MIP imaging and processing and Radiopharmacuticals with procedures
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
245 Terms
What are the two main reasons we would perform planar MPI imaging over SPECT?
if pt is claustrophobic or exceeding weight limit of SPECT table
How is the gamma camera set up for planar imaging? (what FOV, and collimator do we use?)
SFOV or LFOV with zoom
LEAP collimator for Tl, or LEHR for Tc
T/F: when performing planar imaging, both sets of images should be acquired in the same way (positioning, angles)
true
Why is it important that both sets of planar images images be acquired in the same way
so that they’re comparable
What are we looking at with MPI(myocardial perfusion imaging)
blood flow to left ventricle
How do we position the patient for MP imaging?
either both arms or left arm over head
pt should be made as comfortable as possible
can be imaged supine, prone, or decubitis position
If we were imaging the patient in a decubitis position, which side should they be laying on?
right side (so that left side is up)
What is the benefit of imaging a patient in a prone position?
helps eliminate diaphragm artifact
What types of planar views are we acquiring during MPI?
anterior
LAO (45-55 degree)
left lateral (90 degree)
Why do we acquire LAO (45-55 degree) planar views?
best for septal visualization
What is the idea patient positioning for L. lateral planar views and why?
decubitus - decreases diaphragm attenuation, which can cause false postiive defect in inferior wall of L. ventricle
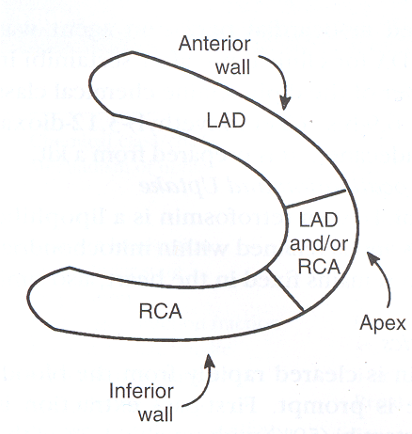
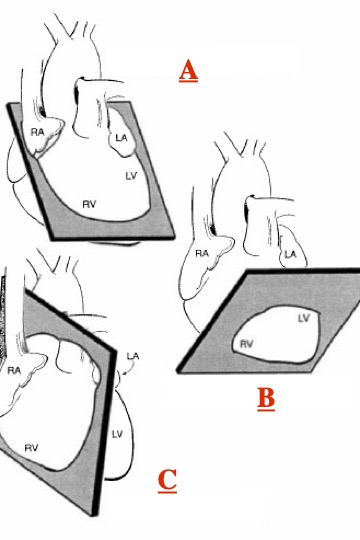
What view of the heart is represented in this image?
anterior
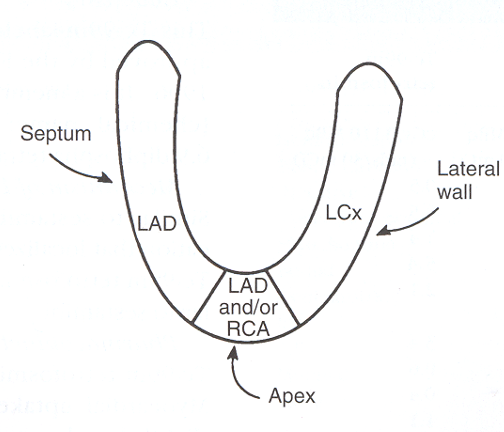
What view of the heart is represented in this image?
LAO (left anterior oblique)
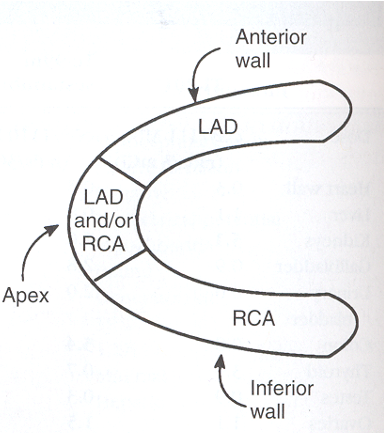
What view of the heart is represented in this image?
Left lateral
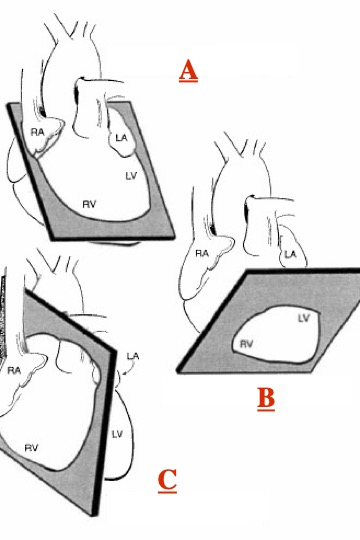
What view of the heart is represented in this image?
anterior
What view of the heart is represented in this image?
LAO (left anterior oblique)
What view of the heart is represented in this image?
Left lateral
When do we begin our first set of Tl-201 planar images? Are we taking stress or rest images.
5-10 min post-injection
stress
What is the imaging parameters for Tl-201 planar images?
30% window centered over 72keV
optional 20% window on 167 keV
128×128 matrix
minimum 600,000 counts/image or 8min/image
When would we perform redistribution planar images when using Tl-201?
3-4 hrs post injection
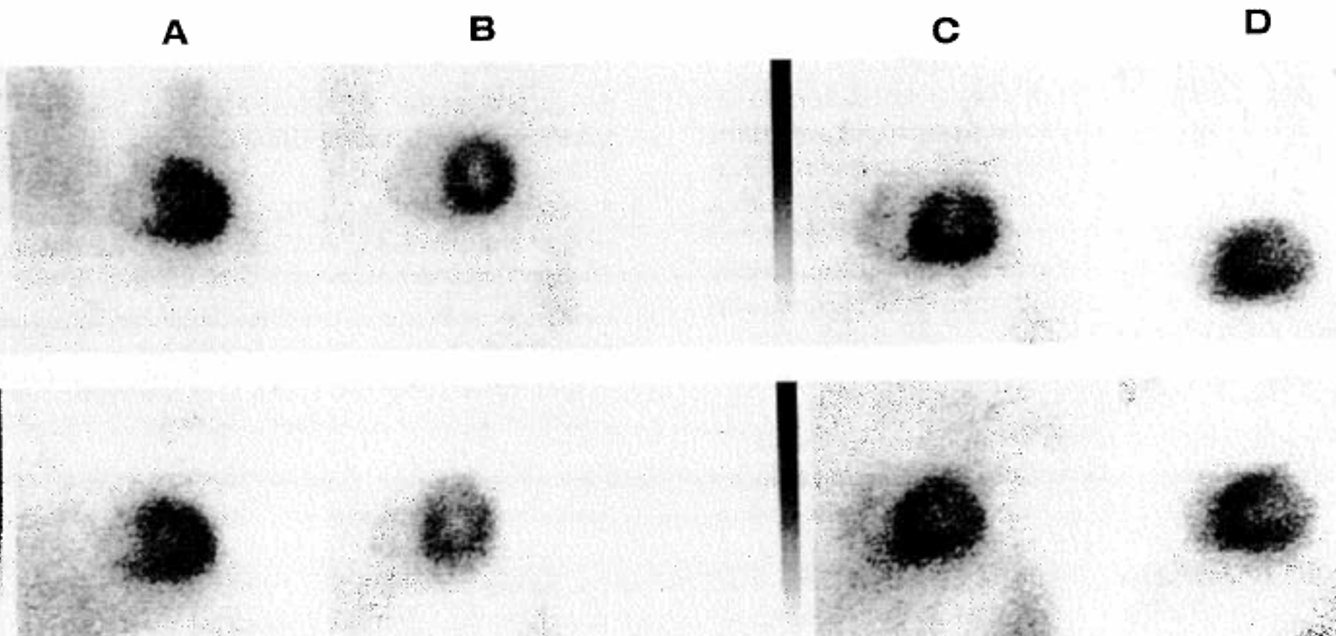
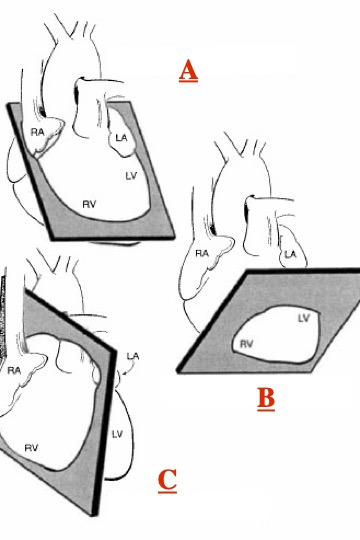
What view is shown in A?
anterior
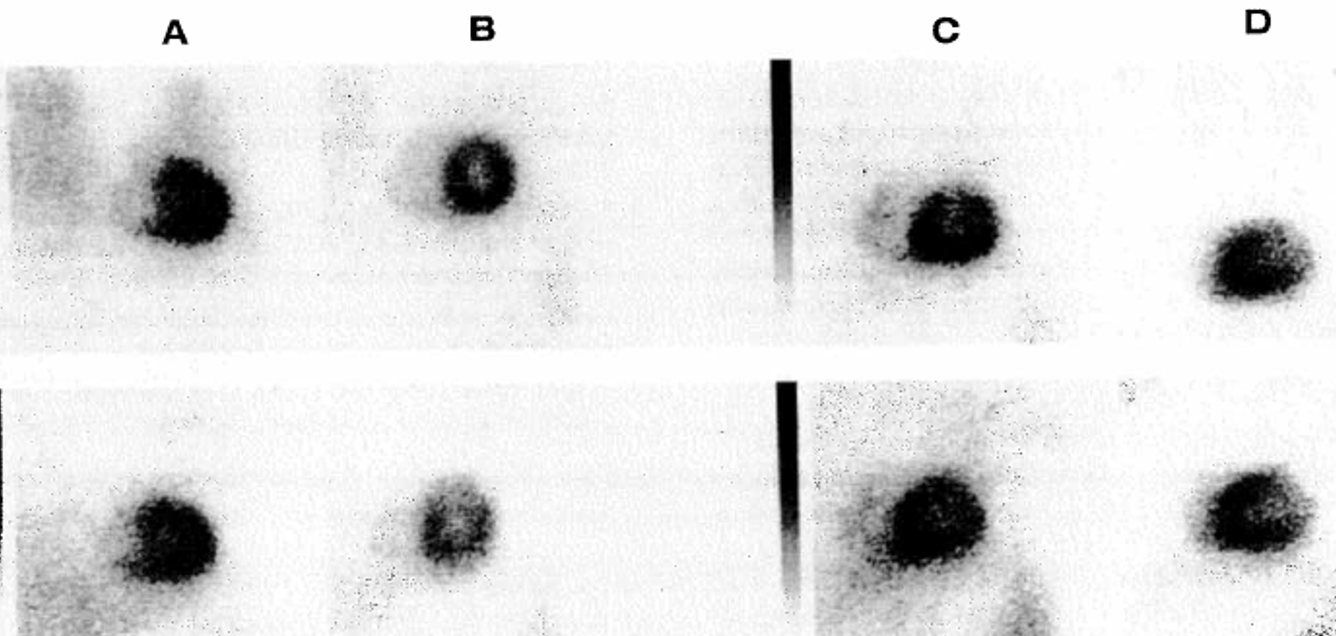
What view is shown in B?
LAO (30 degree)
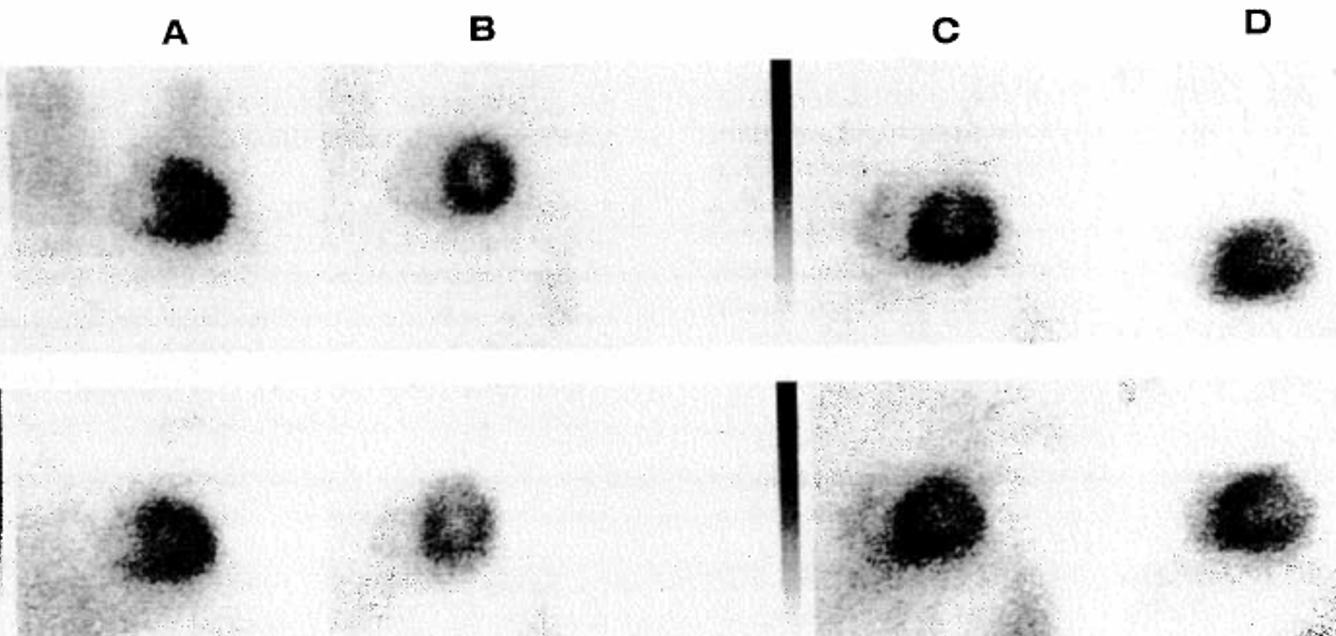
What view is shown in D?
left lateral
When do we begin stress imaging when taking Tc planar images?
15-60 min after stress injection
When do we begin rest imaging when taking Tc planar images?
30-90min after rest injection
What is the energy window for tc planar imaging?
20% window over 140keV
When performing planar MPI images, we take ___min/images, or ___min/image if gated.
5, 10
How are planar MPI images processed?
Side-by side display of background subtracted and smoothed stress and rest or redistribution images
if using Tl-201 - Heart lung ratio can be calculated
When processing Tl-201 planar images, what does a high heart-lung ratio likely indicate?
greater chance PT has CAD
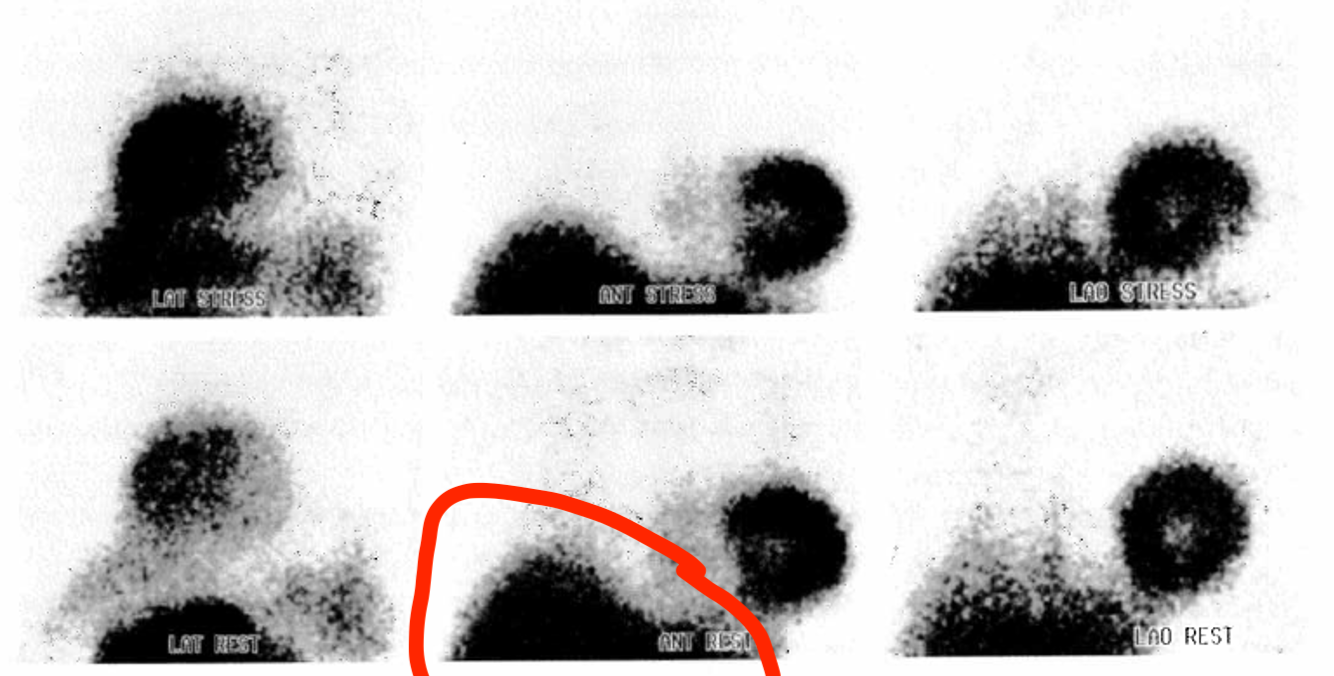
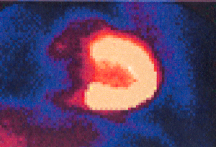
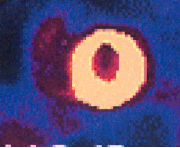
This is a photo of a planar Sestamibi MPI image, what might the circled object be?
Liver (MPI tc agents leave body thru liver)
How many images are acquired each stop in gated SPECT imaging?
8 images at each stop then put together in composite to make beating heart
What triggers data collection during gated SPECT imaging?
R-wave of ECG
What can be assessed with gated SPECT acquisition
wall motion
wall thickening
estimate of EF
ventricular volume
How is gated data useful?
helps differentiate true perfusion defect from attenuation
Female with fixed defect in anterior wall
if it’s MI or breast attenuation
How can gated data be used when determining if its MI or breast attenuation?
if wall motion and thickening are normal in anterior wall, physician can confidently interpret study as being normal with attenuation artifact
What is the gamma energy level for Tl-201 SPECT imaging?
very low gamma energy (68-80keV)
What is the physical half-life of Tl-201?
73.1 hr
How is Tl-201 produced?
in a cyclotron
How many injections are given during a Tl-201 SPECT imaging? What is the dose?
1 injection
3-4mCi
In what order are the rest/redistribution and stress images performed using Tl-201 SPECT imaging
Stress-rest protocol only
When is the pt placed under the camera immediately after stress?
immediately after stress
What is the general Tl-201 SPECT imaging protocol?
Typically 1 injection used (3.0-4.0 mCi)
Stress-Rest protocol only
Patient placed under camera immediately after stress
3-hour rest period required before delay images
Redistribution begins at about 10-15 minutes post injection
What is the mechanism of uptake of Tc-Sestamibi?
mitochondria of myocardium
Which Tc agent has a higher extraction fraction, Sestamibi or Tetrofosmin?
Sestamibi
What is the benefit of using Tc agent Tetrofosmin over Sestamibi
Tetrofosmin has faster liver clearance, can image quicker
T/F: uptake of Tc agents is dependent on mitochondrial membranes
True
T/F: Tc agents have minimal redistribution, especially compared to Tl-201
true
What is the major pathway for clearance of Tc agents?
hepatobilliary system (liver)
What is the general dose range for Tc-99m agents?
10-30mCI
How does the dosage differ when using Tc-99m in a 1 day protocol?
2nd dose is 3 times that of first
ex. if first dose was 10mCi, 2nd dose is 30mi
When imaging patients with a large body habitus using Tc-99m, is a 1-day or 2-day protocol better?
2 day
If performing a 2 day protocol using Tc-99m, is it more ideal to perform the stress or rest first?
stress
If we wanted a TRUE rest image, should we perform the stress or rest images first?
rest
What is the protocol for a Dual isotope imaging protocol? (dose, timings, processing precautions)
3mCi Tl-201 - rest images
wait 10-15min
20-30mCi Tc-99m agent - stress images
wait desired time
processing - use different filters
For all protocols, what are the two most important things to remember?
all counts count
ALALRA
What types of protocols can we perform using Tc-agents only?
1 day R/S - Tc99m (most typical)
1 day S/R - Tc99m
2 day - Tc99m (preferred for obese patients)
What protocols use Tl (not exclusively)
1 day Tl only
1 day dual isotope Tl/Tc99m
What are the indications for myocardial perfusion imaging?
Assessment of the presence, location, extent, and severity of CAD
Risk stratification of patients after MI
Risk stratification before non-cardiac surgery in patients with known CAD or high risk factor of CAD
What is the patient prep for MPI?
NPO for 4 hrs
no caffeine 12 hrs before the stress test
certain medications may need to be stopped for stress test
i.e. beta blockers
What is the general protocol for a 1 day R/S Tc-99m stress test?
inject low dose at rest [8-10mCi]
wait 30min for myoview, 45min for Mibi
image rest
stress test
inject high dose [24-30mCI] at peak exercise or peak coronary vasodialation
wait 30-45 min
image stress
process images
always review images for movement and artifacts (bowel or liver interference)
What should MPI images always be reviewed for before releasing patients?
movement and artifacts (from bowel or liver interference)
What is the general protocol for a dual isotope Tl/Tc protocol?
inject Tl at rest
wait 20min
image rest
Stress: inject high dose of Tc-99m agent (24-30mCi) at peak exercise or peak coronary vasodilation
image stress
always review images for movement and artifacts (from bowel or liver interference)
Describe the 1 day protocol using Tl
Inject 3-4mCi TL at peak exercise or peak coronary vasodilatation
Wait 10min
Image Stress
Wait 4hours
Image Rest
Describe a 2 day protocol using Tc-99m agents
Day 1
Inject high dose of Tc99m agent (24-30mCi) at peak exercise or peak coronary vasodilatation
Wait 30-45min
Image Stress
Day 2
Inject low dose at rest (24-30mCi)
Wait 30min for myoview
Wait 45min for Mibi
Image Rest
What tracer/agent protocol is best for image quality?
Dual tracer protocol using Tl for stress and Tc for rest
Why is the Dual tracer protocol (Tl/Tc) best for best image quality?
◦Has a better extraction fraction w/TL
◦Maximizing dosage
◦Saves money
What are the downfalls of a Dual tracer protocol (Tl/Tc)?
◦Increased radiation exposure
◦Lots of scatter radiation in the body
◦Motion after stress
◦Long study
Which is preferred in a SPECT image study, circular or elliptical orbit?
elliptical orbit
Are SPECT images typically acquired in 180 degrees or 360?
180
When acquiring images for Tl SPECT study in step-and-shoot mode, for how long is each image acquired? (answer in ___sec/stop)
40 sec/stop
When acquiring images for Tc-agents SPECT study in step-and-shoot mode, for how long is each image acquired? (answer in ___sec/stop)
20-25 sec/stop
What are the different methods of attenuation correction?
transmission source
CT
computer based programs
none
What is a flood uniformity correction?
correct images for uniformity by applying flood correction
What is involved in SPECT imaging processing?
define reconstruction boundries
manually draw line thru heart cavity parallel to long axis of ventricle
reconstruction performed w/ either back-projection or iterative reconstruction
What would happen if the long axis of the ventricle is selected incorectly during SPECT image processing?
reconstructed images and polar plots will be distorted
What is the purpose of image filters?
enhance resolution and supress noise
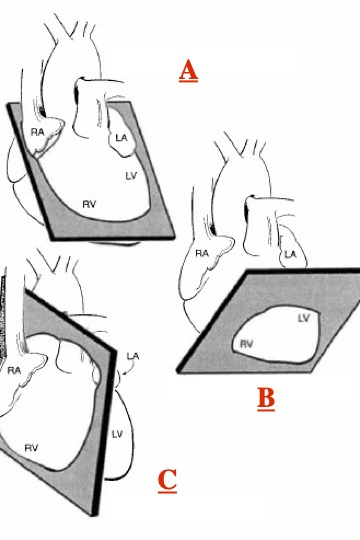
What plane is A?
horizontal long axis
From what to what is A “slicing”?
from inferior to anterior [superior]
What plane is B?
Short axis
From what to what is B “slicing”?
from apex to base
What plane is C?
Vertical Long axis
C is slicing ___ to ___ (hint-anatomical directions/landmarks)
medial to lateral (septal to lateral)
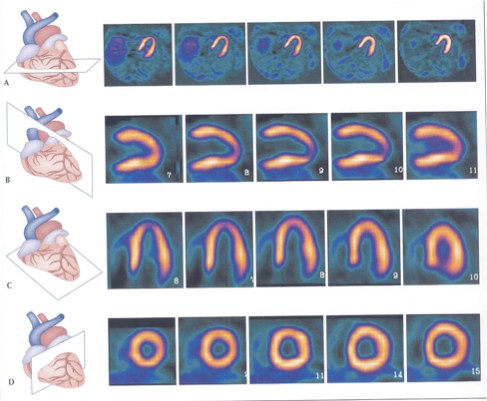
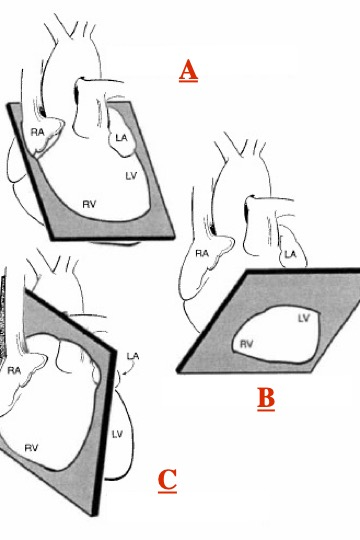
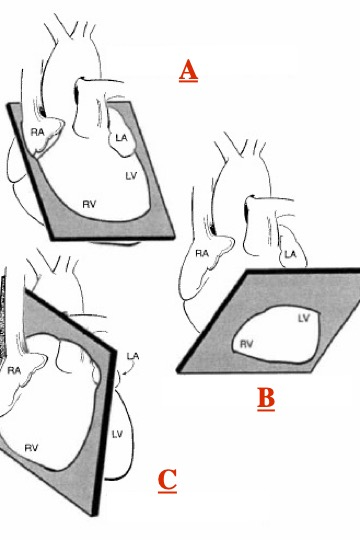
What type of slice is A?
top transaxial
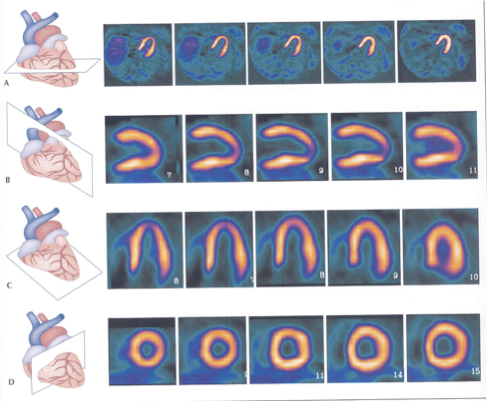
What slice is B?
vertical long axis
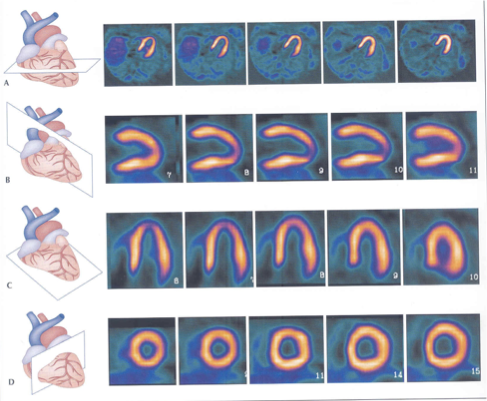
What slice is C?
Horizontal long axis
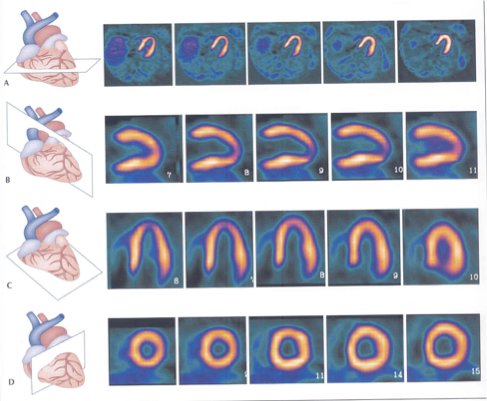
What slice is D?
Short axis
Which artery supplies the septum?
left anterior descending
Which artery supplies the apex?
left anterior descending
Which artery supplies the anterior wall of the heart?
left anterior desending
Which artery supplies the lateral wall of the heart?
circumflex
Which artery supplies the inferior wall?
Right main coronary
What are the other types of plots we can generate for MPI?
reversibility plot
blackened pixel plot
standard deviation plot
What is the purpose of a quantitative polar plot?
provides way to visualize entire left ventricle in one image
analysis of SPECT data can detect and/or verify perfusion abnormalities
What are volume images?
3d images that allows for surface of heart to be viewed in systole and diastole
Can we generate volume images without gated imaging?
no - need gated info to generate volume images
What is the purpose of a reversibility plot?
generated to show extent of reversibility
What is the purpose of a blackened pixel plot?
shows which areas are greater than a specified standard deviation below the mean
What is the purpose of a standard deviation plot?
color codes myocardium based on number of standard deviations below the mean of the normal database
What are the two types of Radiopharmaceuticals we can use for a cardiology procedure?
Thallium-201 chloride
Tc-99m labeled agents`
What is the extraction Fraction?
amount of radioisotope taken up in myocardium the first pass thru the heart