HPG Axis and puberty
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
HPG Axis System Overview
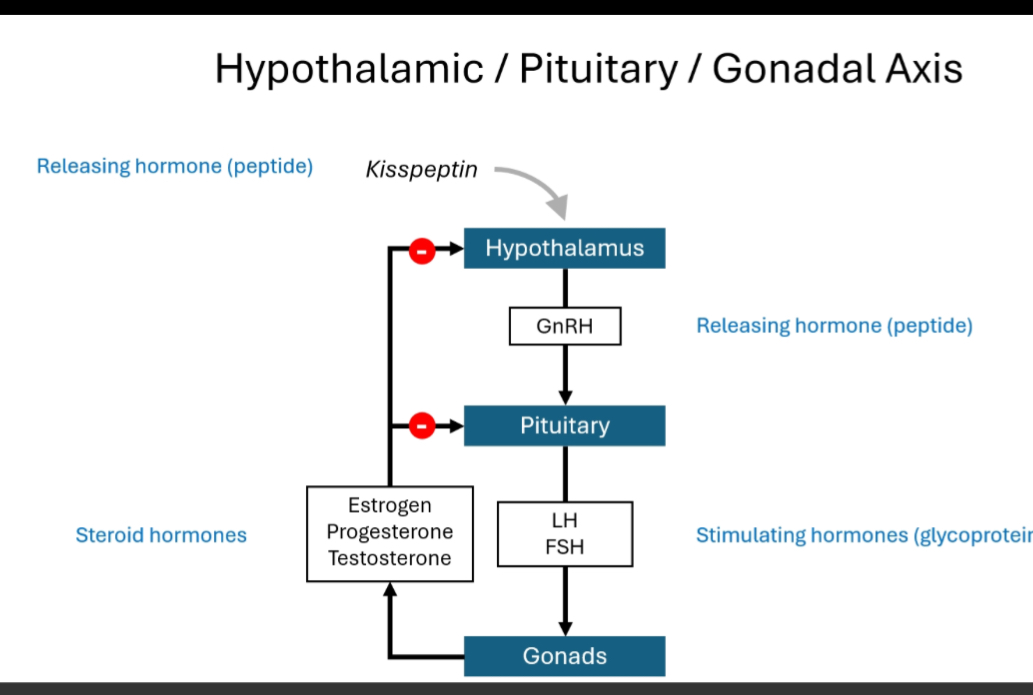
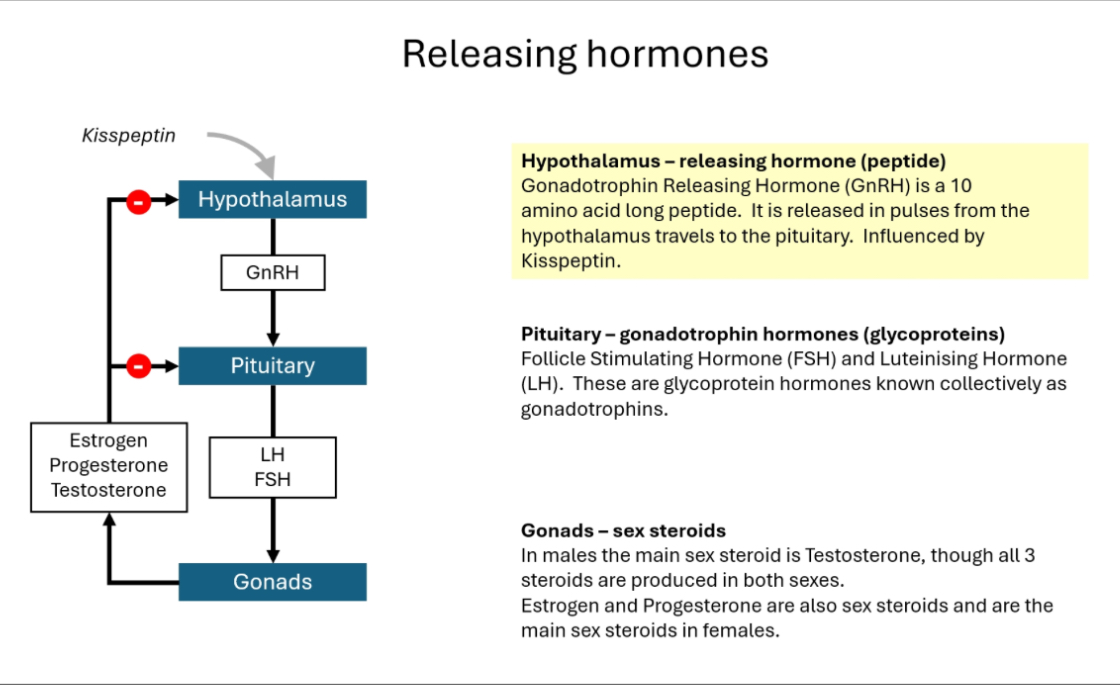
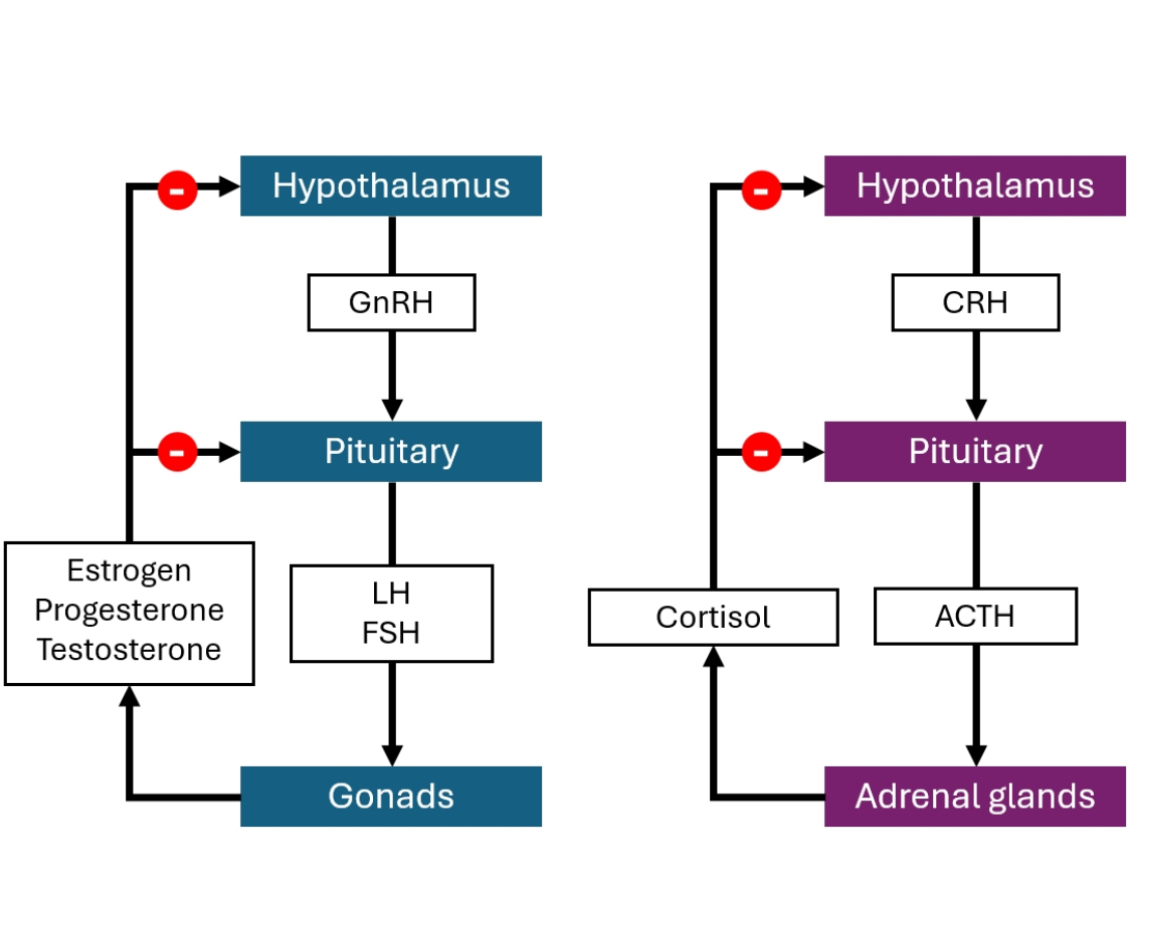
The HPG axis (Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal axis) is a top-down hormonal control system that regulates sexual development, puberty, gamete production, and sex steroid levels through hierarchical signalling and negative feedback.
Step-by-step definition
Hypothalamus releases GnRH in a pulsatile manner.
Pituitary gland responds to GnRH by releasing LH and FSH.
Gonads (testes or ovaries) respond to LH/FSH by:
Producing sex steroids (testosterone, oestrogen, progesterone)
Producing gametes (sperm or oocytes)
Sex steroids feed back negatively to the hypothalamus and pituitary to regulate output.
Why pulsatile GnRH matters:
Continuous GnRH would switch the system off; pulses keep the axis active and tunable.
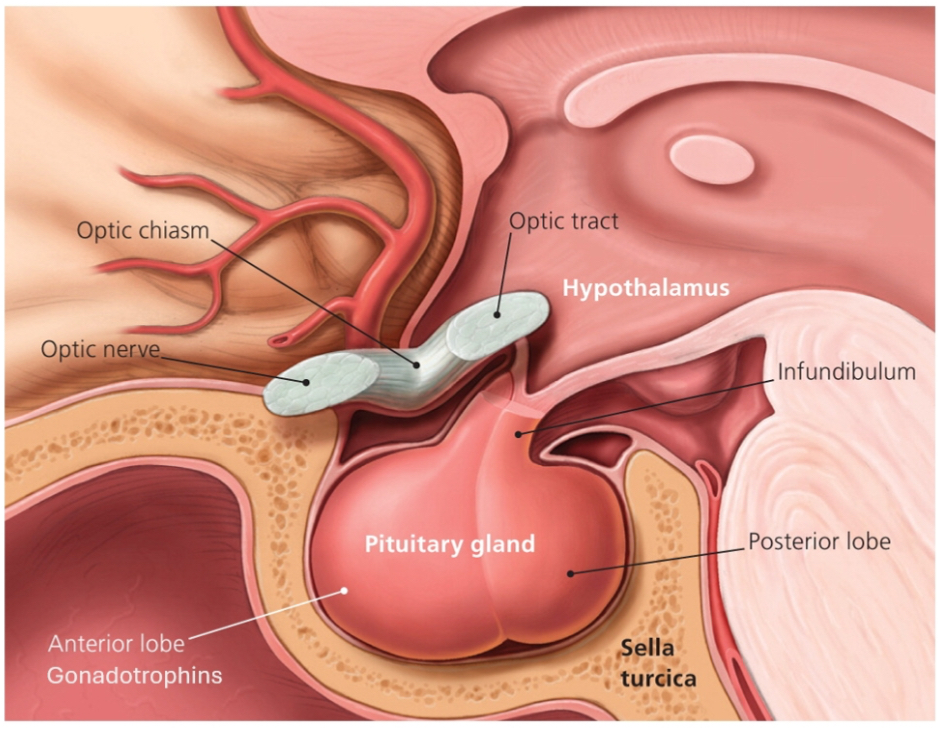
HPG axis
A) Hypothalamus (top of the diagram)
Produces GnRH (a peptide hormone).
GnRH release is pulsatile.
Kisspeptin stimulates GnRH neurons (important for puberty onset).
Red “minus” symbols show negative feedback from sex steroids.
B) Pituitary (middle)
Responds to GnRH by releasing LH and FSH (glycoprotein hormones).
LH and FSH are the output signals to the gonads.
C) Gonads (bottom)
In testes:
LH → Leydig cells → testosterone
FSH → Sertoli cells → spermatogenesis + inhibin
In ovaries:
LH → theca cells → androgen production
FSH → granulosa cells → oestrogen production + follicle development
D) Steroid hormones and feedback
Testosterone, oestrogen, progesterone:
Act on target tissues
Feed back to both hypothalamus and pituitary
This feedback:
Reduces GnRH
Reduces LH/FSH
Prevents hormone overproduction
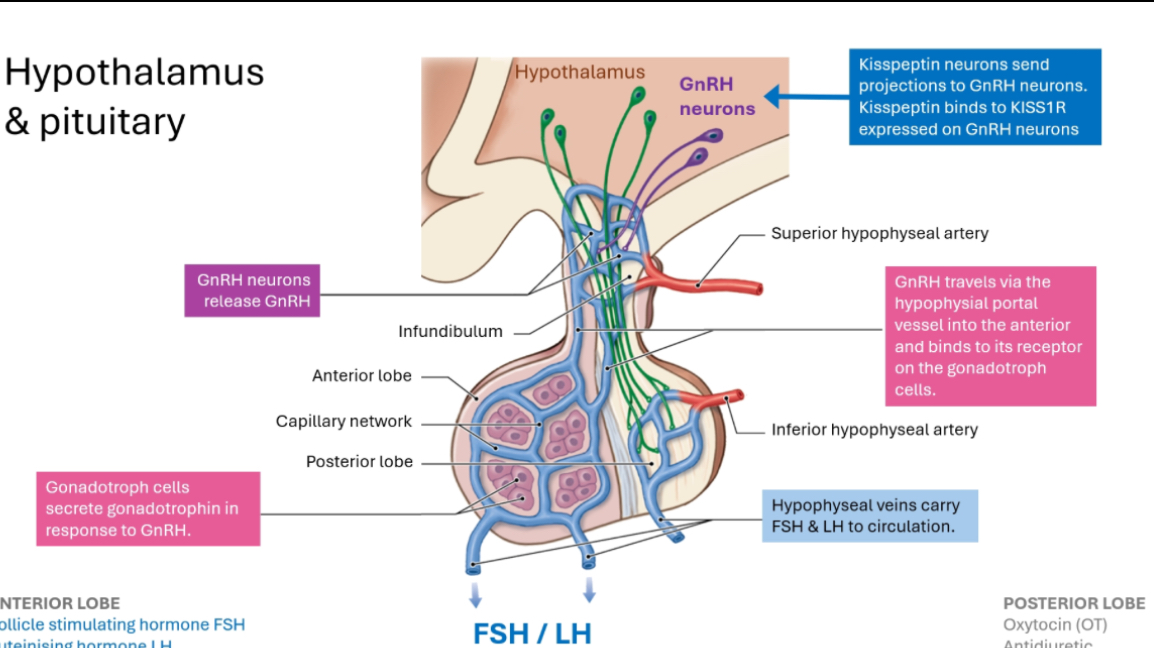
GnRH pathway
1) GnRH neurons (top of the diagram)
These neurons live in the hypothalamus.
They release GnRH.
GnRH release is pulsatile (short bursts).
Important:
Kisspeptin neurons stimulate GnRH neurons.
Kisspeptin is what helps switch puberty on.
2) GnRH does NOT go to the whole body
GnRH is released into a local capillary network at the base of the hypothalamus.
This is called the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system.
Why this exists:
GnRH would be diluted and broken down if released into general circulation.
The portal system delivers GnRH directly and efficiently to the pituitary.
3) GnRH reaches the anterior pituitary
GnRH travels down the infundibulum (the pituitary stalk).
It reaches the anterior pituitary only.
It binds GnRH receptors on gonadotroph cells.
Key cell to remember:
Gonadotrophs = LH + FSH producers
4) Pituitary response
Gonadotroph cells release:
LH
FSH
These are released into normal bloodstream.
5) LH and FSH go to the gonads
LH and FSH travel via circulation to:
Testes or ovaries
They stimulate:
Sex steroid production
Gamete production
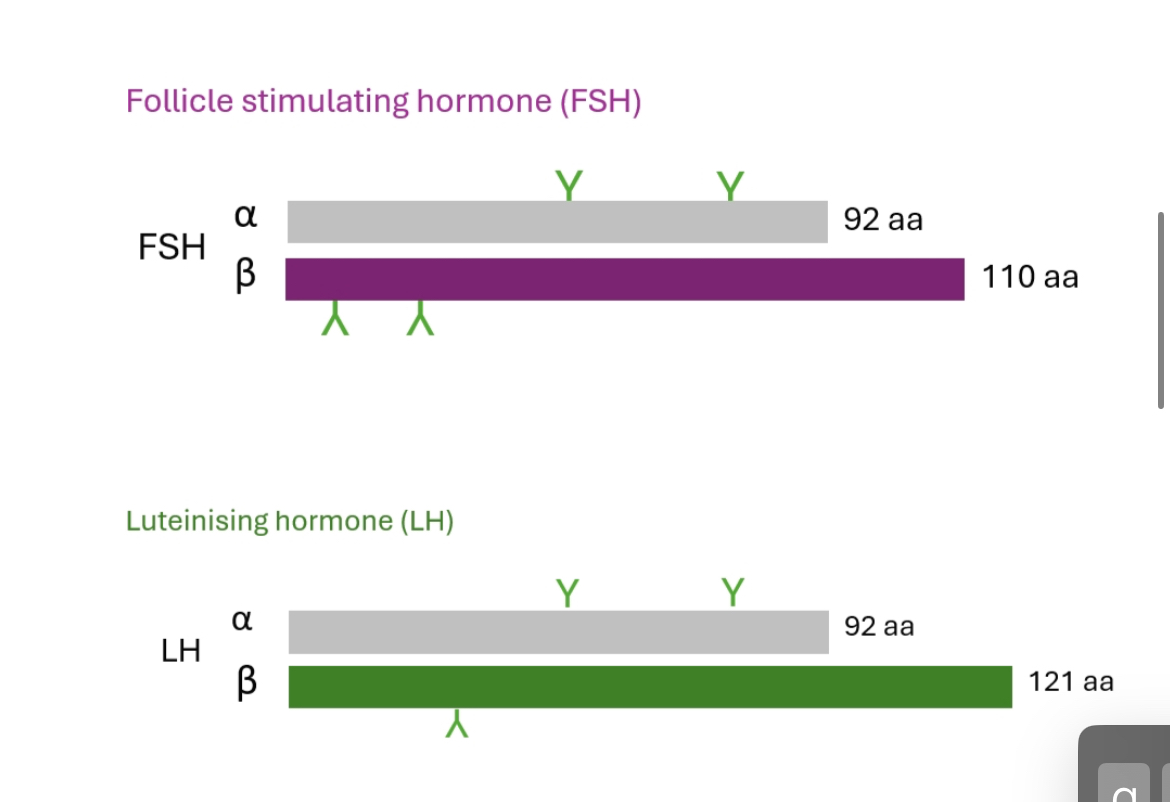
Gonadotrophin hormones
Heterodimeric glycoproteins with shared α-subunit but different b subunits
LH: steroidogenesis (ovulation/testosterone)
FSH: follicle growth/testicular Sertoli cell activation → gametogenesis.
Pulse frequency dictates hormonal outcome:
Slow pulses → ↑ FSH
Rapid pulses → ↑ LH
Mechanism: Differential β-subunit gene transcription.
Puberty
Puberty is the transition from a non-reproductive state to a reproductive state, driven mainly by sex steroids.
A) Changes common to puberty
• Growth spurt
• Epiphyseal plate closure
• Skin changes (acne, oiliness)
• Pubic and axillary hair (androgen-dependent)
B) Male puberty (testosterone-driven)
Main hormone: Testosterone
Effects shown on the slide:
• Increased muscle mass and strength
• Shoulder broadening
• Facial and body hair
• Voice deepening (larynx growth)
• Adam’s apple prominence
• Penile and testicular growth
C) Female puberty (oestrogen-driven)
Main hormone: Oestrogen
Effects shown on the slide:
• Breast development (thelarche)
• Hip widening
• Increased subcutaneous fat
• Female pattern pubic/axillary hair
• Growth spurt followed by epiphyseal closure
• Softer skin and higher-pitched voice
How the two slides connect (this is the exam logic)
• Adrenarche explains:
• Pubic/axillary hair
• Acne
• Gonadarche explains:
• Breast development
• Voice deepening
• Muscle mass
• Fertility
You need both for normal puberty.
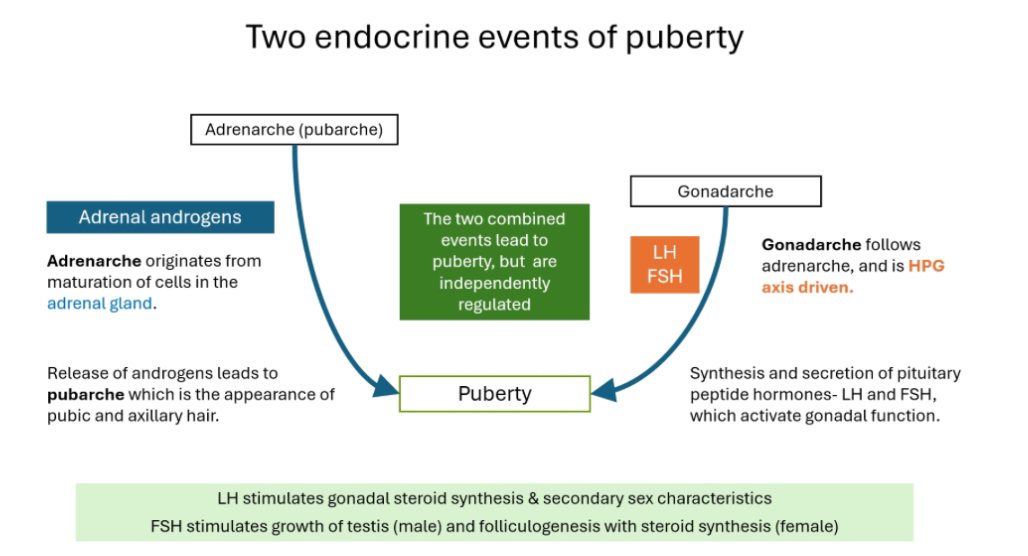
Puberty happens because two different hormone systems switch on, and they are independent but combine to produce puberty.
A) Adrenarche
What it is:
Adrenarche = maturation of the adrenal glands.
Hormones involved:
• Adrenal androgens (DHEA, DHEAS, some testosterone-like effects)
What it causes:
• Pubic hair
• Axillary hair
• Body odour
• Acne
This is called pubarche.
Important:
• Adrenarche is NOT driven by the HPG axis
• It can happen even if the gonads are not working
B) Gonadarche
What it is:
Gonadarche = activation of the HPG axis.
Hormones involved:
• GnRH (hypothalamus)
• LH and FSH (pituitary)
• Sex steroids from gonads (testosterone or oestrogen)
What it causes:
• Gonadal growth
• Sex steroid production
• Secondary sexual characteristics
• Fertility
Important:
• Gonadarche usually follows adrenarche
• It is essential for true reproductive puberty
Continuous GnRH Mechanism in Therapy
Continuous receptor binding → desensitisation → ↓ LH/FSH → ↓ gonadal steroids.
Used in precocious puberty, IVF, hormone-dependent cancers.
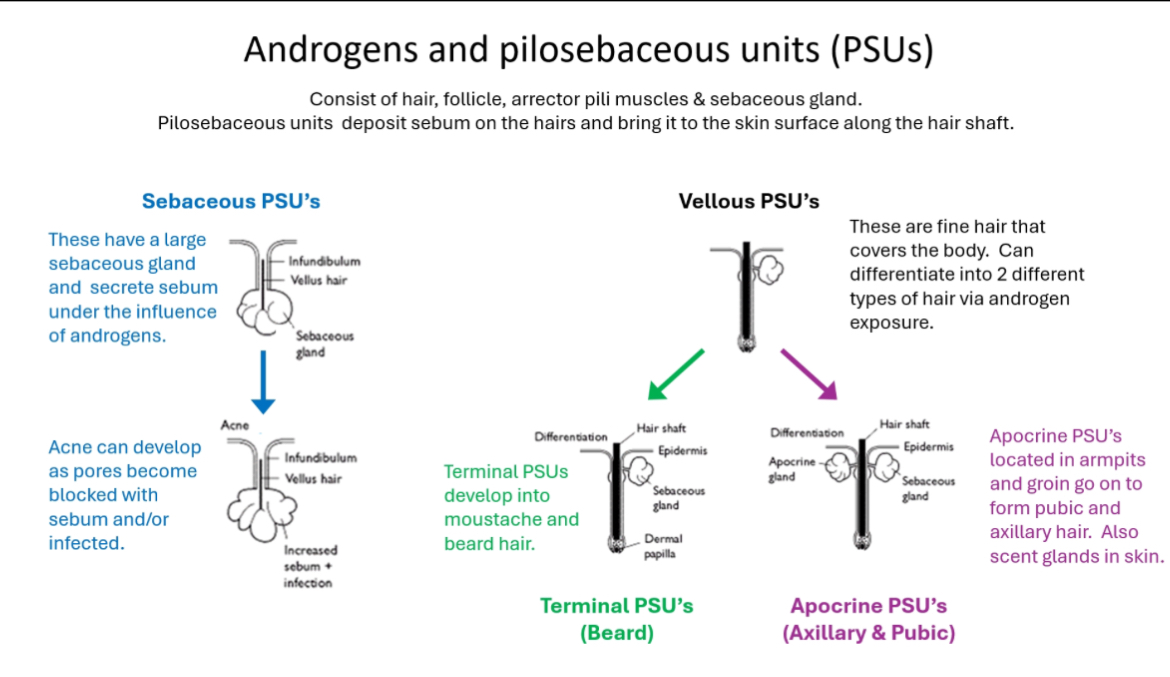
Androgens and PSUs
Androgens act on hair + skin
Androgens act on pilosebaceous units (PSUs), causing:
• Increased sebum production
• Transformation of fine hair into thicker hair
• Development of acne, pubic hair, axillary hair, and facial hair
What a pilosebaceous unit (PSU) is
A PSU is a functional skin unit made of:
• Hair follicle
• Hair shaft
• Sebaceous (oil) gland
• Arrector pili muscle
Function:
• Produces sebum
• Sebum travels along the hair shaft to the skin surface
Types of PSUs in the diagram
1) Sebaceous PSUs (acne pathway)
• Have large sebaceous glands
• Highly androgen-sensitive
• Androgens → ↑ sebum production
• Excess sebum blocks pores ± infection
Result:
• Acne
2) Vellus PSUs (starting point)
• Produce fine, soft vellus hair
• Cover most of the body
• Androgen exposure can change them
They can differentiate into:
3) Terminal PSUs (beard/facial hair)
• Under high androgen exposure
• Vellus hair → terminal hair
• Thick, coarse, pigmented hair
• Seen in:
• Beard
• Moustache
• Chest (in males)
4) Apocrine PSUs (pubic & axillary hair)
• Found in:
• Armpits
• Groin
• Under androgen influence:
• Form pubic and axillary hair
• Act as scent glands
Why this matters in puberty and disease
• Adrenarche:
• Androgens → pubic & axillary hair + acne
• CAH:
• Excess androgens → early pubic hair + acne
• AIS:
• Androgens present but receptors don’t work → reduced body hair
LH Pulses as Clinical Surrogate of GnRH Activity
We can’t measure GnRH directly, so we use LH pulses as a stand-in.
Why we can’t measure GnRH
• GnRH is released in tiny pulses
• It has an extremely short half-life (minutes)
• It travels only in the portal circulation
• It is rapidly degraded
So in blood tests, GnRH is basically invisible.
2) What GnRH does instead
• Every time the hypothalamus releases a GnRH pulse,
• The pituitary responds by releasing an LH pulse.
Important:
• This happens one-to-one.
• No GnRH pulse → no LH pulse.
3) Why LH is useful
• LH lasts longer in the blood than GnRH.
• LH enters the systemic circulation.
• We can measure LH repeatedly with blood samples.
So:
• LH pulse frequency and size reflect GnRH pulse activity.
LH pulses = surrogate marker
• GnRH activity = real driver
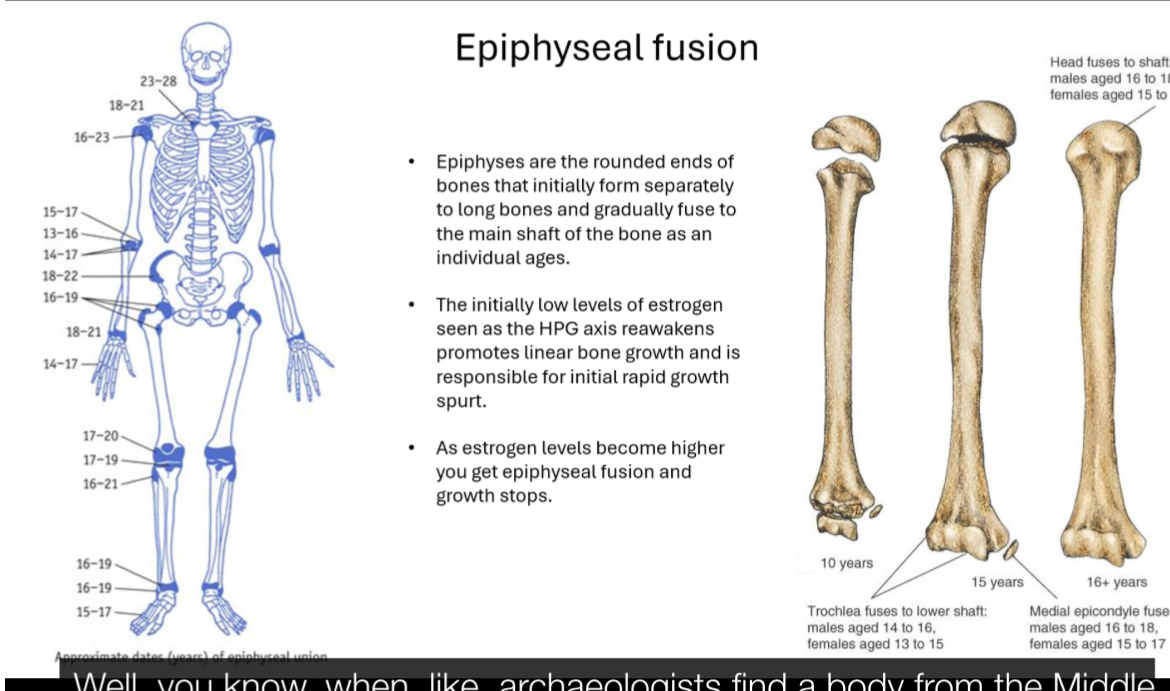
Epiphyseal fusion
Epiphyses are the rounded ends of long bones that start separate from the shaft and fuse with age.
When puberty begins, low levels of oestrogen (from reactivation of the HPG axis) stimulate rapid linear growth (growth spurt).
As puberty progresses, rising oestrogen levels cause the growth plates to close (epiphyseal fusion).
Once fusion occurs, longitudinal bone growth stops.
Fusion happens earlier in females than males, which is why females typically stop growing sooner.
Early puberty:
Adrenal androgens are noticeable (hair, acne)
Later puberty:
Gonadal steroids dominate (breasts, voice, muscle)
This is shift in visible effects, not suppression of HPA activity
Silent Period → Reactivation by Kisspeptin Increase
Fetal HPG activity → postnatal quiescence → Kisspeptin-driven reactivation.
Consonance
Puberty doesn’t always happen at the same age for everyone,
Central Precocious puberty: Precocious puberty is the onset of secondary sexual characteristics before age 8 in girls and before age 9 in boys, due to EARLY activation of pubertal hormone pathways.
Peripheral Precocious puberty:
Cause: Sex steroids produced independently of the HPG axis
Sources:
Adrenal (e.g. CAH)
Ovarian/testicular tumours
Exogenous hormones
Features:
Abnormal or incomplete pubertal sequence
LH/FSH are low
What “consonance” means
Pubertal changes occur in a smooth, ordered sequence.
One change does not skip ahead of another.
A child may start earlier or later, or progress faster or slower, but the sequence stays the same.
Think: same order, different clocks.
Boys: typical order of changes
Growth of testes and scrotum (first true sign of puberty)
Penile lengthening
Pubic hair growth
Growth spurt
Voice deepening
Change in body shape (more muscle, broader shoulders)
Underarm and facial hair
Key point:
Testicular enlargement always comes first
Facial hair comes late, never early
Girls: typical order of changes
Breast budding (thelarche) – first sign
Pubic hair growth
Growth spurt
First period (menarche) – occurs after the growth spurt
Underarm hair growth
Change in body shape (hips widen, fat redistribution)
Adult breast size
Key point:
Menarche is not the start of puberty
It happens after several other changes
Why this matters clinically
If the order is abnormal, think pathology (e.g. precocious puberty, endocrine disorders).
If the order is normal but timing is early/late, this can still be normal variation.
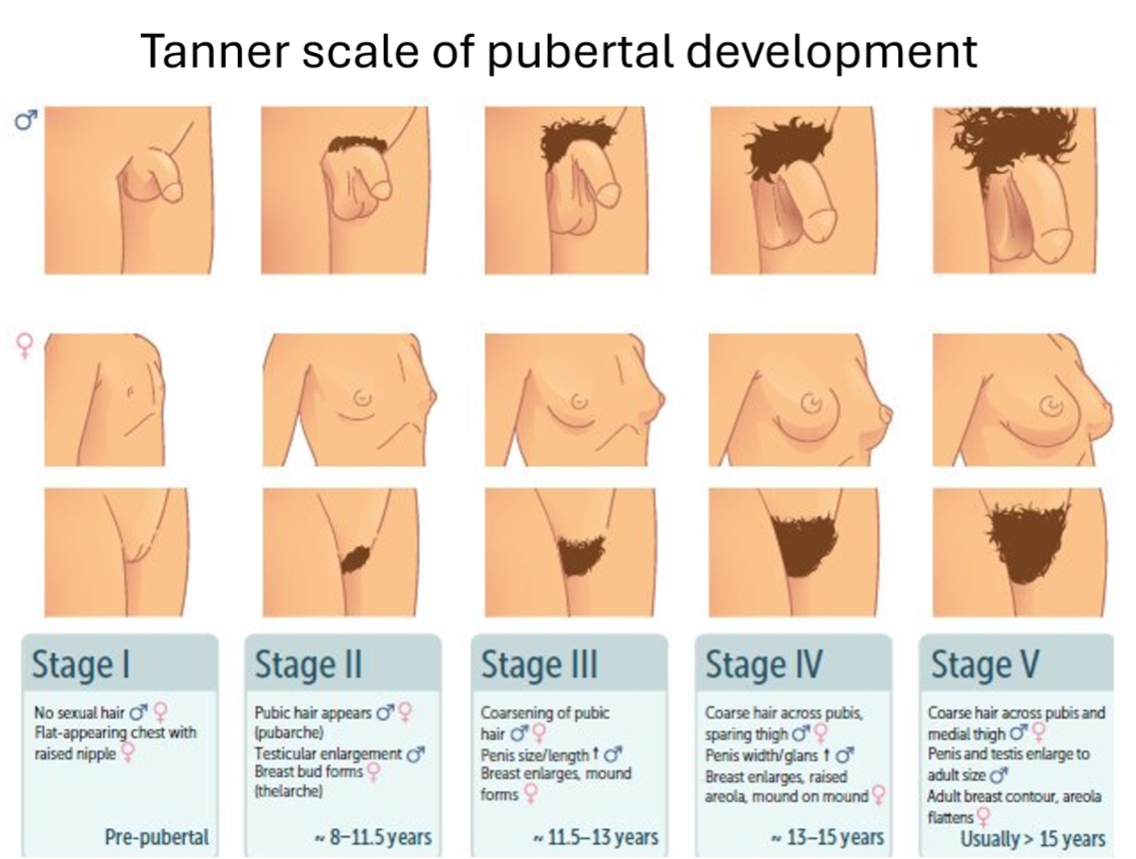
Tanner scale of pubertal development
The Tanner scale is a clinical staging system (Stages I–V) used to describe physical pubertal development, based on external genitalia/breast development and pubic hair, not age.
Stage I: Pre-pubertal
Stage II: Puberty begins
Stage III: Progressive pubertal development
Stage IV: Advanced pubertal development
Stage V: Adult sexual maturity
GnRH Pulse Maturation: Night-time to Circadian Pattern
In puberty → mostly nocturnal; adulthood → daytime pulses stable.
Gonadal Steroidogenesis & Gamete Maturity
FSH: Sertoli/granulosa → gamete development
LH: Leydig/theca → steroid output
Final output: fertility capacity.
Metabolic Regulation: Leptin
Threshold for Puberty Initiation
Body fat ~17–18 percent required to trigger; ~22 percent to maintain cycles.
Leptin → stimulates Kisspeptin → activates GnRH.
Environmental/Nutritional Influences
Higher nutrition → earlier puberty
Anorexia/chronic illness → delayed puberty.
Psychosocial Development During Puberty
Autonomy, sexual awareness, identity consolidation; risk-taking increases.
Central (GnRH-Dependent) Precocious Puberty Mechanism
↑ GnRH pulses → ↑ LH/FSH → ↑ sex steroids.
Consonance preserved; bone age advanced.
Treatment: continuous GnRH analogues.
Peripheral (GnRH-Independent) Precocious Puberty Mechanism
Sex steroids ↑ despite suppressed LH/FSH.
Loss of consonance → discordant development.
Examples: Testotoxicosis & McCune-Albright Syndrome
Testotoxicosis: constitutive LH receptor activation → Leydig steroidogenesis
McCune-Albright: activating cAMP pathway → autonomous hormone synthesis
Delayed Puberty Diagnostic Criteria
Girls: no secondary sex characteristics by 13, no menarche by 18
Boys: no testicular enlargement by 14
Pubertal delay
What “pubertal delay” means
Definition:
Boys: no secondary sexual characteristics by 14 years
Girls: no secondary sexual characteristics by 13 years, or no menarche by 18 years
Causes of pubertal delay (3 main groups)
1) Constitutional delay
(most common)
What it is:
A normal variant — puberty happens late but normally.
Key features:
Affects growth and puberty
~90% of pubertal delay cases
Much more common in boys
Often familial
Can be worsened by chronic illness (e.g. diabetes, cystic fibrosis)
Hormones:
HPG axis intact, just late to activate
Outcome:
Normal adult height and sexual development
2) Hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism
(Low LH and FSH)
Problem location:
Hypothalamus or pituitary
Mechanism:
GnRH or gonadotrophin deficiency → gonads not stimulated
Causes:
Kallmann syndrome (failed GnRH neuron migration)
Hypopituitarism
Long-term opioid or glucocorticoid use
Other genetic causes
Hormones:
Low LH/FSH
Low sex steroids
3)
Hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism
(High LH and FSH)
Problem location:
Gonads themselves
Mechanism:
Gonads fail → low sex steroids
Loss of negative feedback → high LH/FSH
Causes:
Gonadal dysgenesis
Turner syndrome (XO)
Klinefelter syndrome (XXY)
Acquired gonadal damage (e.g. mumps)
Hormones:
High LH/FSH
Low sex steroids