hurricanes and tornadoes
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
rhian
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
hurricane def
tropical cyclone (typhoon)
rapidly rotating storm system
thick clouds spiral around clear eye
high pressure centre (950mb)
strong winds (>32m/s)
500km diameter
hurricane structure
most intense activity in eye wall
conditions in the eye are calm
centrifugal forces and pressure gradients cause spinning
warm core causes high pressure and sinking air, stopping clouds from forming
conditions for hurricane formation
Atlantic hurricane season- 1st June- 30th Nov
warm ocean surface temperatures (>26.5)
water with a depth of 50m
require convection and a strong Coriolis effect
hurricanes form at 5-20 degrees N or S
small amounts of wink shear
saffir simpson scale
1-5
hurricane dissipation
tropical cyclones can last 7-20 days
storms hits land or reaches cold waters
supply of latent heat is cut off
high wind shear
weakens and dissipates over a few days
hurricane hazards
strong winds- 120-250km/h
heavy rain- 250mm/day
storm surges
secondary events- floods, landslides, tornadoes
hurricane katrina facts
hit louisiana 29th august 2005
category 3, 193km/h (119mph)
most expensive hurricane ($108 billion)
1800 fatalities
7.5m storm surge
weakened to a tropical storm following day
mitigation: evacuation
mandatory- New Orleans
10-30,000 in New Orleans Superdome (sustained damage)
Many stayed (poor, elderly, limited transport)
Mitigation: Flood protection systems
levees were poorly constructed and dated
over 50 levees failed, causing widespread flooding in New Orleans
Over 80% of city flooded, up to 2m in some areas
failure of levees caused most impacts and deaths
drowning- 1/3 of all deaths
aftermath
1,800 deaths
drinking water contaminated for 5 months
1 million houses damaged, 300,000 destroyed by flood
500,000 people homeless
230,000 jobs lost
more than 50,000 pets missing
recovery
existing socio-economic inequalities created difficulties for some groups
overwhelming demands, limited resources
lack of training and capacity
failure of coordination and communication
gendered and racialized marginalization
exclusion from decision-making
controversy and criticism
criticism towards the slow response at the state- and local level
failure of federal emergency management agency
pre existing vulnerabilities:
failure of flood protection due to poor funds, information and construction
low income communities in New Orleans tend to live in lower lying areas
long term socio-economic impacts: demographic
400,000 people permanently displaced
population of new orleans decreased by 29% between 2005 and 2011
long term socio-economic impacts: employment
230,000 jobs lost
employment recovery:
better for higher income groups
other groups disadvantaged (women, black communities, those who moved)
long term socio-economic impacts: mental health
5 years after Katrina
PTSS- post traumatic stress symptoms
PD- psychological distress
secondary trauma- loss of home/ community
higher earning individuals had less of a risk of developing PTSS/PD
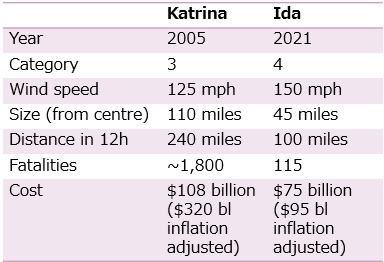
Katrina vs Ida
hurricane defences in New Orleans were rebuilt by 2018 and cost $14.6 billion
hurricane Ida damaged power grids and the water treatment system, but the levees held and didn’t cause floods
Mitigation: Forecasting
weather satellites
sea surface temps
wind speeds
moisture content in the atmosphere
scientific aeroplanes
computer modelling and statistics
spaghetti plots
climate change and storm events
2020 Atlantic hurricane season- 30 storms
increase in Atlantic tropical storm count and accumulated energy since 1990s
tornadoes def
violently rotating column of air in contact with the ground and a cumulonimbus cloud
tornadoes formation
moist air ahead of a strong cold front
duration: minutes to hours
size: <1km across
travel a few km
wind speeds 105-450km/h
tornado classification
Enhanced Fujita Intensity Scale
USA tornadoes: 69% weak, 29% strong, 2% violent
tornado occurrences
USA: 900 per year
UK: 34 per year
Bangladesh: 250 reported 1865-2014
USA tornadoes
In 2017:
18 tropical storms (10 hurricanes)
1418 confirmed tornadoes
Hurricanes: affect a larger area
Tornadoes: small but frequent
Notable disasters:
Hurricane Katrina (2005) >1000 fatalities
Tri-State Tornado (1925) 695 fatalities
mitigation: tornado forecasting
forecasting is complicated
development of temperature and wind flow patterns
mitigation: tornado safety
know where to go
communication aware of surroundings
education is key
tornado vulnerability
mobile homes: 82% fatalities
houses: 87% fatalities