IB Psychology - Biological Approach
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
localization
refers to the idea that the brain is made up of specialized modules, and that each module has a certain function
prefrontal cortex
the outermost layer of the frontal lobe and is responsible for many of the executive functions in the brain
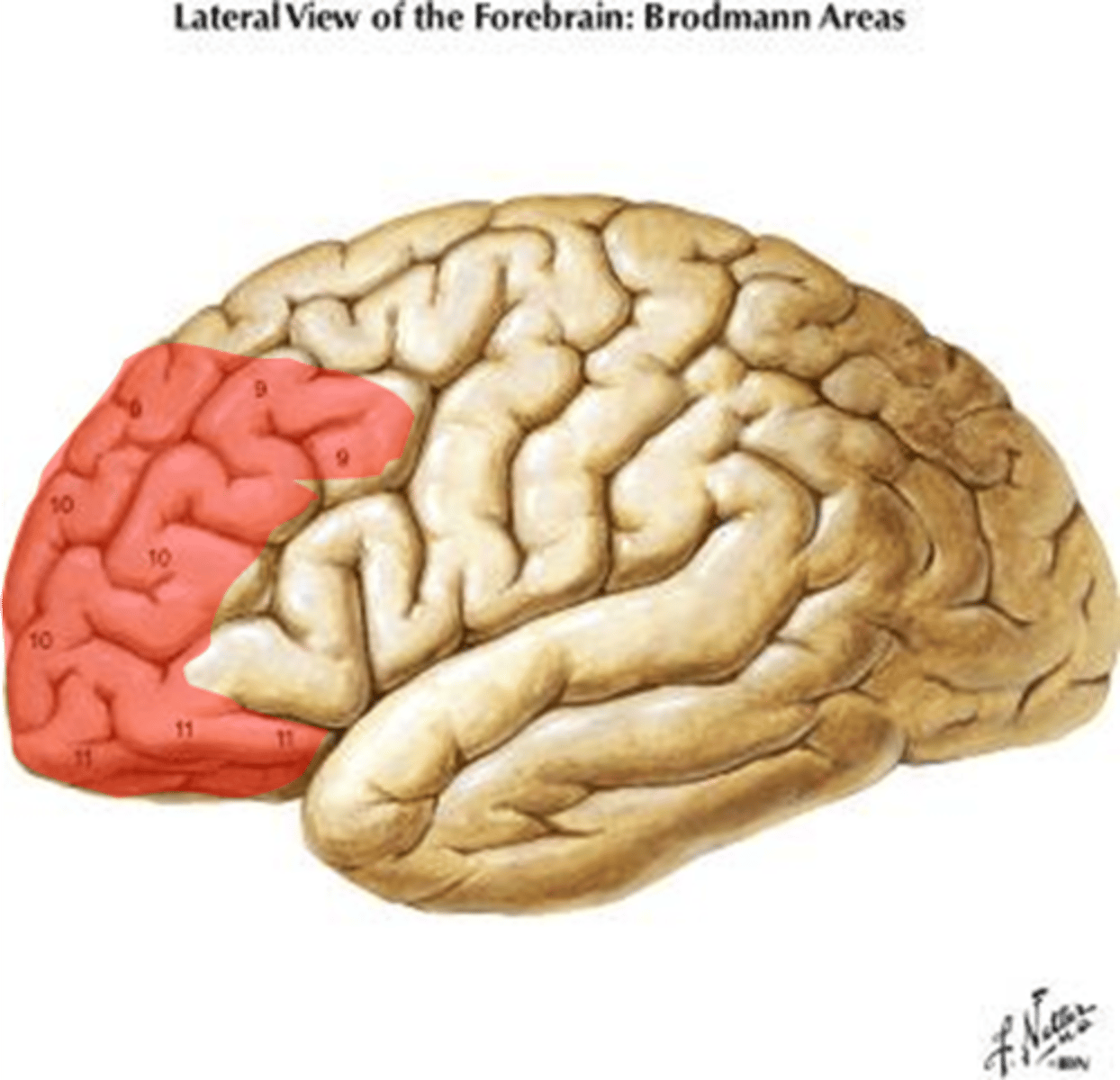
Broca's area
localization - suggests that speech articulation is controlled by the left frontal lobe
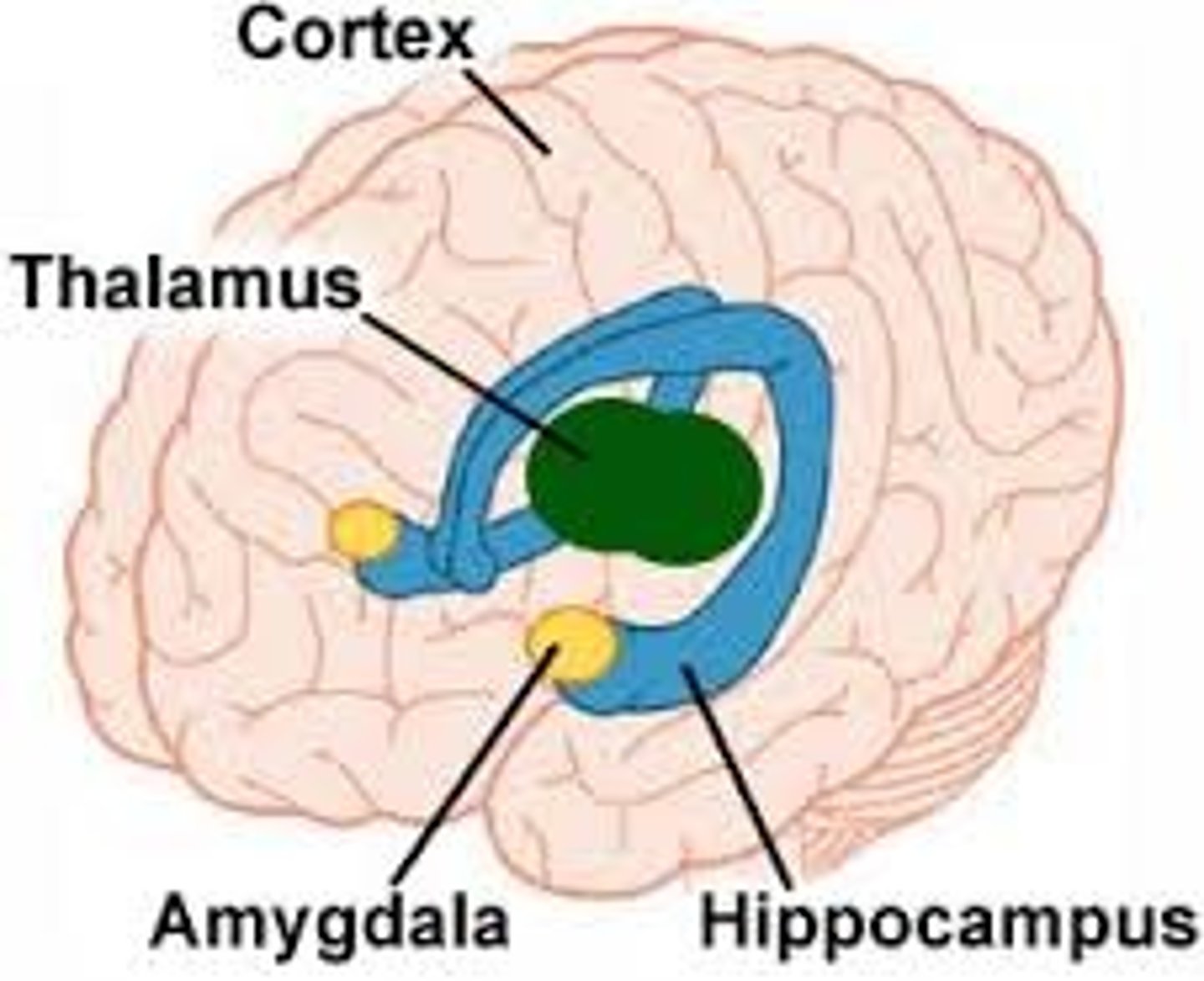
amygdala
emotional center of the brain and is part of the limbic system. It activates our stress response and our ability to experience emotions such as fear.
localization criticisms
some functions may be focused in a specific module while others are widely distributed - demonstrated in Lashley
neuroplasticity
refers to the brain's ability to adapt by forming new connections as a result of experience, learning, or following an injury. Reasons for change are both genetic and environmental - as a result of experience
dendritic branching
the process by which the part of one neuron establishes a connection with other neurons
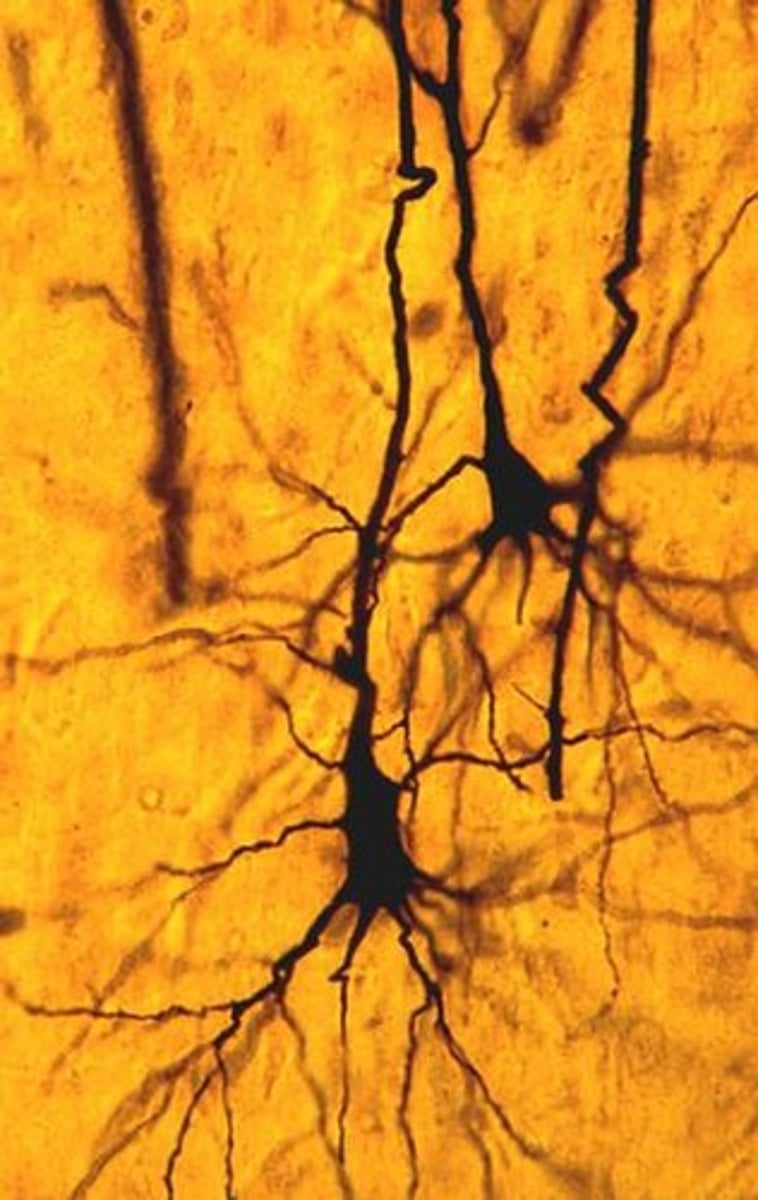
neural network
sum total of all your brain's neurons, and the connections between them. The stronger the pathway becomes, the more likely this pathway will become activated in the future.
synaptic plasticity
the ability of one neuron to form new connections and break up the old ones
corticial remapping
when brain area X assumes the functions of brain area Y due to injury
Maguire et al. (2000)
neuroplasticity - London cab drivers showed an increase in the posterior of the hippocampus as a result of their day to day lives

Neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
excitatory neurotransmitters
allows the impulse to cross the synapse and produce a stimulating effect on the brain
inhibitory neurotransmitters
stops the impulse, preventing it from crossing and produces a calming effect on the brain
agonists
chemical substances that mimic or enhance the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receptor sites of the next cell, increasing or decreasing the activity of that cell
antagonists
drugs that block the function of a neurotransmitter
limitations of neurotransmitters
reductionist explanation for behaviour. There could be many other things affecting behaviour.
pheromones
Chemical signals released by an animal that communicate information and affect the behavior of other animals of the same species. Inconclusive evidence that they exist in humans.
pheromones and animals
are processed in a different part of the brain than ordinary smells. It is processed in the vomeronasal organ (VNO) and is connected to a special region called the accessory olfactory bulb.
pheromones and humans
don't have a functional VNO or the accessory olfactory bulb so the effect of pheromones is debatable
Lundstrom and Olsson (2005)
pheromones - the study suggests that the androstadienone found in sweat may serve the function of signaling sexual attractiveness

criticisms of human pheromones
research is inconclusive, contradictory findings, biased because of backing by commercial interests, and limitations in methodology
hormones
chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
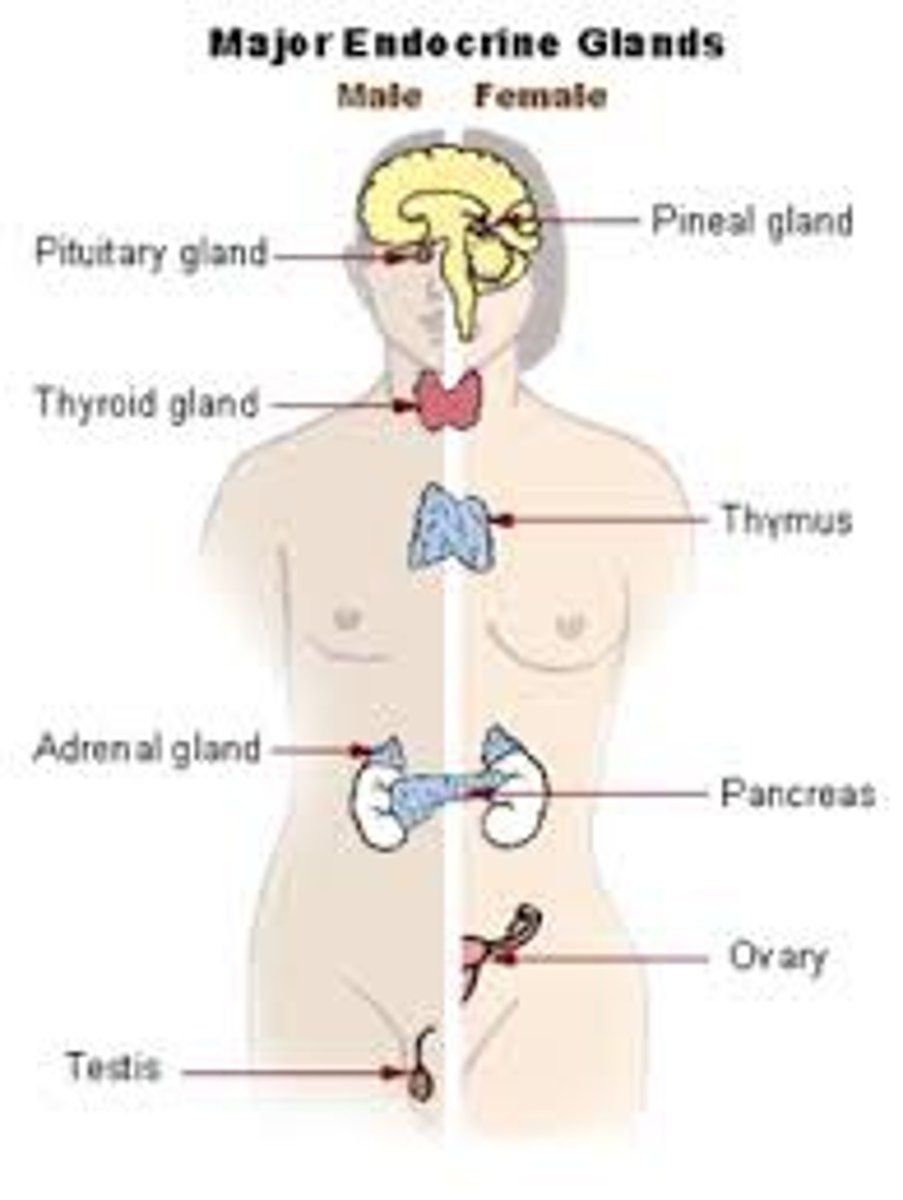
endocrine glands
release hormones. Parts include adrenal gland, pineal gland, thyroid, thymus, etc.
target cells
receptors for a particular hormone
gene activation
when a hormone binds to a receptor and launches a sequence of changes
examples of hormones
adrenaline, insulin, oxytocin, testosterone, cortisol, etc.
impacts of testosterone
deepened voice, muscle development, increased competitiveness and violence
Effects of Cortisol (glucocorticoid)
1. longer-term stress response, 2. increases blood [glucose], 3. increases protein degradation, 4. decreases inflammation & immunity
Albert et al. (1986)
hormones - the study suggests that testosterone plays an important role in aggression and status seeking in rats
Kiecolt-Glaser
stress of caring for someone with a chronic illness delays wound recovery due to chronic stress - increase in cortisol (glucocorticoids) in bloodstream

genetics
The scientific study of heredity. DNA can be found in the nucleus of each cell and is organized into tiny units called genes
genotype
the genetic structure an organism inherits from its parents
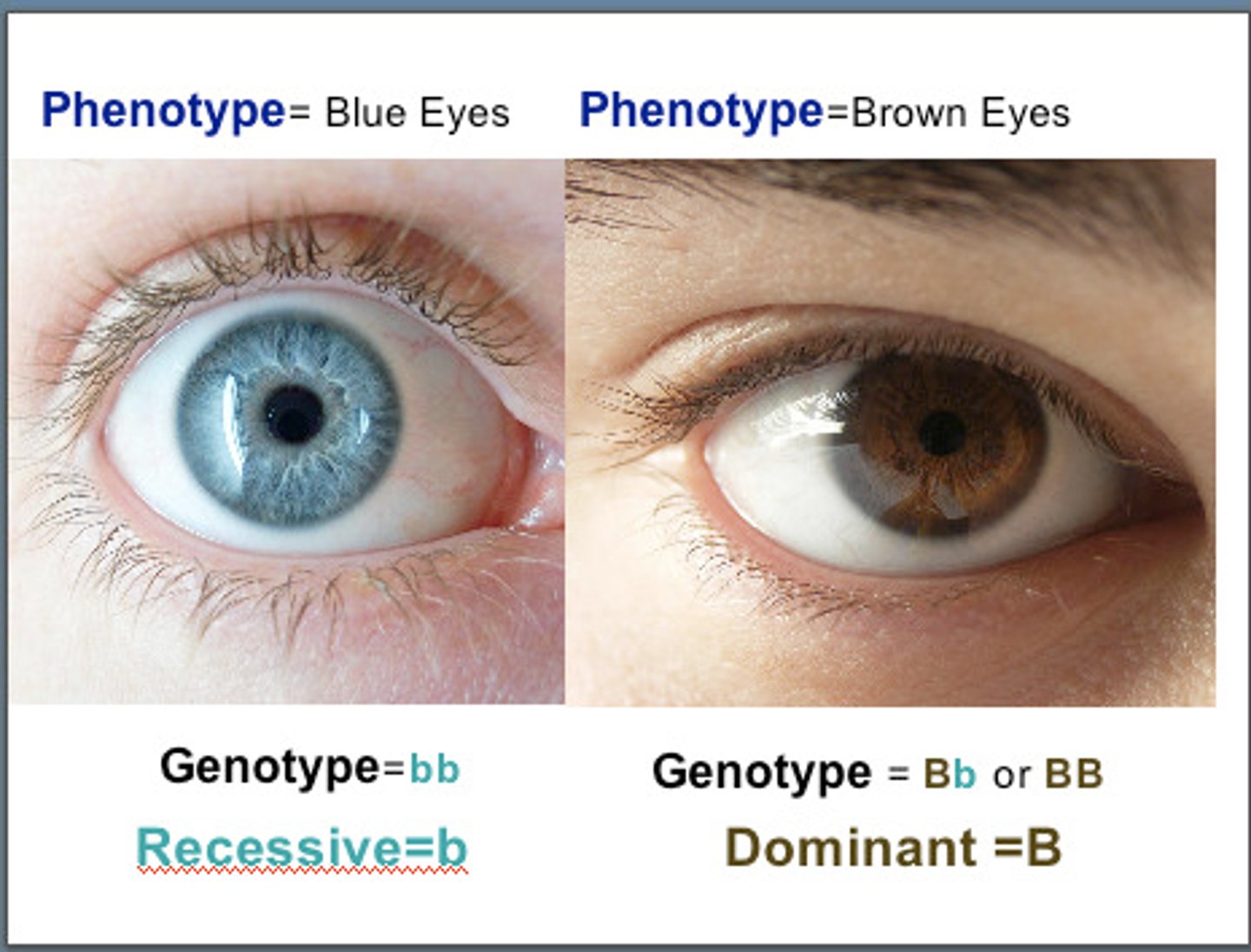
phenotype
the observable characteristics of an organism resulting from the interaction between the organism's genotype and its environment
genes and behaviour
contain the instruction for the production of proteins which regulate the body's processes and the expression of the phenotypic traits such as intelligence
chromosomes
humans have 46 and each one contains thousands of genes and are located in the nucleus of every human cell
epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
genetic similarities
a quantitive measure of the relative contribution of genetic factors into a trait/behaviour. Methods include twin studies, family studies, and adoption studies.
concordance rate
The degree to which a condition or traits shared two or more individuals or groups
Caspi et al. (2003)
genetics and behaviour - the study suggests that individuals with the 5-HTTT gene reacted to stressful life events with more depressive symptoms
criticisms of genetics
different traits are influenced by genetic inheritance to different degrees and environmental factors can influence biological factors through the regulation of gene expression
theory of evolution
states that organisms are driven to survive and reproduce and organisms of the same population are born with randomly different traits which may help in their survival
survival of the fittest
favourable characteristics which help an organism survive and reproduce
natural selection
organisms that are better adapted and pass on their genes to help strengthen the gene pool
monozygotic (MZ) twins
Twins who originate from one zygote that splits apart very early in development. (Also called identical twins.) Share 100% of genes.
dizygotic twins
fraternal twins - no more genetically similar that regular siblings
3 R's of animal research
replacement, refinement, reduction
4 types of Animal models used in experimental research
Genetic, environmental, invasive (nervous), invasive (bodily parts)
Strengths of animal research
- Relatively small and easy to handle, so procedures can be more feasible
- Short gestation periods and reproductive cycles, so generations can be studied
- Similar brain structures to humans, can be related to humans
Limitations of animal studies
-ethical issues
-generalizability between animals and humans
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer-generated images of soft tissue. MRI scans show brain anatomy.
fMRI
a form of magnetic resonance imaging of the brain that registers blood flow to functioning areas of the brain
Strengths of fMRI
- show how the blood is flowing in the brain
- used to identify problems with blood circulaition
- early detection of alzheimers disease
- safe to use
MRI strengths
The image created from MRI has high spatial resolution, and is thus very detailed.
It is safe to use because it does not use radioactive materials, meaning individuals can be tested repeatedly.
MRI scans are fast and practical, as they are easy to operate, and are therefore placed in almost every hospital.
Limitations of fMRI
Very loud and claustrophobic, can't detect which brain receptors are being activated by the drug/treatment being looked at, doesn't show the sequence of activation, just the area involved.
Limitations of MRI
• They are very expensive
• Movement may affect the pictures
• They cannot say anything about cause-effect relationships
Brain Imaging Techniques
Pictures of the living human brain to establish a correlation between the brain and behaviour
Includes MRI and fMRI..