Muscle tissues
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
skeletal muscle
attached to bone; voluntary; striated muscle
cells are long and multinucleated
smooth muscle
do not exhibit cross-striation; involuntary; cover wall of internal organs
cells are narrow and spindle-shaped, single and centrally located nucleus
cardiac muscle
wall of heart; involuntary; striated muscle
cells are branched, intercalated discs
fusiform muscles
Cylindrically shaped in the center and tapers at the ends
Ex: biceps, triceps
unipennate muscle
Fibers that run only one side of the muscle
Ex: palmar interosseous
bipennate muscle
Two rows of oblique muscle fibers run both sides of tendon
Ex: dorsal interosseous
digastric muscle
double belly; parallel muscle fibers
Ex: omohyoid
Quadrate muscles
multi-belly muscle with tendinous intersection
Ex: rectus abdominis
levels of organization of skeletal muscle
muscle>fascicle>myofibers (muscle fiber)>myofibrils>myofilaments>actin (thin filaments) & myosin (thick filaments)
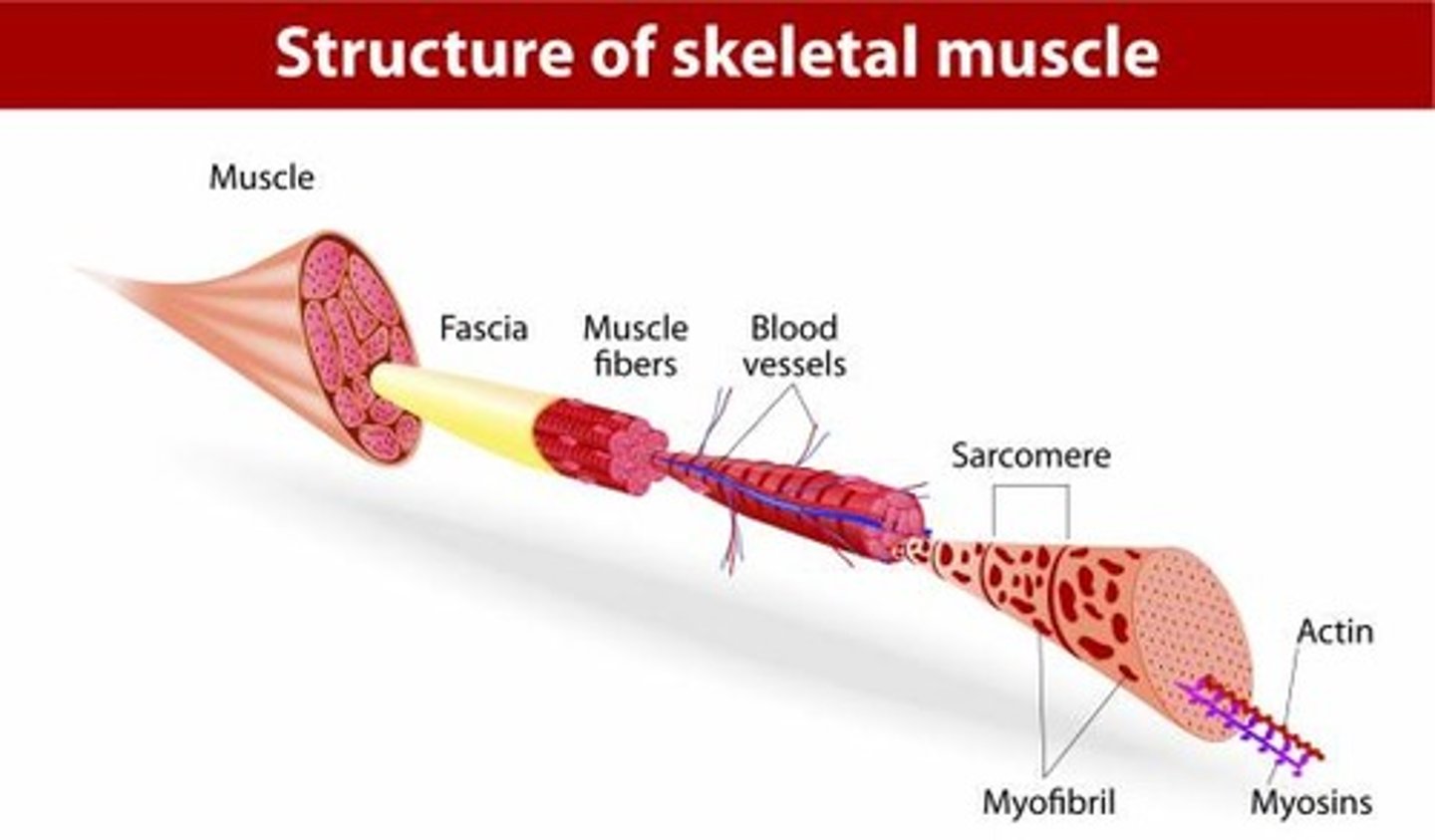
Epimysium
surrounds entire muscle
Perimysium
surrounds fascicles
Endomysium
Surrounds individual muscle fibers
muscle fiber (myofiber)
bundle of myofibrils; nuclei + mitochondria + T-tubules + sarcoplasmic reticulum + terminal cisternae
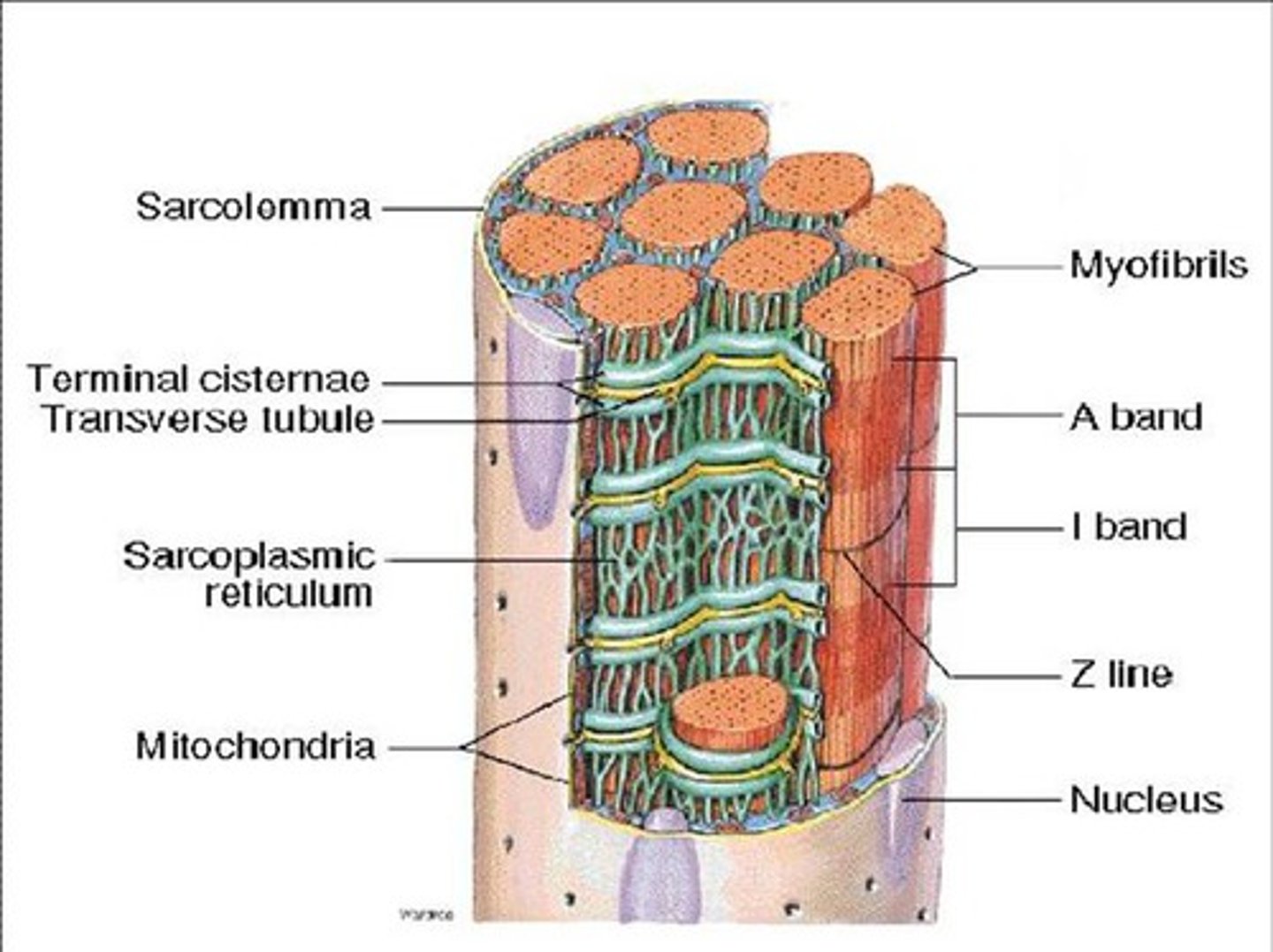
Triad of a muscle fiber
T-tubule + 2 terminal cisternae of SR
cross bridge cycle
repeated interactions between myosin and actin filaments -> muscle contraction
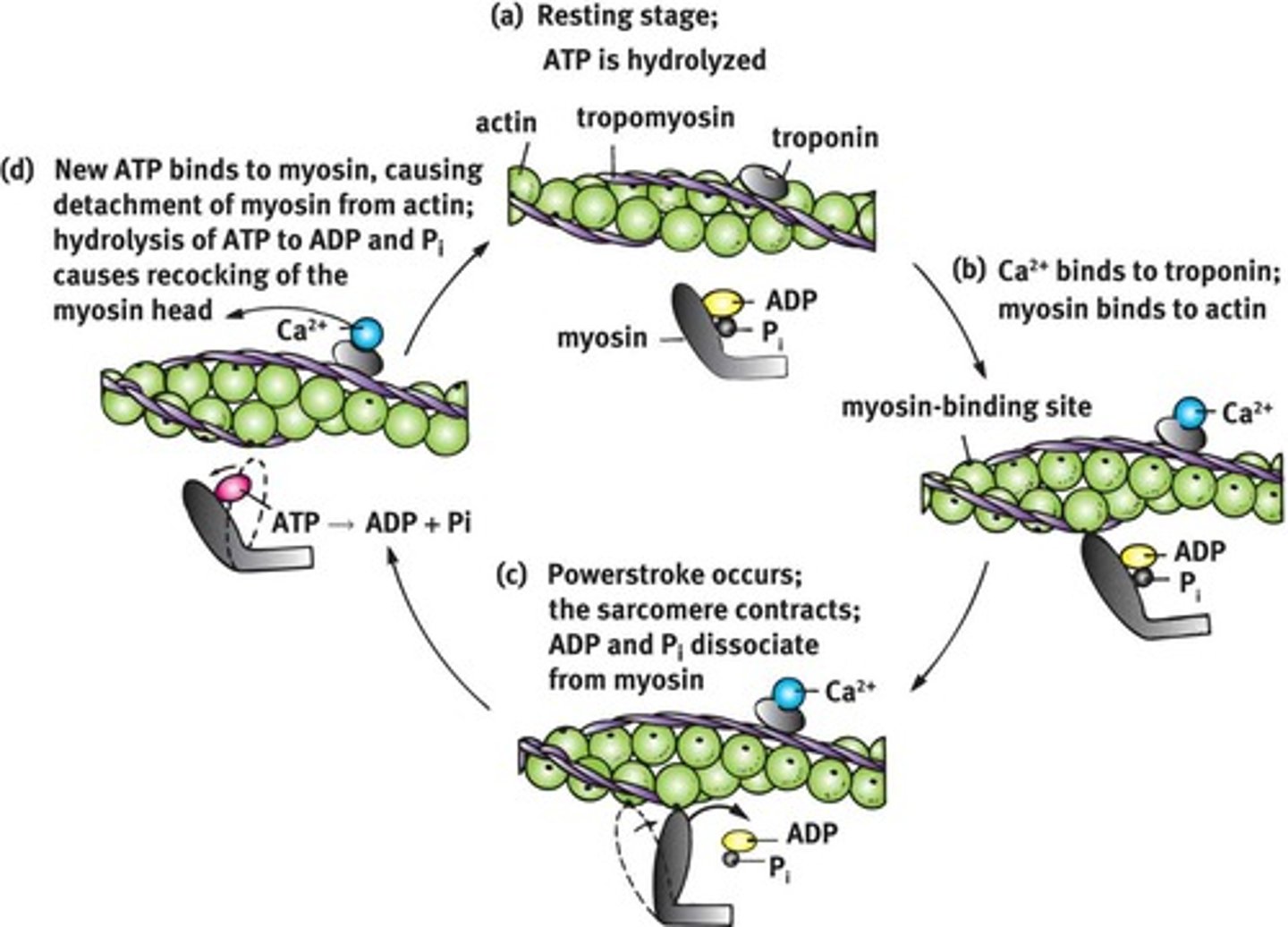
thin filaments
double-stranded helix actin
tropomyosin and troponin complexes: masks myosin-binding site
thick filaments
myosin
Sacromere
contractile unit of a muscle fiber
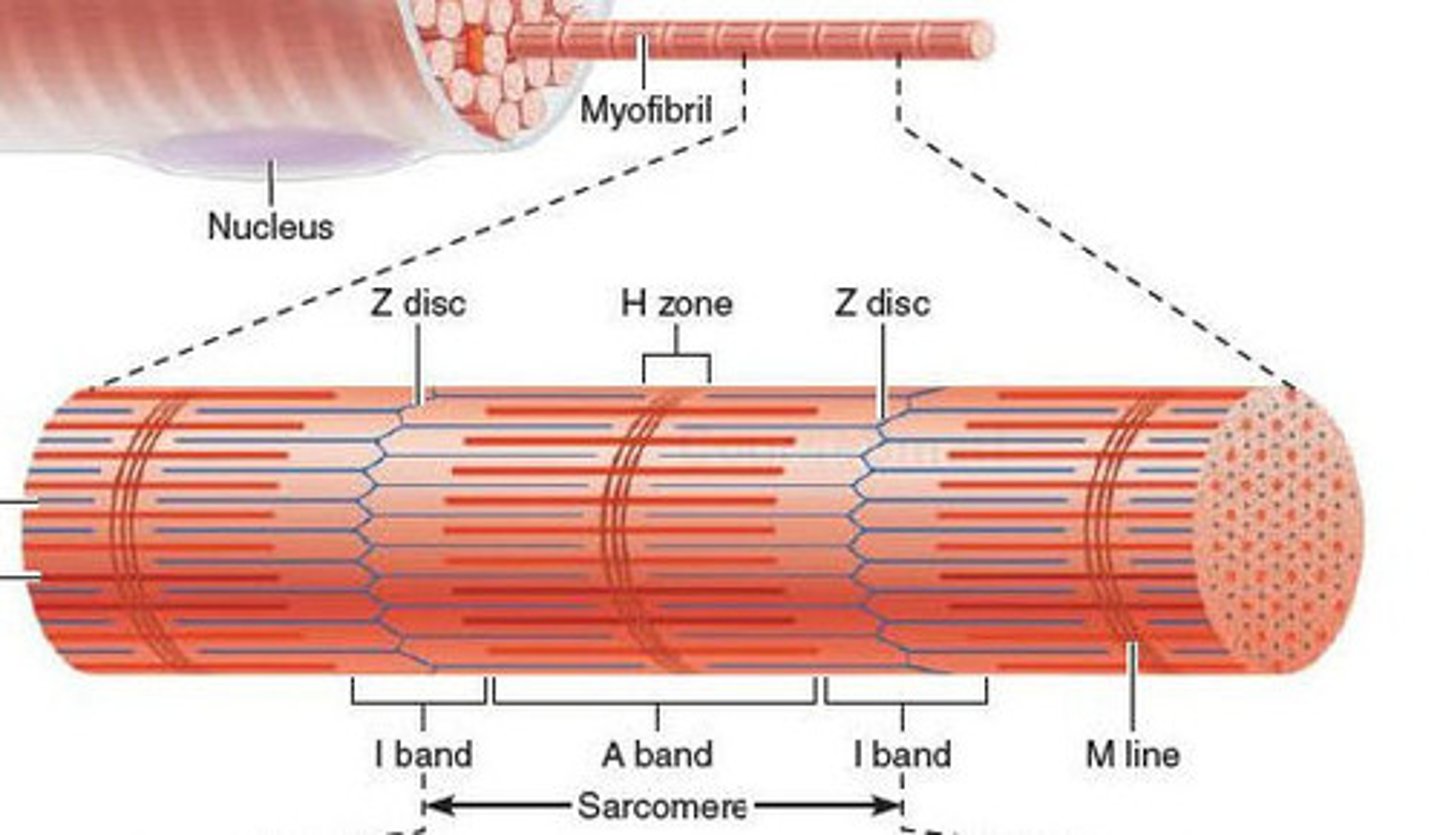
muscle contraction steps
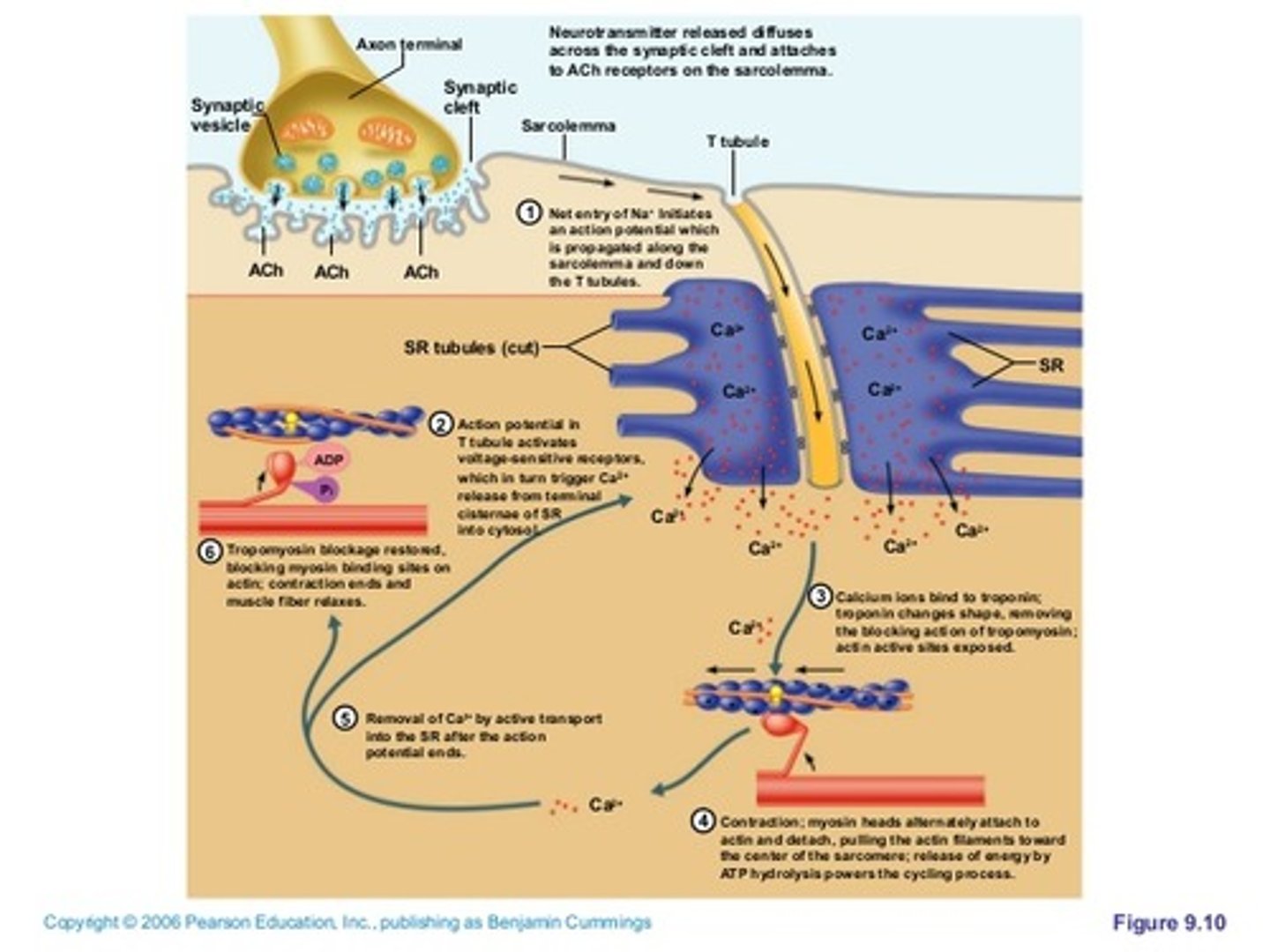
1) Motor neuron releases acetylcholine into the neuromuscular junction and causes the depolarization of the sarcolemma.
2) Depolarization spreads down the sarcolemma to the T-tubules, triggering the release of Ca2+ ions.
3) Ca2+ binds to troponin, causing a shift in tropomyosin and exposure of the myosin-binding site on the actin filament.
4) Shortening of the sarcomere occurs as the myosin head binds to the exposed sites of actin, forming a cross-bridge and pulling the actin filament along the thick filament, resulting in contraction.
5) Muscle relaxes when acetylcholine is degraded by acetylcholine esterase and the allowing Ca2+ is brought back into the SR. ATP binds to myosin head, allowing it to relax from actin.
red fibers
slow-twitch; many myoglobin and capillaries -> oxidative phosphorylation to produce ATP; slow contraction but fatigue resistant
muscles to maintain erect posture, leg muscles of marathon runners
white fiber
fast-twitch; abundant glycogen -> anaerobic glycolysis to produce ATP; fast contraction but fatigue-prone
leg muscles of short-distance sprinters
extreme muscle work -> oxygen deficiency -> ischemic pain -> lactic acid -> muscle fever
intermediate fibers
fast-twitch; both myoglobin & glycogen -> oxidative and glycolytic activity; intermediate contraction speed and fatigue
leg muscles of middle-distance runners, swimmers and hockey players
isotonic contraction
muscle shortens against a constant load to produce movement
isometric contraction
muscle tension increases as the muscle maintains a fixed overall length
concentric action
insertion approach origin
concentric inverse: origin approach insertion
eccentric action
origin and insertion move away from each other