Human Anatomy Exam 1
1/234
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
235 Terms
Eponym
associated with the name of a person after whom a structure is named or thought to be named
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
Right lobe of liver, gallbladder, right kidney, portions of stomach, small and large intestine
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
Left lobe of liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen, portions of large intestine
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
Cecum, appendix, portions of small intestine, reproductive organs (right ovary in female and right spermatic cord in male), and right ureter
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
Most of small intestine, portions of large intestine, left ureter, and reproductive organs (left ovary in female and left spermatic cord in male)
Cephalic
Head
Cervical
Neck
Thoracic
Chest
Brachial
Segment of the upper limb closest to the trunk; the arm
Antebrachial
Forearm
Carpal
Wrists
Manual or Manus
Hand
Abdominal
Abdomen
Pelvic
Pelvis
Pubic
Anterior pelvis
Inguinal
Groin
Lumbar
Lower Back
Gluteal
Buttock
Femoral
Thigh
Patellar
Kneecap
Crural
Leg, from knee to ankle
Sural
Calf
Tarsal
Ankle
Pedal
Foot
Plantar
Sole region of foot
Pericardium
Membrane surrounding heart
Right hypochondriac region
Upper Right Region
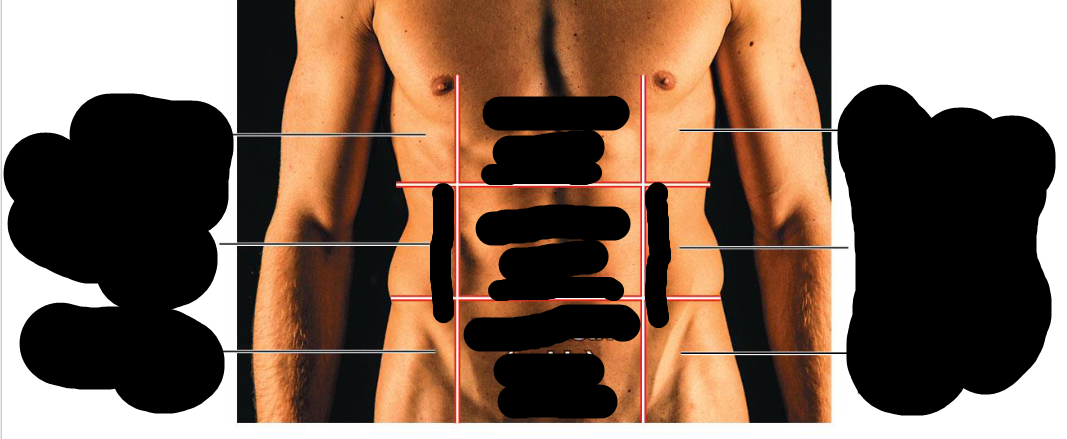
Right lumbar region
Right middle region
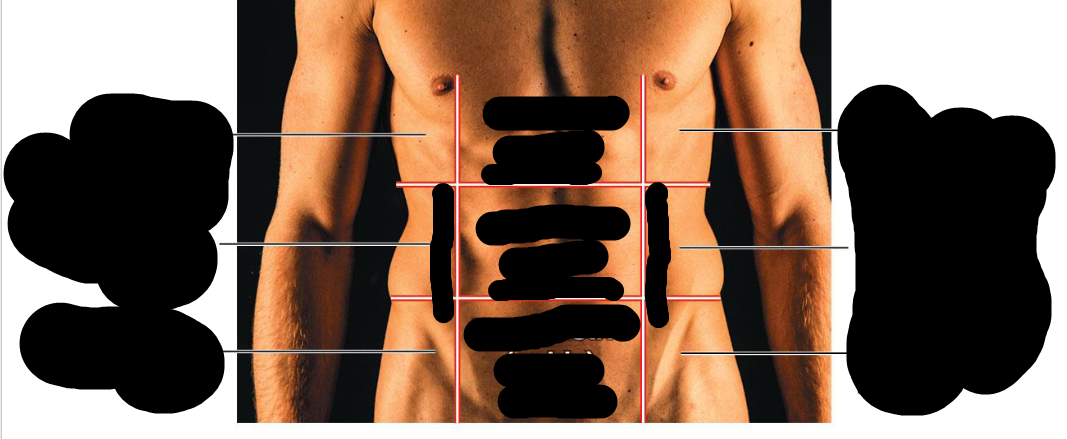
right inguinal region
bottom right region
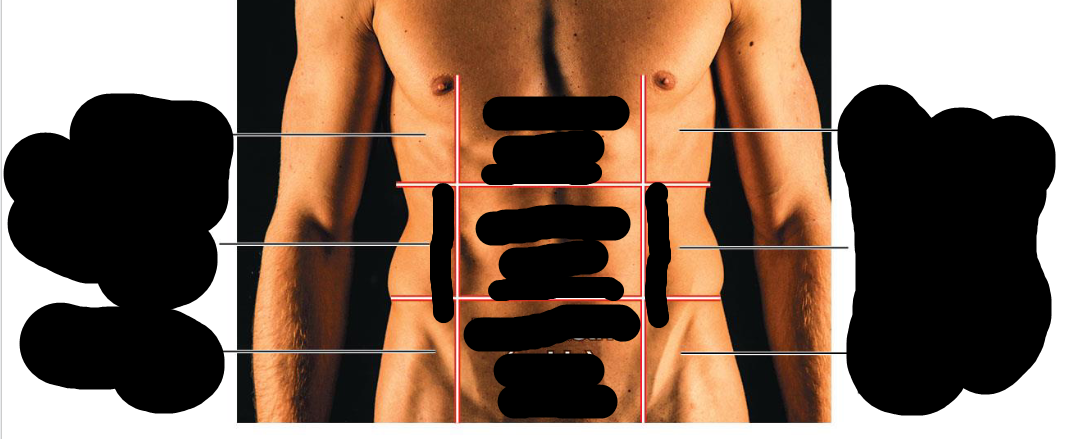
Epigastric region
Upper middle region
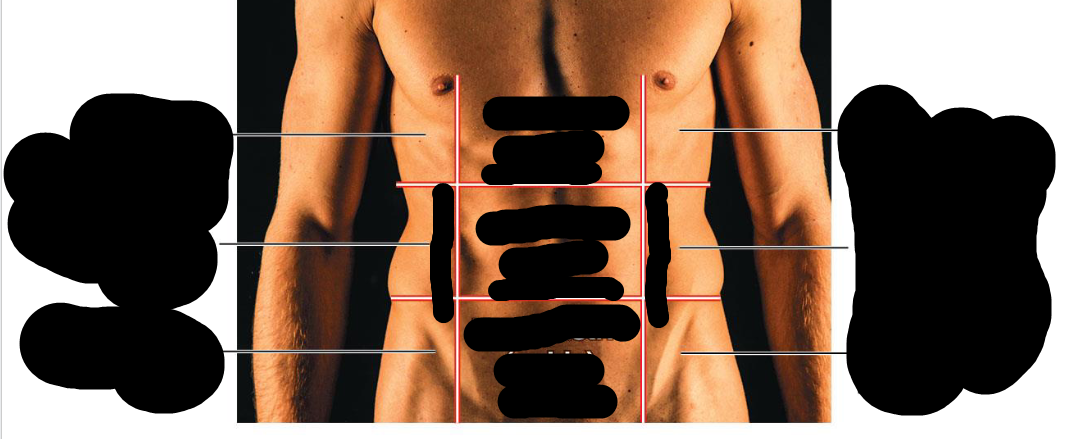
Umbilical region
Middle region
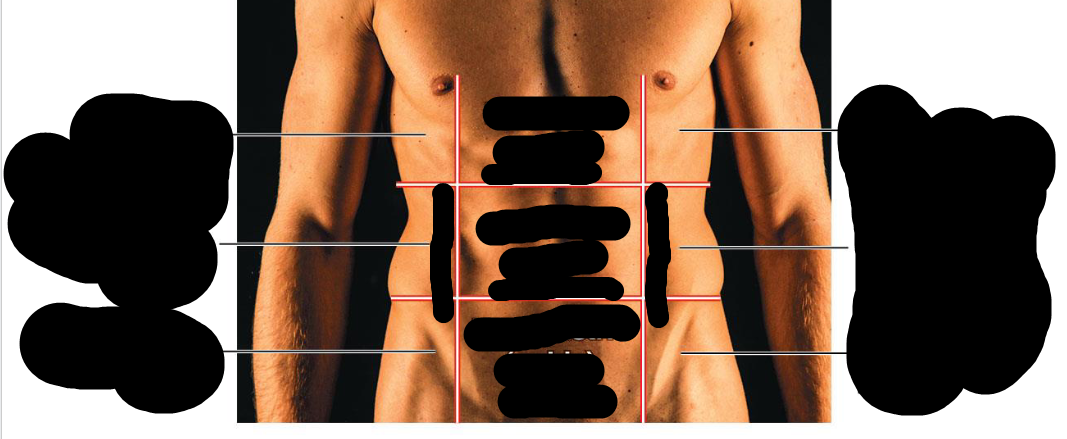
hypogastric region
Lower middle region
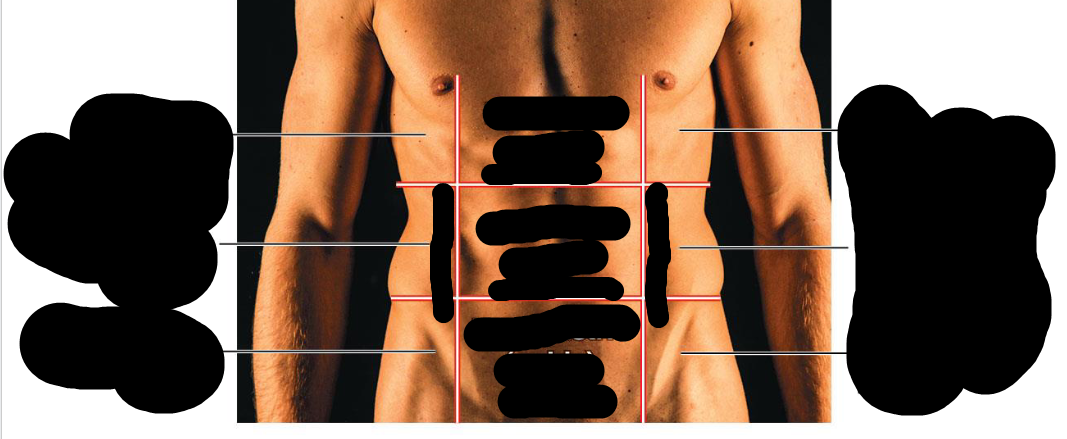
Left hypochondriac region
Left upper region
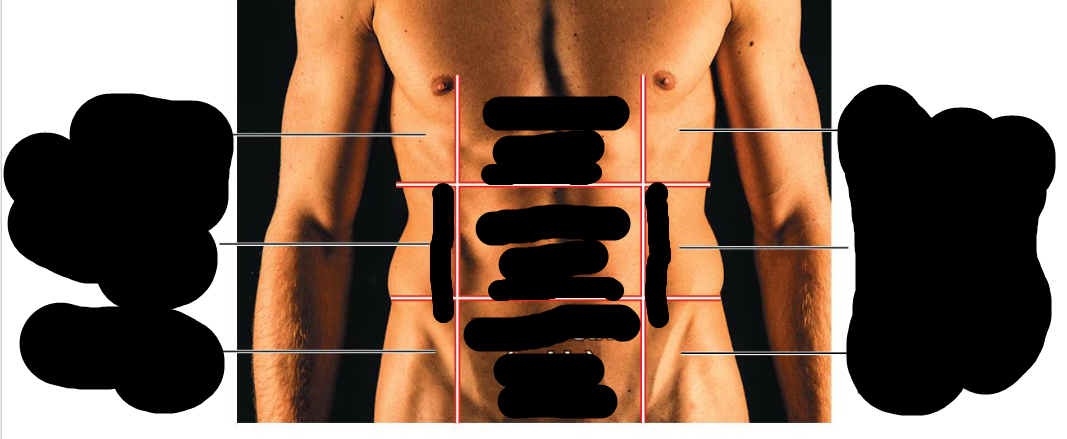
Left lumbar region
left middle region
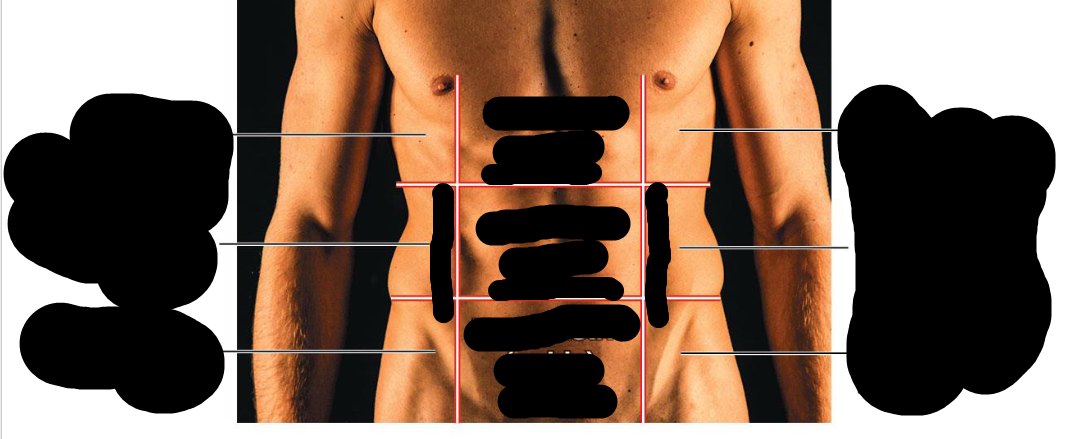
left inguinal region
bottom left region
Frontal
Forehead
Orbital
Eyes
Nasal
Nose
Oral
Mouth
Mental
Chin
Sternal
Sternum (middle chest area)
Axillary
Armpit
Mammary
Breasts
Umbilical
Belly button
Inguinal
groin
Otic
Ears
Occipital
Back of the head
Scapular
Shoulder blades
Vertebral
Spinal area
Sacral
Bottom of spine
Perineal
between anus and external genitalia
Acromial
Top of arm
Brachial
arm
Antecubital
anterior elbow
Pollex
thumb
Palmar
Palm
Digital
Fingers and Toes
Coxal
hip
Fibular or peroneal
lateral side of leg
Metatarsals
Bones in the foot
Hallux
Big toe
Olecranal
posterior elbow
Metacarpal
Back of the hand
Popliteal
Back of the knee
Calcaneal
Heel
Frontal or Coronal Plane
Front and back sections
Transverse Plane
Superior and Inferior sections
Sagittal Plane
Left and right sections
Midsagittal
Left and right sections equal
Parasagittal
Left and right side unequal
Cell Junction
Intracellular attachments
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs)
transmembrane proteins responsible for cell junctions.
Tight Junctions
Impermeable junctions
Form continuous seals around the cell
Prevent molecules from passing between cells
Stomach
Tight Junctions found commonly in:
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions
Bind adjacent cells together like molecular velcro
Help keep cells from tearing apart
Skin
There are many desmosomes in:
Gap Junctions
Communicating junctions
Allow ions and small molecules to pass from cell to cell
Particularly important in heart cells and embryonic cells
Connexon
Channel between cells in gap junctions
Gap junctions
Necessary for heart function
Desmosomes
Resist damage for stretching and twisting (blister)
Hemidesmosomes
Tie epidermal cells to fibers of the basal lamina
Basal Lamina
an acellular membrane between epidermis and dermis
Pemphigus
Autoimmune disease associated with cell junctions; causes blisters in mouth, esophagus, eyes, nose, vagina, and anus
Epithelial tissue
Covers exposed surfaces
Lines internal passageways and chambers
Produces glandular secretions
Connective tissue
Fills internal spaces
Provides structural support
Stores energy
Muscle tissue
Contracts to produce movement
Includes skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle
Nervous tissue
Conducts electrical impulses
Carries information
Epithelial Tissue
Sheets of cells that cover exposed surfaces, line internal cavities and passageways
Apical Membrane
Part of epithelial tissue that faces the lumen
Basolateral Membrane
Part of epithelial tissue that faces the extracellular fluid
connective tissue
Almost all epithelial cells are supported by:
apical membrane
Tight junctions are very close to the:
Avascularity
Does not contain blood vessels
Regeneration
Epithelial cells have high:
Neuroepithelia
Epithelia found in special sense organs
Microvilli
Absorption and secretion
Cilia
Movement
reproductive organs
Cilia are commonly found in:
Stereocilia
Found in sensory organs (like the inner ear). Long cilia
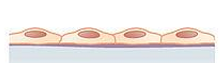
Simple squamous epithelium