Economics 102: Macroeconomics Ch 11. Money, Banking and Financial Markets
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
financial asset
something you can own
something of monetary value
that monetary value is derived from a contractual claim
Money
official medium of exchange
Stock
piece of paper that represents something of value
Bonds
contractual claim is with the municipality, corporation, or individual that issued the bond
Which of the following financial assets is a debt instrument - a promise by the issuer to pay the holder their principal plus interest at some future date?
Bonds
Stock
Legal Tender
Money
Bonds
What are the conditions for something to qualify as a financial asset?
something you can own, something with monetary value, something where that monetary value is derived from a verbal agreement
something you can own, something with monetary value, something where that monetary value is derived from a contractual claim
something you can hold, something with monetary value, something where that monetary value is derived from a contractual claim
something you can own, something with potential investment value, something where that monetary value is derived from a contractual claim
something you can own, something with monetary value, something where that monetary value is derived from a contractual claim
George reaches into his wallet and pulls out a $20 US bill to pay for his coffee. By using currency to make a purchase, what is George actually doing?
George is bartering with an established IOU.
George is exchanging value for the ownership in the underlying asset.
George is offering a trade in the amount of value of the medium of exchange.
George is paying with a government guaranteed note.
George is paying with a government guaranteed note.
Which of the following BEST explains the contractual obligation associated with stock?
The promise by a central bank to keep the economy strong so the business represented by the stock can be financially stable.
Commitment by the company that issued the stock to buy the stock of cash whenever the holder of the stock requests.
A commitment to the owner of stock to make the value of the stock increase, no matter what.
An ownership interest in a company.
An ownership interest in a company.
Which of the following lists is in the correct order, from least to most, of the market value of each of these financial assets?
Stock, Money, Bonds
Money, Bonds, Stock
Bonds, Stock, Money
Money, Stock, Bonds
Money, Stock, Bonds
time value of money
money that you have right now will be worth more over time
future value
how much money put in the bank today will turn into at some point in the future with the interest
present value
how much you need to save today to have a specific amount at some point in the future
annuity
a stream of equal payments
future value of an annuity
how much a stream of A dollars invested each year at r interest rate will be worth in n years
present value of an annuity
how much you will need today to receive a stream of payments A each year for n years if the money is invested at r interest rate
Which of these is an annuity?
Betty gets $50 in six months and $20 six months later
Bob gets $10 this year and $20 next
Jack gets $10 in three months and $10 six months later
Joan gets $100 every year for the rest of her life
Joan gets $100 every year for the rest of her life
How much will Bill and Mary need to put in the bank today at 4% interest to have $20,000 in five years for a down payment on a house?
$20,000
$16,000
$16,439
$17,439
$16,439
The time value of money means that:
A dollar received today is worth the same as a dollar received tomorrow
A dollar received tomorrow is worth more than a dollar received today
A dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received tomorrow
A dollar received two years from now is worth more than a dollar received today
A dollar received today is worth more than a dollar received tomorrow
If Martha puts $100 in the bank today at 6%, how much will she have in three years?
$124.10
$119.10
$112.10
$106.00
$119.10
If a couple saves $5,000 a year for five years at 5% interest, what is the future value of this annuity after those 5 years?
$30,000
$32,680
$27,628
$35,680
$27,628
The Money Supply
is the total quantity of money in the economy at any given time
M1
small savings accounts
money market funds
small time deposits
M2
large time deposits
large money market funds
repurchase agreements
Liquid
means that you can convert something into cash quickly
Which of the following measures of the money supply is largest?
M2
M1
Coins and currency
Time deposits
Checkable deposits
M2
Which of the following statements is true regarding the money supply?
M1 is more liquid than M2.
M1 is larger than M2.
M2 is more liquid than M1.
M2 is composed primarily of coins in circulation.
M2 is no longer used by the Federal Reserve.
M1 is more liquid than M2.
Loretta deposits money into her savings account. If all other factors are held constant, how does this affect M2?
M2 stays constant
M2 decreases
M2 increases
M2 decreases by the M3 amount
M2 stays constant
Which of the following is a component of M1?
Cash and coins in circulation
Government bonds
Gold
Certificates of deposit
Savings accounts
Cash and coins in circulation
In economics, the word 'liquid' refers to which of the following?
The ability to quickly and easily convert an asset to cash.
Water used in the sprinkler system at the Federal Reserve bank.
The nature of the product market.
The amount of free flow involved in the money supply.
The ability to convert money into gold.
The ability to quickly and easily convert an asset to cash.
Money
is anything that is widely accepted in exchange for goods and services
A Coincidence of Wants
when two parties to an exchange value the good they would receive as much as the good they would give away
Commodity money
money that’s in the form of a commodity with intrinsic value
Representative money
is not money itself, but something that represents money. it is exchangeable for a commodity
Fiat money
is money with absolutely no intrinsic value that is used as money. only has value because the government says it’s valuable
The government issues a new two-dollar and fifty cent bill. What is the intrinsic value of the new currency?
$2.50
Nothing
Always greater than $2.50
$2.50 plus or minus inflation
$2.50 plus or minus nominal interest
Nothing
Why was money created?
To provide the government with quick tax revenue.
As a means of taking advantage of people in lower income brackets.
To reduce the costs of making transactions in the economy.
It was created by the central bank to control interest rates.
To reduce the costs of making transactions in the economy.
Which of the following insures that the US dollar maintains its value?
The amount of gold on deposit with the Federal Reserve
The price of silver
Only the promise of the United States government
The intrinsic value of the paper it is printed on
The price of gold
Only the promise of the United States government
Assume that there are two parties to an exchange and that they value the goods they would receive as much as the goods they would give away. What do economists call this?
An exchange
A coincidence of coinage
Transactions costs
An alignment of barter
A coincidence of wants
A coincidence of wants
Money that has an intrinsic value is called what?
Commodity money
Gold
Fiat money
Representative money
Barter
Commodity money
What does it mean if everything in an economy can be quoted in terms of money?
It refers to money as the foundation of every transaction.
It means money is plentiful.
It means the Central Bank has increased the money supply.
It refers to money having a terminal value.
It refers to money as the foundation of every transaction.
Money is a medium of exchange because:
It fuels the stock market.
Two bills of like denomination have the same value.
Two bills of like denomination can be exchanged.
It can be used to satisfy any number of needs and desires.
It can be used to satisfy any number of needs and desires.
How does inflation prevent most of the money in use today from serving as a pure store of value?
During economic uncertainty, the purchasing power of money increases.
Inflation causes the purchasing power of money to increase over time.
Inflation causes the purchasing power of money to decrease over time.
Inflation causes consumers to invest in gold over time rather than spend money.
Inflation causes the purchasing power of money to decrease over time.
Money serves as a standard of deferred payment when:
it is no longer divisible.
it has intrinsic value.
it is used to buy something now and make payments later on.
it is exchanged for goods and services.
it is used to buy something now and make payments later on.
Why is gold NOT considered money?
Because despite being a unit of account, it is not a store of value.
Because despite being a medium of exchange, it is not a store of value.
Because despite being a store of value, it is not a medium of exchange or a unit of account.
Because despite being a standard of deferred payment, it is not a store of value.
Because despite being a store of value, it is not a medium of exchange or a unit of account.
The Fractional Reserve Banking System
a system in which banks hold back a small fraction of their deposits in a reserve and loan out the rest of their deposits in a reserve and loan out the rest of their deposits to borrowers
legally permits banks to hold less than 100% of their deposits as a reserve
The Required Reserve Ratio
the percentage of deposits that banks are required to reserve
Excess Reserves
bank reserves above and beyond the reserve requirement set by a central bank
money the bank has available to loan out
When someone deposits money into a savings account, this demand deposit becomes _____ to the bank?
A stock
An asset
A liability
A bond
A risk
A liability
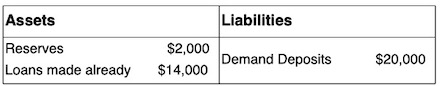
According to the T-account shown, if the required reserve ratio is 10%, what is the maximum amount of additional loans this bank can make?
$6,000
$26,000
$14,000
$4,000
$20,000
$4,000
How do banks make money?
Loaning out their excess reserves
Collecting interest on deposits
Money is moved not made
Loaning out required reserves
Fundraising
Loaning out their excess reserves
Under fractional banking, when a bank lends to a customer, which of the following happens?
Only a small fraction of deposits gets loaned out.
The money supply increases.
The banks go bankrupt.
The Banks make less money.
The money supply decreases.
The money supply increases.
A bank gets a demand deposit of $50,000. If the reserve requirement is 10%, what is the maximum the bank can loan out at this time?
$50,000
$65,000
$45,000
$15,000
$35,000
$45,000
The fractional reserve banking system
is a system in which banks hold back a small fraction of their deposits in a reserve and loan out the rest of their deposits to borrowers
Lydia deposits $70,000 into the First National Bank of Ceelo. The required reserve ratio is 9%. How much will the money supply increase if the bank loans out excess reserves?
$63,700
$6,300
$70,000
$77,000
$7,000
$63,700
When a deposit is made into a bank, what does the bank do?
The bank sets aside the entire amount for safekeeping.
The bank pays this amount to another bank.
The bank sets aside a required reserve and loans out the rest.
The bank loans out 120% of it.
The bank transfers all of it to the Federal Reserve.
The bank sets aside a required reserve and loans out the rest.
Which of the following is NOT true regarding the role of banks in the economy?
Banks connect savers with borrowers.
Banks control the fiscal policy of the country.
Banks are required to set aside a fraction of all deposits.
Banks provide the funds that people need to invest.
Banks increase the money supply.
Banks control the fiscal policy of the country.
How do banks make money?
Loaning out excess reserves
Borrowing from the Federal Reserve
Loaning out all their reserves
Making and selling coins
Paying interest to savers
Loaning out excess reserves
How does the economy change every time banks loan out excess reserves?
The long-run aggregate supply curve shifts inward.
The price level goes down.
Interest rates go down.
The money supply decreases.
The money supply increases.
The money supply increases.
The Multiplier Effect
describes how an increase in one economic activity leads to a much greater increase in economic output
Reserve Ratio
the fraction of a customer’s deposits that a bank is required to withhold on reserve in their vault or on deposit with the central bank
set by the Federal Reserve
gives the central bank power to influence and change the money supply
Excess Reserves
the fraction of a customer’s deposits a bank is able to loan out to borrowers, so they can earn a profit
The Money Multiplier
the relationship between the reserves in a banking system and the money supply
Required Reserves
the fraction of a customer’s deposits that a bank is required to withhold on reserve in their vault or on deposit with the central bank
When $1,000 gets deposited into the banking system, and the reserve ratio is 10%, what is the increase in the money supply?
$9,000
$1,000
$5,000
$10,000
$10,000
If banks have excess reserves of $5,000, and the money supply increased by $20,000, what is the reserve ratio?
20%
10%
15%
25%
25%
Besides being known as the reserve ratio, what is the fraction of a customer's deposits that a bank is required to hold in reserve also called?
Total reserves
Excess reserves
Federal Reserve
Required reserves
Required reserves
Assume that the reserve requirement is 25%. If banks have excess reserves of $10,000, which of the following is the maximum amount of additional money that can be created by the banking system through the lending process?
$2,500
$250,000
$40,000
$50,000
$40,000
The money multiplier is a relationship between which two drivers?
Reserves loaned out by banks and the total reserves.
Reserves in a banking system and the money supply.
Required reserves and the money supply.
Reserves in the banking system and the interest rate.
Reserves in a banking system and the money supply.
Money
the portion of your wealth that you choose to hold in the form of cash or checking accounts
Personal Income
the ongoing flow of money into an individual’s life, including compensation from salaries, wages, bonuses and dividends or distributions from investments such as real estate or a business
The demand for money
the relationship between the quantity of money people want to hold and the factors that determine that quantity
Which of these is TRUE regarding money demand and price level?
It varies directly with the price level.
It does not vary with the price level.
It varies logarithmically with the price level.
It varies inversely with the price level.
It varies directly with the price level.
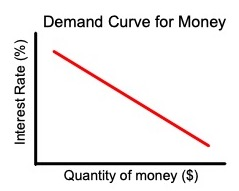
When looking at the demand curve for money, which of the following completes this sentence?
When interest rates are 20%, the demand for money is _____.
low but increasing rapidly before interest rates increase.
higher than it would be if interest rates are 10%.
lower than it would be if interest rates are 2%.
the same as it would be if interest rates are 15%.
lower than it would be if interest rates are 2%.
What coincides with an increase in the demand for money when the supply of money is unchanged?
Higher interest rates
No change in interest rates
Money demand soon declines
Lower interest rates
Lower interest rates
How does the demand curve for money shift?
It shifts down as the price level decreases.
It shifts down as real GDP increases.
It shifts up as interest rates increase.
It shifts up as the price level decreases.
It shifts down as the price level decreases.
As the price level decreases, how is the value of money impacted?
Increases, so people want to hold more of it.
Decreases, so people want to hold less of it.
Increases, so people want to hold less of it.
Decreases, so people want to hold more of it.
Increases, so people want to hold less of it.
The Money Market
an economic model describing the supply and demand for money in a nation
Because the central bank controls the money supply, it also controls what other economic driver?
It also controls market interest rates.
It also controls exchange rates.
It also controls the demand for money.
It also controls the demand for products and services.
It also controls taxes on savings and investment.
It also controls market interest rates.
What happens when money demand increases and all other things remain constant?
The money market finds a new equilibrium and the market interest rate falls
The money market remains at the same equilibrium
The demand curve for money shifts leftward, leading to a lower interest rate
The supply of money falls by an equal amount to compensate
The money market finds a new equilibrium and the market interest rate rises
The money market finds a new equilibrium and the market interest rate rises
When economists illustrate the money market, the demand curve is _____ while the supply curve is _____.
upward sloping; vertical
upward sloping; downward sloping
downward sloping; upward sloping
horizontal; vertical
downward sloping; vertical
downward sloping; vertical
How does high economic output lead to higher nominal interest rates?
It leads to higher income which leads to an equilibrium position for money
It leads to equilibrium in the economy which leads to higher rates
It leads to higher income which leads to lower demand for money
It leads to lower income which leads to higher demand for money
It leads to higher income which leads to higher demand for money
It leads to higher income which leads to higher demand for money
What is the economics model that describes the demand and supply of money in a nation called?
The money supply
The demand for money
The product market
The market for loanable funds
The money market
The money market
Maturity
the point at which the loan was due
Par value
face value
initial loan amount
Coupon rate
the annualized interest, also referred to as the coupon, divided by the initial loan amount
What is a coupon rate?
Annualized coupon divided by par value.
Quarterly coupon divided by par value.
Semi-annual dividend divided by current value.
Quarterly dividend divided by future value.
Annualized coupon divided by par value.
Most bonds pay interest:
Annually
Monthly
Quarterly
Semi-annually
Semi-annually
In the formula C = i / p, what does the p represent?
Interest rate
Present value
Property value
Par value
Par value
There is a company offering $5000 bonds which will earn an annual interest of $200. What is the coupon rate?
5%
7%
4%
10%
4%
Most bonds have par values of:
$500
$1,000
$25
$10,000
$1,000