MED SURG FINAL EXAM
1/266
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
267 Terms
benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
increase in the number of epithelial cells and stromal tissue within the prostate (benign growth)
what is an early symptom of BPH?
decrease in force of urine stream
manifestations of BPH
-decr in urine flow
-hesitancy in initiating stream
-dribbling upon completion
-urinary retention
diagnostic tests for BPH
1. digital rectal exam (finger up butt)
2. urinary flow test
but also:
-history
-urinalysis (urine culture&sensitivity)
-incr creat
-post void residual
-transrectal ultrasound
-prostate biopsy
-cystoscopy
what must you rule out with a BPH diagnosis?
prostate cancer (look for PSA antigen)
what two med classes are used to manage BPH?
typically BOTH are used
1. alpha blockers
2. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors
examples of alpha blockers
-doxazosin
-terazosin
-tamsulosin
what do alpha blockers do?
relax smooth muscle in prostate and bladder neck to help decr urine blockage!
adverse effects of alpha blockers
1. orthostatic hypotension
2. ejaculation changes
examples of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors
-dutasteride
-finasteride
what do 5-alpha reductase inhibitors do?
inhibit hormone responsible for enlarging prostate thereby reducing prostate size
-long onset of action, but also very much longer duration of action!!!
I am a young woman and I am administering dutasteride to my old man pt... any concerns?
women of child-bearing age need to WEAR GLOVES! (its a teratogen)
surgical tx of BPH
transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): excision of prostate using a resectoscope through the urethra
-creates an open passageway for urine flow!!!
what is inserted after a TURP and why?
a large 3-way foley catheter is inserted for continuous bladder irrigation: decr bleeding and clear blood clots
what is needed for bladder irrigation?
an order and sterile technique!
After TURP, urine color is pink to light yellow... is this normal?
yes!
what do you do if urine output is bright red after TURP?
up flow rate of irrigation
how do you measure accurate I&Os with continuous bladder irrigation?
subtract how much irrigation has been infused from the output
after TURP, pt c/o bladder spasms... what do you do?
make sure catheter system is PATENT
-if not patent, and there is an order to irrigate, try and flush any blockages out!
post-op management after TURP
-medicate for pain
-medicate for bladder spasms (ditropan)
-administer antibiotics
-instruct pt not to strain to void or have BM
-monitor for TURP syndrome
why should a pt not strain after TURP?
can cause a bladder spasm
TURP syndrome
hyponatremia and water intoxication (resembling brain stroke) caused by an overload of fluid absorption from the open prostatic sinusoids during TURP procedure
manifestations of TURP syndrome
-hyponatremia
-fluid overload: CHF, pulm edema, hypertension
-decr HCT
-bradycardia
-confusion!
overall, what is the most significant nursing intervention in a TURP pt?
if pt complains of bladder spasm, ensure system is patent (catheter may be clogged from blood clot)
renal calculi
stones made of minerals or acids that form in renal pelvis, ureter, or bladder and cause urinary obstruction
types of stones
1. calcium oxalate
2. calcium phosphate
3. struvite
4. uric acid
5. cystine
which type of stone is associated with UTIs, bacteria, and WOMEN?
struvite
which type of stone is the most common in the US?
calcium oxalate
which type of stone is due to a hereditary congenital defect?
cystine (high levels of cystine in urine, thus seen in adolescents also)
which type of stone may be related to gout?
uric acid (gout pts have deposits of uric acid crystals in joints)
diagnostics for calculi
-urinalysis, culture&sensitivity
-24hr urine collection: measure Ca, Phos, uric acid levels
-microscopic crystals
-urine pH... alkaline vs. acidic?
-UTI... struvite
-elevated WBCs... struvite
type of stone associated with alkaline urine pH
calcium phosphate
type of stone associated with acidic urine pH
uric acid
nursing management of calculi
-control pain
-tamsulosin (alpha blocker!) to relax muscles and promote flow!!
-force fluids: 8 glasses/day
-void q 2
-strain all urine!
-dietary changes...
dietary changes for all stone types
decrease sodium and animal protein intake
increase fluid intake
diet changes for calcium oxalate stone
restrict oxalate :O!!!! (and vitamin C?)
dark leafy greens, chocolate, strawberries, nuts, beets, tea
dietary changes for uric acid stone
restrict purine (meats basically)
surgical management of renal calculi
lithotripsy
indications for lithotripsy (or really any surgical procedure for stones)
-stones TOO LARGE for spontaneous passage
-infection (bacteria or symptomatic)
-causing impaired renal function
-PERSISTENT pain, nausea, or ileus
-unable to be treated medically
-only got ONE kidney
what is a lithotripsy?
a procedure that uses ultrasound shock waves to break the stones
-non-invasive but yes-painful
post-op care for lithotripsy
-strain the urine!!!
-maintain fluid balance
-control thy pain!
what may be placed after a lithotripsy and why?
a temporary NEPHROSTOMY TUBE to preserve renal function if there is complete obstruction of the ureter (perhaps from swelling post-op)
-prevents hydronephrosis
pt is sitting on their nephrostomy tube, it is super kinked up, and the PCT clamped it for the sake of vibes... thoughts?
NO!!!!! to all of it
MD orders irrigation of nephrostomy tube... what 3 things must you do?
1. use STRICT ASEPTIC technique
2. do not instill more than 5-10cc of sterile solution
3. irrigate SLOWLY (pls don't waterboard the kidney)
cystitis
infection and inflammation of the bladder
lab findings for cystitis
-elevated serum WBCs
-urinalysis: bacteria, WBCs, nitrate, incr pH
-urine C&S: erm bacteria
Pharmacologic management of cystitis involves...
using both analgesics and antibiotics... cannot just alleviate symptoms, must rid of infection
Analgesic used for cystitis
pyridium
Antibiotics used for cystitis
1. macrobid: 5-7 days
2. bactrim: 3 days
3. cipro: 3 days
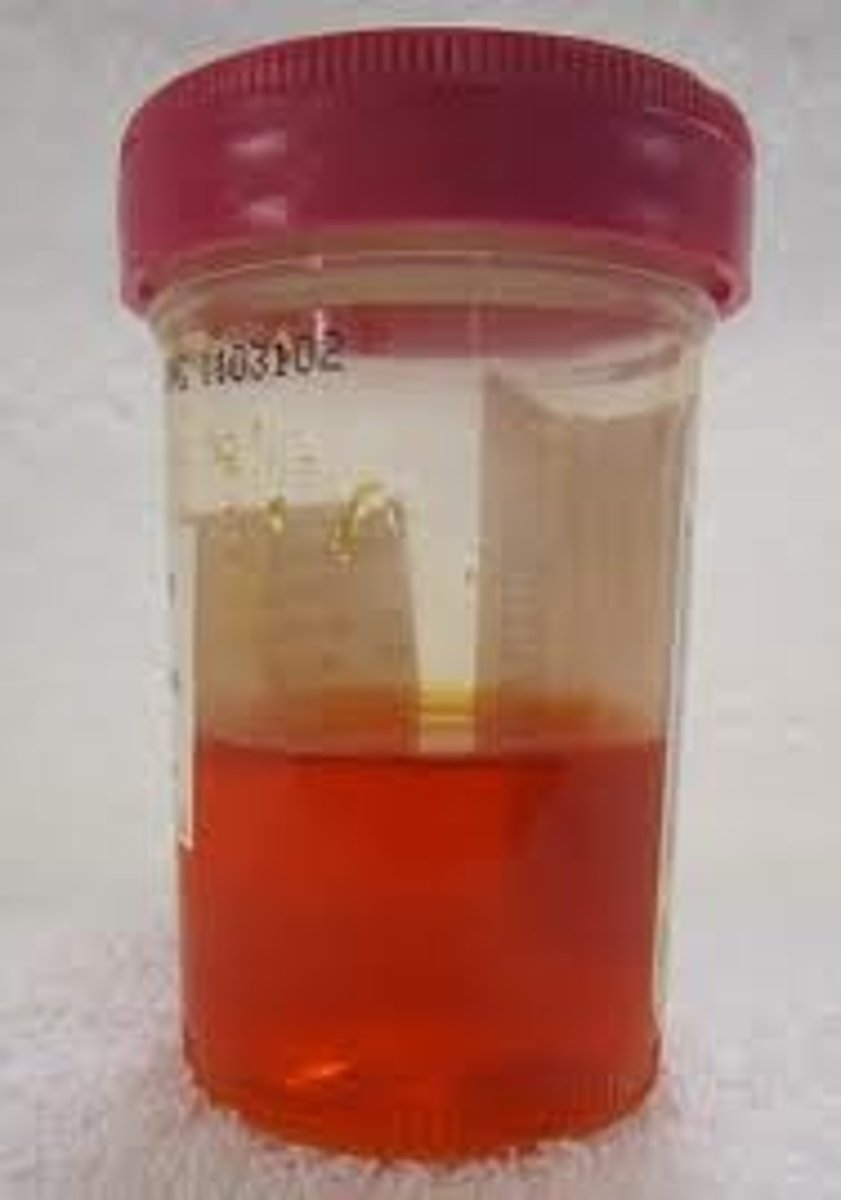
what must you educate your pt about with pyridium?
fanta orange piss

nutritional interventions for cystitis
1. incr fluid intake: 8 glasses/day
2. avoid: caffeine, alcohol, citrus
health promotion tips to prevent cystitis!!!
mostly for the ladies bc we got issues
-wipe front to back
-shower, no bath!
-COTTON underwear
-avoid pantyhose pls
-incr fluids! (water)
-contraceptives: ill fitting diaphragms and spermicides are just.. no
-void immediately after sex
urethritis
inflammation and infection of the urethra
causes of urethritis
tag yourself!
1. e coli
2. gonorrhea
3. chlamydia
tx of urethritis
1. antibiotics
2. fluids
3. avoid sexual intercourse until symptoms subside
acute pyelonephritis
infection and inflammation of the kidney/renal pelvis
manifestations of acute pyelonephritis
-RECENT SIGNS OF CYSTITIS!
-high fever, chills, nausea
-flank pain, tenderness, muscle pain
why is there recent signs of cystitis with acute pyelonephritis?
ascending infection!
tx of acute pyelonephritis
1. PO antibiotics (7-14 days) or IV antibiotics if severe
2. incr fluid intake
3. follow-up urine culture and if you relapse... SIX WEEK course of antibiotics for you!
if moving a fractured limb... how should you support it?
support ABOVE and BELOW the fx to help decrease pain and muscle spasms!
what do you assess q 1-2 hours with fractures?
neurovascular function distal to fx via the 5 P's: pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesia, paralysis
fx complications
1. compartment syndrome
2. fat embolism syndrome
compartment syndrome
swelling in a confined space that produces dangerous pressure; may cut off blood flow and damage nerves, muscle, and other tissue
early symptoms of compartment syndrome
1. severe pain out of proportion to injury
2. pain exacerbated by PASSIVE STRETCH of muscle within compartment
symptoms of compartment syndrome
-severe pain out of proportion to injury
-pain exacerbated by passive stretch of muscle within compartment
-paresthesia
-decr sensation
-muscle weakness
-pallor
-pulselessness
potential cause of compartment syndrome... and what do you do???
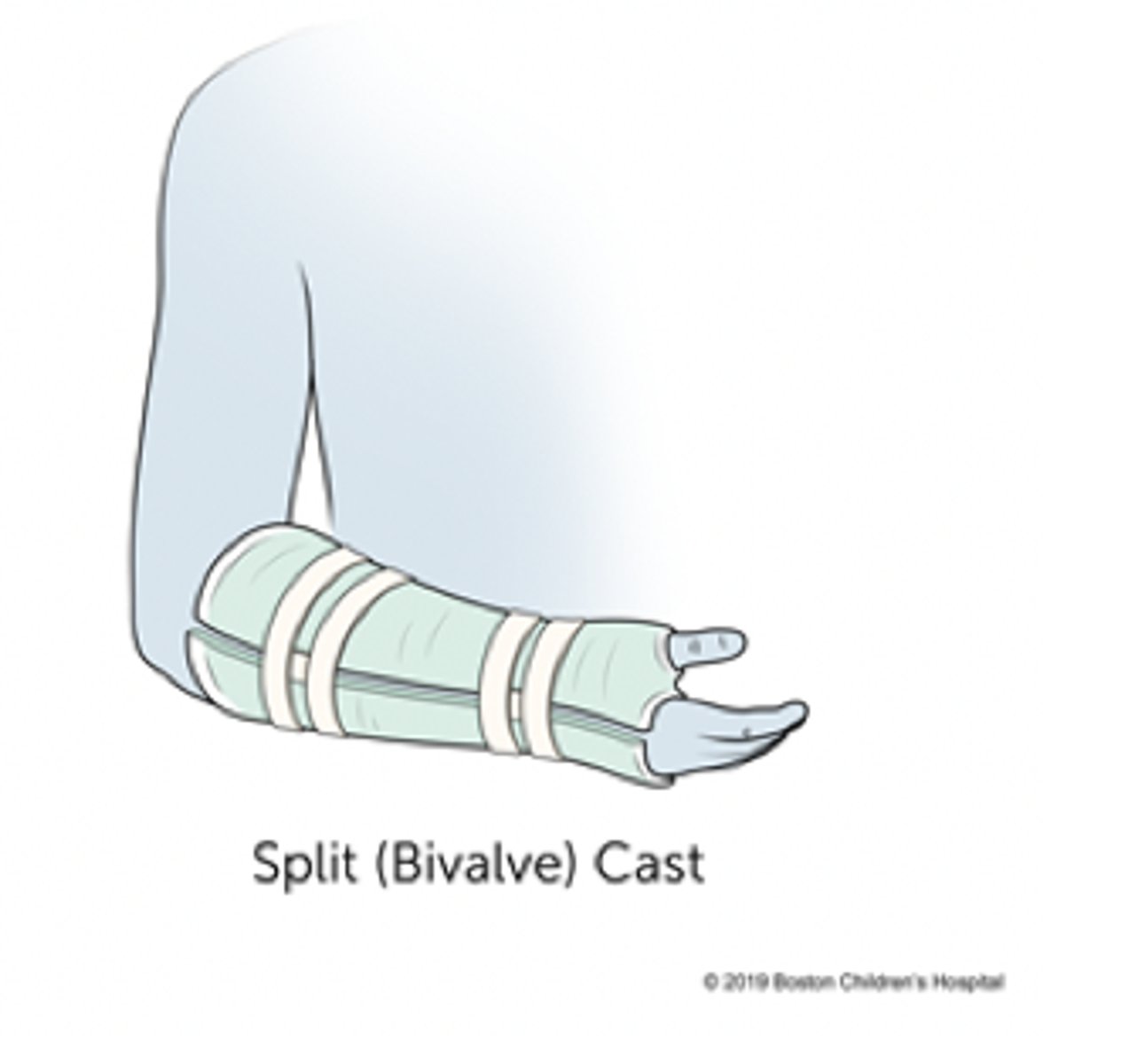
compartment syndrome can be caused by a cast if put on while extremity still swelling (thus extremity swells UNDER CAST)
this is an EMERGENT situation in which the cast needs to be CUT (bivalved) to relieve the pressure
fat embolism syndrome
fat globules leave bone marrow due to incr pressure, enter the bloodstream, and lodge in the pulmonary vascular bed or peripheral circulation
symptoms of fat embolism syndrome
develop in a few hours to a few weeks
-respiratory insufficiency: ARDS
-change in LOC: confusion
-clotting activation: thrombocytopenia and petechiae
types of casting materials
1. fiberglass: drys and hardens w/in minutes
2. plastic: erm takes 24-73 hours
what pt eduction should you give concerning plaster casts?
1. they get WARM for approx 15 min.. warn pts of this sensation!
2. need to be exposed to AIR to facilitate drying, so should remain uncovered until hard!
general cast care
-handle with palms of hands to avoid denting of cast
-avoid pressure on cast
-avoid putting powder or objects into cast pls
external fixators are for...
severe or comminuted fractures
-permits active tx of soft tissue injury
Once soft tissue injury healed, an ex fix can be changed to a...
Cast
nursing interventions with external fixators
-perform neurovascular checks
-inspect pin site...
What kind of drainage is expected from a pin site?
Serous (not bloody)
what is the purpose of traction?
reduces, aligns, and immobilizes fractures which:
-MINIMIZES MUSCLE SPASMS
-reduces deformity
-incr space between opposing surfaces
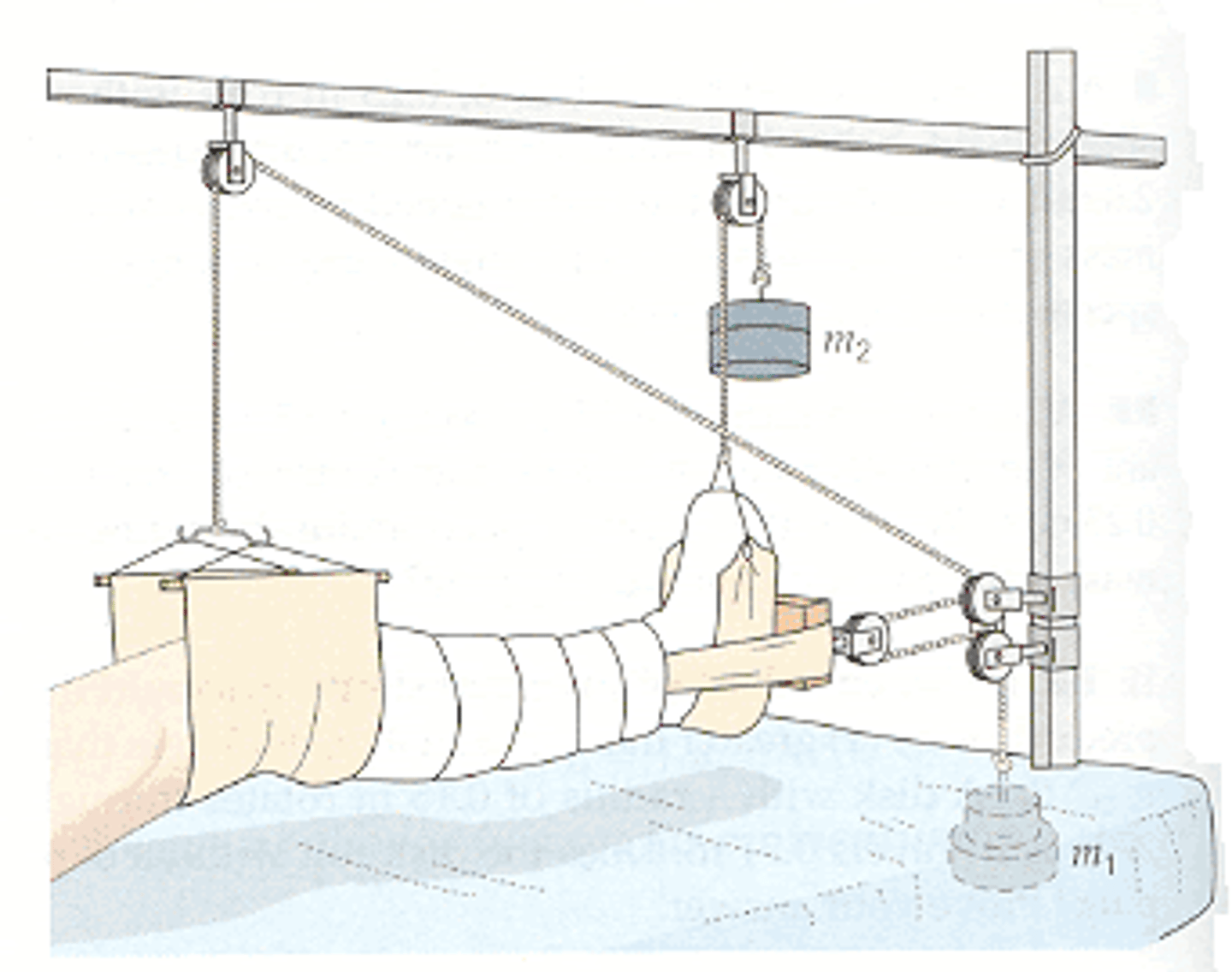
types of traction
1. skin
2. skeletal
what are the 3 principles of traction?
1. must be CONTINUOUS
2. skeletal traction is NEVER interrupted
3. ELIMINATE any factor that might reduce effective pull or alter line of pull
—weights, ropes, knots must hang FREELY!!
—maintain body alignment!!
3 possible ways to infect your BONE (osteomyelitis)
1. direct contamination: fx
2. continuous infection: surrounding tissue
3. hematogenous: blood
common manifestations of osteomyelitis
-draining and ulceration at involved site
-swelling, redness, warmth
-acute or chronic pain of incr intensity
-incr WBCs
medical management of osteomyelitis
-prolonged IV antibiotic therapy (often w PICC line so pt can continue at home)
-wound care
surgical management of osteomyelitis
debridement or amputation!
gout is a _________________ disorder caused by what?
metabolic; high levels of uric acid in blood
high serum uric acid = formation of MONOSODIUM URATE CRYSTALS = deposition in joint space = INFLAMMATION + PAIN
gout onset is __________, occurs at ___________, and is characterized by...
ABRUPT! AT NIGHT!
-severe pain
-redness
-swelling
-warmth
over affected joint
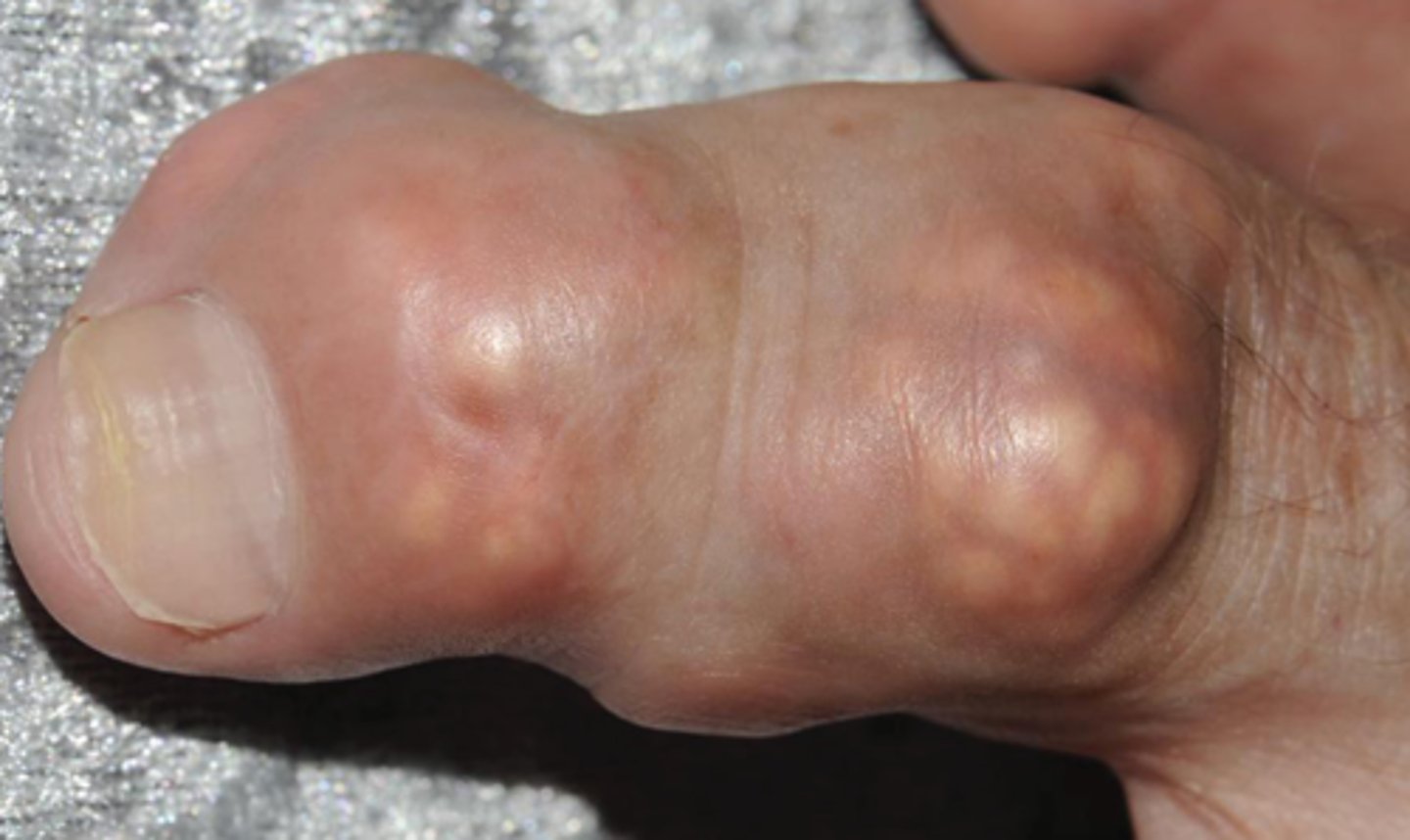
what are tophi?
chalky deposits of sodium urate that may form due to gout
-not painful usually but decr ROM
what is the goal of pharmacotherapy for gout?
treat hyperuricemia, tophi, joint destruction, and renal problems!
treated after acute inflammatory process subsides
medical management of gout
1. uricosuric agents: pee out uric acid...
2. colchicine or NSAID: anti-inflammatories to relieve acute attacks
3. allopurinol: antigout girl
nursing management of gout
-diet: restriction of foods high in purine!
-maintain normal body weight
-pain management is critical!!!!
-monitor renal function
-monitor for tophi (w/in 10 yrs typically)
why monitor renal function w gout pt?
possibility of uric acid calculi
rheumatoid arthritis is an _______________ disease that results in...
autoimmune; synovitis (inflammation of joint tissue) and pannus formation
RA results in cartilage, bone, ligament, and tendon damage that is...
progressive and permanent
manifestations of RA
remissions and exacerbations of BILATERAL joint...
-pain
-swelling
-warmth
-erythema
-lack of function
what joints are typically involved first in RA?
small joints in hands, wrists, and feet
diagnosis of RA
most of these just test for autoimmune response by body
-positive rheumatoid factor (75%)
-ESR is significantly ELEVATED
-RBC DECREASED
-POSITIVE C reactive protein
-positive ANA (20-30%)
-X-ray changes show narrowing joint space and erosion of articular surface
goal of tx/medication w RA
relieve pain, control inflammation, and prevent bone erosion
pt education for RA tx
-balance of rest and exercise is important!
-take meds REGULARLY to maintain blood levels
early, aggressive (FIRST LINE) drug therapy for RA involves...
NSAIDS
surgical tx of RA includes _______________ and involvement of ____________ is necessary
arthroplasty (replace/repair joints to incr functional ability); PT/OT (assist w ADLs)
what exercise is the most effective for arthritis (RA/OA) pts?
aquatic exercises
osteoarthritis is a ____________________ disease that results in...
degenerative joint; thinning of articular cartilage and bone spur formation