Chapter 18: Variation and selection
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
variation
difference between individuals of the same species
causes and result of continuous variation
influenced by genes and environment, resulting in a range of phenotypes between two extremes
e.g. height and body mass
investigation of continuous variation
causes and result of discontinuous variation
caused by genes alone and results in a limited number of distinct phenotypes
e.g. ABO blood groups, seed shape and colour in peas
investigation of discontinuous variation
mutation
genetic change, the way new alleles are formed
gene mutation
random change in the base sequence in DNA
what increases the rate of mutation
ionising radiation and some chemicals
sources of genetic variation in populations
mutation, meiosis, random mating, and random fertilisation
adaptive features
an inherited feature that helps an organism to survive and reproduce in its environment
xerophytes
live in deserts where water is scarce and evaporation is rapid, or in windy habitats
adaptive features: xerophytes
deep roots to reach water far underground
leaves reduced spines with minimum surface area for transpiration
shallow spreading roots to collect occasional rain
rolled leaves, leaf hairs and stomata sunk in pits to trap moist air
waxy leaf cuticle, impermeable water
stomata opening at night and closed at midday when evaporation is highest
hydrophytes
live in fully or partly submerged in water
adaptive features: hydrophytes
natural selection
the individuals that have the best adaptive features are the ones most likely to survive and reproduce
individuals show a range of variation caused by differences in genes
they reproduce more offspring than the environment is able to support
leading to competition for food and other resources which results in a ‘struggle for survival’
individuals with characteristics most suited to the environment have a higher chance of survival and more chances to reproduce
therefore the alleles resulting in these characteristics are passed to their offspring at a higher rate than those with characteristics less suited to survival
meaning that in the next generation, there will be a greater number of individuals with the better adapted variations in characteristics
theory of natural selection was put forward by Charles Darwin and became known as ‘survival of the fittest’
example of natural selection
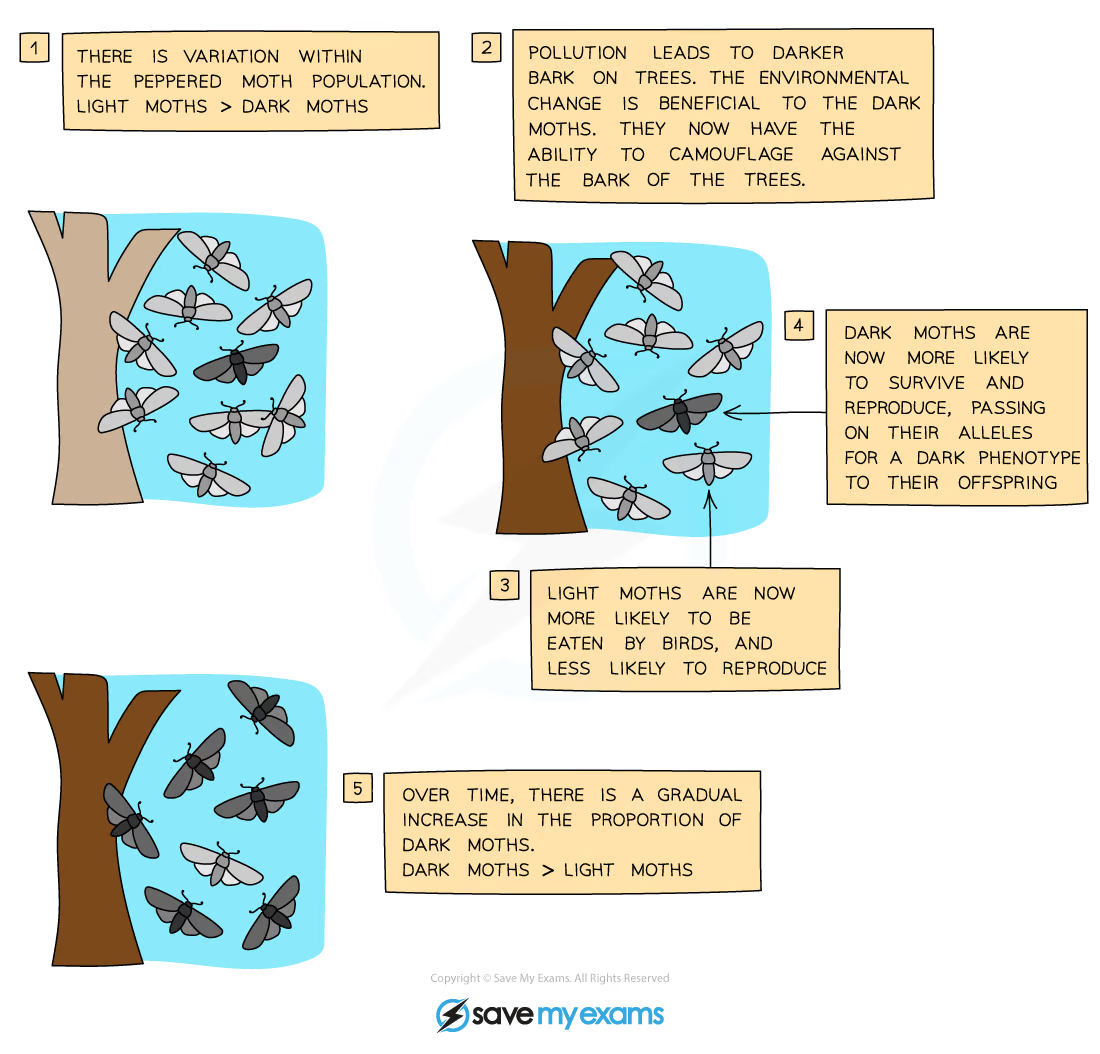
adaptation
Natural selection results in a process of adaptation, which means that, over generations, those features that are better adapted to the environment become more common
selective breeding
to select individuals with desirable characteristics and breed them together
process doesn’t stop there though because it’s likely that not all of the offspring will show the characteristics wanted so offspring that do show the desired characteristics are selected and bred together
This process has to be repeated for many successive generations before a ‘new breed’ is said to be made which will reliably show those selected characteristics in all offspring
e.g. selective breeding is dog breeders who select which dogs can mate together to increase the likelihood of puppies displaying desirable characteristics eg. coat colour
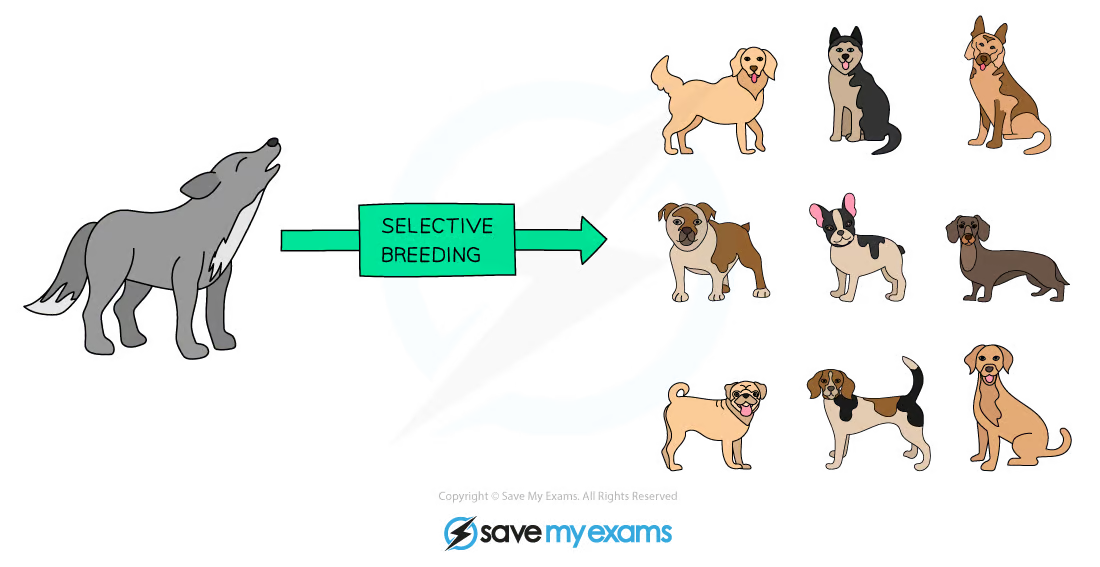
differences between natural selection and artifical selection