Stat 1401 online GSU
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
cluster sample
selecting groups and then including all individuals of the groups within the selected groups
stratified random sample
a sampling method in which a population is divided into distinct subgroups, called strata, that share a common characteristic, and then random samples are taken from each stratum.
simple random sample
every individual in a population has an equal chance of being selected,
multistage sample
selecting a sample in multiple stages, typically combining different sampling techniques. It is often used when dealing with large, geographically dispersed populations
biased sample
sample that does not accurately represent the population from which it is drawn, resulting in distorted or unreliable results. This bias occurs when certain members of the population are more or less likely to be included in the sample, leading to a lack of fairness or accuracy.
unbiased sample
a sample that accurately represents the population it is drawn from, without any systematic overrepresentation or underrepresentation of certain groups or individuals. This ensures that the results and conclusions of the study are valid and applicable to the entire population.
what is standard deviation
a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of data values. It indicates how spread out the values are around the mean (average) of the dataset.
mean
average (add up then divide)
median
the middle value (ascending order then cross them out)
mode
The value(s) that appear most frequently in the dataset
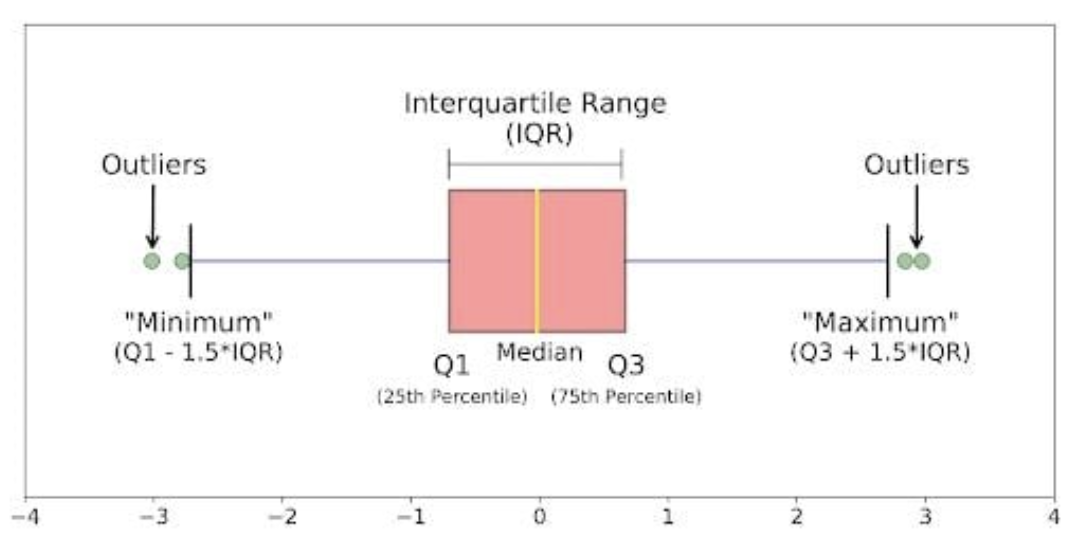
how to read a box plot
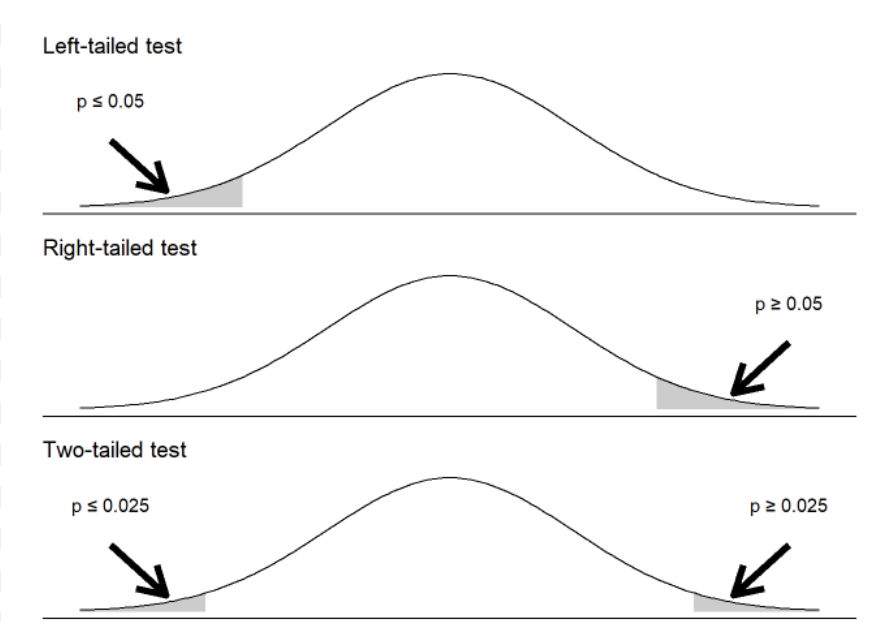
right tailed, left tailed, vs two tailed