Lecture 5: Understanding the Telencephalon and the Amygdala's Role in Behavior and Emotion
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
which of following are part of telencephalon
a. lateral ventricles
b. corpus callosum
c. deep subcortical nuclei (basal ganglia)
d. cerebral cortex
all are true
basal ganglia - 3 nuclei made up of
caudate , putamen & globus pallidus
basal ganglia
project to motor areas of cortex & play important role in motor system
- damage here results in loss of movement as in Parkinsons disease
amygdala
adj to hippocampus
functions: arousal, endocrine, emotions, autonomic responses related to fear
* deep in temporal lobe
functions hippocampus
functions : memory (forming, storing, retrieving) , spatial navigation, limbic (connecting emotions & senses, such as smell & sound, to memories)
looks like seahorse
which structure is found in telencephalon & controls aggression & fear responses
a. basal ganglia
b. amygdala
c. mammillary body
d. reticular formation
e. hippocampus
b. amygdala
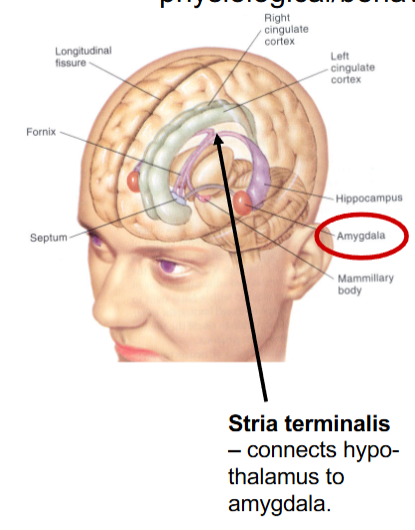
which fiber bundle connects hypothalamus to hippocampus
a. fornix
b. anterior commissure
c. stria terminalis
d. internal capsule
e. mammillary body
a. fornix
functions of amygdala
fear (arousal responses) , attention, reward behavior, emotional memory
lesions in amygdala
deficits in ability to assess danger ; reduce fear & aggression ; monkeys lose rank in social hierarchy
electrical stimulation in amygdala
done in cats
- produce repeated defense reactions (physiological changes, defensive attack, retreat)
disorders from amygdala
anxiety disorders (panic attacks, social phobias) , autism , OCD
in which conditions would you expect amygdala to be activated
a. anxiety (panic) attacks
b. PTSD
c when confronted by snarling pit bull
d. social phobias
e. all of above
all of above
is amygdala part of the limbic system
yes bc its role in emotions
limbic system
on medial walls of brain form ring around brain stem & corpus callosum ; cingulate gyrus, medial temporal cortex, amygdala, hypothalamus , hippocampus
papez circuit
papez believed that emotional experience was determined by activity in cingulate cortex (amygdala, AMG)
- emotional expression (behavior) was thought governed by hypothalamus
- to store memories (emotional coloring ) cingulate cortex projects to hippocampus, which projects to hypothalamus by way of fornix
- hypothalamic effects reach the cortex via relay in anterior thalamic nuclei & brainstem for physiological responses
damage to limbic system
reduced aggression & relief from fear
bilateral damage to amygdala kluver bucy syndrome
- reduced fear & agression
- oral tendencies due to poor visual recognition
-disordered personality --> blunted or "flattened" emotions
- hypersexulaity
clinical treatment using lesions for limbic system
temporal or frontal lobectomy or amygdalectomy performed by cutting conx w/ prefrontal corte
- still in use to treat severe aggression & violent behavior
What connects hypothalamus to amygdala?
Stria Terminalis