Color Vision
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What did Thomas Young theory state about color vision, the trichromatic theory.
color info is decoded by a limited number of cones (<3) and the cones activity leads to color vision; earlier people thought we had a cone for each color (but there’s not enough space or processing ability)
What is normal human vision?
trichromacy, within each class of a cone is a specific photopigment with a peak sensitivity to a specific wavelength.
s-cone *cyanolabe: 426 nm
m-cone *chlorolabe: 530 nm
l cone *erythrolabe: 557 nm
rod: rhodopsin (can’t see color)
Can trichromats distinguish colors based solely on wavelength?
yes, you would need 4 wavelengths to fool them.
Staring at at bright red screen when you switch to white you would see
a blue screen
Flickering between the yellow and white screen you observe
blue instead of white
Your neural processing becomes numb and consequently
you have a reduction in your CSF to that
What is monochromacy?
wavelength discrimination with only one class of retinal photoreceptors
ex. blue cone or s-cone monochromacy
If a pt were presented with two stimuli that differ in wavelength, could this patient tell them apart based on wavelength?
Yes a trichromat would, they could tell two wavelengths apart because photopigments have an absorption spectrum that varies on wavelength which translates to perceived brightness. So two wavelengths have different absorption rates
Why is it easy for a monochromat to tell two different wavelengths apart and match them?
they can adjust their relative intensities which is how we can fool them too as they they can’t distinguish based on wavelength alone, their perceived differences are based on brightness
A person with peak sensitivity at 507 nm would see which one brightest? 505 nm (green), 570 nm (blue), or 620 nm (red)
the green and the red would be the dimmest
What is dichromacy?
retina with two different photoreceptors (M&L cones, and rods).
Can trichromats distinguish colors based solely on wavelength?
yes, you would need 4 wavelengths to fool them
Can a dichromate distinguish two wavelengths based on wavelength solely?
yes, only two they have superior discrimination to monochromats
Why do dichromats have superior discrimination than monochromats?
due to presence of additional photopigments
How many wavelengths needed to trick a dichromat?
3 wavelengths
What is a metamer?
two stimuli that contain different wavelengths, yet appear identical
We have established that the human eyes typically has __________ types of cone photopigments
3 types of cone photopigments
What are the three different methods to determine the absorption spectra of each cone?
electrophysiological
densitometry
genetic modifications
What are the electrophysiological thresholds?
a microelectrode measures electrical response of an isolated cone to monochromatic light
minimum radiance needed to elicit a response = threshold for that wavelength
repeat for many wavelengths to determine the threshold spectrum
What does the threshold spectrum inverse give you?
the sensitivity spectrum for each types of cone
What is densitometry
shining different wavelengths of light into the eye and measuring the amount of light reflected back
unreflected light indicates absorption
What did Molecular Geneticist Jeremy Nathans do?
isolated the genes that encode for each photopigment
Genes for each photopigment isolated & transfected into cell cultures.
Cells expressed 3 unique cone pigments, allowing measurement of each of their spectra.
revealed the wavelength of light each photopigment is most sensitive to
Cone photopigment molecules are composed of two things:
chromophore (identical for all cone photopigments)
opsin (each cone has a different type of opsin)
Chromophores
identical for all cone photopigments
composed of retinal (der. of Vit A (retinol))
Absorbs light → initiates vision.
Opsin
Chain of amino acids in the outer segment discs.
Determines spectral sensitivity of the cone.
Different opsins → S, M, L cone differences.
consistent with inheritance of color deficiencies, X-chromosome contains the genetic coding for
M and L-cone opsins
typically only 1 L cone opsin copy and multiple M cone copies
What are the coding cone photopigments?
Cone Type | Gene Location | Notes |
|---|
L- & M-cones | X chromosome | Explains X-linked inheritance of red–green color deficiencies. |
S-cones | Chromosome 7 | Not sex-linked. |
Rods (rhodopsin) | Chromosome 3 | — |
Which genes are very similar showing 98% homology?
M and L-cone opsin
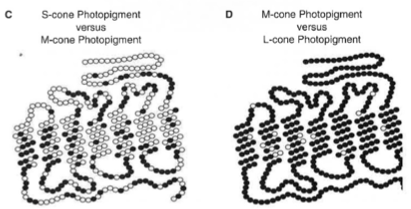
Which opsin genes are only 40% homologous to M or L-cone opsin genes?
s-cone opsin genes
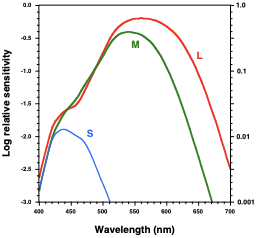
Nathan’s research revealed the wavelength of light that each photopigment is most sensitive to, what was determined by doing so?
S-Cones: maximal absorption at 426nm
M-Cones: maximal absorption at 530nm
L-Cones: two variants found
Variant 1: maximal absorption at 552nm
Variant 2: maximal absorption at 557nm
Vλ (luminance function), is aroung 555nm, what could be supposed if you have variant 1 of L cones?
That your peak would be lower around 550 nm because variant 1 is 552 nm and variant 2 is 557.
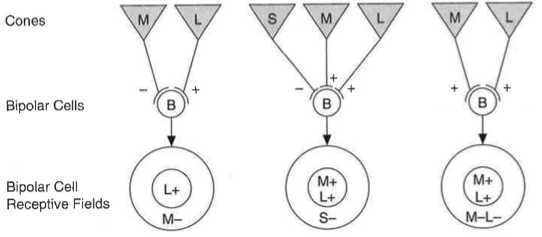
What do studies show about signals from the S, M, and L-cones
they are combined and processed by three neural channels:
red-green color opponent channel
blue-yellow color opponent channel
non-color opponent channel (encodes brightness only)
What did Hering hypothesize about color processing?
color is processed by bipolar hue channels referred to as red-green and blue-yellow- not simultaneously but one at a time,
red elicits a green afterimage and so does yellow with blue
What is color opponent cells?
neurons in the channels that modulate their response (excitation/inhibition) depending on the stimulus wavelength
What are non color opponent cells?
cells that respond with the same polarity (excitation) for all wavelengths varying magnitude of the response
What are the two theories of color opponent cells?
Theory 1: color opponent cells are devoted exclusively to encoding Hue and have no role in brightness info (fits with non-color opponent cells)
Theory 2: color opponent cells encode hue and brightness (Double Duty hypothesis)