Alkene Addition Reactions
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
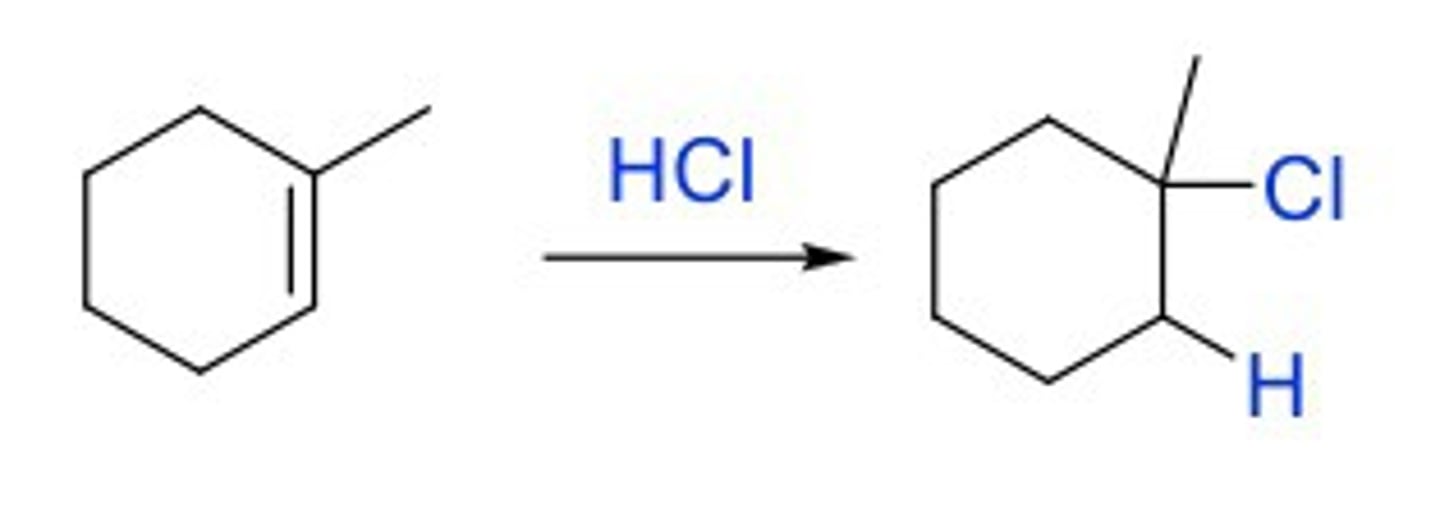
Hydrohalogenation (HBr, HCl, HI)
Markovnikov addition of H and Br/I/Cl on each side of double bond
Look out for hydride shift
Cl to the more sub., H to the less sub. (more H)
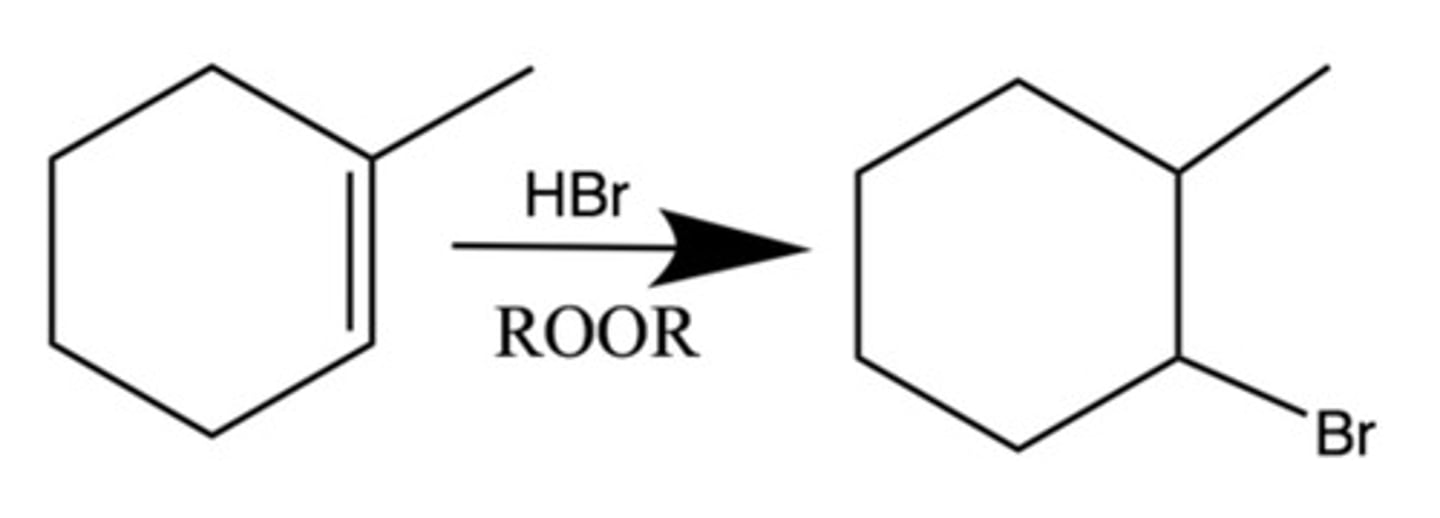
Hydrohalogenation (HBr with ROOR)
Addition of H and Br on each side
Anti-markovnikov
Br on the side w less sub. (more H), H on the side with more sub.
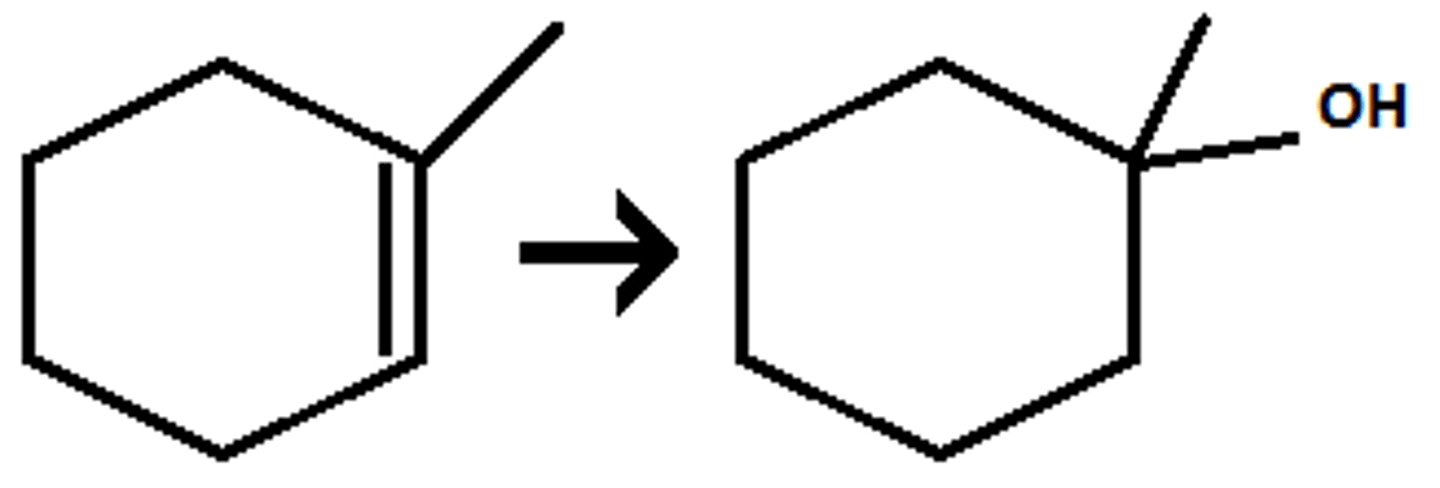
Dihydroxylation (Dilute and HX)
1. Double bond attacks H in the solvent
2. hydride/methyl shift
3. when OH is final product:
- H3O being attacked ->forms H2O
- H2O attaches to + carbon
- H2O comes back to take away an H from the attached H2O
oxymercuration Hg(OAc)2, H2O NaBH4
- Normally: attaches one planar OH on the side with more sub.
- When H2O is changed: attach whatever the thing is - H
Markovnikov and Anti
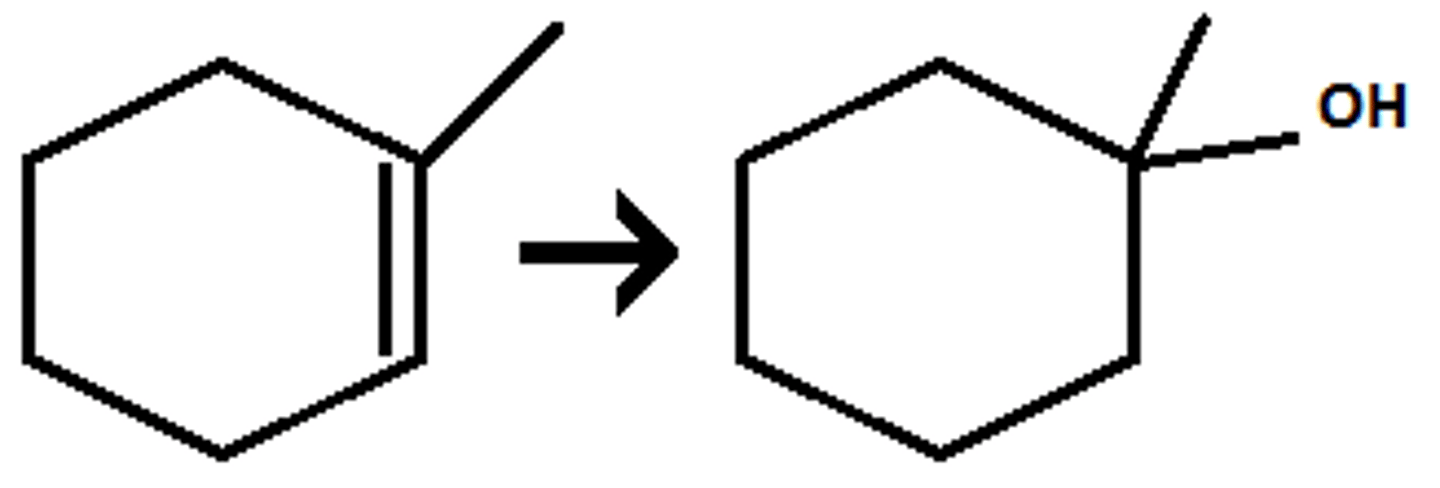
hydroboration BH3, THF, NaOH, H2O
BH3, THF, NaOH, H2O
One OH but with in or out of page + En
Anti-mark and syn
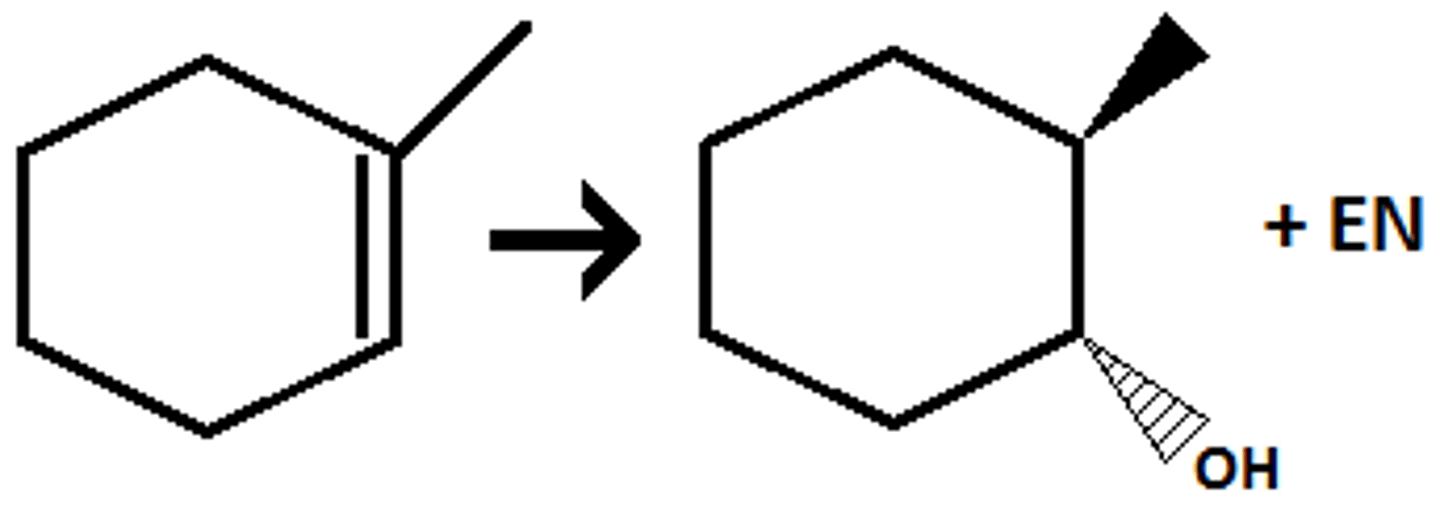
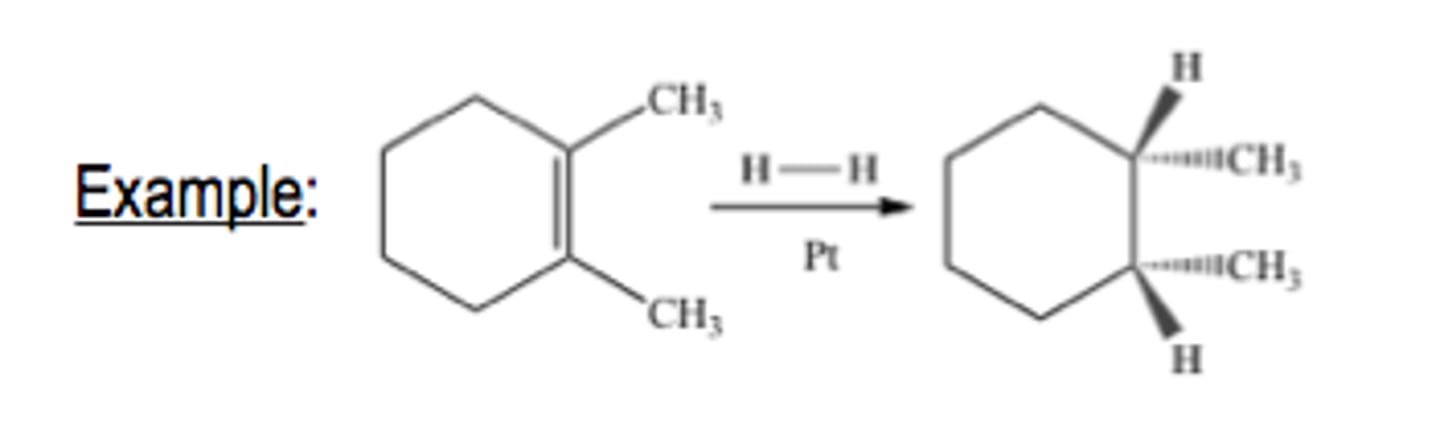
Hydrogenation H2
syn: both has wedges or dashes
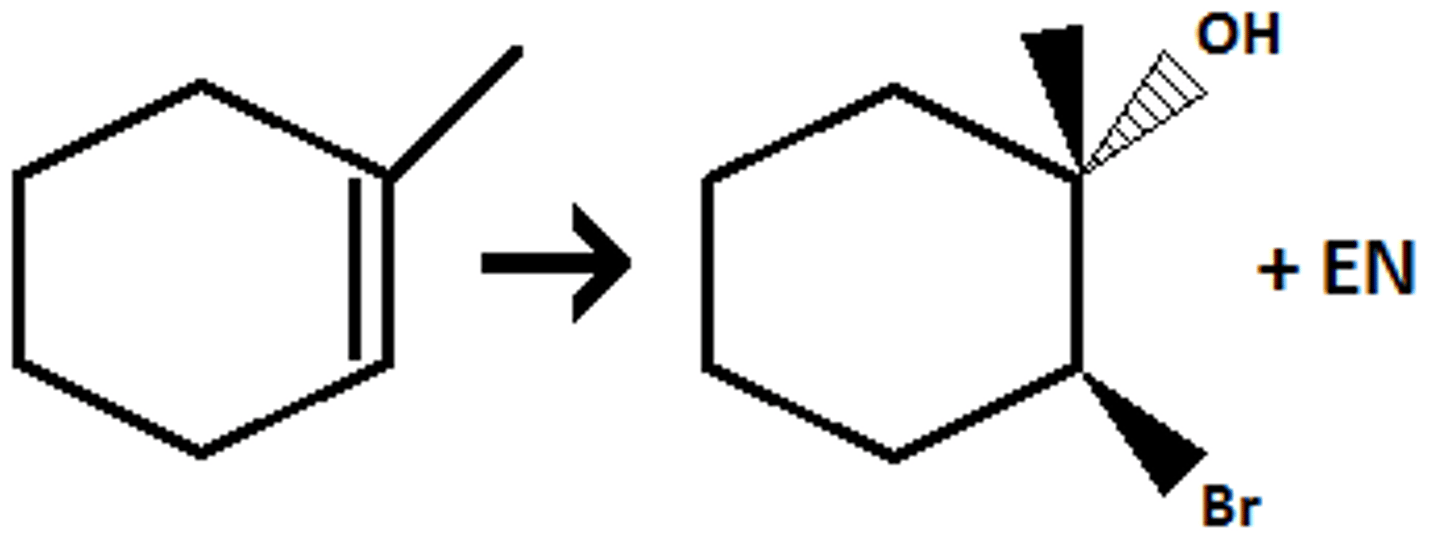
Halohydrin (Br2, H2O)
Halides adds to less sub
OH adds to more sub
Anti- addition
Epoxidation (mCPBA/RCO3H)
Anti addition
OH on each side
draw formation when chiral
OsO4 or KMnO4
syn addition
two OH on each side
draw formation when chiral
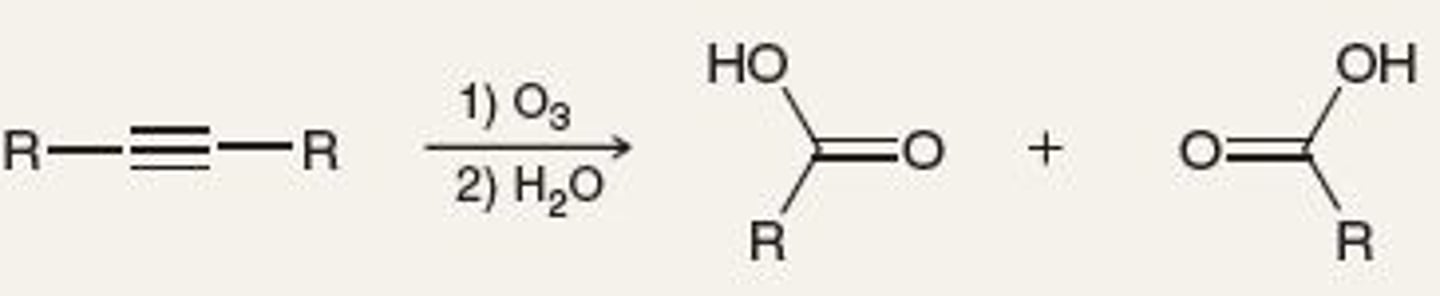
O3 Oxidative Cleavage
Cut double bond in half and add O on each side