Cystic fibrosis + bronchiectasis
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is Bronchiectasis?
Persistent or progressive, chronic, lung condition characterised by permanent dilation of the bronchi due to irreversible damage to the elastic and muscular components of the bronchial wall
Symptoms of bronchiectasis
Persistent cough
Large volumes of purulent sputum
Dyspnoea
Fatigue and reduced exercise tolerance
Non-pleuritic chest pains present between exacerbations
Haemoptysis
Signs of bronchiectasis
Inspiratory coarse crackles, especially lower zones
Wheeze
High-pitched inspiratory squeaks
Large airway rhonchi (low pitched snore-like sounds)
NO SMOKING HISTORY
Risk factors of bronchiectasis
Women > men
Increasing age
Recurrent and/or severe lower respiratory tract infection
COPD / asthma/CF
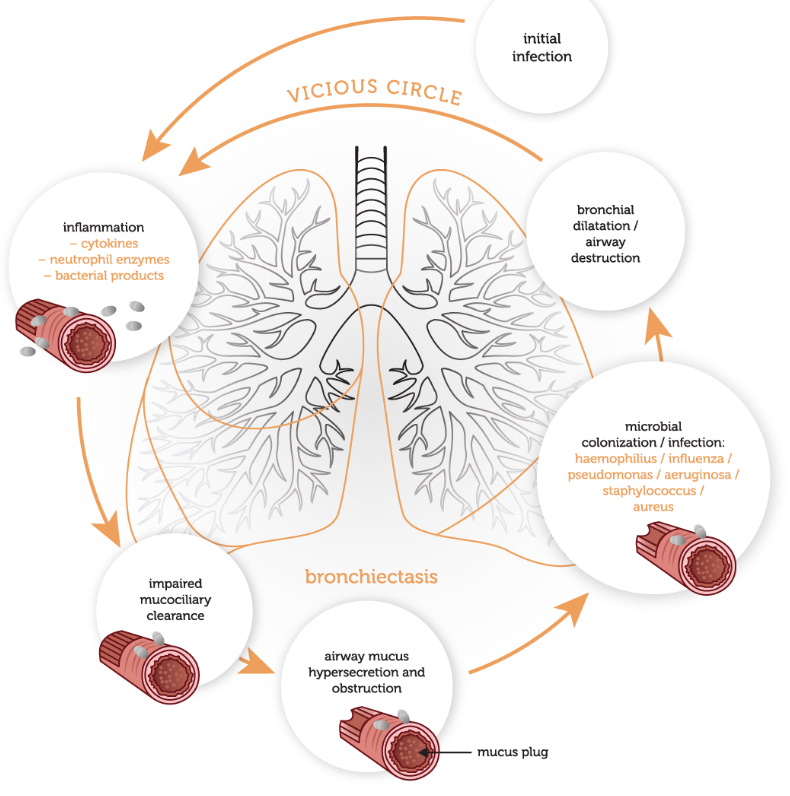
Pathophysiology of bronchiectasis
Persistent airway inflammation → bronchial wall oedema → increased mucus production
→ Inflammatory cells (neutrophils, T cells) recruited to the airways
→ Cytokines, proteases, and R.O.S destroy the airways
Bronchial damage leads to colonisation of the airways
** Cycle of colonisation and subsequent chronic inflammation leads to progressive airway damage and recurrent infection
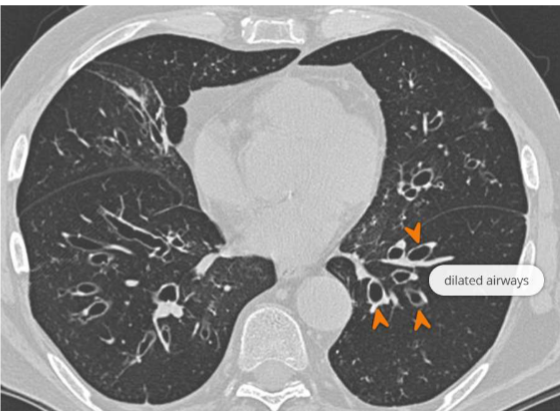
What investigations do you carry out to diagnose brochesctasis
High Resolution CT – gold standard → Signet ring sign: bronchus > accompanying pulmonary artery
Sputum culture
Chest x-ray:
Oxygen saturation levels
Full blood count incl. WCC, CRP
Spirometry – identify severity of airflow obstruction
Management of bronchiectasis
Treatment goal – prevent/slow down progression of disease
Respiratory physiotherapy (airway clearance techniques)
Mucolytic agents
annual influenza vaccine
Antibiotics (for longer duration)
Bronchodilators
Pulmonary rehabilitation
Lung resection surgery
What mutation leads to cystic fibrosis and how is the gene affected?
Autosomal recessive
deletion of phenoalynine in CFTR gene of Chromosome 7
Misfolded CFTR protein synthesised in ER
Protease-sensitive
Readily degraded before entering Golgi complex
What is the role of the CFTR protein?
It is a Cl- transport protein found in the plasma membrane of epithelial cells → facilitates passive movement of Cl- across an electrochemical gradient
ATP binding and hydrolysis in the CFTR protein open and close a continuous ion channel
Pathophysiology of cystic fibrosis
Sweat glands: Impaired Cl- reabsorption → high salt sweat
Decreased Cl- secretion at the apical membrane → thickened, dehydrated secretions/mucus
Lungs: mucus plugging → colonisation → bronchiectasis
decreased mucocilliary clearance
Pancreas: stagnant enzymes → auto-digestion → pancreatic insufficiency + diabetes mellitus
Liver: cholestasis → inflammation → fibrosis ± cirrhosis
Clinical manifestations of cystic fibrosis
salty sweat → increased risk of dehydration
nasal congestion and discharge
nasal polyposis
sinus infections
chronic bronchiecstasis
male infertility: bilateral absence of vas deferens + reduced female fertility: abnormal cervical mucous
How do we test for cystic fibrosis
Antenatal testing (if high risk)
• Chorionic villus sampling (11-14 weeks)
• Amniocentesis (15-20 weeks)
Newborn blood spot screening
• Usually performed at day 5 of life
• Immunoreactive trypsinogen (IRT)
also need +ve sweat test: Cl- ≥ 60 mmol/L
Management of cystic fibrosis
Mucolytics:
rhDNase (e.g. dornase alfa)
Inhaled Hypertonic NaCl
Inhaled mannitol dry powder
Chest physiotherapy
Airway clearance techniques
Regular monitoring:
Respiratory secretion samples (sputum)
Spirometry
Chest x-ray
What are some lifestyle changes/ modifications recommended for patients with CF?
Immunisations and vaccinations#
No smoking/vaping
Regular exercise
Monitor BMI
Glucose monitoring
Monitoring blood tests (FBC/U&Es/CRP/LFTs/vitamin levels)
Targeted CF therapies
CFTR potentiators: Increases flow of Cl- ions through the mutant channel
+
CFTR correctors: Migrate misfolded CFTR protein to plasma membrane, partial restoration