Anatomy & Physiology I - Exam 1
1/241
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
242 Terms
What are the 5 components of the skeletal system?
Bone tissue, cartilage, blood, dense connective tissue, nervous tissue
How many named bones are in the skeleton?
206
The axial skeleton consists of
Skull, vertebral column, rib cage (thoracic cage)
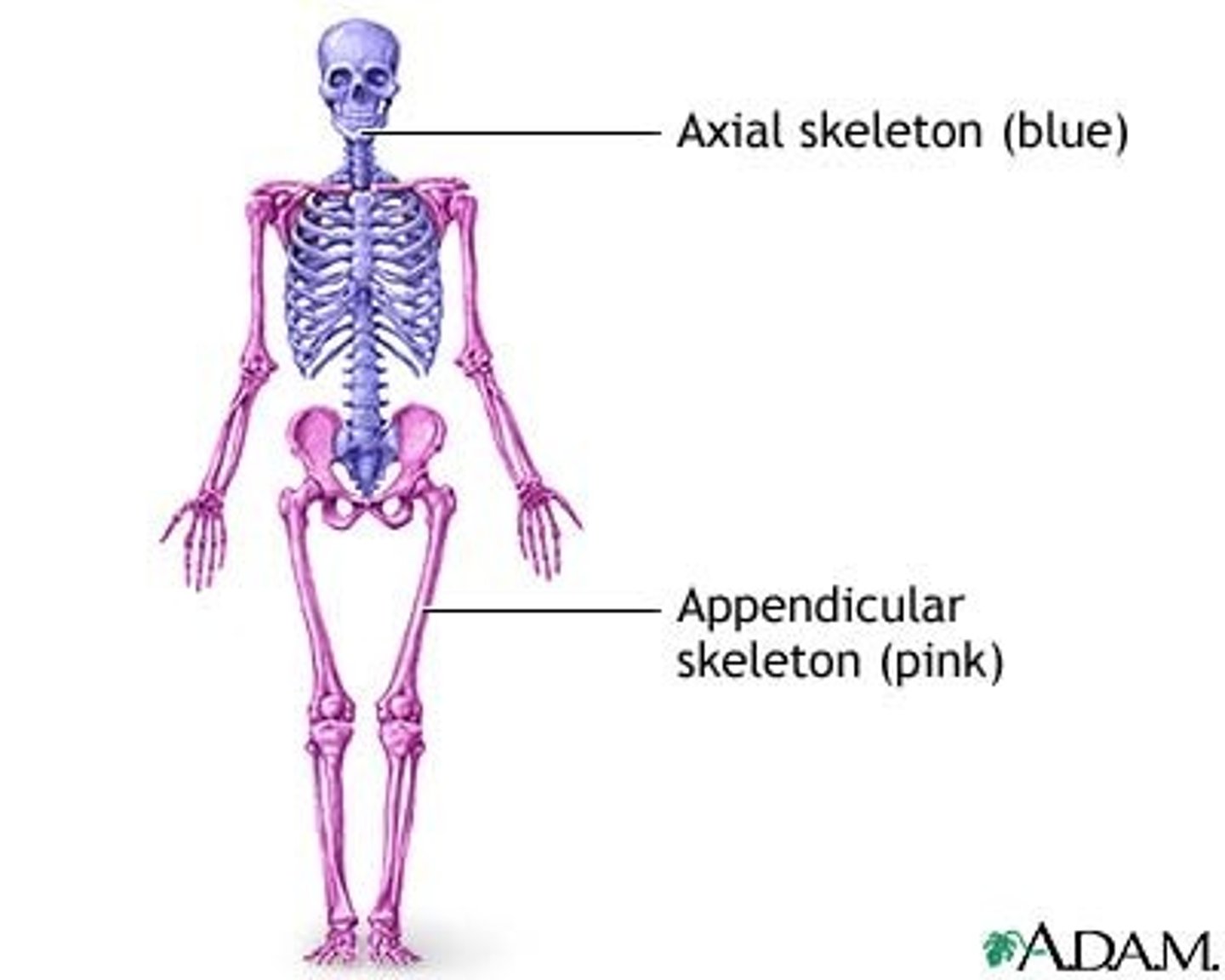
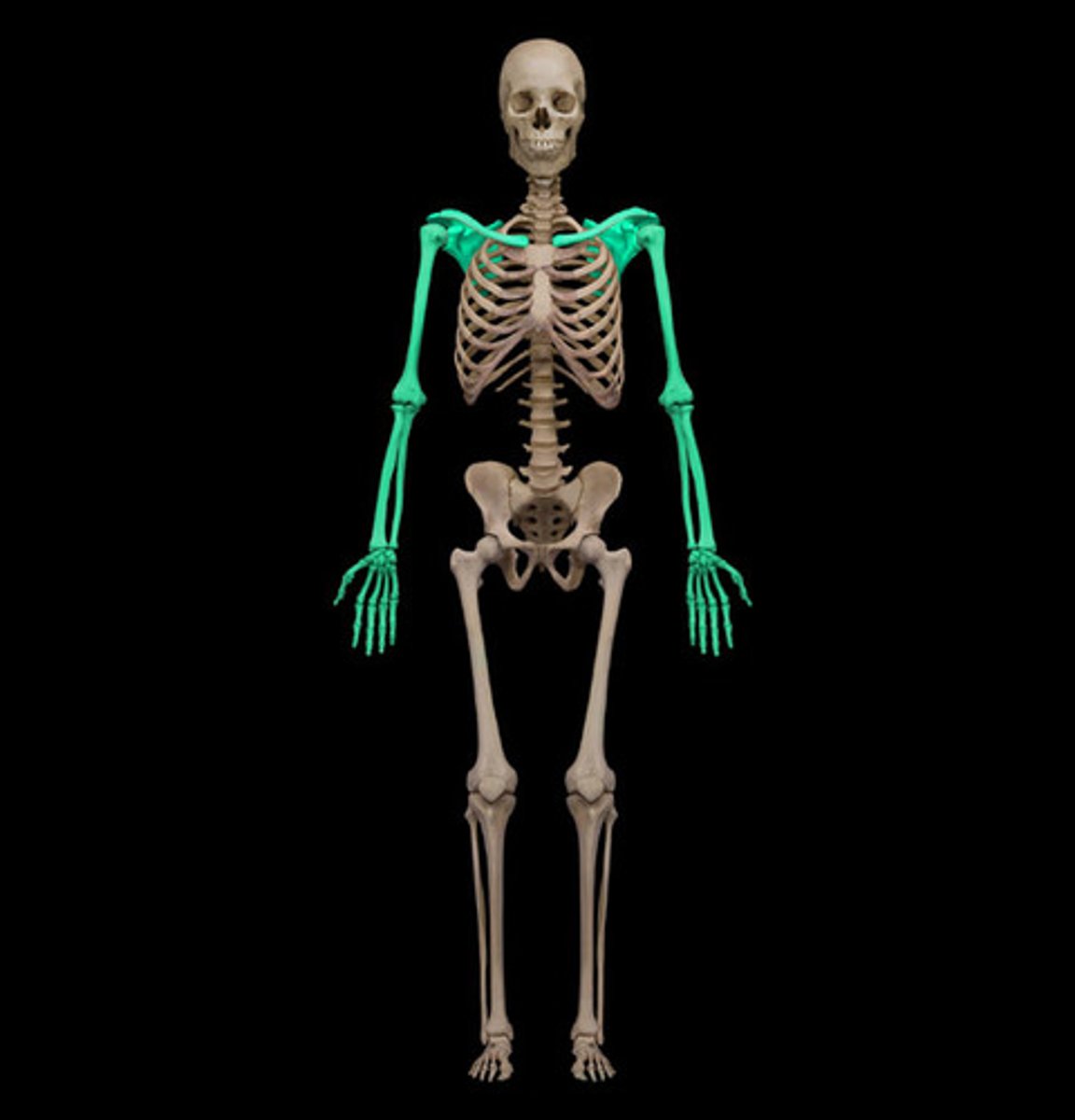
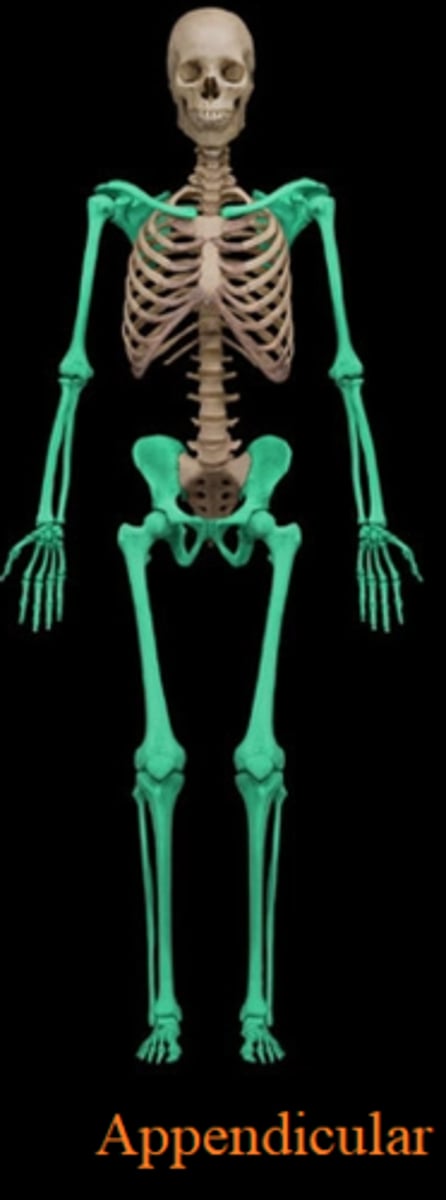
The appendicular skeleton consists of
Pectoral girdle, pelvic girdle, upper and lower limbs
Bone shapes
Flat, irregular, short, long, sutural (wormian), sesamoid (round)
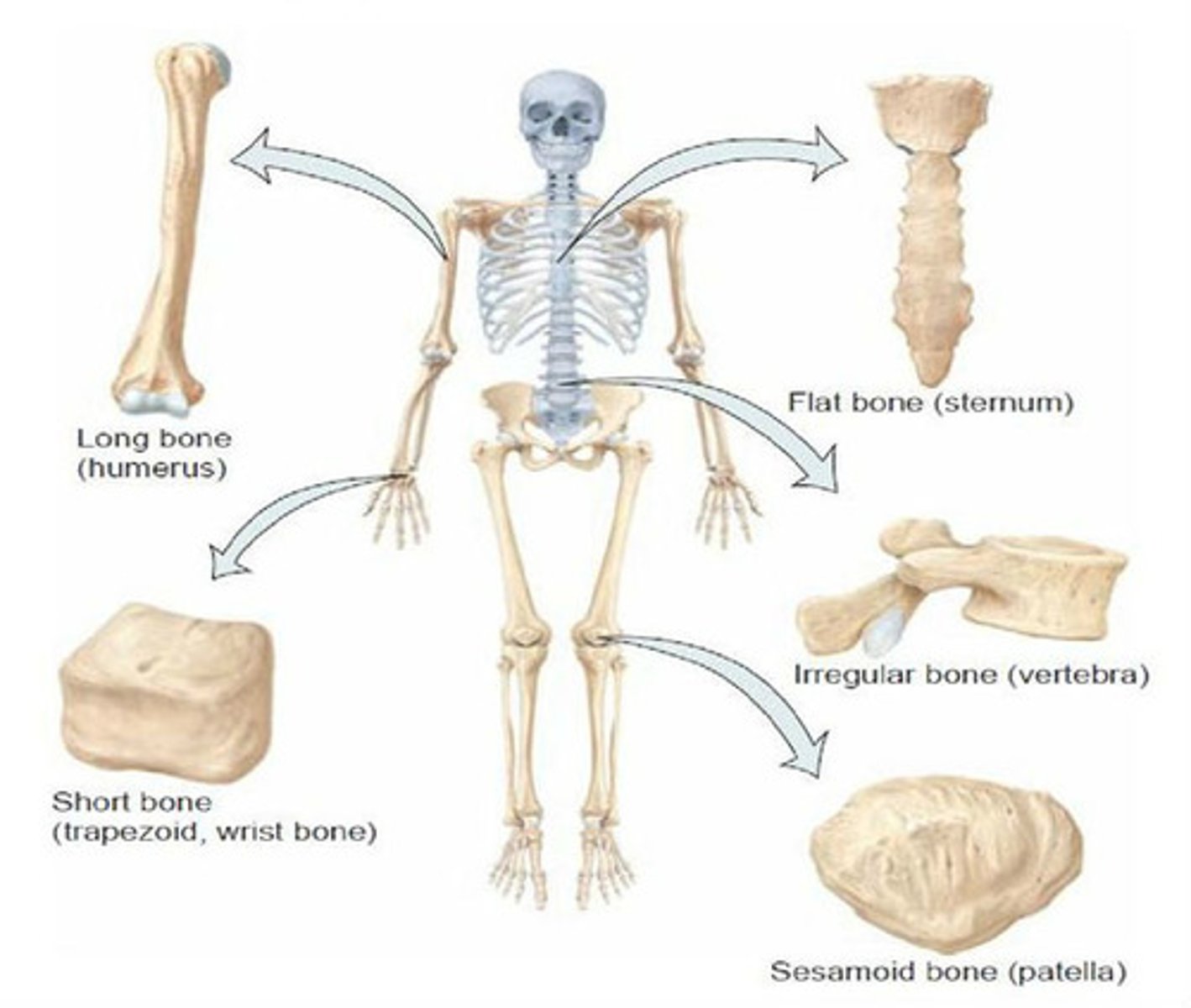
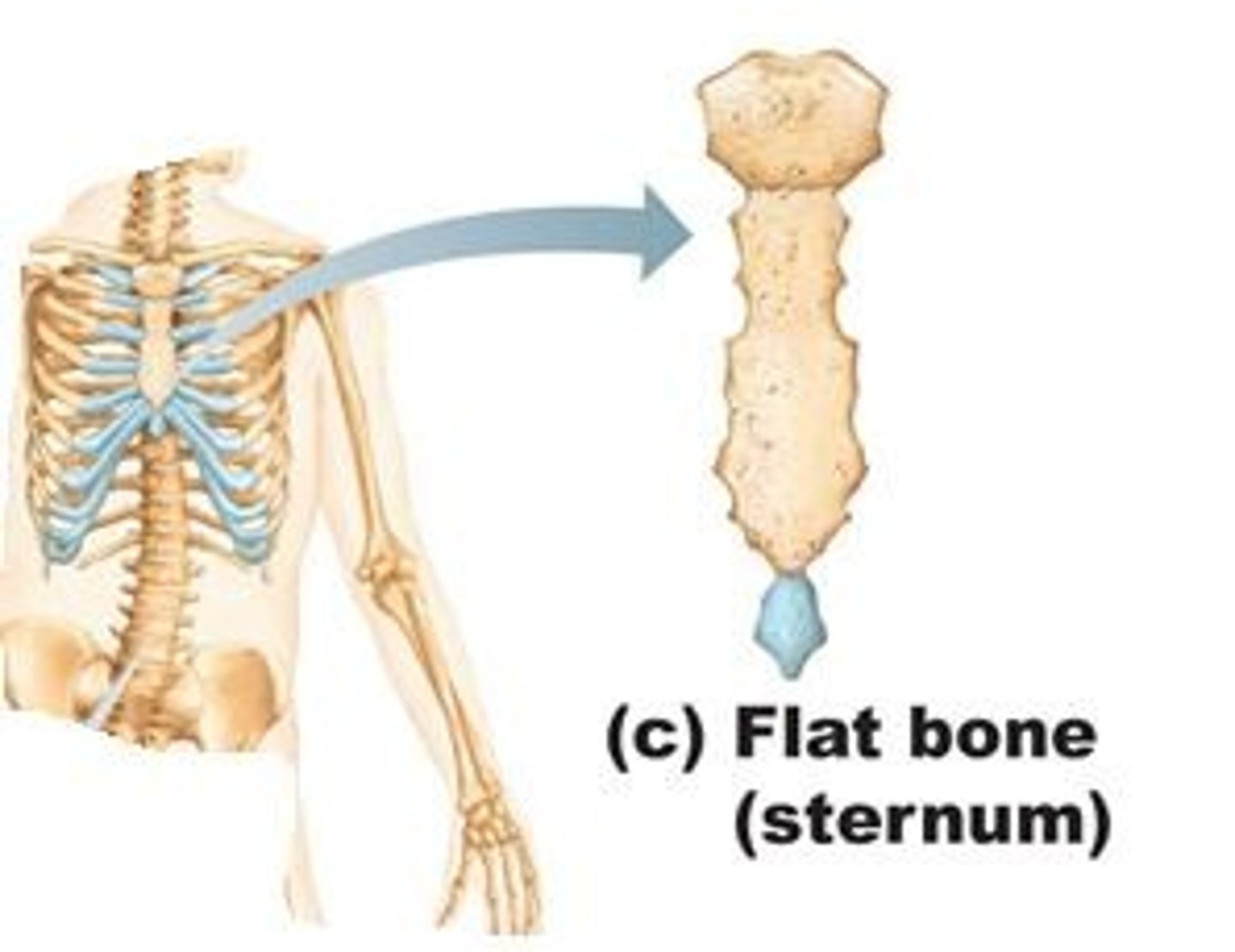
Flat bones
Ribs, shoulder bones, some skull bones
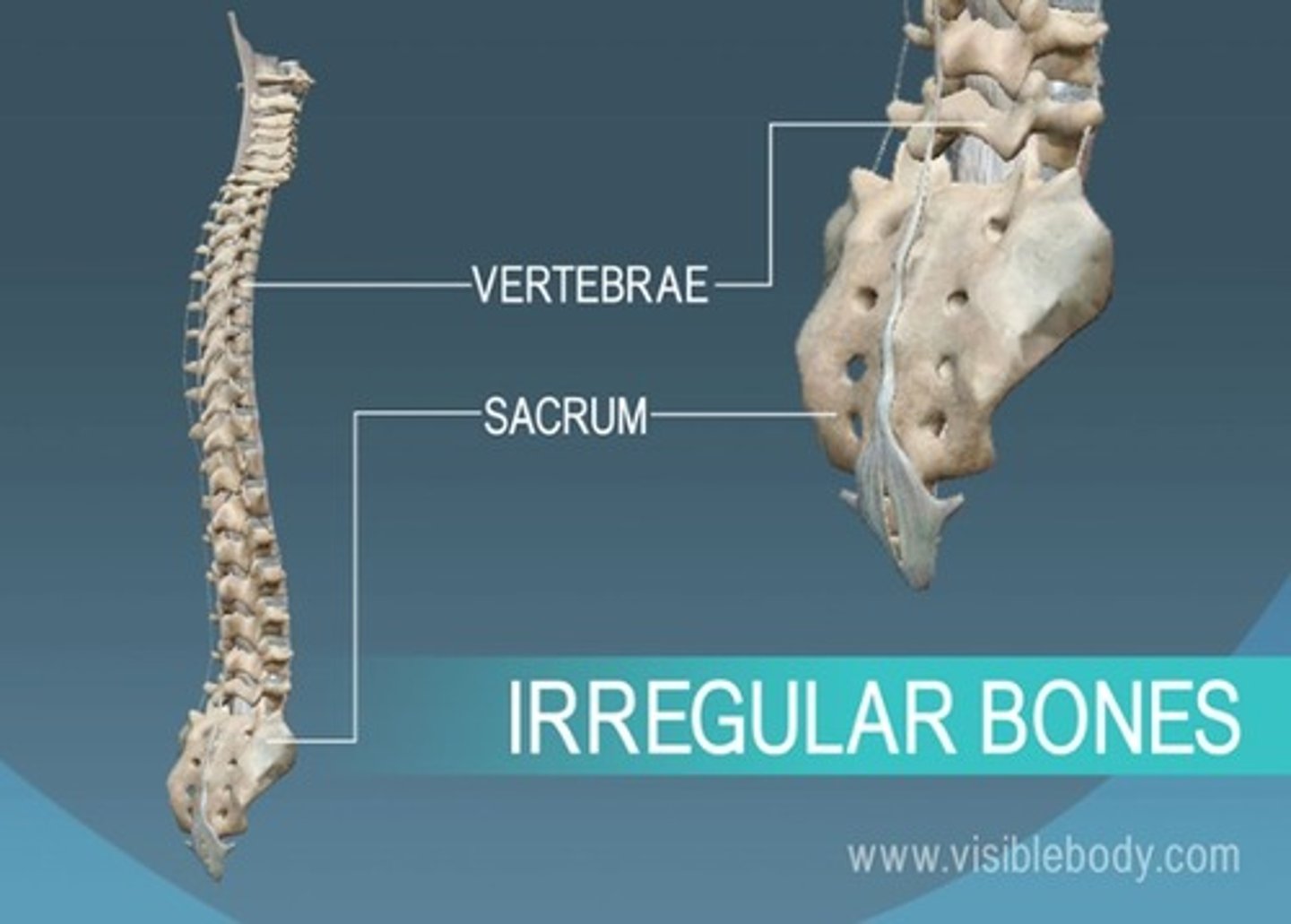
Irregular bones
Many facial bones, spinal/pelvic vertebrae
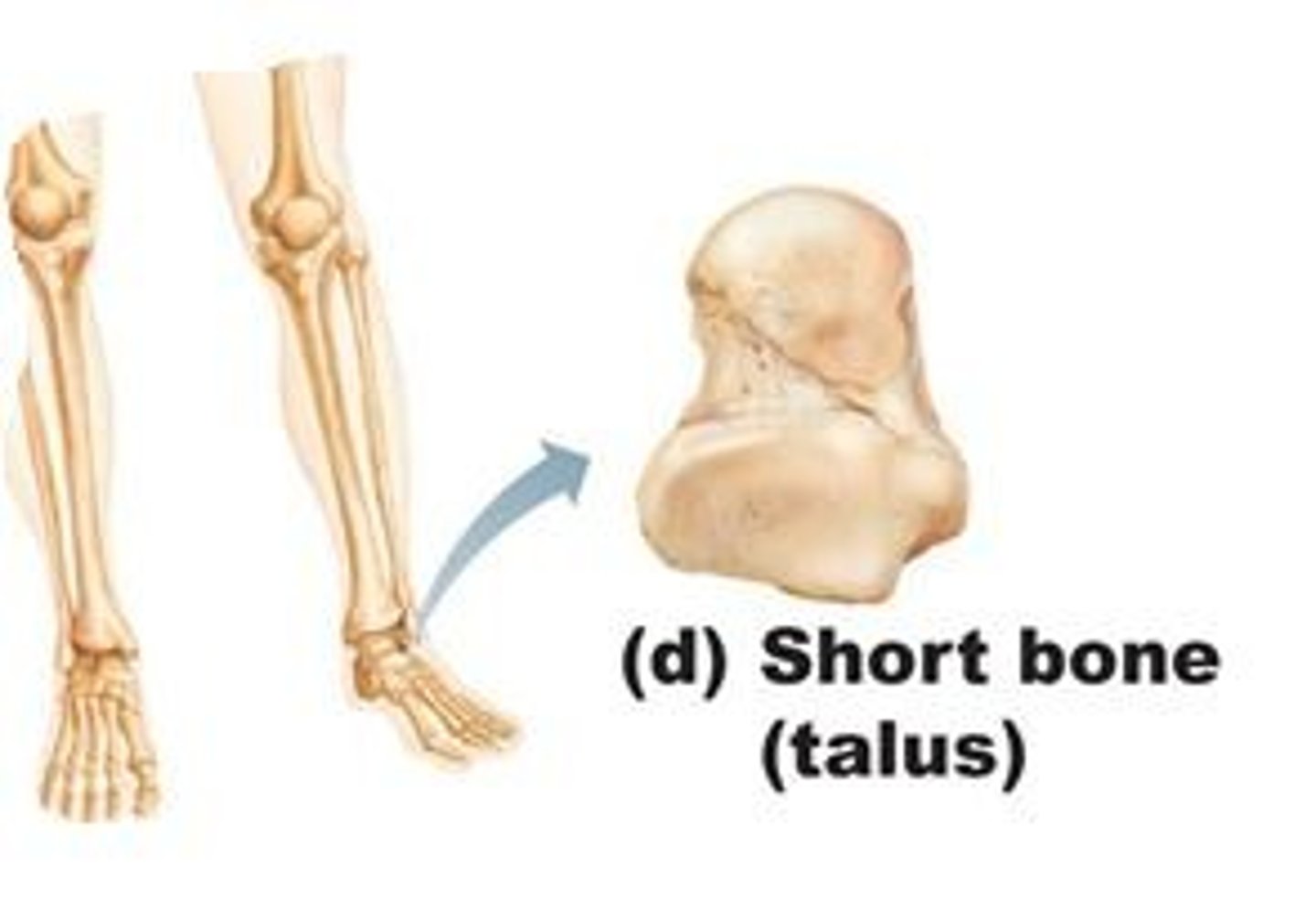
Short bones
Wrist and ankle bones
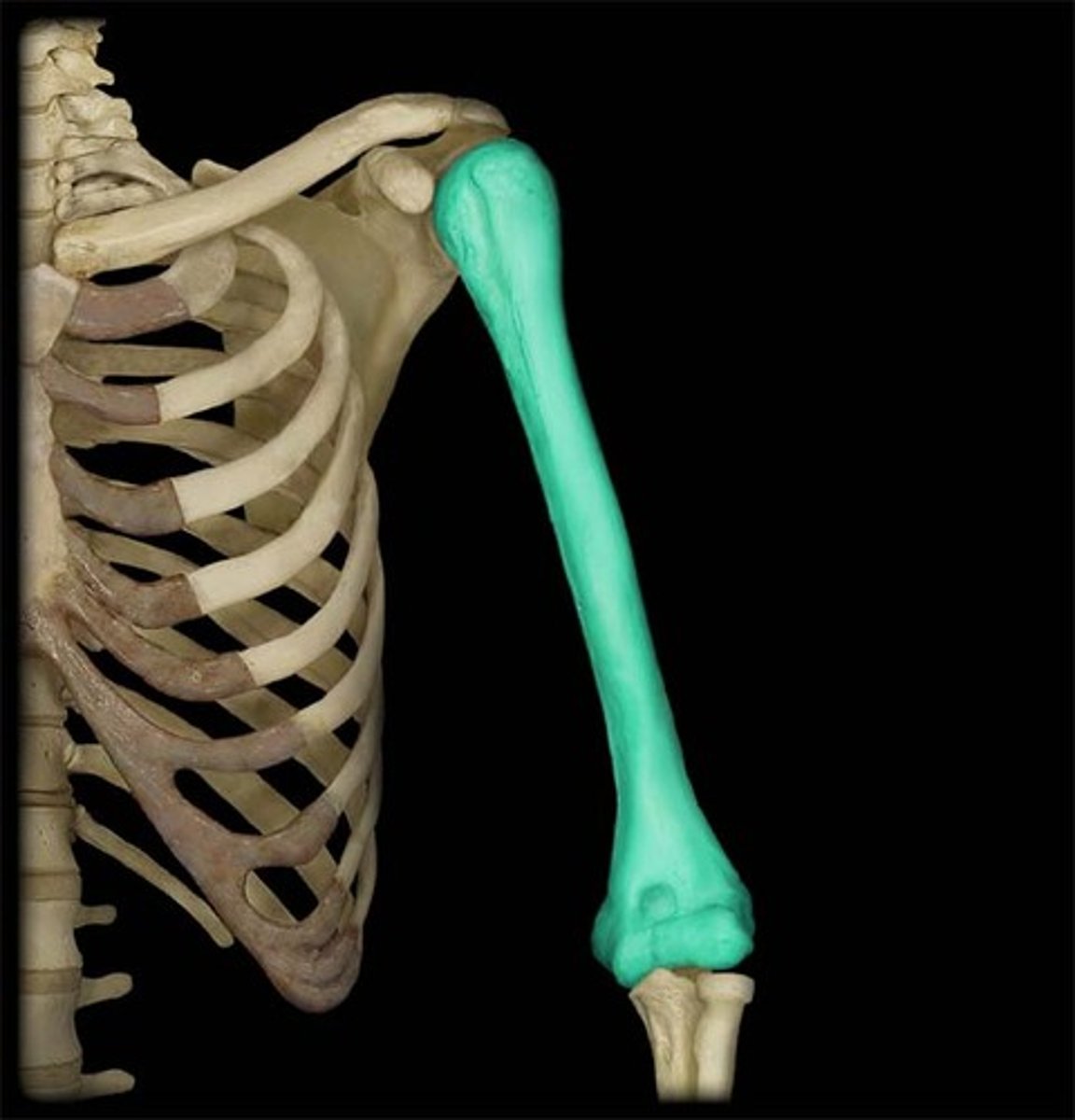
Long bones
Arm, forearm, thigh, leg, palms, soles, fingers, toes
Sutural (wormian) bones
Between flat skull bones
Sesamoid (round) bones
Inside tendons near joints in the knees, hands, and feet
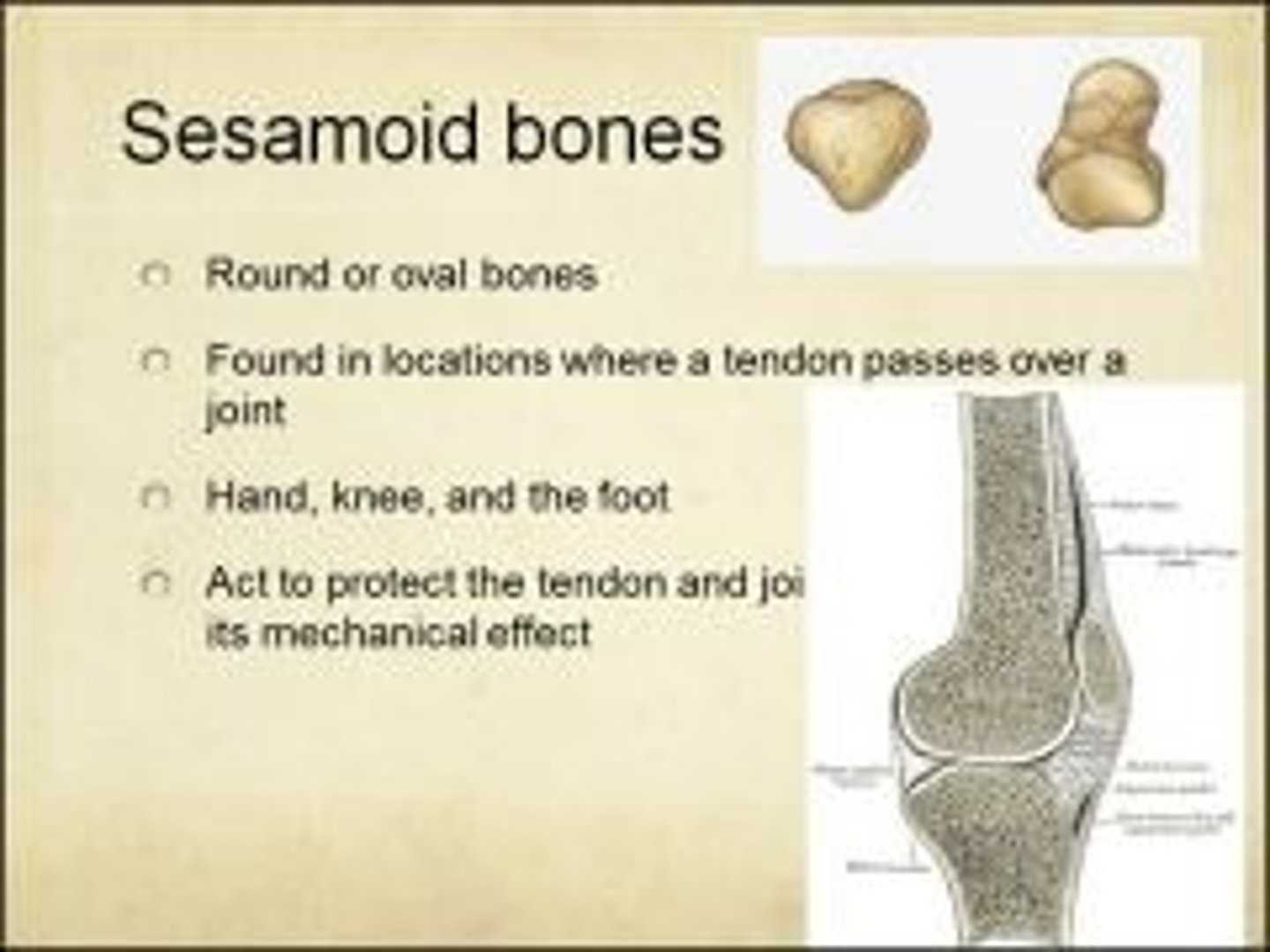
Structures of bones
Dominated by osseous (bony tissue)
Bone structure contains
Nervous tissue, cartilage, fibrous connective tissue
Compact bone
Dense outer layer; solid; contains central space and marrow cavity; layer lining endosteum filled by soft marrow
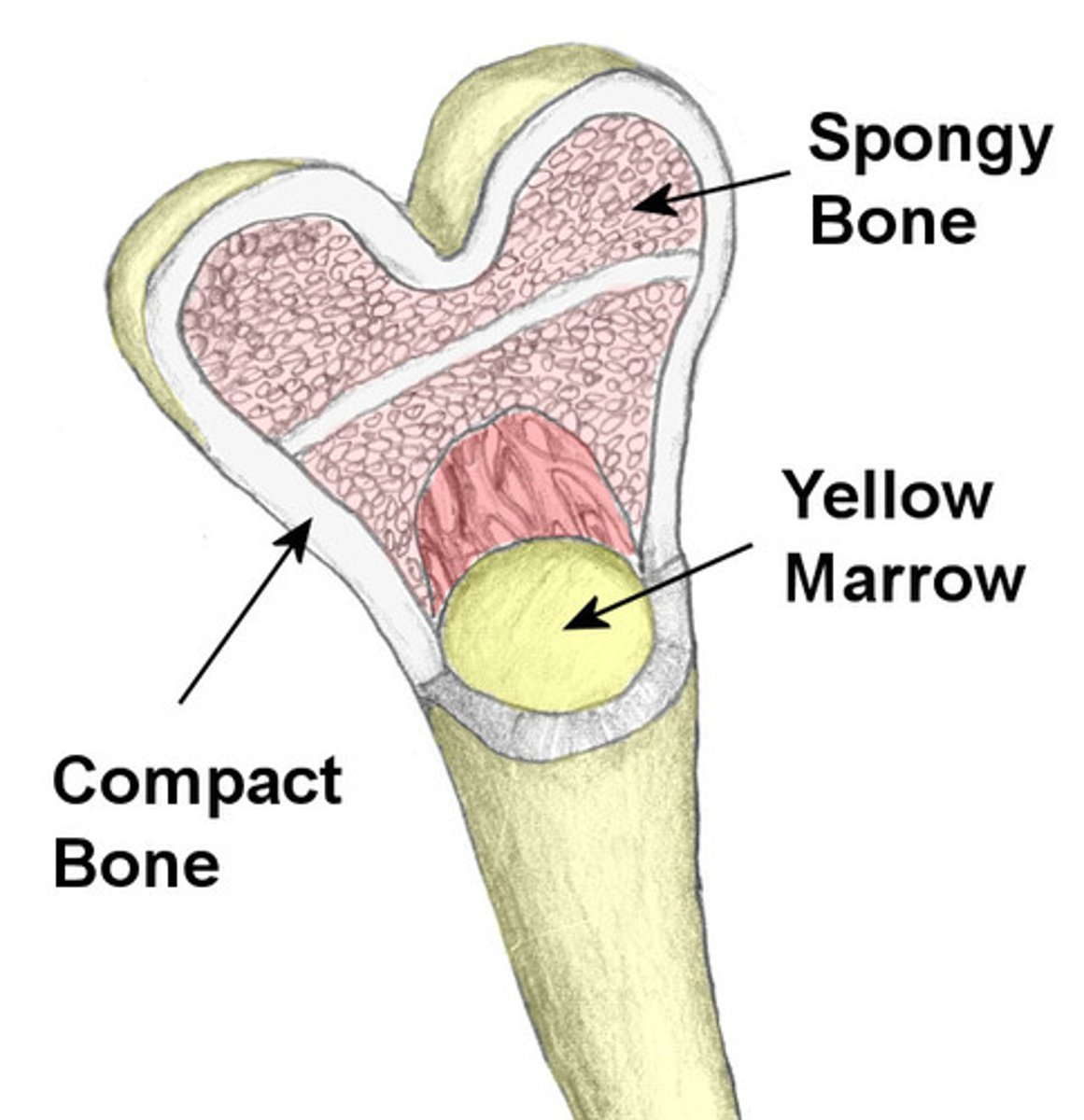
Spongy bone
Needle-like pieces called trabeculae; porous
Diaphysis
Connected to epiphysis; walls of compact or dense bone
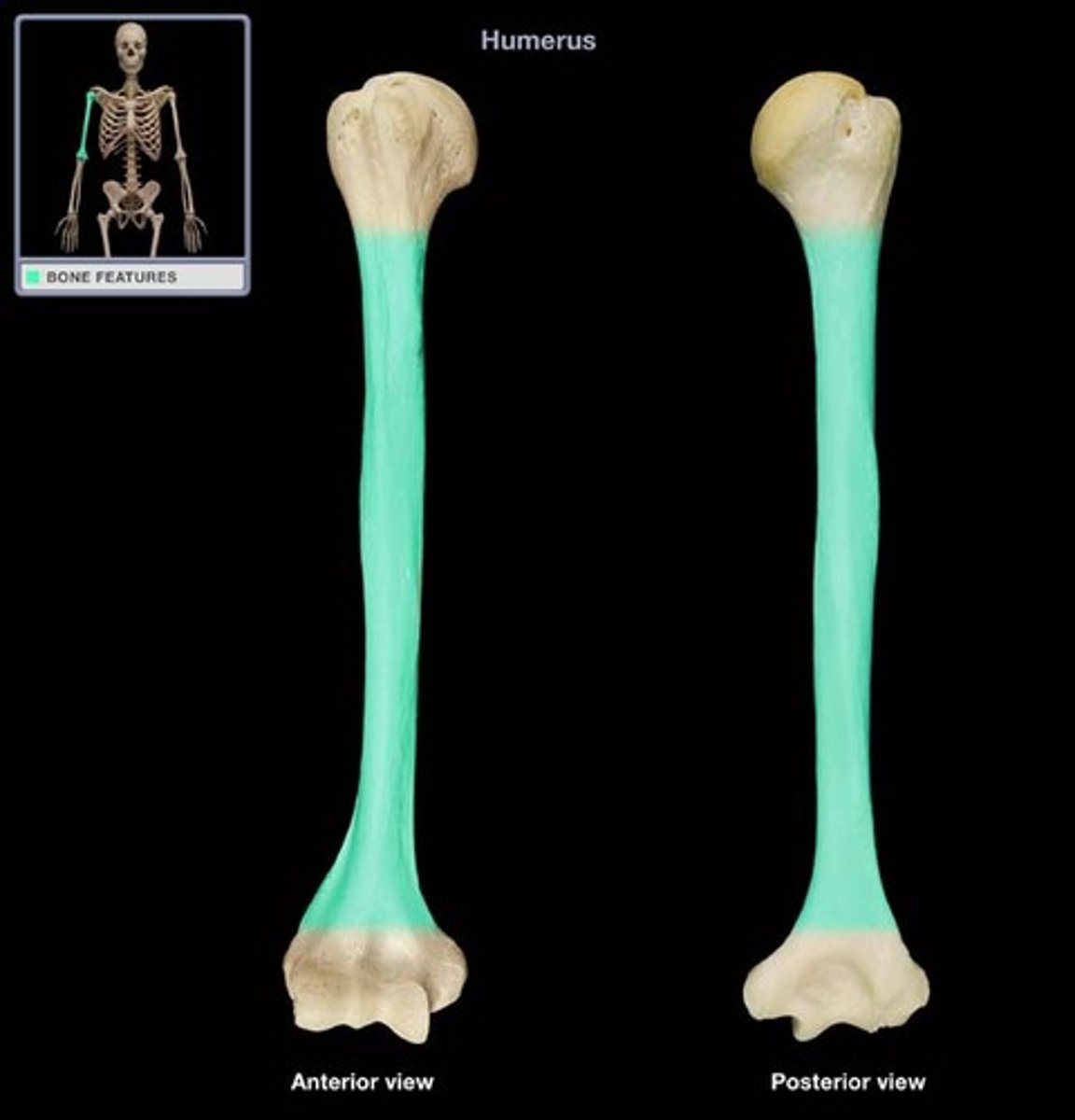
Diaphysis forms a tube with hollow what?
Medullary cavity
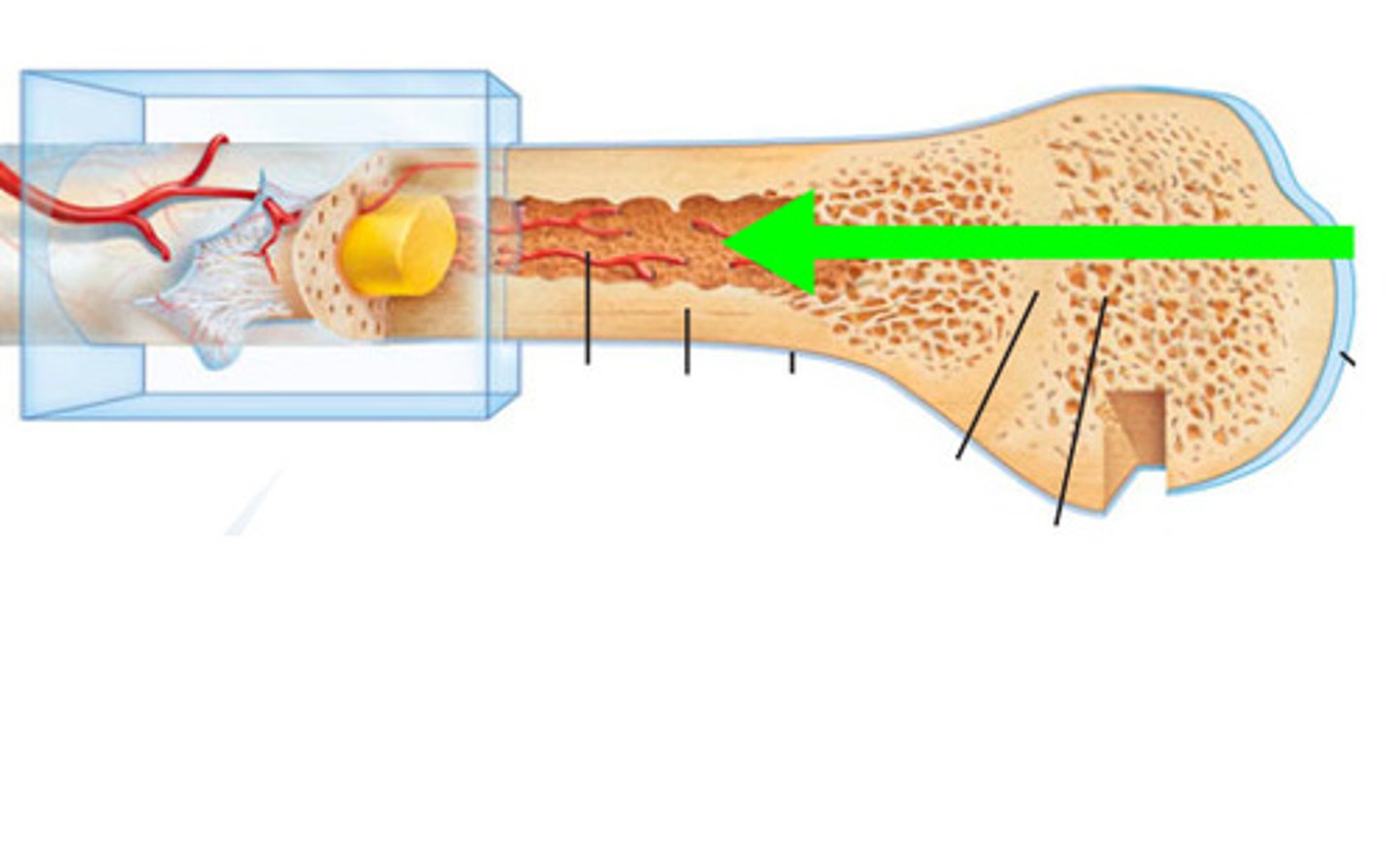
All bones are covered by what?
Superficial periosteum
Bony processes
Where ligaments and tendons can attach
Bone markings
Depressions, projections, openings, where ligaments, muscles, tendons attach, or may occur at joint surfaces (7 types)
Fissures
Narrow, slit like openings
Fossae
Deeper depression; articular surface
Foramina
Oval or round opening through the bones
Meatuses
Passageways that resemble canals
Grooves
Shallow depressions
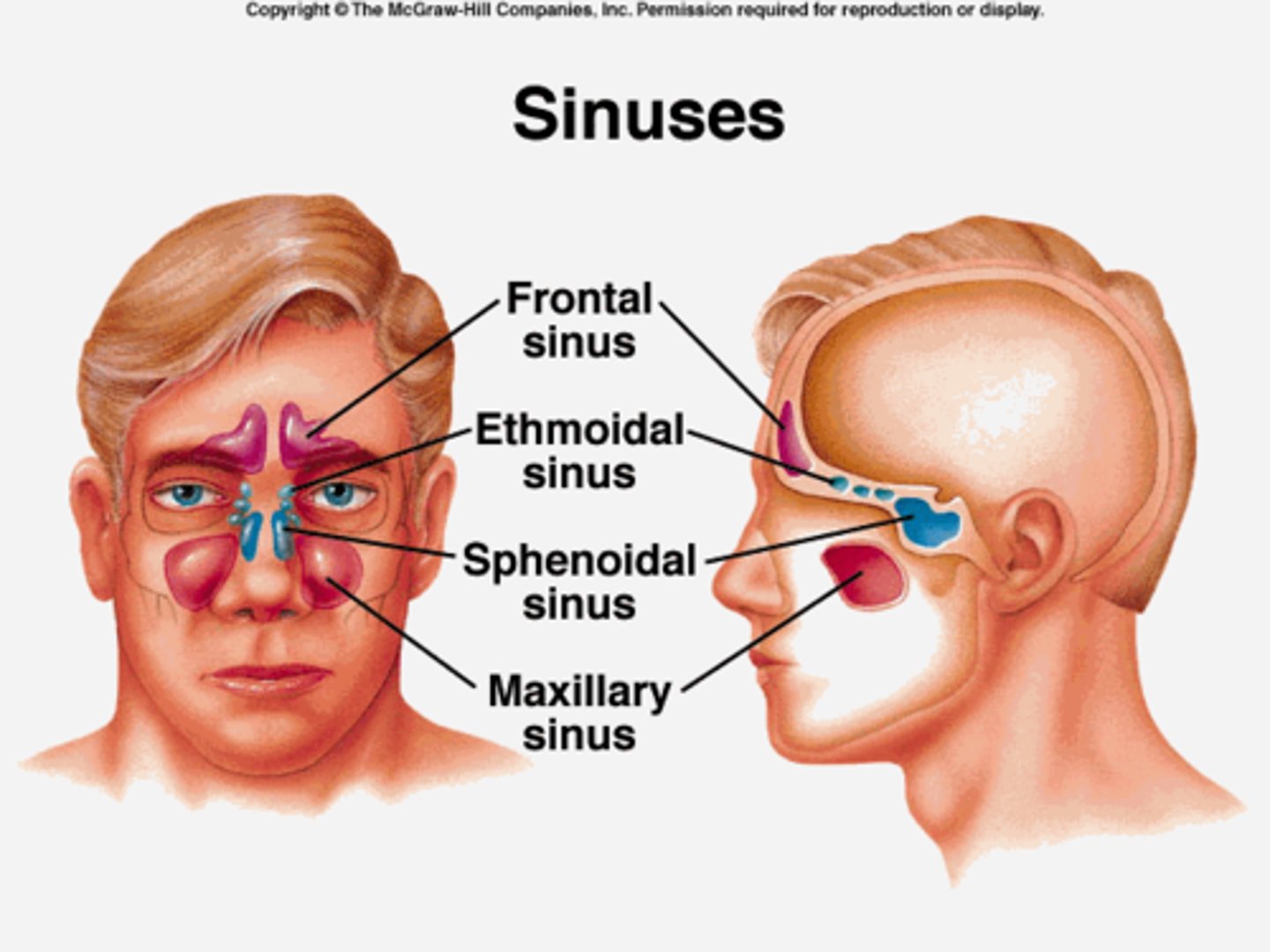
Sinuses
Air filled cavities
Notches
Indentations at edges of structures
Bone projections
Allow for the passage of nerves and blood vessels, and where muscles and ligaments attach OR help to form joints
Crests
Narrow, prominent ridges
Spines
Pointed, sharp, slender
Epicondyles
Raised areas on or above condyles
Trochanter
Large, blunt (only on femurs)
Lines
Narrow ridges, not as prominent
Tubercles
Small, rounded
Processes
Bony prominences
Tuberosities
Large, rounded; may be rough
Condyles
Rounded, articular
Facets
Smooth, almost flat, articular
Heads
Expansions on narrow necks
Rami
Arm-like bars
Microscopic anatomy of bone cells
Includes five different types
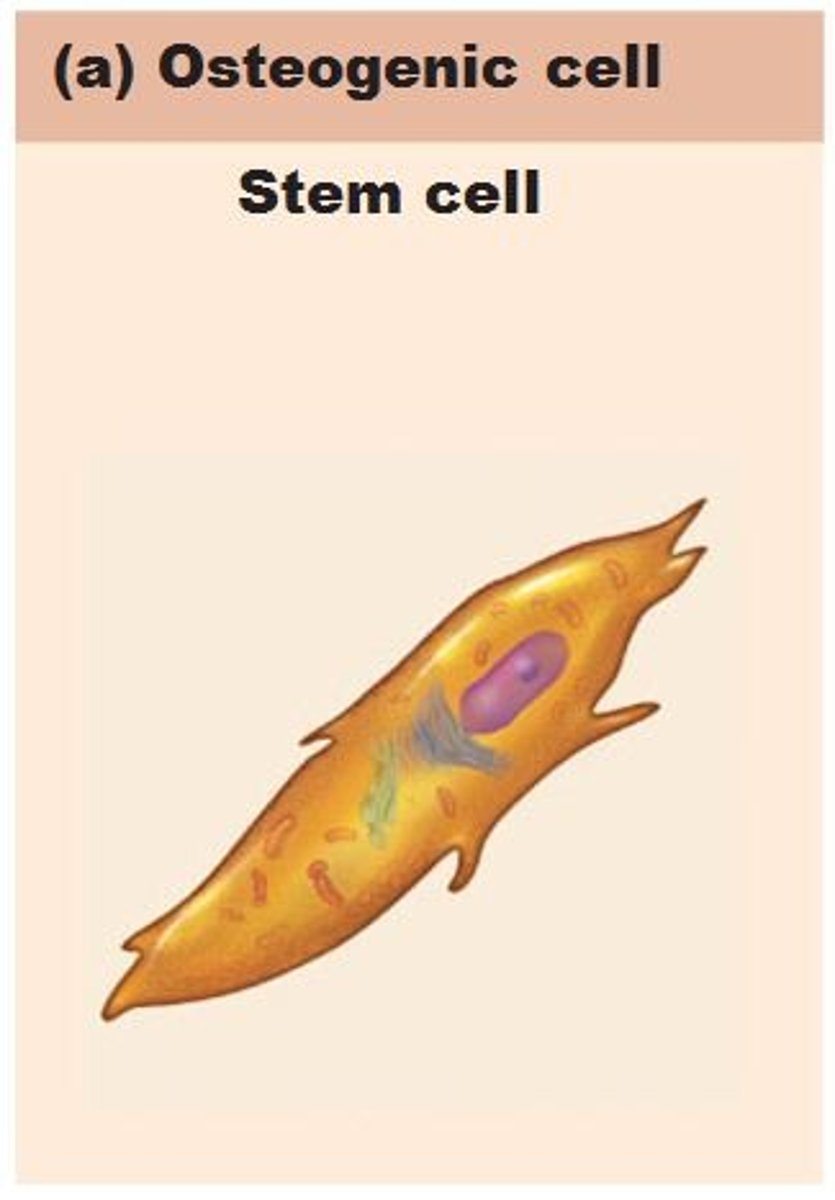
Osteogenic cells
Active stem cells that may differentiate into osteoblasts or bone lining cells
Osteoblasts
Produce bone matrix; related to osteoprogenitor cells and osteocytes
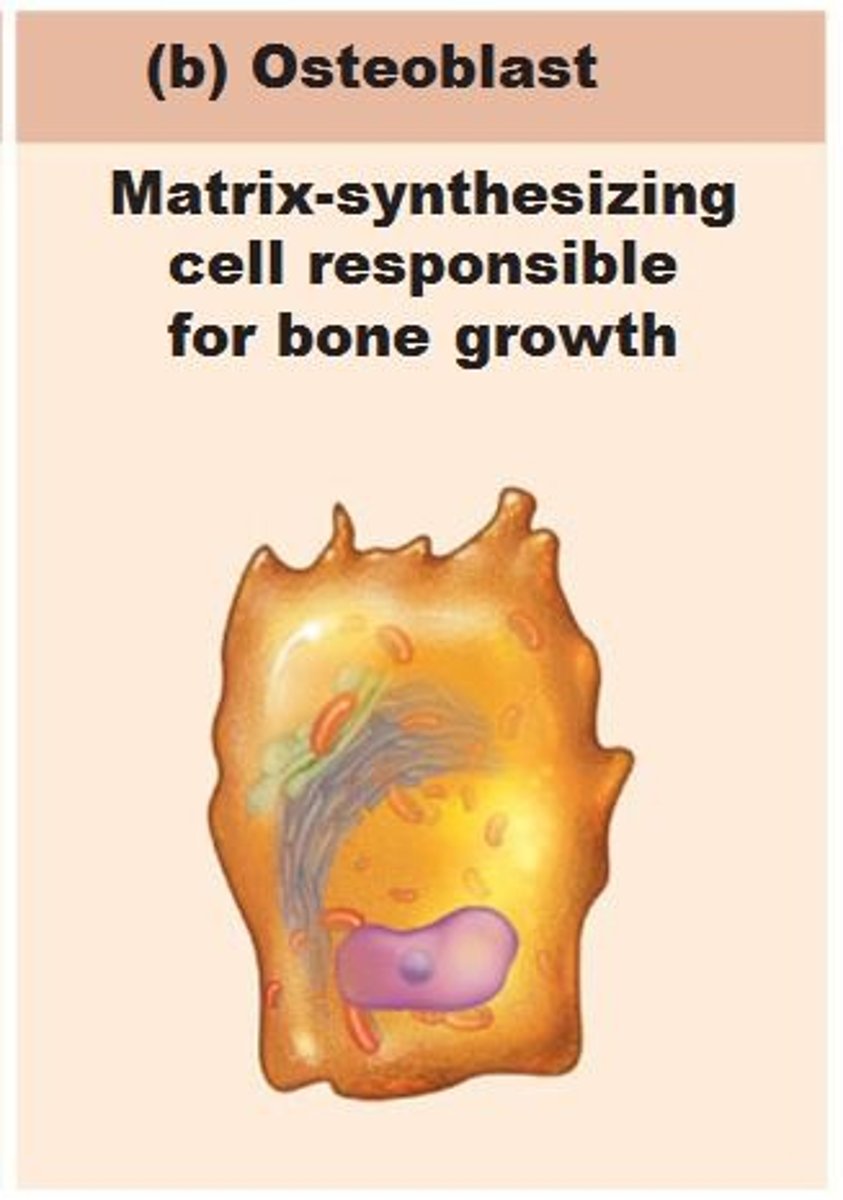
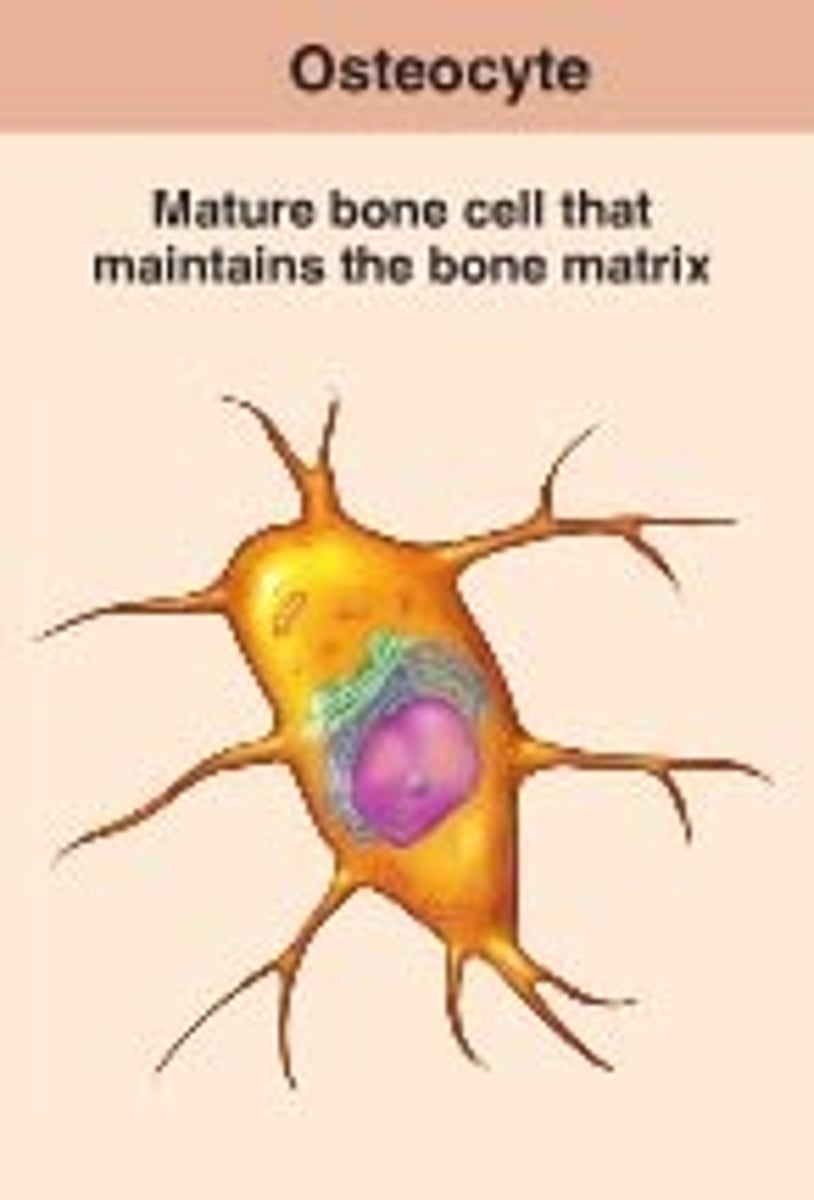
Osteocytes
Mature osteoblasts in the bone matrix
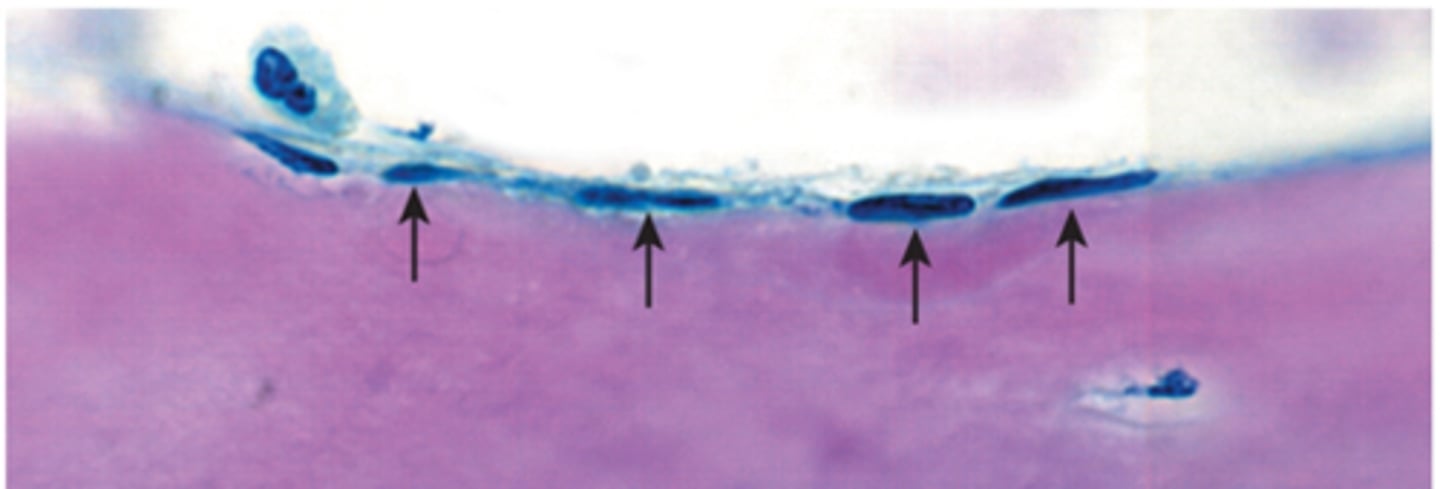
Bone lining cells
Help maintain bone matrix
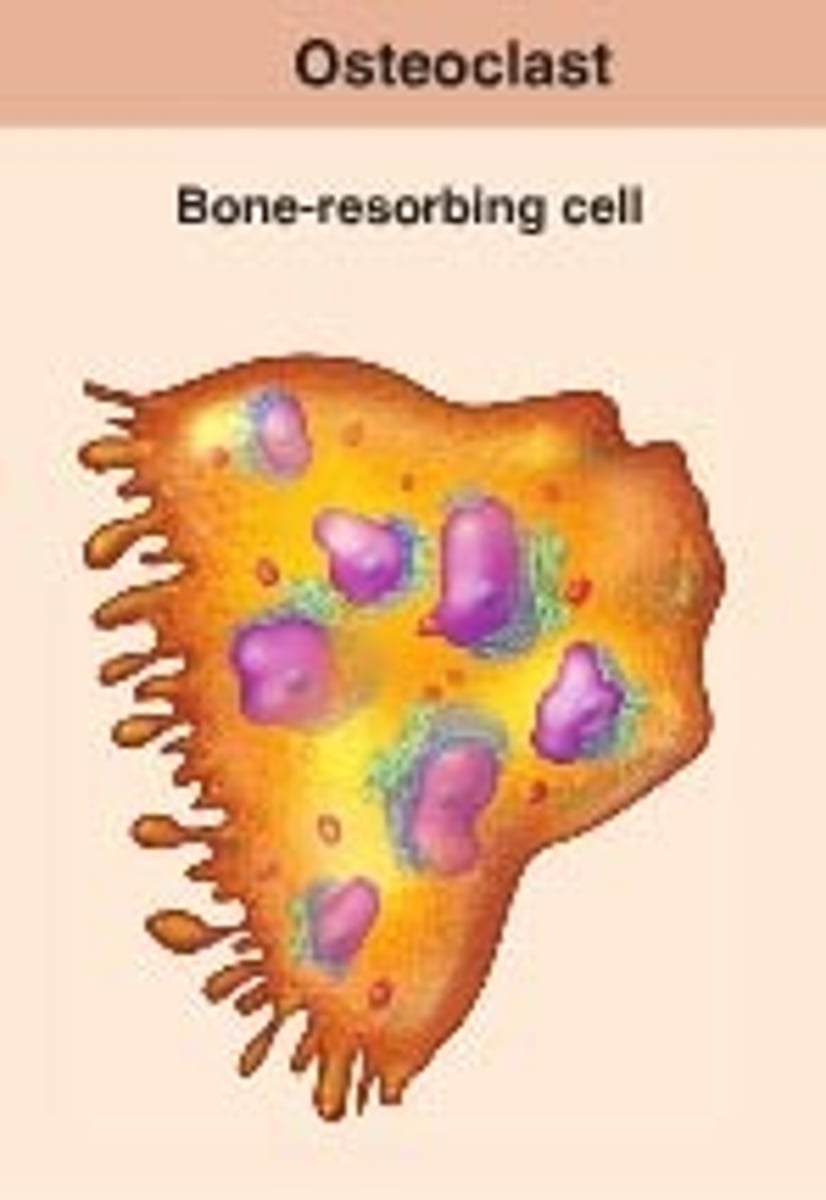
Osteoclasts
Multinucleated bone cells, also known as osteophages
Osteon or haversian system (compact bone)
Structural unit of compact bone, cylinder parallel to long axis of bone, contains hollow tubes of bone matrix called lamellae
Lamellae
Collagen fibers in adjacent rings run in different directions
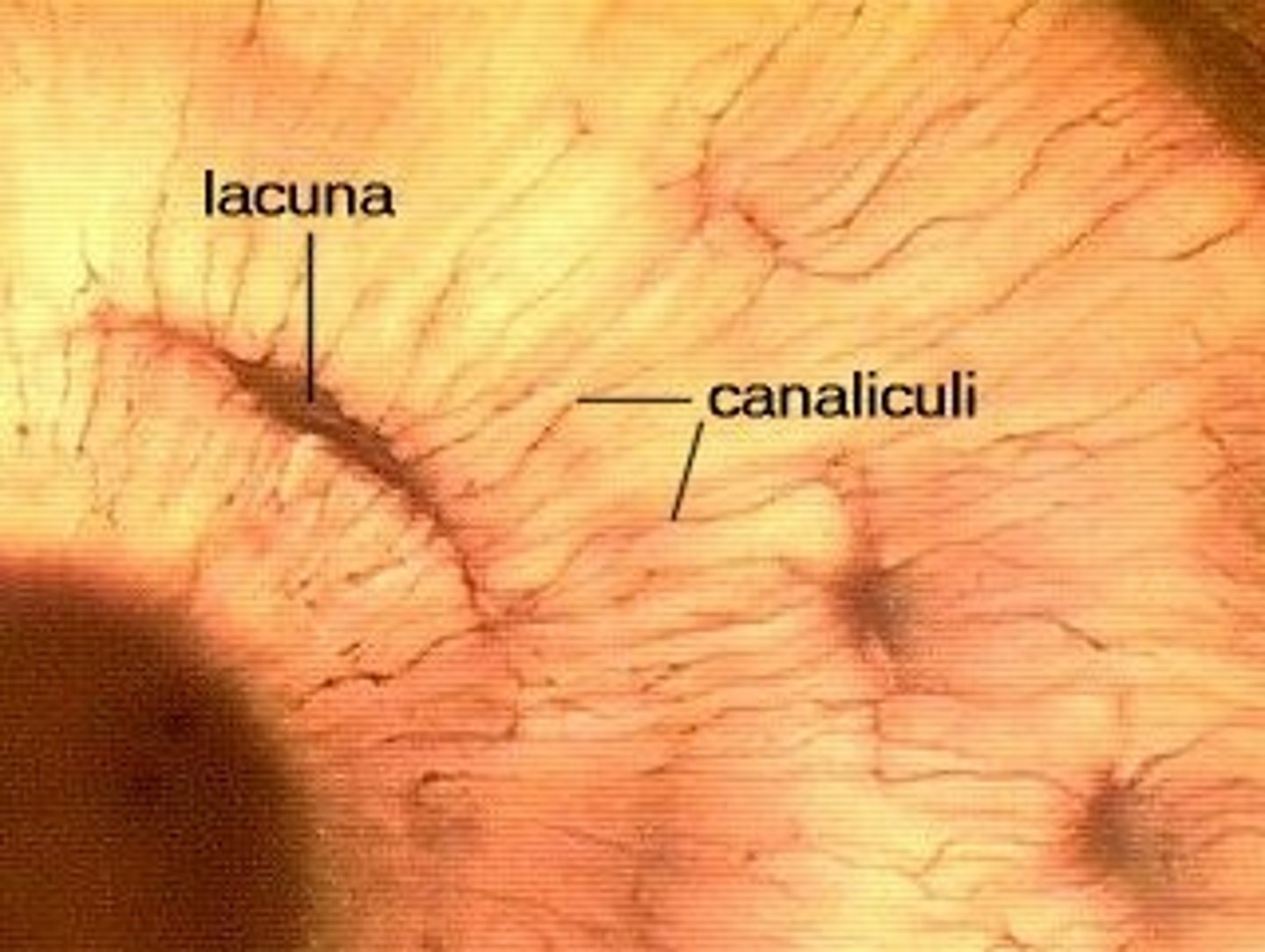
Lacunae
Small cavities containing osteocytes
Canaliculi
Hair-like canals that connect lacunae to each other and the central canal
Chemical composition of bone
Contains organic components and inorganic components
What are the inorganic components of bone?
Hydroxyapatites or mineral salts; 65% of bone by mass
In embryos, what leads to the formation of the skeleton?
Ossification and osteogenesis
What leads to the development of long bones?
Endochondral ossification
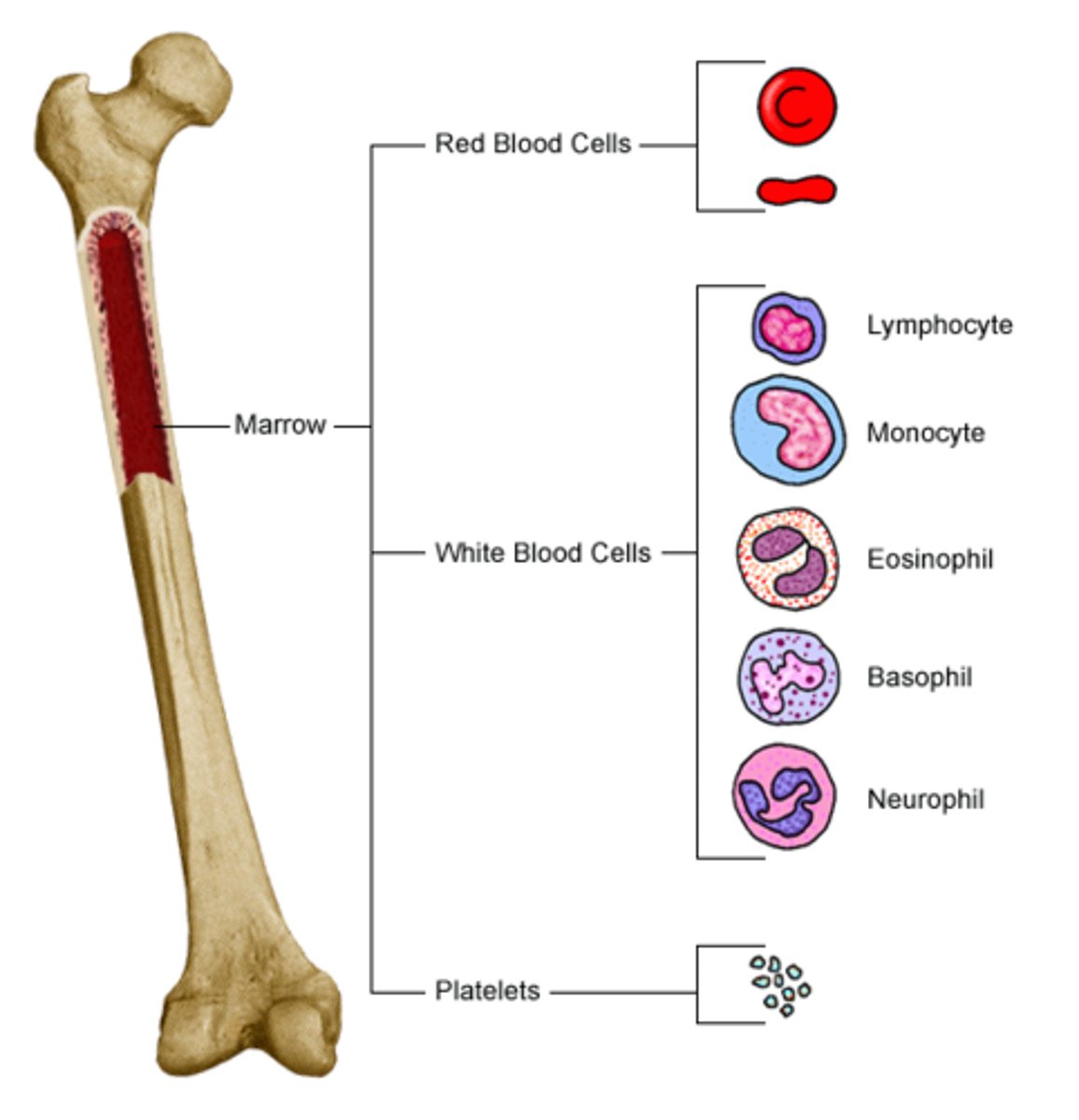
Functions of bones
Hemopoiesis, movement, support and protection, fat and mineral storage, hormone production
What is hemopoiesis?
The process by which the body produces blood cells and blood plasma
Bone homeostasis
Bone self-repair, 5% to 7% of bone mass recycled every week
What is the most common disorder of bone homeostasis?
Bone fracture
Compact bone is replaced how often?
Every 10 years
Spongy bone is replaced how often?
Every 3 to 4 years
Bone fracture is classified by what?
Positioning, completeness of fracture, penetration of skin by bones
Nondisplaced fracture
Bone ends stay in normal position
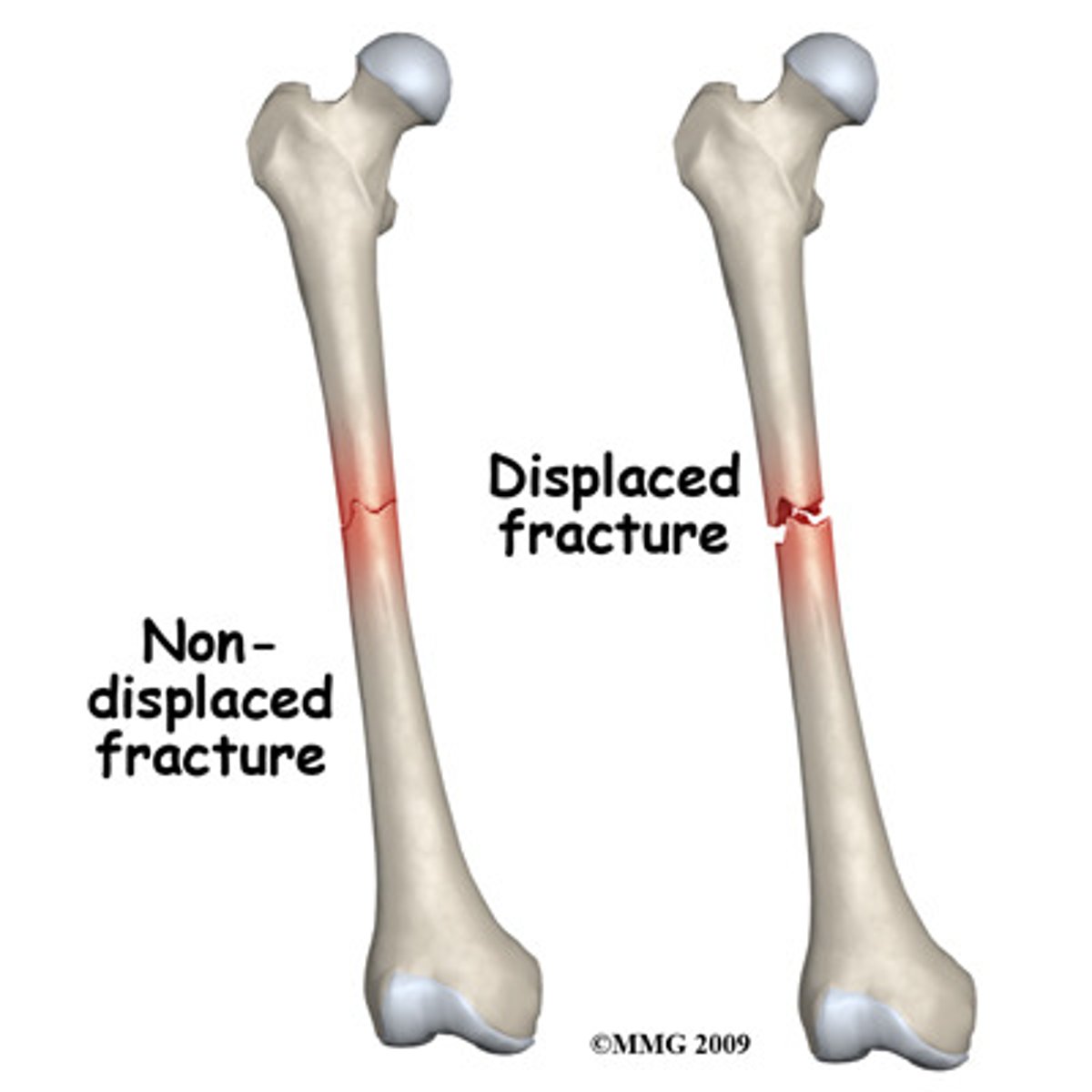
Displaced fracture
Bone ends are out of alignment

Complete fracture
Bone is broken completely through
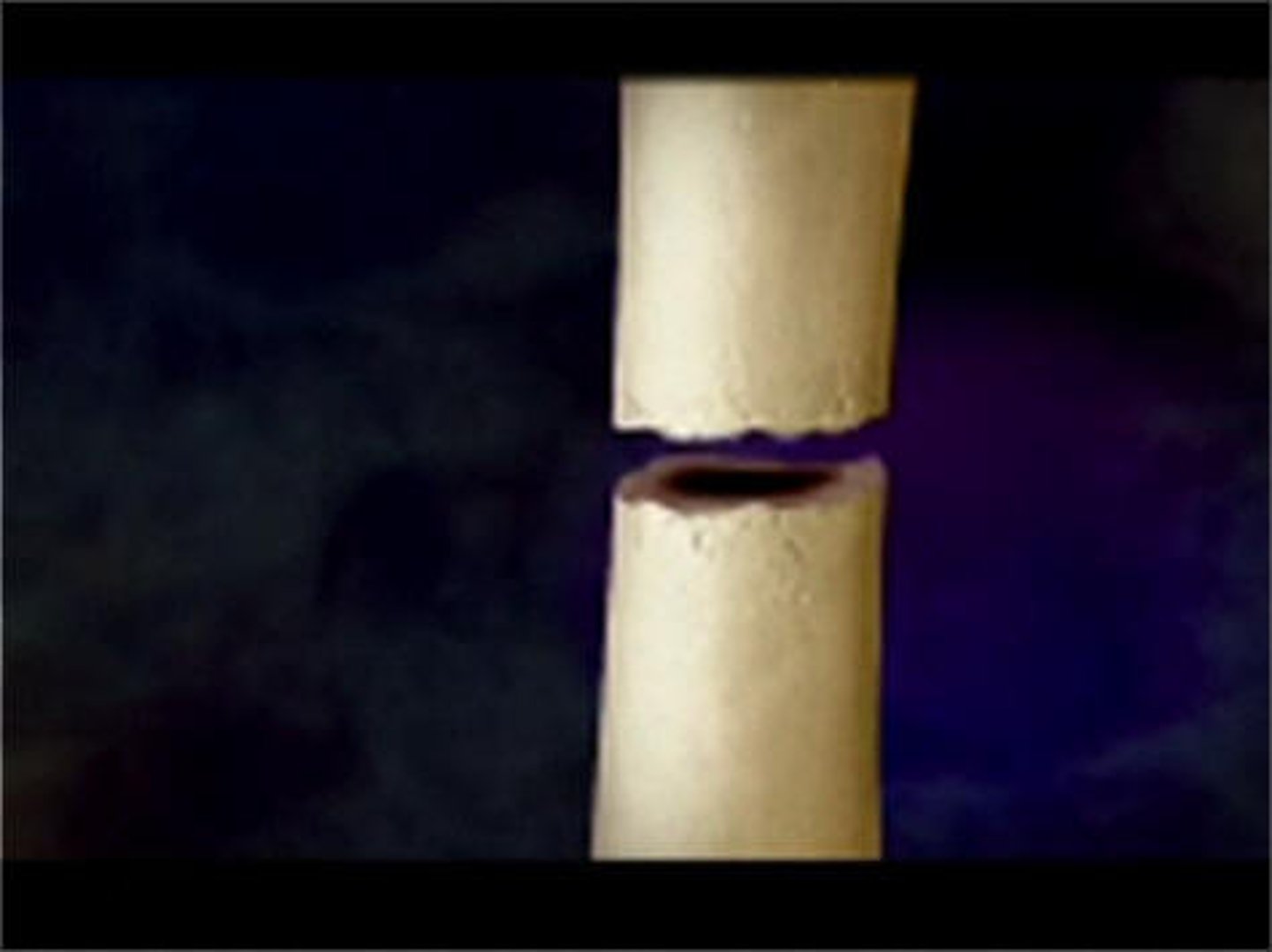

Incomplete fracture
Bone not broken completely through
Open or compound fracture
Bone penetrates skin
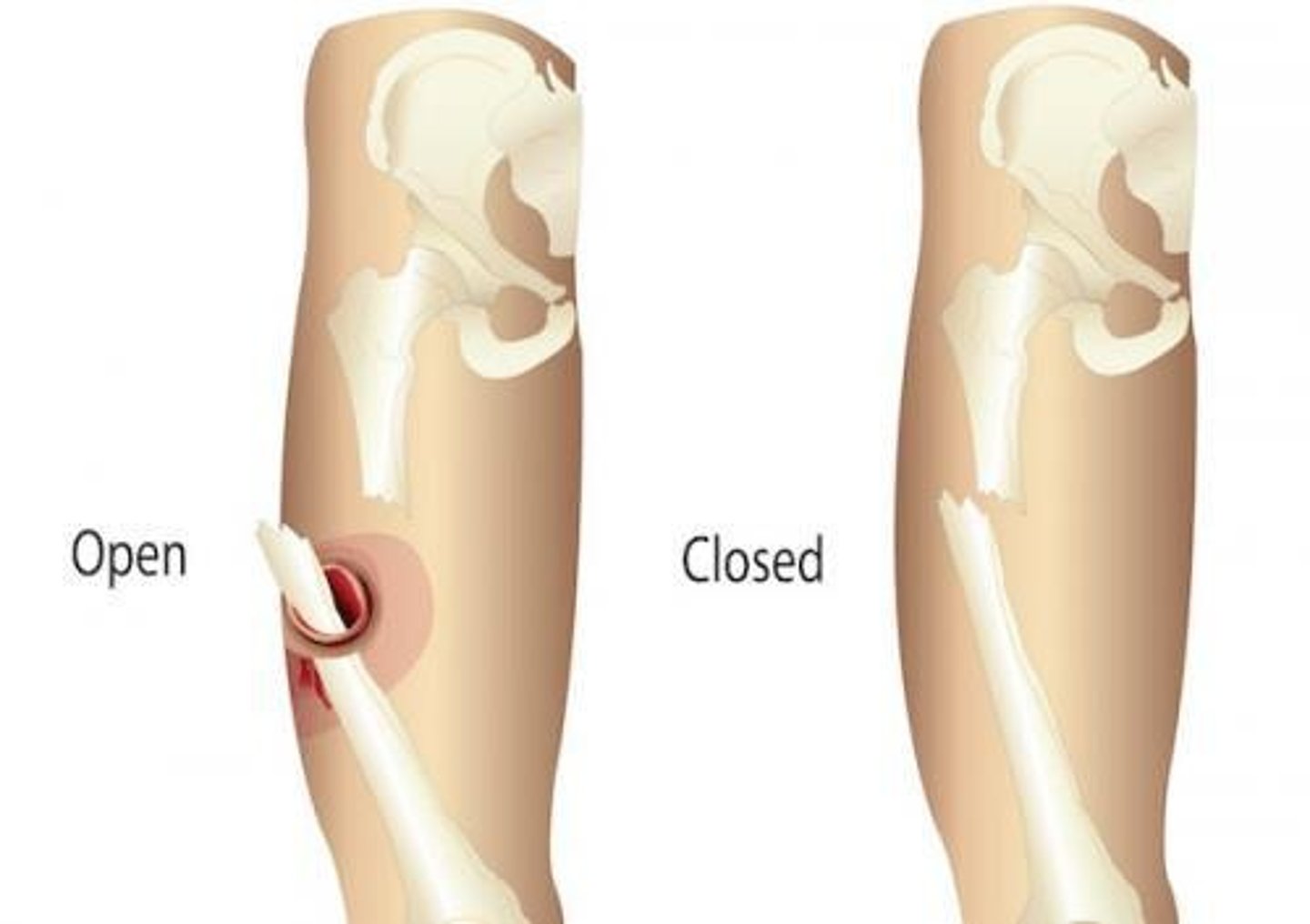
Closed or simple fracture
Bone does not penetrate skin
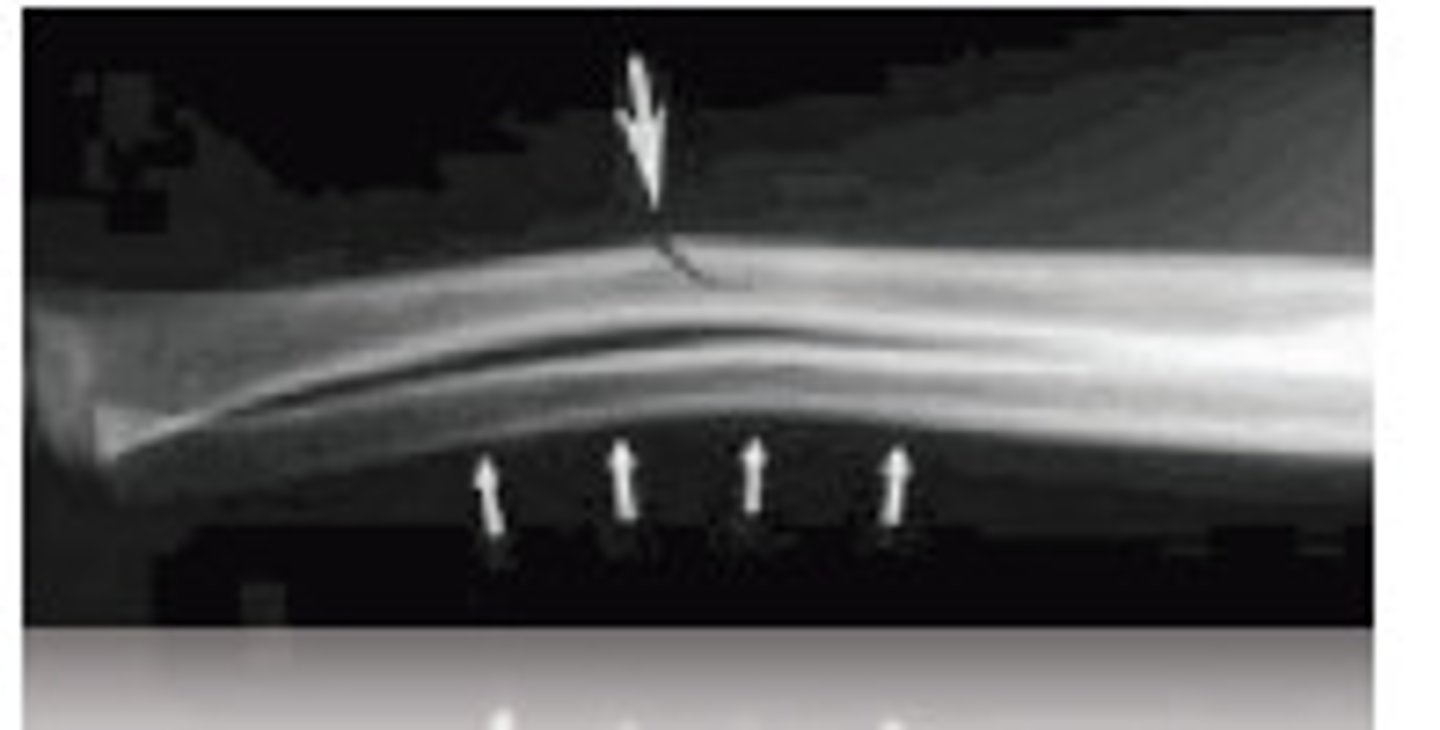
Comminuted fracture
Bone breaks into many fragments
Skull fracture
A break in one or more of the bones that form the cranium, usually because of blunt force trauma
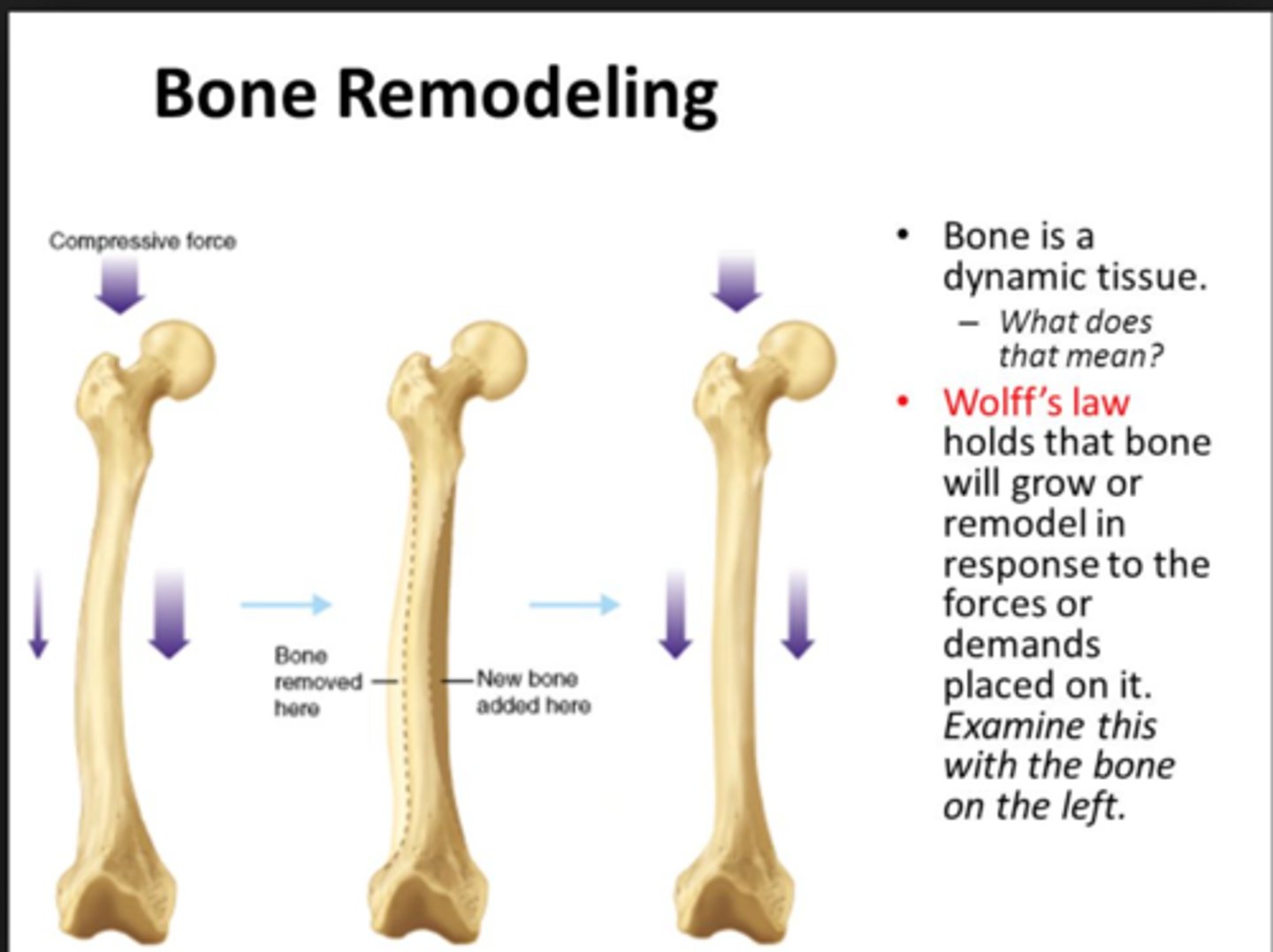
Wolff's Law
Bones grow or remodel in response to forces or demands placed upon them
Rickets
Bowing of a child's legs, deformities of pelvis, rib cage, skull; due to a deficiency of calcium or vitamin D
Osteomalacia
Poor bone mineralization in adults may cause abnormal gait, decreased muscle tone, weakness, and immobility
Osteoporosis
Bone resorption is quicker than bone deposition; spongy bone of the spine is most vulnerable, most common in postmenopausal women
Skull contains how many bones?
22
The only movable bone in the skull is the?
Mandible
The facial skeleton contains how many bones?
14
How many vertebrae form the spine?
26
The spinal vertebrae are separated by what?
Intervertebral discs of cushioning cartilage, connected by ligaments
What does the vertebral column support?
Head and trunk
How many cervical vertebrae are there?
7
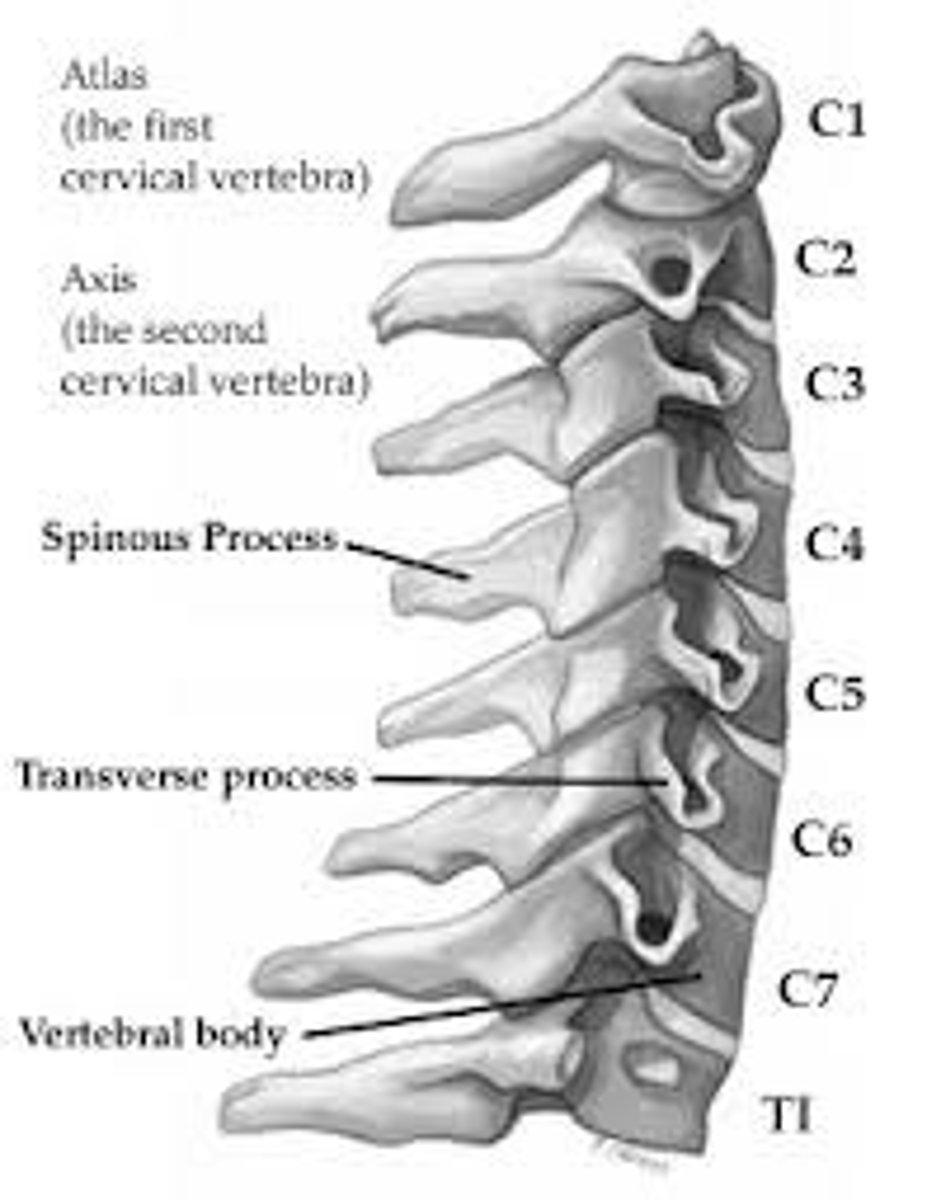
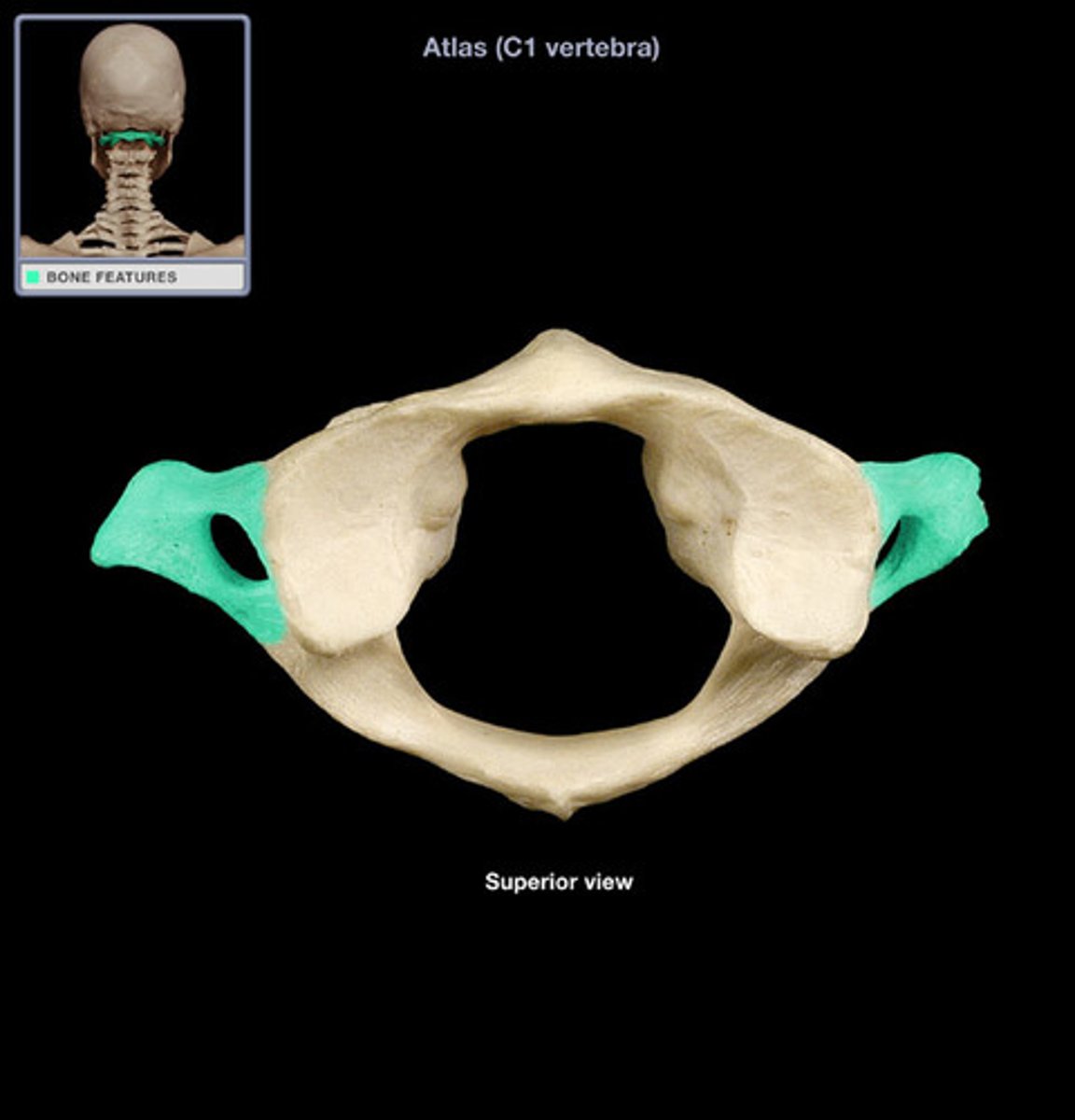
What is the vertebra that supports the head?
Atlas (C1)
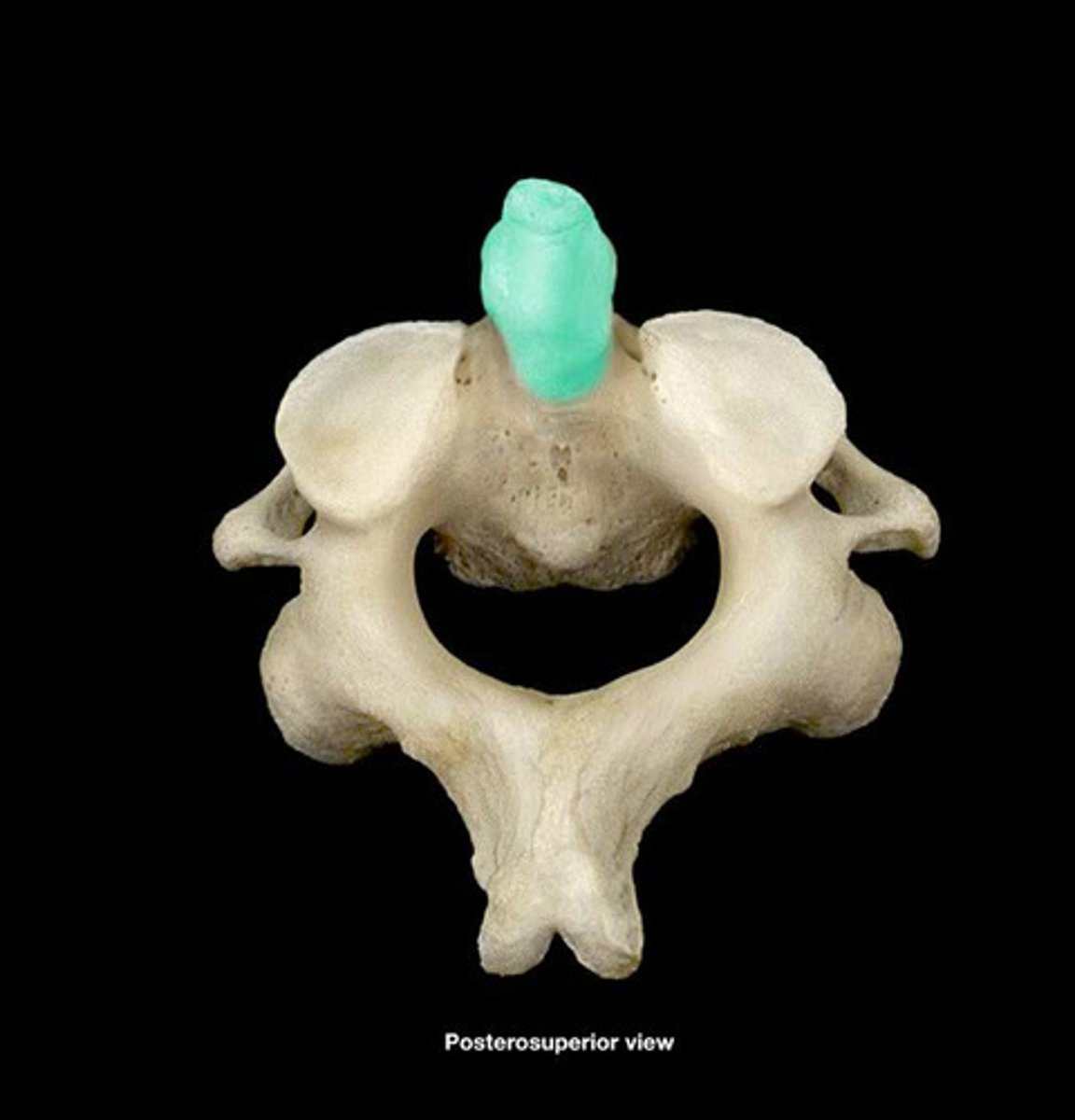
What is the vertebra that comes after atlas?
Axis (C2)
How many thoracic vertebrae are there?
12
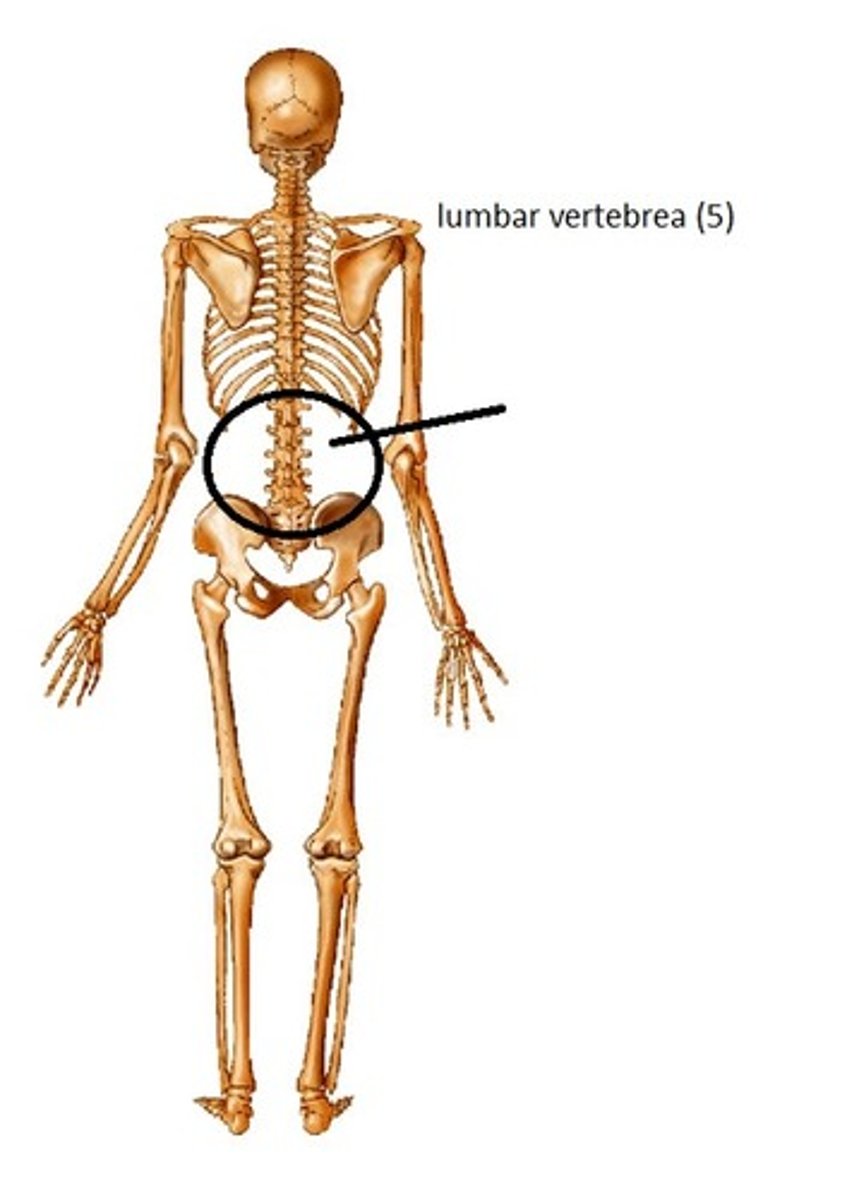
There are how many lumbar vertebrae?
5
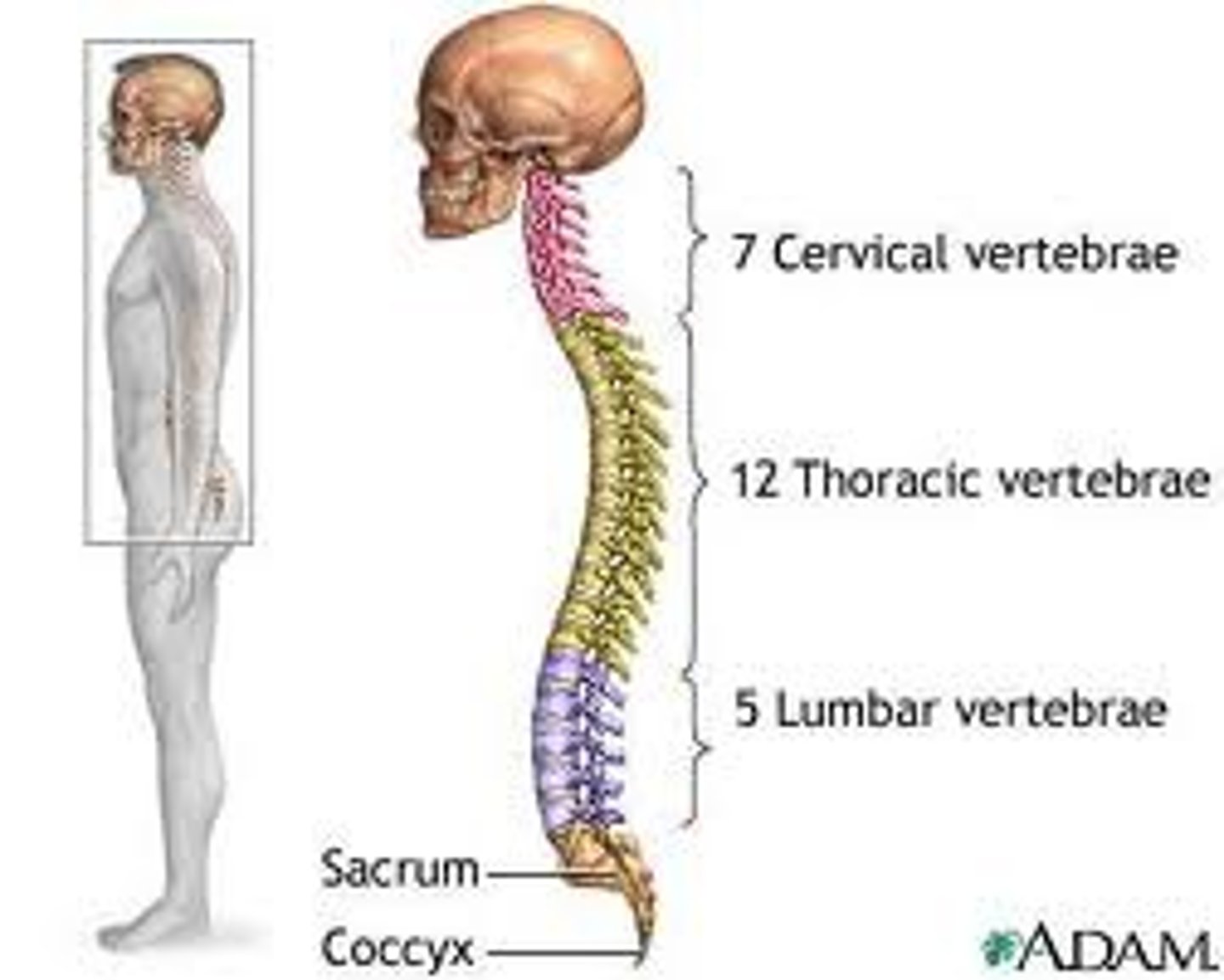
The largest vertebrae are the?
Lumbar because they support more weight
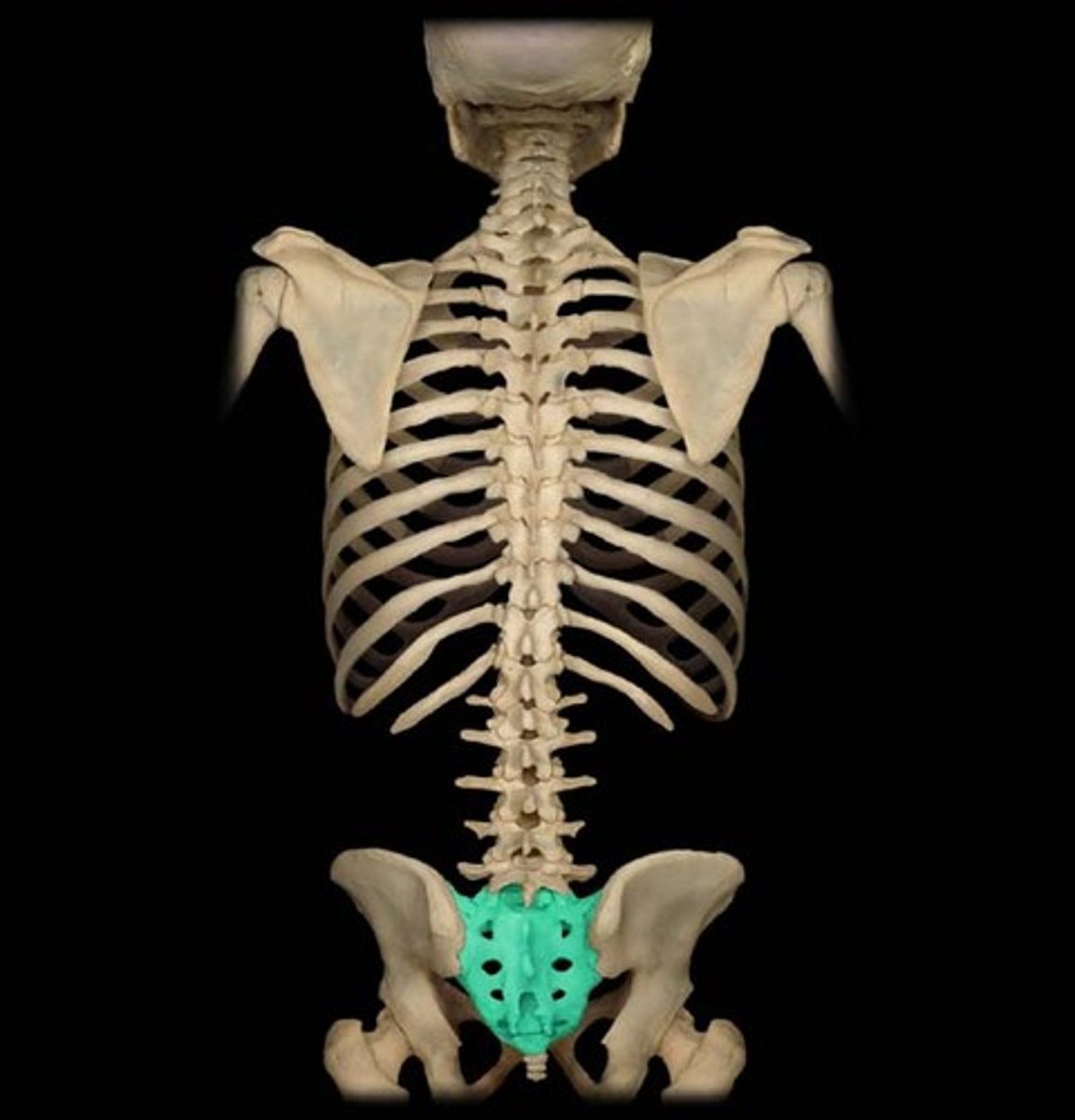
Sacrum
Triangular structure of 5 fused vertebrae
Coccyx (tailbone)
Lowest part of vertebral column; composed of 4 fused vertebrae
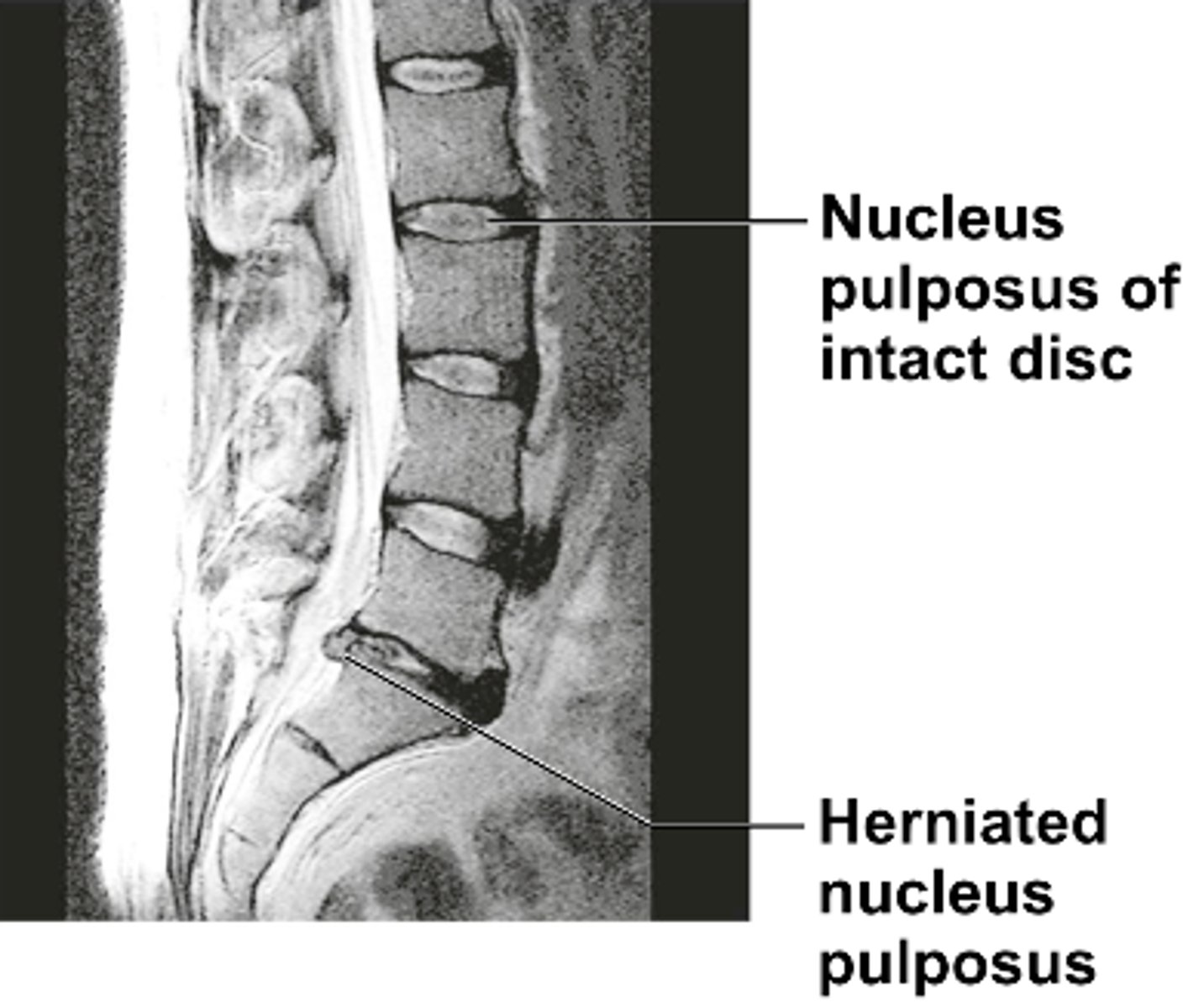
Intervertebral Disc Herniation
Common in lumbar spine; outward bulging causes pressure on spinal cord
Kyphosis
Exaggeration of dorsal curvature in the thoracic region (often due to osteoporosis)
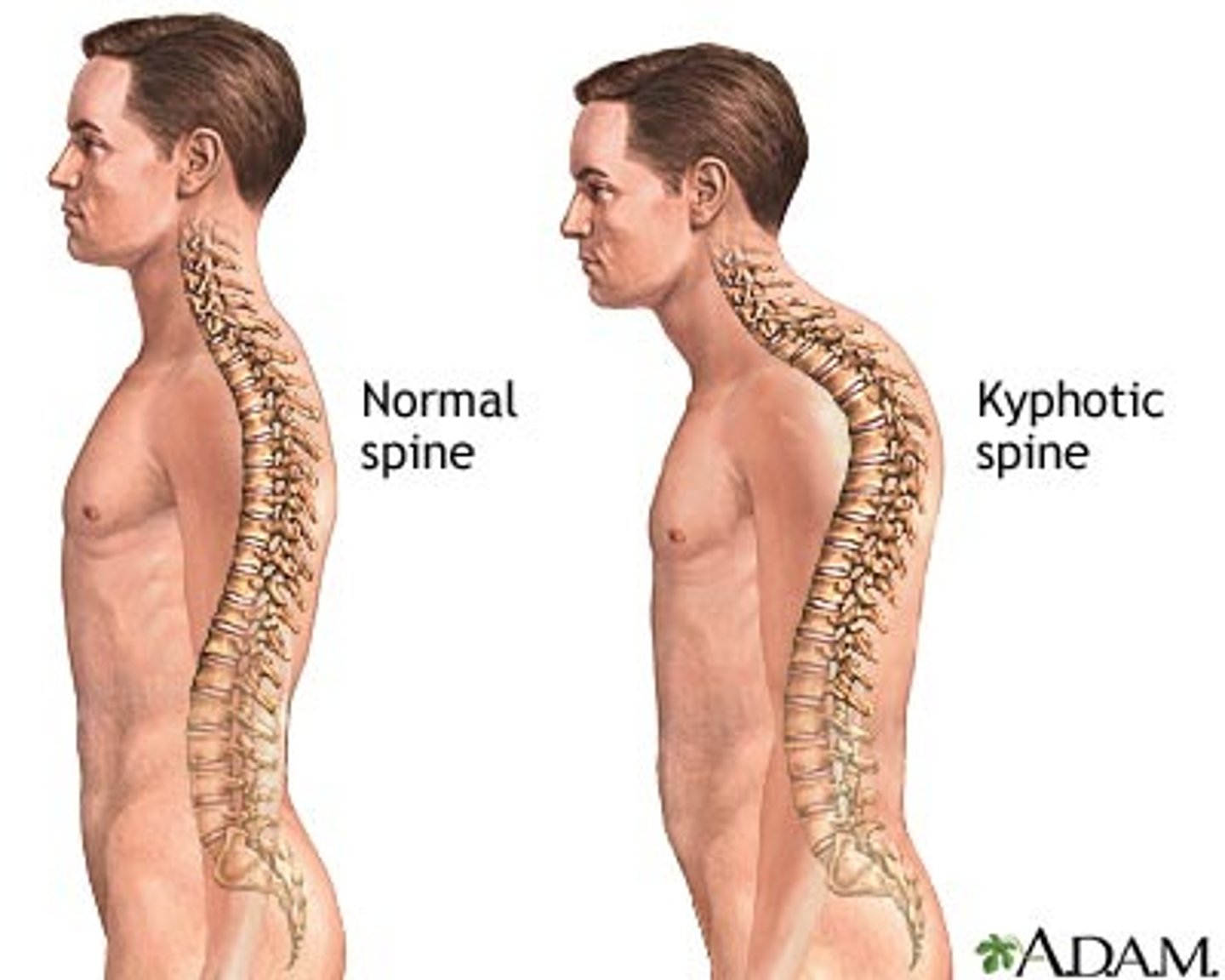
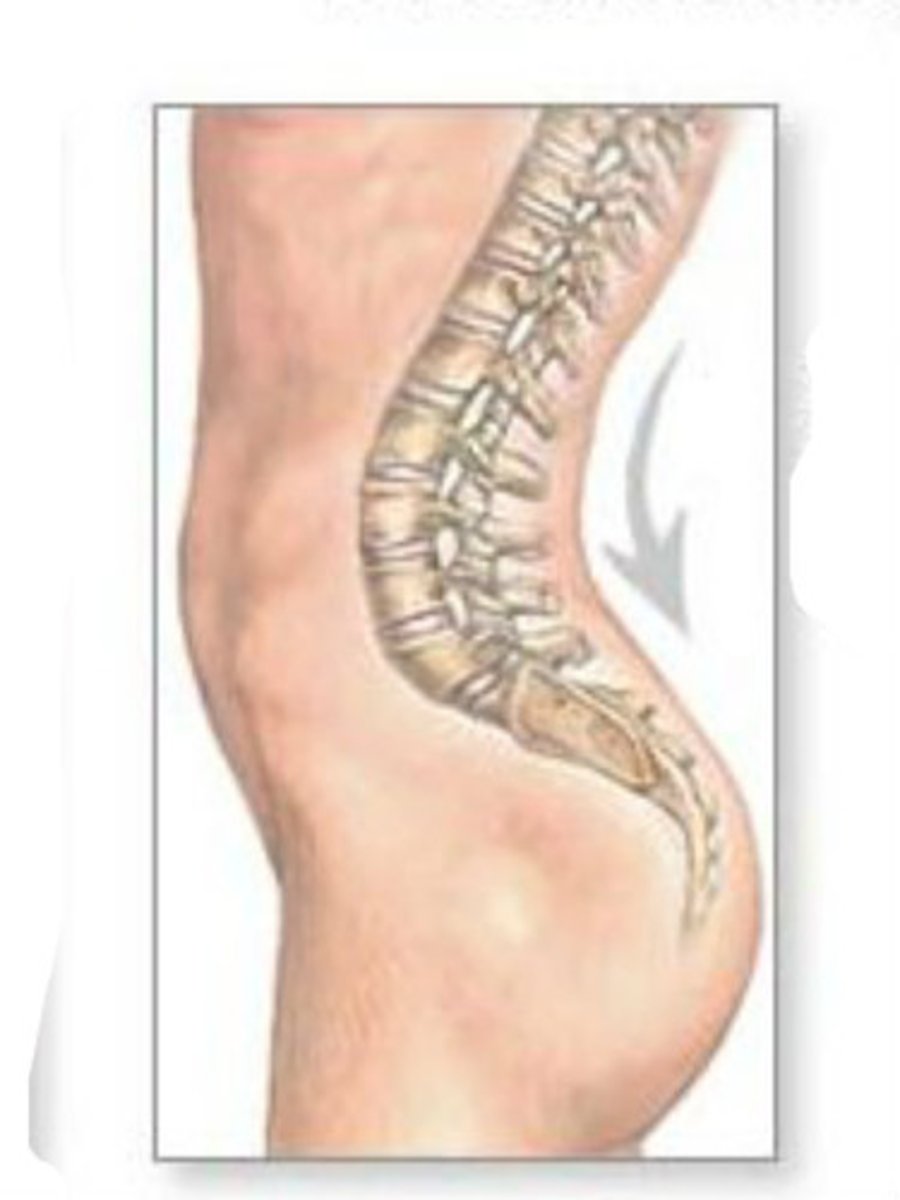
Lordosis
Inward lumbar curvature
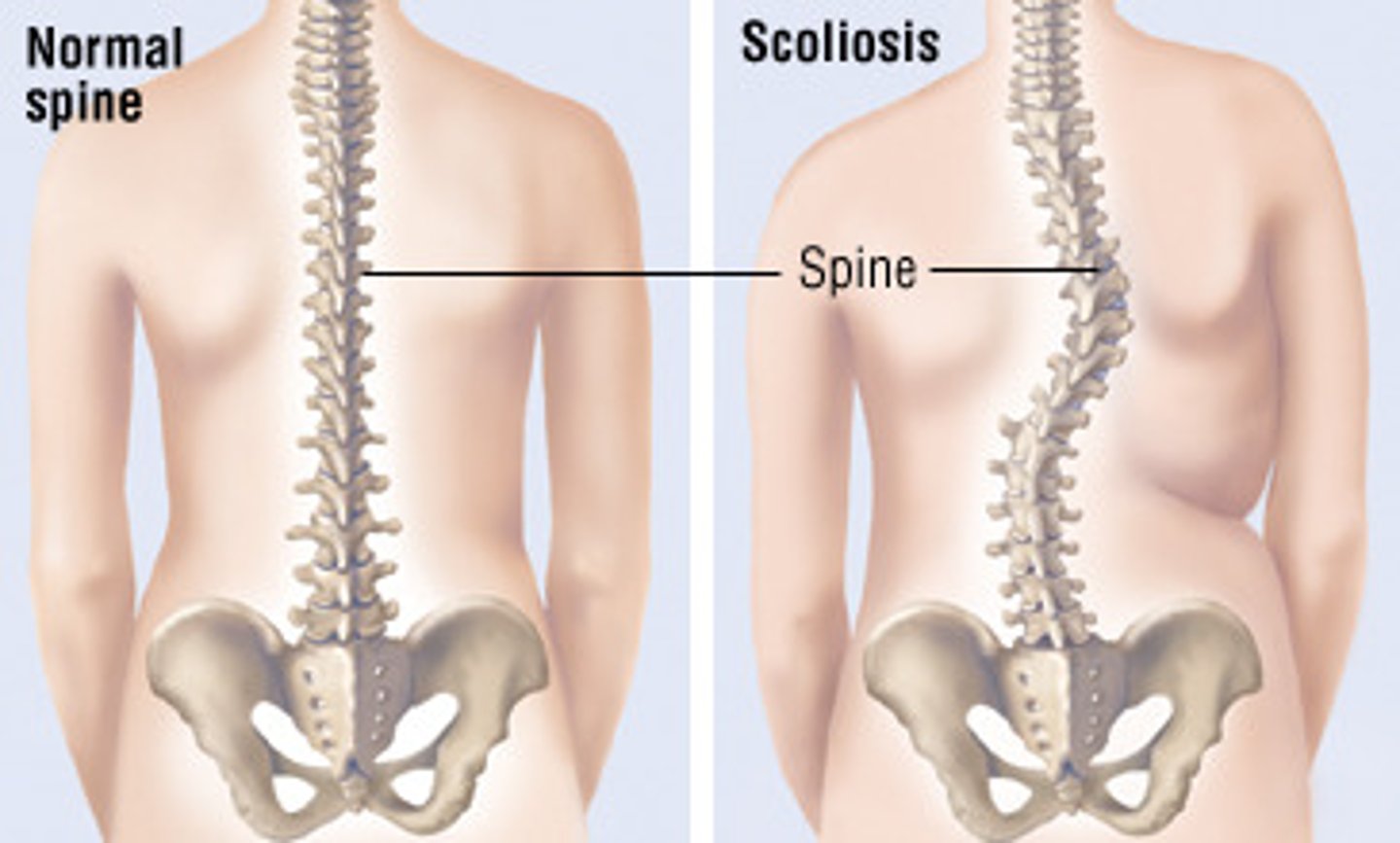
Scoliosis
Abnormal lateral curvature, usually thoracic
Thorax contains how many ribs?
12
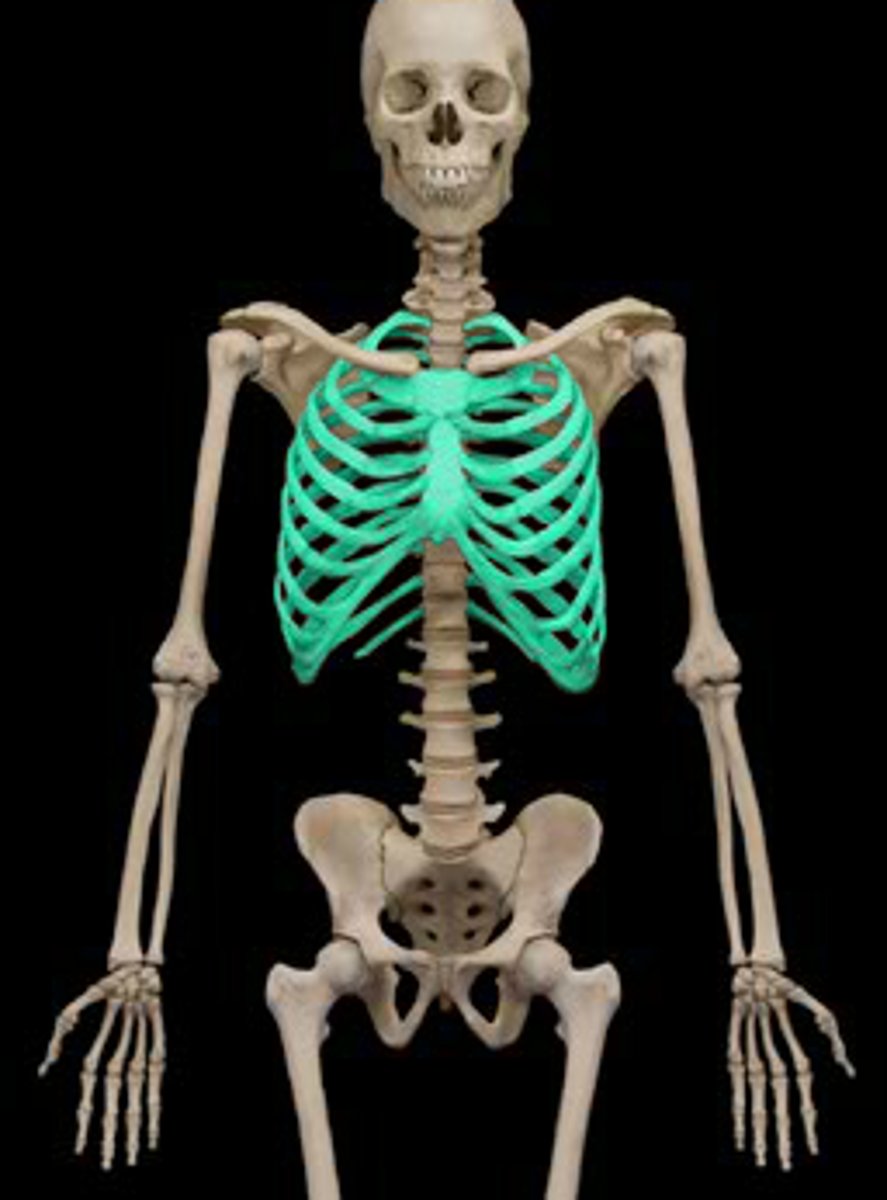
How many ribs are there in total?
24 (12 pairs for each thoracic vertebrae)
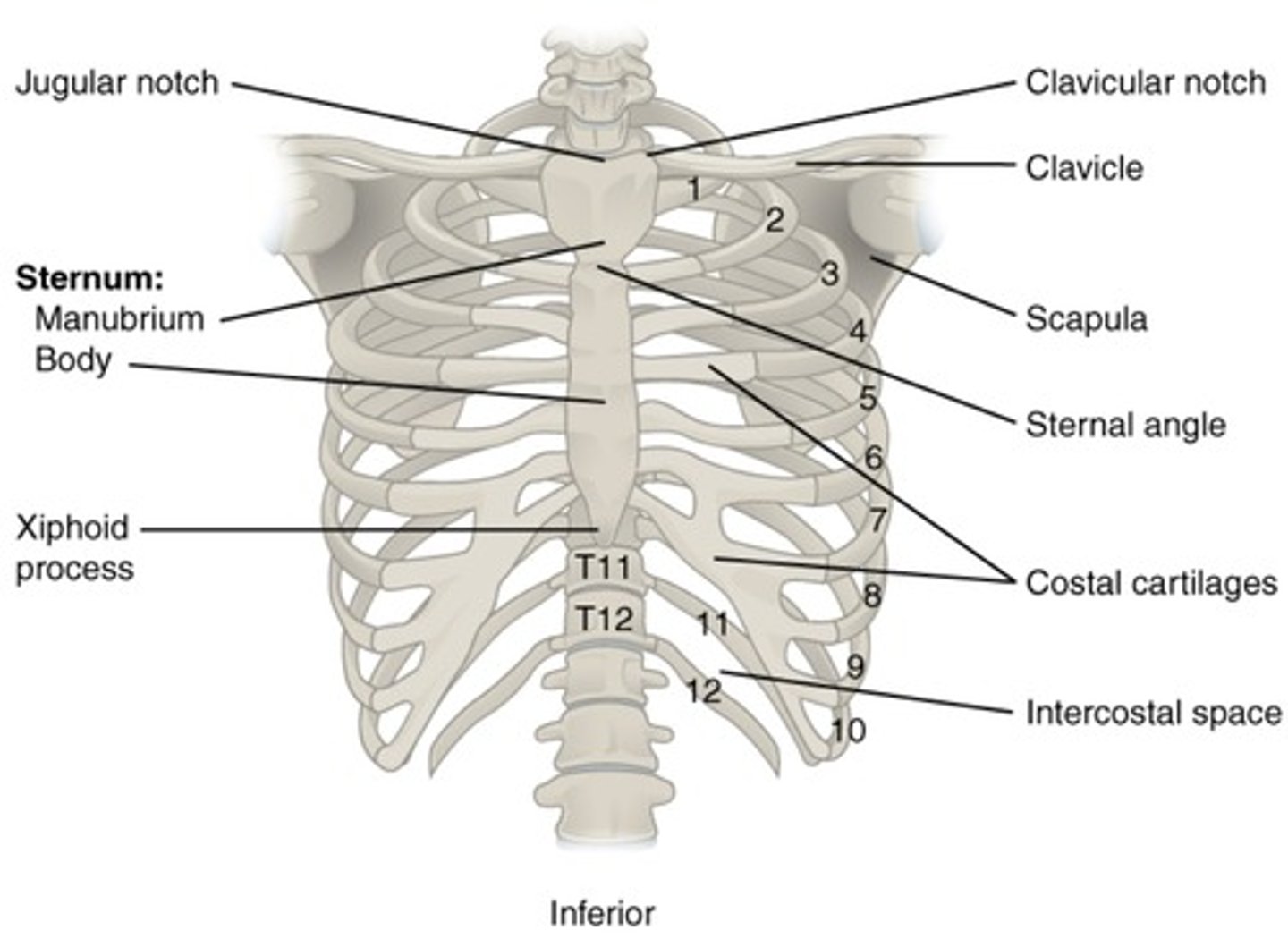
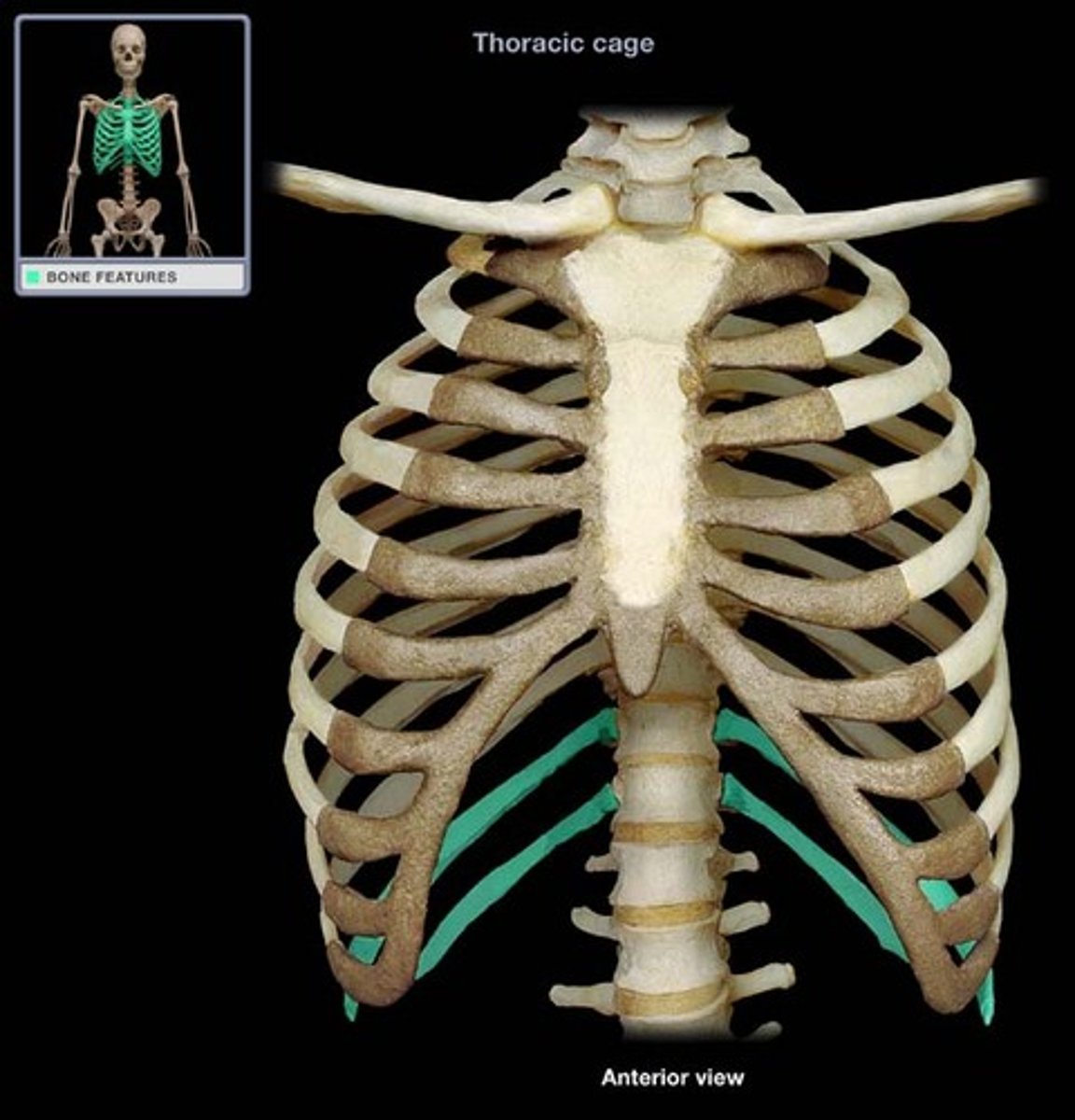
True ribs
The first seven pairs of ribs are attached directly to the sternum
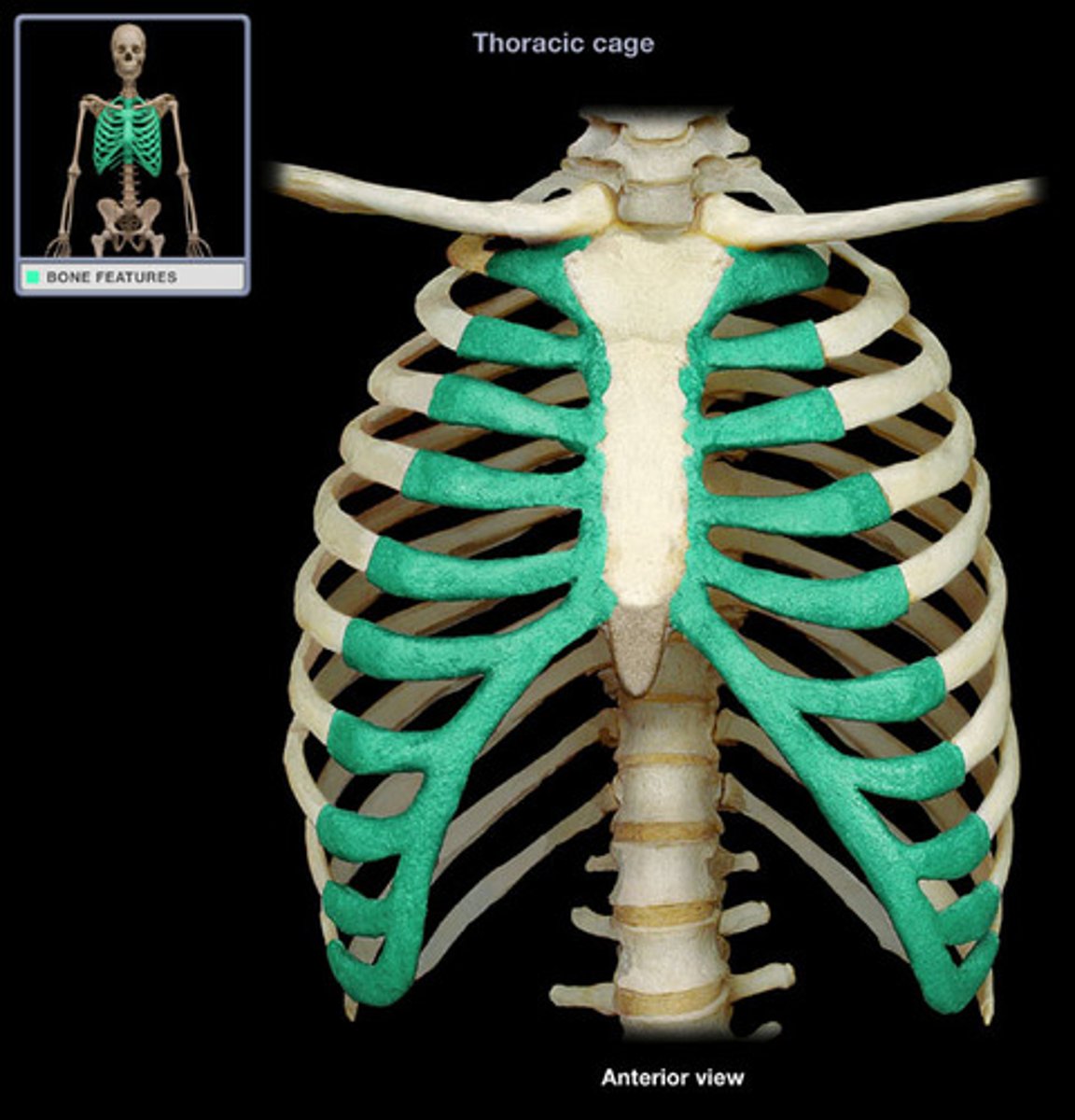
False ribs
Last 5 pairs, do not attach to sternum directly
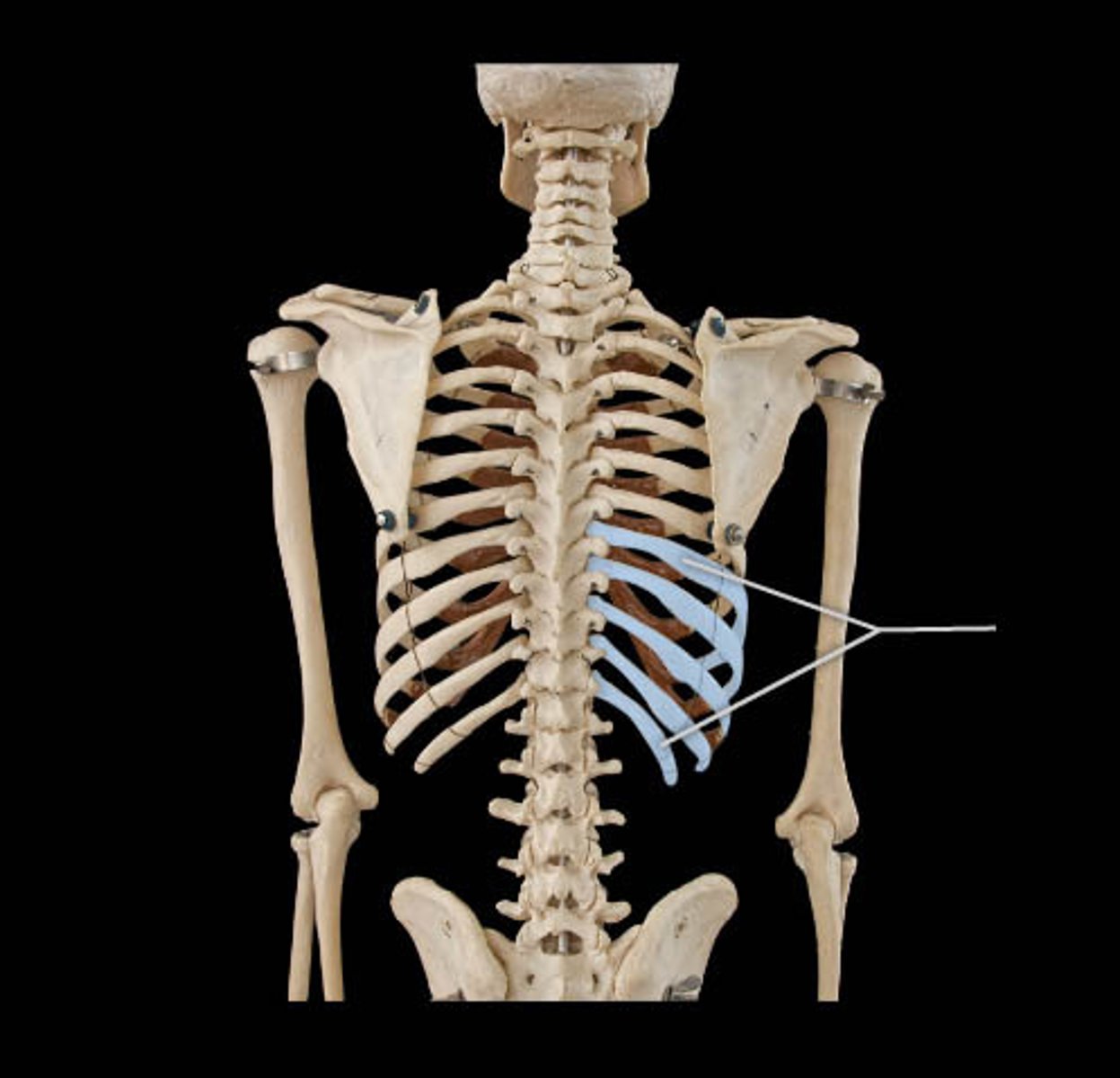
Floating ribs
Ribs 11 and 12 do not attach to the sternum
Ribs attach to the sternum by way of?
Costal cartilage
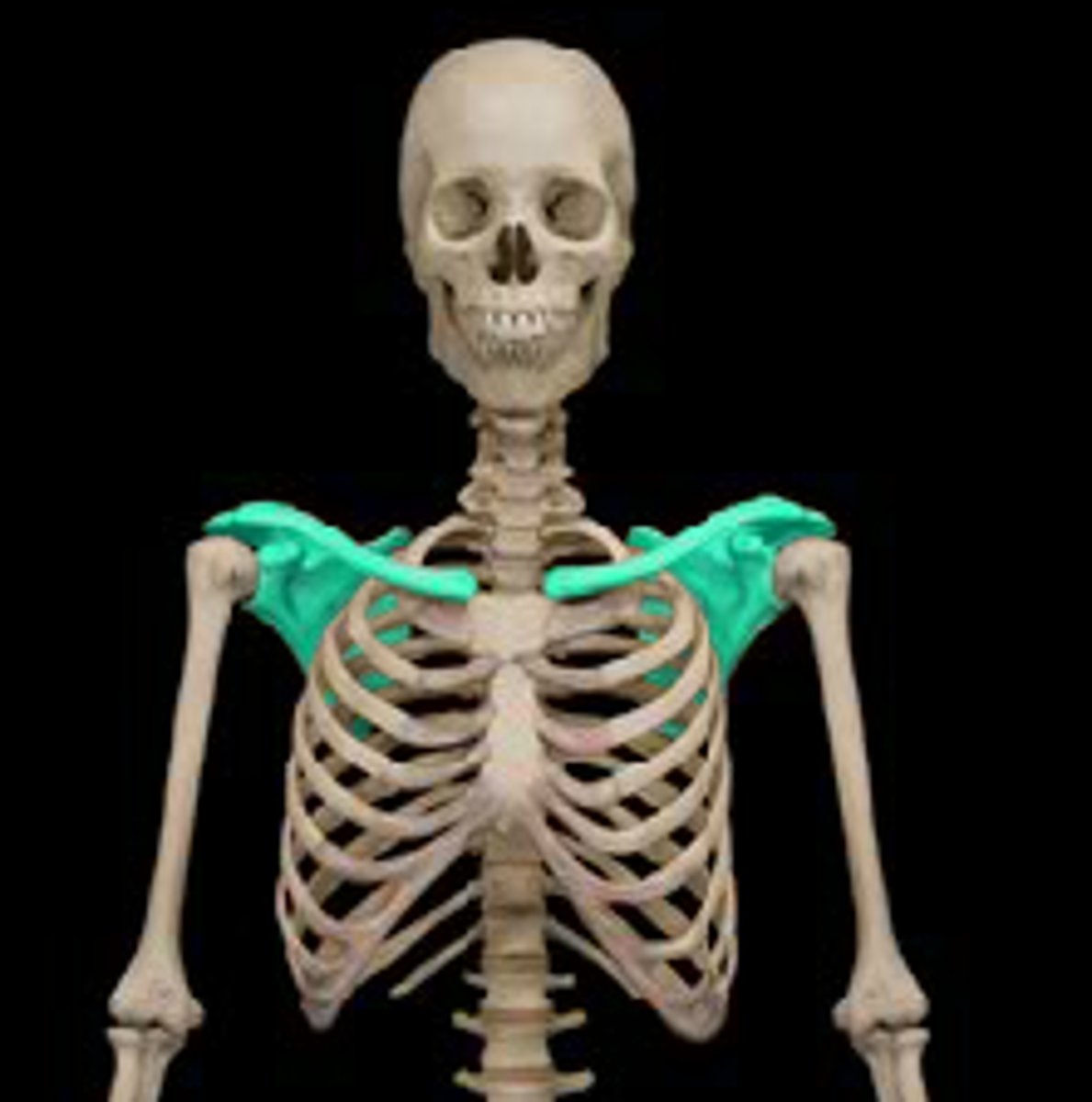
Pectoral girdle (shoulder girdle)
Clavicle and scapula on each side, connects the upper limb bones to the axial skeleton
Upper limbs
Includes arm bones, forearms, and hand bones
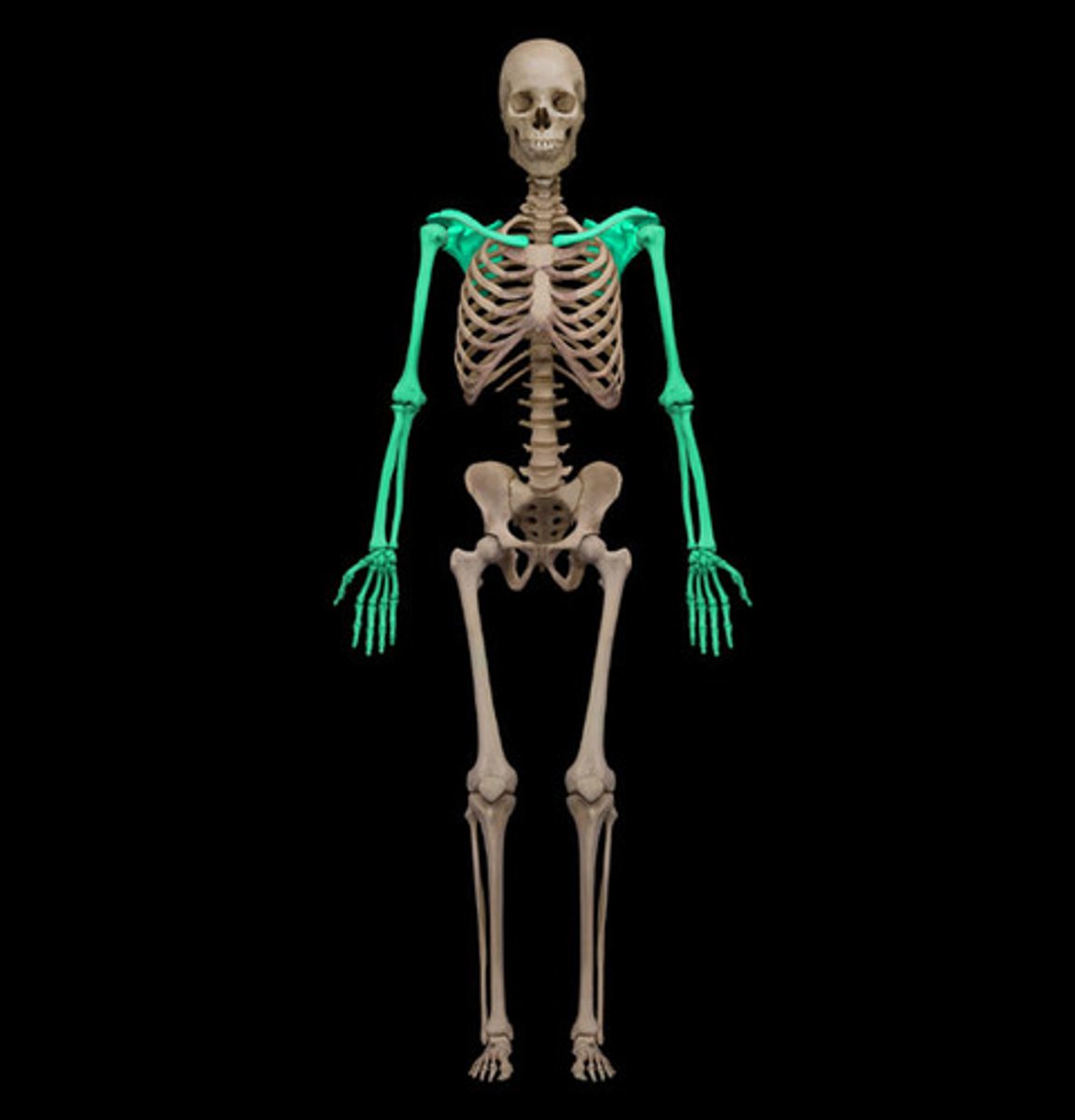
Upper limbs function
Provide muscle attachments, function to move limb parts