thermochemistry
1/49
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
chemical change
a process in which a substance's physical or chemical properties are altered
other definitions for chemical change
rearrangement of ions or atoms
how can chemical change be identified?
by changes in colour, odour, temperature, pH, smell, or state
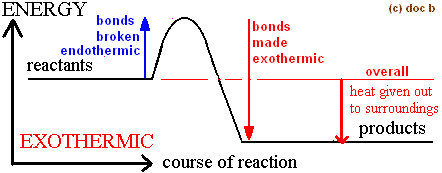
what do chemical changes do to the bonds of the reactants and the products?
they BREAK the reactants' bonds and FORM the products' bonds
breaking bonds is an ___ process
endothermic!
forming bonds is an ___ process
exothermic!
what is potential energy derived from?
position (e.g. changing an atom's arrangement is a change in its position)
chemical reactions are a change in what form of energy?
potential energy
what is kinetic energy derived from?
motion
how can kinetic energy be measured? (give an example)
a thermometer! e.g. as a hot liquid cools off to match its surroundings, you can see the thermometer drop as the particles of that liquid begin to slow down
what is thermodynamics?
the study of the interconversion of heat and other forms of energy
what must you always do in thermodynamics?
define a system and contrast it with the surroundings
what is a calorimeter? give two examples
an insulated container in which the amount of heat absorbed or released by a chemical reaction or physical change is noted; a styrofoam cup or a bomb calorimeter
why are calorimeters useful?
they localize surroundings; usually these are far too vast (the surroundings is literally everything in the universe)
let's say you use a bomb calorimeter and inside you have methanol burning. what does the change in temperature tell you?
the energy absorbed by the water indicates the energy released by the combustion of methanol!
what are the three types of systems?
open (can exchange matter and energy)
closed (can only exchange energy NOT matter)
isolated (doesn't really exist, but doesn't exchange energy nor matter)
what are sign conventions defined by?
the terms of the system
draw a potential energy diagram for an exothermic reaction
draw a potential energy diagram for an endothermic reaction
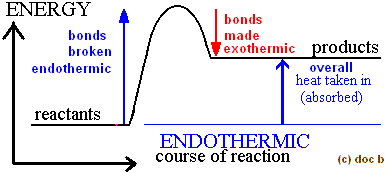
do potential energy changes result in a change in temperature?
no! potential energy changes are a change in POSITION not motion
what is enthalpy change?
potential energy change or chemical change (they’re the same thing)
what is the first law of thermodynamics?
the total quantity of energy in the universe is constant
energy is neither lost nor created; only transformed from one form to the next
what equation is almost always used in calorimetry?
Esys = -Ecal
nΔH = -mcΔT
what are words used that are signs of a potential energy change?
dissolved, dissociate, combust/burn, ionize, neutralize, react, replace, formation, decomposition
are neutralization and combustion reactions endothermic or exothermic?
exothermic?
what assumptions are made with calorimetry?
the calorimeter and the system are isolated from the universe
when the temperature stops changing, the process is complete
the predicted reaction is the one that took place
when using a metal can (such as in the lab) for a calorimeter, we assume that both the water and the metal can had the same temperature change
what are the three forms of the calorimetry equation?
nΔH = -mcΔT
nΔH = -ΔT(mcwater + mcmetal)
nΔH = -CΔT
what is complete combustion?
hydrocarbon + O2(g) —> CO2(g) + H2O
what is incomplete combustion?
hydrocarbon + O2(g) —> CO2(g) + H2O + CO(g) + C(s)
what is open combustion?
water exists as water vapour (H2O(g))
what is closed combustion?
water exists in a liquid state (H2O(l))
in a combustion reaction, what is the system made of and how does it show chemical change?
the system is all of the carbons, oxygens, and hydrogens involved
by rearranging itself and changing its position, chemical change is initiated
what is molar enthalpy measured in?
kJ/mol
what is total enthalpy measured in?
kJ
what are calorimeters used for?
to measure energy changes
what are the two main types of calorimeters?
a bomb calorimeter and a polystyrene cup calorimeter
describe the structure of a bomb calorimeter.
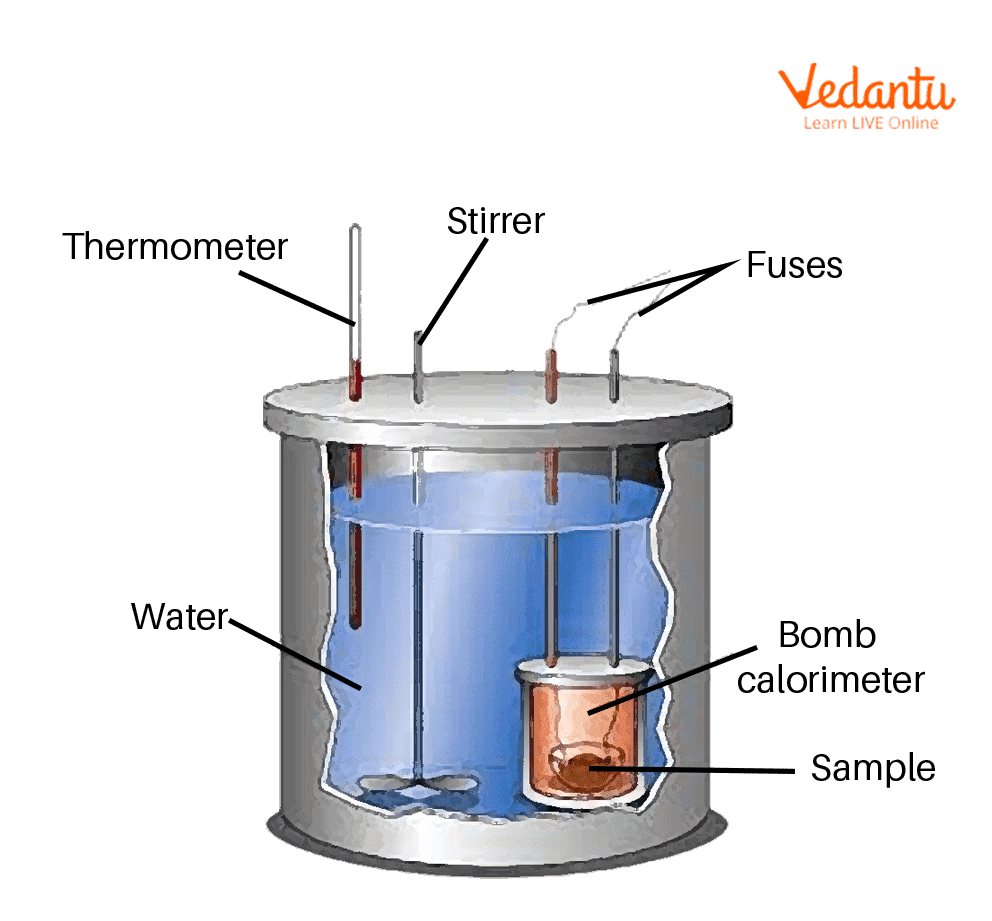
there is an enclosed bomb immersed in water surrounded by an insulated container
heat given off or absorbed by a reaction goes into water and we can note temperature changes to find the energy change of the reaction!
when are polystyrene cups useful?
when measuring energy changes that occur in solutions
what is hess’ law?
when products are converted into reactants, the change is enthalpy is ALWAYS the same even if the reaction happens in one or multiple steps
four steps of hess’ law
Overall (write what reaction you want)
Manipulate (switch around the given equations to get what you need. note that multiplying by -1 switches the arrow of the reaction)
Iterate (rewrite new equations and enthalpy changes)
Cancel add (cancel off what can be cancelled and add enthalpy changes once final equation is met)
what is the other form and equation of hess’ law?
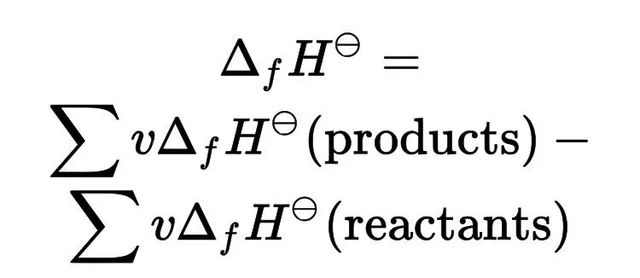
what are rates of reaction affected by?
temperature, surface area (linked to stirring)
what state has the highest surface area?
gases! liquids have lower surface area
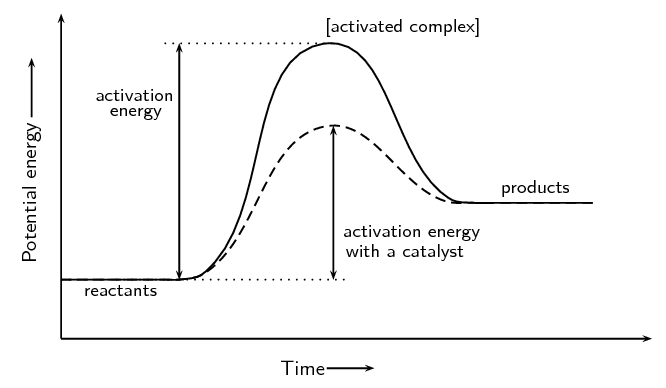
how do catalysts make reactions happen quicker? what does this do to the rate of reaction?
catalysts lower the activation energy by providing an alternate reaction pathway
this increases the rate of reaction
what is activation energy?
the minimum amount of energy a reactant needs to start a chemical reaction
do catalysts affect enthalpy change?
no! catalysts only change the number of steps or the pathway
they do NOT affect enthalpy because it is the exact same reaction
just affects how reactants become products
if a compound has high chemical energy what does that mean?
more unstable
if a compound has low chemical energy what does that mean?
more stable
draw a potential energy diagram for a reaction with a catalyst (this is an endothermic reaction)
what are some errors with calorimetry experiments?
open container and uninsulated calorimeter —> energy leaks out
flame not close enough to calorimeter; heat is lost elsewhere
not stirring; heat is centralized in one area