Animal Models in Research: Rabbits, Dogs, Cats, and NHPs
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
152 Terms
Rabbits scientific name?
Oryctolagus cuniculus
What is the rabbit Order?
Lagomorpha
What is the most common breed of rabbit?
New Zealand White
whats the small breed of rabbit?
Dutch-belted
A large breed of rabbit.
Flemish giant
Common Usage of rabbits?
Antibody production, drug screening.
Adult Weight of rabbits
2-6 kg
how much Water consumption do rabbits intake?
50-100 ml/kg
how much Food consumption do rabbits intake?
50 g/kg
what is the Life span of rabbits?
5-7 years
What is the Heart rate in rabbits?
200-300/min
What is the Respiration rate in rabbits?
32-60/min
What is the Rectal temperature of rabbits?
38-40 °C
What is Night coprophagy in rabbits?
A behavior where rabbits consume a special kind of stool called 'night feces' for nutrient conservation.
What are specific feeding requirements for rabbits?
Rabbit diets should have high fiber and limit pelleted feed to avoid obesity.
how to sex a rabbit?
Differentiating male and female rabbits based on physical characteristics.
female rabbits have a narrowhead and a large dewlap under their chins
Malerabbits lack the dewlap, and have a much larger head thanthe females
What is the Breeding age for small rabbit sized breeds?
Approx. 3.5-4 months.
What is the Breeding age for medium sized rabbit breeds?
4-4.5 months
What is the Breeding age for large sized rabbit breeds?
6-9 months
What type of ovulators are rabbits?
induced ovulators
What does Monogastric mean?
one stomach
single-chambered stomach - which have a large cecum for fermentation
What does Polyestrous mean?
more than one estrus cycle
go into heat multiple times throughout the year
What is the Gestation length in rabbits?
30-33 days
Lactation duration in rabbits
6-8 weeks
Weaning age in rabbits
4-6 weeks, but can be up to 8 weeks.
Average litter size in rabbits?
litter 4-10; mean 7-8
cannibalism occasional in young or nervous does
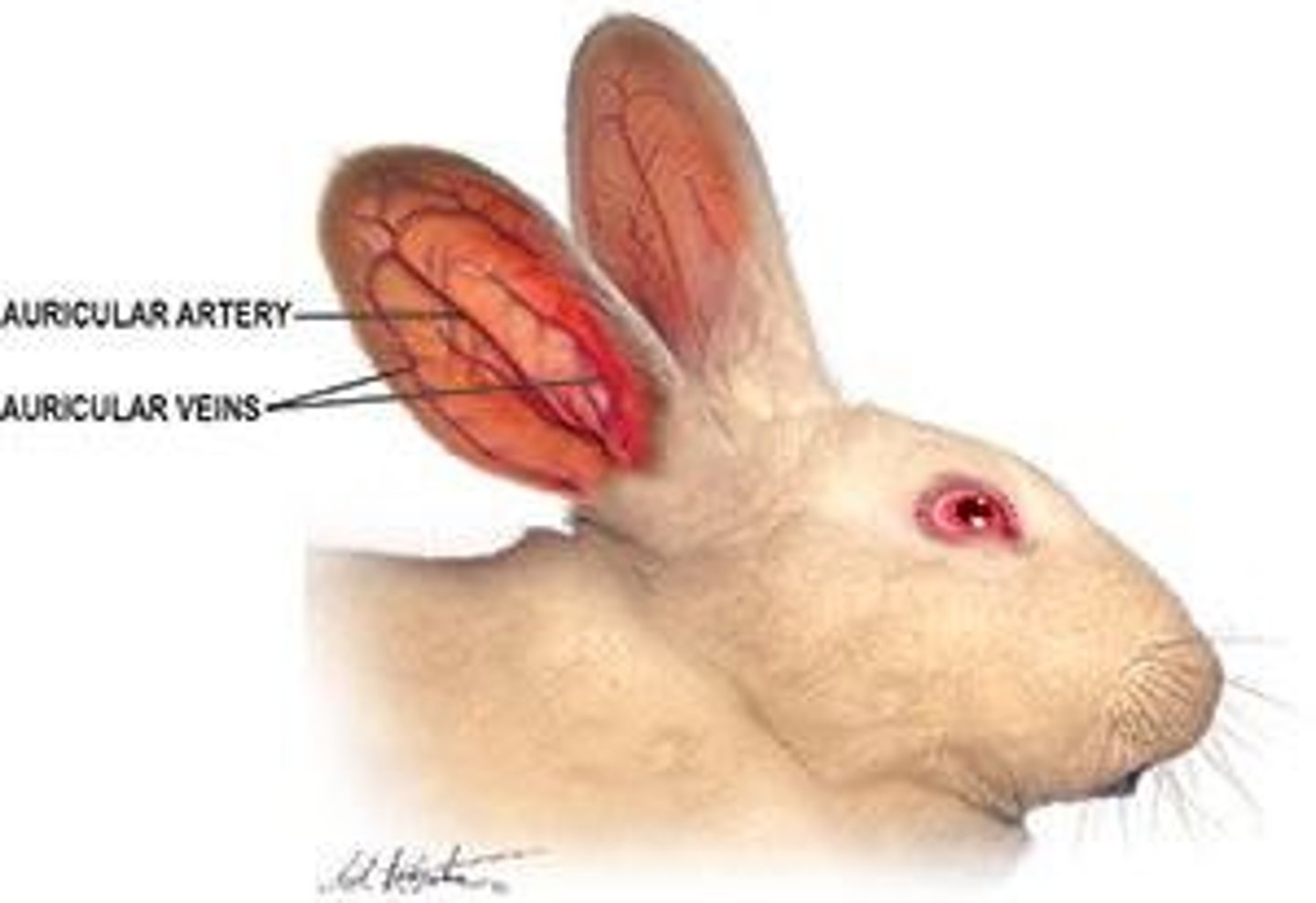
What is a Unique anatomical features in rabbits?
Ear can function in thermoregulation and for blood collection.
What is a Unique anatomical features of rabbits teeth?
Teeth are open-rooted and continuously grow, causing malocclusion.
Rabbits Unique anatomical features - Toenails
Rabbit toenails grow rapidly.
Rabbit Skeleton Weight
Rabbits have very light skeletons that make up only about 8% of their body weight.
Rabbit Musculature
Rabbits are also very muscular, especially in the hind limbs.
what is Rabbit Injury Risk?
The combination of a light skeleton and very strong muscles can result in injuries, the most common being a broken back.
Where should you never grasp rabbits by, and where should you grasp/support while holding them?
Never grasp rabbits by the ears; grasp by scruff and always support hindquarters.
Why should you restrain a rabbit from kicking?
Don't allow animal to kick while being restrained (may result in broken back).
What should you do when Carrying Rabbits?
Carry with head tucked and eyes covered whenever possible.
What is a Mechanical Restraint that can be used for rabbits?
Use mechanical restrainer or wrap in towel for study procedures.
how to deal with Aggressive Rabbit Handling?
For aggressive rabbits, who are defending their cage - 'throwing towel' may work best; once out of their cage: they are calmer.
How do you place a rabbit in a cage?
Place into cage backwards.
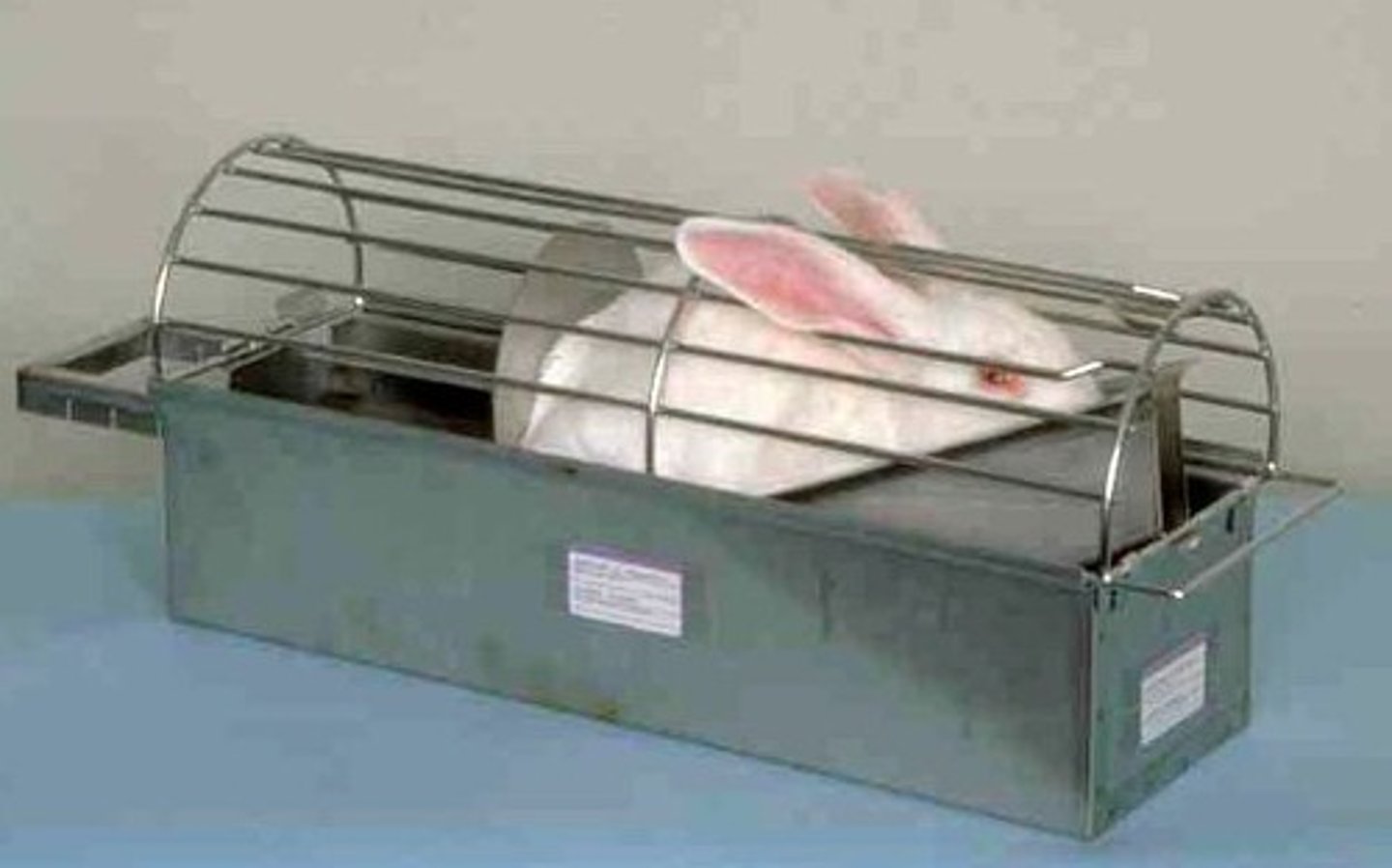
What is a rabbit Restraint Box?
Device prevents rabbit from kicking backward and injuring the spine.
What are Hair Balls (trichobezoars)?
Rabbits ingest hair while grooming, leading to a ball of hair forming in the stomach due to the lack of ability to vomit and the small diameter of the pylorus.

What are rabbit Hairball Symptoms?
Hairballs are often asymptomatic in the rabbit, but they may cause obstruction of the gut and result in anorexia.
how can Room Temperature Effect rabbits shedding?
Hot room temperature may have compounding effect as they shed more (best is 16-22 C).
What are the Domestic Dog Ancestors?
The ancestors of the domestic dog are wolves (Canis lupus) who long ago roamed Europe, Asia, and North America in large numbers.
how are dogs used as Animal Models?
Dogs serve as animal models in a variety of areas, such as cardiovascular research and orthopedic (bone) studies.
Where are dogs acquired from?
Acquired from licensed dealers, pounds or individuals
history and disease status unknown - usually quarantined 30-60 days.
What does condition for research mean?
Random source animals already quarantined and conditioned; conditioning programs directed towards eliminating infectious agents, parasites and acclimation to lab environment.
Does NIH fund research that use random cats and dogs?
NO! NIH does not fund research that are using random source cats and dogs.
What are benefits in animals that are bred for research?
More uniform and have fewer health problems; pedigrees are available; animals accustomed to cage life.
What is Record Keeping?
- Permanent proper ID (tattoo number)
- physical characteristics
- genetic heritage
- behavioral information
- medical history
- reproduction history
What is a Normal Canine Physiological Data in beagles?
Body Weight: 10.5 kg (male) - 9.9 kg (female)
Avg Lifespan = 12 years
Body Temp = 38.9 °C; 102 °F;
Birthweight = 250g
Heart Rate = 70-160 beats/min
Respiratory rate = 22 breaths per min.
What are distinguishing features of dogs?
- carnivorous diet
- have canines
- feces are firm
- urine is clear and yellow
- short alimentary tract with simple stomach.
What are concerns in dogs pharmaceutically and disease wise?
sensitive for certain drug or anesthetics
rabies, canine distemper
what is special about Dog Vision?
They can see well at lower levels of illumination.
Dogs External genitalia identification
The external genitalia of dogs are easily identified, and the sex differences are obvious from birth.
when do dogs reach puberty?
Dogs reach puberty between 6-12 months.
Breeding frequency in dogs?
Dogs breed year-round, with mating permitted by the female only during estrus.
Estrus cycle in dogs?
Estrus occurs every 7-8 months in dogs (mono-estrus type).
Estrus length in dogs?
The length of estrus is 7-10 days.
Estrus detection methods in dogs?
Estrus can be detected by visual observation of swollen vulva and vaginal discharge, vaginal cytology, or Progesterone (P4) levels.
When should first time breeding occur in dogs?
Breed at the first heat after 1 year of age.
what should be the Breeding frequency during estrus in dogs?
Place the female with the male every other day during estrus.
Ovulation in dogs is...
Ovulation is spontaneous.
how can you detect pregnancy in dogs?
Detection of pregnancy can be done by abdominal palpation at 21-28 days post conception (dpc).
Average gestation period in dogs?
The average gestation period for dogs is 63 days.
Signs of pregnancy in dogs?
Teats become larger and more prominent in color and may produce clear fluid; weight gain and a swollen, round abdomen after 40 dpc.
When should you move female dog to whelping area?
Move the female into a whelping area 10-14 days prior to whelping, ensuring it is warm and secluded.
What are Behavioral changes in pregnant females?
Pregnant females may seek seclusion or the company of the handler, exhibit some nest building, and show signs of anorexia or emesis.
what is Tenesmus in dogs?
straining and attempted defecations and urinations without result.
what is the duration of Uterine contractions in dogs?
Uterine contractions last 6-12 hours.
what is the Puppy delivery process?
Uterine contractions increase pressure which ruptures membranes and expels pups, with membranes usually delivered within 15 minutes and typically 30-45 minutes between pups.
What is Licking behavior after birth?
Bitches lick pups vigorously after delivery.
what is Litter size in dogs?
Litter size ranges from 4-12, with an average of 2 litters per year
When does weaning occur in dogs?
weaning occurring at 7-8 weeks.
What are some characteristic of housing for dogs?
Dogs are social animals and can be group housed in pens or runs, with outdoor runs acceptable if they have appropriate heating, cooling, shade, and protection from rain and wind.
what are the Dietary needs of dogs?
Dogs are primarily carnivores but require a balanced diet including meat, grain, and vegetables.
how often should adult dogs be fed?
Adult dogs are typically fed once daily.
How often should water be given to dogs?
Fresh water should be provided ad libitum.
Social hierarchy in groups (dogs)
In groups, dogs establish social hierarchy, so adequate feed and water should be provided for less dominant individuals.
what are some enrichment components for dogs?
Human contact, training, toys, treats, and exercise are important components of enrichment for dogs.
what is the dog scientific name?
canis familiaris
Normal feline physiological data
- Average body weight: 3.5 kg (male) vs 2.5 kg (female),
- average lifespan = 12 years
- body temperature = 38.6 °C; 101.5 °F
- birth weight = 110-120g
- heart rate = 110-140 beats/min, respiratory rate = 26 breaths/min.
What is the cats scientific name?
felis catus
What two wild types were crossed to make the domesticated cat?
Felis sylvestris x Felis lybica
What are Distinguishing features in cats?
- Features include retractable claws
- purring vocalization, normal
-feces that are firm and brown, and pale yellow urine with a faint odor.
What is different about Male cat urine odor?
Male urine has a musky pervasive odor.
why are cats poor subject for research?
they are Prone to respiratory infections
Pathogen-free breeders in cats
There are specific pathogen free breeders of cats.
what is dangerous about cat bits?
Cat bites can lead to dangerous infection.
what are common diseases in cats?
Toxoplasmosis - cats are host for Toxoplasma gondii.
respiratory infections
How to determine sex in Male cat ?
In male cat (tom), testes are contained in an easily seen external scrotal sac.
Male cat penis...
The penis and penile sheath are small and point towards the tail.
Extending male cat penis...
The penis can be extended out of sheath by applying gentle pressure on both sides of the base of the sheath.
Female cat anatomy...
The female has a visible vulva and anus. Breeding female is known as a queen.
Anogenital distance in kittens
In young kittens, AGD is slightly greater in the male. The genital opening is round in male and slit-like in the female.
when does Puberty occur in cats?
Puberty = 36 weeks or 9 months (males), 5-12 months (females).
what is the Breeding cycle in cats?
Polyestrous breed all year long under laboratory conditions.
what is the estrus duration in cats?
Estrus lasts 1-4 days if mating occurs; if not, can last up to 10 days.
what Behavioral changes during estrus in cats?
Behavioral changes during estrus: may display lordosis (inward curve of spine) and are generally very vocal with no obvious physical signs.
Why are cats considered induced ovulators?
they ovulate after 24 hour post-coitus (mating)
what are mating methods in cats
Can be mated in pairs or harem breeding (a week or 10 days).