Hemodynamics Final - 125 DMS
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
174 Terms
Which of the following definitions, best describes the term "hemodynamics"?
study of the anatomy of the heart and blood vessels
study of blood vessels and how they interact at the cellular level
study of blood components
study of blood moving through the circulatory system
study of blood moving through the circulatory system
All of the following would be considered part of the Four Pumps that assist blood flow throughout the body EXCEPT:
heart pump
vertebral pump
aortic pump
calf muscle pump
respiratory pump
vertebral pump
When discussing or measuring "flow", AKA "volume flow rate", one would most likely be measuring what and using which units of measure?
discussing the number of blood cells passing through a vessel wall and using a concrete number such as 320
discussing the amount of blood flow and using a volume unit such as liter
discussing the amount of blood flow over a specified period of time and using a volume unit such as liter divided by a unit of time such as minute
discussing the speed of blood flow over an hour and using an area unit such as centimeter squared and a time unit such as hour
discussing the amount of blood flow over a specified period of time and using a volume unit such as liter divided by a unit of time such as minute
If a sonographer were to measure flow velocity, he would most likely record the flow velocity and report it to the physician in which of the following units of measure?
miles per hour
millimeters per microsecond
meters per hour
centimeters per second
centimeters per second
Of the following forms of flow, which is most likely associated with the arterial system?
pulsatile
phasic
steady
pulsatile
Of the following forms of flow, which is most likely associated with the venous system?
pulsatile
phasic
steady
phasic
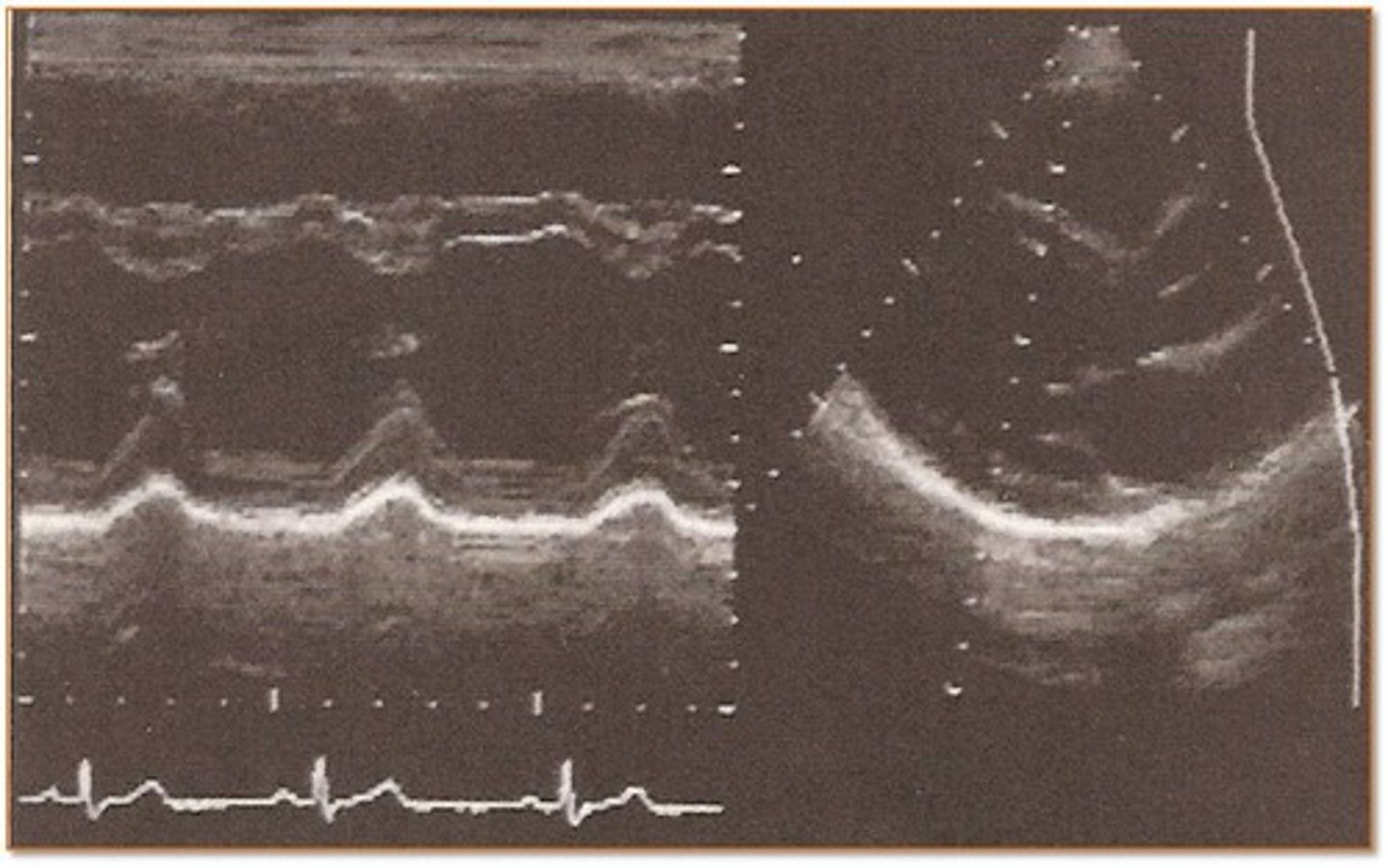
Referencing the image at the right, what type of flow pattern is demonstrated?
pulsatile
Correct! phasic
steady
phasic
Referencing the picture at the right, if this were representing blood flow through a vessel, which of the following best describes the conditions of blood flow?
wide, smooth, laminar, low velocity
narrow, turbulent, changing directions, high velocity
narrow, turbulent, changing directions, high velocity
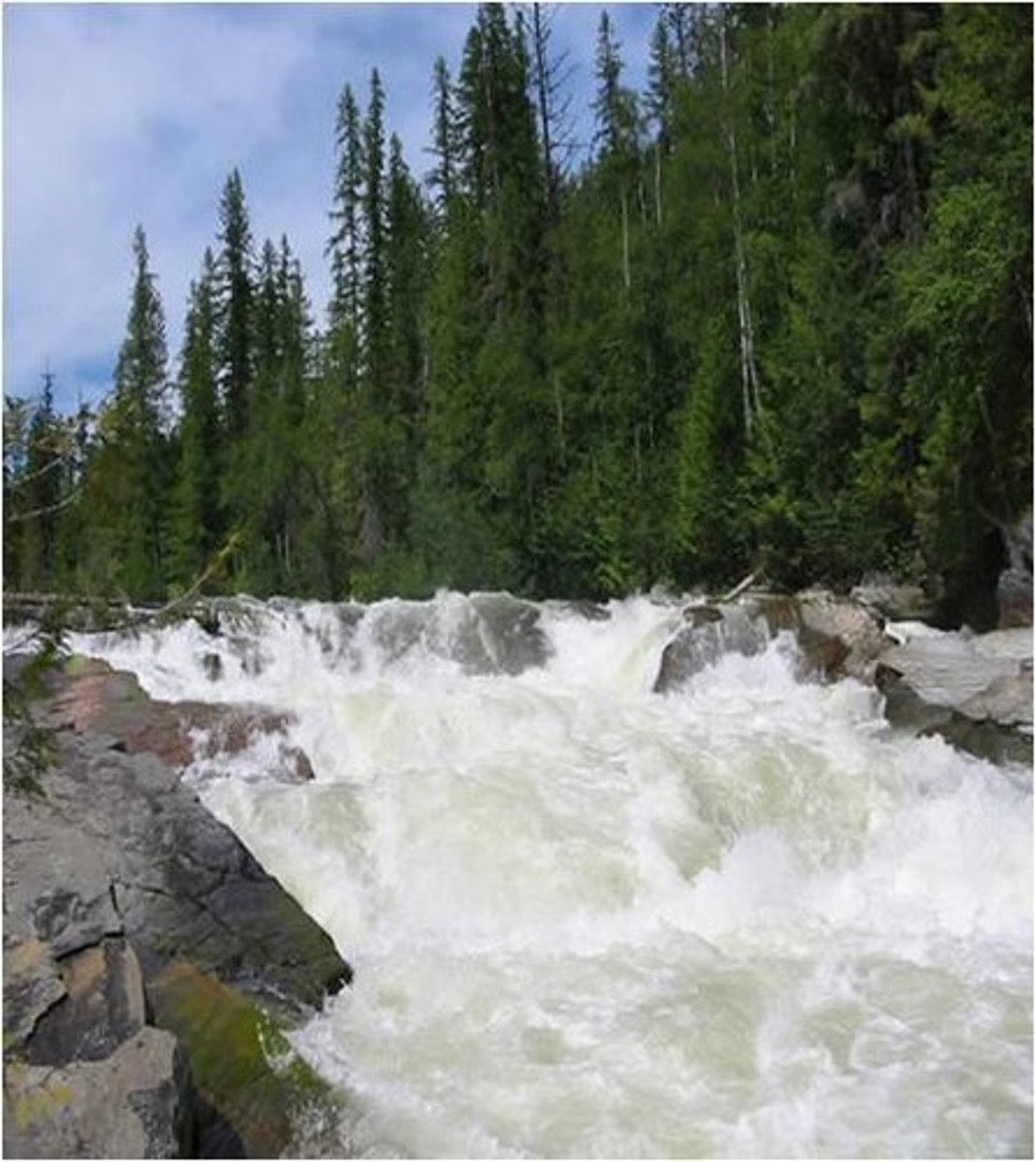

Referencing the image at the right, what type of flow pattern is demonstrated?
pulsatile
phasic
steady
pulsatile
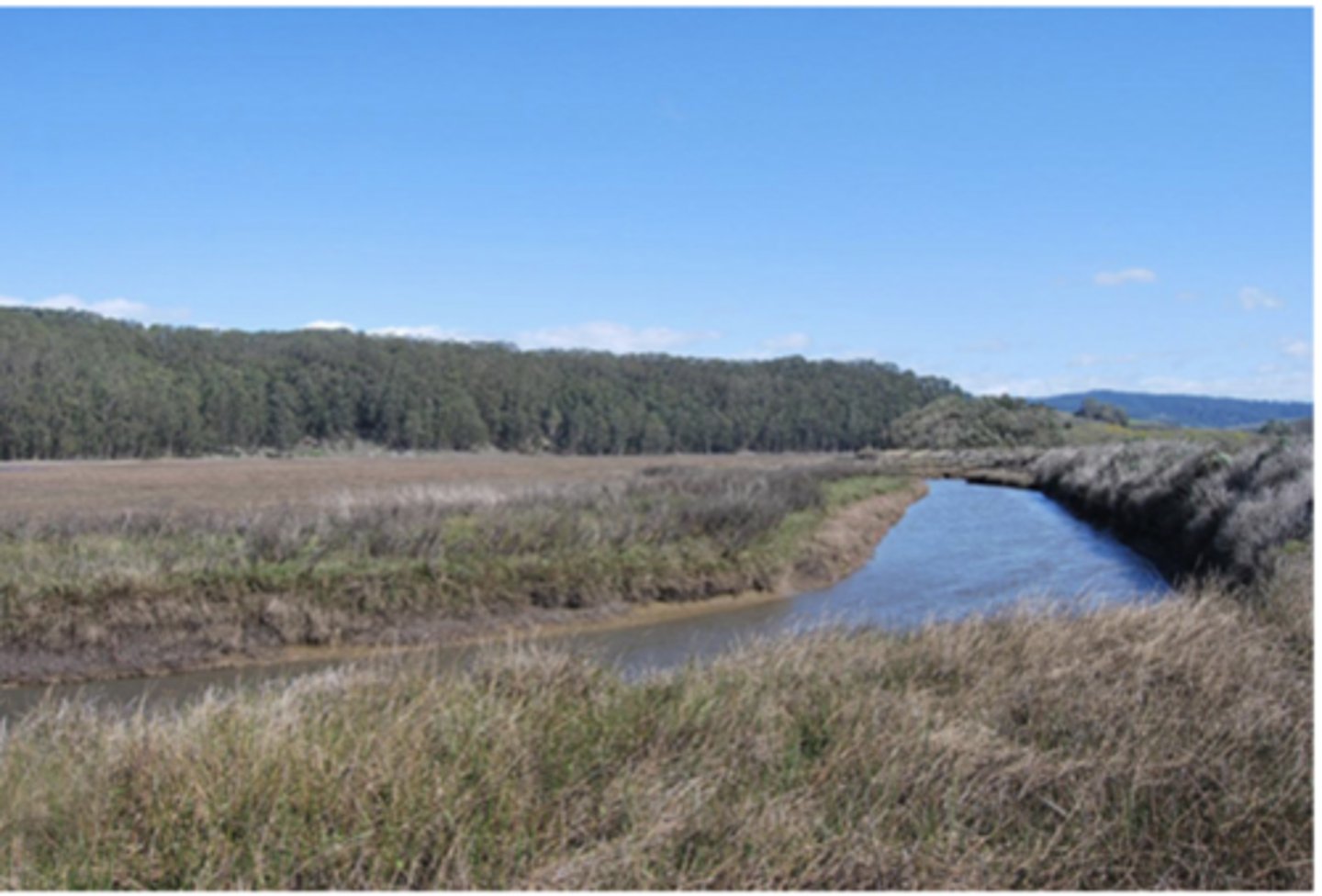
Referencing the image to the right, if you were to compare this river to blood flow through a vessel, which statement best describes the characteristics that would be found within that vessel?
slow flow, laminar, slower in the middle, faster along the walls
turbulent, high velocity flow, faster in the middle, slower along the walls
slow flow, laminar, faster in the middle, slower along the walls
turbulent, low velocity flow, slower in the middle, faster along the walls
slow flow, laminar, faster in the middle, slower along the walls

In order for fluid to flow from one place to another, there must be a...
difference in temperatures (temperature gradient)
difference in velocities (velocity gradient)
difference in pressures (pressure gradient)
difference in molecular density (density gradient)
difference in pressures (pressure gradient)
When the left ventricle contracts, blood leaves the heart with a particular force or energy, but it immediately begins to lose steam (energy). What characteristic of blood contributes to this loss in energy?
viscosity
plasma
platelets
White Blood Cells
viscosity
Which of the following results in energy loss as blood moves through a vessel?
pressure
blood type
friction
content of the blood cells mitochondria
friction
Which statement best describes the concept being illustrated by the diagram to the right?
The pressure wave of blood moves slowest in the center of the stream and fastest along the outer walls, resulting in the backwards parabolic appearance.
The friction along the walls of the vessel results in an energy loss and a reduction in the velocity of blood cells moving along the walls while the velocity of flow of the blood cells in the center of the vessel continue to move more quickly, resulting in the bullet shape.
The maximum velocity is in the center of the vessel due to the pressure being in the center and not on the walls.
The friction along the walls of the vessel results in an energy loss and a reduction in the velocity of blood cells moving along the walls while the velocity of flow of the blood cells in the center of the vessel continue to move more quickly, resulting in the bullet shape.
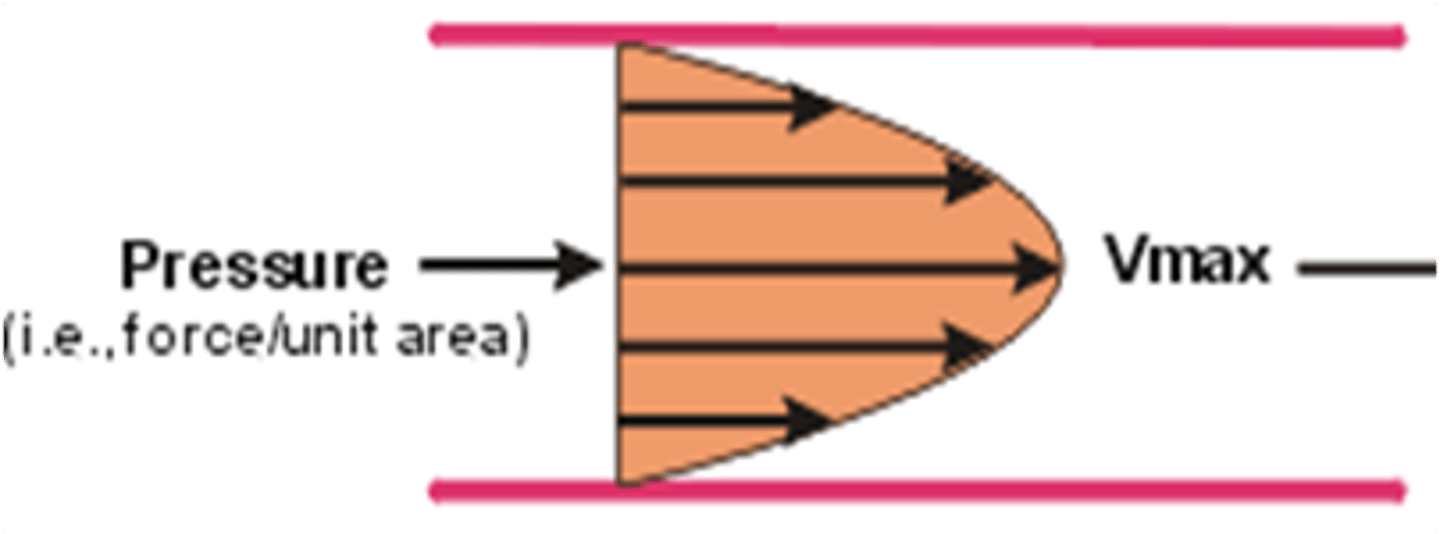
Using your critical thinking skills, if inertial energy loss occurs when there is a change in the motion of blood (Newton's Law of Motion), then in which of the following situations would it be least likely for an inertial energy loss to occur?
pulsatile blood flow
phasic blood flow
turbulent blood flow
steady blood flow
steady blood flow
You learned that a pressure gradient (or change/difference in pressure) is needed for blood to flow. For example, blood moves from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure, just as humans avoid areas of high pressure in their lives and move to areas of comfort or low pressure.
If the concept is represented by the following: Pressure Gradient = flow x resistance, what happens to the pressure gradient if resistance increases?
The pressure gradient or difference in pressure also increases.
The pressure gradient or difference in pressure decreases.
The pressure gradient or difference in pressure does not change at all.
The pressure gradient or difference in pressure also increases.
Voltage = current x resistance is a formula that described by...
Newton's First Law of Motion
Doppler's Law
Reynold's Law
Ohm's Law
Ohm's Law
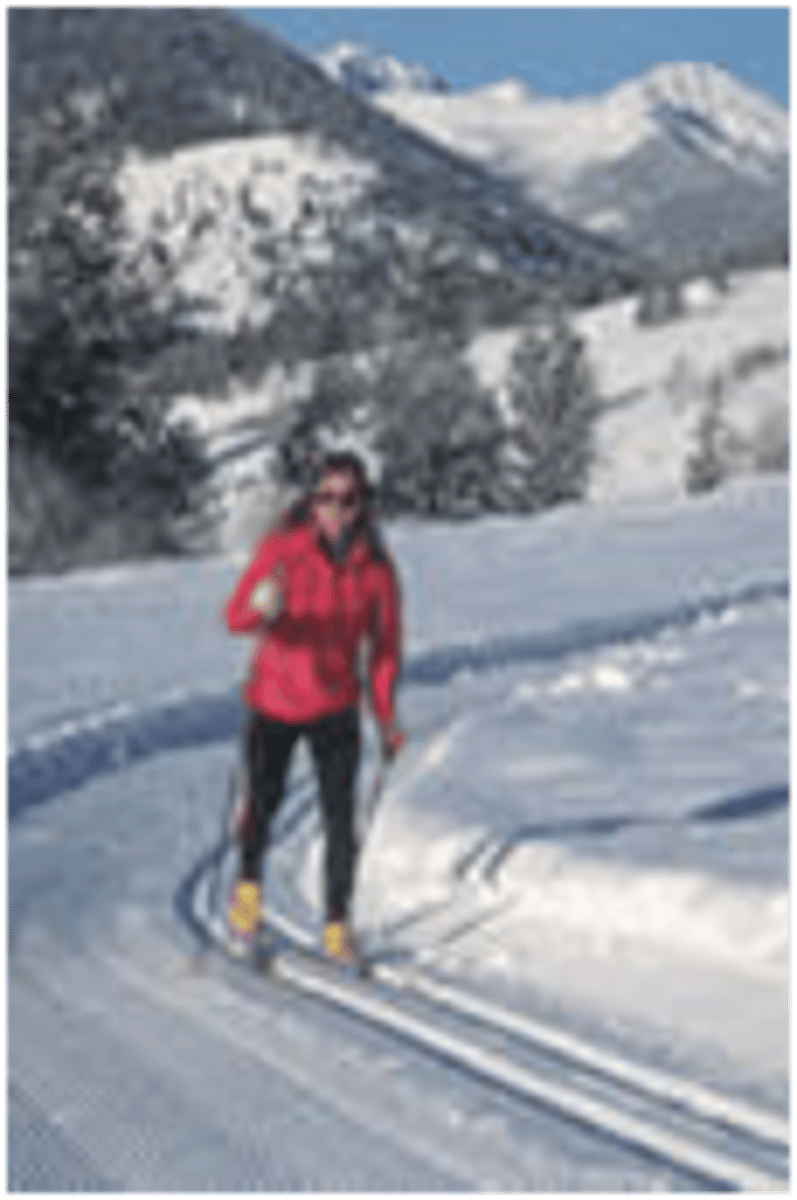
Referencing the skiier on the right, if she was spending the day cross country skiing and a friend was spending the day downhill skiing, which one would have benefited from the effect of gravitational energy?
the downhill skier
the cross country skier
the downhill skier

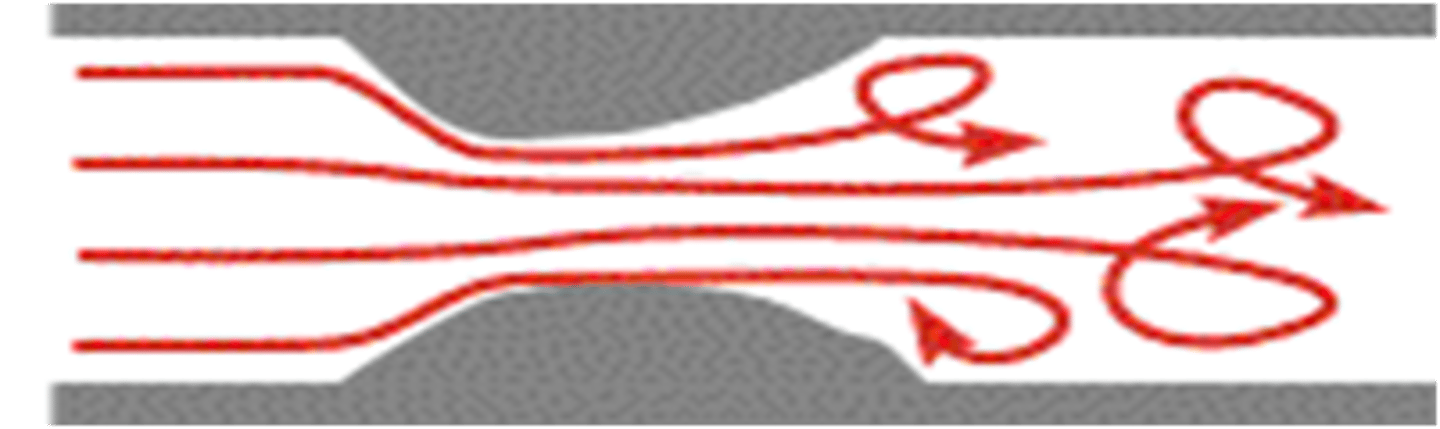
Referencing the diagram to the right, what hemodynamic principle is illustrated:
flow disturbance post-stenosis demonstrating turbulent flow reversal and loss of energy due to friction
laminar flow appearance downstream from a bifurcation
laminar flow appearance through a pulsatile artery
flow disturbance post-stenosis demonstrating turbulent flow reversal and loss of energy due to inertia
flow disturbance post-stenosis demonstrating turbulent flow reversal and loss of energy due to inertia
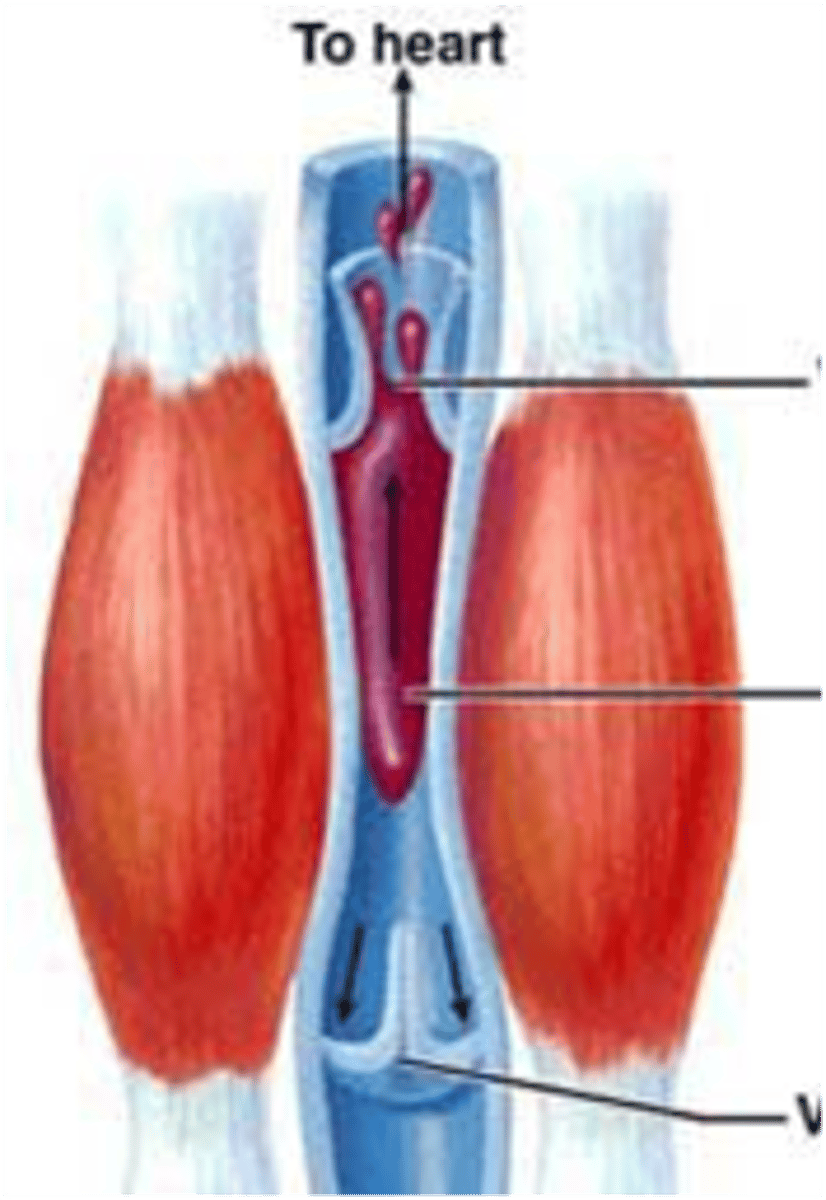
Of the four pumps that cause blood to flow throughout the body, which one is represented by the diagram on the right?
heart pump
aortic pump
calf muscle pump
respiratory pump
calf muscle pump
All of the following are pumps that help circulate blood throughout the body EXCEPT:
heart pump
aortic pump
digestive pump
calf muscle pump
respiratory pump
digestive pump
Which of the following best describes the role of the heart pump?
starts the flow of blood to the legs
starts the flow of blood to the heart
starts the flow of blood to the brain
starts the flow of blood to the body and lungs
starts the flow of blood to the body and lungs
All of the following are required for blood to flow out of the heart EXCEPT:
chemical change in the blood
electrical conduction
mechanical contraction of the heart muscle
pressure gradient between one side of a heart valve and the other
chemical change in the blood
Pertaining to the electrical conduction system, which component is known as the pacemaker of the heart?
Bundle of HIS
Purkinjie Fibers
Internodal Tract
Sino-atrial Node
Sino-atrial Node
The muscle layer of the heart responsible for effective pumping is known as the...
endocardium
epicardium
myocardium
pericardium
myocardium
All of the following are functions of the heart and circulation EXCEPT:
provide blood and nutrients
regulate fluids in the body
supply cells with oxygen
remove carbon dioxide and wastes
regulate fluids in the body
Which valve separates the left ventricle from the aorta?
tricuspid valve
pulmonary valve
mitral valve
aortic valve
aortic valve
The heart needs its own blood supply but does not get it from the blood going through the chambers. Which of the following supplies the heart with blood and oxygen needed to maintain cardiac health?
coronary sinus
coronary plexsus
coronary arteries
coronary ligament
coronary arteries
The test that records the electrical activity of the heart is called...
an electroencephalogram
an echo-cardiogram
an electrocardiogram
a pulmonary function test
an electrocardiogram
Referencing the picture at the right, if this were representing blood flow through a vessel, which of the following best describes the conditions of blood flow?
wide, smooth, laminar, low velocity
narrow, turbulent, changing directions, high velocity
narrow, turbulent, changing directions, high velocity
The valve that separates the right atrium from the right ventricle is the...
tricuspid valve
mitral valve
aortic valve
pulmonary valve
tricuspid valve
In order for blood to flow from one chamber to the next, there must be a...
pressure gradient
the same pressures in both chambers
papillary muscles
chordae tendinae
pressure gradient
In order for there to be mechanical contraction of the heart, there must be...
electrical activity
muscular system
circulation
de-oxygenated blood
oxygenated blood
electrical activity
Which of the following separates the right ventricle from the left ventricle?
Tricuspid valve
Interatrial septum
Mitral valve
Interventricular septum
interventricular septum
Referencing the image to the right, which imaging mode is illustrated and what function is demonstrated?
Doppler mode illustrating blood flow through the heart
Spectral Doppler mode illustrating flow velocities
Gray scale mode illustrating heart valve motion
M-mode illustrating heart wall motion and heart valve motion
M-mode illustrating heart wall motion and heart valve motion
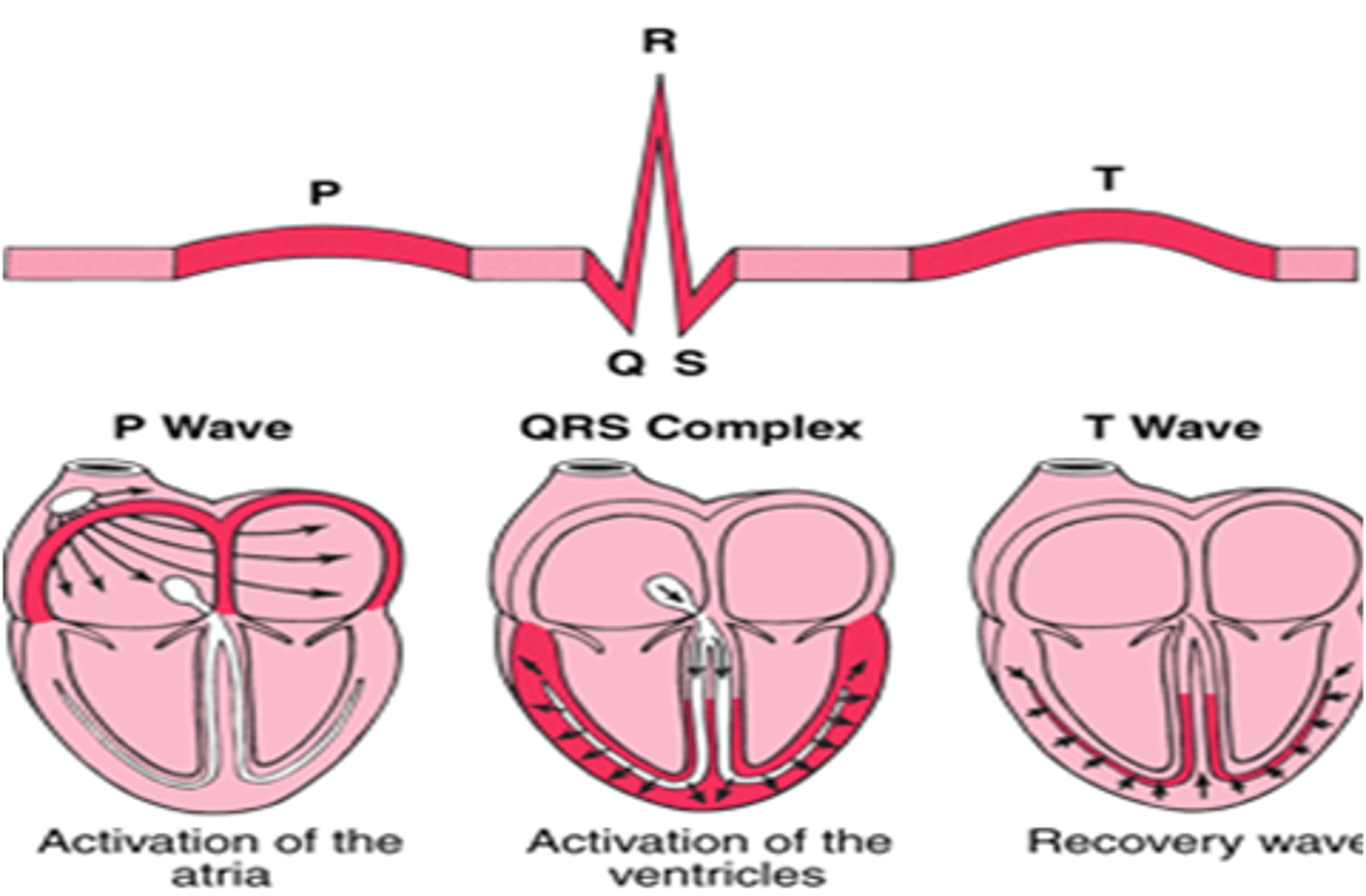
Which of the following waveforms of the EKG represent ventricular contraction?
P wave
QRS complex
T wave
QRS complex
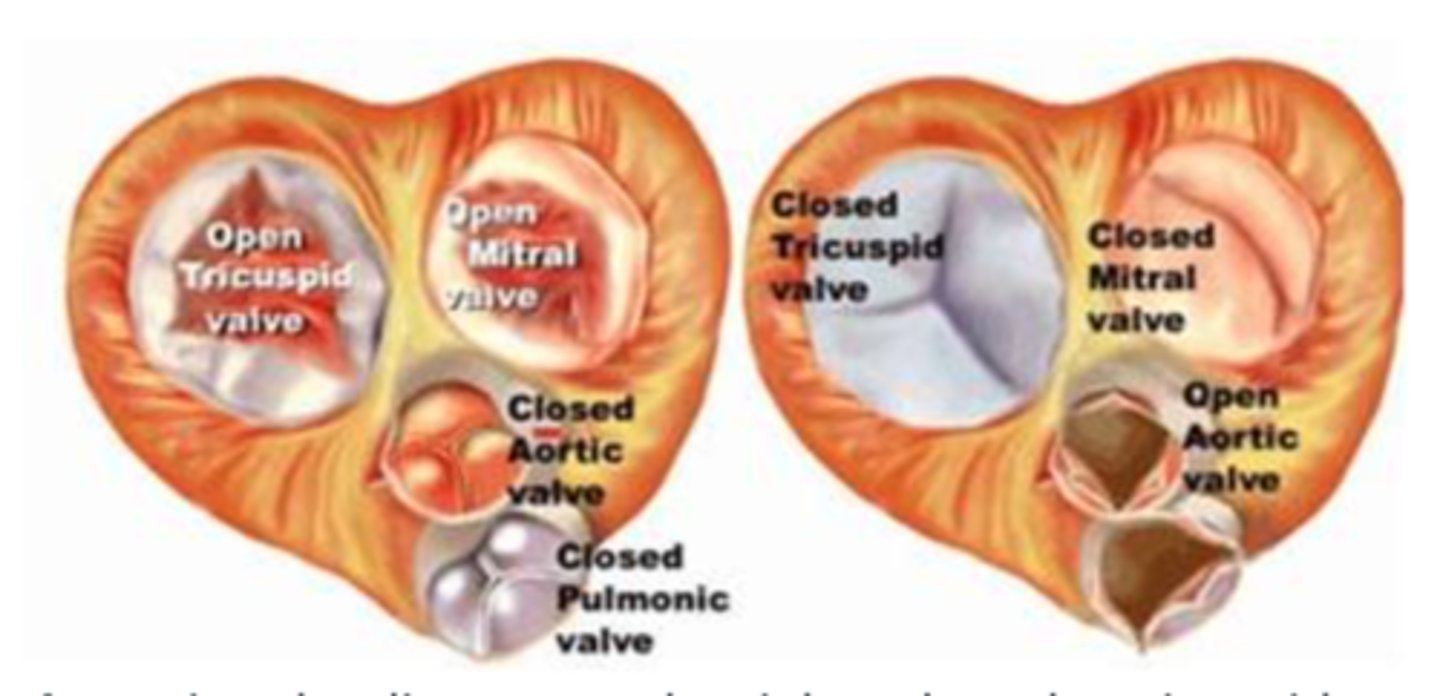
Referencing the diagram to the right, when the tricuspid and mitral valves are open, but the aortic and pulmonic are closed, the heart is in which phase of the cardiac cycle?
systole
diastole
diastole
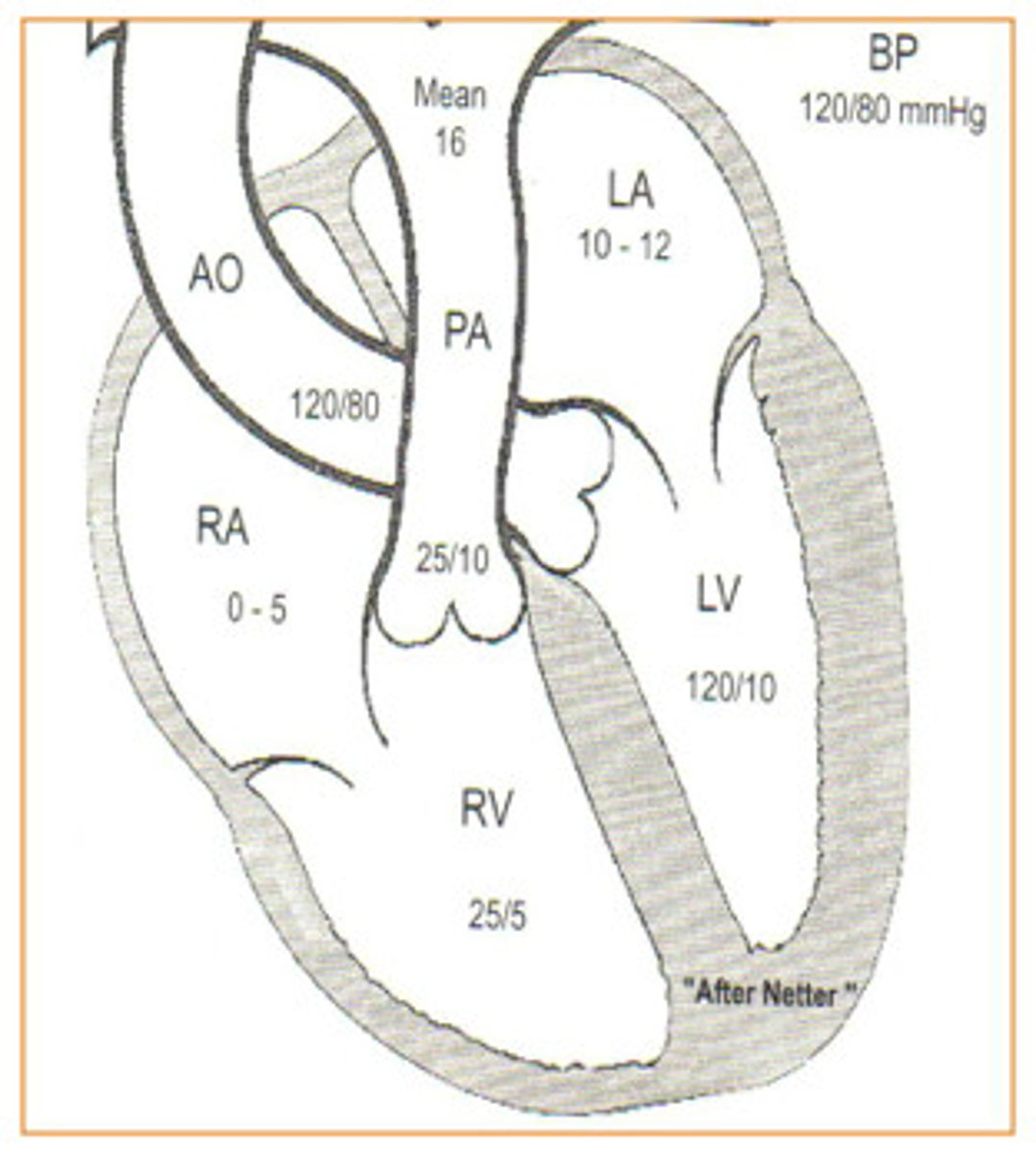
Referencing the diagram to the right, the pressures within different locations within the heart have been labeled. Based upon this information, what must the pressure be in the left ventricle before the aortic valve will open?
greater than 120/80
greater than 120/10
greater than 25/10
greater than 25/5
greater than 120/80
Which of the following best describes the concept of "pre-load"?
relates to what happens to blood after it leaves the heart (arterial outflow)
relates to what happens prior to blood entering the heart (venous return)
relates to what happens prior to blood entering the heart (venous return)
Of the four pumping mechanisms that cause blood to circulate throughout the body, which of the following has the thick media walls that accepts a bolus of blood that with contractile recoil pushes blood through the vessel?
heart pump
aortic pump
calf muscle pump
respiratory pump
aortic pump
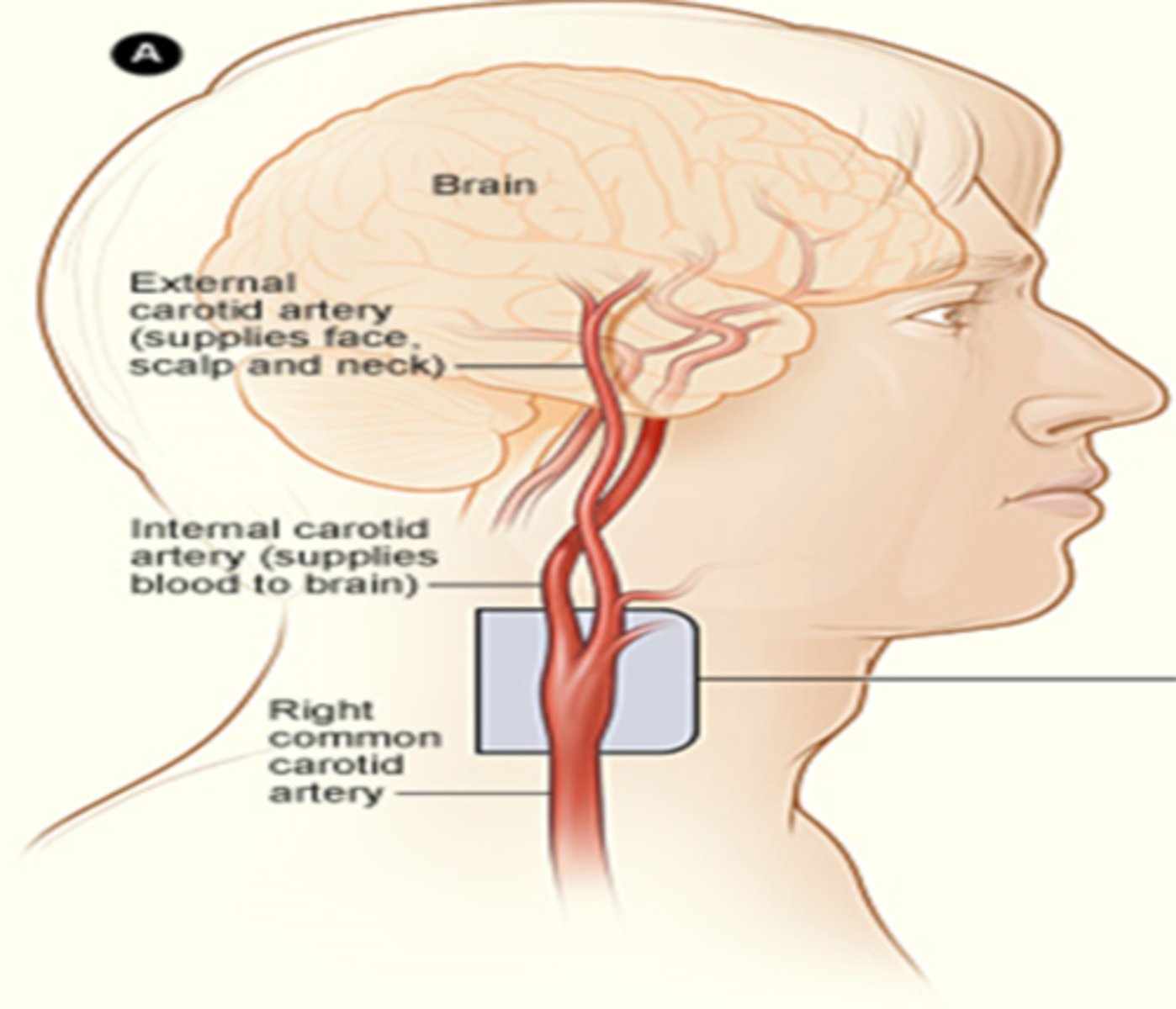
While the Left Common Carotid Artery branches directly from the aortic arch, bifurcates into the Internal Carotid Artery and External Carotid Artery, the Right Common Carotid Artery has a slightly different route. Which of the following best describes how blood gets to the right side of the face and brain?
blood travels off the aortic arch, through the brachiocephalic or innominate artery to the right common carotid artery to the right internal and right external carotid arteries
blood travels off the aortic arch, through the brachiocephalic or innominate artery to the right common carotid artery to the right internal and right external carotid arteries
The descending aorta provides blood to all of the following organs, tissue, cells EXCEPT:
abdominal organs
pelvic organs
upper extremities
lower extremities
upper extremities
The term "bolus" refers to...
a small quantity of red blood cells
a large quantity of something administered all at once, such as blood or nutritional supplement or medication
a small quantity of something administered all at once, such as blood or nutritional supplement or medication
a large quantity of white blood cells
a large quantity of something administered all at once, such as blood or nutritional supplement or medication
It is extremely important for sonographers to recognize the difference between blood flow patterns associated with the Internal Carotid Arteries that bring blood to the brain and the External Carotid Arteries that bring blood to the face and scalp. What percentage of blood from the Common Carotid Artery (CCA) branches to the ICA?
10%
20%
50%
80%
80%
It is extremely important for sonographers to recognize the difference between blood flow patterns associated with the Internal Carotid Arteries that bring blood to the brain and the External Carotid Arteries that bring blood to the face and scalp. If the capillary vascular bed that receives blood from a vessel is said to be "low resistance", which of the statements below best describes the characteristics of blood flow.
blood flow is forward during diastole, but reversed during systole
blood flow is forward during systole, but reversed during diastole
blood flow is forward during both systole and diastole
blood flow is reversed in both systole and diastole
blood flow is forward during both systole and diastole
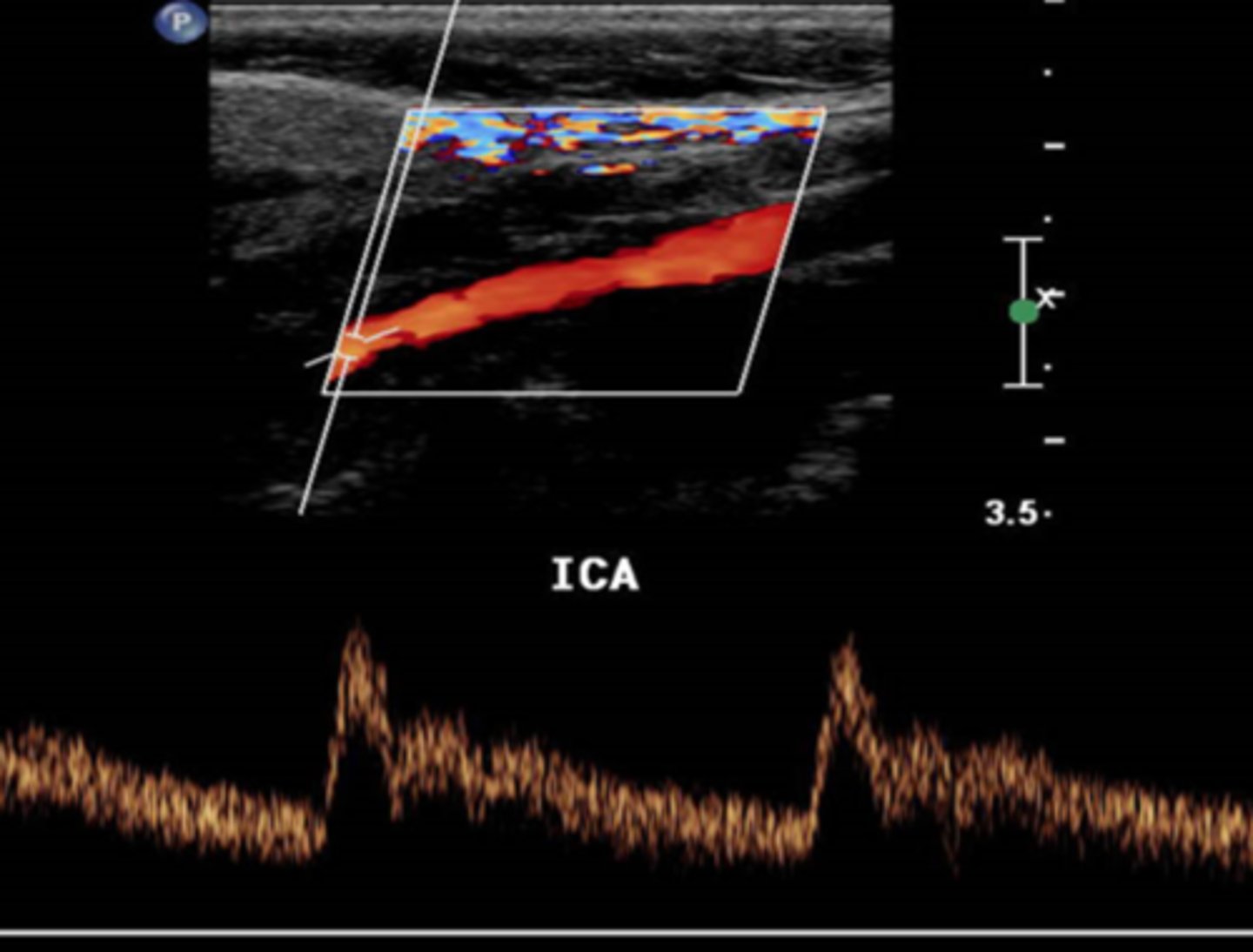
It is extremely important for sonographers to recognize the difference between blood flow patterns associated with the Internal Carotid Arteries that bring blood to the brain and the External Carotid Arteries that bring blood to the face and scalp. If a sonographer were to describe the flow in a high resistance vascular bed and how that would look on a spectral Doppler waveform, the sonographer might say...
the spectral Doppler tracing accelerates to a peak in systole and then touches the baseline during diastole
the spectral Doppler tracing accelerates to a peak in systole, decelerates in diastole, but does not touch the baseline
the spectral Doppler tracing accelerates to a peak in systole and then touches the baseline during diastole
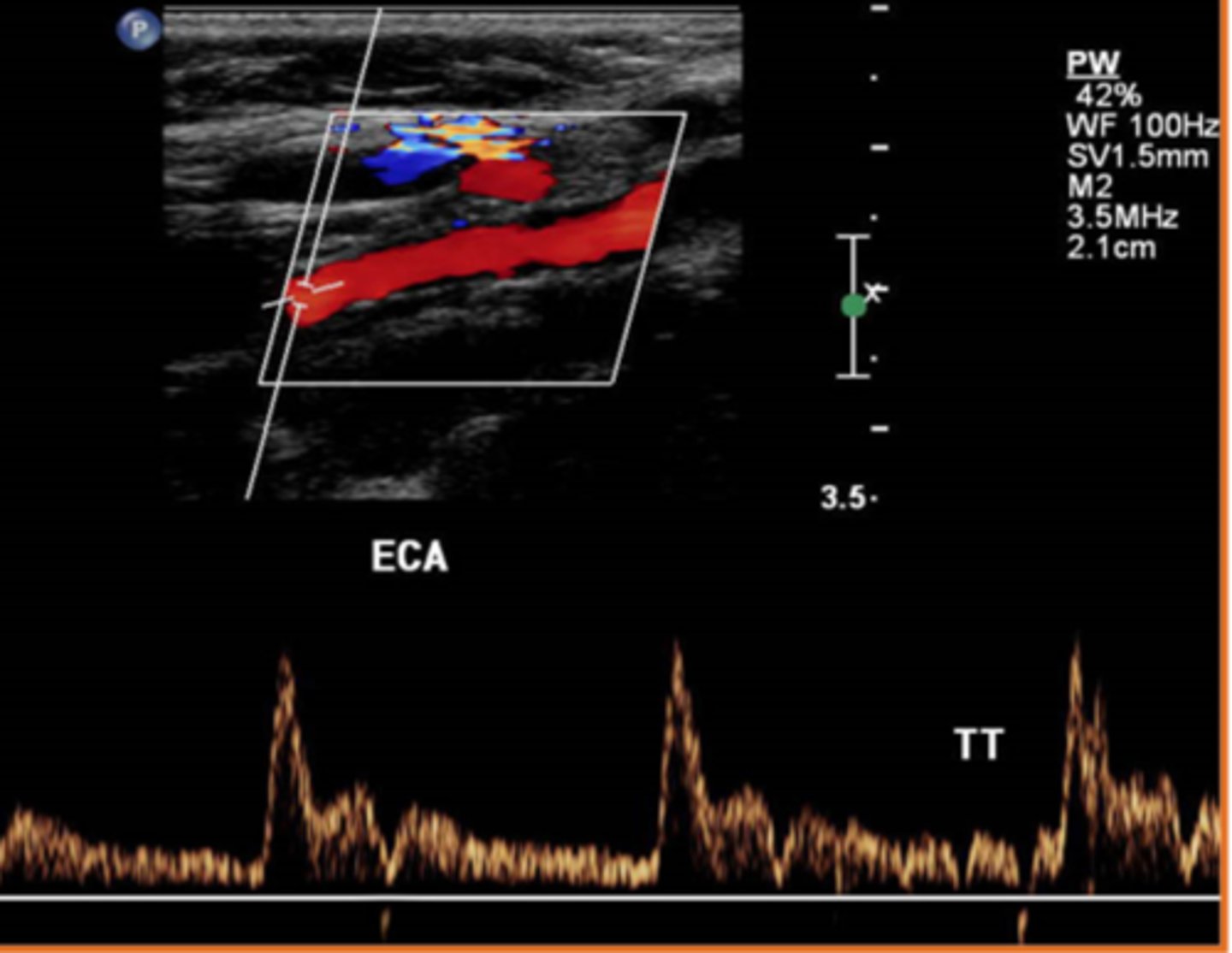
Which of the following best describes the term "peak systole"?
the lowest velocity throughout the cardiac cycle
the highest velocity during the ventricular relaxing phase of the cycle
the highest velocity during the entire cycle (contracting and relaxing)
the lowest velocity during the ventricular contracting phase of the cycle
the highest velocity during the entire cycle (contracting and relaxing)
Which of the following statements best describes the term "end-diastole"?
the lowest velocity, just prior to the upstroke associated with the next cardiac cycle
the highest velocity, just prior to the down stroke associated with the next cardiac cycle
the lowest velocity, just prior to the down stroke associated with the next cardiac cycle
the highest velocity, just prior to the upstroke associated with the next cardiac cycle
the lowest velocity, just prior to the upstroke associated with the next cardiac cycle
Which of the following statements best describes the term "window filling"?
a recording of the highest velocities associated with blood flowing through a window
a recording of the highest velocities associated with blood flowing through a sample gate
a recording of the varied velocities between the highest and the baseline flowing through a window
a recording of the varied velocities between the highest and the baseline flowing through the sample gate
a recording of the varied velocities between the highest and the baseline flowing through the sample gate
Which of the following statements best describes the term "dicrotic notch"?
small downward deflection in the arterial pulse (pressure wave) immediately after the closure of the semi-lunar valves
small upward deflection in the arterial pulse (pressure wave) immediately after the closure of the semi-lunar valves
small downward deflection in the venous flow pattern after the patient takes a step
small downward deflection in the venous flow pattern after the patient takes a step
small downward deflection in the arterial pulse (pressure wave) immediately after the closure of the semi-lunar valves
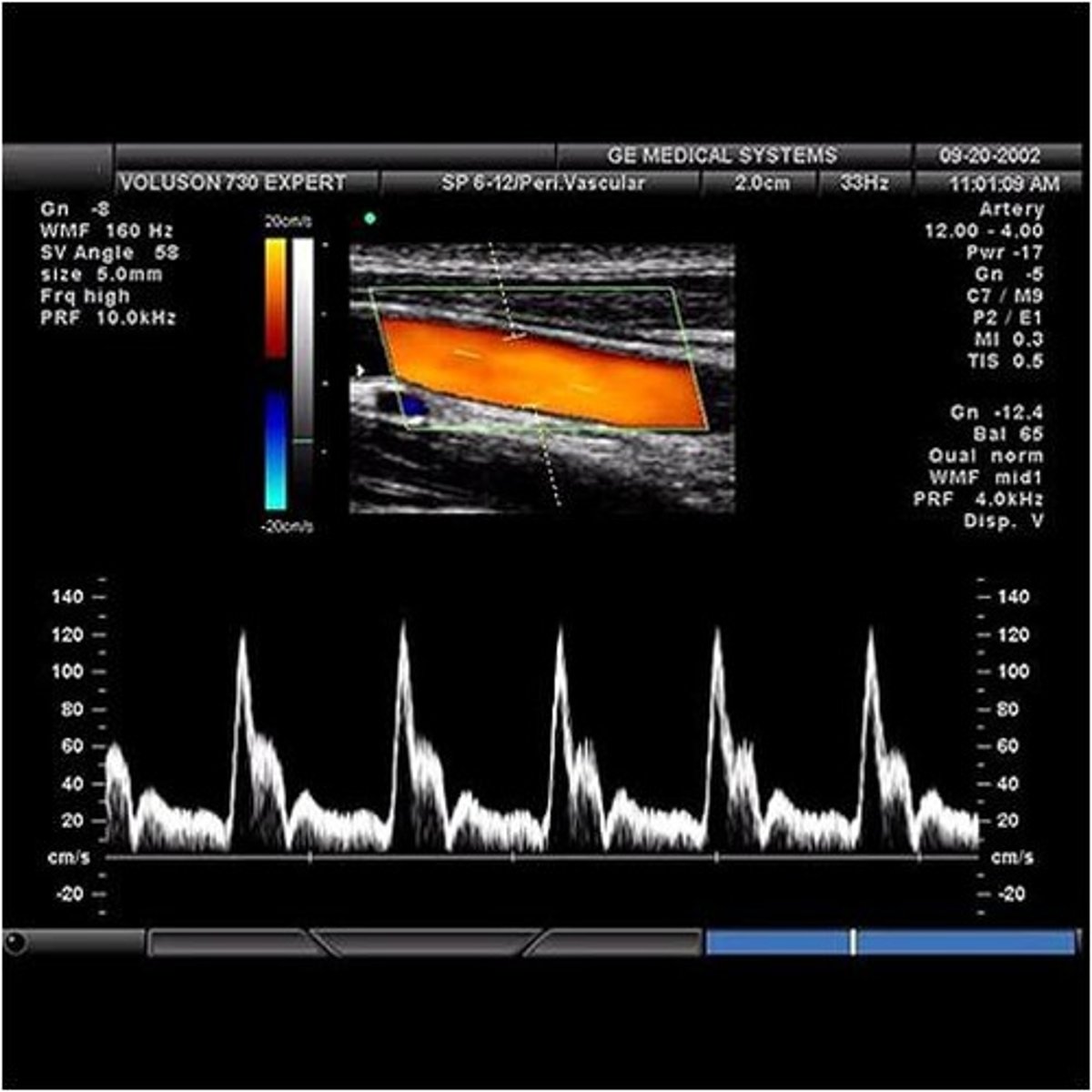
What characteristics do the CCA and ICA have in common?
sharp systolic upstroke
constant forward flow in diastole
rapid deceleration
constant forward flow in diastole
Color Doppler can provide all of the following information about blood flow EXCEPT:
absence or presence of flow
direction of flow
mean velocities of flow
smooth or turbulence of flow
quantifiable flow velocity
quantifiable flow velocity
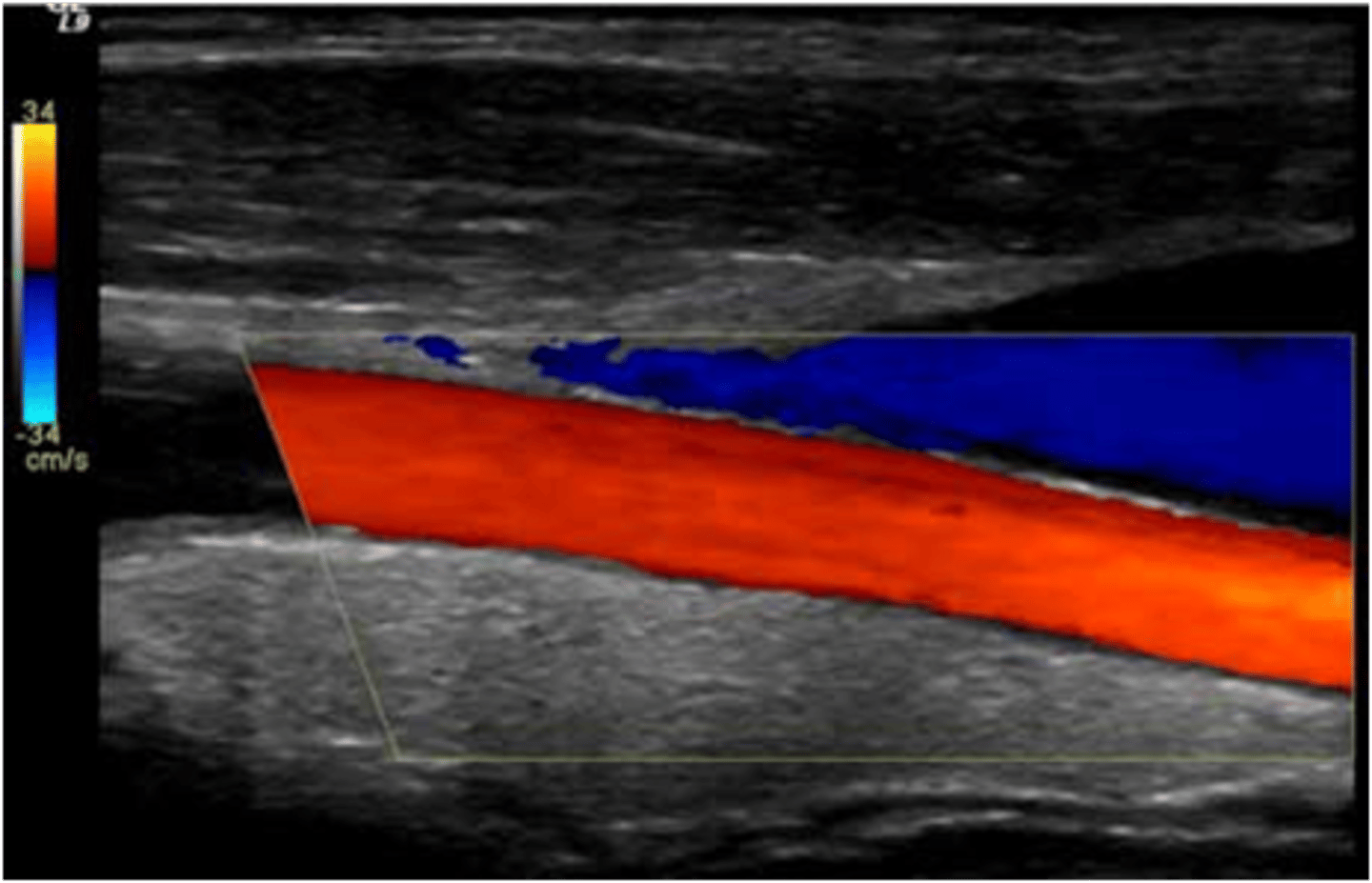
When scanning a carotid artery study on a patient, the sonographer notes a small area of reversed flow as detected by color flow Doppler in the area of the carotid bulb (bifurcation). Should the sonographer report this finding as normal or abnormal?
normal, this is a result of boundary layer separation due to change in flow direction at the bulb
abnormal, there is very likely an obstruction in this area that has resulted in blood flow reversal
normal, this is a result of boundary layer separation due to change in flow direction at the bulb
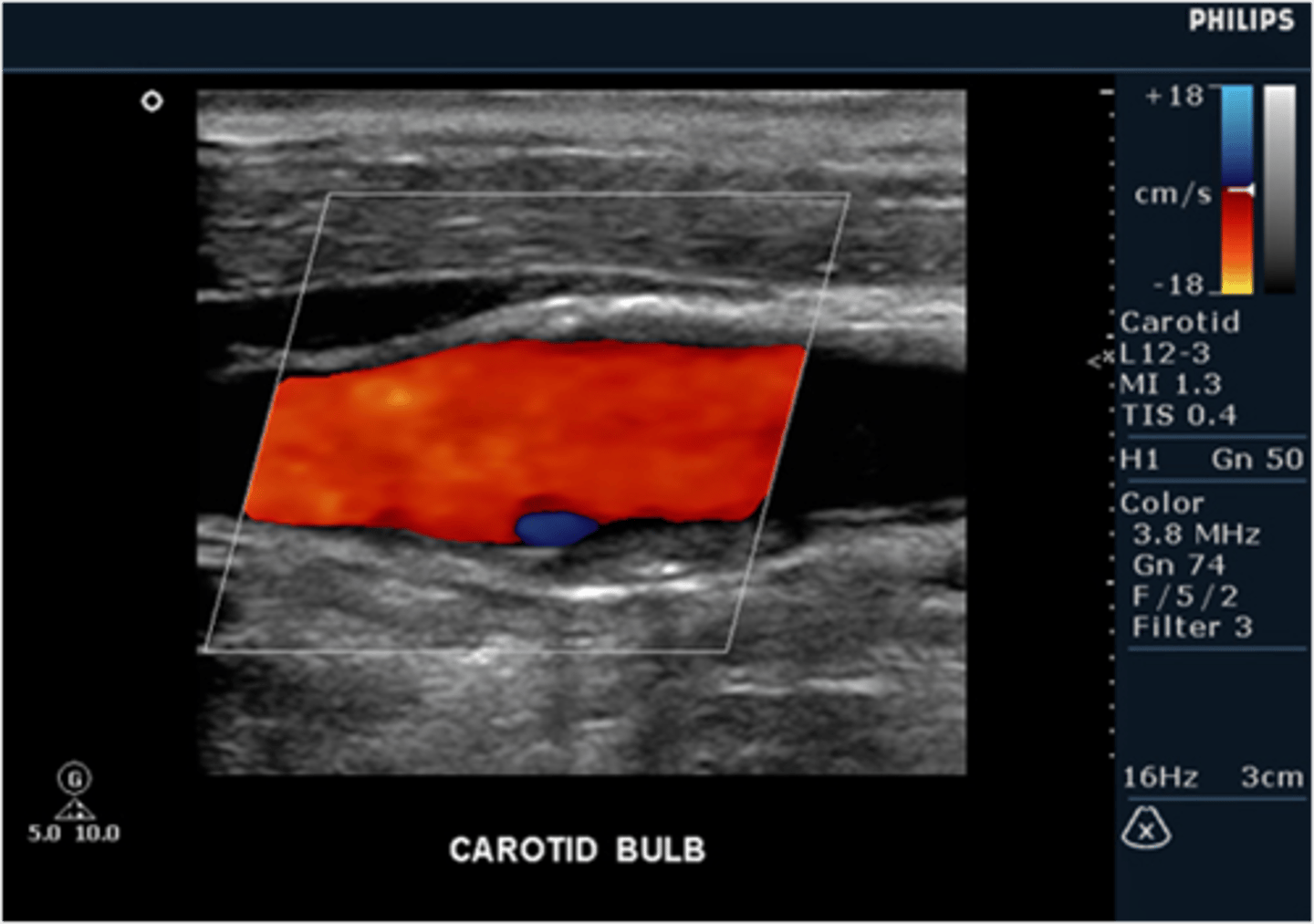
When scanning the cerebrovascular system (carotid arteries and vertebral arteries), the sonographer is ready to demonstrate flow in the vertebral arteries. What combination of ultrasound system adjustments should he/she make to properly visualize the vertebral arteries?
increase velocity scale and increase depth
decrease velocity scale and increase depth
decrease velocity scale and decrease depth
increase velocity scale and decrease depth
decrease velocity scale and increase depth
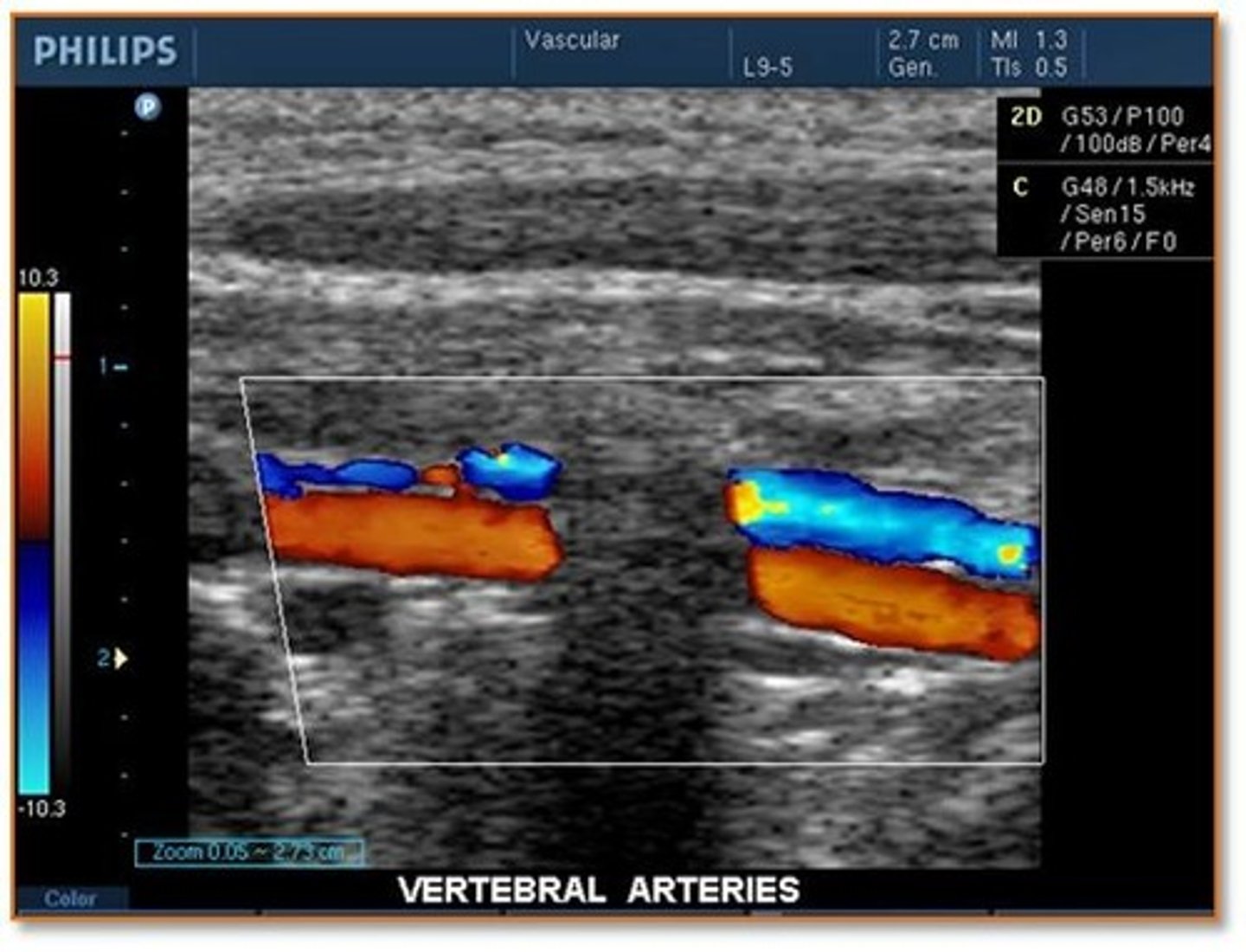
While scanning the vertebral arteries, the sonographer notes a significant shadowing effect through the vessel that interrupts the color Doppler information. How should the sonographer report this finding to the physician?
normal shadowing from the spinal processes
abnormal shadowing from plaque on the anterior wall of the vertebral artery
normal shadowing from the spinal processes
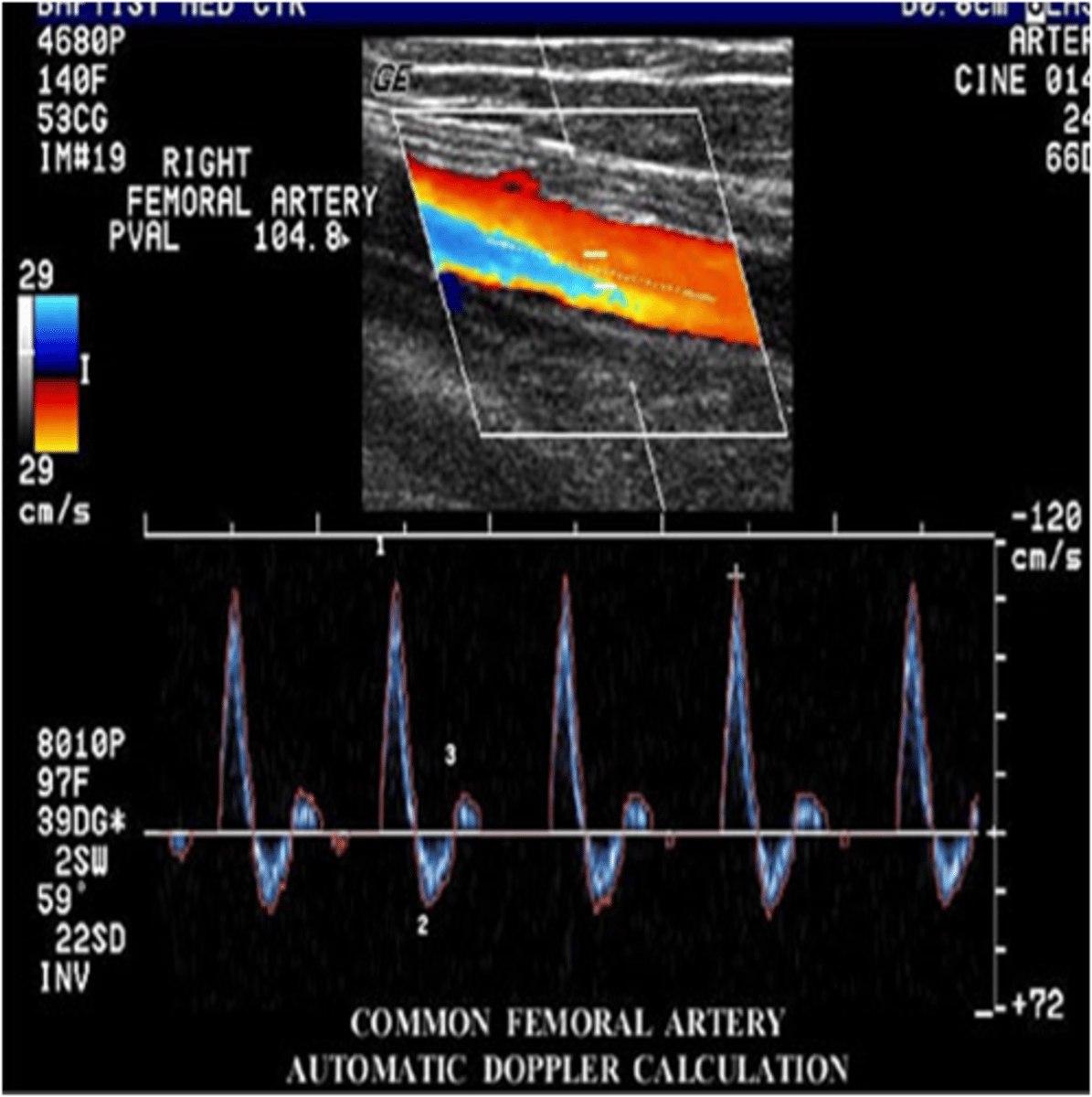
Unlike the cerebrovascular system that feeds the brain and requires continuous blood flow even during diastole when the heart is relaxing, the peripheral vascular system that feeds blood to the upper extremities (arms) and lower extremities (legs)has a very different waveform pattern. The term that best describes the normal waveform pattern associated with the peripheral arterial system of the legs is...
uniphasic
biphasic
triphasic
quadriphasic
triphasic
How does an increase in peripheral resistance to blood flow affect blood pressure?
it also increases
it decreases
it has no effect
it also increases
To which circulatory system does the concept of "peripheral resistance" apply?
all blood flow throughout the entire circulatory system
only the cerebrovascular system that has high and low resistance flow patterns and brings blood to the vital brain
only the peripheral vascular system that brings blood to non-vital organs
only the centralized circulatory system that brings blood to the vital organs of the abdomen such as the liver and kidneys
only the peripheral vascular system that brings blood to non-vital organs
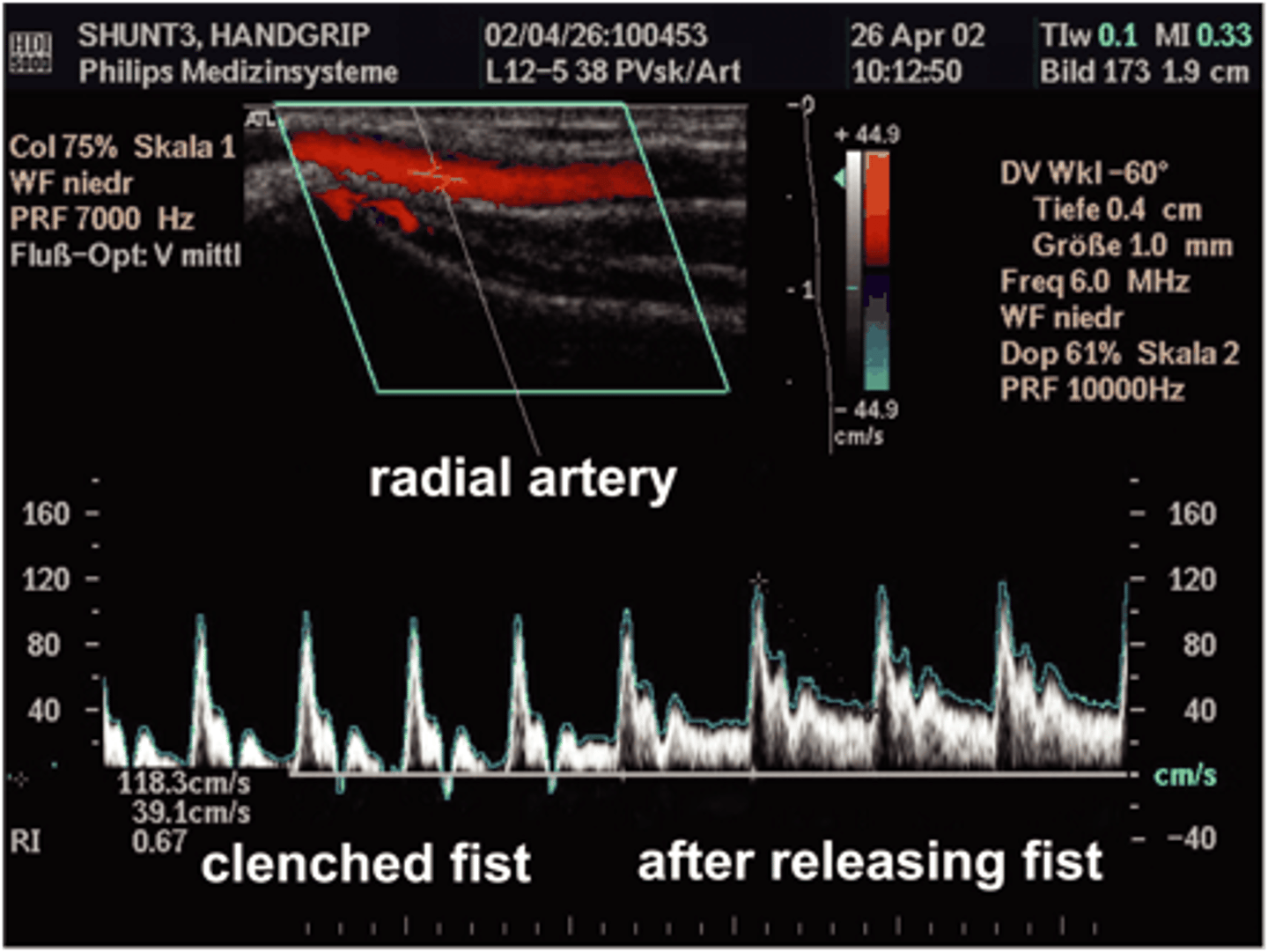
When the patient clenches and releases his fist, the waveform pattern of blood flow in his upper extremity changes. Which of the following statements provides the best explanation for why this occurs?
the fist clenching causes blood to flow more freely into the hand so it would be triphasic
the fist clenching increases peripheral resistance so the waveform becomes triphasic but when the fist is released blood flow freely and continuously so it becomes a low resistance pattern
the fist clenching decreases peripheral resistance so the waveform becomes low rsistance
the first clenches has not real effect on peripheral resistance
the fist clenching increases peripheral resistance so the waveform becomes triphasic but when the fist is released blood flow freely and continuously so it becomes a low resistance pattern
At what anatomical location on the body will the patient's measured pressure be less than his actual circulatory pressure?
the level of the head
the level of the heart
the level of the waist
the level of the knees
the level of the ankles
the level of the head

When veins are under their normal low pressure, which of the following shapes most represents their normal appearance?
hourglass
oval
round
hourglass
With exercise, blood flow increases through the artery to the muscle and therefore there is also an increase in blood volume that must be drained from the muscle by the vein. Which of the following statements best describes the change in a vein when a person exercises?
The vein expands to accommodate the increase in blood volume, but by increasing in size, there is little increase in pressure.
The vein collapses under the extra pressure from the increasing volume of blood draining from the muscle.
The vein expands to accommodate the increase in blood volume, but by increasing in size, there is little increase in pressure.
As veins increase in size to accommodate the increase in blood volume, what happens to resistance to flow?
it increases, restricting flow back to the heart
it increases, increasing flow back to the heart
it decreases, restricting flow back to the heart
it decreases, increasing flow back to the heart
it decreases, increasing flow back to the heart
Once a vein's cross sectional shape has progressed from hour glass to oval to round, what happens to the transmural pressure?
It ruptures the vein and then the pressure decreases.
It increases significantly if there is continuing need to increase volume further.
It decreases significantly as the need to increase volume increases.
There is no change to the transmural pressure as the vein cross sectional shape changes.
It increases significantly if there is continuing need to increase volume further.
When you are at the doctor's office and they take your blood pressure, they could take the pressure at any location where a pulse can be found. Which statement best describes why they select the brachial artery of the arm to take blood pressures?
The brachial artery pressure is closest to the level of the heart so the measurement will be the most accurate.
The arm is easier to reach than the wrist.
If they used the carotid pulse, it would be difficult to put a cuff around the patient's neck and also the reading would be erroneously high.
If they used an ankle pressure, it would be erroneously low.
The brachial artery pressure is closest to the level of the heart so the measurement will be the most accurate.
What is the hydrostatic pressure for someone who is supine (lying on his back)?
0 cm/sec
0 mmHg
140 mmHg
180 mmHg
0 mmHg
For a supine individual whose actual circulatory pressure is 120 mmHg, what pressure reading would be obtained if his brachial blood pressure were taken?
0 cm/sec
0 mmHg
120 mmHg
180 mmHg
120 mmHg
At what anatomical location on the patient does the measured pressure = the accurate circulatory pressure?
the level of the head
the level of the heart
the level of the waist
the level of the knees
the level of the ankles
the level of the heart
Referencing the image at the right, what type of flow pattern is demonstrated?
pulsatile
phasic
steady
phasic
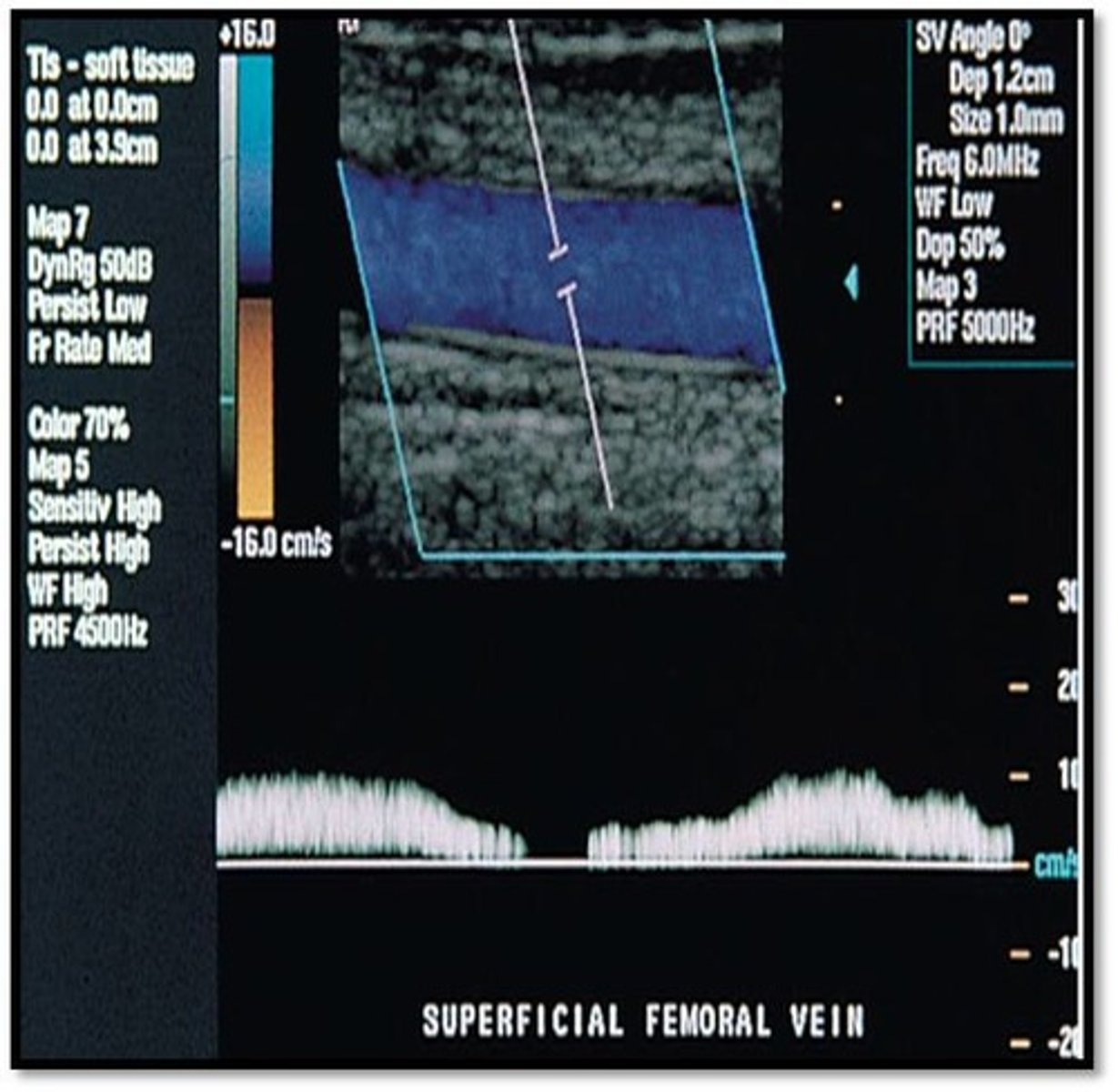
To which part of the respiratory cycle is the yellow arrow pointing in the spectral Doppler image of the lower extremity vein?
inspiration
expiration
expiration
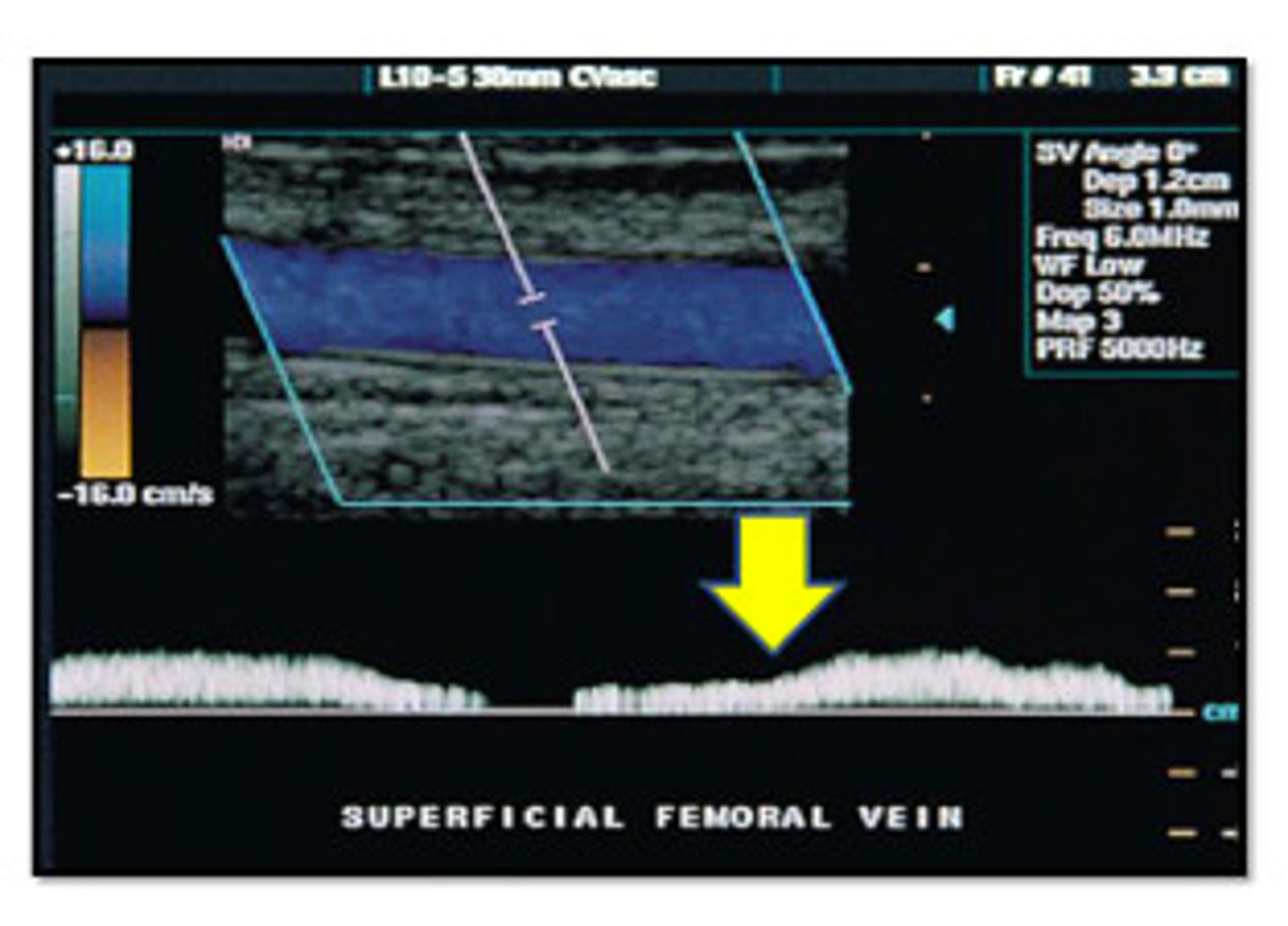
From the appearance of the vessel in this image, is this an artery or a vein?
artery
vein
vein
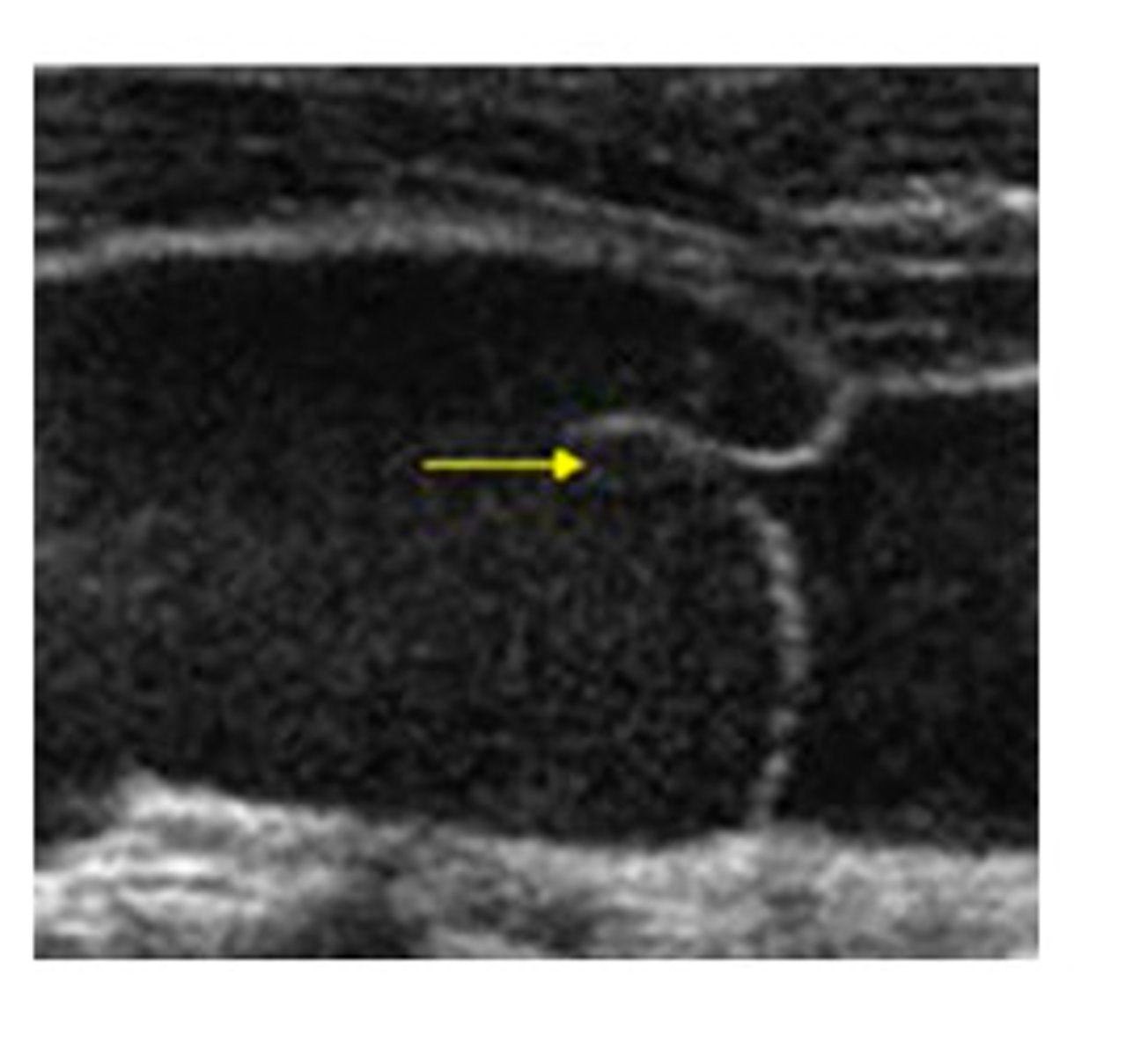
The yellow arrow is pointing to which of the following:
septation
tumor
valve
muscle
valve
A normal vein is which of the following?
non-compressible
compressible with light transducer pressure
compressible only with Valsalva
compressible with light transducer pressure
Movement of blood in the lower extremity venous system is influenced mainly by all of the following EXCEPT:
respiratory variation
aorta pump
valves
calf muscle pump
aorta pump
Which of the following has an artery paired with it?
deep vein
superficial vein
perforating vein
capillary
deep vein
A benign tumor of the heart that blocks flow, most commonly into the left ventricle, reducing the cardiac output is called:
myxoma
tumoroma
sarcoma
lipoma
myxoma
If the the heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the metabolic needs of the body, view the image and predict what the pathology might be.
angina pectoris
CHF (congestive heart failure)
myocardial infarction
arrhythmias
CHF (congestive heart failure)
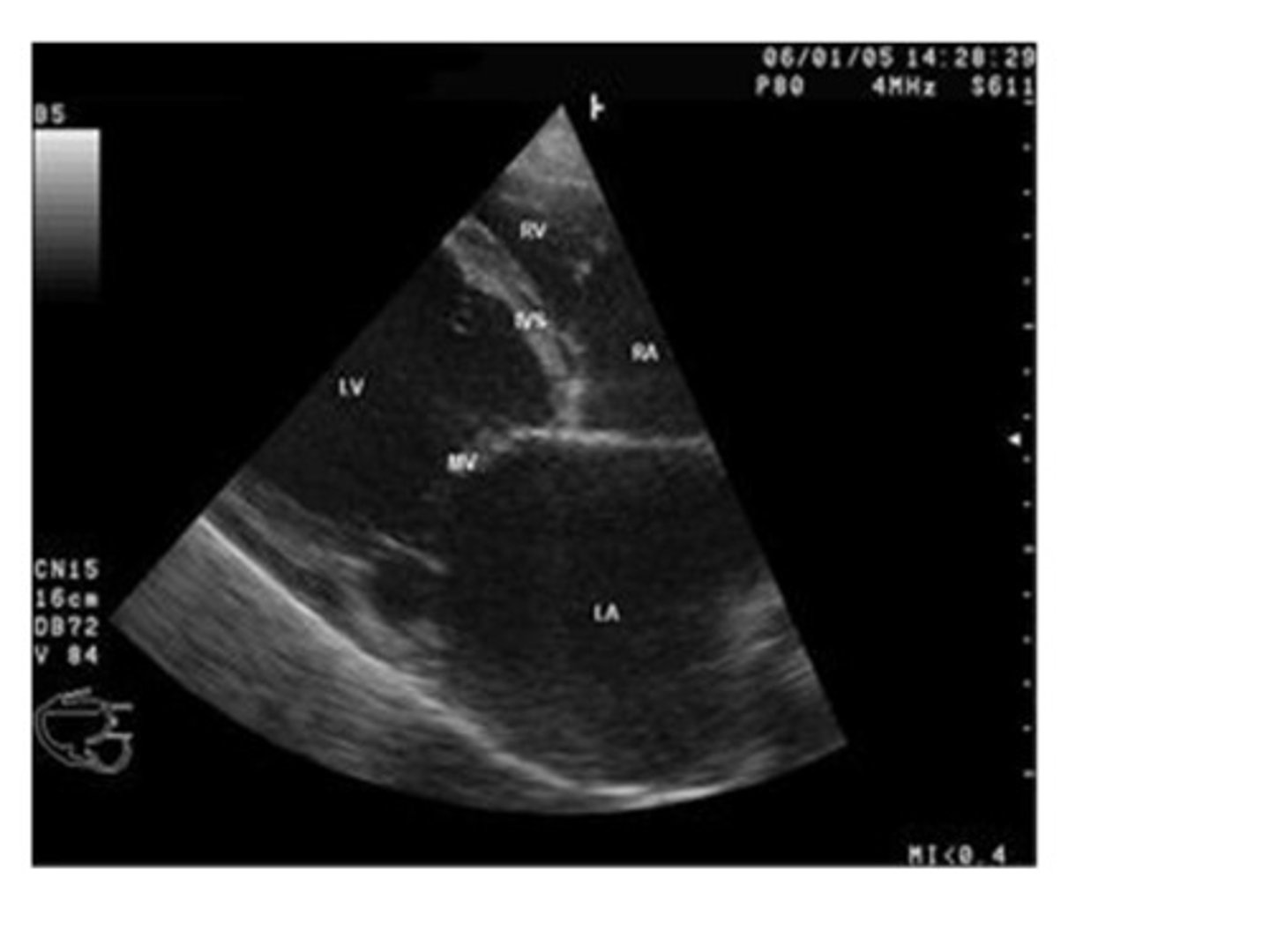
CHF (congestive heart failure) can be referred to as right sided or left sided heart failure depending on the cause and which side of the heart fails first. Even if all valves are functioning normally, a patient with pulmonary disease is at risk for right sided CHF.
True
False
True
All of the following are common occurrences immediately following an infarction or also at a later time EXCEPT.
arrhythmias
cardiogenic shock
aneurysm
rupture of necrotic tissue
healing of necrotic tissue
healing of necrotic tissue
The volume of blood in the ventricles prior to ejection, which is dependent on venous return, is called:
preload
afterload
contractility
stroke volume
preload
The resistance the ventricles have to pump against to eject blood into the great vessels is called:
preload
afterload
contractility
cardiac output
afterload
Obstruction of venous flow toward the heart will do all of the following EXCEPT:
increase venous return
decrease venous return
decrease stroke volume
decrease contractility
increase venous return
An infection of the inner lining of the heart and heart valves that may cause vegetations or perforations of the valves is known as:
myocarditis
epicarditis
endocarditis
pericarditis
endocarditis
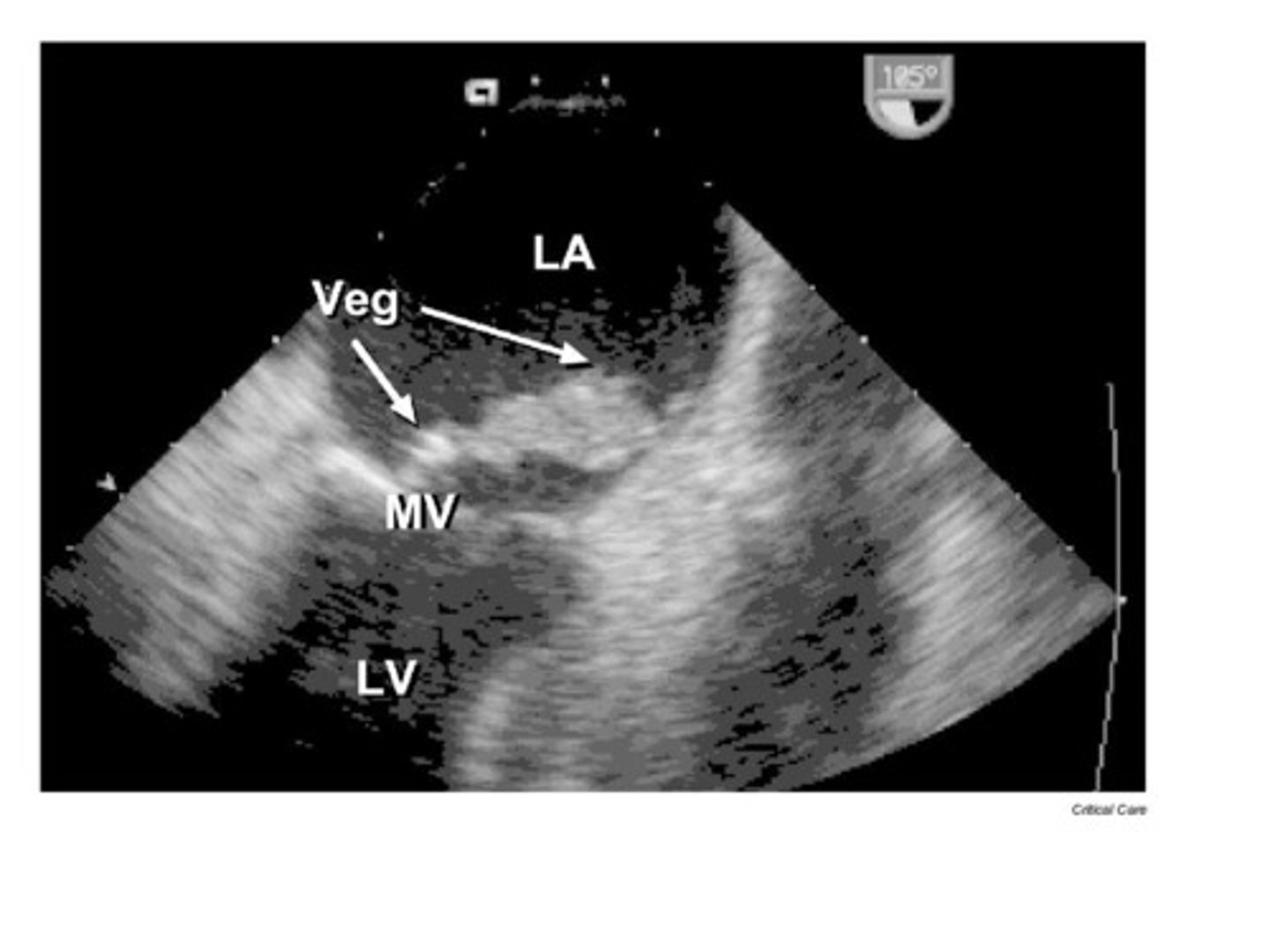
The purpose of the valves of the heart is which of the following?
obstruct blood from moving forward
keep blood moving in a one way direction
allows blood to move where it is needed
valves are really not necessary in the heart
keep blood moving in a one way direction
When blood leaks back into the chamber it came from, it is known as:
reflux
stenosis
regurgitation
spontaneous
regurgitation
Looking at the color map on the image, the red color represents:
flow toward the transducer
flow away from the transducer
flow toward the transducer
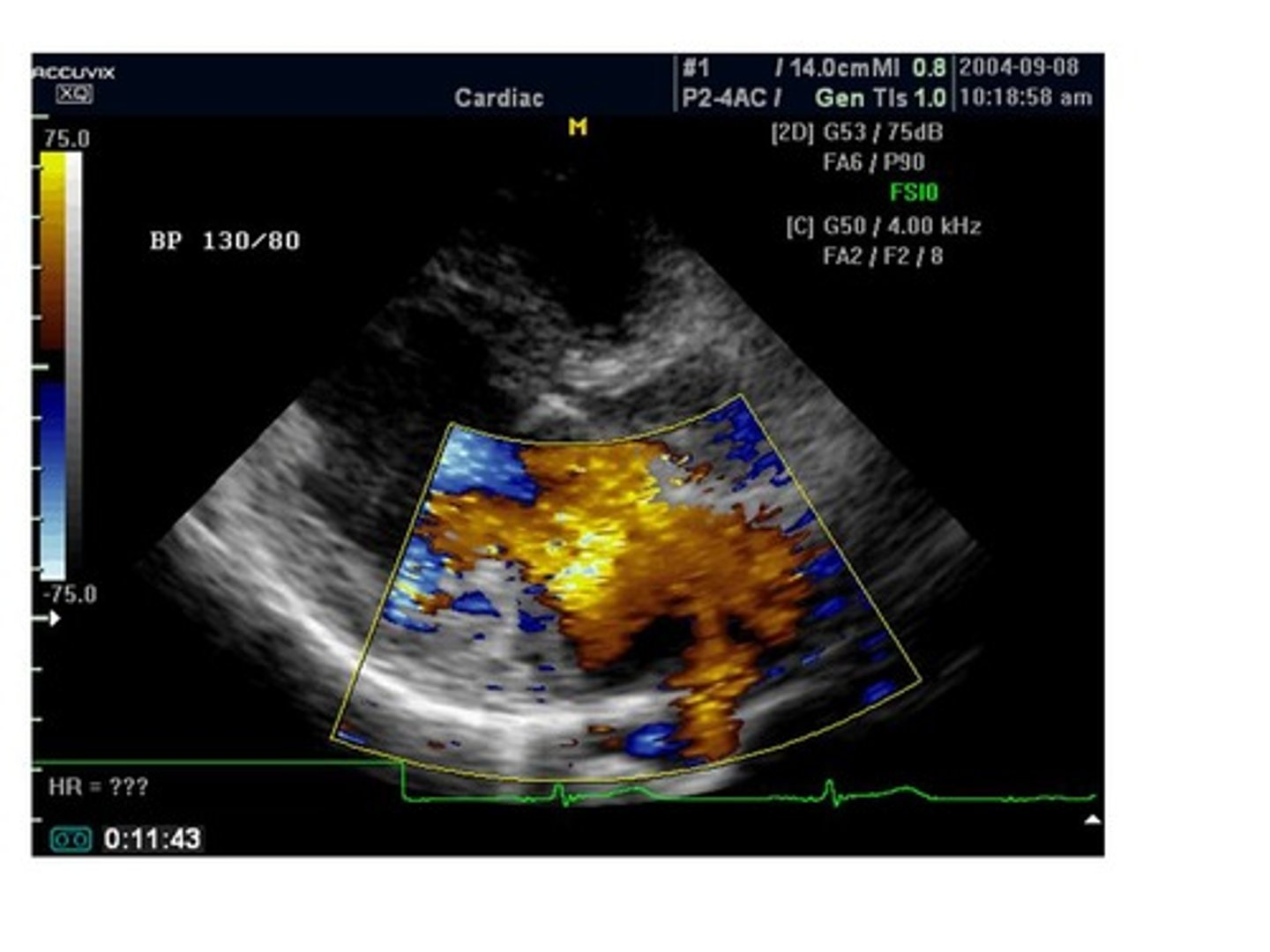
This image is demonstrating which type of color flow?
normal color flow
disturbed flow
spontaneous flow
steady flow
disturbed flow
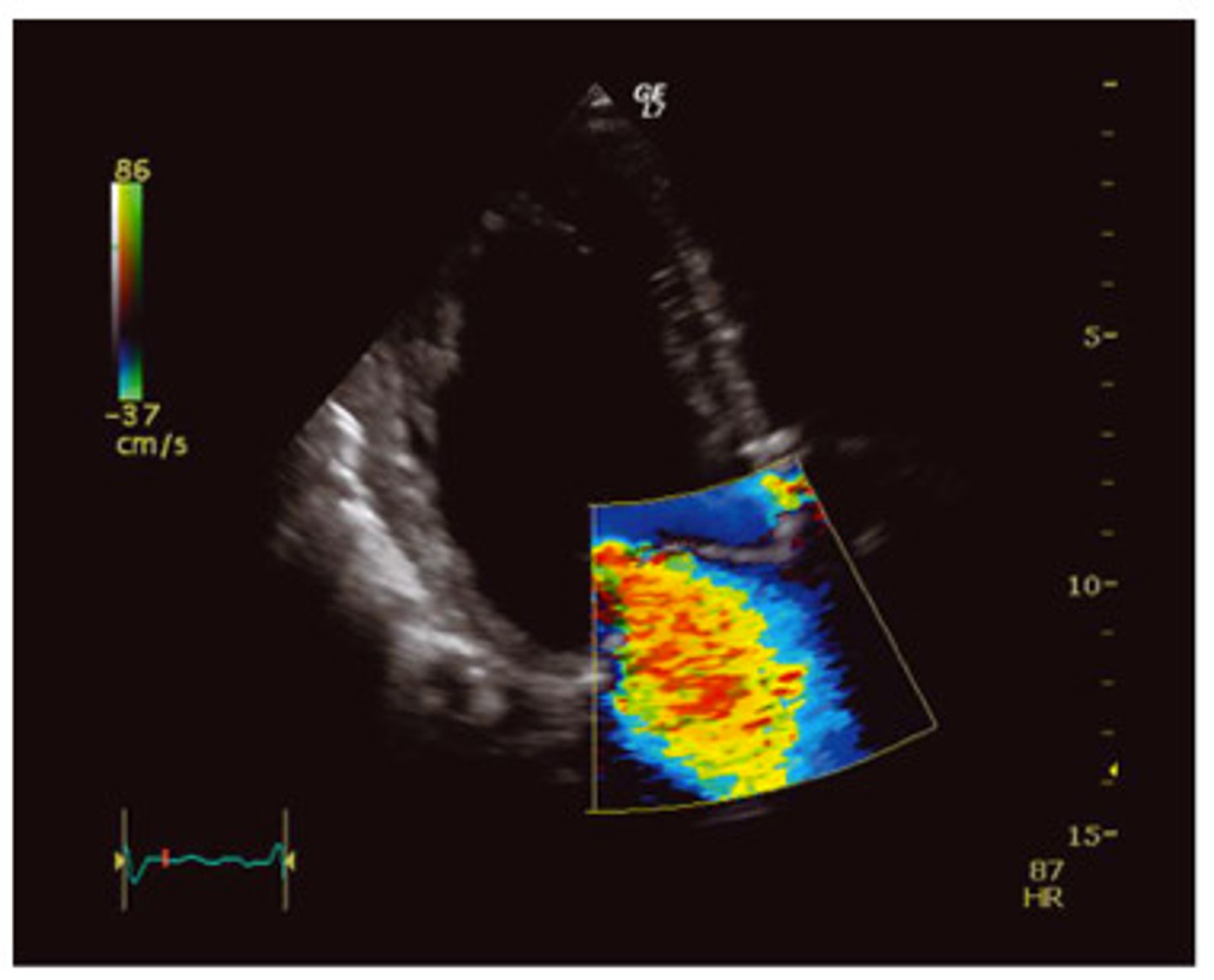
The blue color is demonstrating which of the following?
flow toward the transducer
flow away from the transducer
the transducer has nothing to do with the direction of flow
flow away from the transducer
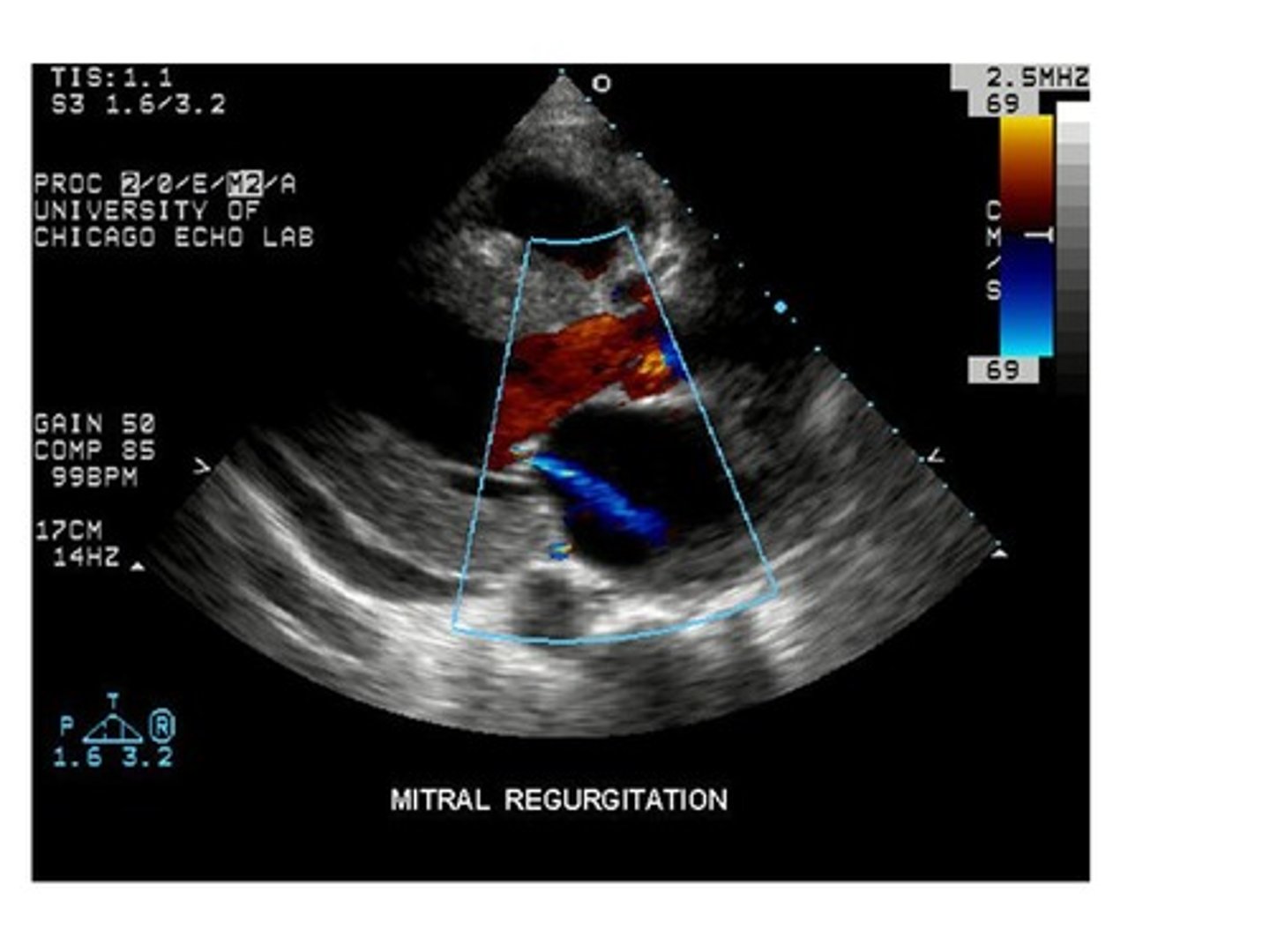
Reviewing the image, the left ventricle has a bulge in the apex which could have been caused by a myocardial infarction. The bulge in the apex is known as:
thrombus
aneurysm
clot
stenosis
aneurysm
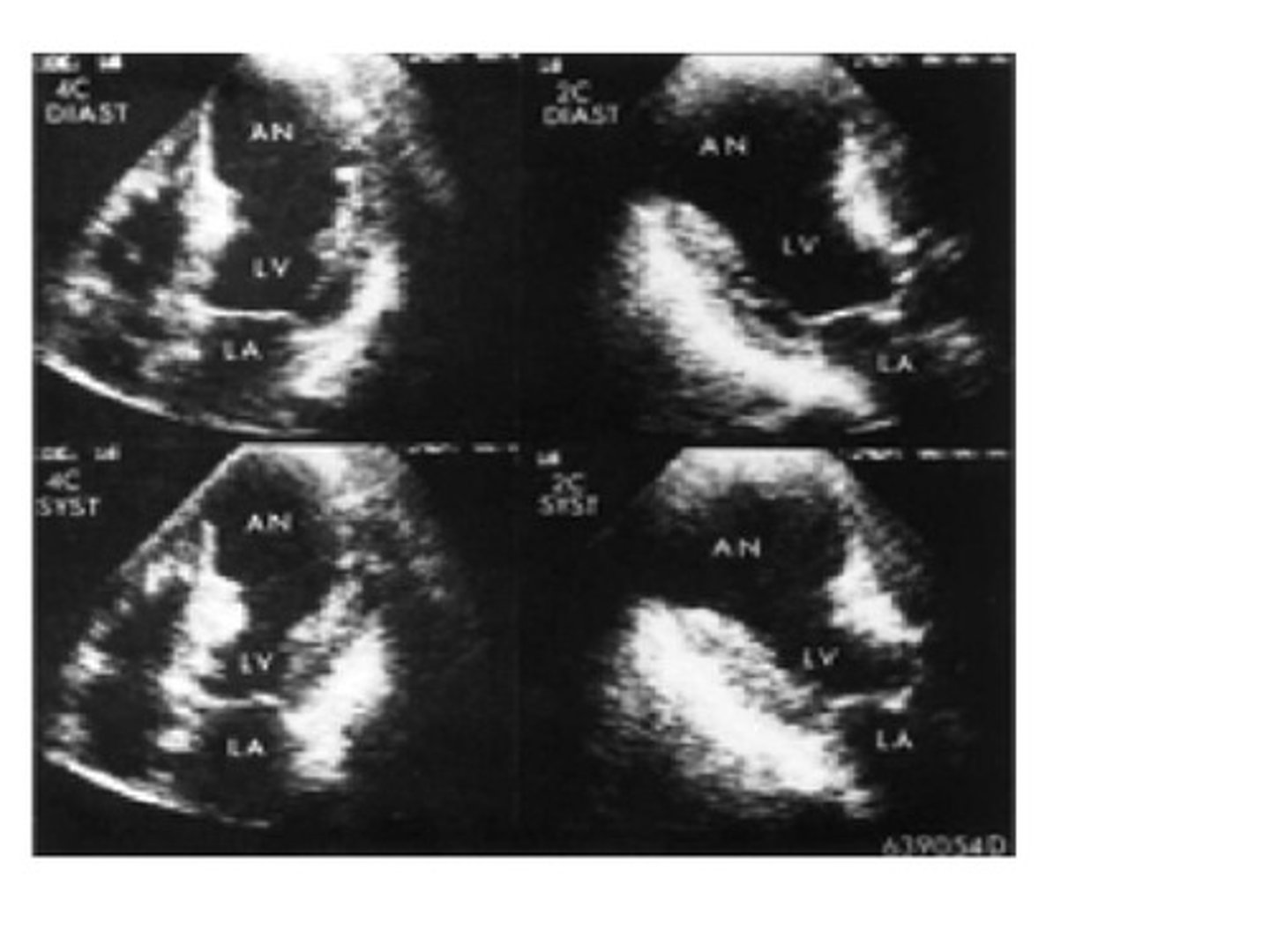
A bulge in the left ventricle along with the thinning of necrotic tissue of the infarcted wall and the high pressure in the ventricle during ejection may cause which of the following?
stenosis
rupture
regurgitation
nothing is at risk of happening
rupture
All of the following are indications to perform an echocardiogram EXCEPT:
murmur of unknown cause heard by the physician on auscultation
entertainment
suspected congenital disease or valve disorders
suspected heart failure, established ischemia or heart disease
patient with shortness of breath with abnormal EKG
entertainment
Which of the following valves are open in diastole? (More than 1 answer is possible.)
aortic valve
mitral valve
pulmonary valve
tricuspid valve
mitral valve, tricuspid valve
Kidneys are responsible for all of the following EXCEPT:
regulation of blood pressure
filter blood
remove waste from urine
require little oxygen
require little oxygen
Fatty Plaques can develop a hard fibrous calcific cap that is at risk of ...
crumbling
rupture
invading tissue
plaque division
rupture
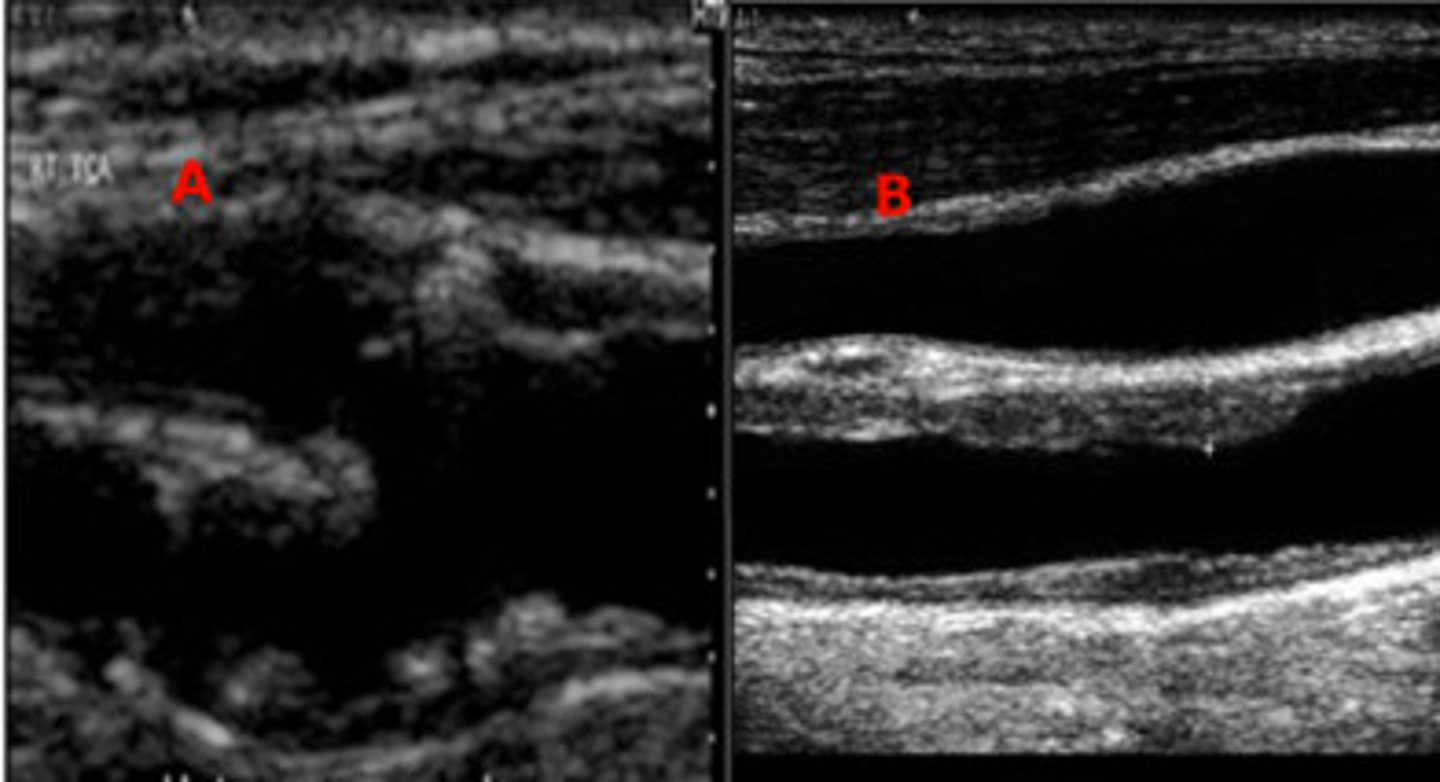
Which one of the two images represents a plaque that is at risk of embolization?
Image A
Image B
Image A
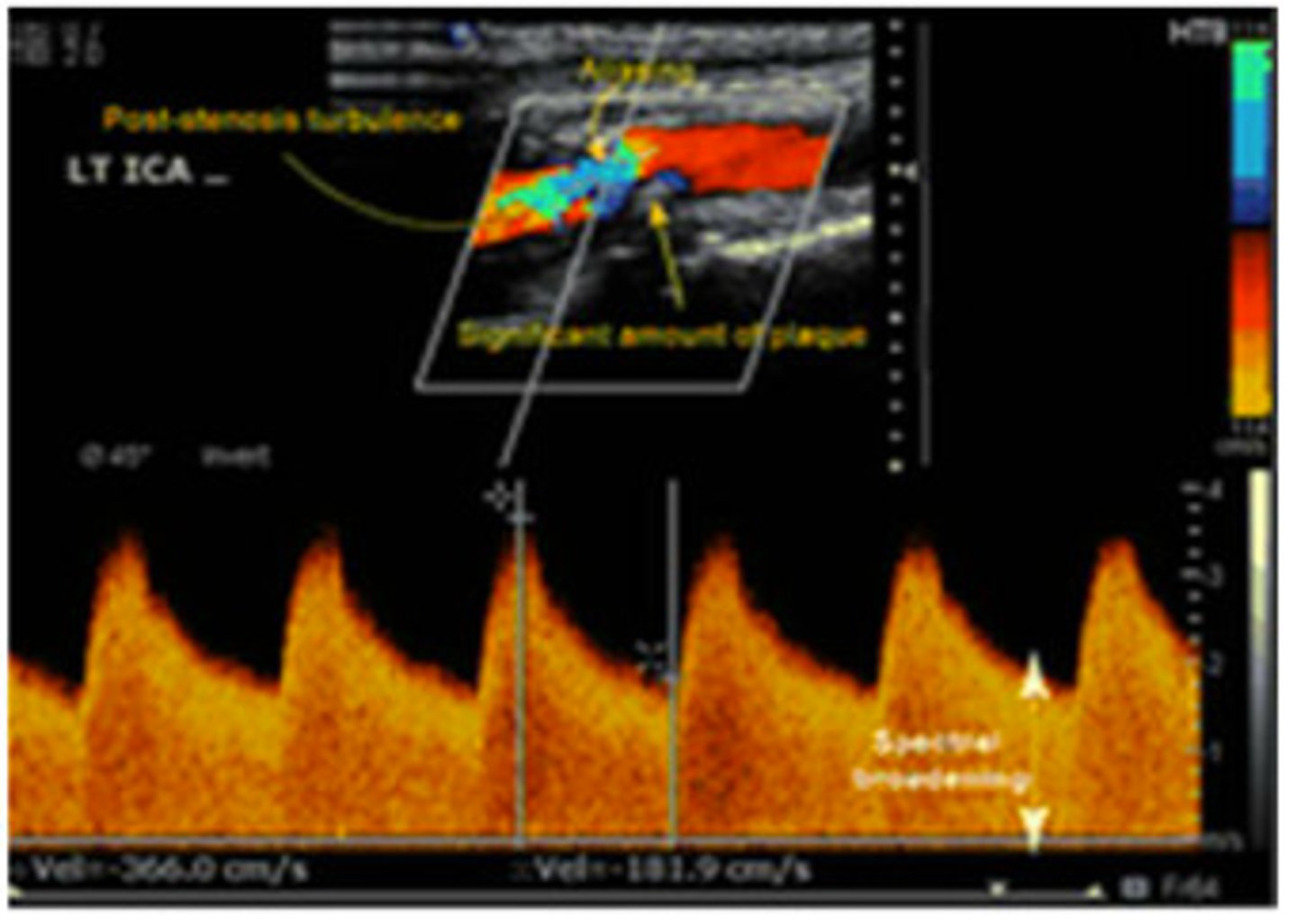
The appearance of the spectral Doppler waveform and the velocity recorded in this image represents...
no stenosis
mild stenosis
significant stenosis
total occlusion
significant stenosis
All of the following are non-modifiable risk factors for atherosclerosis EXCEPT:
age
gender
family history
high cholesterol
high cholesterol
Which one of the following is a TRUE statement about the Ankle/Brachial Index?
an index greater than 1.3 is normal.
the ankle pressure should be equal to or greater than the arm pressure.
the arm pressure should be equal to or greater than the ankle pressure.
pain in the legs or feet at rest is termed intermittent claudication.
the ankle pressure should be equal to or greater than the arm pressure.
A patient with pain in the legs at rest would demonstrate an ABI of less than....
1.3
1
.97
.4
.4
When performing an ABI, the blood pressure cuff should not be inflated greater than __ once the signal has stopped.
100 mmHg
80 mmHg
30 mmHg
10 mmHg
30 mmHg