UC DAVIS BIS 2A
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Design Challenge
A written plan that identifies a problem to be solved together with its requirements and constraints
Hypothesis
A testable prediction, often implied by a theory

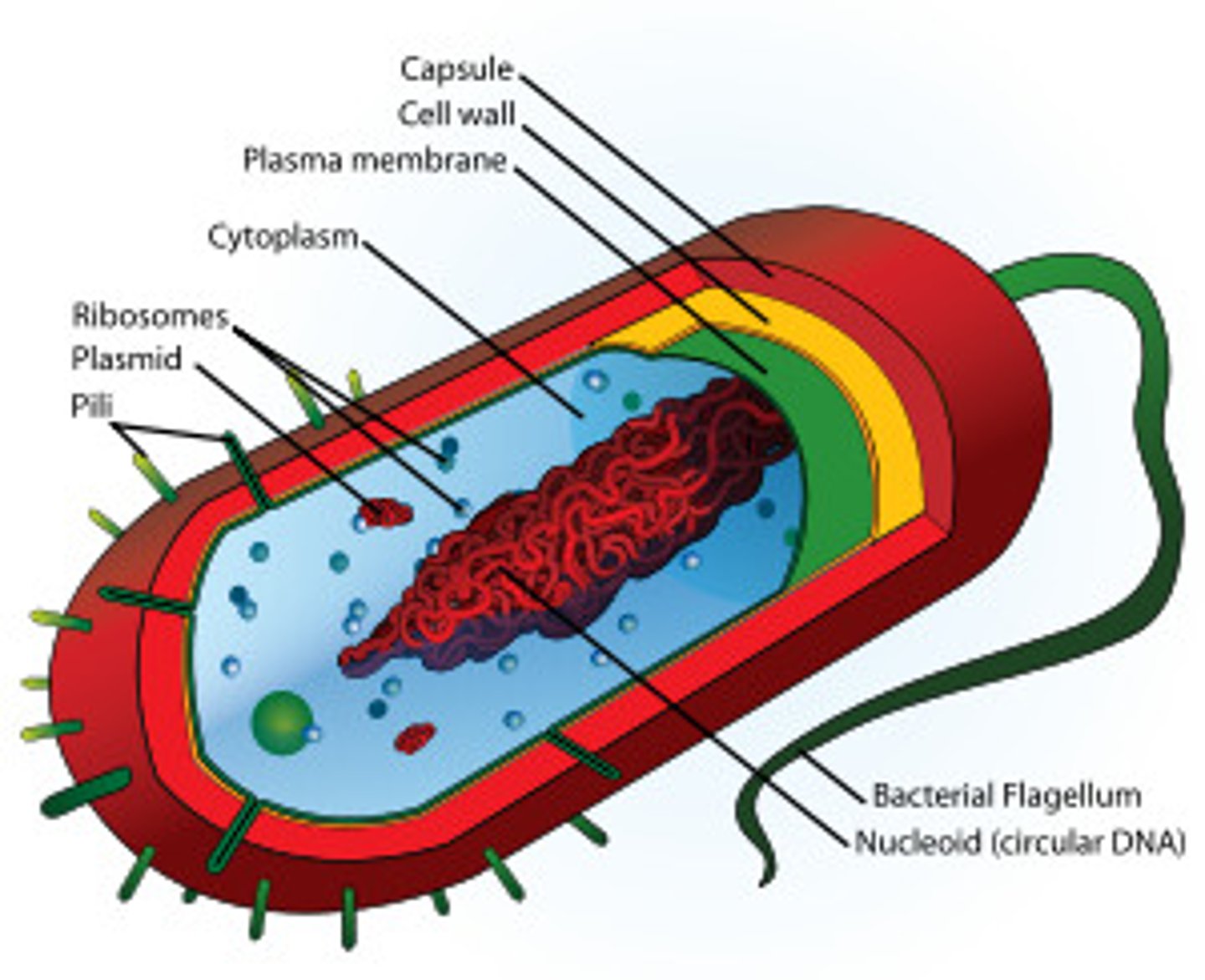
Prokaryote
A unicellular organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
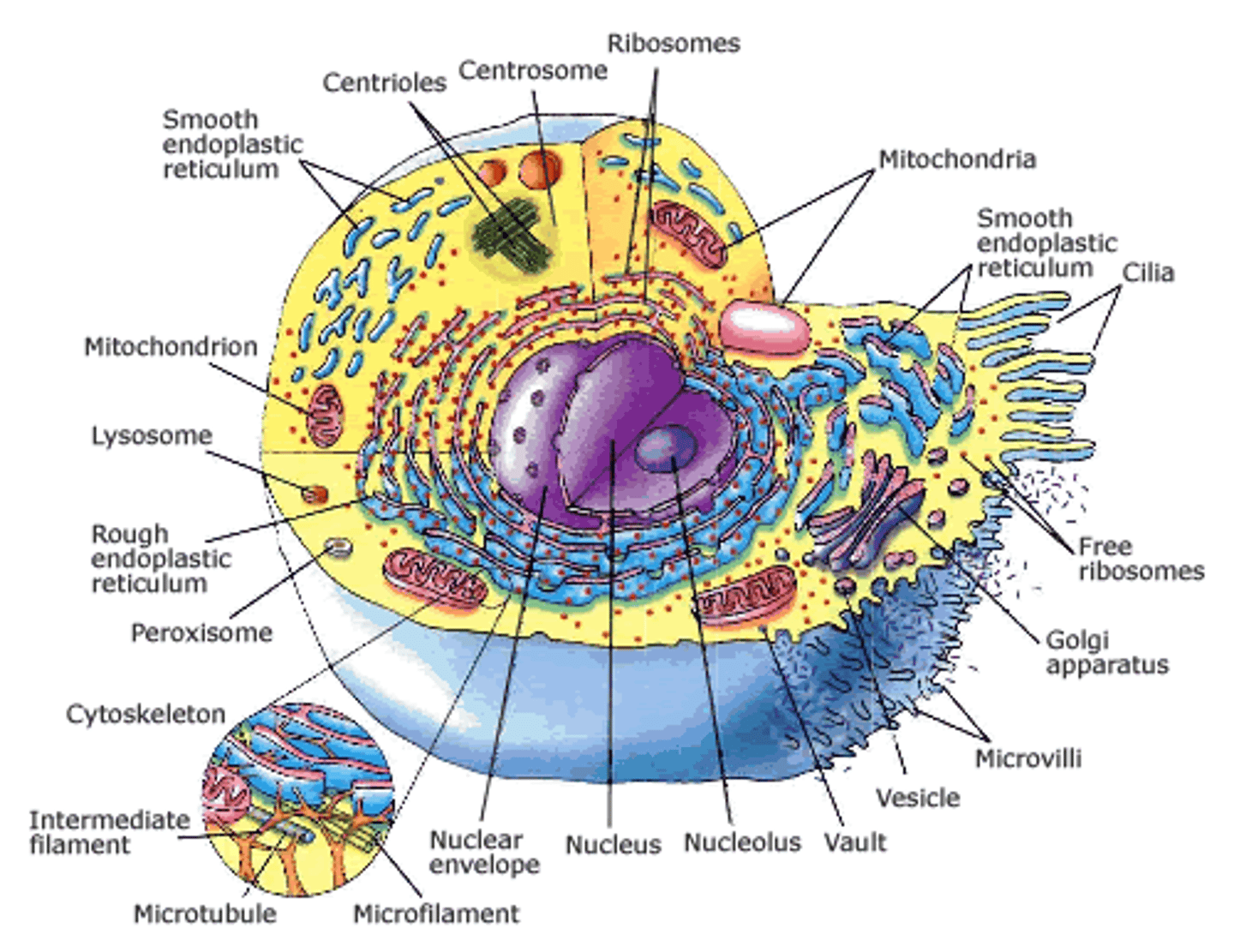
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
Organelle
specialized structure that performs important cellular functions within a eukaryotic cell
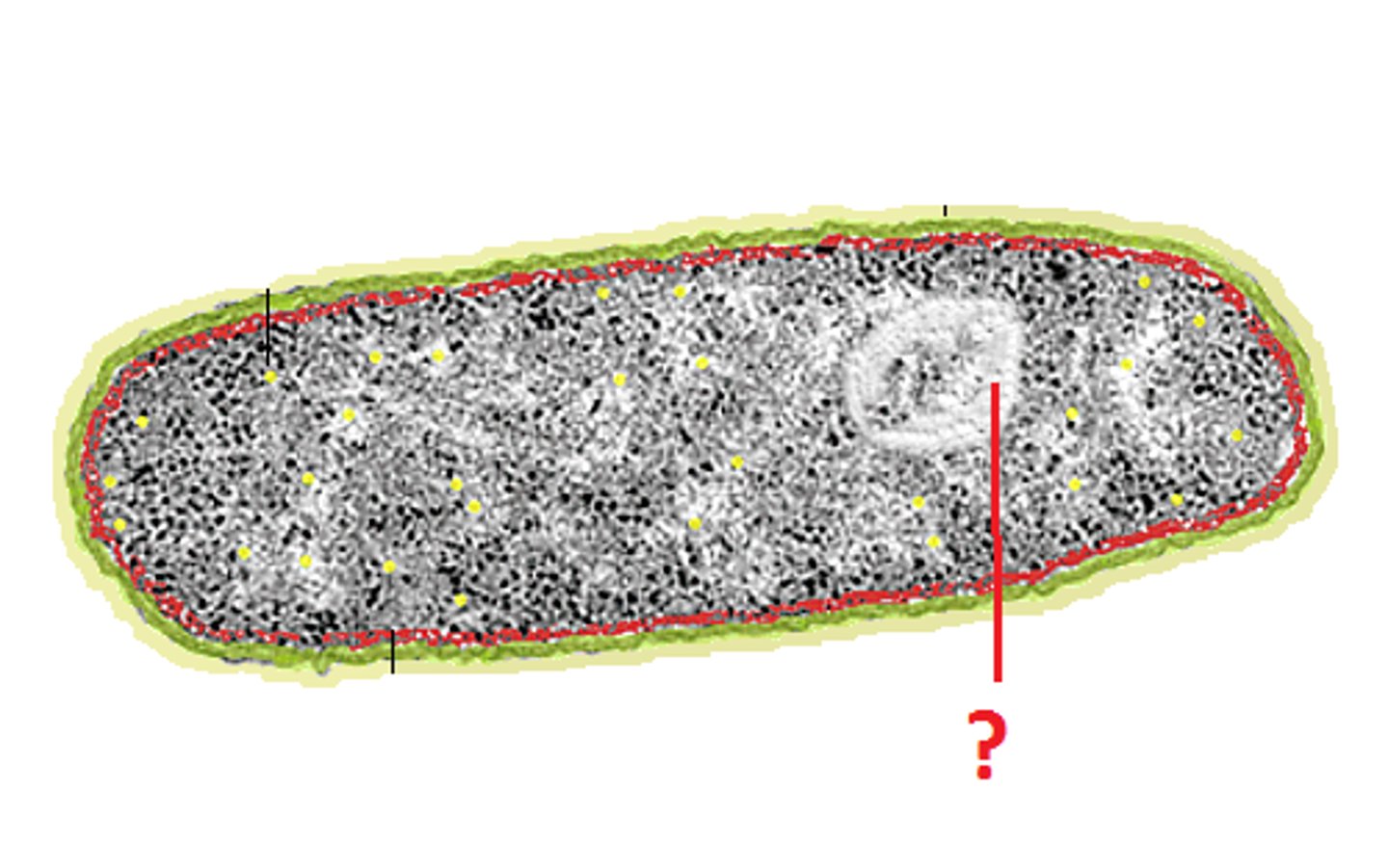
Nucleoid
A dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell.
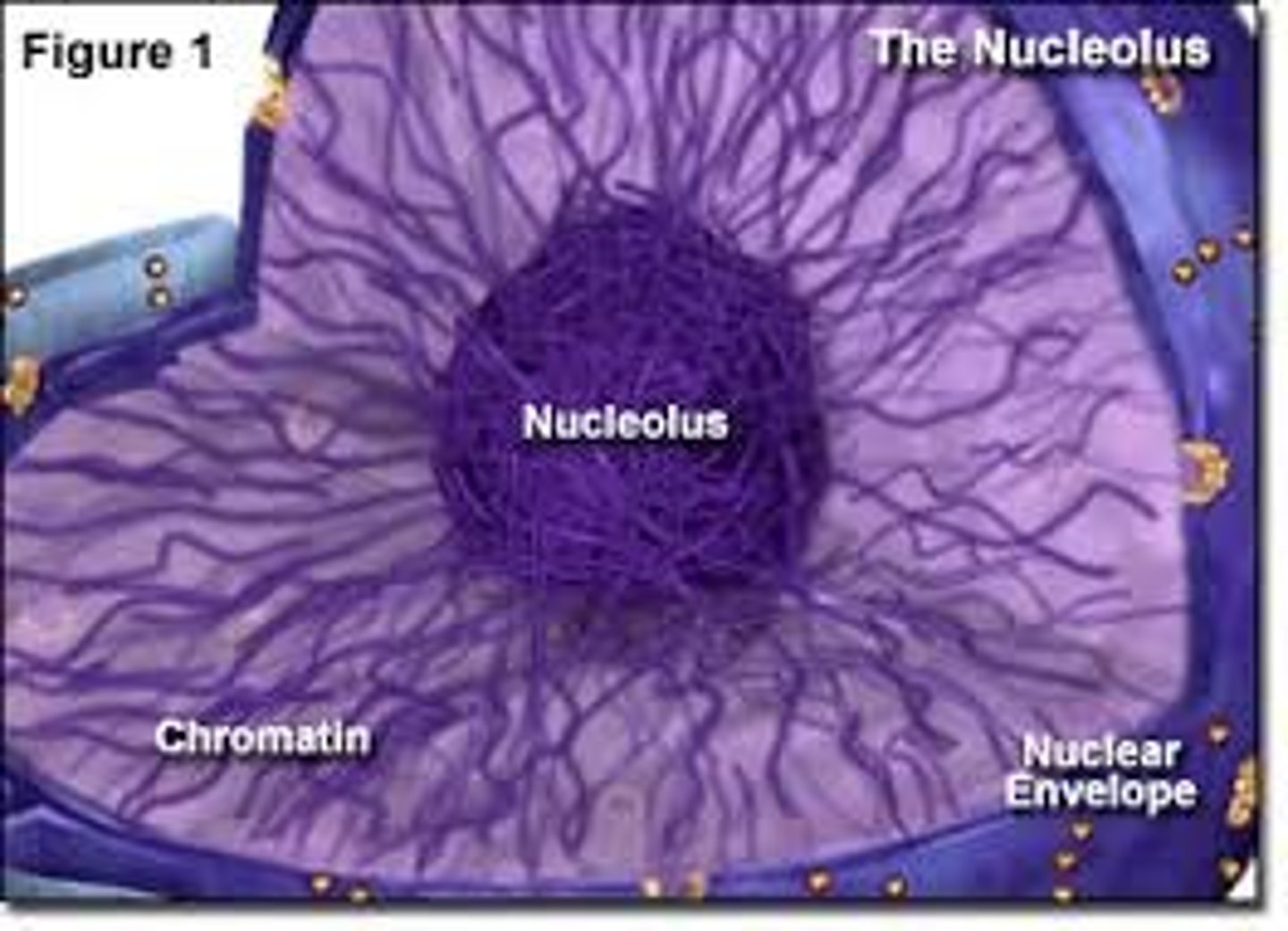
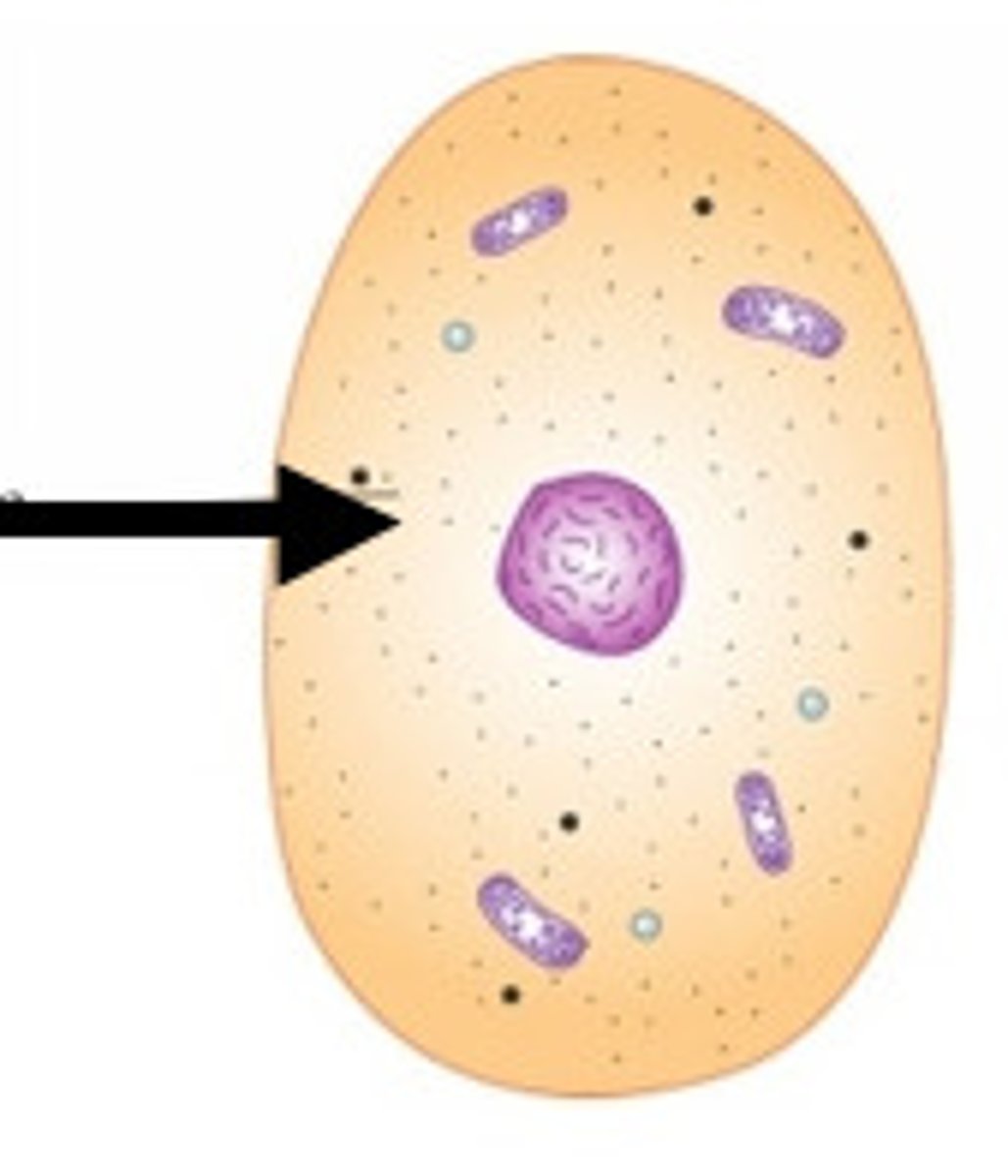
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
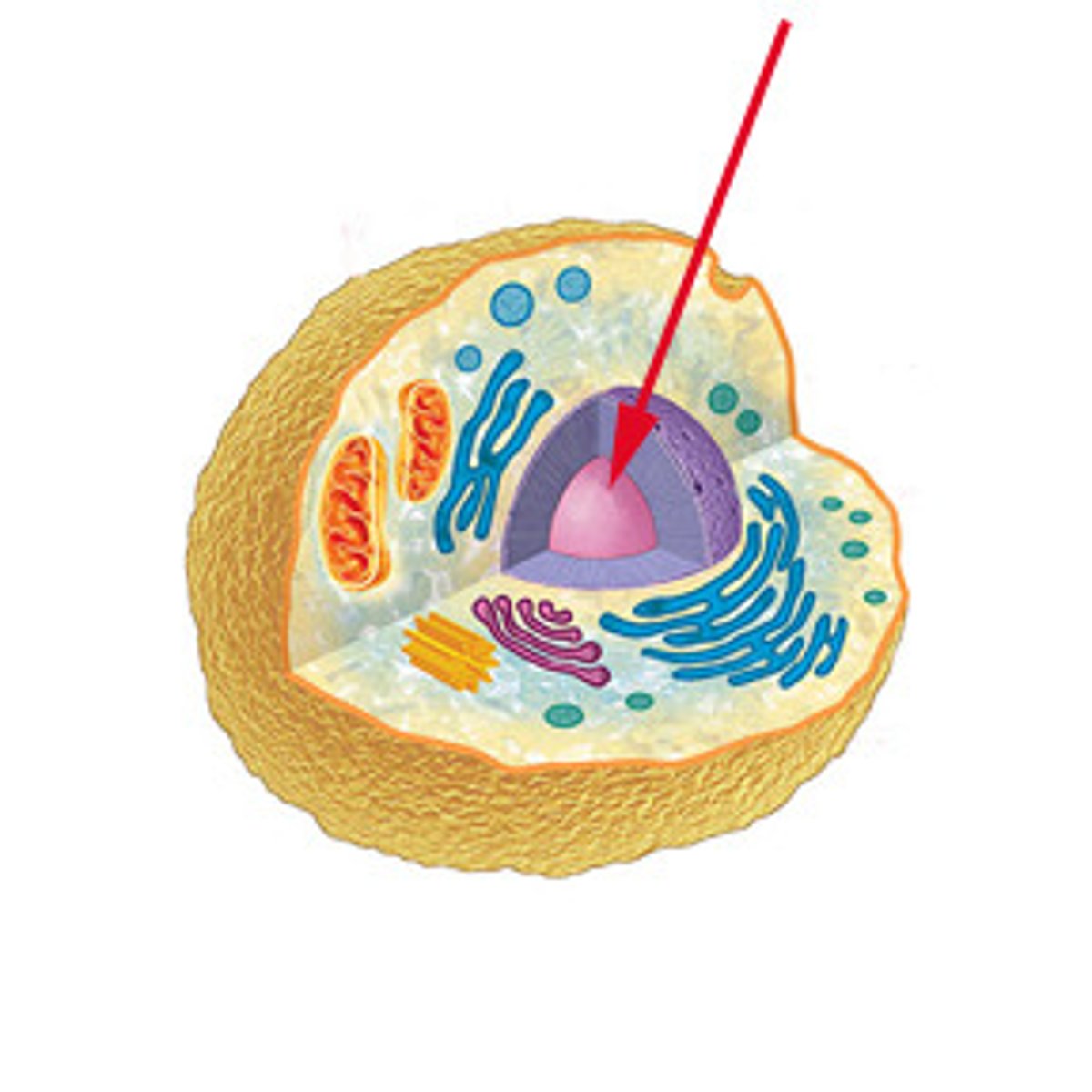
Nucleus
Control center of the cell
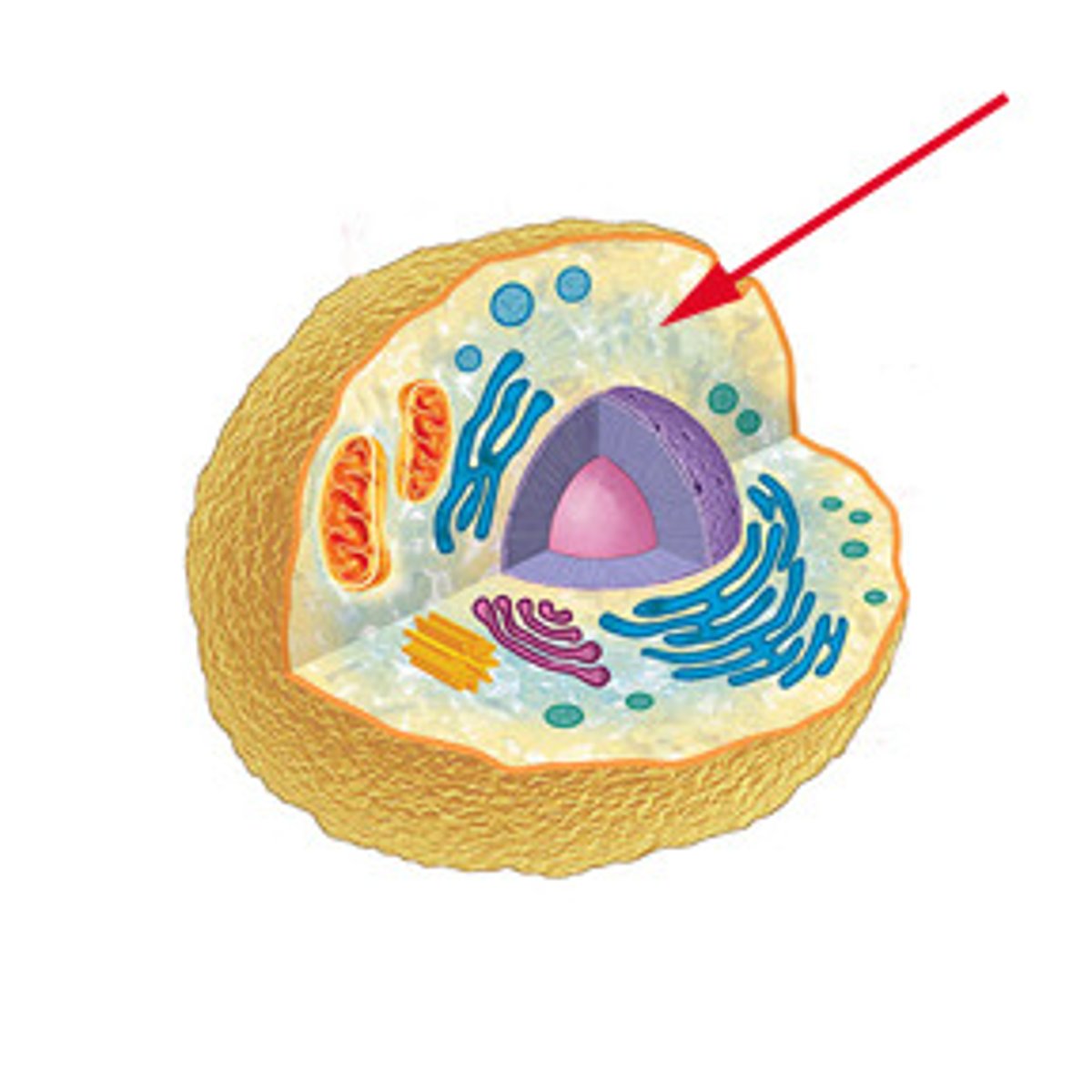
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
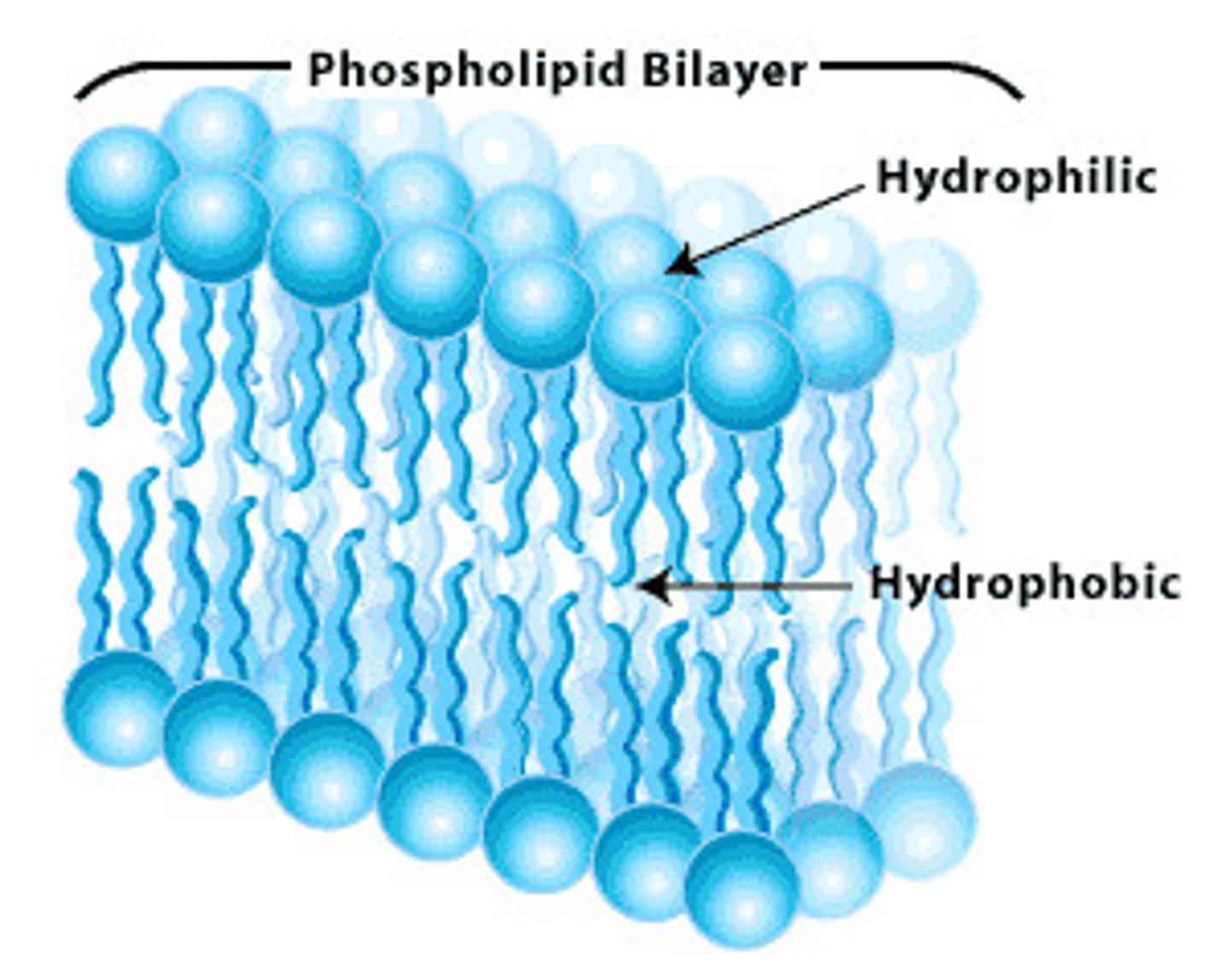
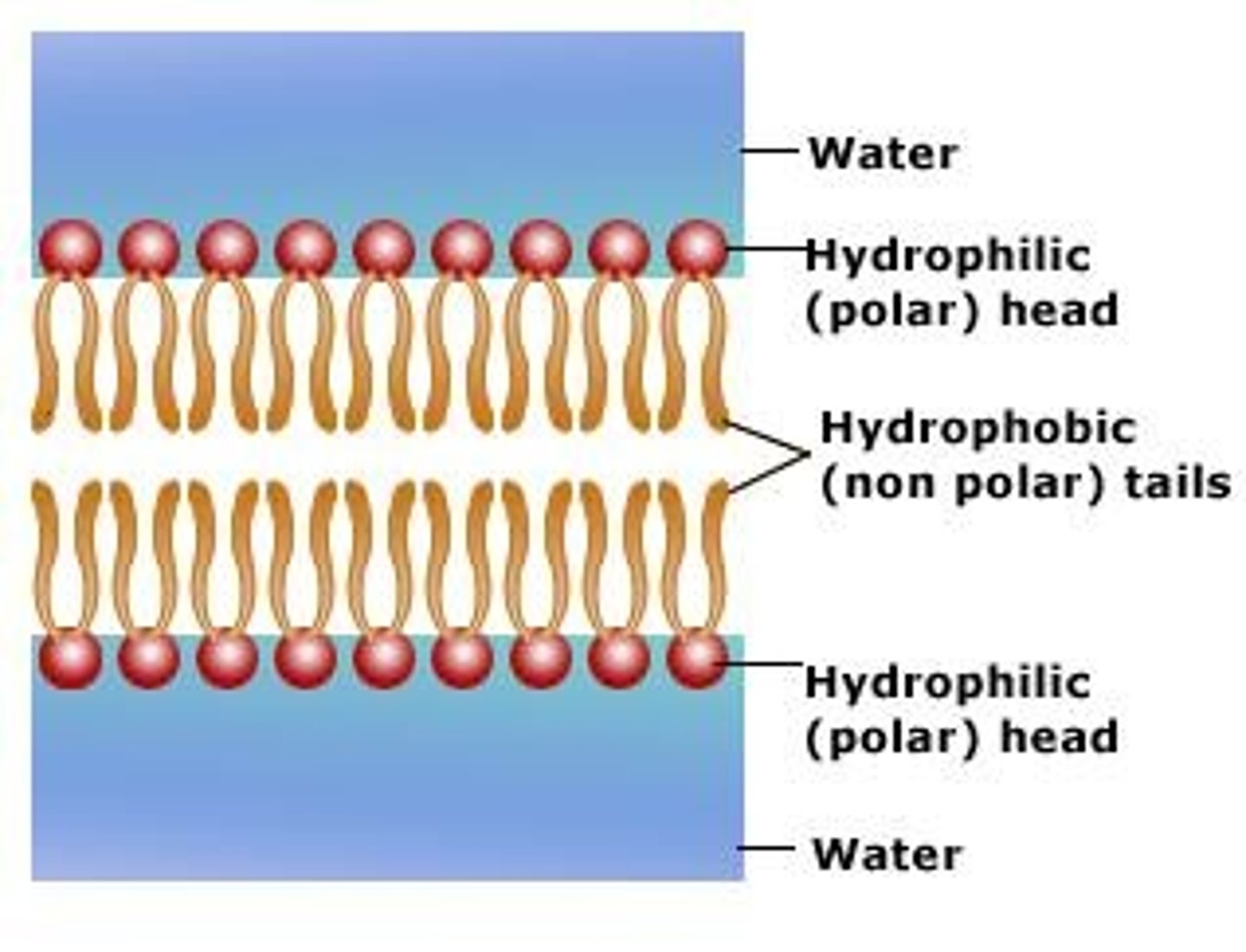
Plasma Membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells.
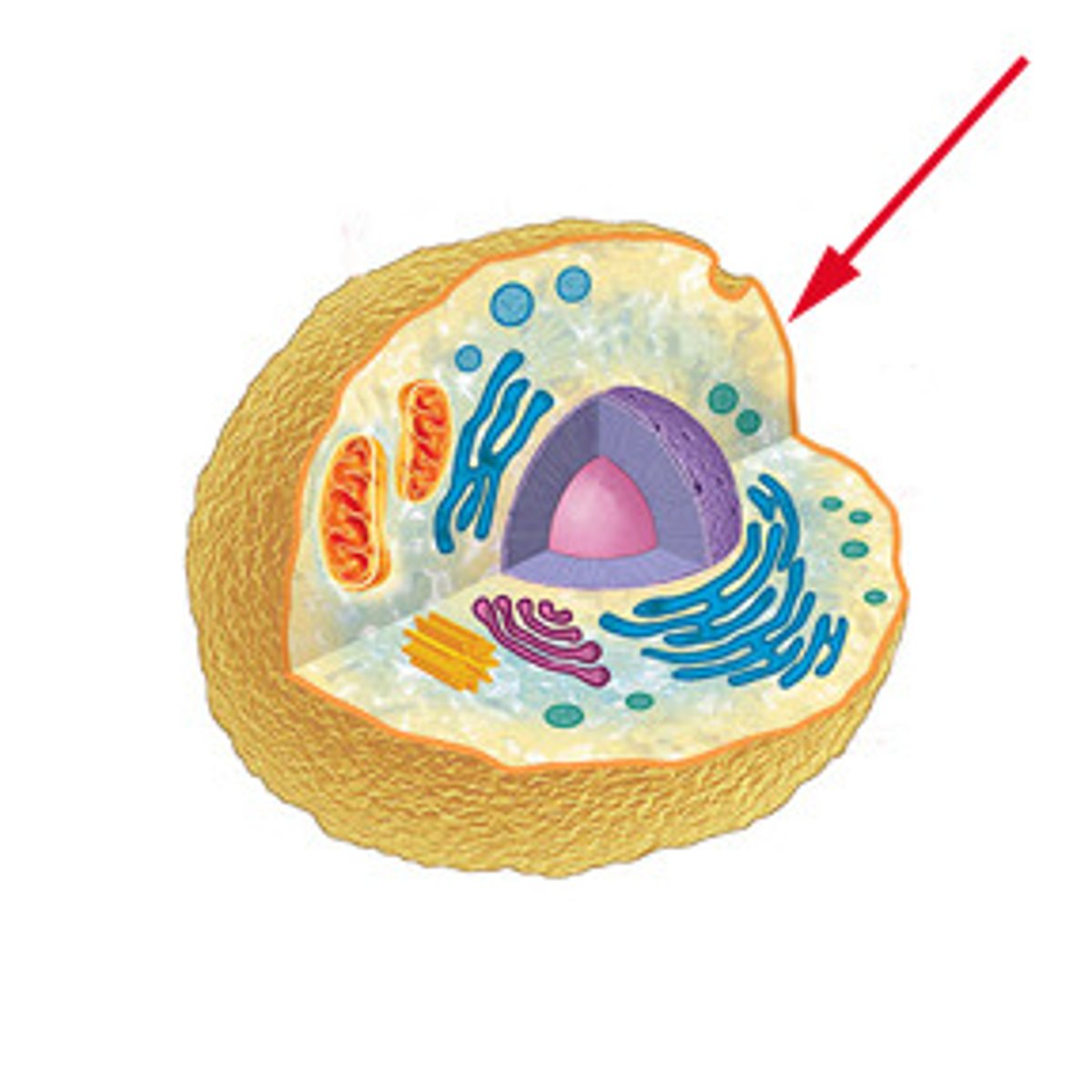
Internal Membranes
membranes surrounding organelles
Inner Membrane
Where is ATP synthase located in the mitochondrion?
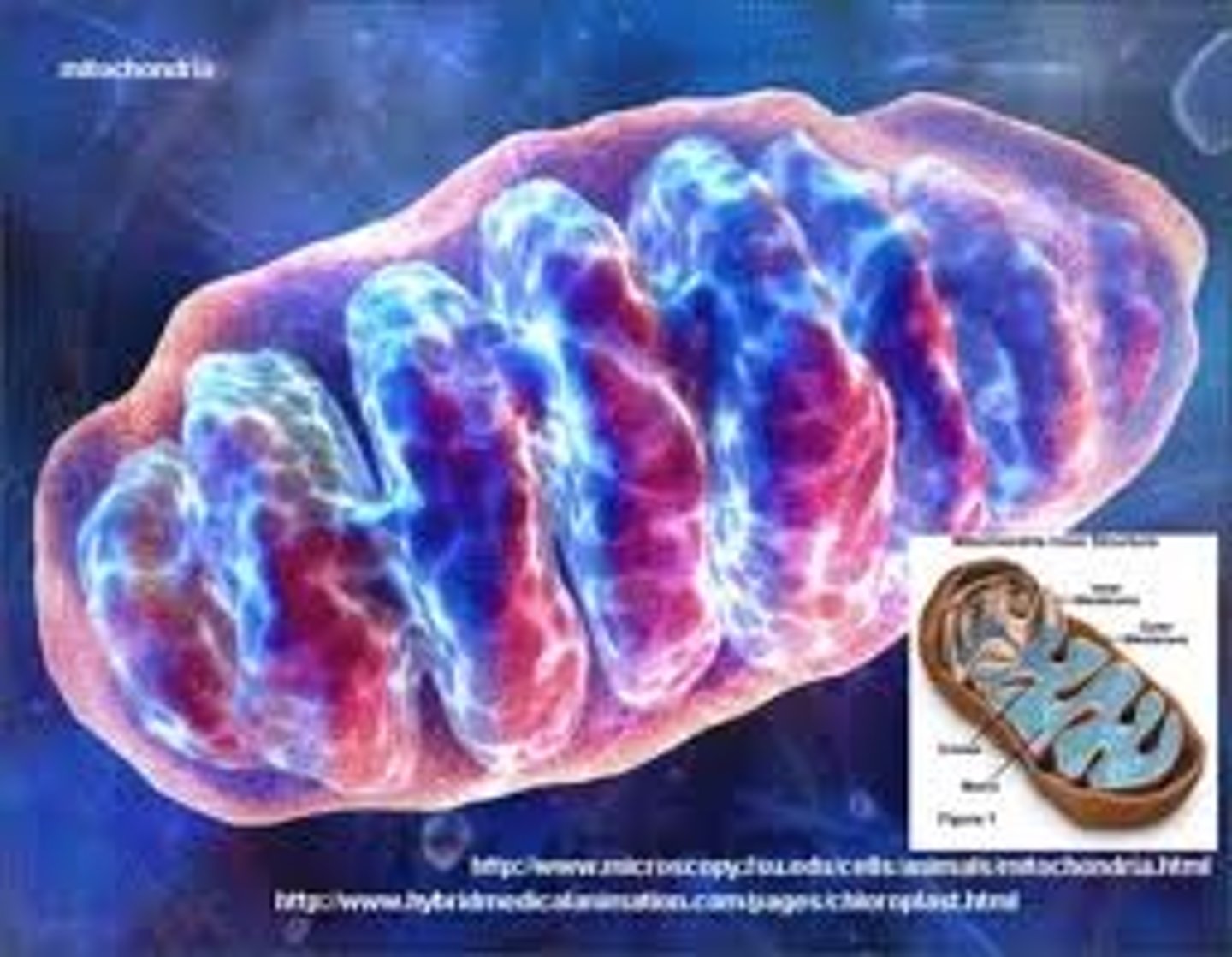
outer membrane
Outermost membrane in the mitochondria that protects and holds the form of the organelle.
Cell Wall
A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms.
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Flagella
whiplike tails found in one-celled organisms to aid in movement
Pilli
Hollow tubes used to move cells or exchange DNA between bacteria by conjunction.
Ribosomes
Makes proteins
Endomembrane System
A network of membranes inside and around a eukaryotic cell, related either through direct physical contact or by the transfer of membranous vesicles.

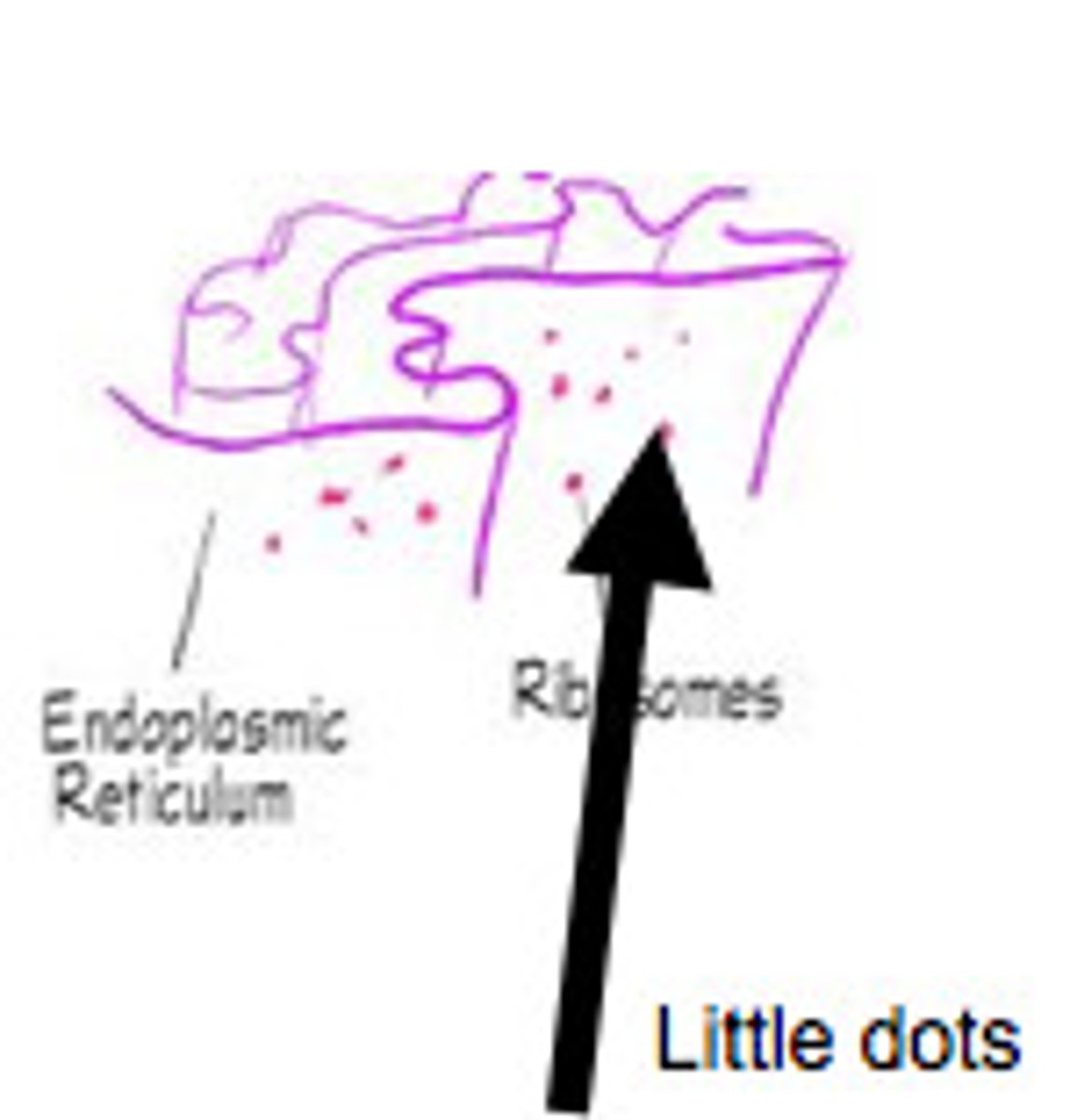
Rough ER
That portion of the endoplasmic reticulum studded with ribosomes.
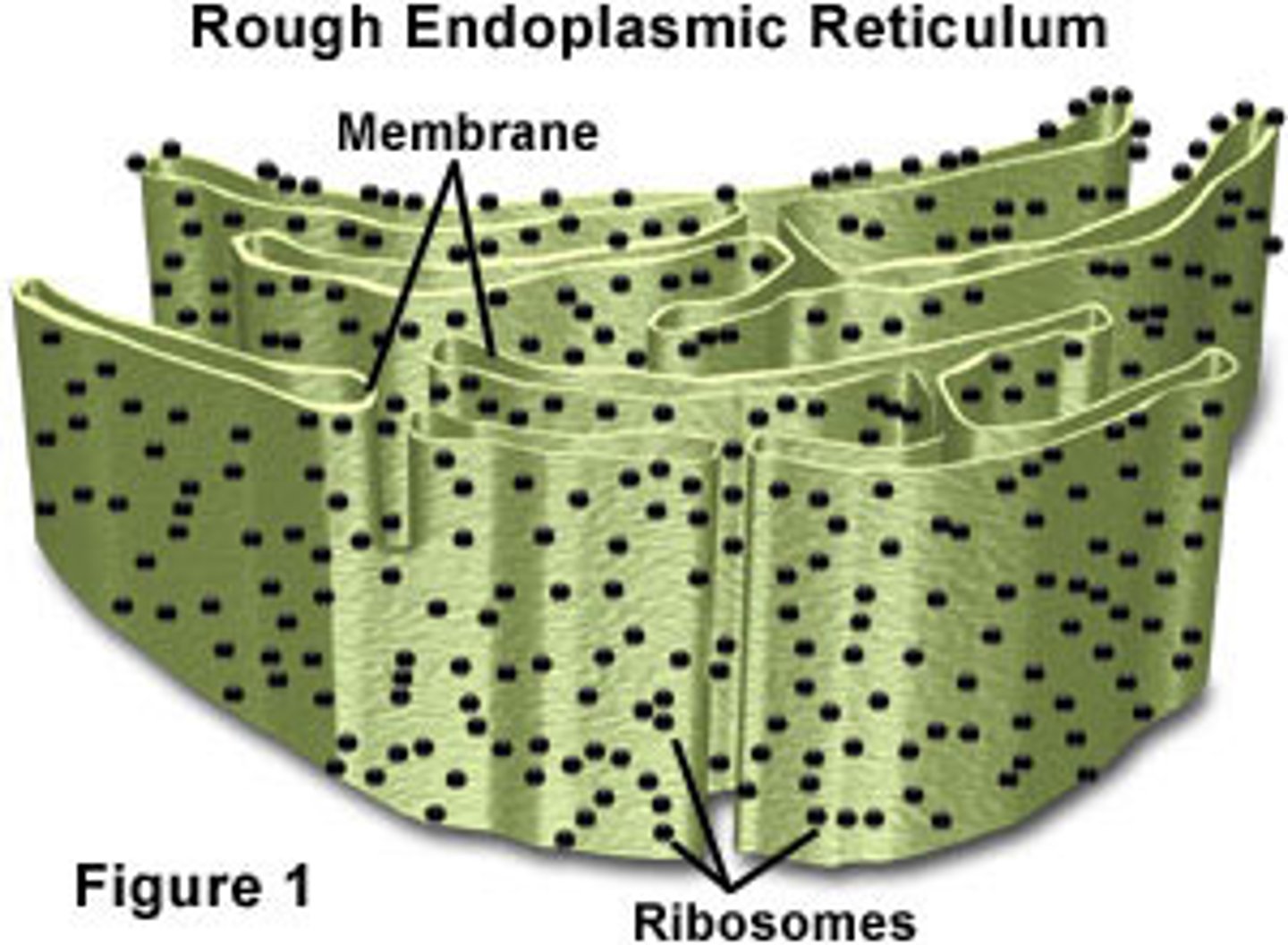
Smooth ER
That portion of the endoplasmic reticulum that is free of ribosomes.
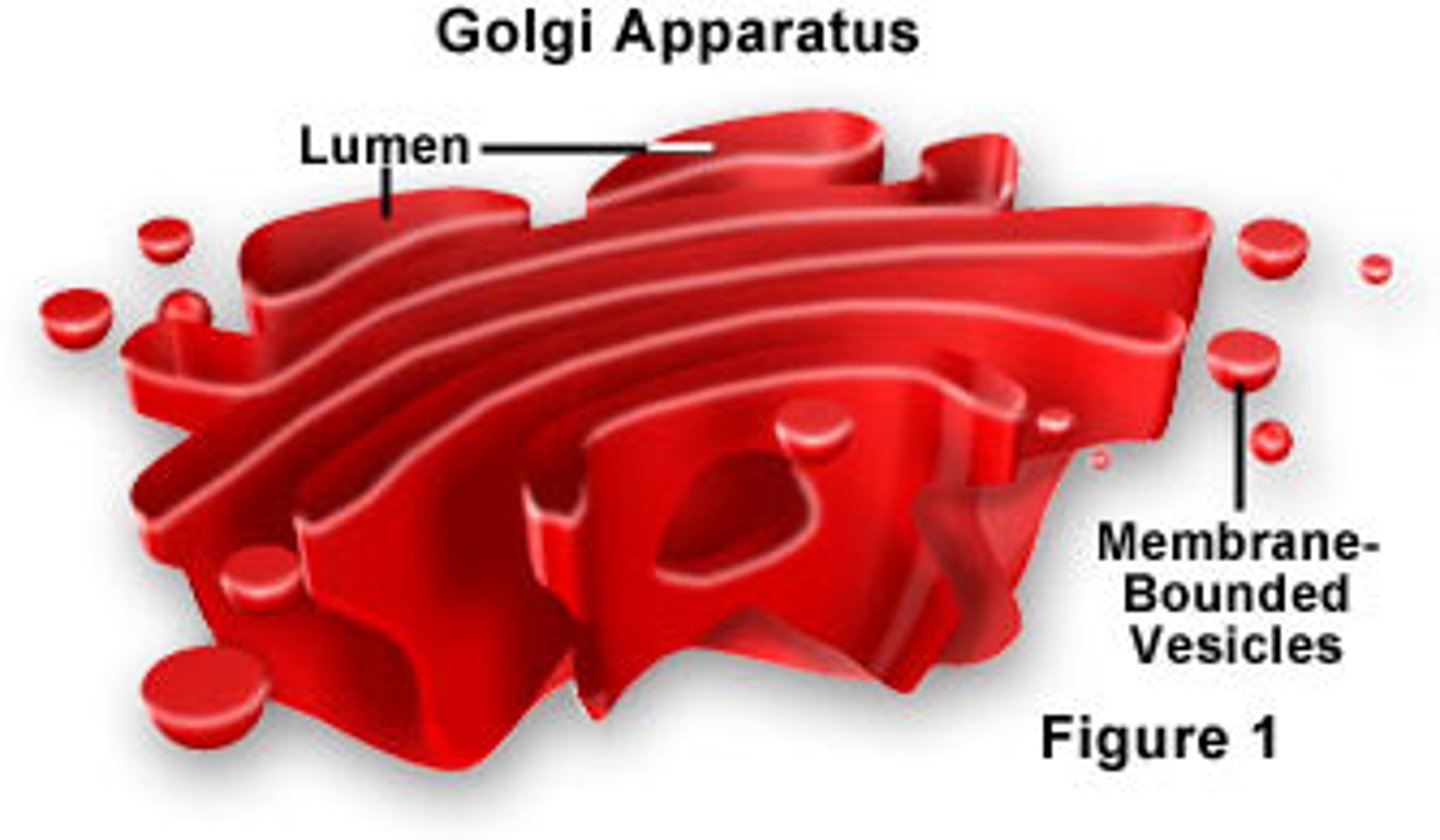
Golgi Apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
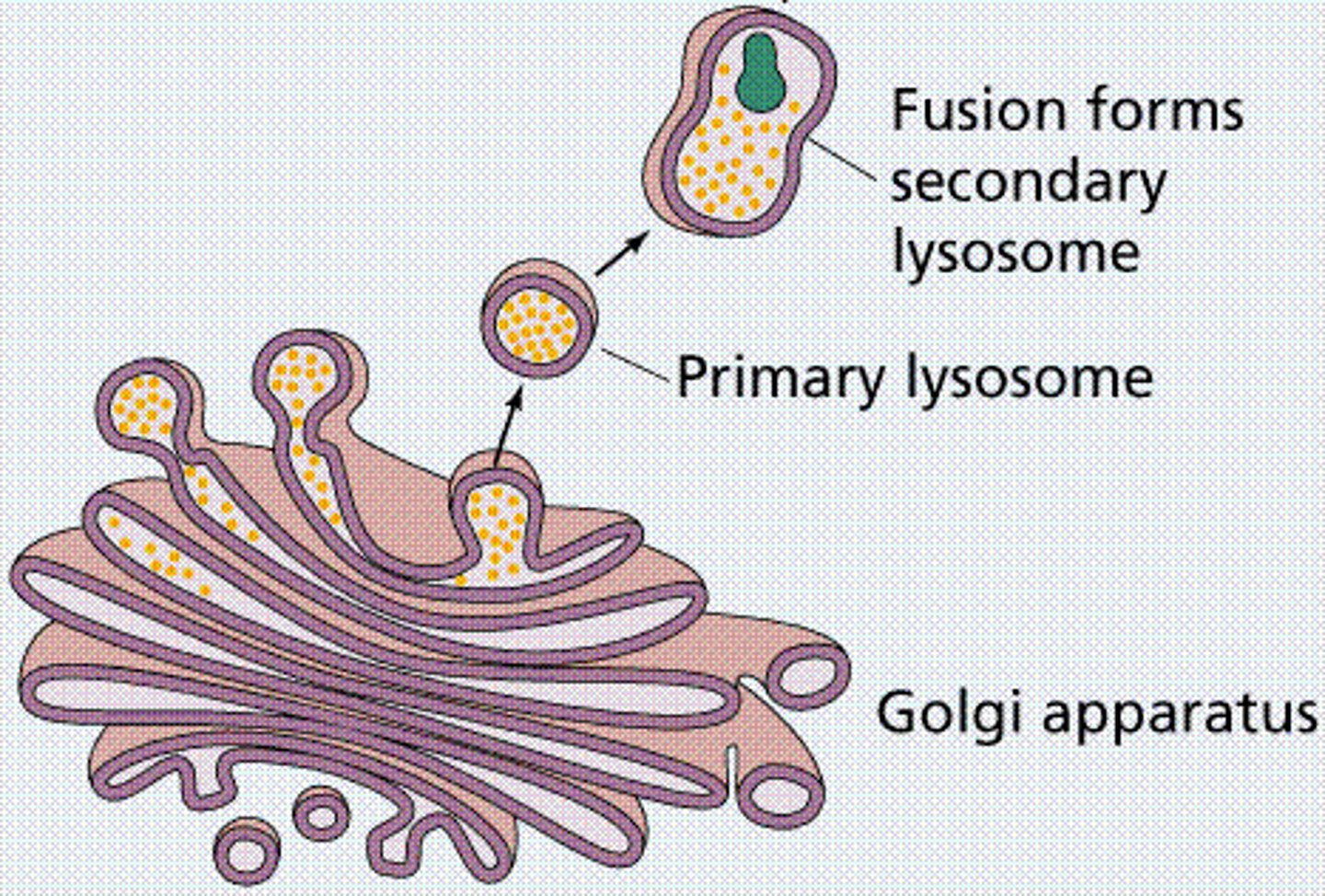
Primary Lysosomes
contain inactive enzymes
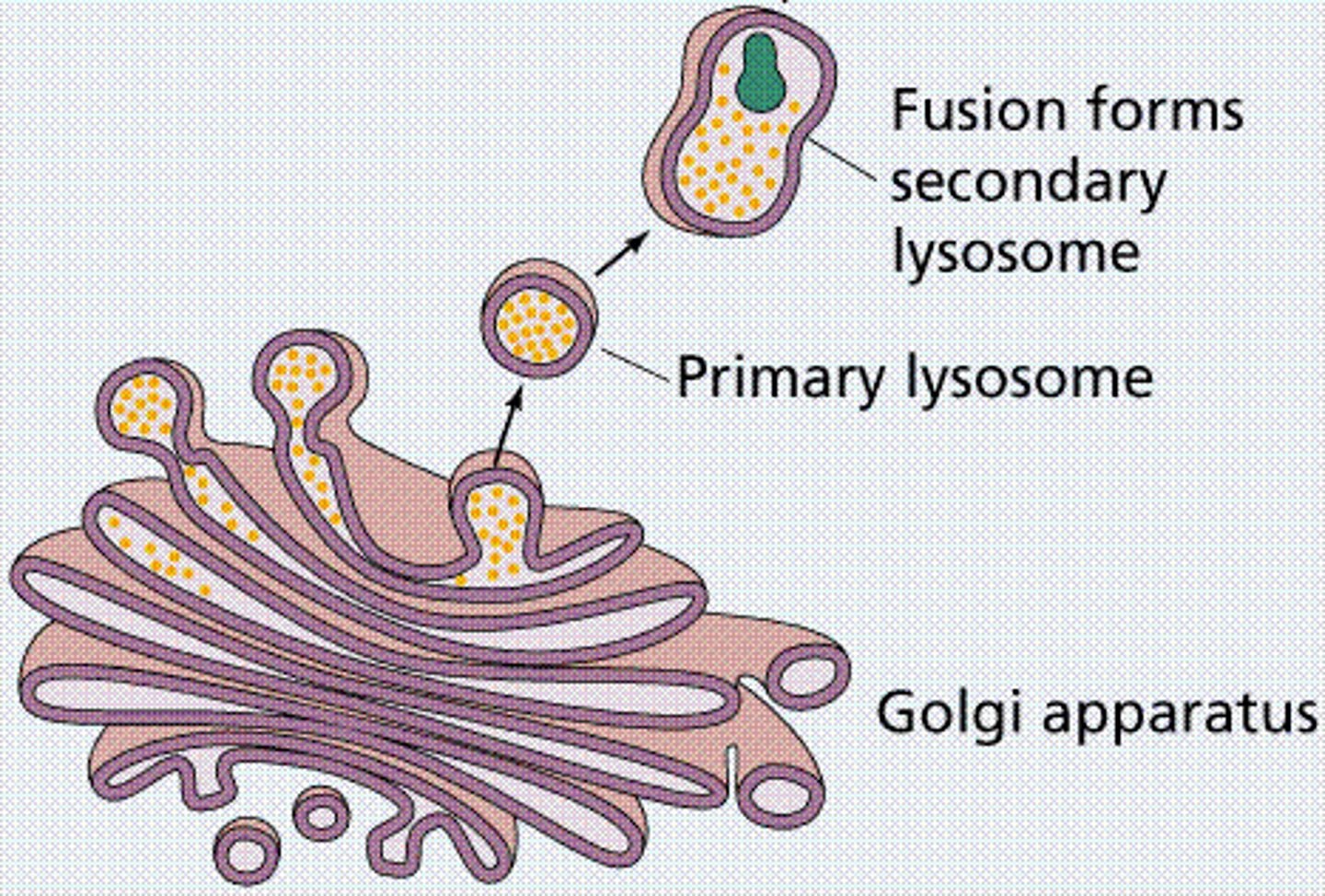
Secondary Lysosomes
Membrane-enclosed organelle formed by the fusion of a primary lysosome with a phagosome, in which macromolecules taken up by phagocytosis are hydrolyzed into their monomers.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell
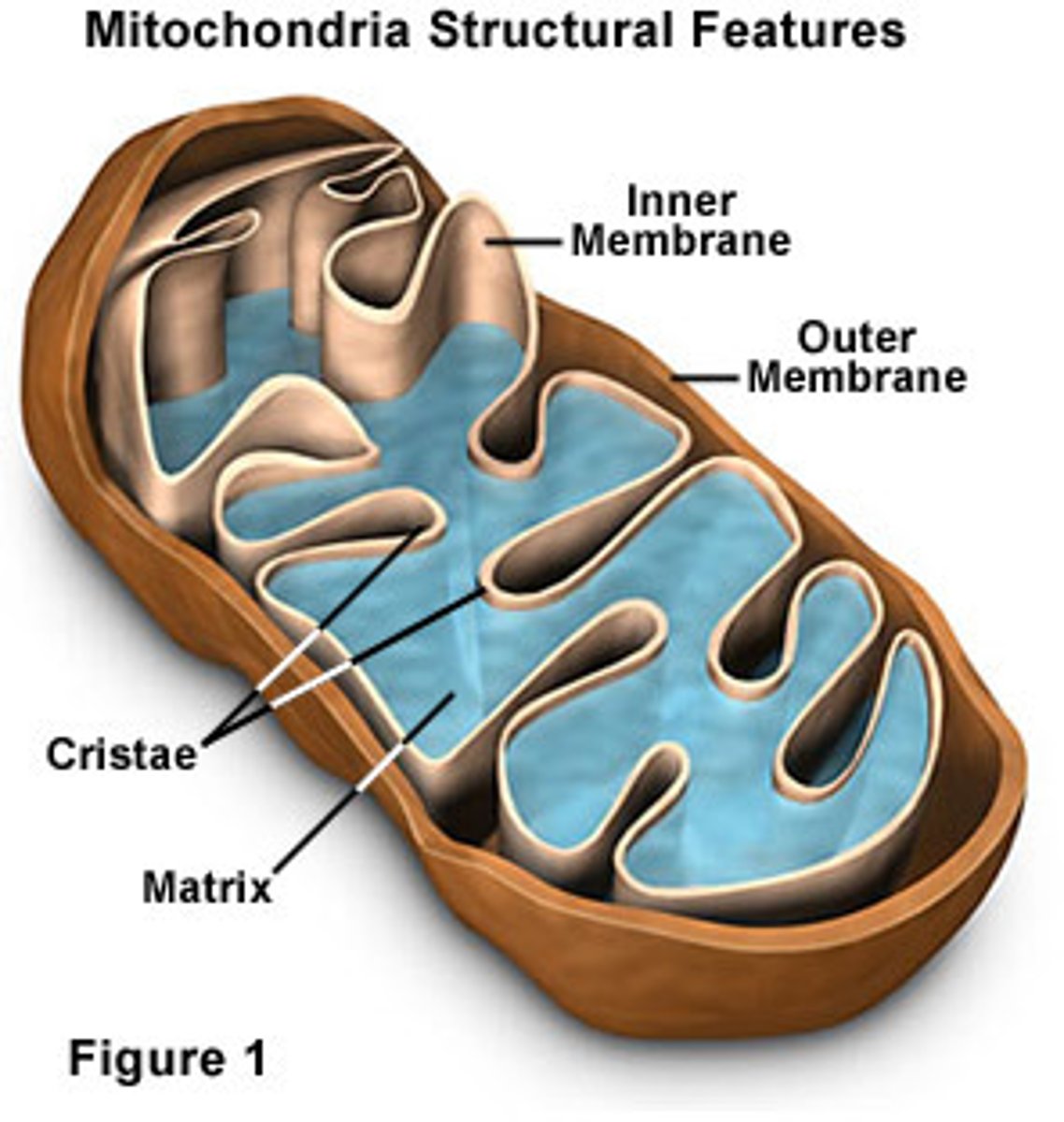
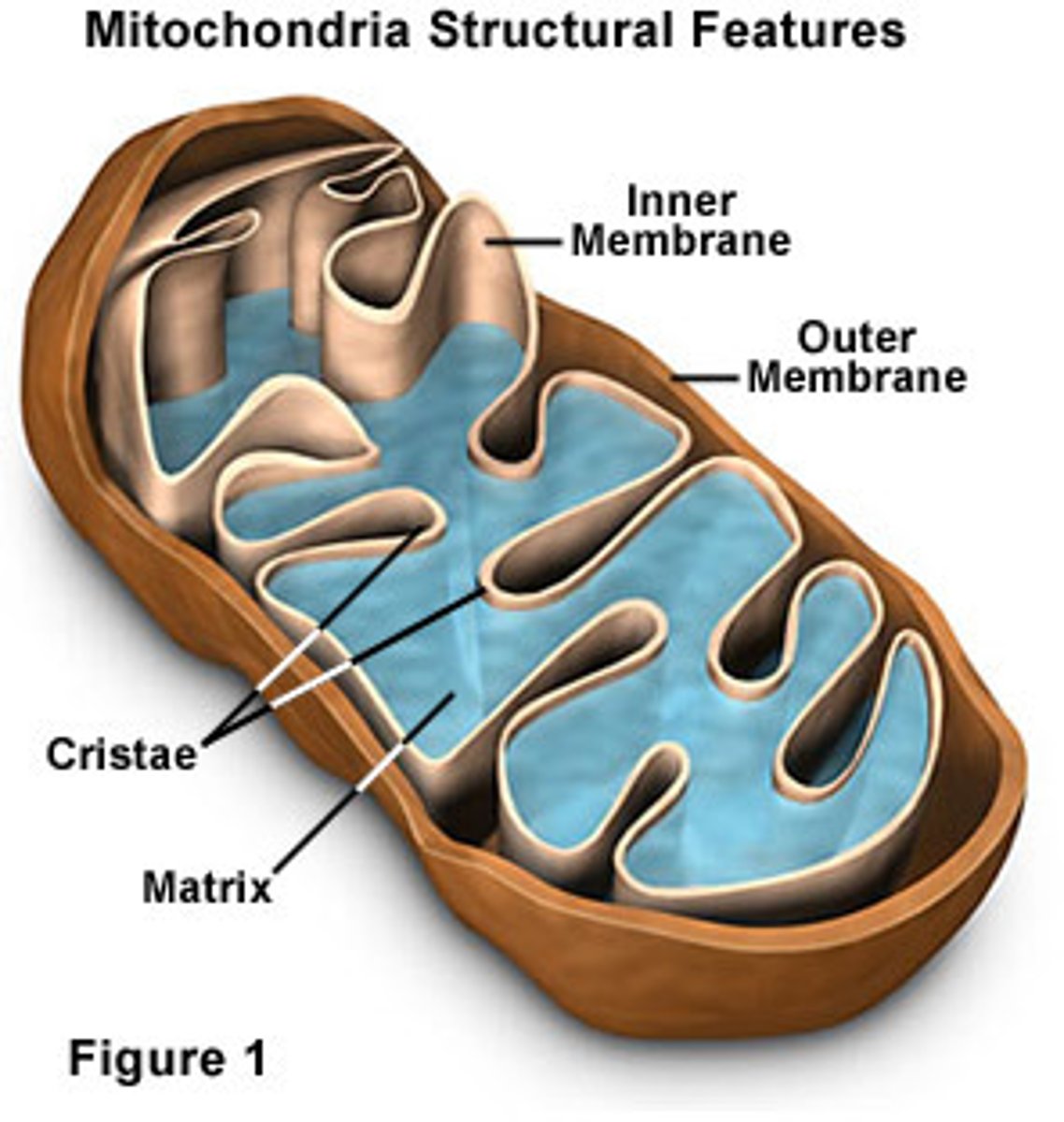
Matrix
Innermost compartment of the mitochondrion
Cristae
Infoldings of the inner membrane of a mitochondrion that houses the electon transport chain and the enzyme catalyzing the synthesis of ATP.
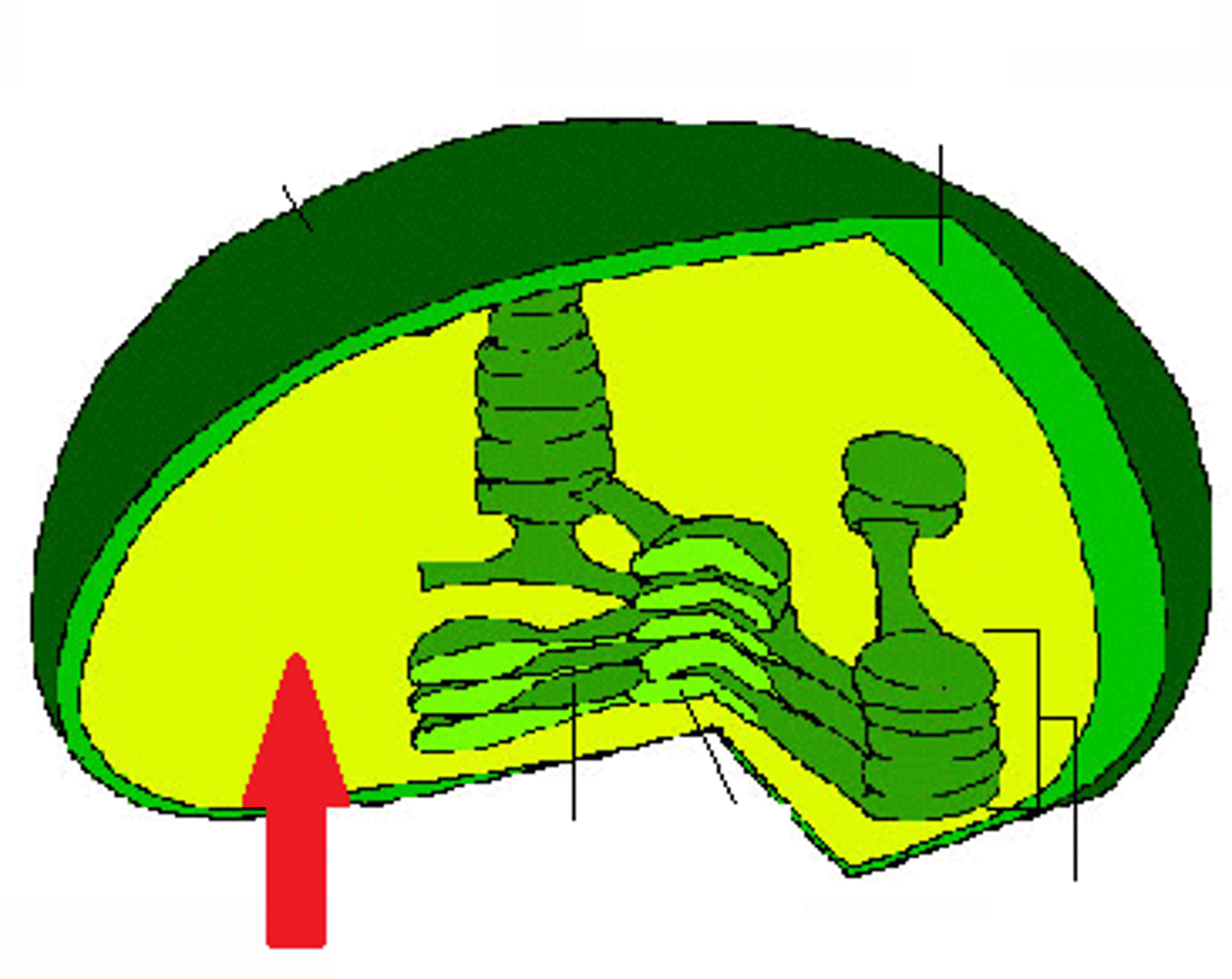
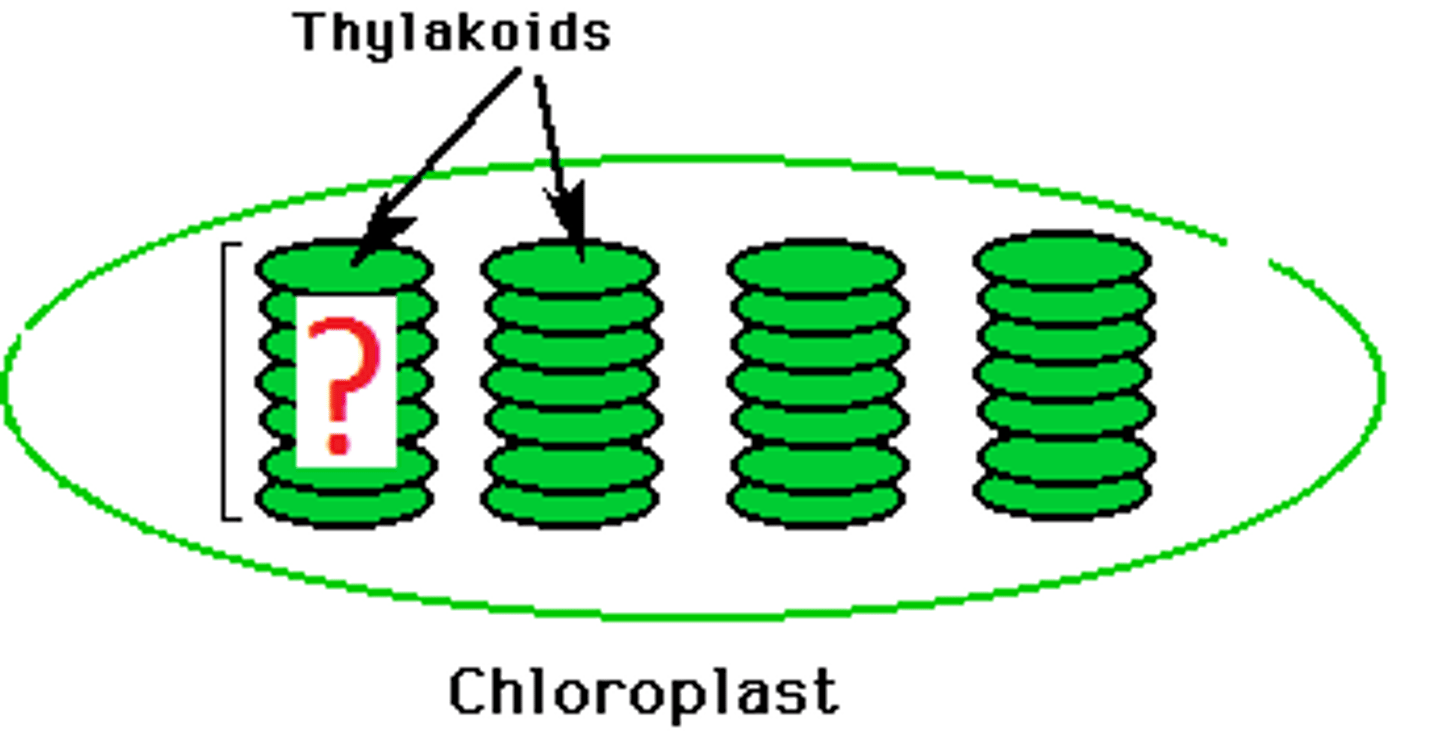
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
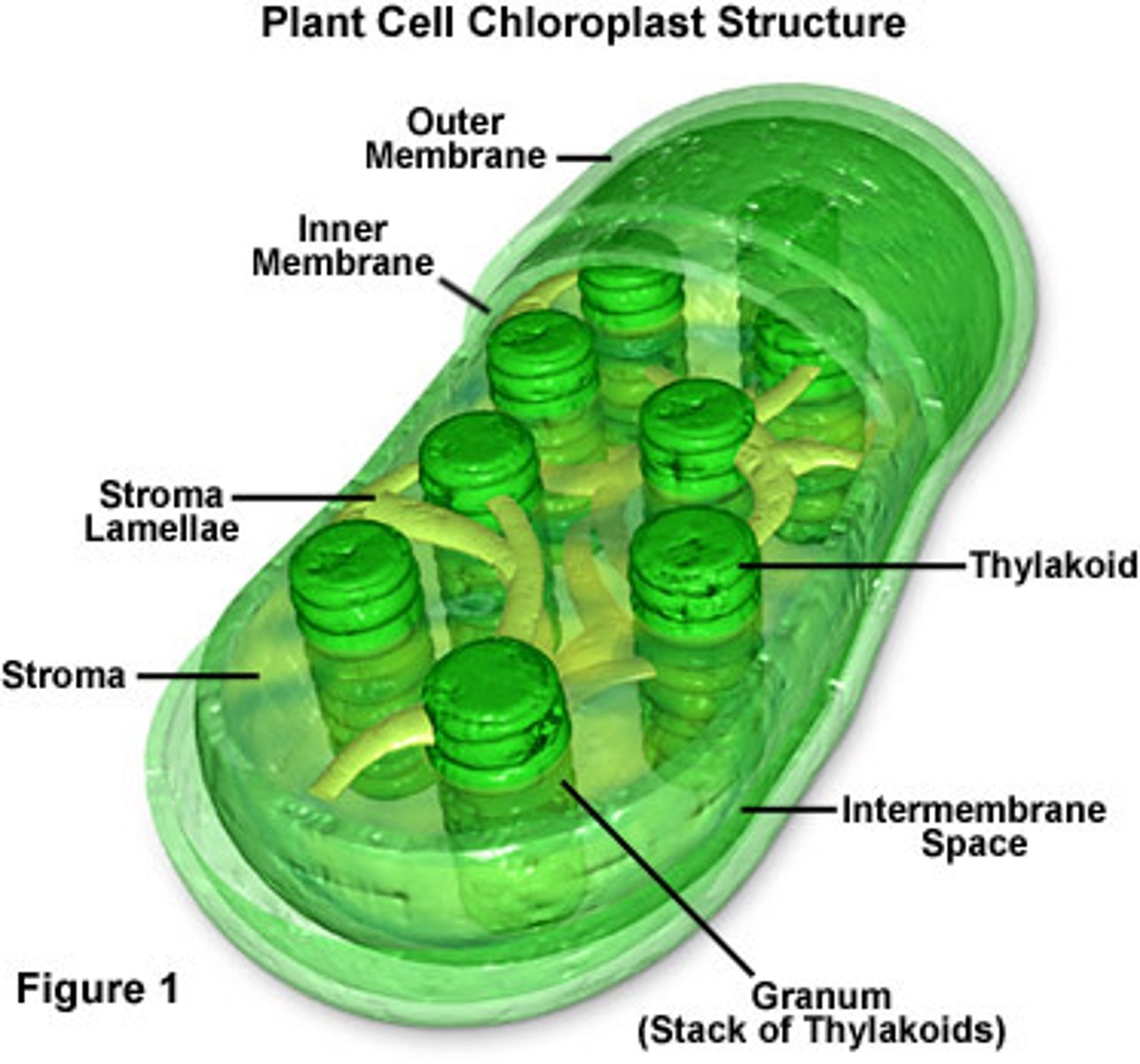
Thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy.
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
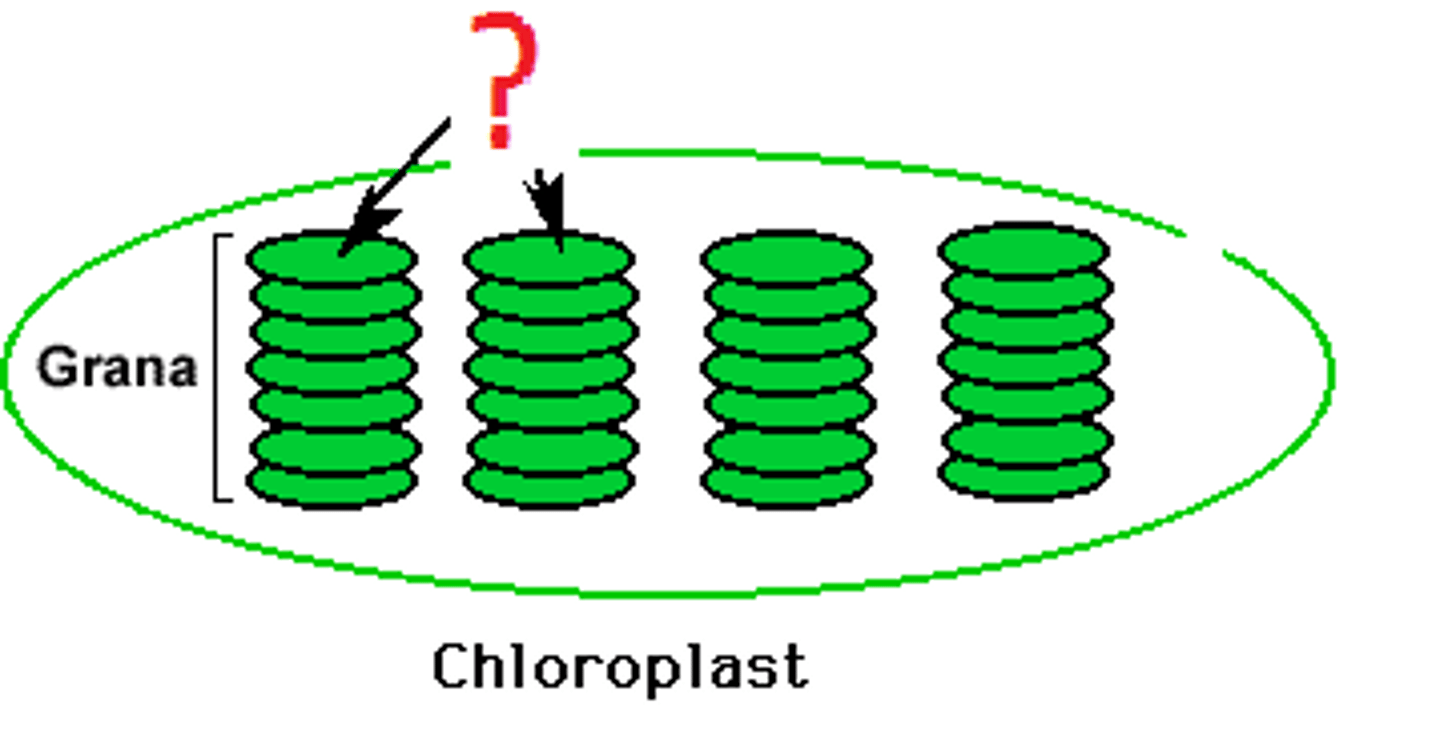
Granum
stack of thylakoids
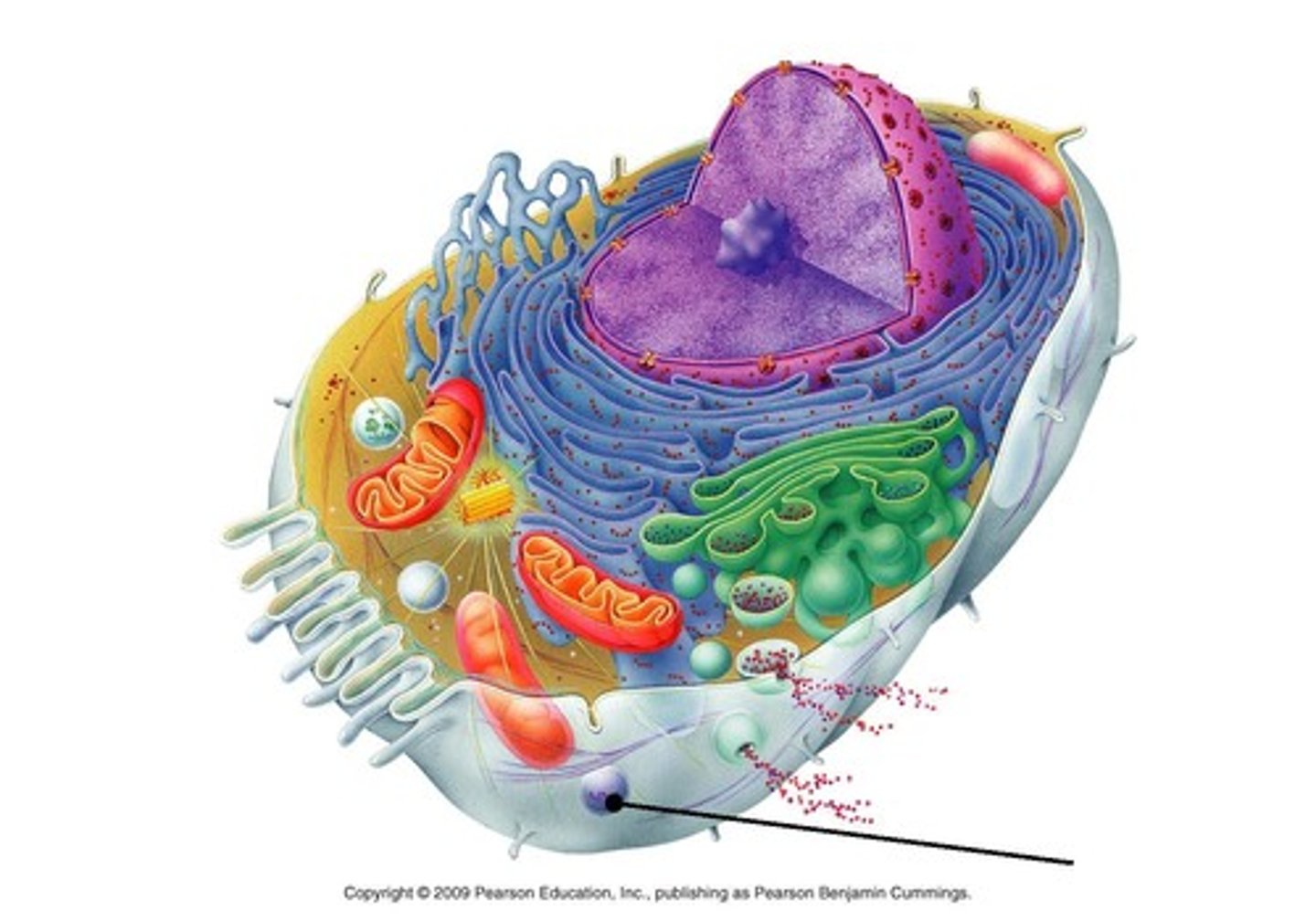
Peroxisomes
Contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals
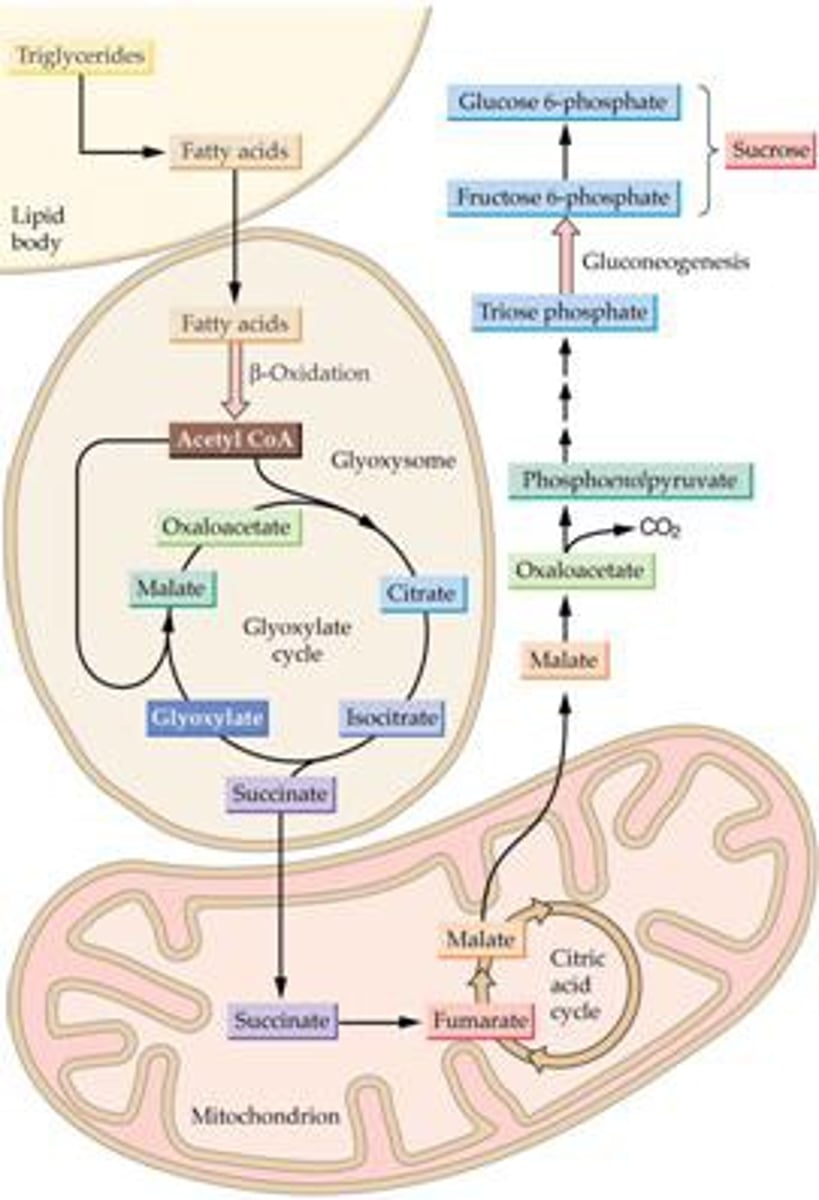
Glyoxysomes
found in fat tissue, converts fat into sugar
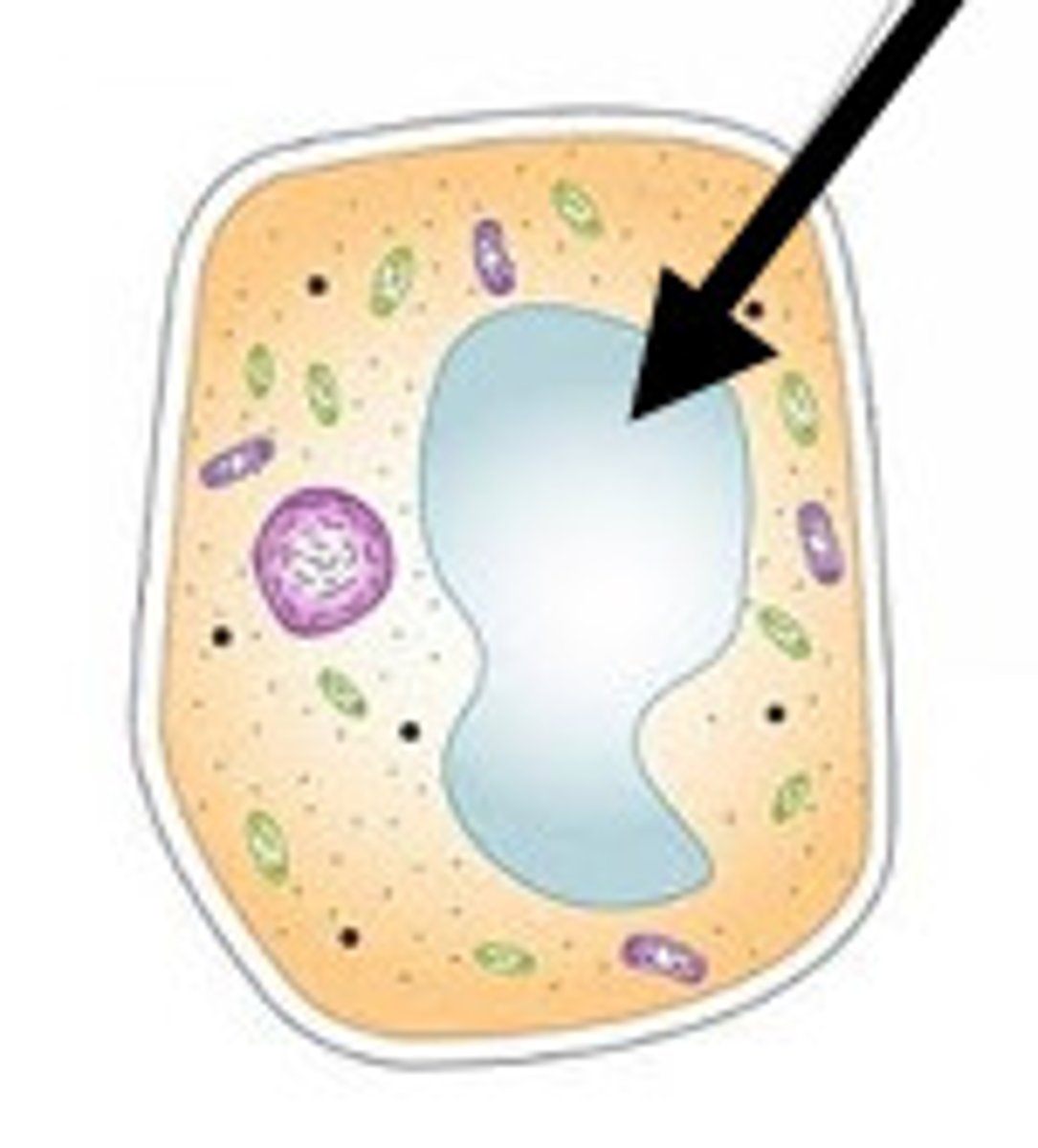
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
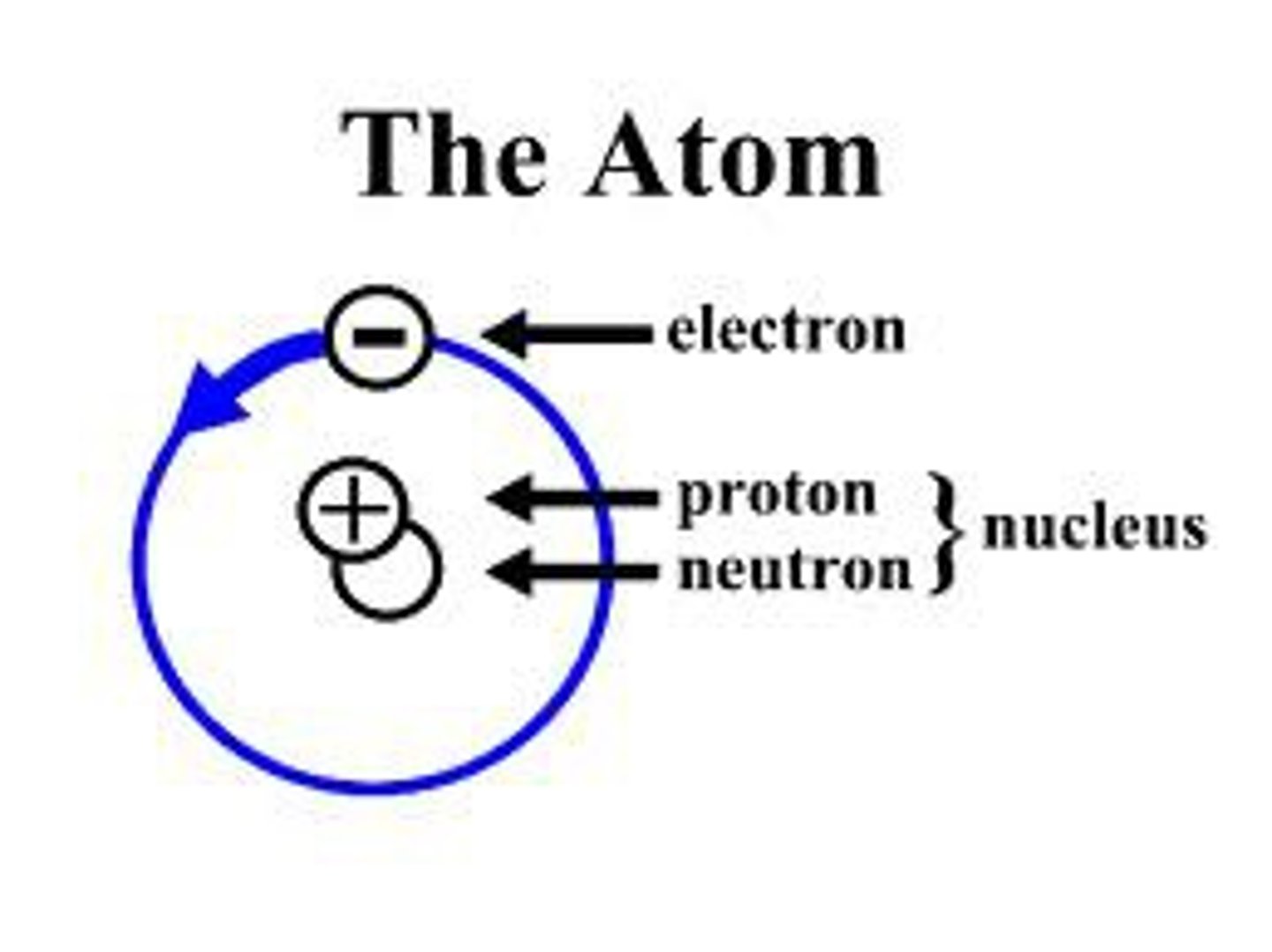
Atom
Smallest unit of matter that retains element properties
The most common atoms in Biology
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur
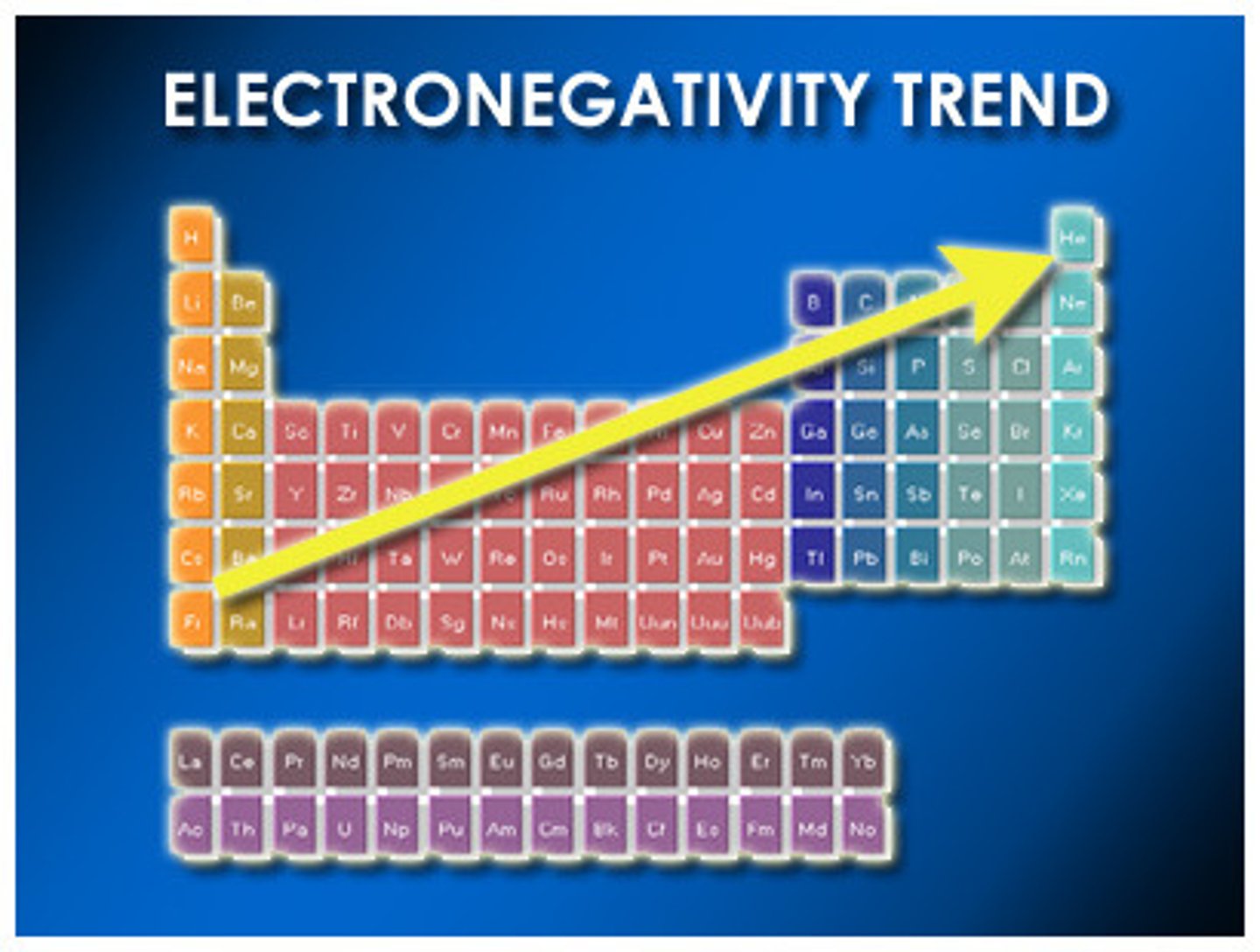
Electronegativity
the tendency of an atom to attract electrons
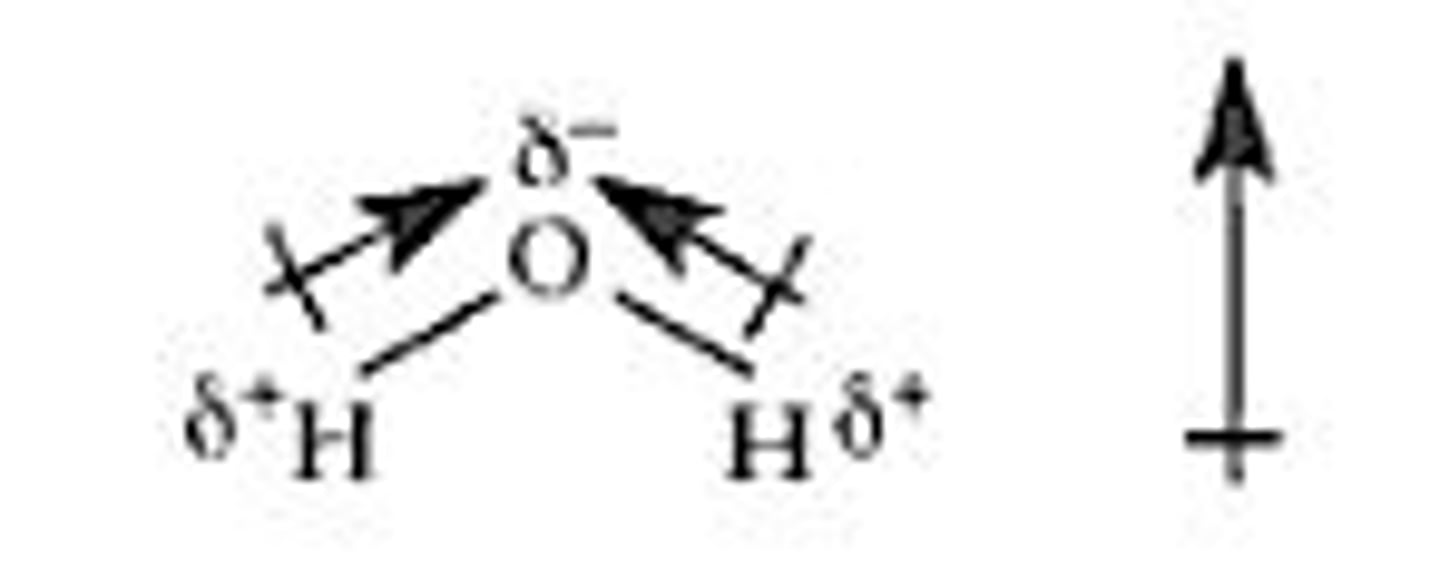
Dipoles
positive and negative charged ends of a polar covalent molecule
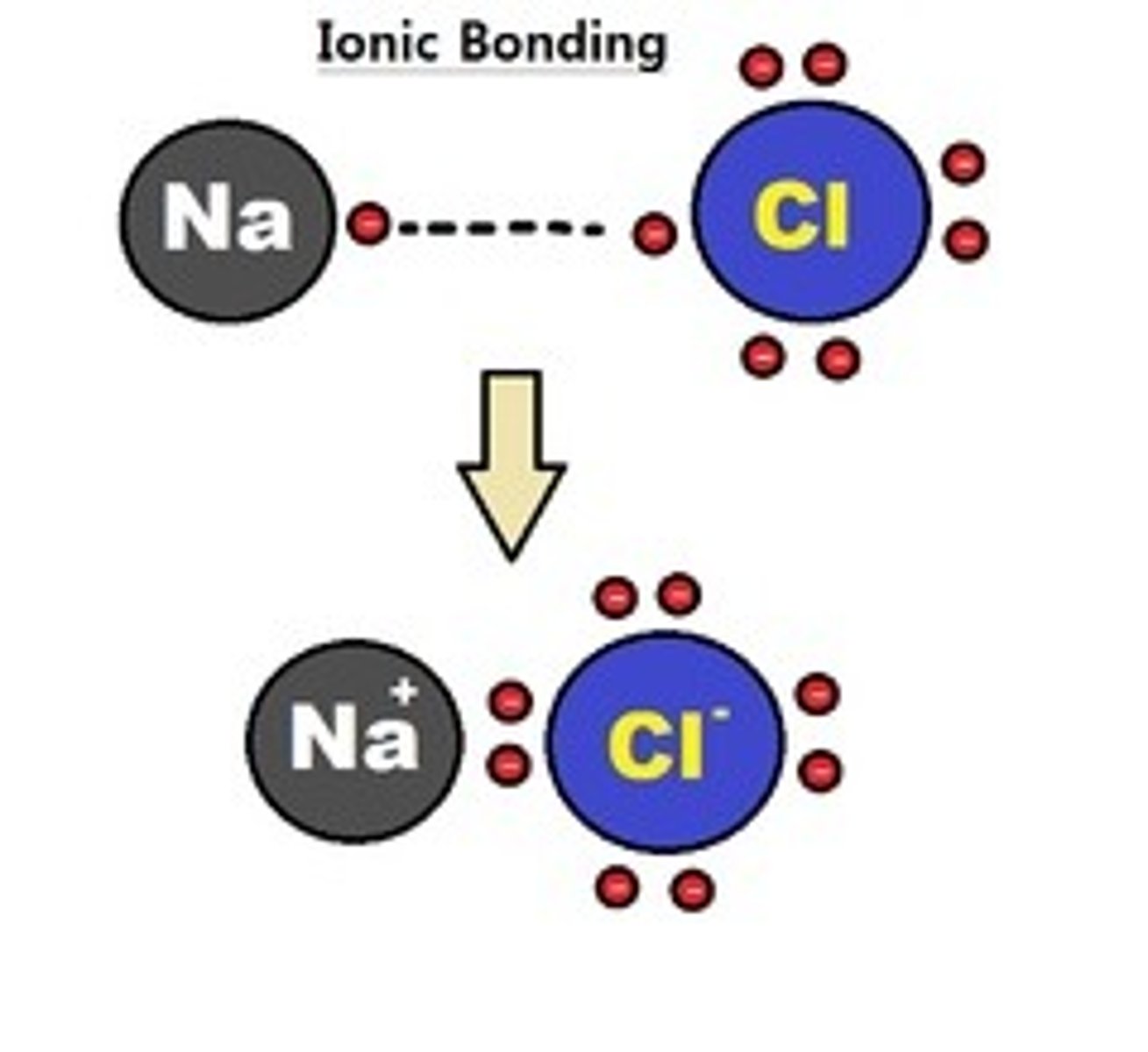
Ionic bonds
Metals interacting with a nonmetal, opposite charges. Takes electrons and aren't usually stable.
Covalent bonds
Nonmetals interacting with nonmetals, shared electrons, and are usually stable.
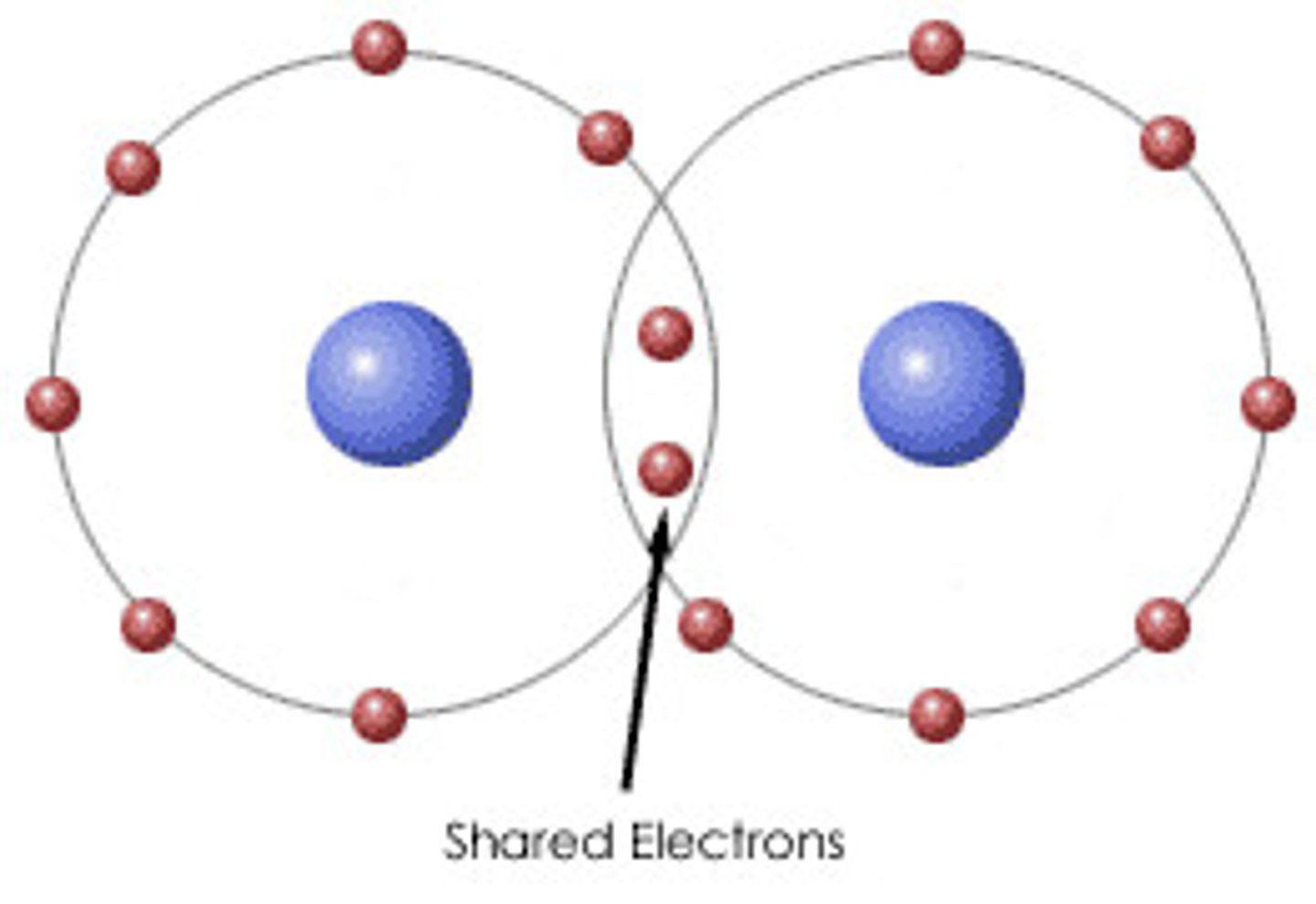
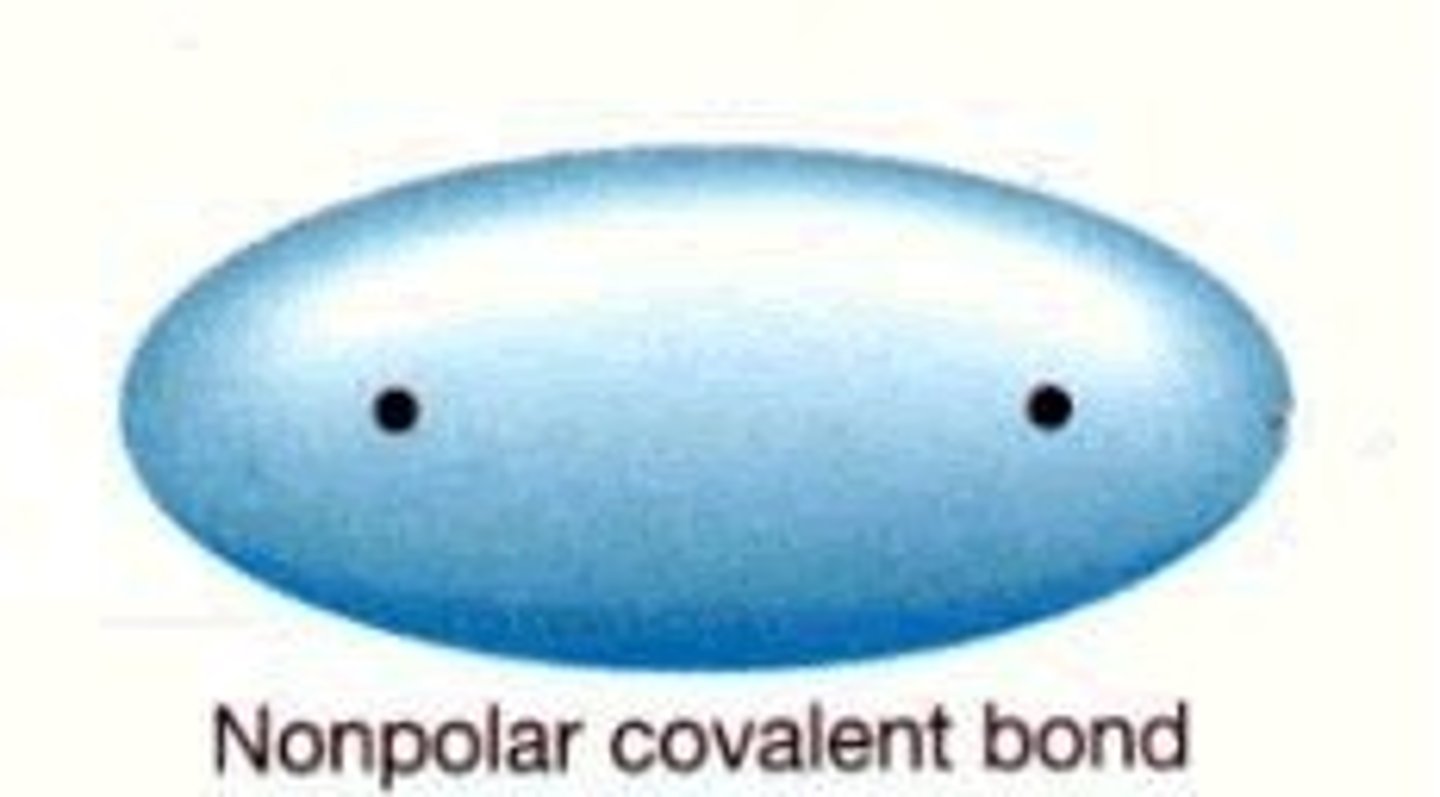
Non polar bonds
When the sharing of electrons is basically equal. Nonpolar covalent
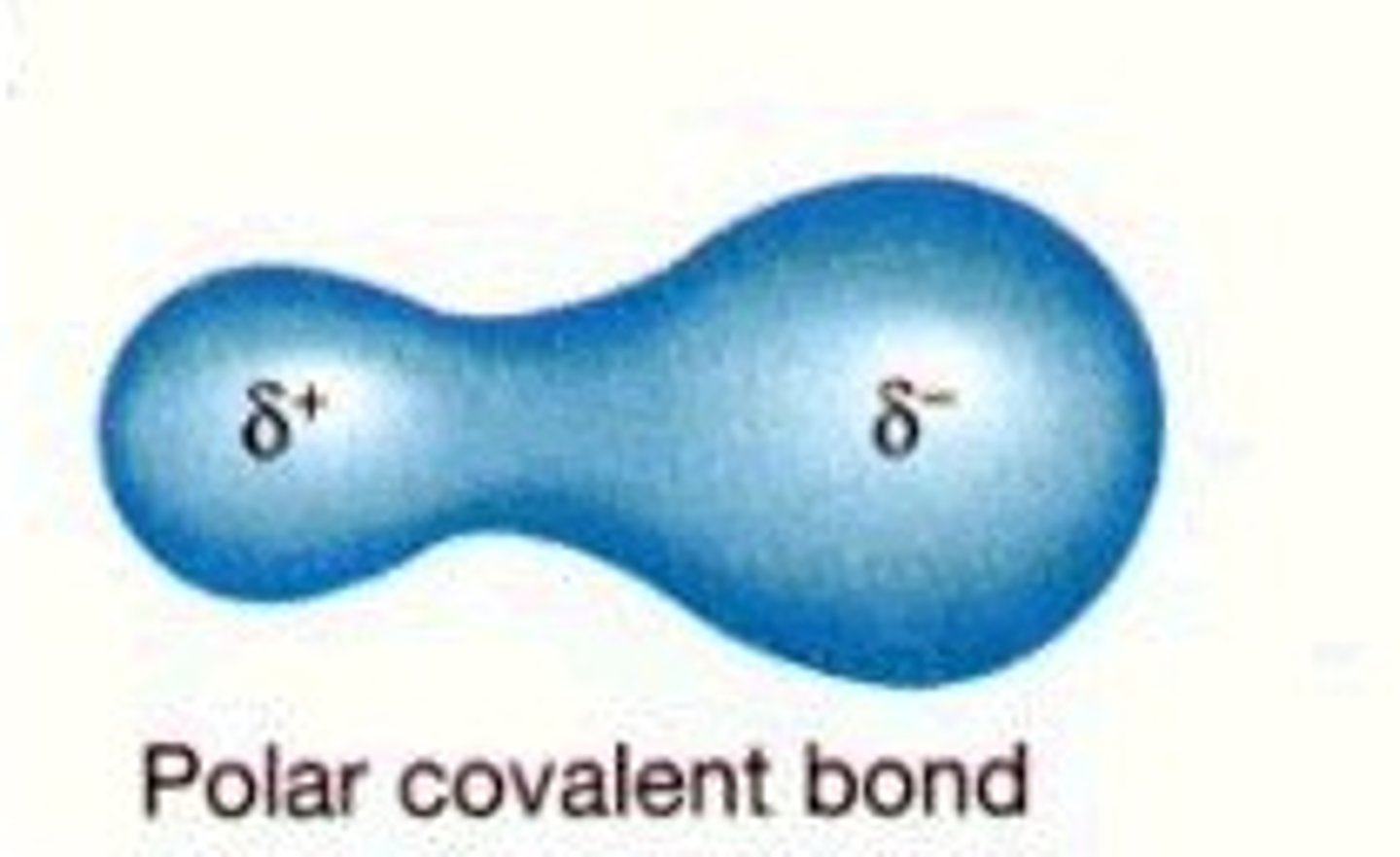
Polar bonds
When the sharing of electrons is not equal. Polar covalent
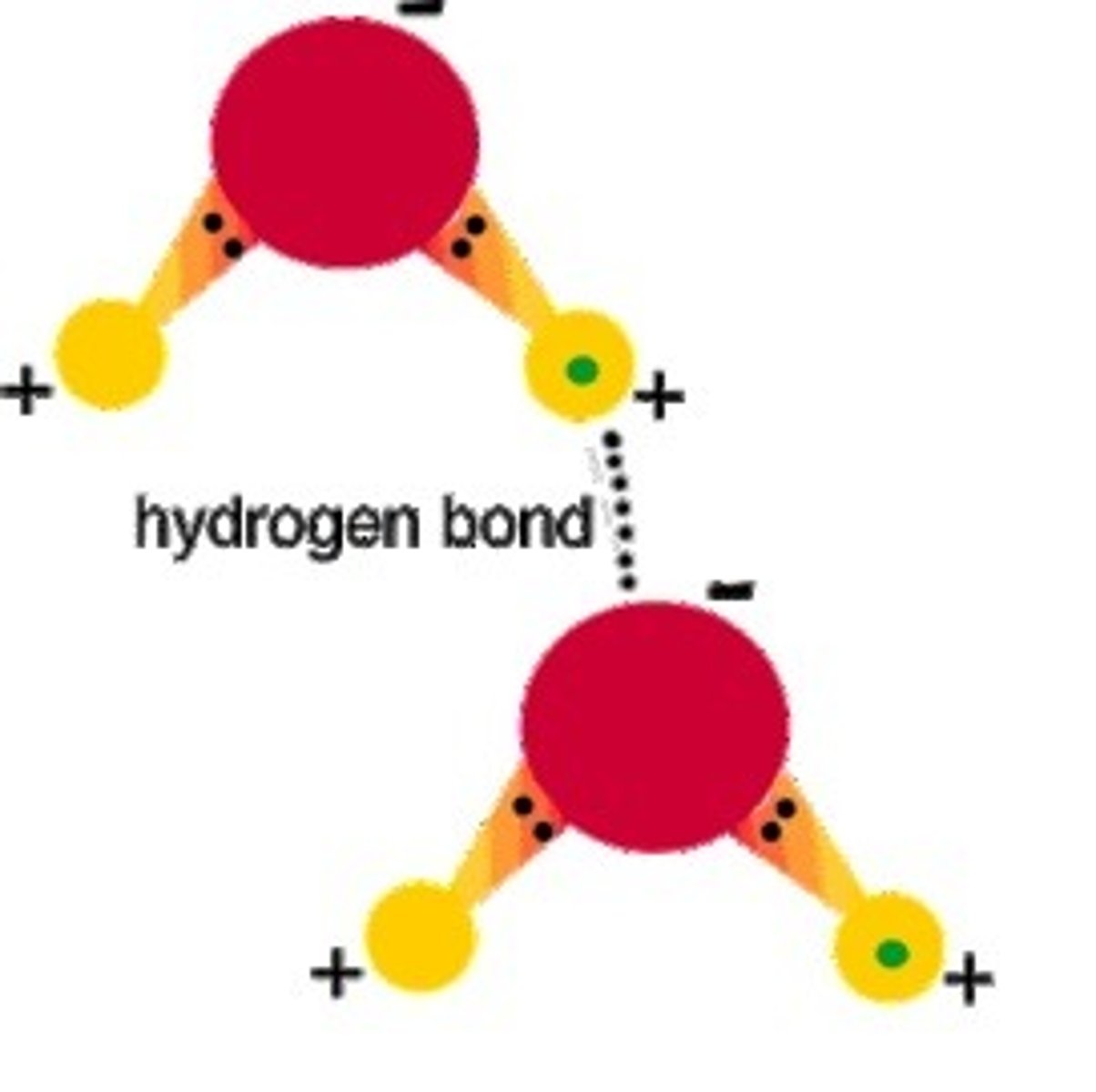
Hydrogen bonds
Type of covalent bond, between a partial positive charge of H and partial negative of other atoms. Usually with O, N, or F.
Van Der Walls bond
Interaction of electrons of nonpolar substances
Water
H20 Polar Covalent

Hydrophilic
Molecules are polar and will interact with water
Hydrophobic
Molecules are nonpolar and won't interact with water
Dissociation
Disrupting the bonds and breaking them apart.
pH < 7
Acid (High H+ proton concentration)
pH = 7
Neutral (water)
pH > 7
Base (Soap)
Are there more or less H+ ions at a higher pH?
less

pH = pKa
[protonated] = [deprotonated]
pH > pKa
Deprotonated predominates
pH < pKA
Protonated predominates
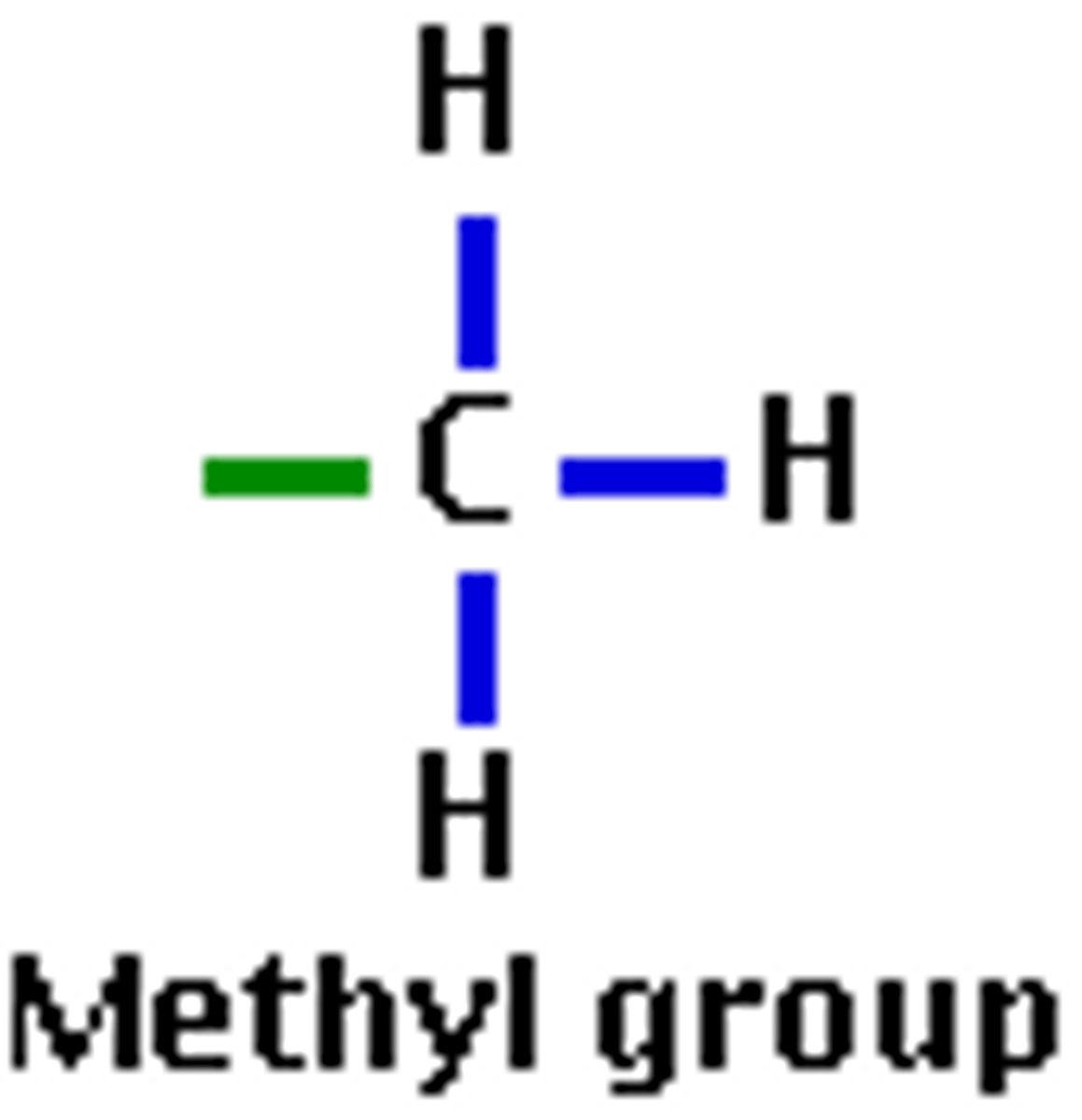
Methyl functional group
Unable to form hydrogen bonds(only one that never can) Nonpolar
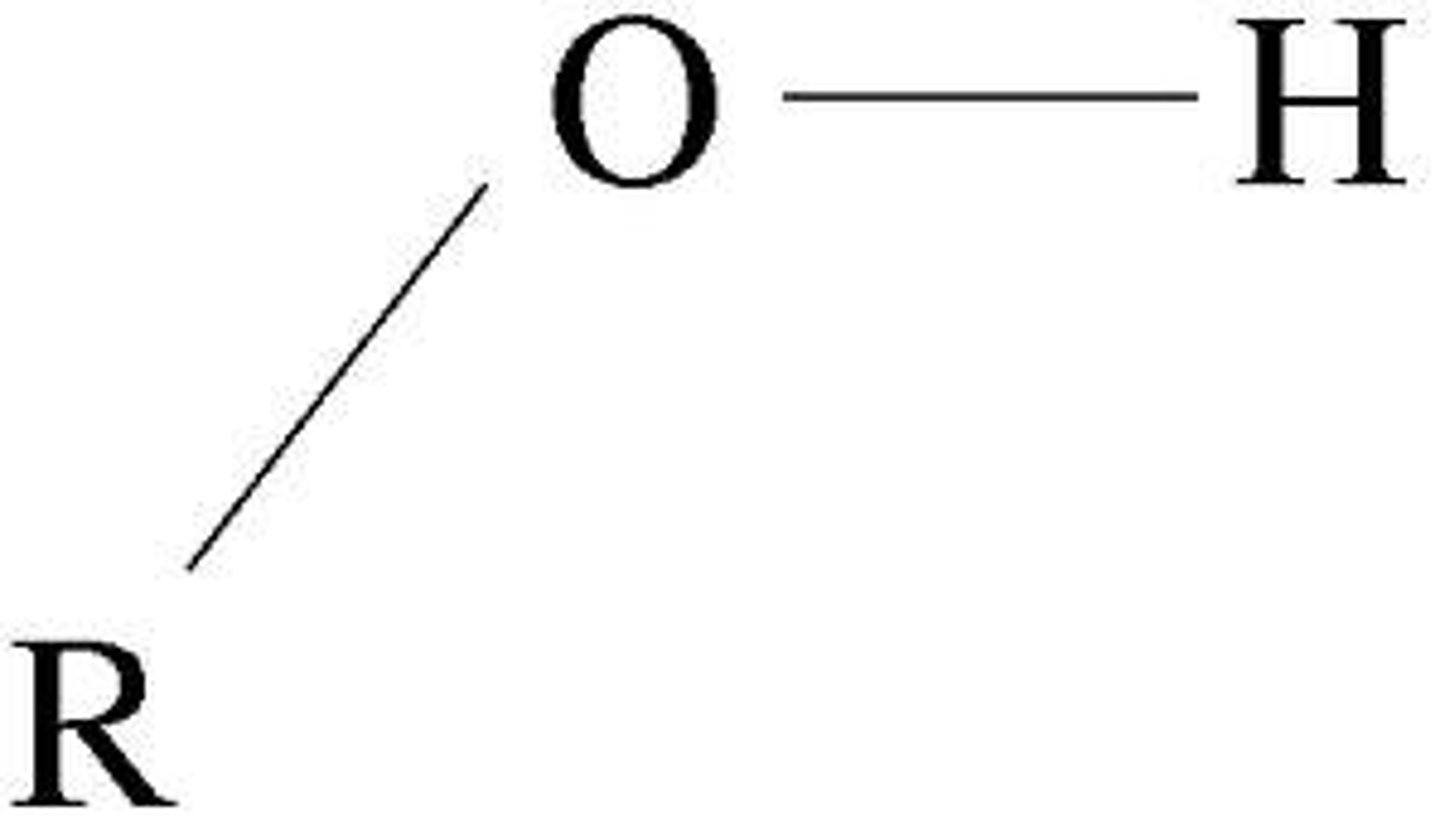
Hydroxyl functional group
Can form hydrogen bonds, Polar
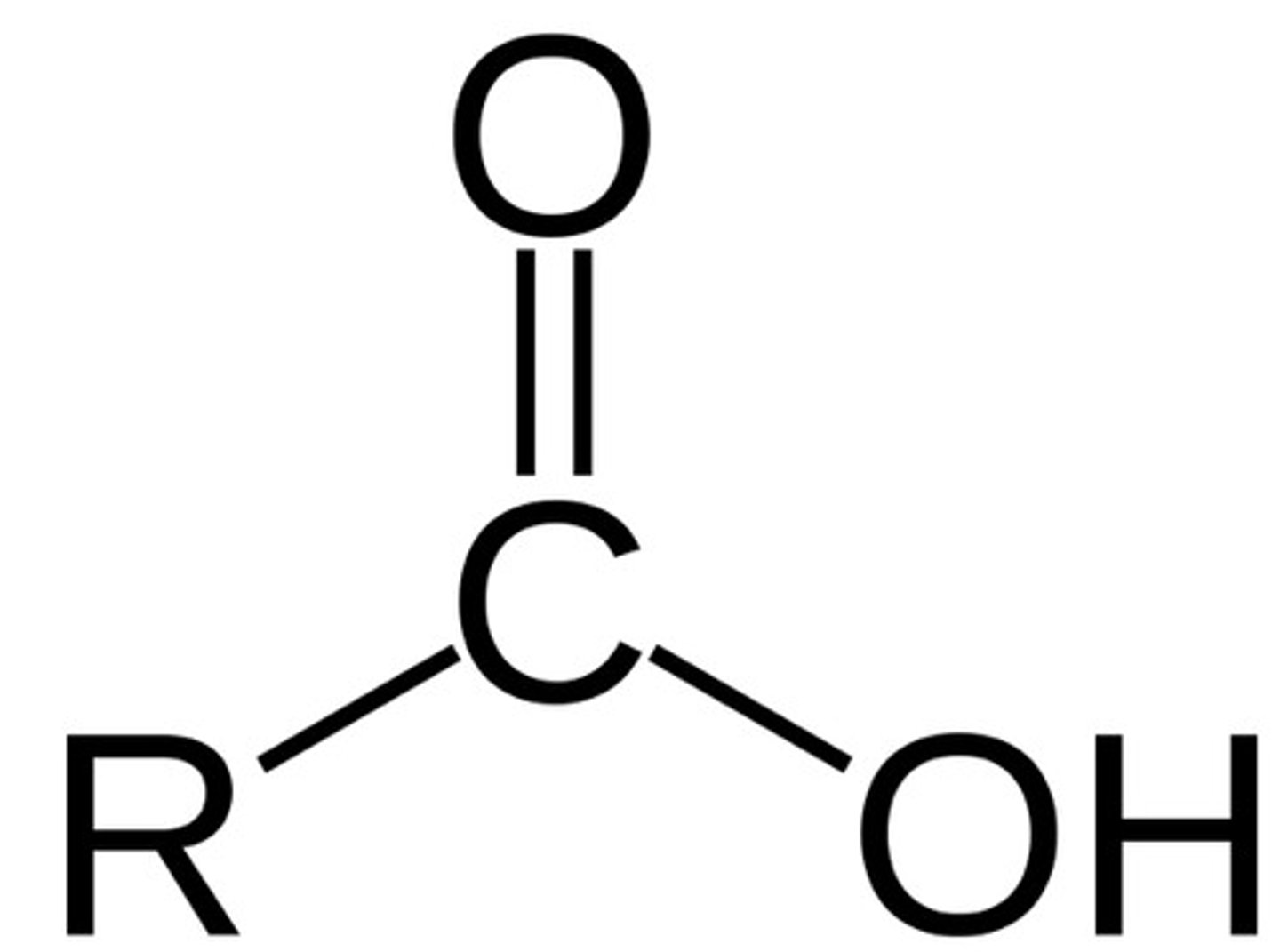
Carboxyl functional group
Can form hydrogen bonds, Polar
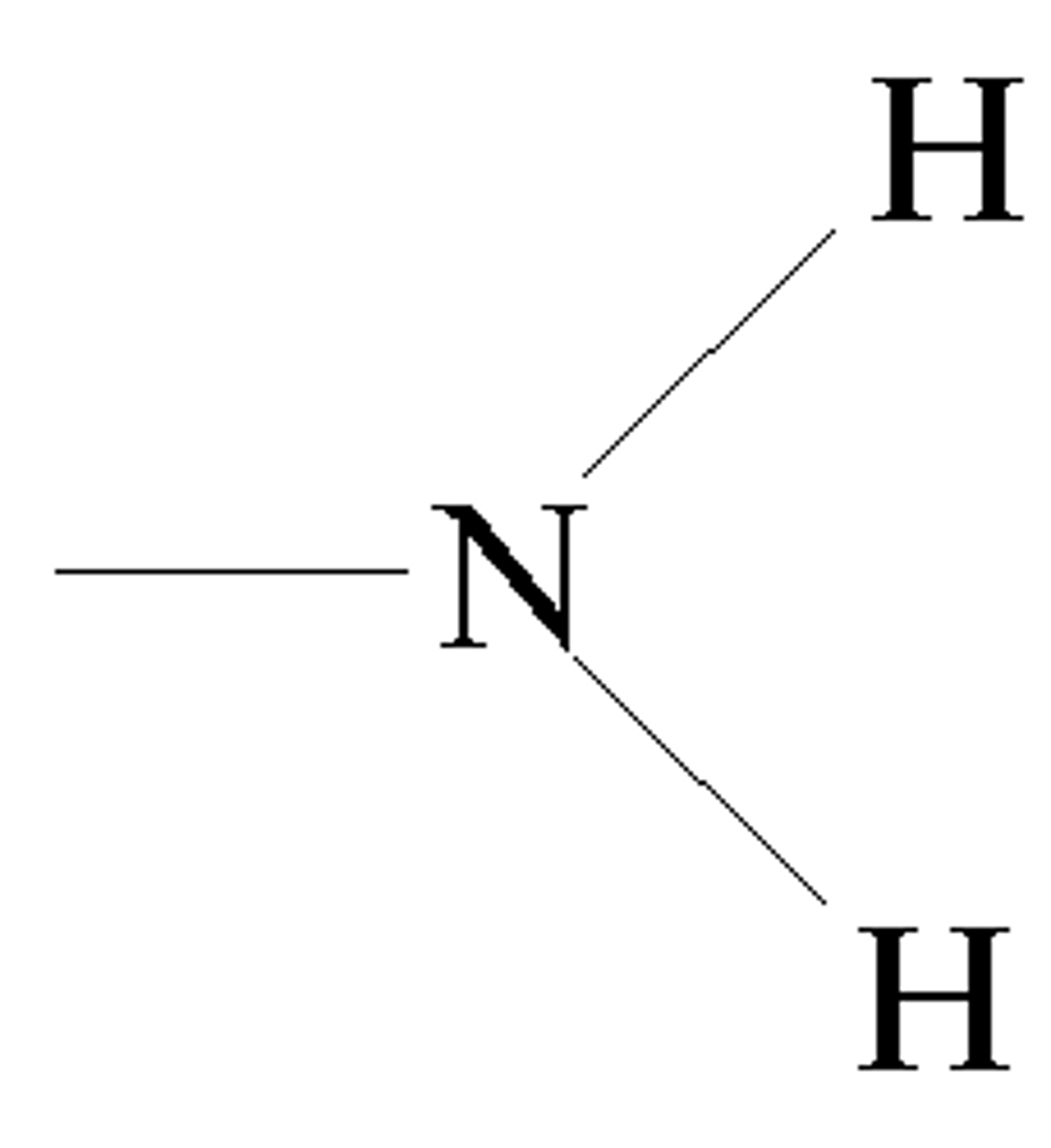
Amino functional group
Can sometimes form hydrogen bonds
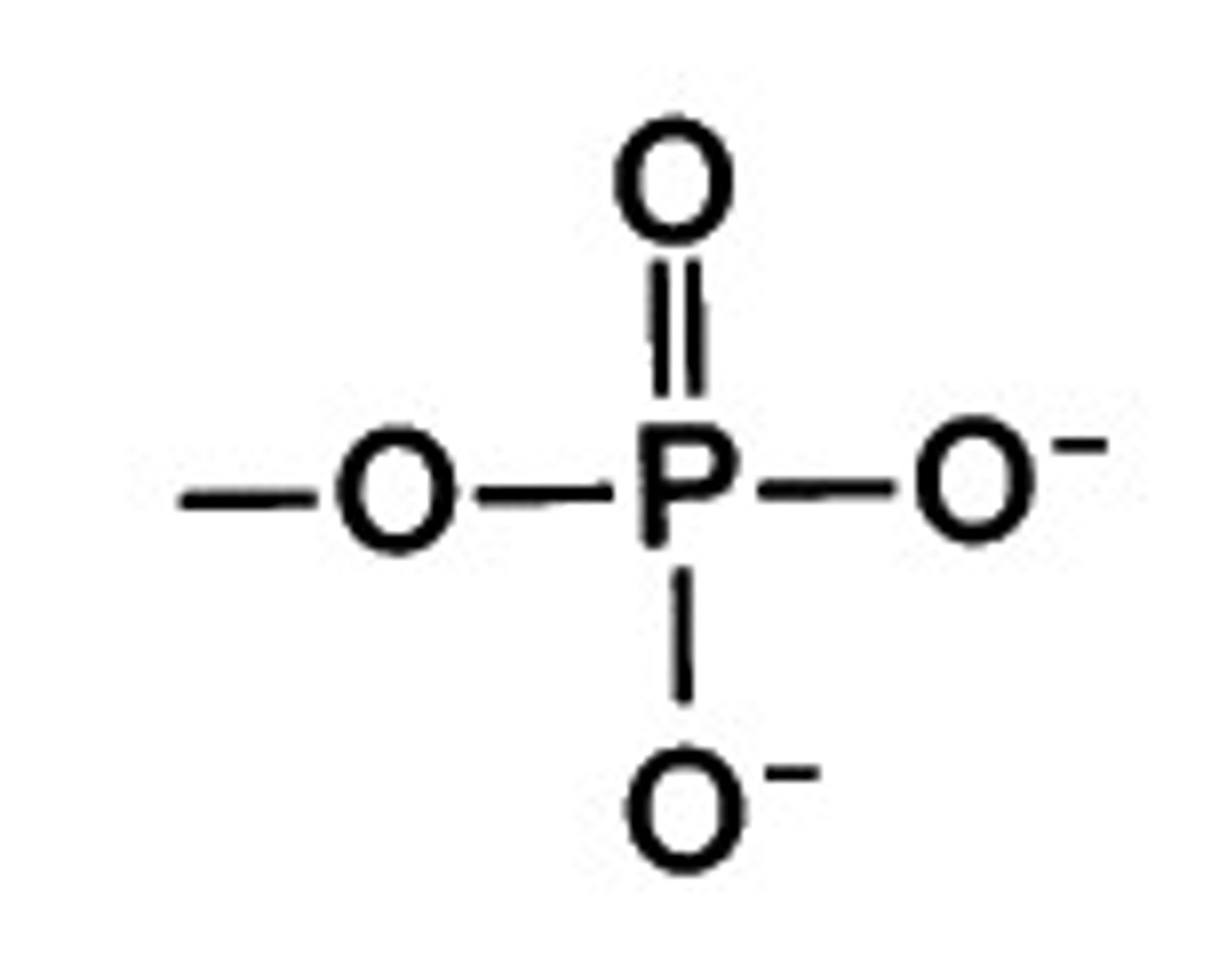
Phosphate functional group
Can form hydrogen bonds
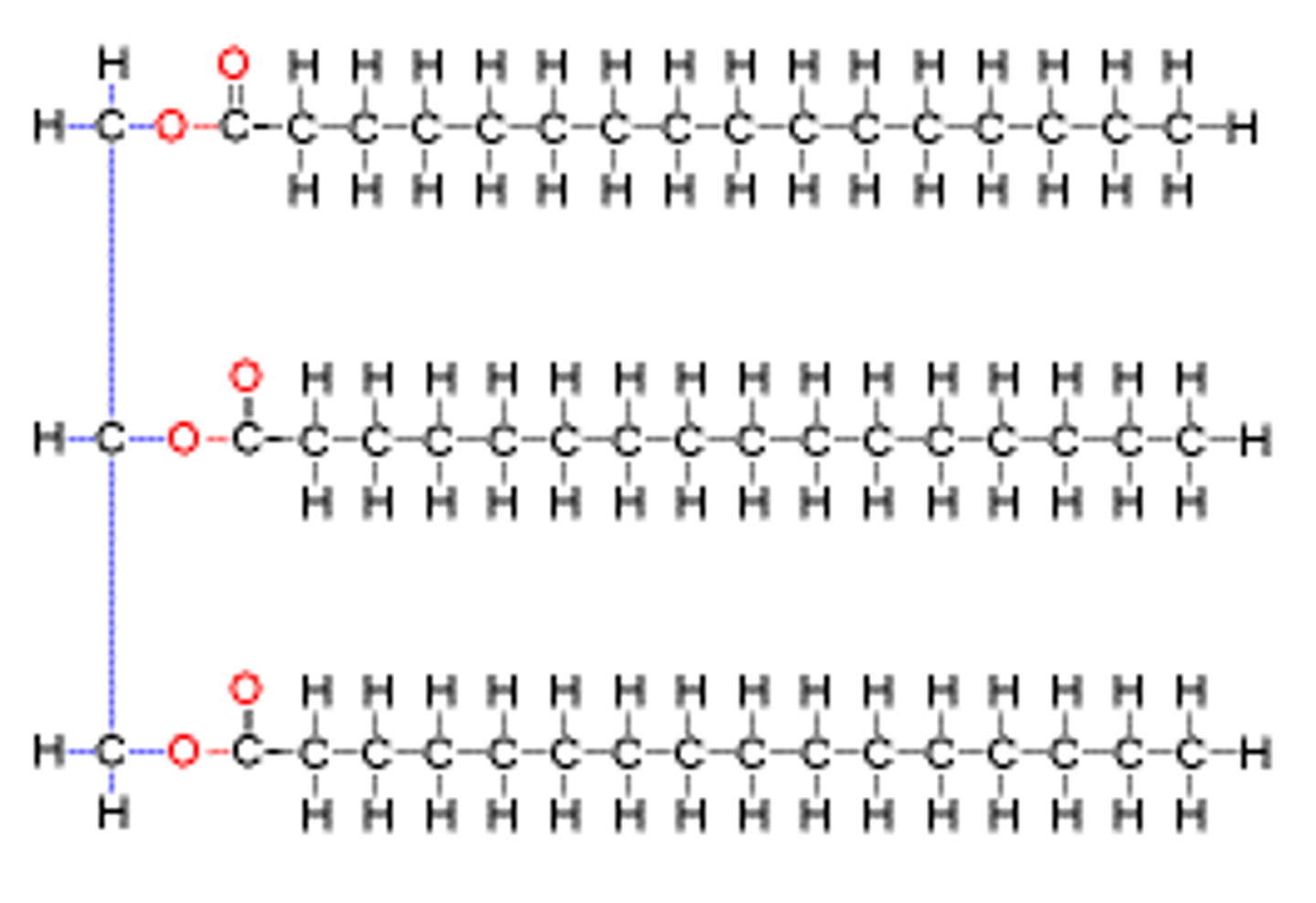
Lipids
Energy-rich organic compounds such as fats and oils. Are Hydrophobic and nonpolar
Steroids
Fats that have 4 carbon rings. Ex. Cholesterol

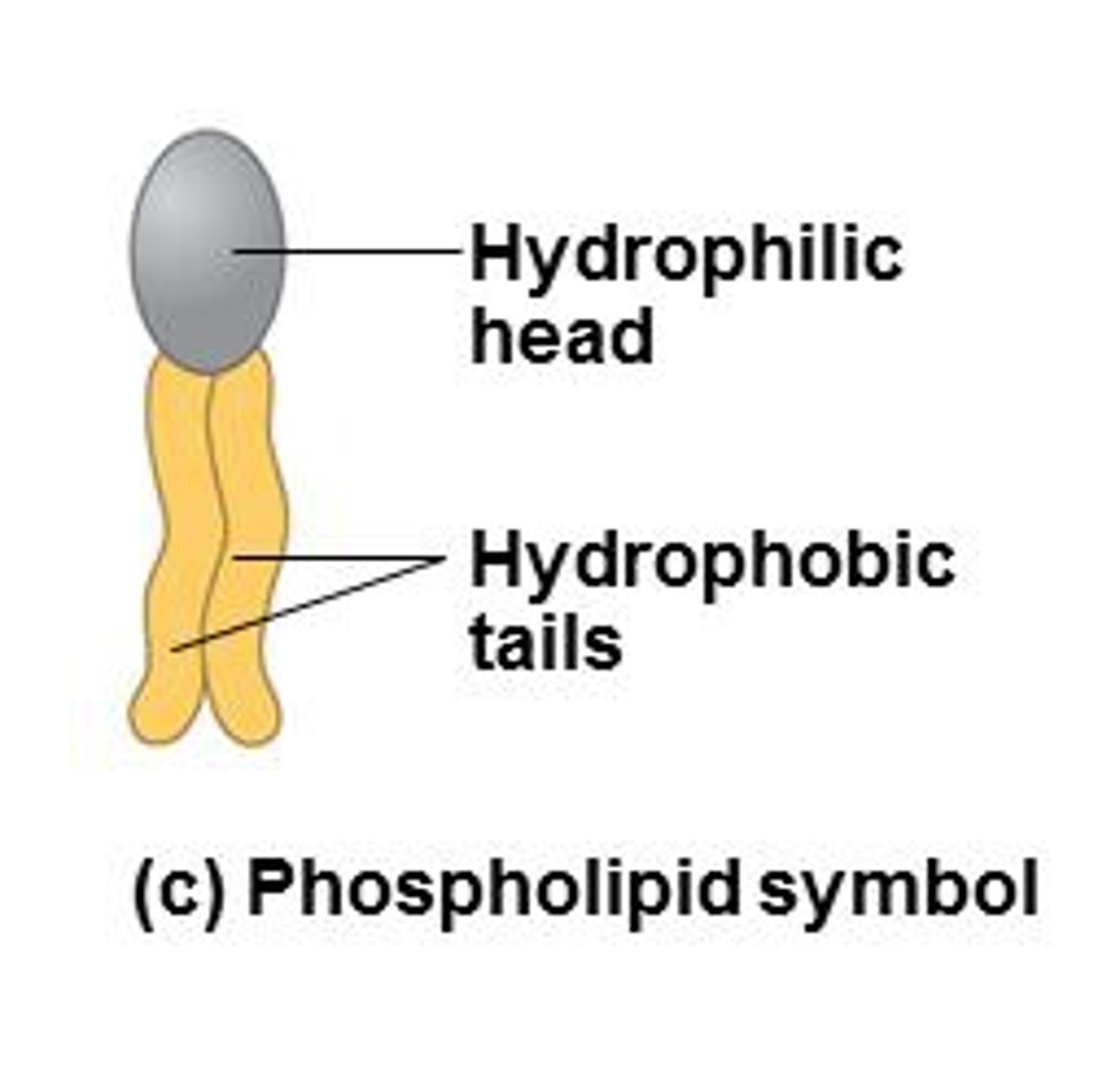
Phospholipids
Make up the duel layer of cell membranes, fatty acid chains and polar head group
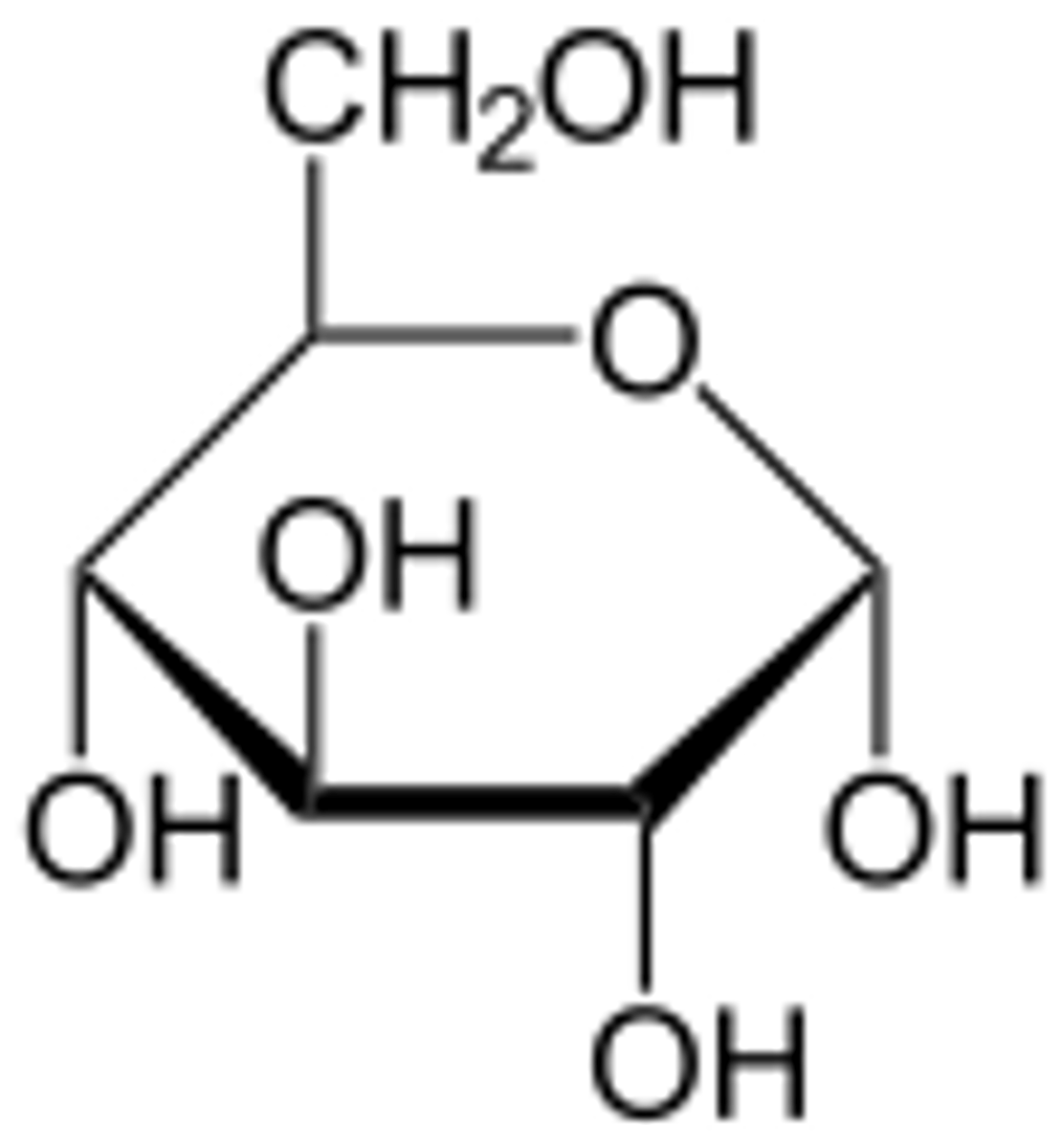
Carbohydrates
The starches and sugars present in foods, have a CH2O forumula.
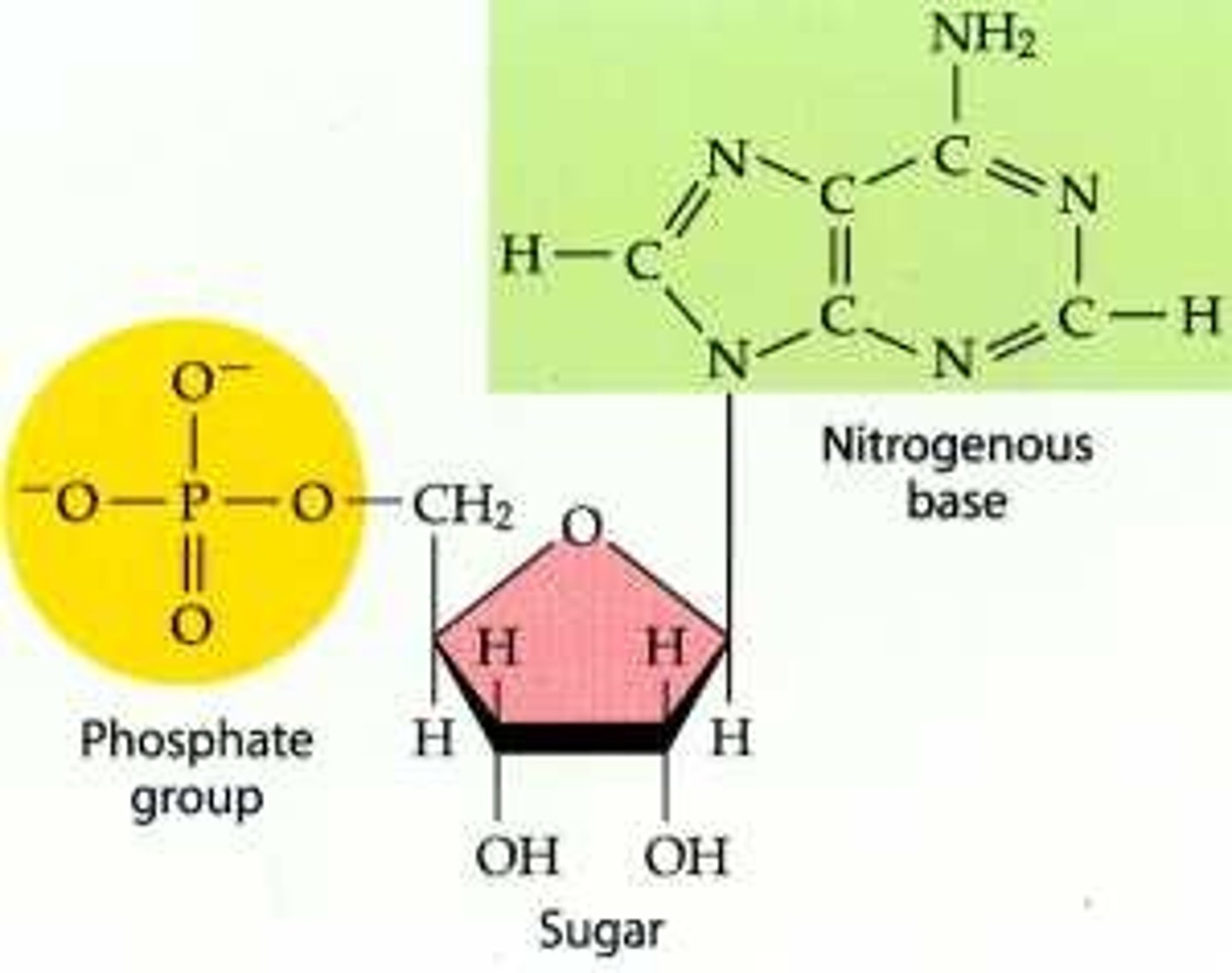
Nucleotides
Made of pentose sugar. nitrogenous base, and phosphate group. Monomers of nucleic acids
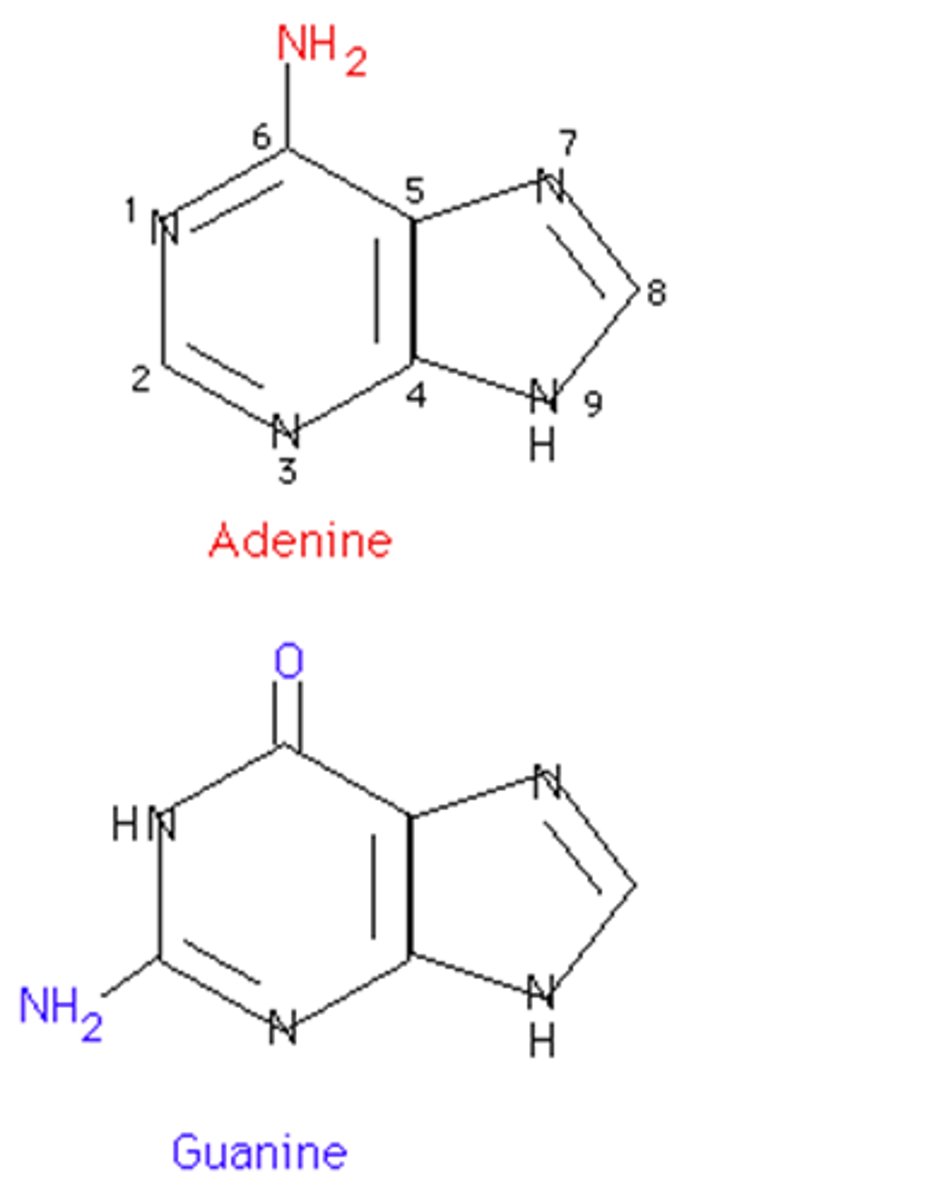
Purines
Adenine and Guanine
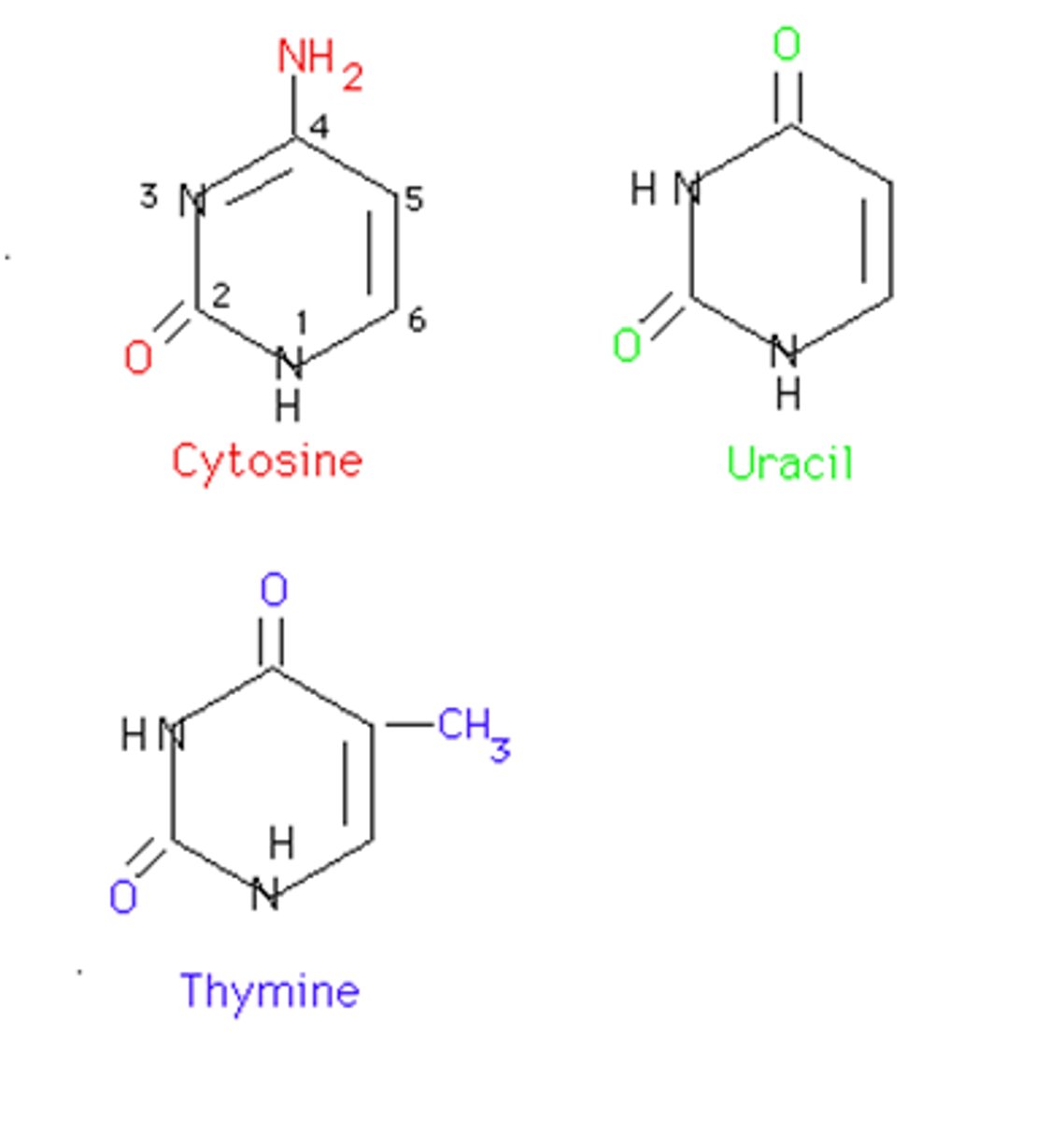
Pyrimidines
Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
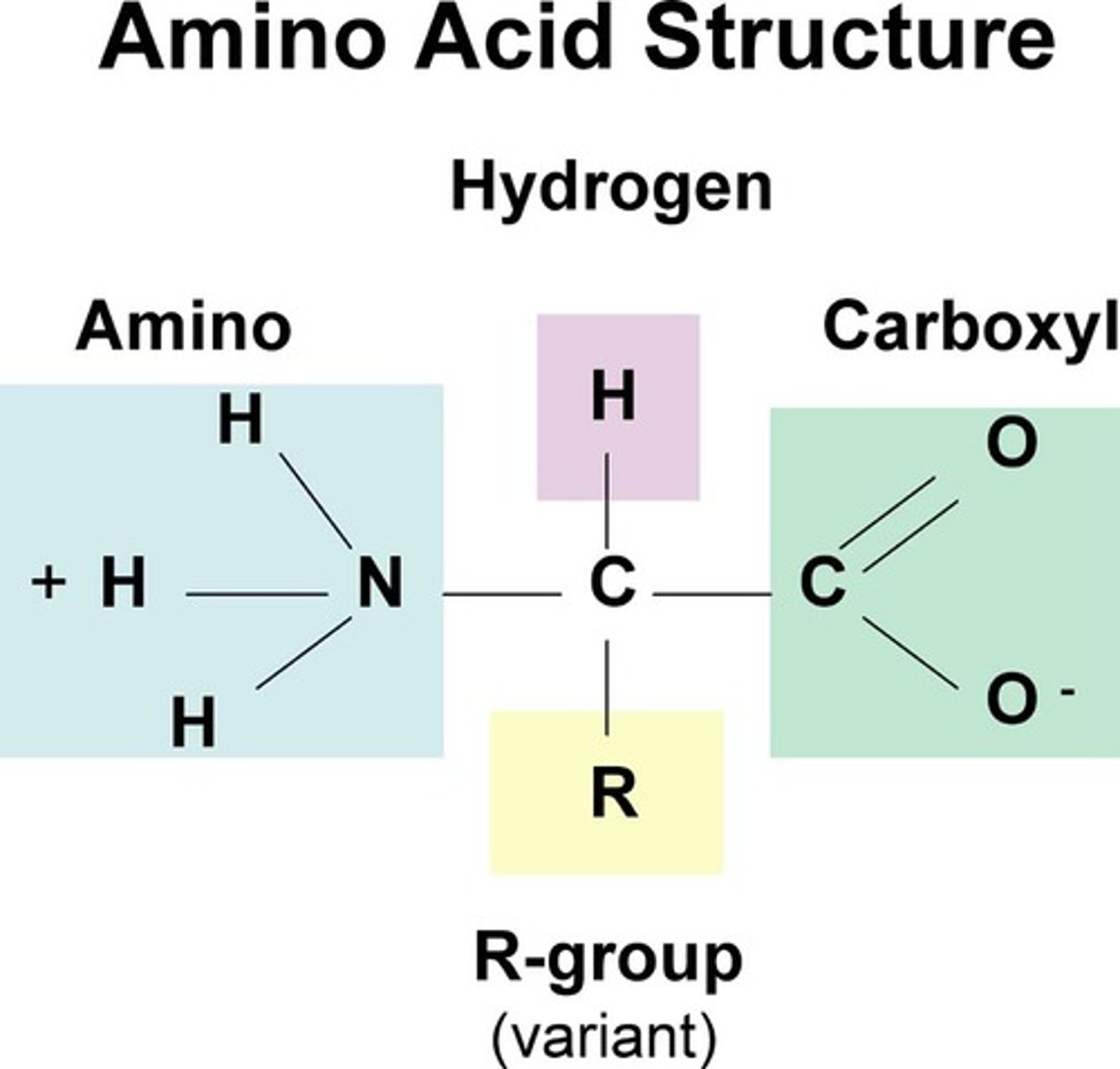
Amino acids
Building blocks(Monomers) of proteins. Structure consists of central carbon bounded to amino group, R group, and a carboxyl group.
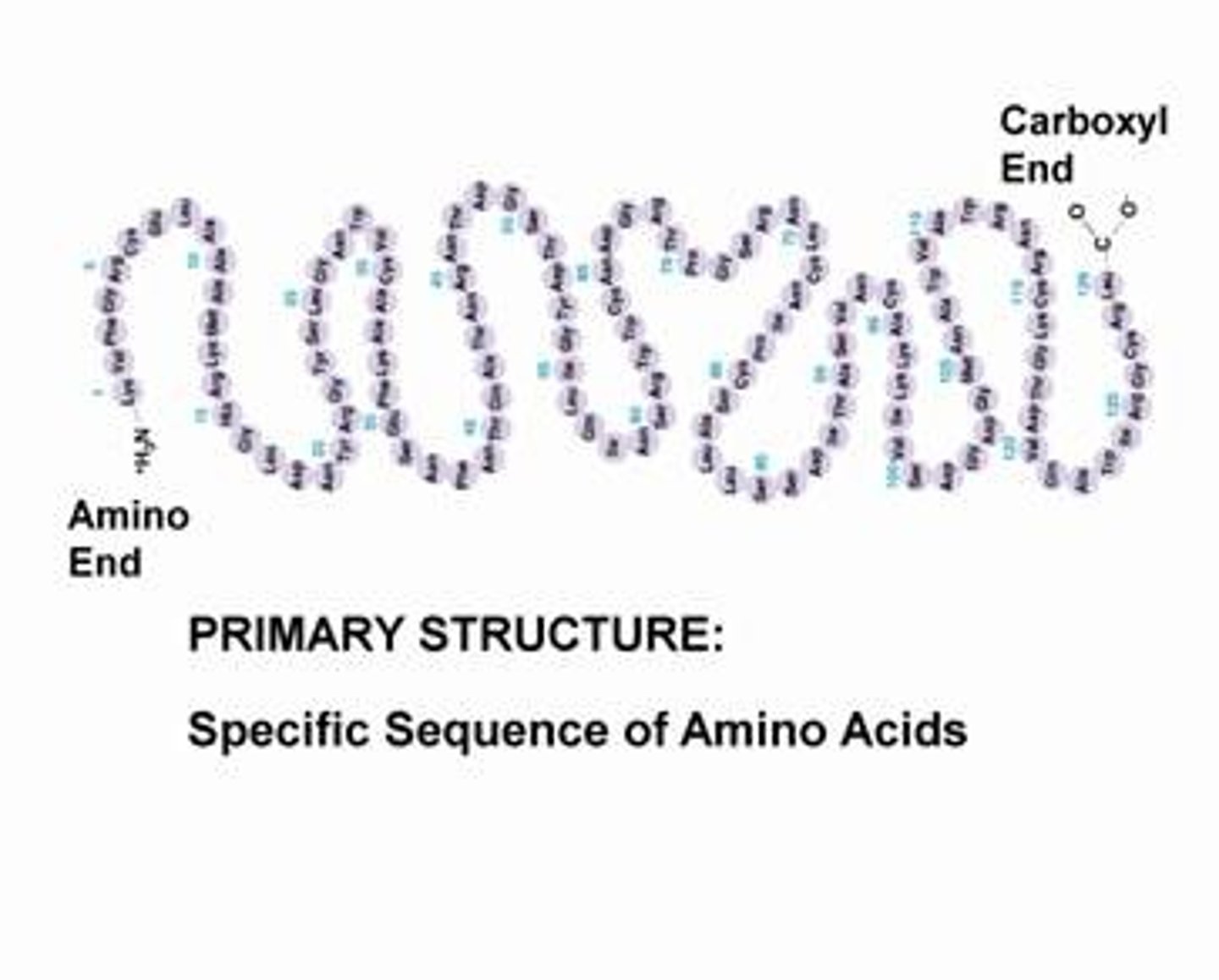
Primary structure of proteins
Linear sequence of amino acids in a peptide bond.
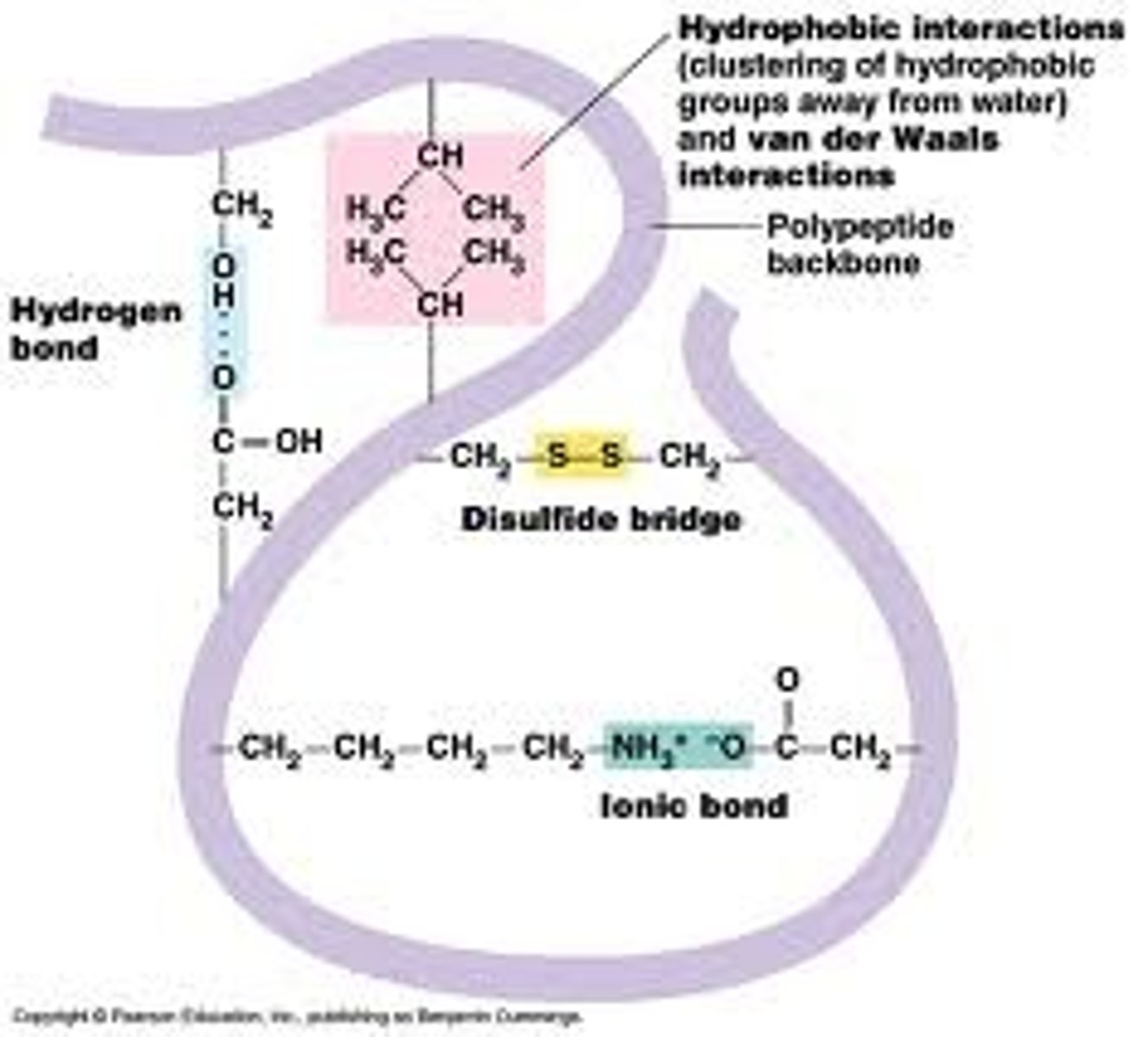
Secondary structure of proteins
Local folding of the polypeptide chain, held together by hydrogen bonds, usually forms a-helix and b-pleated sheets.

Tertiary structure of proteins
Unique 3D structure of a polypeptide, has to do with how the R groups interact, and forms disulfide linkages between areas in the chain.
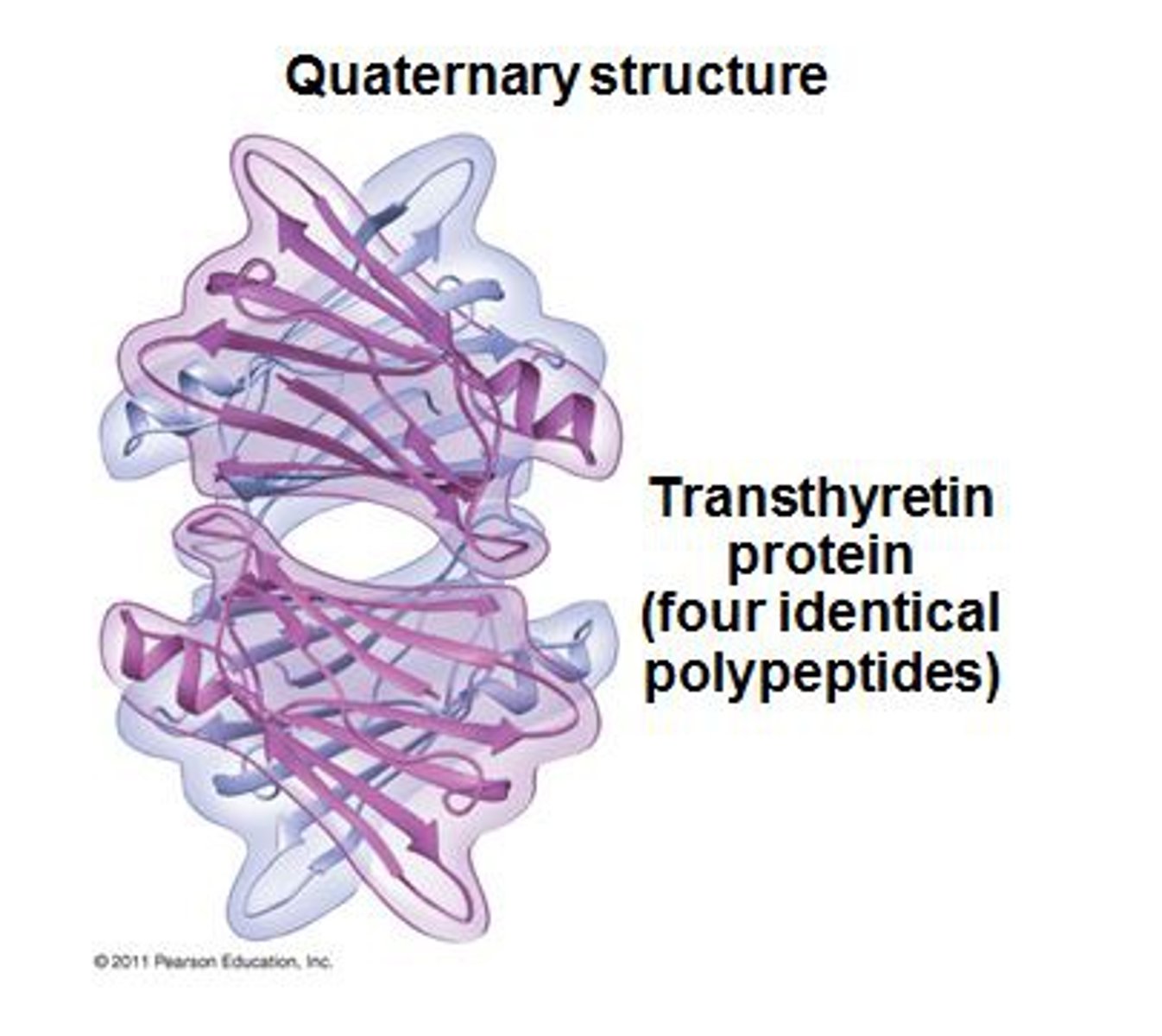
Quaternary structure of proteins
How multiple polypeptide subunits of a protein interact.
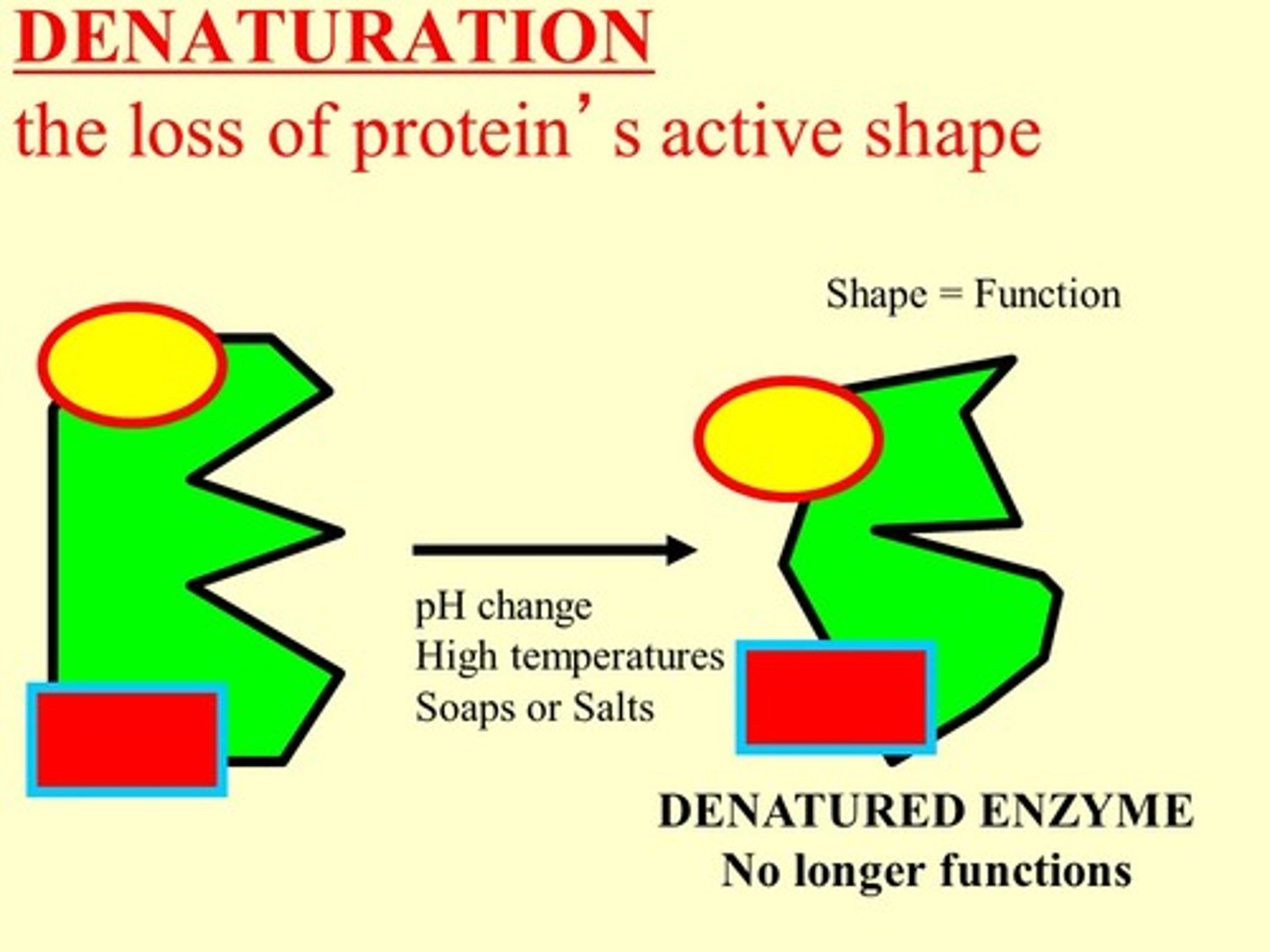
Denaturation
Protein structure changes, but primary sequences don't. Can be reversed, but function of protein is lost.
Catalyst
Helps increase the speed at which the reaction takes place by lowering the activation energy to start the reaction. Doesn't change the reaction or free energy.
Enzymes
Protein catalysts
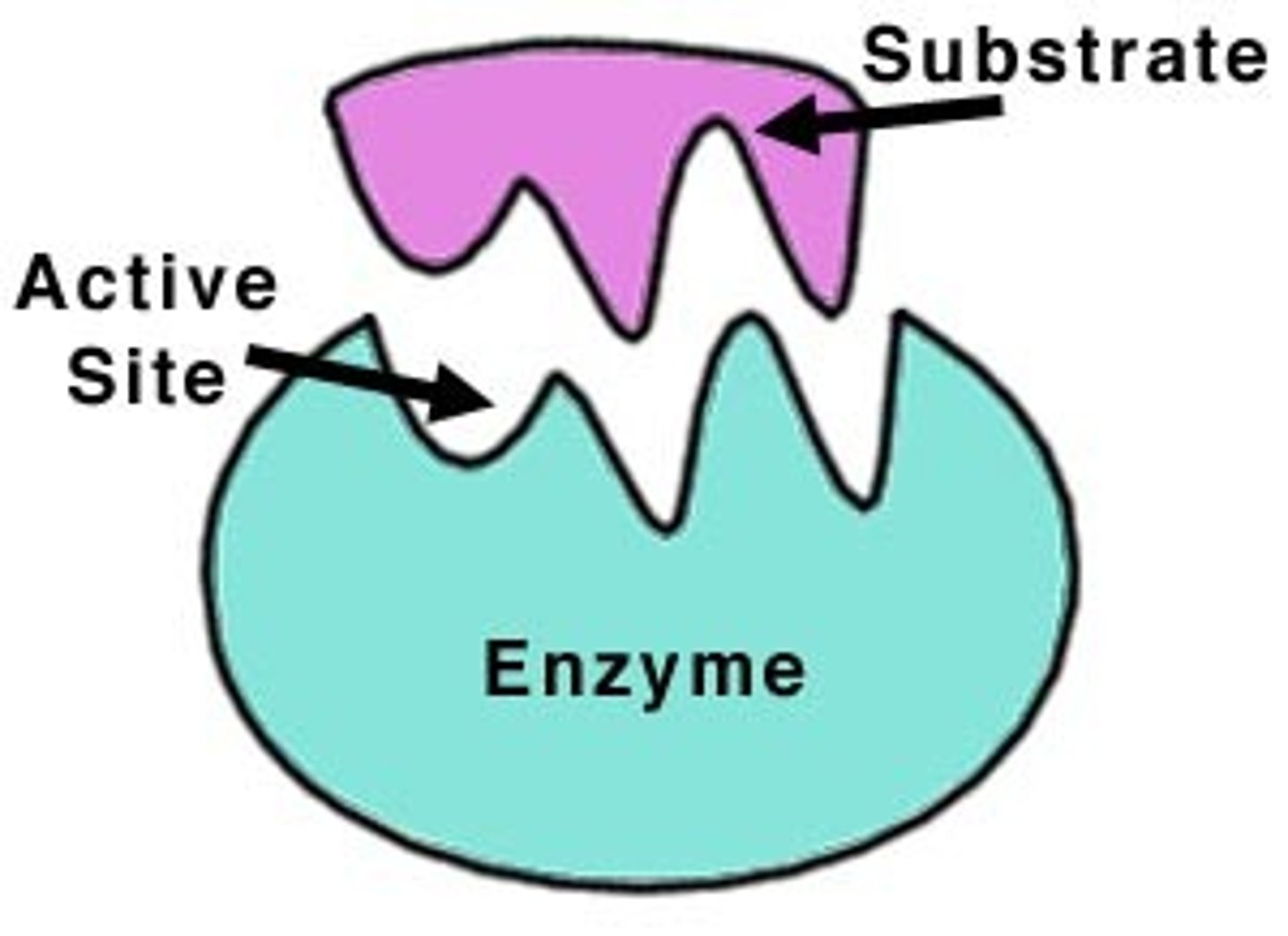
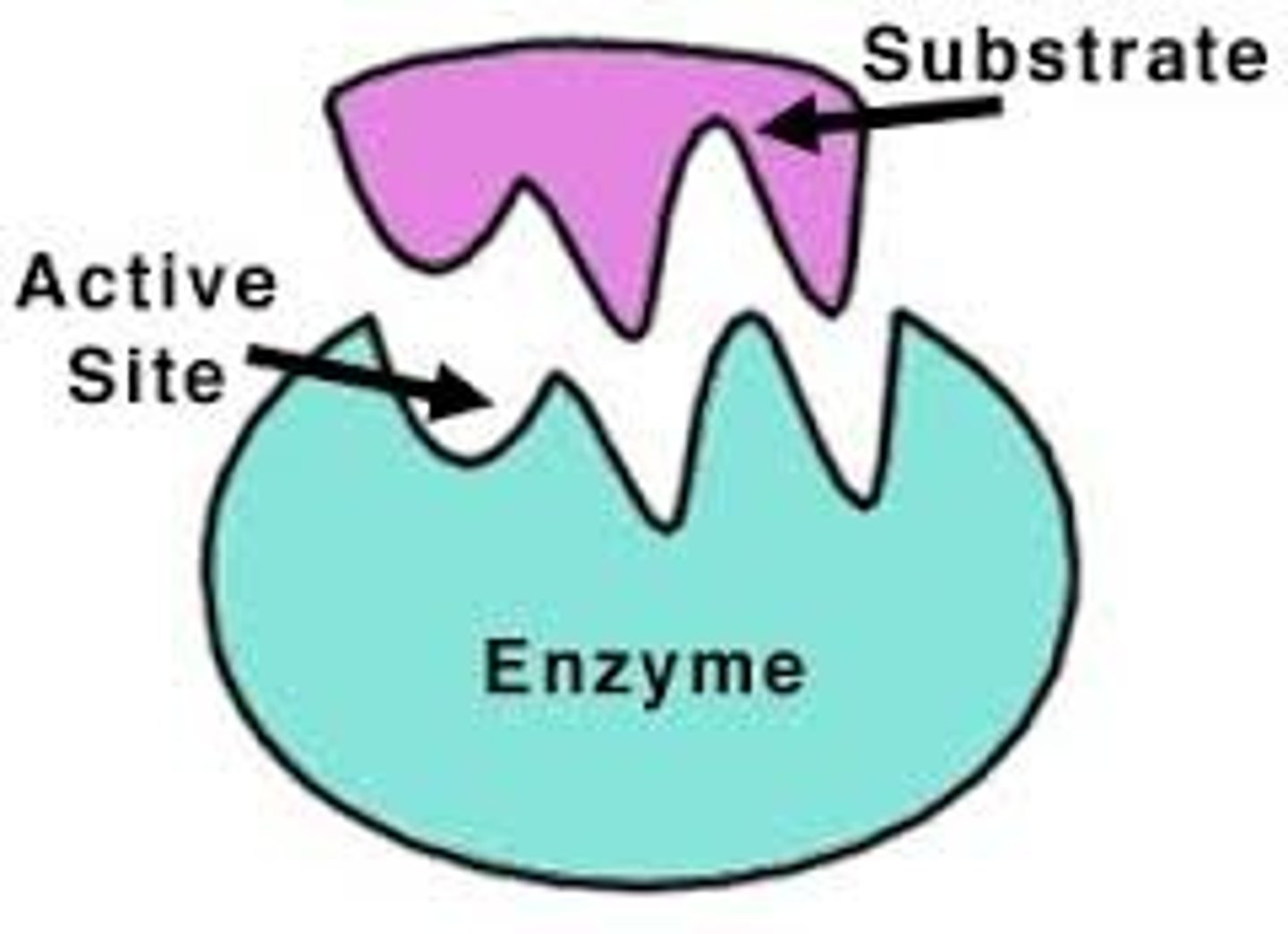
Substrates
The reactants that bind to the enzyme
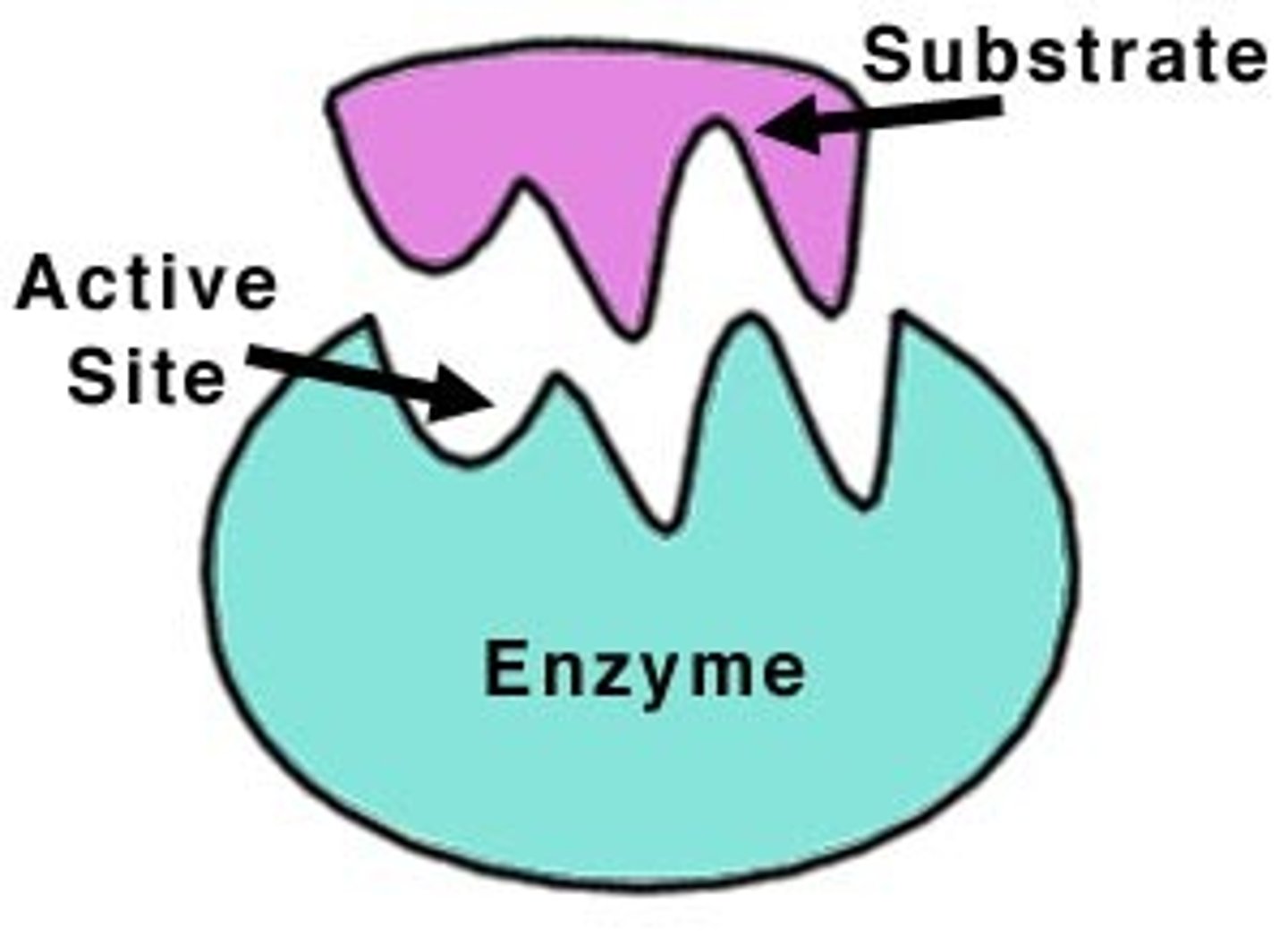
Active sites
the site on an enzyme that attaches to a substrate
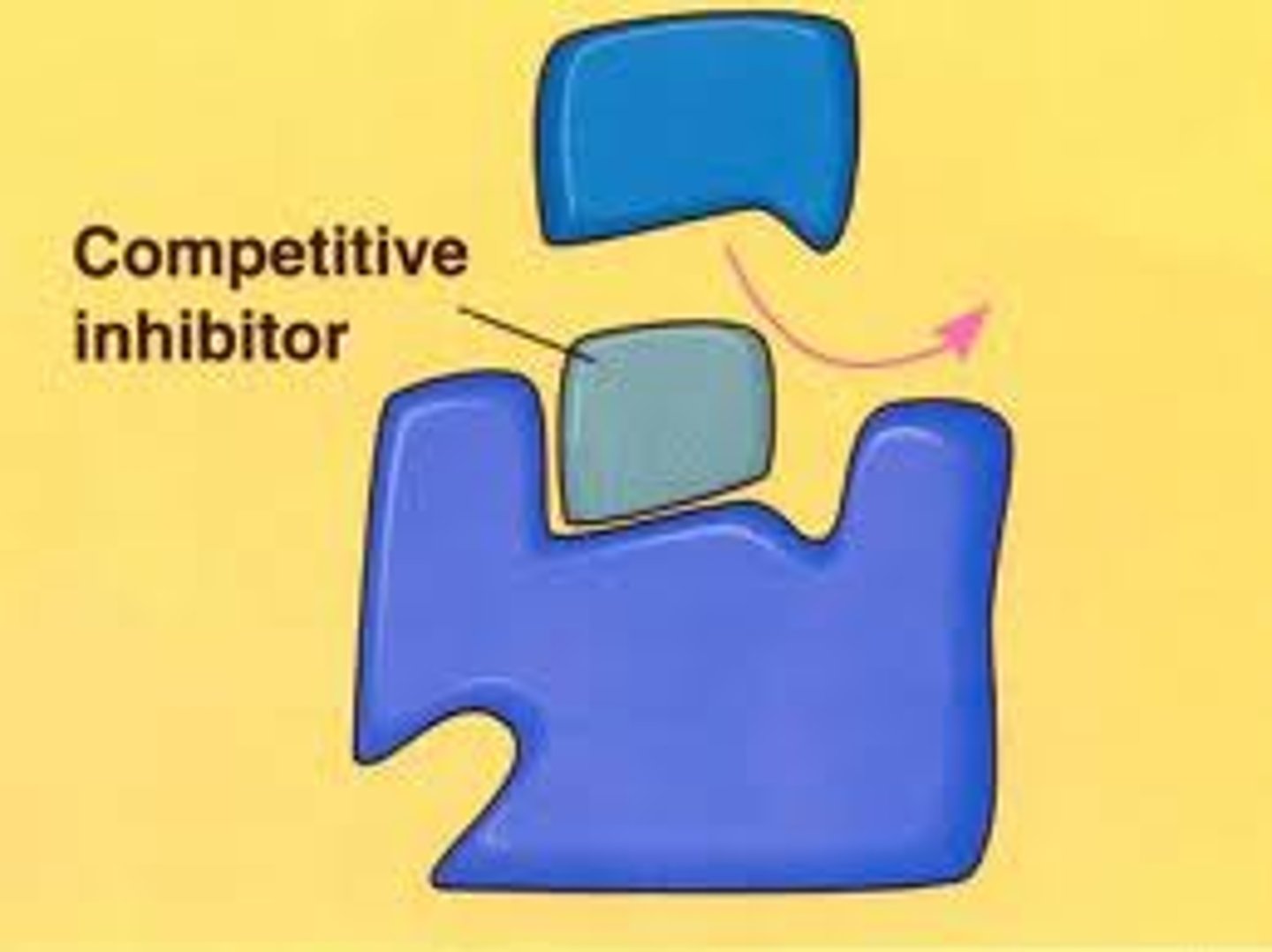
Competitive inhibition
Competes with the substrate for the active site

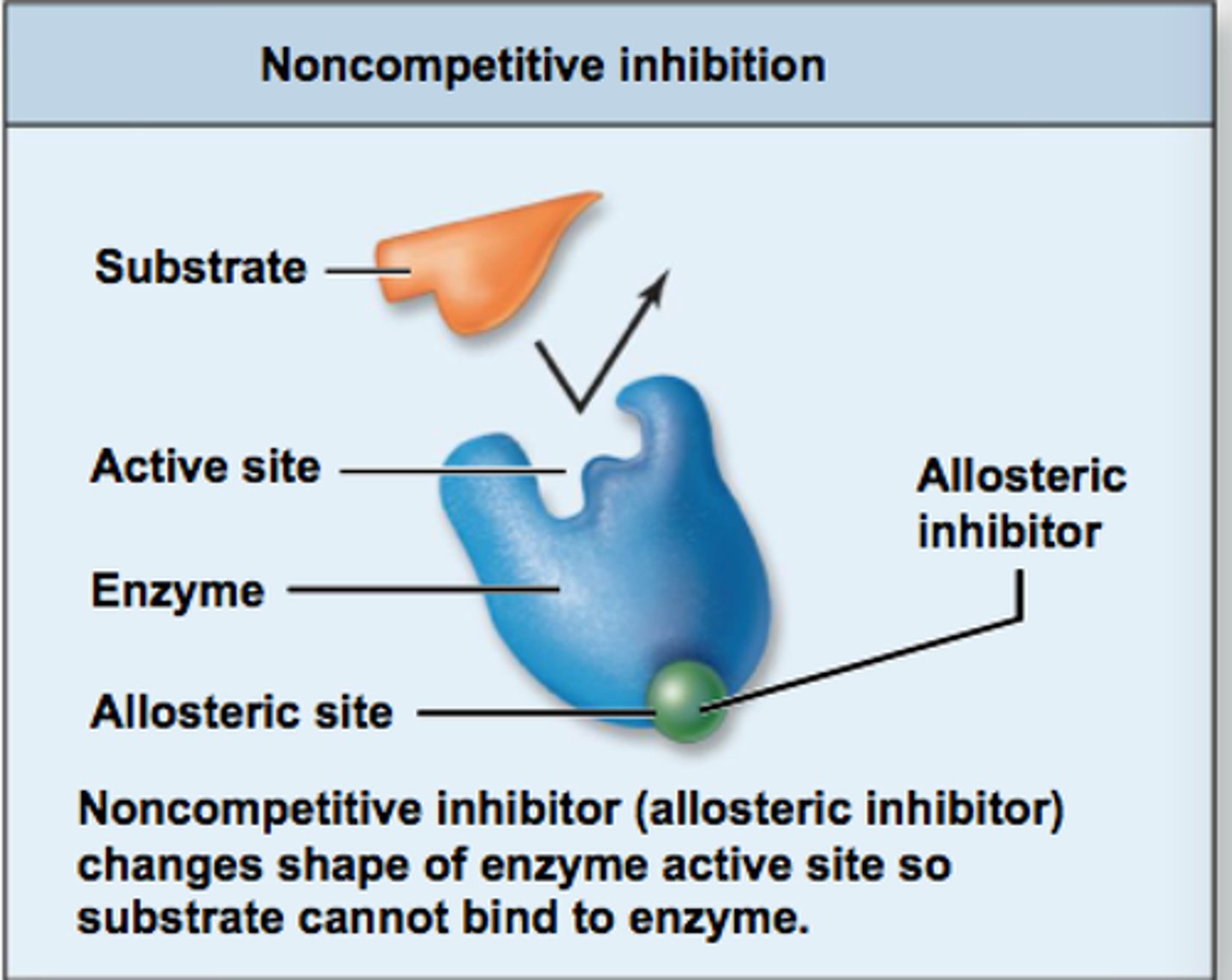
Noncompetitive inhibition (Allosteric inhibition)
Alters enzyme elsewhere.
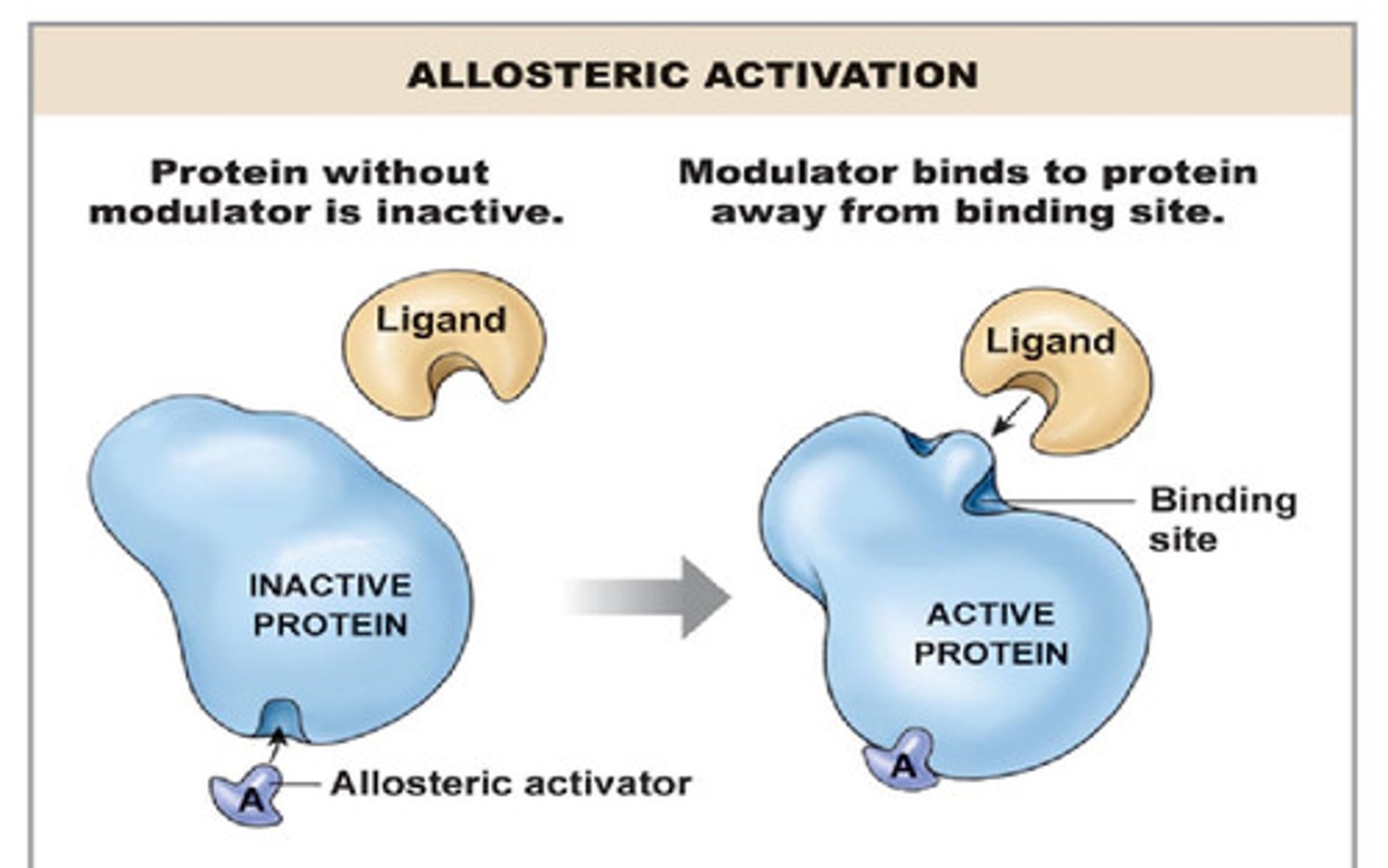
Allosteric activation
Changes the binding site to fit the substance.
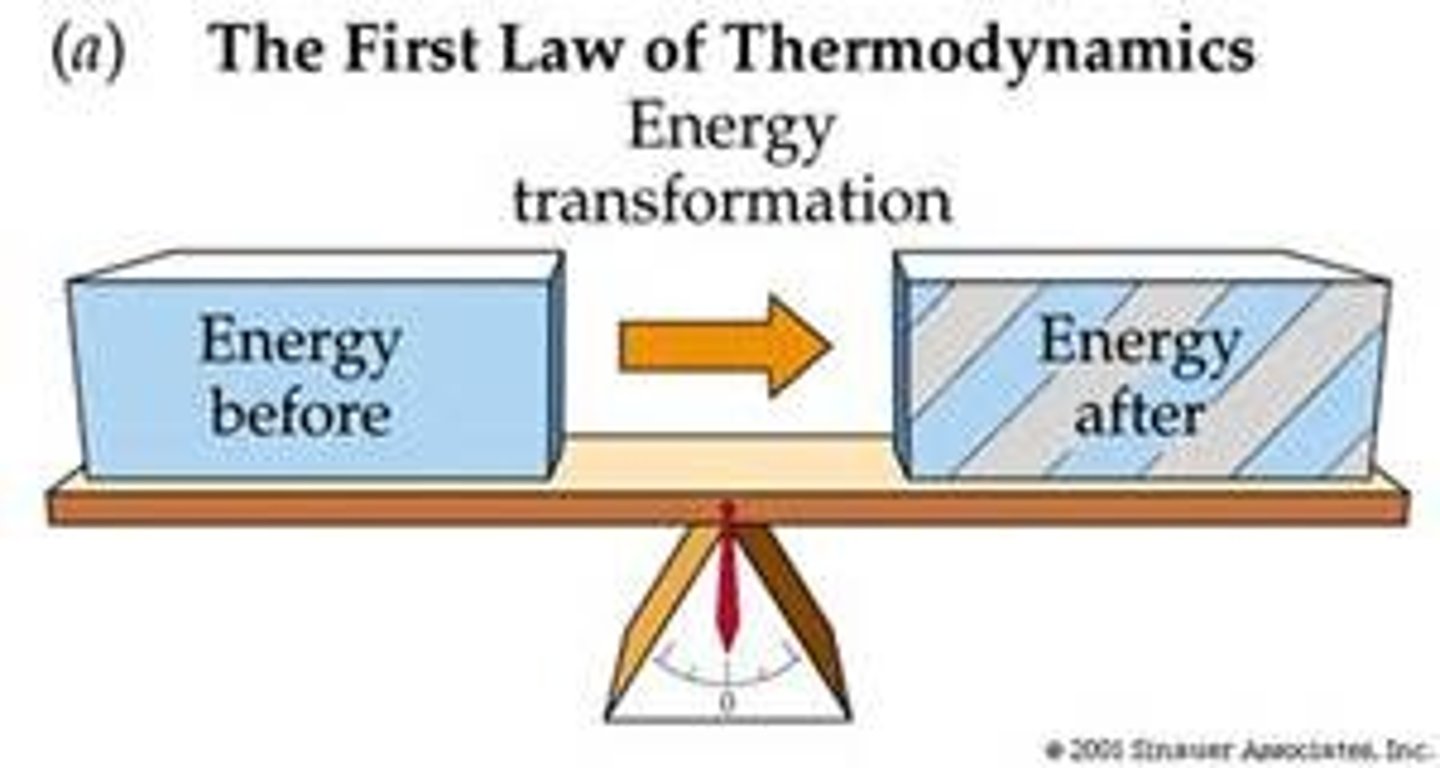
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Energy is constant, it can be moved but not created or destroyed
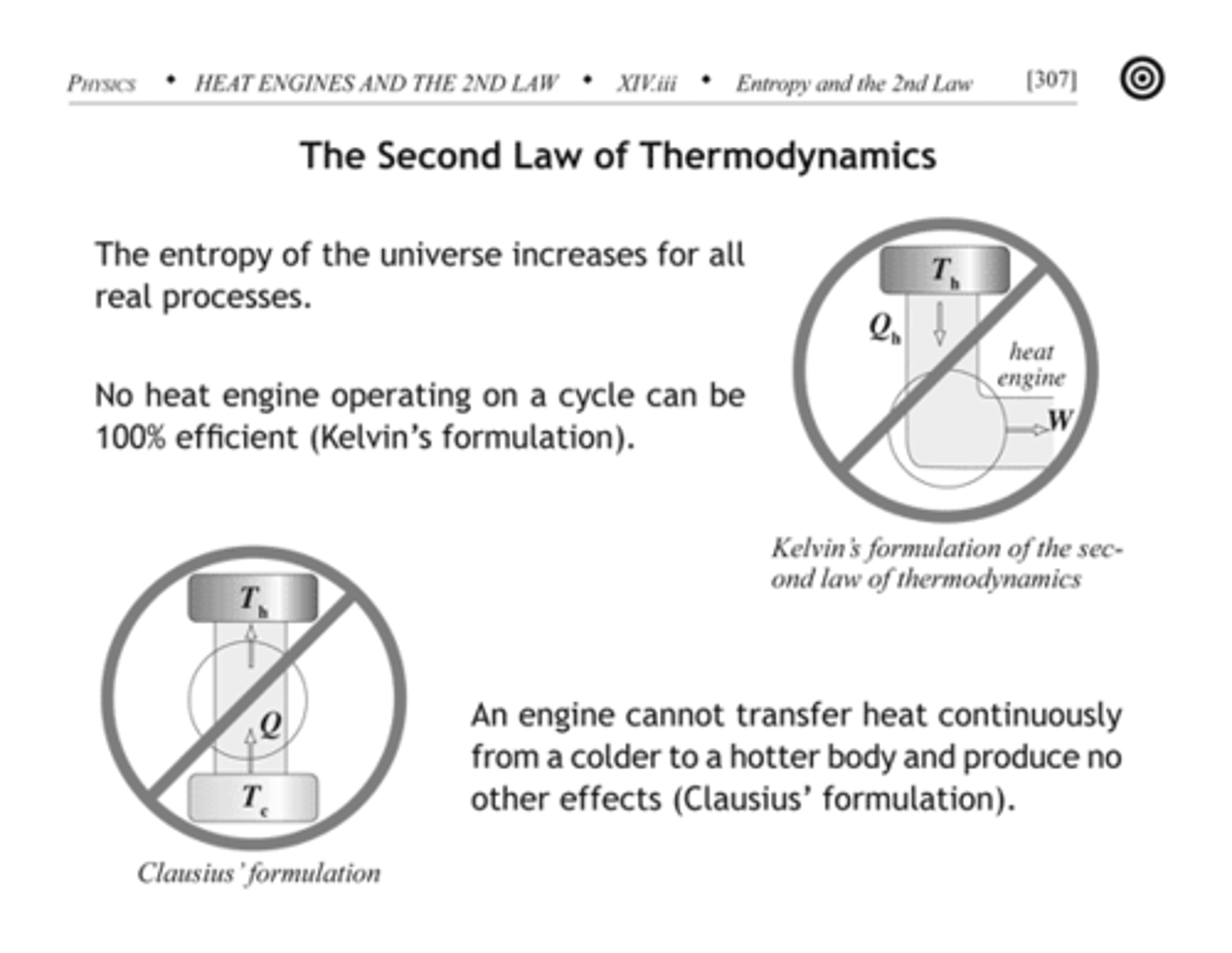
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
Every energy transfer or transformation increases the entropy of the universe.
Gibbs Free Energy (Enthalpy)
Amount of energy available and useful to do work ΔG
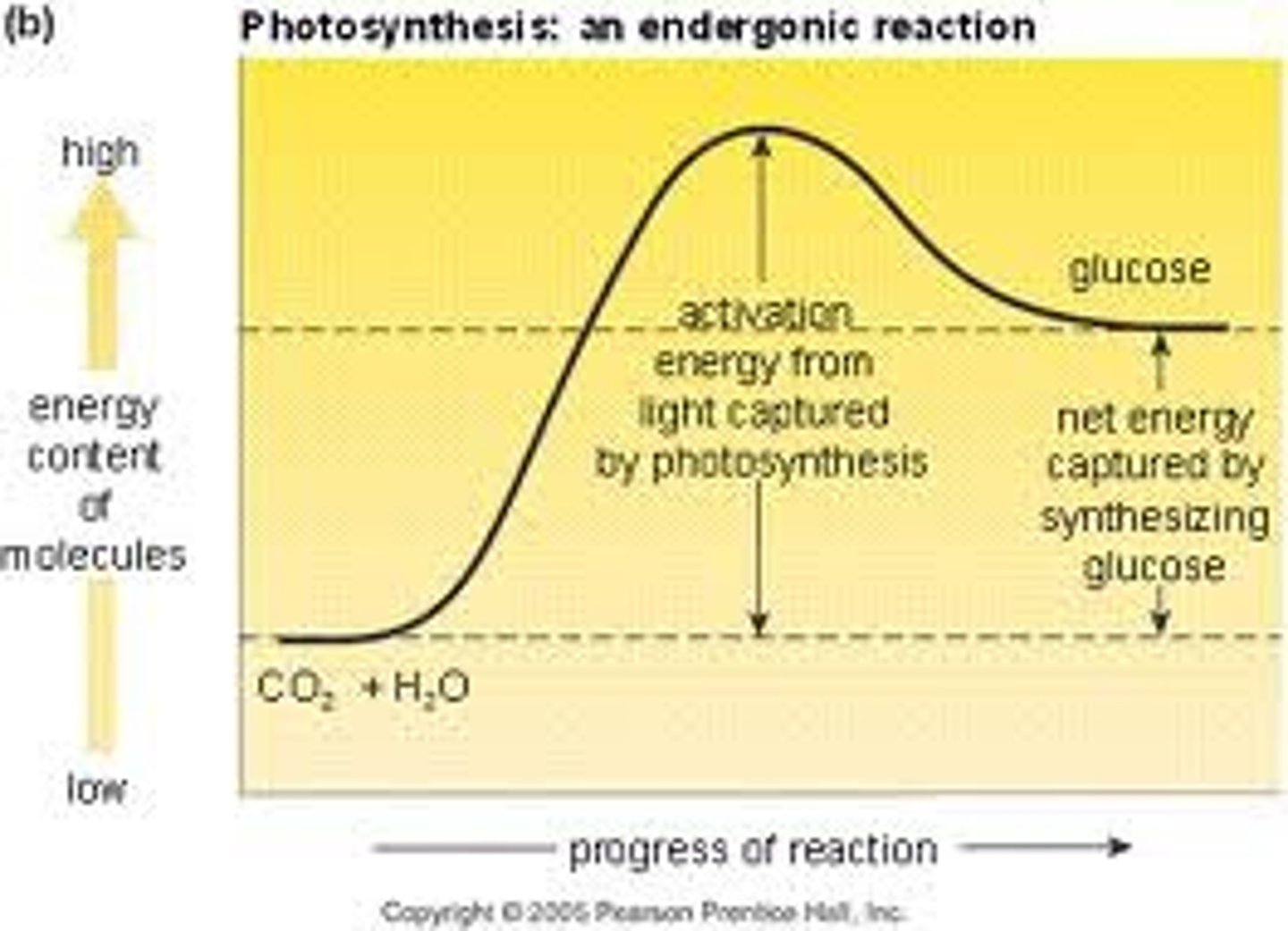
Endergonic
The free energy in a system increases (unfavorable) Absorbed ΔG>0
Exergonic
The free energy in a system decreases (Favorable) Released ΔG<0
OIL RIG
oxidation is loss, reduction is gain
Oxidation half reaction
Loses an electron, becomes positively charged (Reducing agent)
Reduction half reaction
Gains an electron, becomes negatively charged (Oxidizing agent)
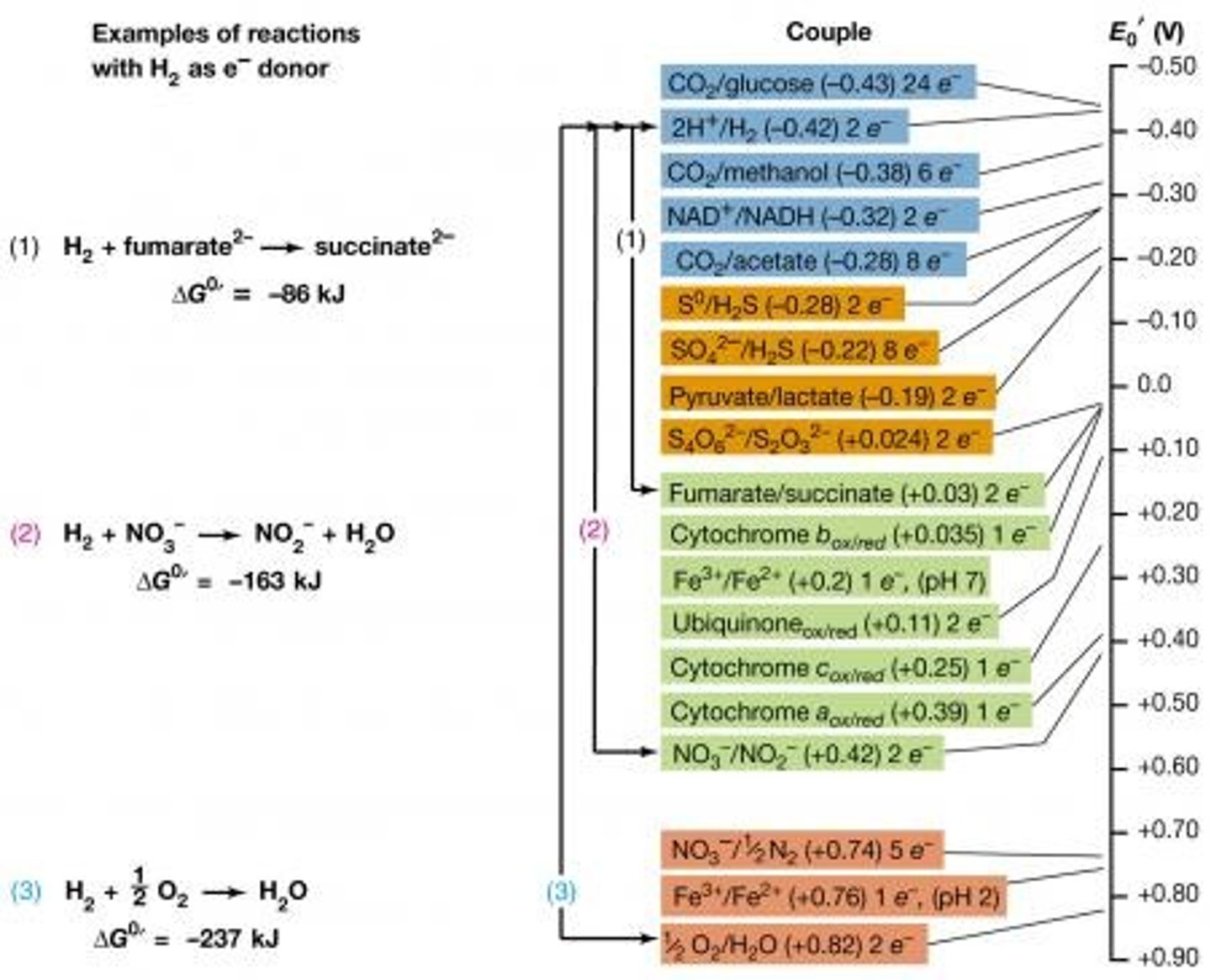
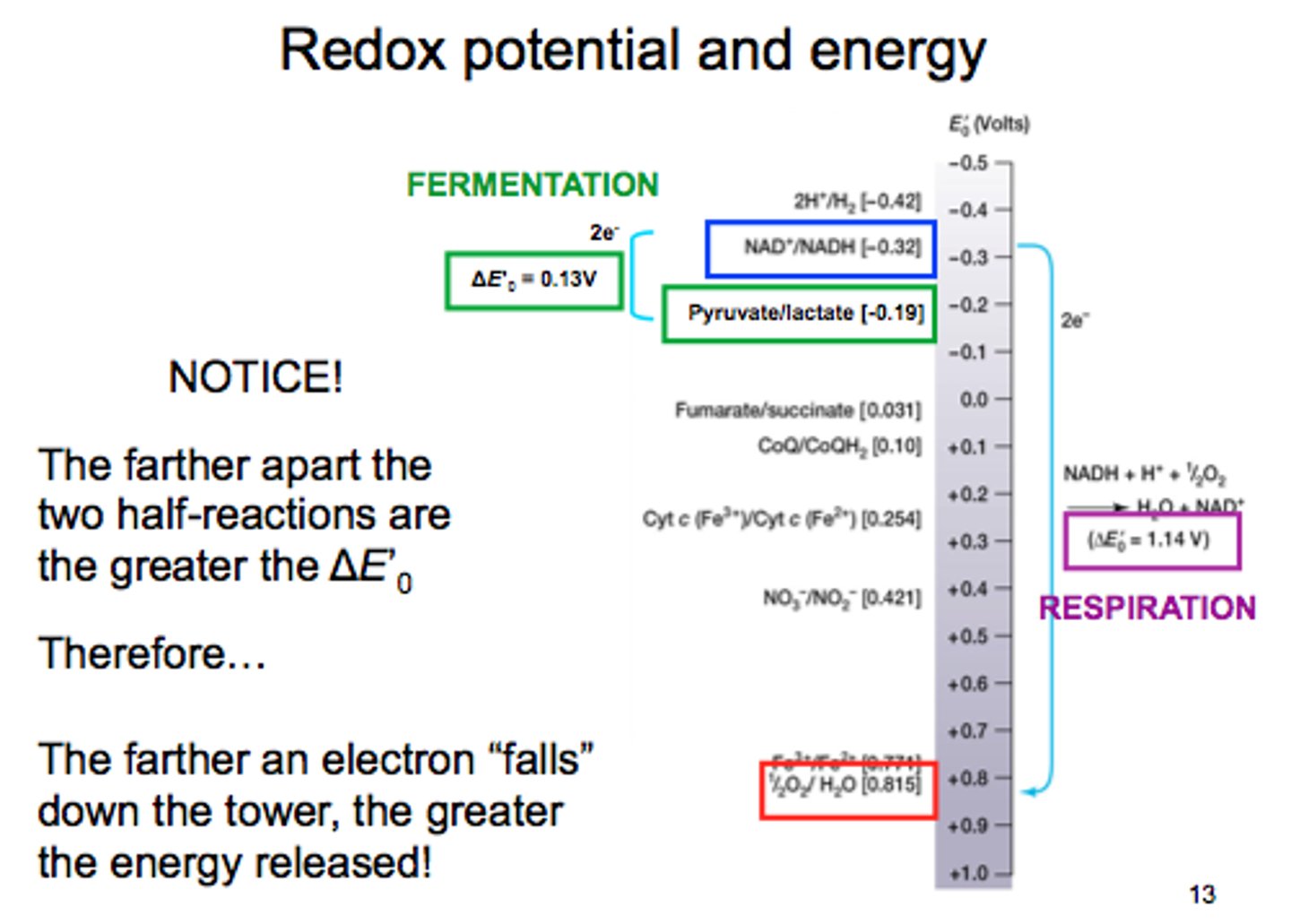
Electron Tower
Tool that ranks different half reactions
A+B -> A+ + B-
Oxidation half: A ->A+
Reduction half B ->B-
The Reduction potential
the tendency of a substance to gain electrons
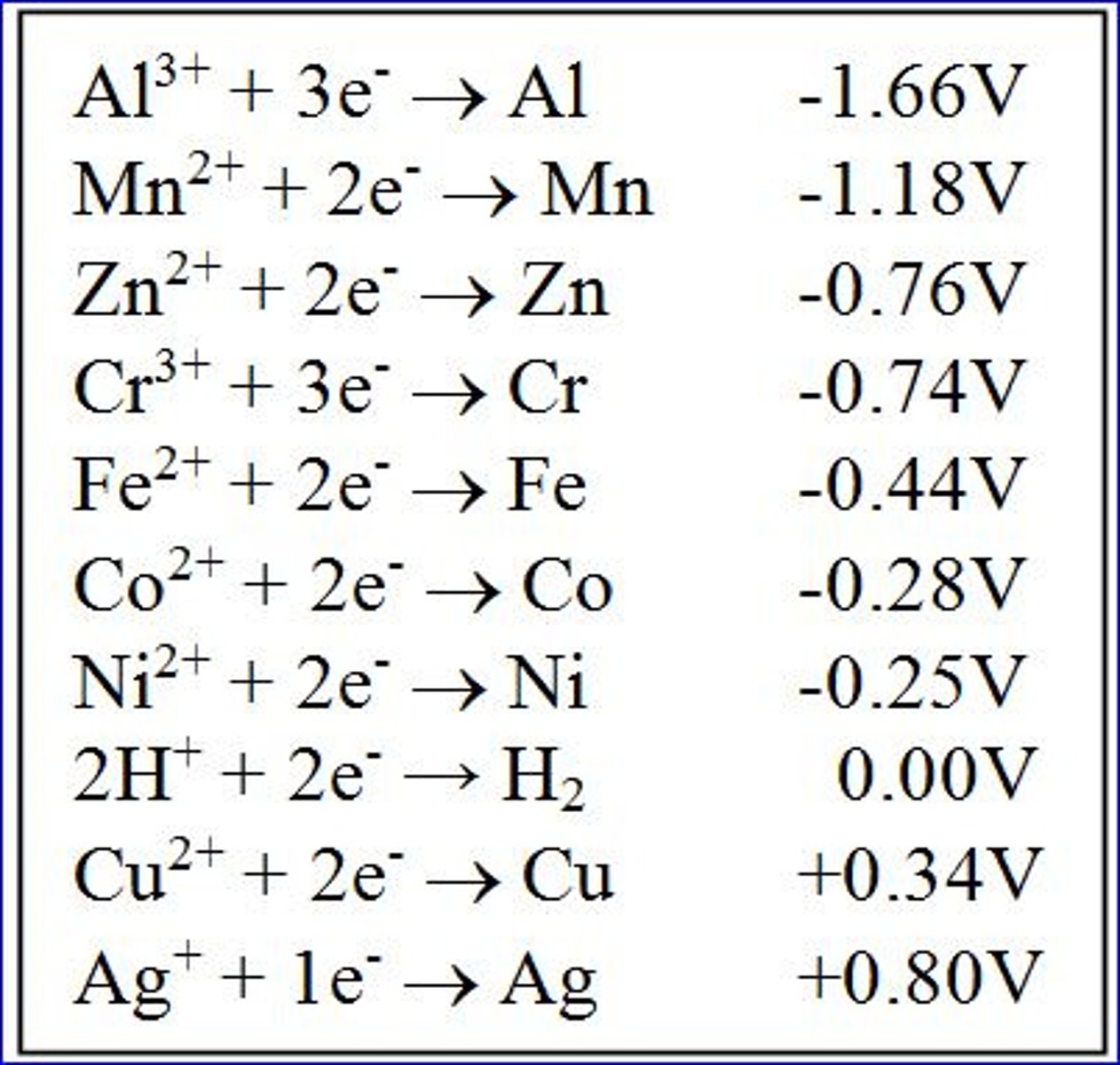
Redox Tower
Tool that ranks the ability to accept or donate in relation to other half reactions. The more positive it is, the more likely it is to accept electrons
ΔG = -nFΔE
ΔG = Gibbs Free energy
-n= Number of moles of electrons transferred
F= Constant 96.485 kJ/V
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work