
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Individual
one organism (elk)
population
group of same species (elk herd)
community
all living organisms in an area
ecosystem
all living and nonliving things
biome
large area with similar climate conditions that determine plant and animal species there
Competition
organisms fighting over a resource like food or shelter: negative, negative
Predation
one organism using another for energy source; positive, negative
Mutualism
both organisms benefit; positive, positive
Commensalism
relationship that benefits one organism and doesn’t impact the other; positive, 0
Predation examples
Herbivores (giraffe and tree), Carnivores (leopard and giraffe), Parasites (mosquitoes, tapeworm, sea lamprey), Parasitoids (lay eggs e.g. bot fly and parasitic wasps)
Symbiosis
any close and long-term interaction between two organisms of different species
resource partitioning
different species using the same resource in different. ways to reduce competition
temporal partioning
using resources @ different times, such as wolves and coyotes hunting @ different times (night vs day)
spatial partioning
using different areas of a shared habitat (different length roots)
morphological partioning
using different resources based on different evolved body features
biome
an area that shares a combination of average yearly temp. and precipitation (climate)
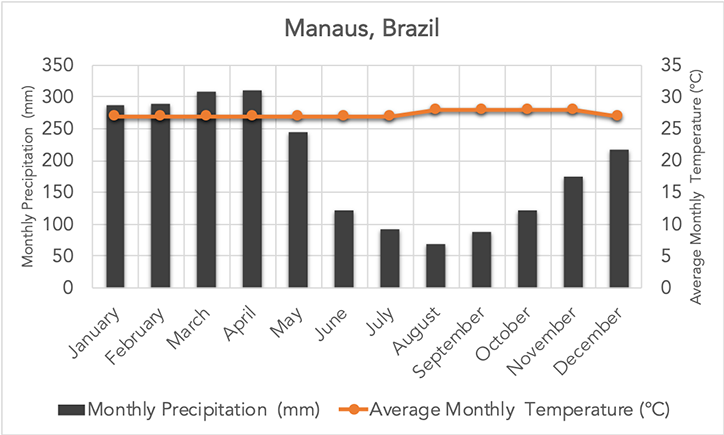
tropical rainforest

taiga (boreal forest)

temperate deciduous forest

grassland

desert

tundra
tropical rf
nutrient-poor soil (high competition from so many diff. species)
taiga
nutrient poor soil (low temp and low decomp. rate of dead org. matter)
temperate forest
nutrient rich soil (lots of dead org. matter-leaves and water temp/moisture for decomp)
biomes shift in location on earth as climate changes
ex: warming climate will shift taiga forests further north as tundra permafrost soil melts and lower latitudes become too warm for aspen and spruce
salinity
how much salt there is in a body of water and determines which species can survive and usability for drinking
depth
influences how much sunlight can penetrate and reach plants below the surface for photosynthesis
flow
determines which plants and organisms can survive and how much oxygen can dissolve into the water
temperature
warmer water holds less dissolved O2 so it can support fewer aquatic organisms
littoral zone
shallow water w/ emergent plants
limnetic
where light can reach (photosynthesis)
No rooted plants, only phytoplankton
profundal
too deep for sunlgiht (no phots.)
benthic
murky bottom where inverts bugs live, nutrient rich sediments
wetlands
area with soil submerged/saturated in water for at least part of the year, but shallow enough for emergent plants
plants in wetlands
they are adapted to living with roots submerged underwater for instance lily pads cattails and reeds
Benefits
stores excess water during floods, recharges groundwater by absorbing rainfall into soil, filters pollutants, high plant growth due to lots of water and nutrients
Swamp
Cyprus tree
Marsh
reed and cattails
Bog
spruce and sphagnum moss
estuaries
areas where rivers empty into the ocean, mix of fresh and salt water
Salt Marsh
estuary habitat along coast in temperate climates and is a breeding ground for many fish and shellfish species
Mangrove Swamps
estuary habitat along coast of trop. climates and has mangrove trees with long stilt roots that stabilize shoreline and provide habitat for many species of fish and shellfish
Coral Reef
Mutualistic relationship; warm shallow waters beyound the shoreline most diverse marine (ocean) biome on earth
Coral and Algae Relationship
coral take CO2 out of the ocean to create calcium carbonate exoskeleton (the reef) and also provide CO2 to the algae and algae live in the reef and provide sugar (energy) to the coral through photosynthesis
Intertidal zones
narrow band of coastline between high and low tide; need to be adapted and survive crashing waves; EX: barnacles, sea stars, crabs
Open Ocean
low productivity/ area as only algae and phytoplankton can survive in most of ocean; they provide a huge part of the oxygen that we need to survive and absorbs a lot of CO2
Photic zone
area where sunlight can reach (photosynthesis)
Aphotic zone
area to deep for sunlight (no photosynthesis)
Photosynthesis
Producers convert CO2 into suga
Respiration
Sugars are converted back into CO2
Burial
slow process that stores carbon in underground sinks like sedimentary rock or fossil fuels
Extraction
Human extraction of fossil fuels brings carbon to Earth's surface, where it can be combusted
Exchange
CO2 in the atmosphere and CO2 dissolved in water are constantly exchanged
Combustion
Combustion converts fossil fuels and plant material into CO2
When does imbalance occur in carbon cycle?
When resorvoris or sinks are storing carbon
Carbon sinks
a carbon reservoir that stores more carbon than it releases (ocean: algae and sediment, plants, soil)
Carbon source
process that add Carbon to atmosphere (fossil fuel - oil n gas, animal agriculture - burping n farting = methane, deforestation - releases carbon from trees)
Photosynthesis process
removes CO2 from the atmosphere and converts it to glucose
glucose
biological form of carbon and stored chemical energy in the form of a sugar it is a carbon sink
Respiration
uses oxygen to break glucose down and release energy thus it is a carbon source
direct exchange
carbon dioxide moves directly between the atmosphere and ocean by dissolving into ocean water at the surface. An increase in atmospheric CO2 leads to a corresponding increase in oceanic CO2, which contributes to ocean acidification
what takes out CO2?
algae, phytoplankton, coral reef, marine org. with shells - carbon sinks
Fossil fuels
coal, oil, and natural gas are formed from fossilized remains of org. matter ex: dead ferns (coal) or marine algae n plankton (oil)
Phosphorus cycle
movement of p atoms and molecules between sources and sinks and it is extremely slow
Weathering
process by which rocks containing phosphorus minerals gradually break down due to natural forces like wind, rain, and temperature changes
Step 1
Weathering of uplifted rocks contributes phosphates to the land. Some phosphates make their way back to the ocean.
Step 2
Phosphate fertilizer applied to fields can run off directly into streams, become part of a soil pool, or be absorbed by plants.
Step 3
Excretion by animals and decomposition of both plants and animals release phosphates on land or in water.
Step 4
Dissolved phosphates precipitate out of solution and contribute to ocean sediments. Conversion of sediments into phosphate rocks is a very slow process.
Step 5
Geologic forces can slowly lift up phosphate rocks from the ocean floor to form mountains.
Synthetic
Humans mine phosphate minerals adding it to products like synthetic fertilizers and detergents/cleaners
Issues
synthetic fertilizers containing phosphates are added to lawns or ag. fields; runoff carries P into nearby bodies of water P from detergents and cleaners enter bodies of water via wastewater from homes
assimilation
occurs when plants absorb phosphate ions from the soil or water and incorporate them into organic molecules, like DNA and ATP, essential for growth and energy transfer. Animals then obtain phosphorus by consuming these plants or other animals.
excretion
when animals release phosphorus back into the environment through waste products
sedimentation
phosphate doesn’t really dissolve well in water so it forms chunks underneath and over time this can become sedimentary rocks
geo uplift
tectonic plate collision forcing up rock layers that form mountains then p cycle starts over again with weathering
Eutrophication
process where excess nutrients, especially phosphorus and nitrogen, enter water bodies (like lakes, rivers, and oceans), leading to an overgrowth of algae and other aquatic plants
Caused by
runoff containing fertilizers, sewage, and industrial waste.
Steps
Nutrient Enrichment → Algae Bloom → Oxygen Depletion → Aquatic Life Decline → Dead Zone
Terrestrial Reservoir
Phosphorus is stored in soil and rocks, particularly in phosphate-rich minerals. Through weathering, phosphate ions are released into the soil, where they become available to plants and enter the terrestrial food web.
Aquatic Reservoir
Phosphates from soil and rocks eventually enter water bodies through runoff and can accumulate in ocean sediments. Over long periods, these sediments may form new phosphate rock on the ocean floor.
evaporation
occurs when liquid water is heated by the sun and transforms into water vapor, entering the atmosphere
transpiration
process by which water is absorbed by plant roots from the soil, moves through the plants, and is released as water vapor through small openings in leaves called stomata
evapotranspiration
amount of water that enters atmosphere from transpiration and evaporation combined
surface runoff
occurs when excess water from precipitation (rain or snowmelt) flows over the land's surface instead of soaking into the ground
condensation
process by which water vapor in the atmosphere cools and changes back into liquid water droplets
infilitration
refers to the process by which water penetrates the soil surface and moves downward into the soil layers