Autonomic Nervous System
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
What is a visceral efferent fiber?
Motor fiber that carries autonomic signals from CNS to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands.
What is a visceral afferent fiber?
Sensory fiber that carries information from organs to the CNS.
What is a paravertebral ganglion?
Ganglia located along either side of the vertebral column; part of sympathetic chain.
What is a prevertebral ganglion?
Ganglia located anterior to the vertebral column near major arteries; part of sympathetic system.
What is the cervical ganglion?
Sympathetic ganglia in the neck; includes superior, middle, and inferior cervical ganglia.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)?
Motor system regulating involuntary functions; includes sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions.
What are sympathetic nervous system targets and functions?
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, glands; promotes "fight or flight" (e.g., heart rate ↑, pupil dilation).
What are parasympathetic nervous system targets and functions?
Smooth muscle, glands of head/viscera; promotes "rest and digest" (e.g., gut motility ↑, pupil constriction).
How does sympathetic system affect cardiopulmonary system?
Increases heart rate and contractility; bronchodilation.
How does parasympathetic system affect cardiopulmonary system?
Decreases heart rate; constricts airways.
How does sympathetic system affect digestive system?
Decreases motility and secretions; contracts internal sphincters.
How does parasympathetic system affect digestive system?
Increases motility and secretions; relaxes internal sphincters.
How does sympathetic system affect genitourinary system?
Promotes bladder storage; inhibits erection.
How does parasympathetic system affect genitourinary system?
Promotes urination and defecation; facilitates erection.
How does sympathetic system affect the eye? Mydriasis
Dilates pupil (mydriasis=larger word so bigger pupils)
How does parasympathetic system affect the eye? Miosis
Constriction of pupil (miosis) and accommodation for near vision.
What are cardiopulmonary splanchnic nerves?
Sympathetic nerves to thoracic organs; arise from cervical and upper thoracic ganglia.
What are abdominopelvic splanchnic nerves?
Sympathetic nerves to abdominal and pelvic viscera; include thoracic, lumbar, and sacral branches.
What are pelvic splanchnic nerves?
Parasympathetic nerves from sacral spinal cord to pelvic organs.
What is the sympathetic chain?
A series of ganglia running parallel to the spinal cord from neck to pelvis; path for sympathetic distribution.
Where are somatic afferent cell bodies located?
Dorsal root ganglia.
How are sympathetic fibers organized?
Preganglionic fibers arise from thoracolumbar spinal cord; synapse in chain or prevertebral ganglia; postganglionic fibers go to target.
How are parasympathetic fibers organized?
Preganglionic fibers arise from brainstem/sacral cord; synapse near/in target organ.
What receptors mediate somatic motor transmission?
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors at neuromuscular junction.
What receptors mediate sympathetic effects?
Adrenergic receptors (α and β); muscarinic Ach receptors in sweat glands.
What receptors mediate parasympathetic effects?
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.
What is the general pathway for autonomic innervation?
Preganglionic neuron in CNS → synapse in ganglion → postganglionic fiber to target.
What is the "fight or flight" response?
Sympathetic activation increasing heart rate, dilating pupils, redirecting blood to skeletal muscle, and mobilizing glucose.
What causes referred pain?
Visceral afferents converge onto somatic pathways in spinal cord; brain interprets organ pain as somatic pain in dermatome.
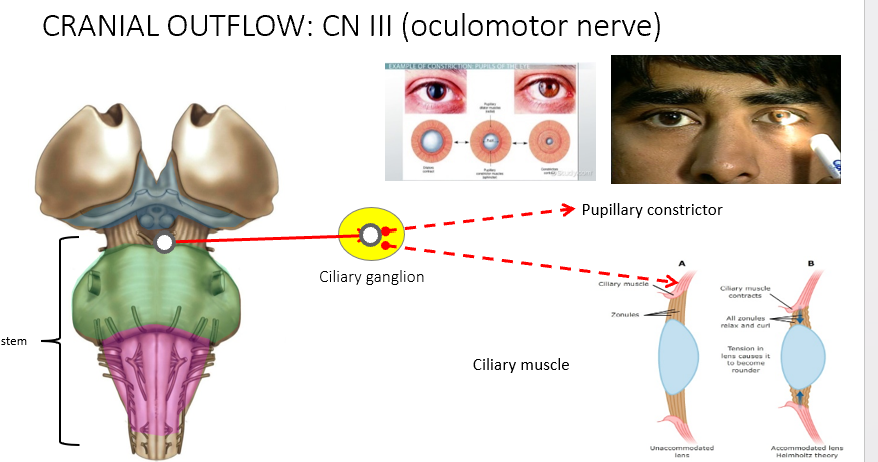
Cranial Nerve III
Oculomotor, innervates muscles that move the eye;
Target: parasympathetic>pupillary sphincter muscle and ciliary muscle of lens
Function:Pupillary constriction, accomodation of lens for near sight

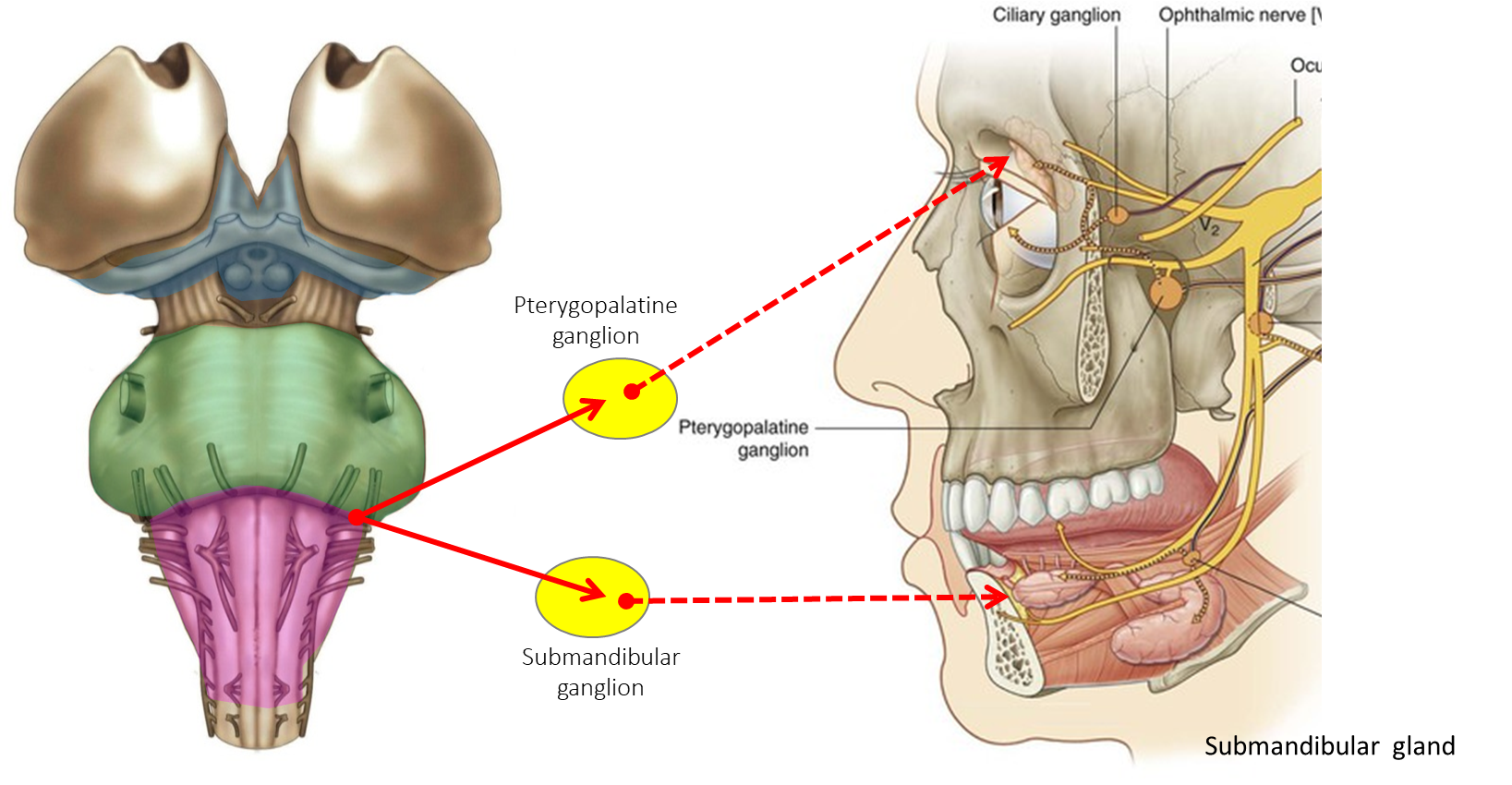
Cranial Nerve VII
Facial nerve
Targets: Lacrimal Gland(leads to tearing or lacrimation) and submandibular/sublingual salivary glands (parasympathetic increases salivation)
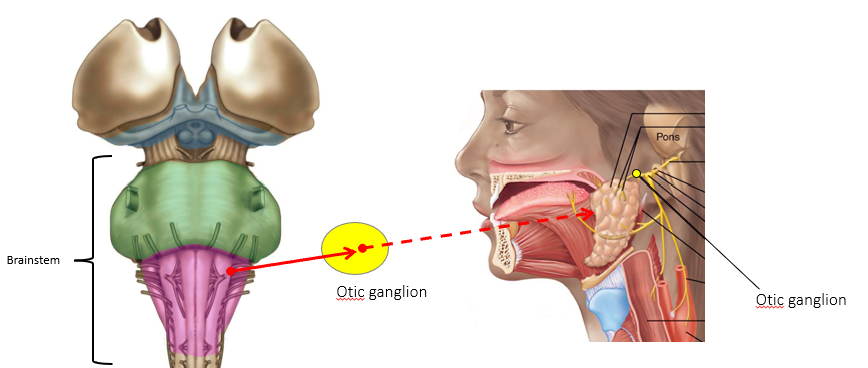
Cranial Nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal Nerve, taste and general sensory fibers to tongue and throat (stimulation increases salivation)
Target: parotid glands