BIO 201: Chapter 4.2 Gross Anatomy of the Nervous System - The Brain
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
66 Terms
brain
complex mass of nerve, connective, and epithelial tissue that is divided into 4 anatomical and functional regions
cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, and brainstem
4 anatomical and functional regions of the brain
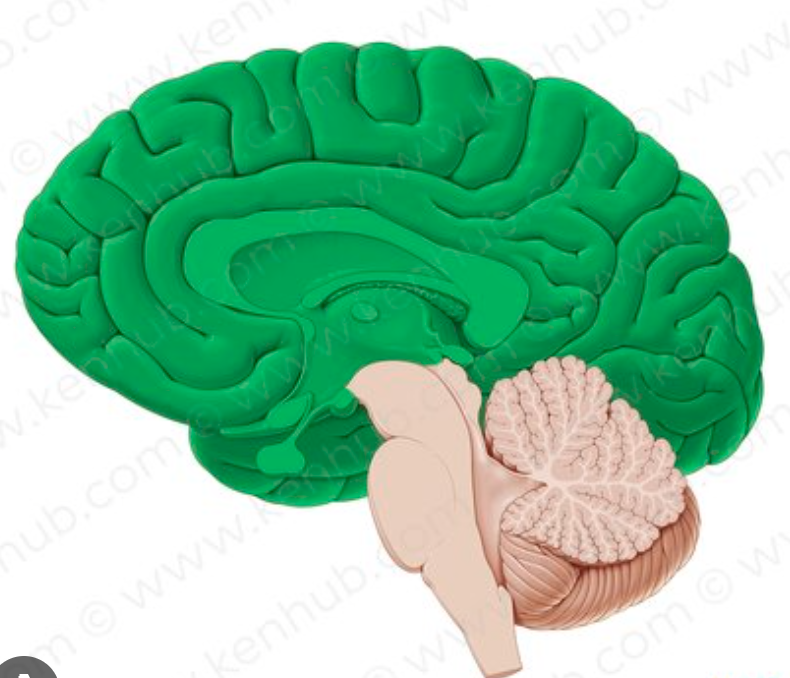
cerebrum
largest region that occupies most of the space in the cranial cavity
split into 2 cerebral hemispheres and made up of 4 lobes
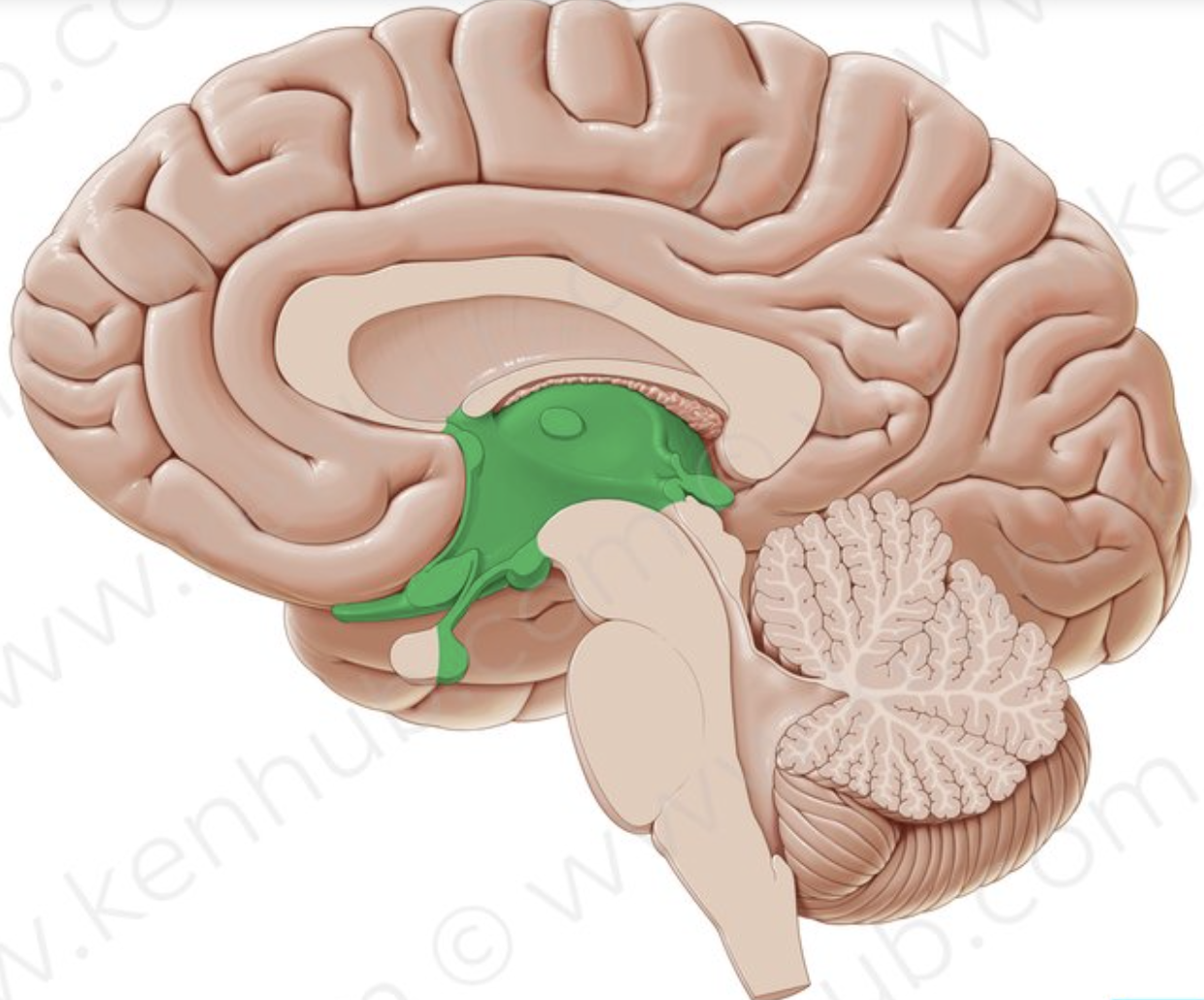
diencephalon
pair of oval shaped structures deep into the cerebrum
contains multiple nuclei
gateway to the cerebral cortex
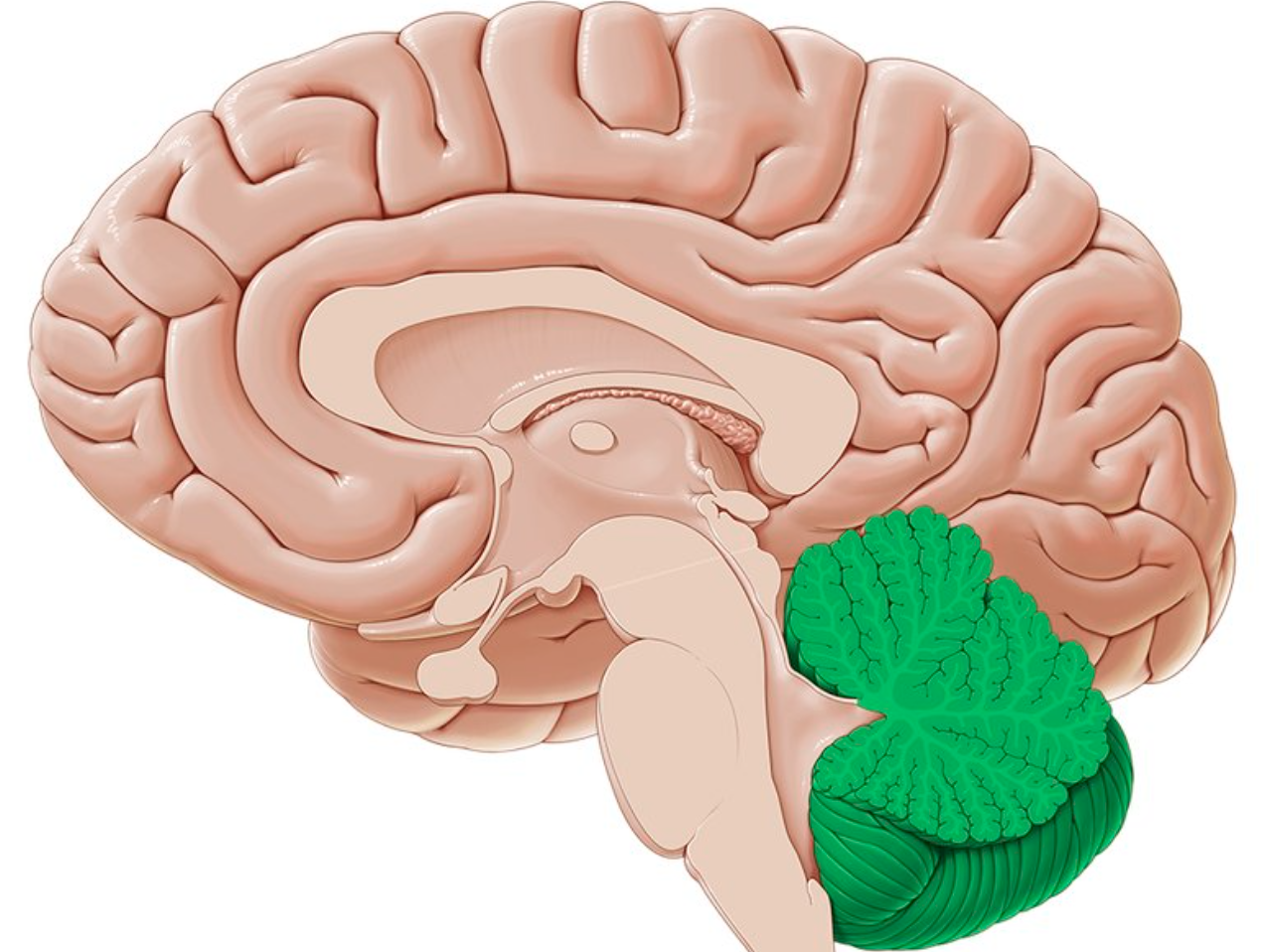
cerebellum
second largest region of the brain
consists of a left and right cerebellar hemispheres
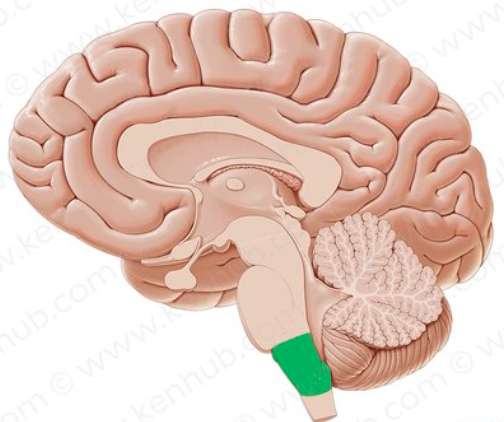
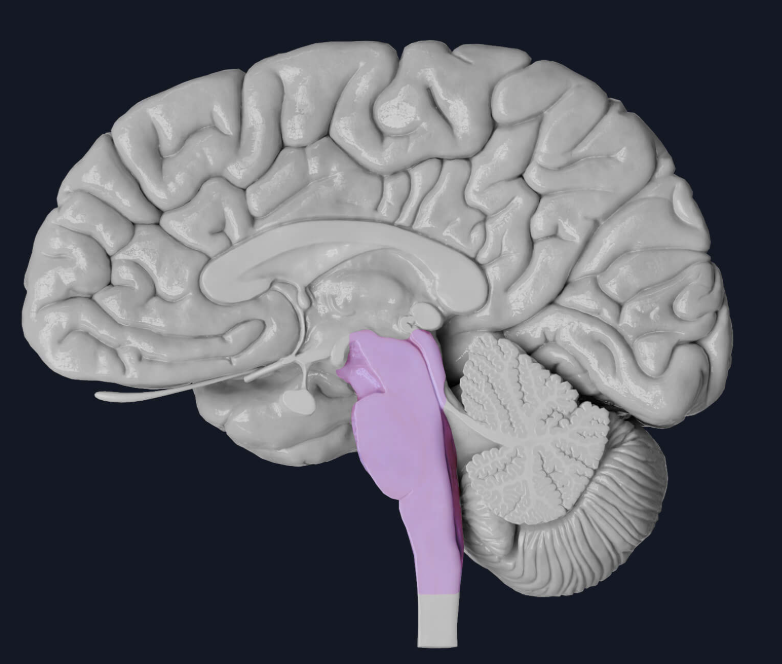
brainstem
long structure that extends inferiorly from the diencephalon
10 of the 12 cranial nerves originate from here
made up of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
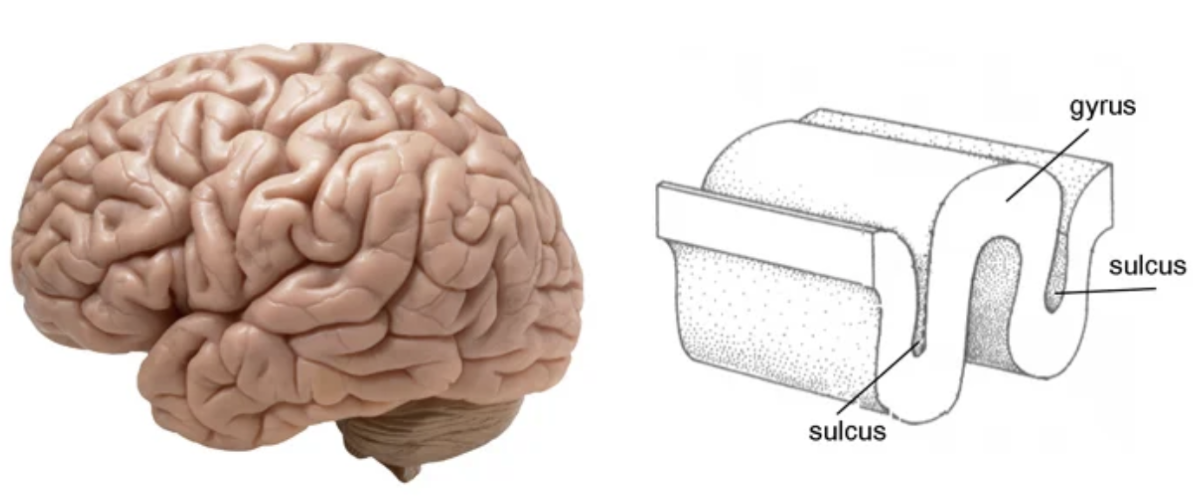
fissures
deeper grooves or furrows that usually separate bigger parts of the brain
sulci
shallow grooves found in the cerebrum
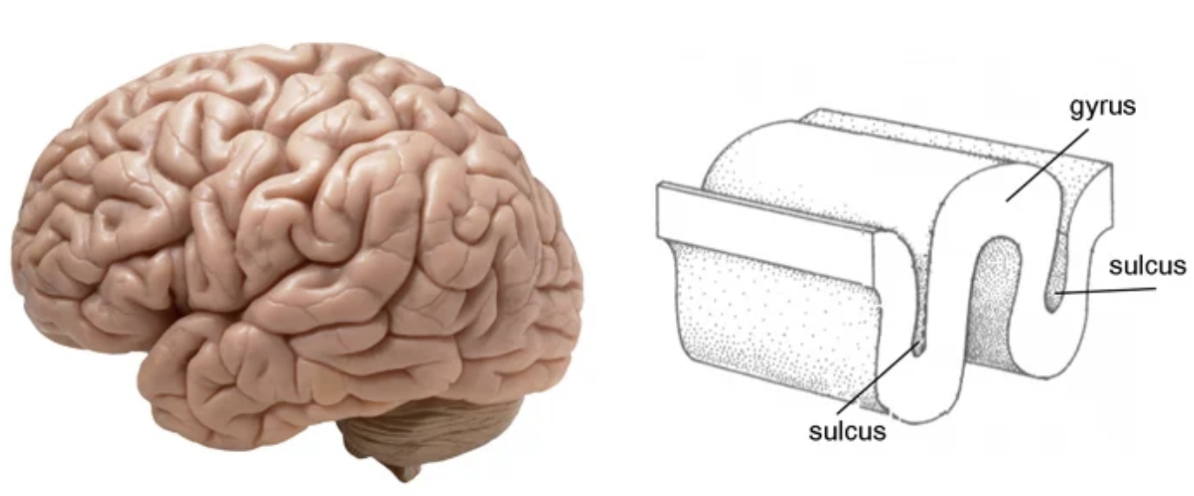
gyri
folds found in the cerebrum
gray matter
located superficial in the cerebrum and cerebellum
composed of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses
nuclei
deeper masses of gray matter surrounded by white matter
white matter
lies deep to the gray matter
composed of bundles of axons and tracts
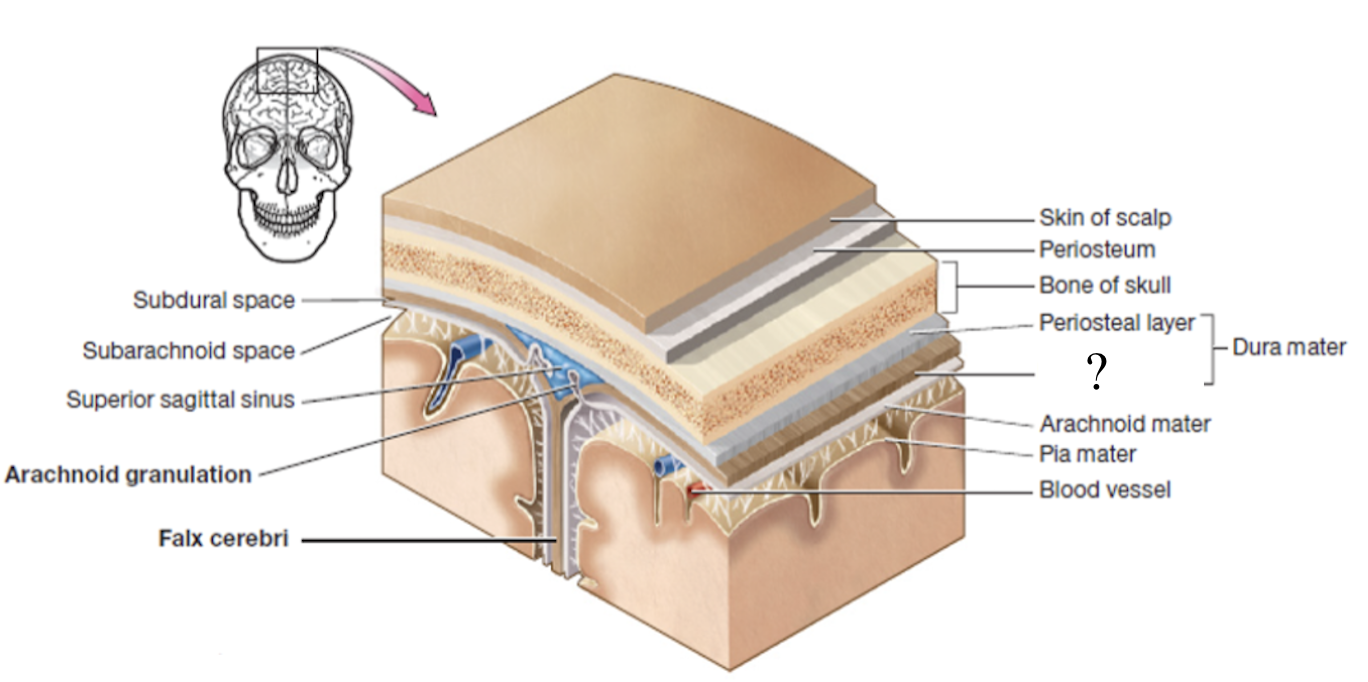
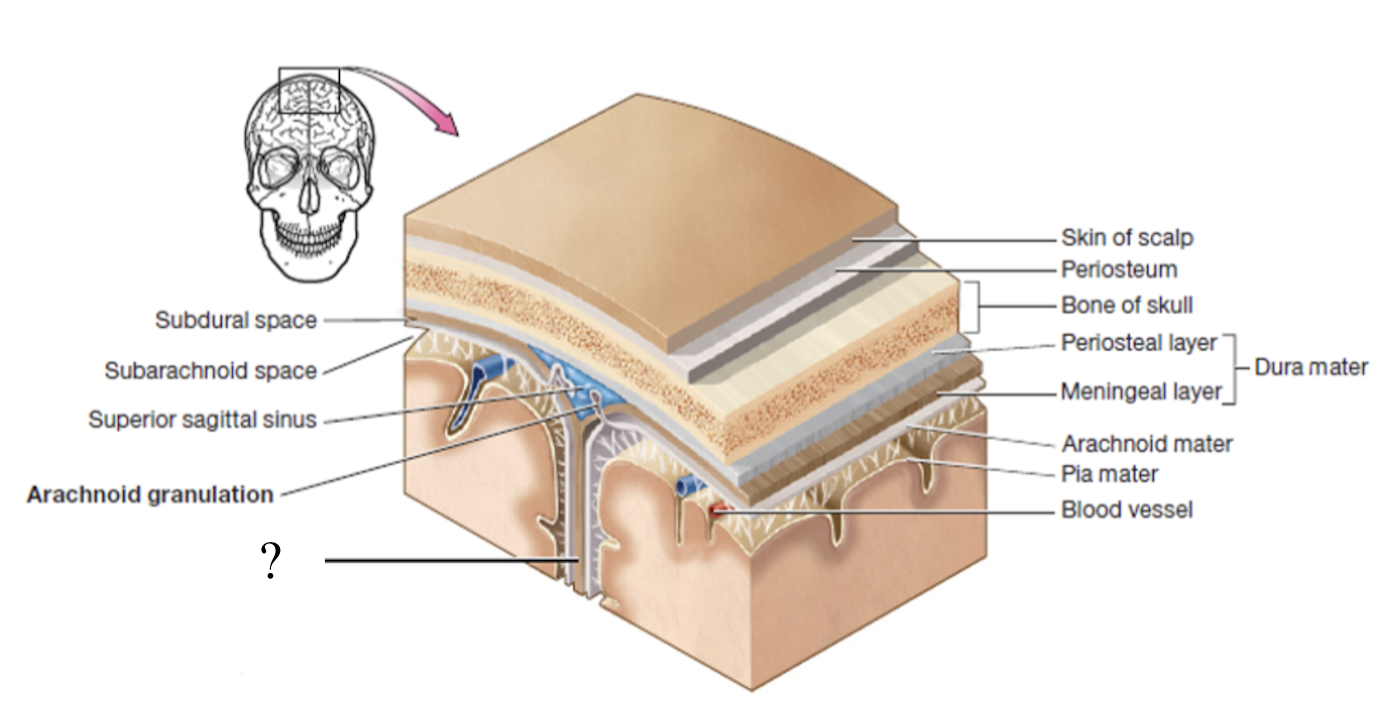
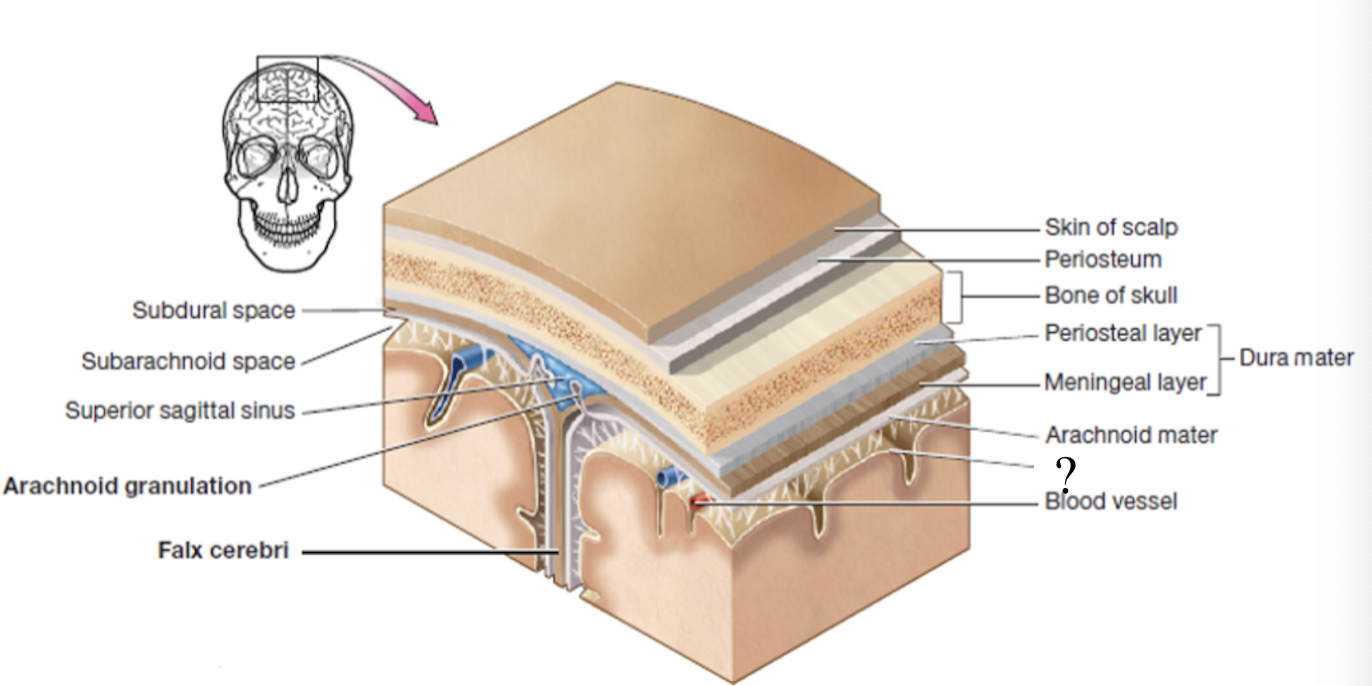
meninges
set of 3 connective tissue membranes that surround the brain and spinal cord
dura mater
most superficial cranial meninge layer that is tough to protect the brain
made up of 2 layers (periosteal and meningeal layers)
periosteal layer
outer layer of dura mater that surrounds the cranial bones
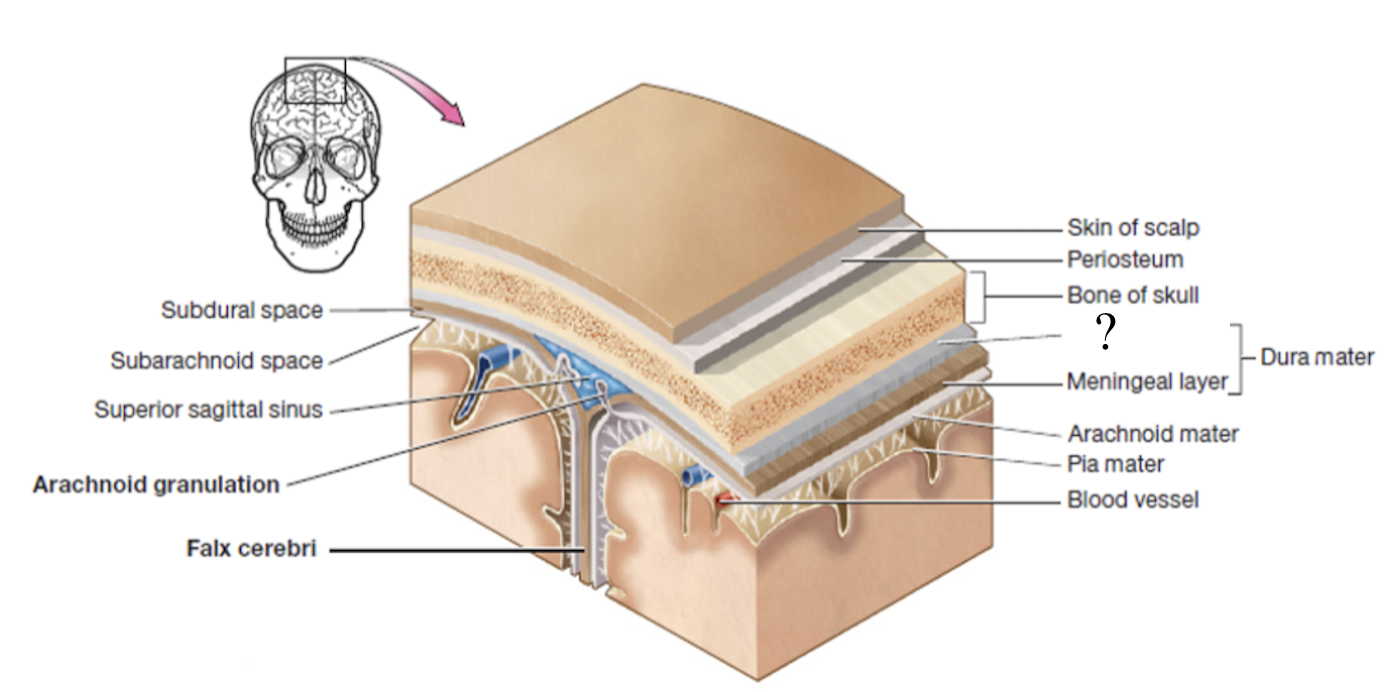
meningeal layer
inner layer of dura mater that faces the other meninges
formed by 3 structures: falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli, and falx cerebelli
falx cerebri
separates each cerebral hemisphere
located in the longitudinal fissure
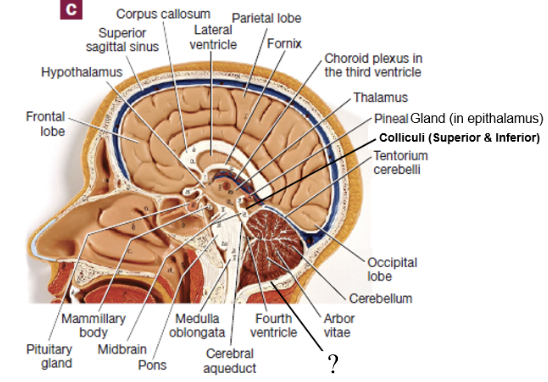
tentorium cerebelli
separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum
located in the transverse fissure
falx cerebelli
separates each cerebellar hemisphere
located inferior to the cerebellum
subdural space
potential space below the dura mater and above the arachnoid matter
potential space as it can be opened if needed in case of brain bleed
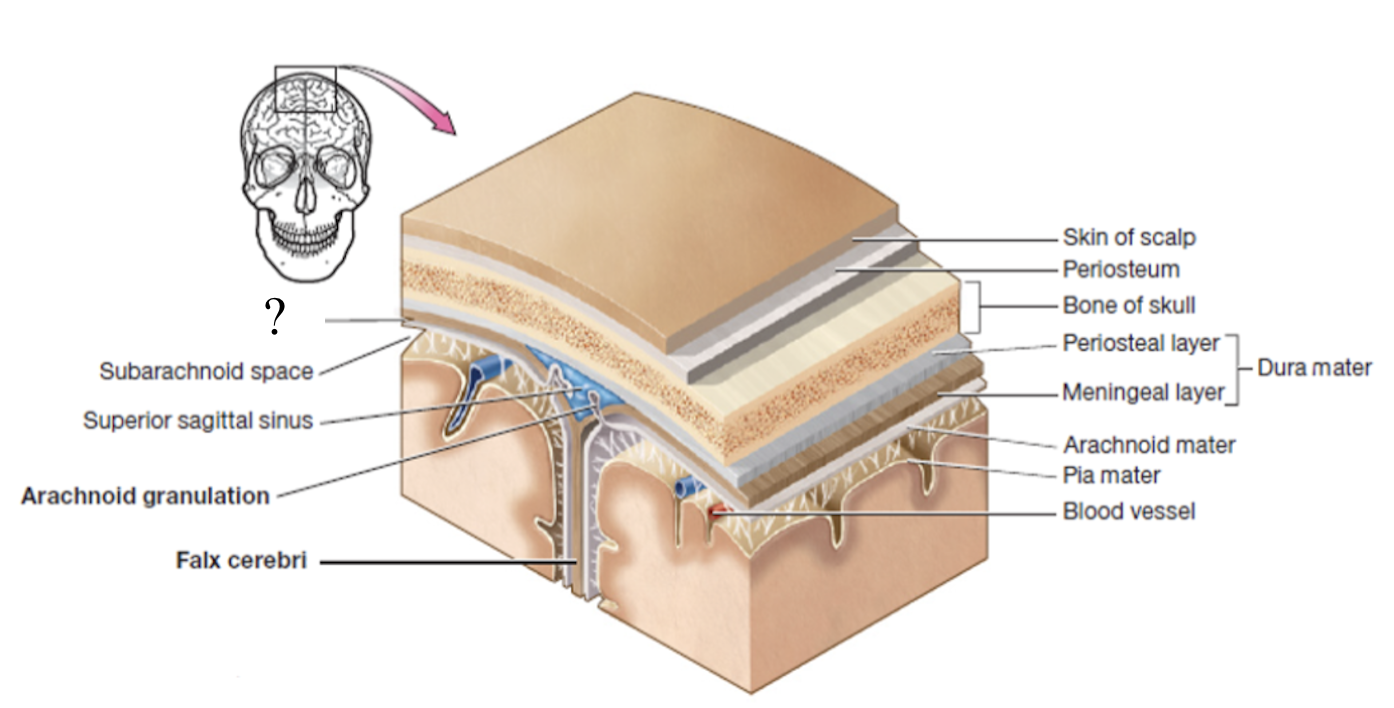
dural sinuses
spaces formed by the layers of the dura mater that collect deoxygenated blood and CSF circulated through the brain
ex: superior sagittal sinus
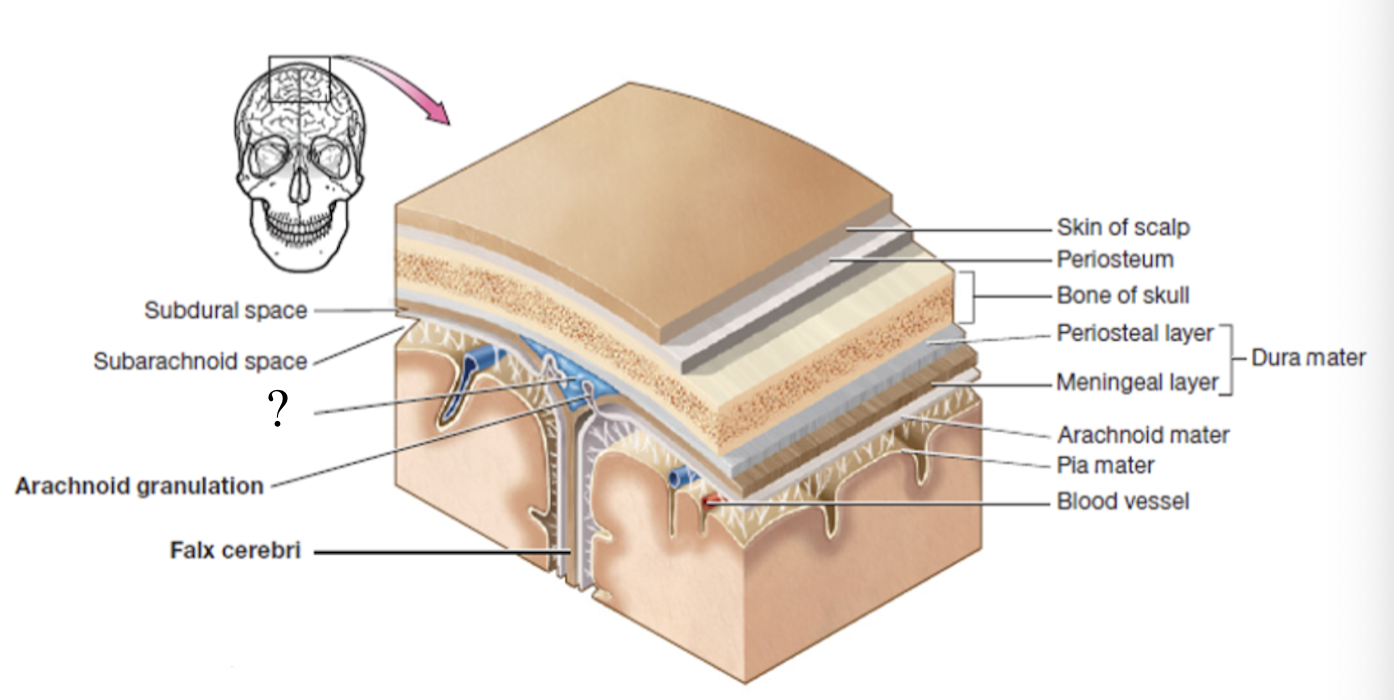
arachnoid mater
second layer of the cranial meninges that resembles a spider web and has small parts called arachnoid granulations
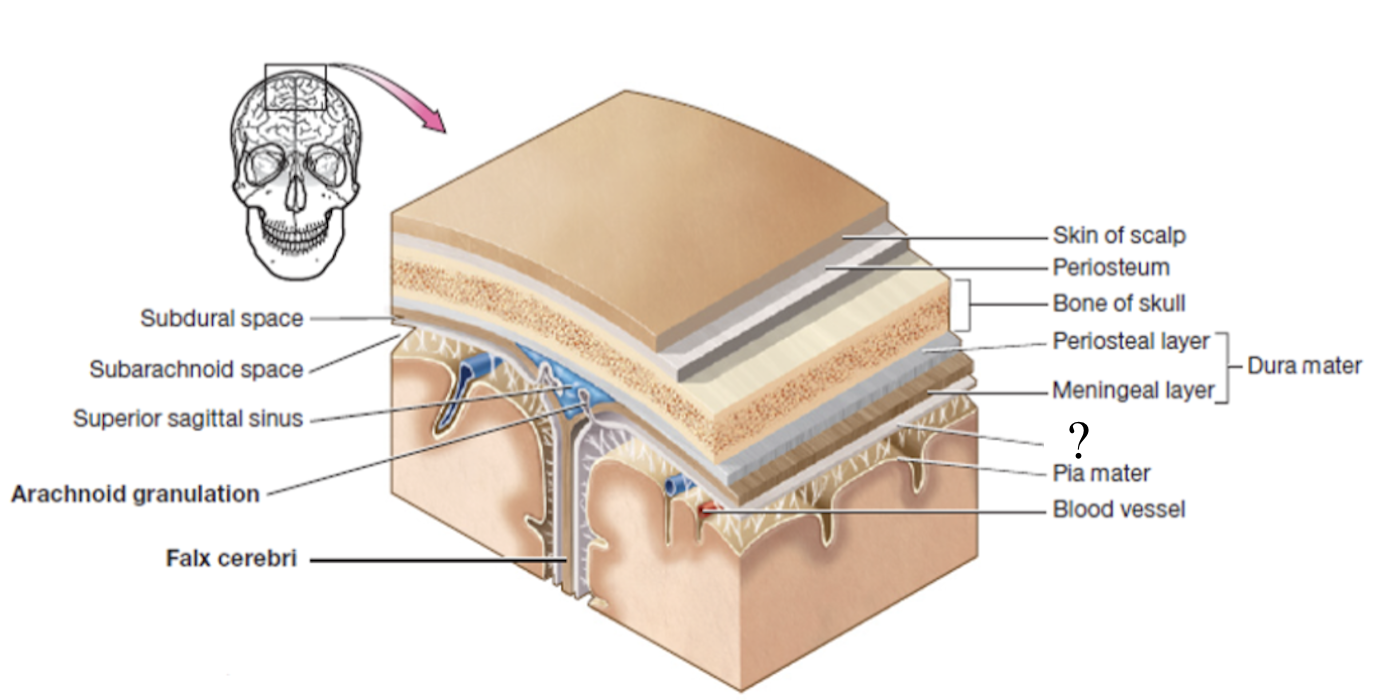
arachnoid granulations
tree-like protrusions piercing through the dura mater which absorb CSF into the dural sinuses
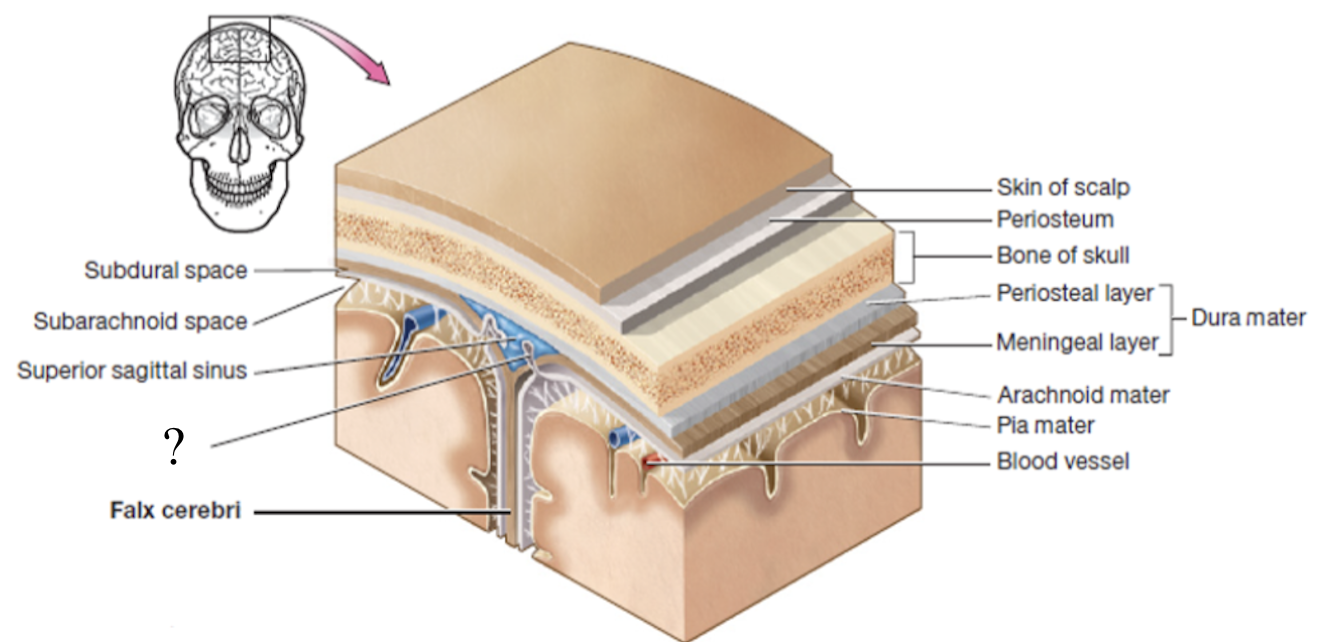
subarachnoid space
actual space below the arachnoid mater where CSF flows and surrounds the brain and spinal cord
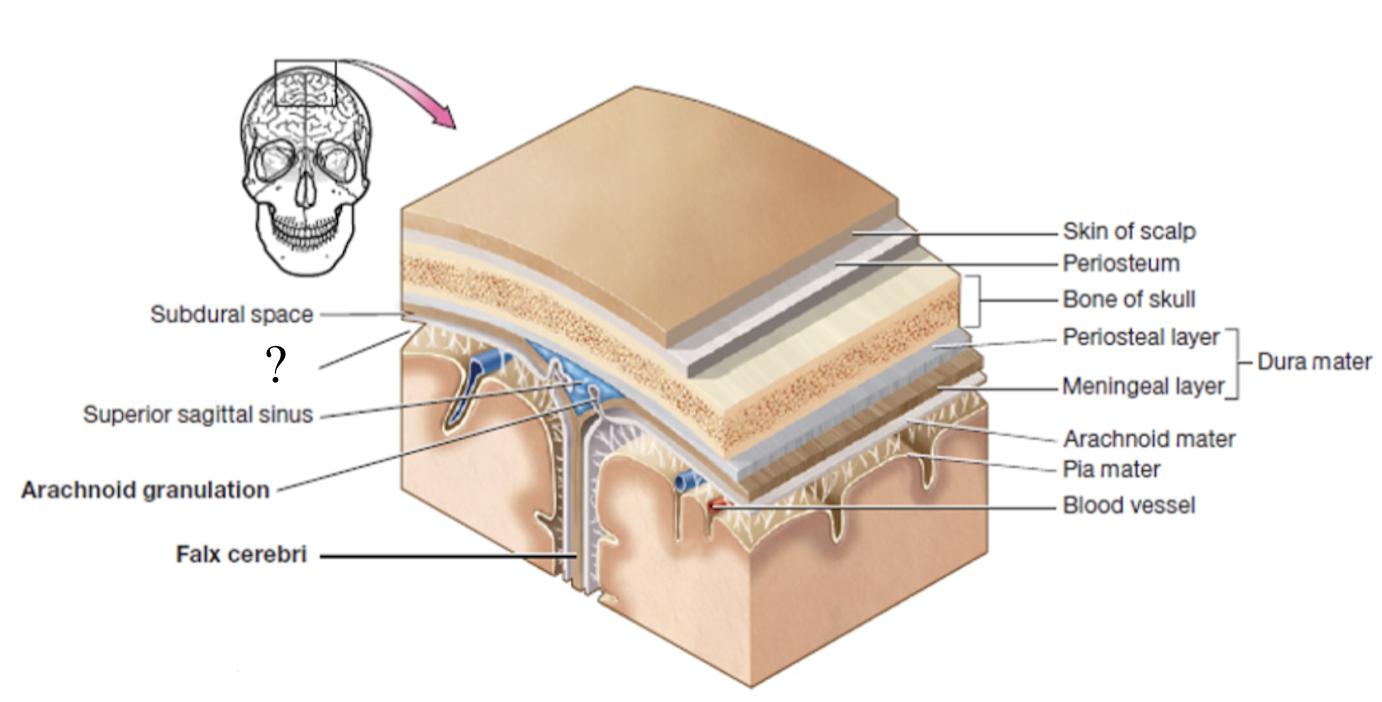
pia mater
deepest layer of the cranial meninges, very thin and closely follows every contour of the brain, including the sulci
ventricles
fluid filled cavities spaces located in different parts of the brain
choroid plexus
spongy mass of capillaries that line ventricles
lateral ventricles
aka the 1st and 2nd ventricles which form an arc with an anterior, posterior, and inferior horns and is located within the left and right cerebral hemispheres
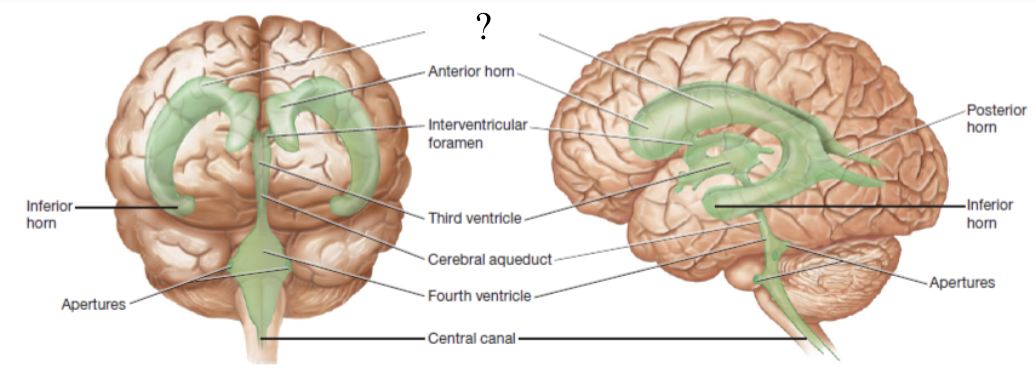
interventricular foramen
located inferior to the anterior horn and functions to connect the lateral ventricles to the 3rd ventricle
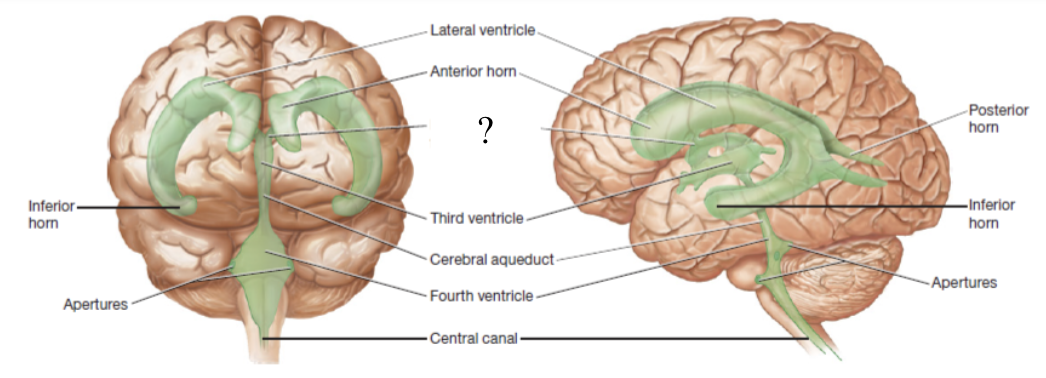
3rd ventricle
ventricle located below the corpus callosum and within the medial part of the thalamus
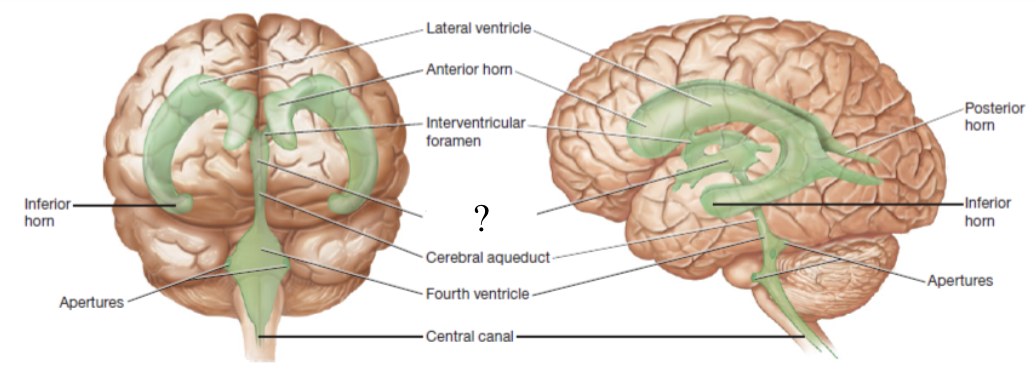
cerebral aqueduct
located in the midbrain and functions to connects the 3rd ventricle to the 4th ventricle
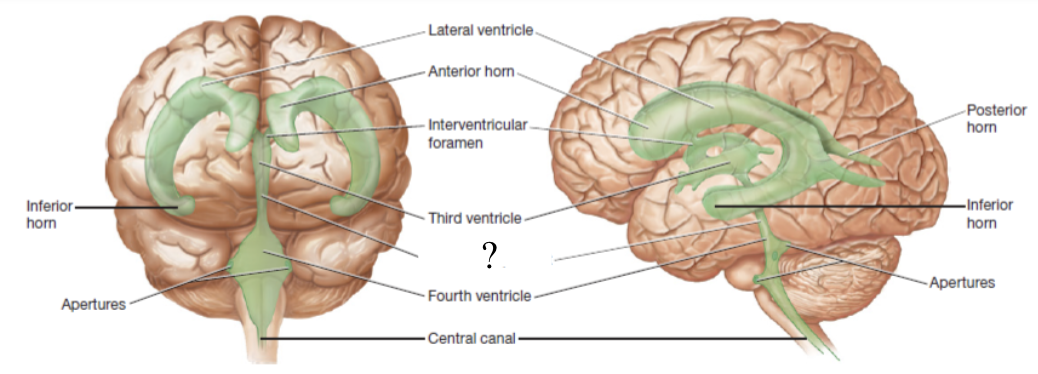
4th ventricle
ventricle located between the pons and cerebellum
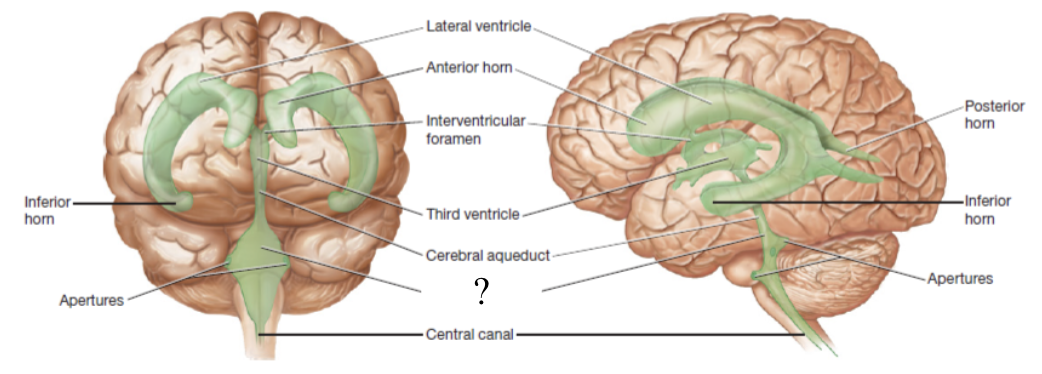
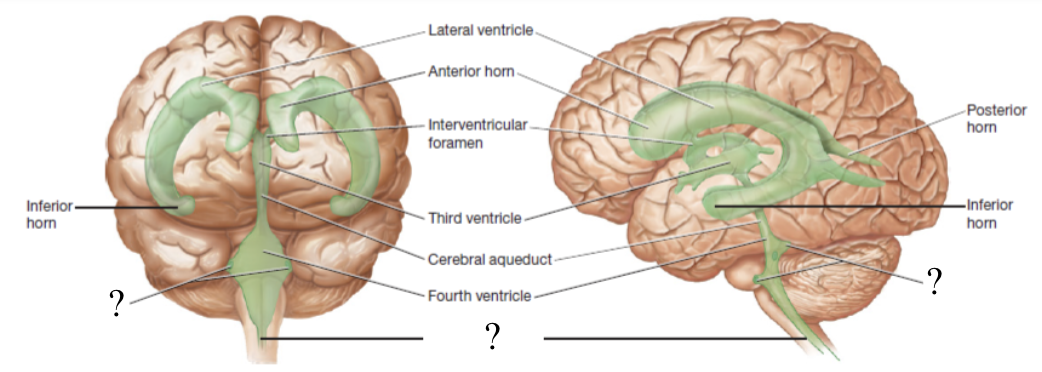
central canal and apertures
located by the medulla oblongata and function to drain CSF into the subarachnoid space
cerebrospinal fluid
clear and colorless fluid that flows in the ventricles to protect the brain
500, ependymal
about ____ mL/day of CSF is produced by _____ cells lining the choroid plexus found in each ventricle
functions of CSF
buoyancy: allows the brain to attain considerable size without being impaired by its own weight
protection: protects the brain from striking the cranium when head is jolted to prevent TBIs or concussions
chemical stability: rinses metabolic wastes from the nervous tissue and regulates its chemical environment
left and right lateral ventricles → interventricular foramen → third ventricle → cerebral aqueduct → fourth ventricle → apertures and central canal → subarachnoid space → reabsorbed by arachnoid granulations into the dural sinuses
CSF flow in the ventricles
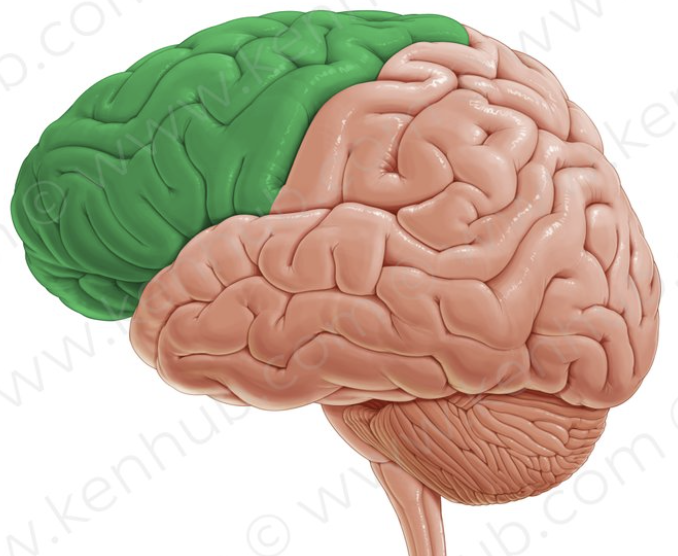
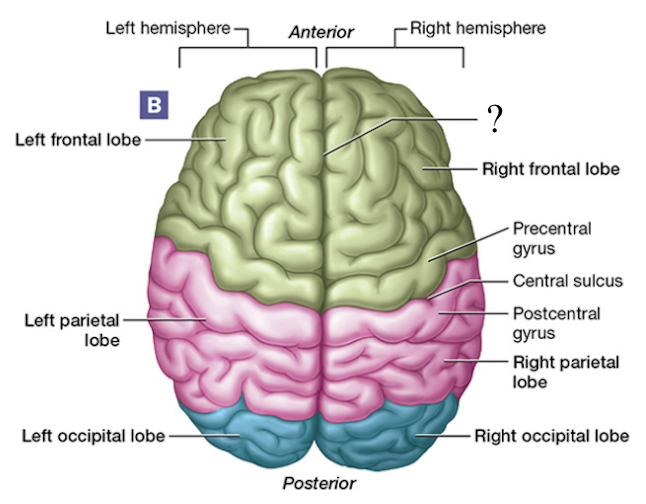
frontal lobe
responsible for emotion, mood, memory, and aggression
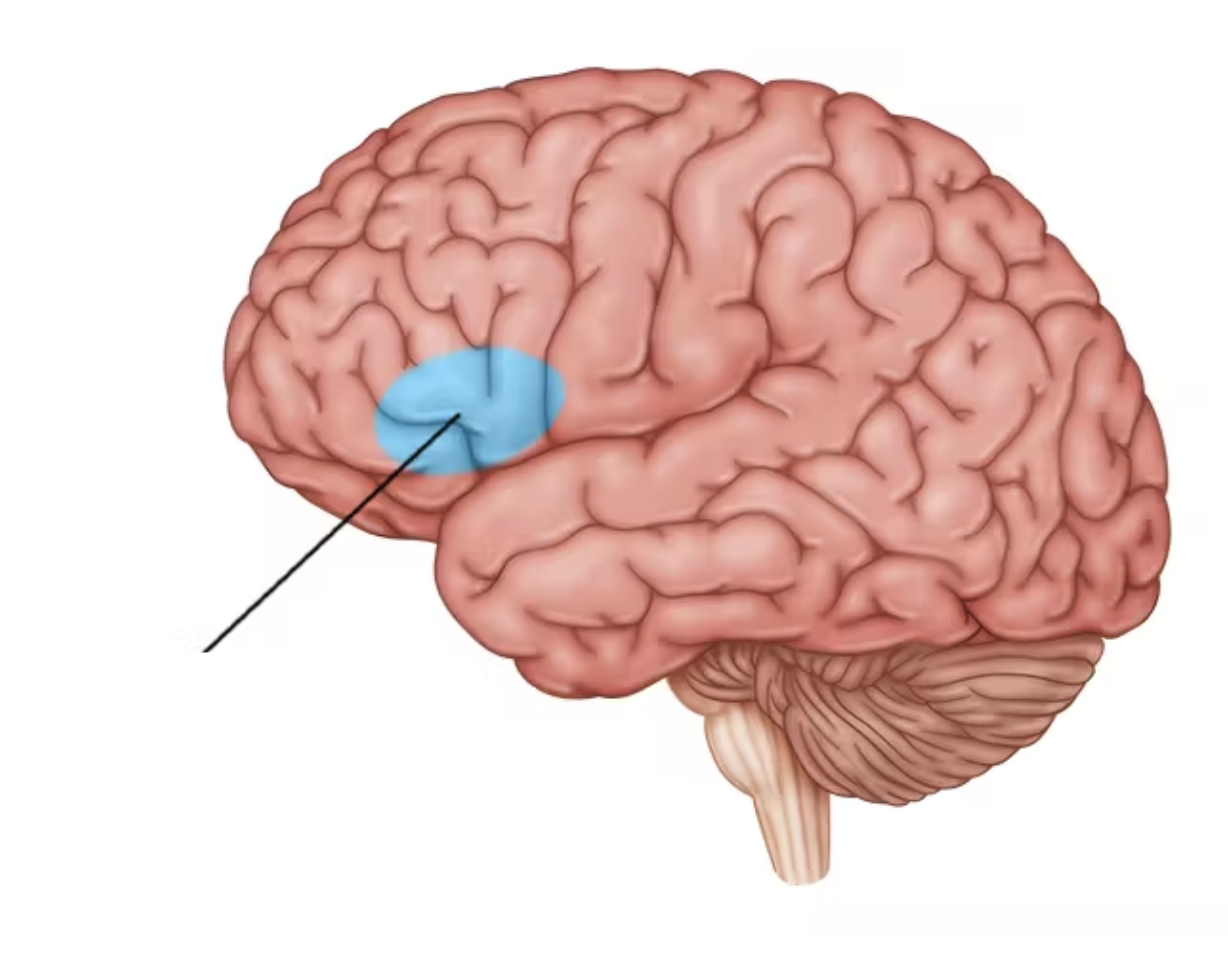
broca area
motor language area for speech or sign language
located anteriorly in the left frontal lobe
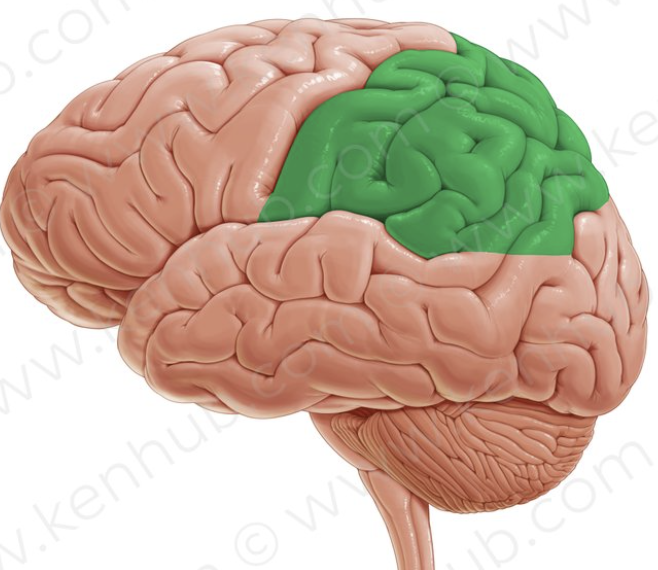
parietal lobe
responsible for sensory and integration of taste
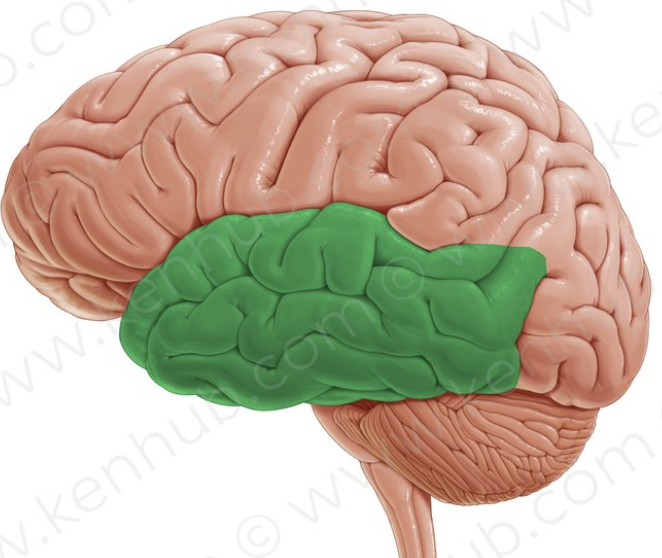
temporal lobe
responsible for hearing, smell, learning, visual recognition, and emotional behavior
wernicke area
recognition of spoken and written language
posteriorly in the left temporal lobe
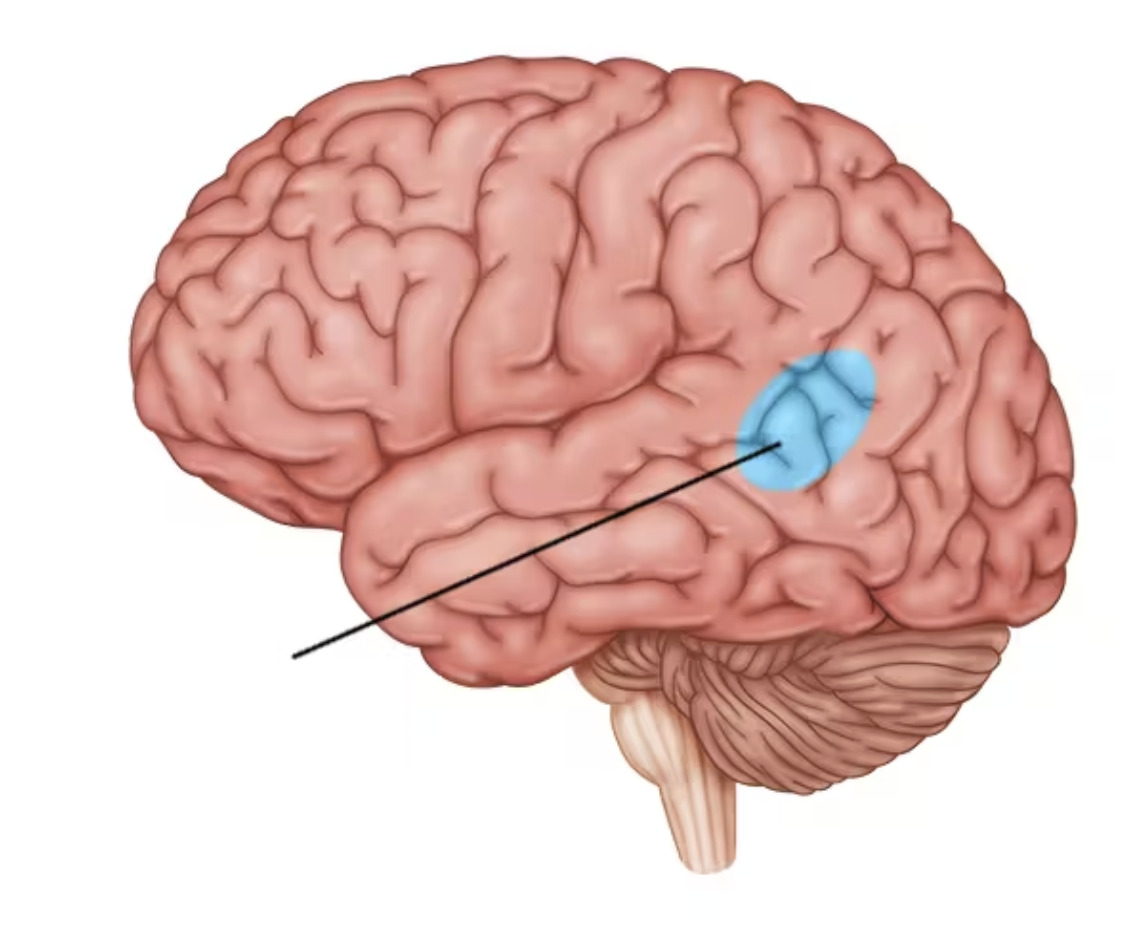
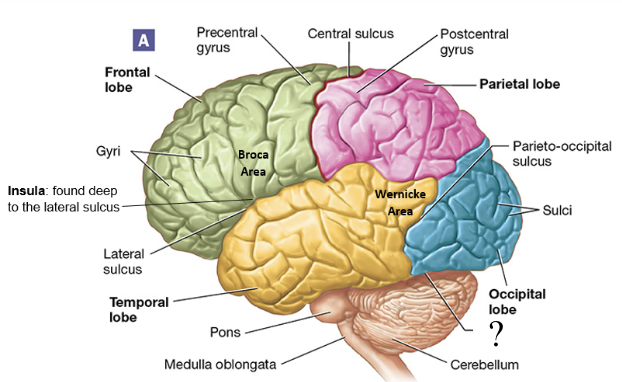
occipital lobe
principal visual center of the brain
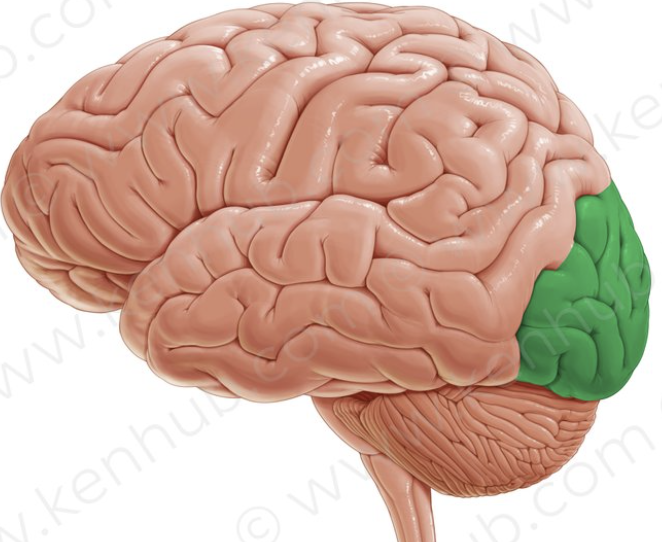
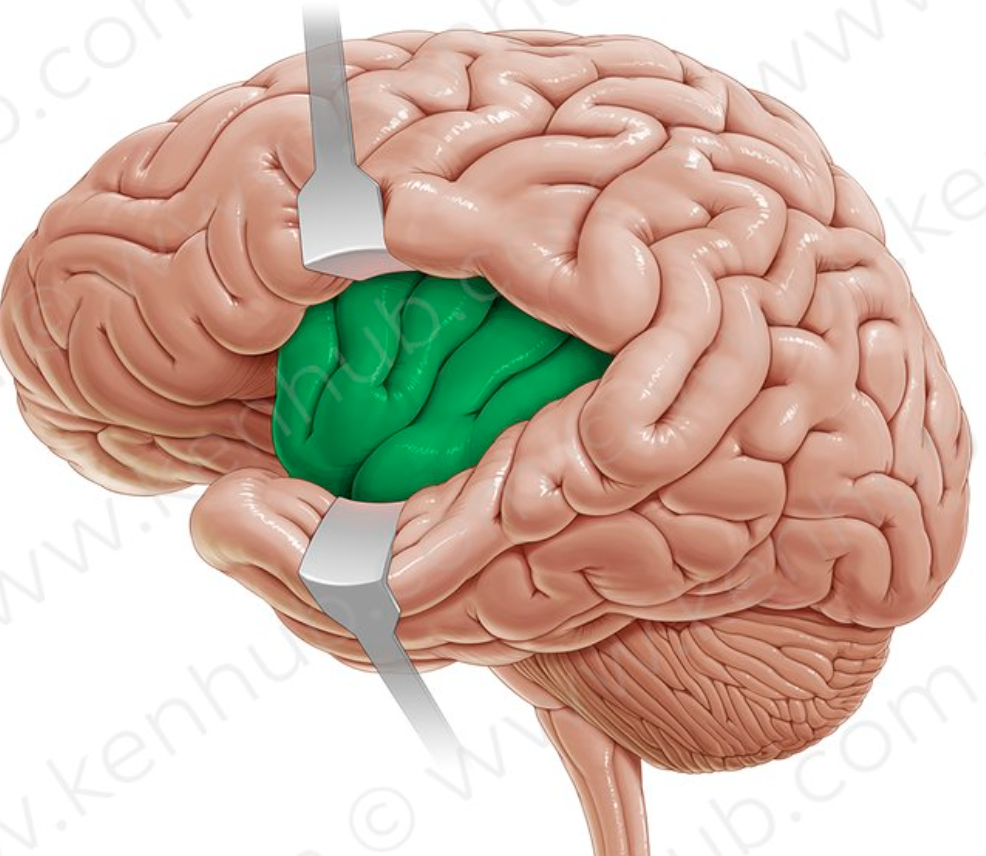
insula
small mass of cerebral cortex deep to the lateral sulcus that plays role in pain and empathy
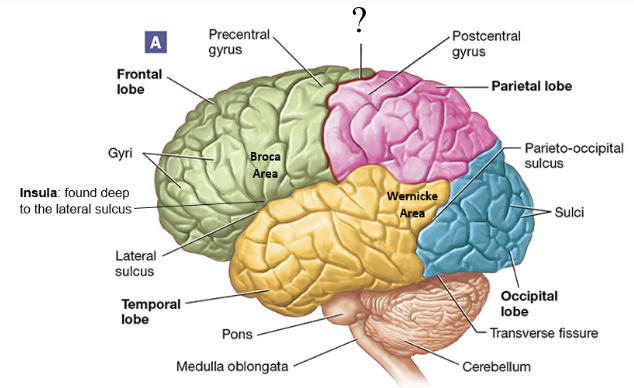
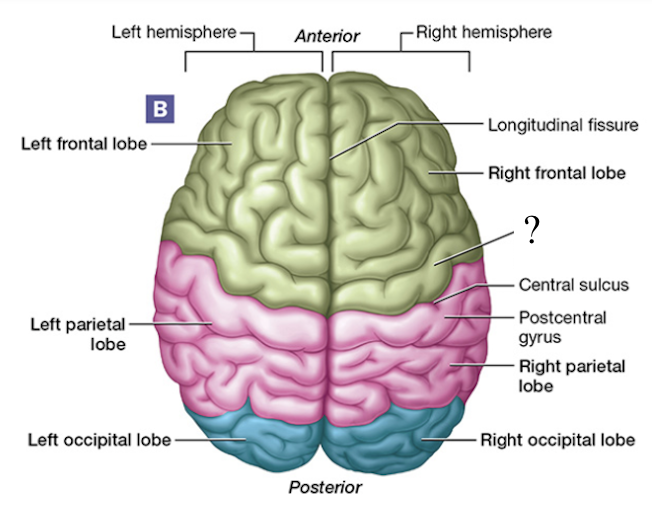
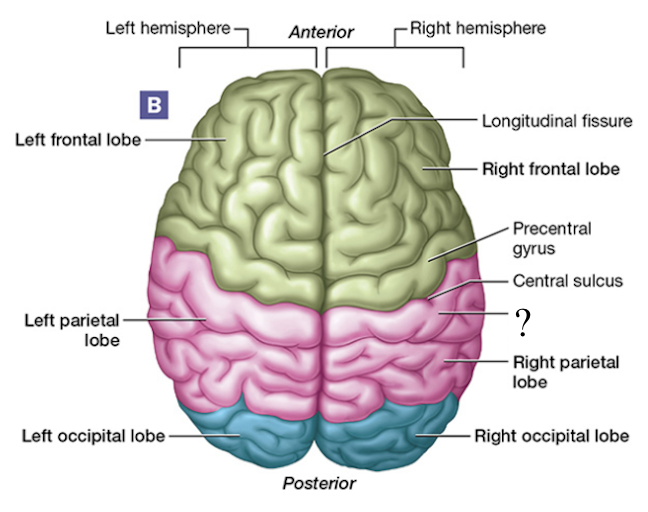
central sulcus
shallow groove found between the frontal and parietal lobes
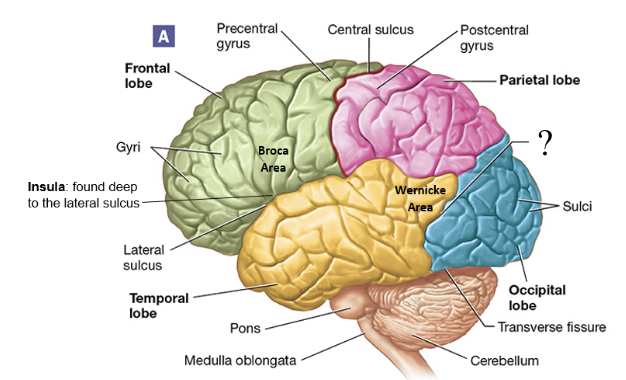
lateral sulcus
shallow groove found between the frontal and temporal lobes
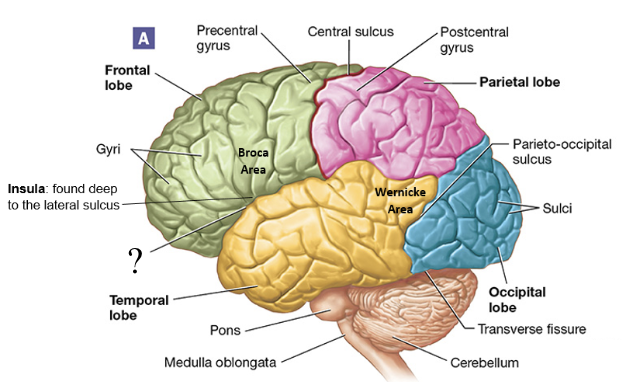
parieto-occipital sulcus
shallow groove found between the parietal and occipital lobes
transverse fissure
deep groove found between the cerebellum and cerebrum
longitudinal fissure
deep groove found between each cerebral hemisphere
precentral gyrus
aka the primary motor cortex, anterior to the central sulcus, located in the frontal lobe
signals sent from here result in muscle contractions
postcentral gyrus
aka the primary somatosensory cortex, posterior to the central sulcus, located in the parietal lobe
awareness of stimulation occurs here
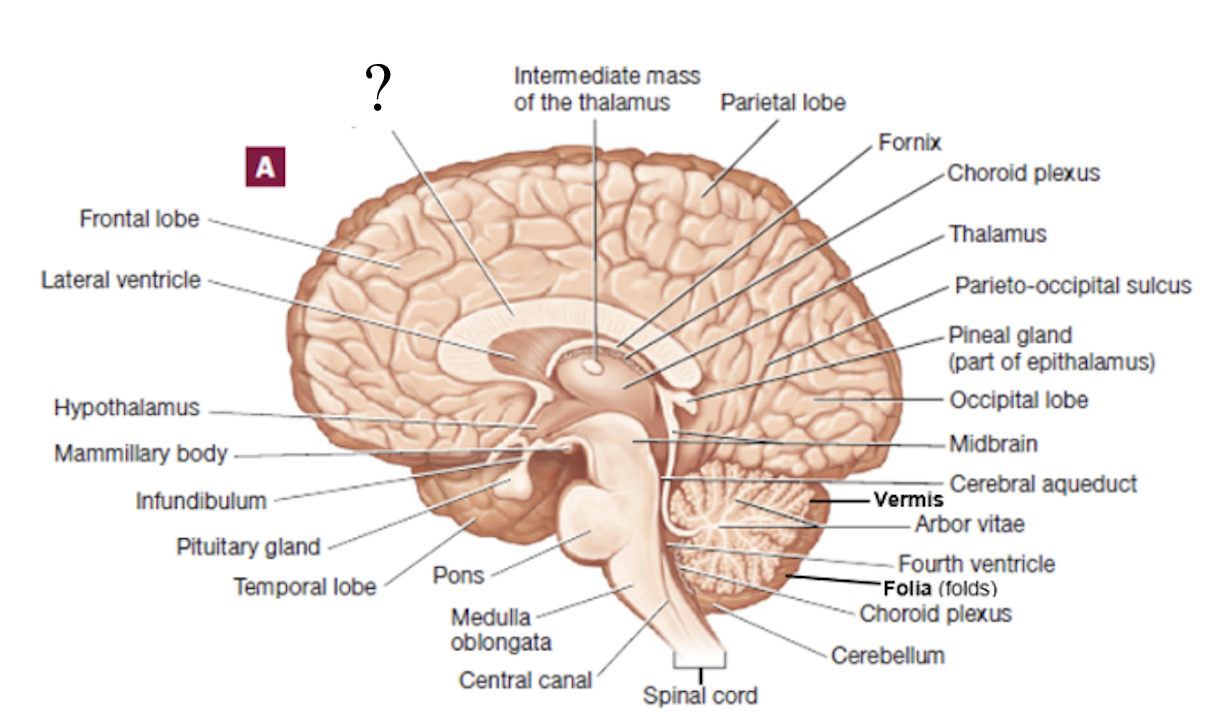
corpus callosum
thick C-shape structure made up of nerve axons/tracts that connect the cerebral hemispheres to each other
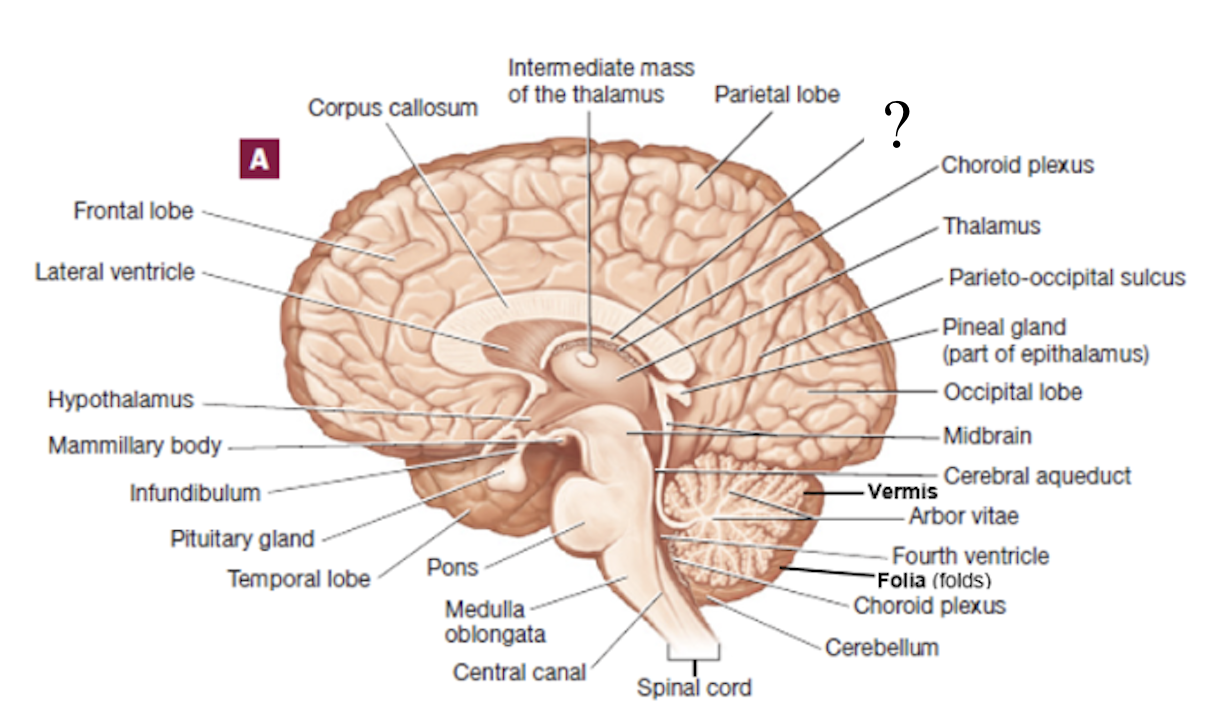
fornix
thin C-shape structure located inferior to the corpus callosum
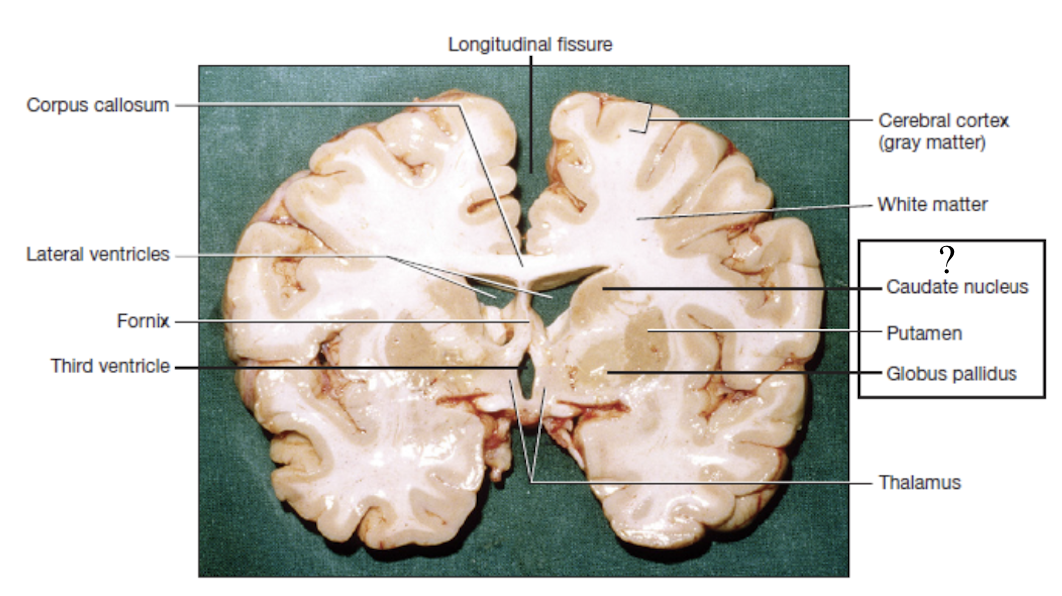
basal nuclei
striped masses of gray matter buried deep in the white matter lateral to the thalamus and are involved in motor control
caudate nucleus: superior and medial
putamen: lateral
globus pallidus: inferior and medial
cerebellar cortex
central control point for muscle contraction
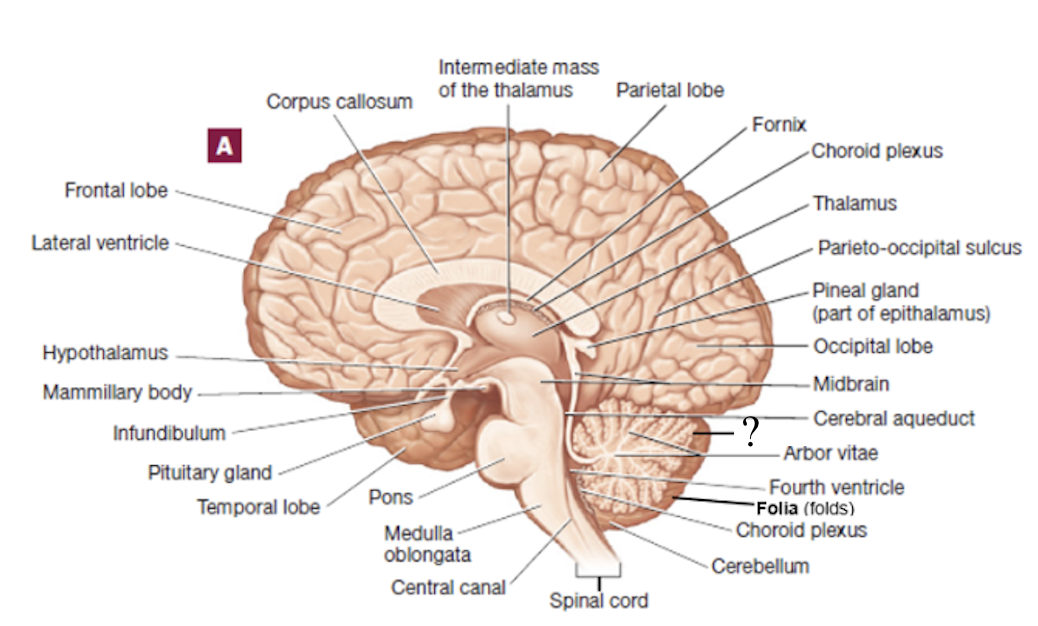
arbor vitae
translates to “tree of life” and is white matter of the cerebellum
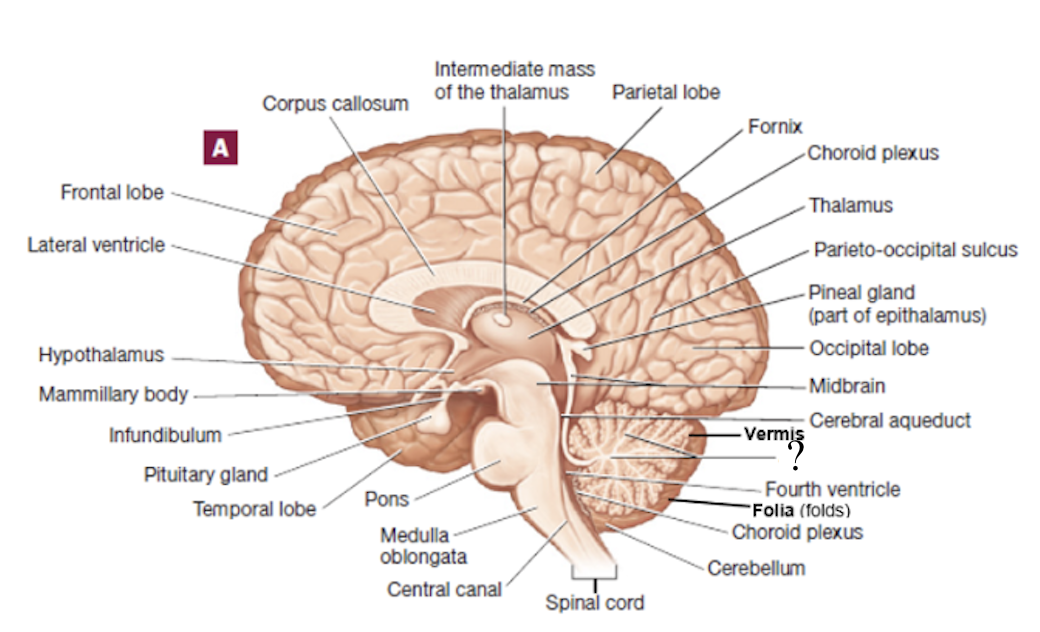
folia
folds found within the cerebellum
vermis
medial structure that connects each cerebellar hemisphere
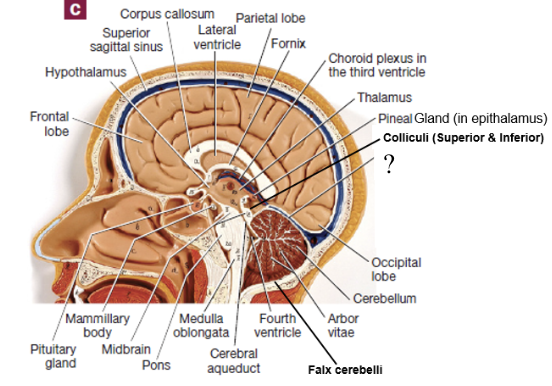
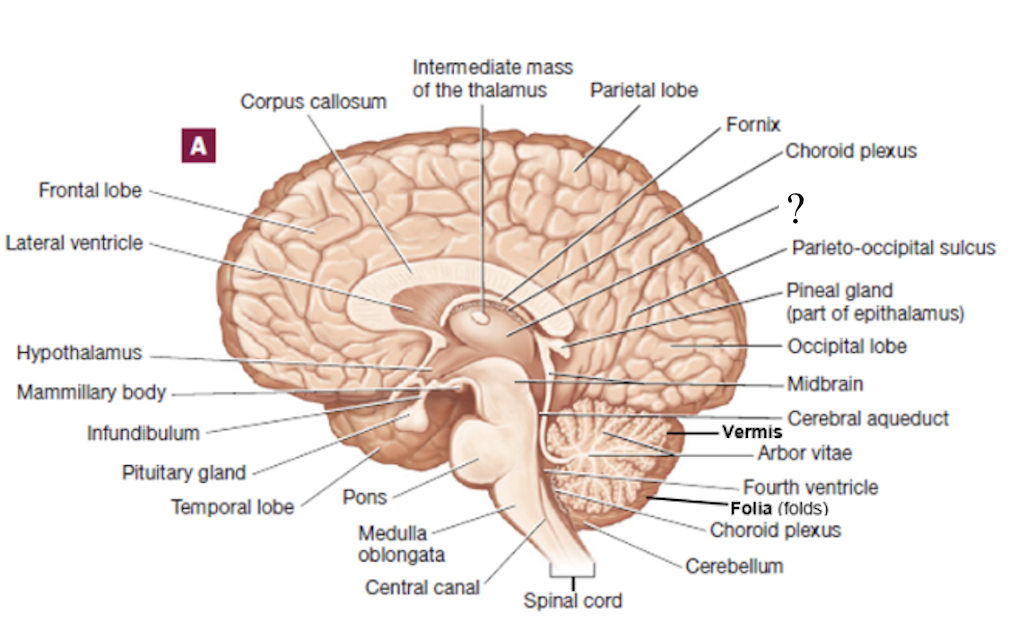
thalamus
filters information and relays a small portion of it to the cerebral cortex
gateway to the cerebral cortex
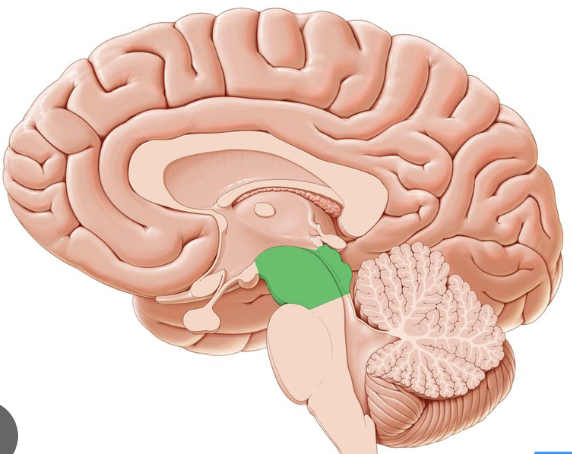
hypothalamus
anterior and inferior to the thalamus and is the major control center of the autonomic nervous and endocrine systems
connected to the pituitary gland via the infundibulum
rests on the hypophyseal fossa
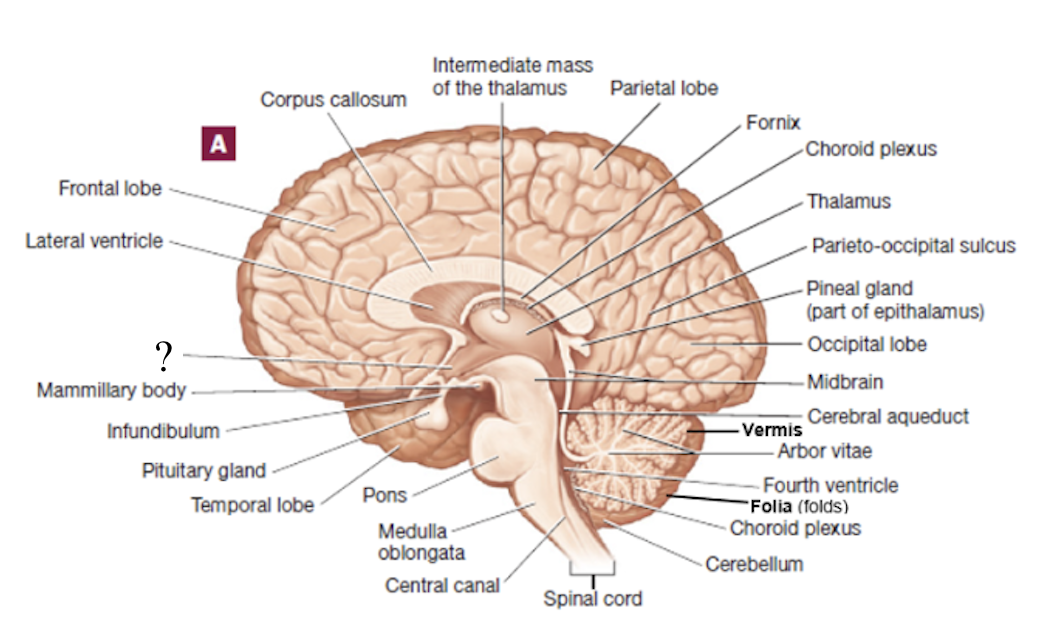
epithalamus
posterior and superior to the thalamus
houses the pineal gland, which releases the hormone melatonin
mammillary bodies
pair of round structures located posterior to the pituitary gland
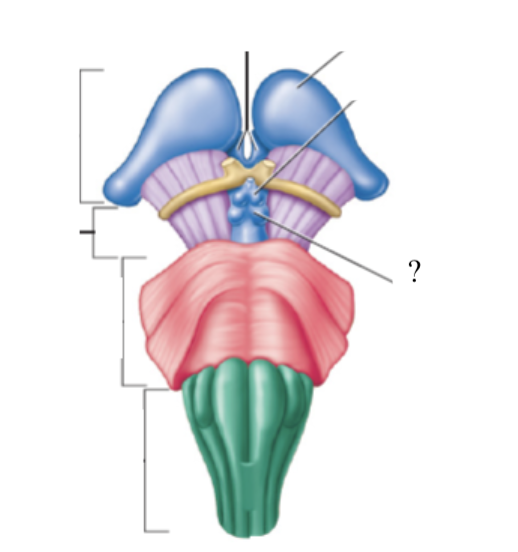
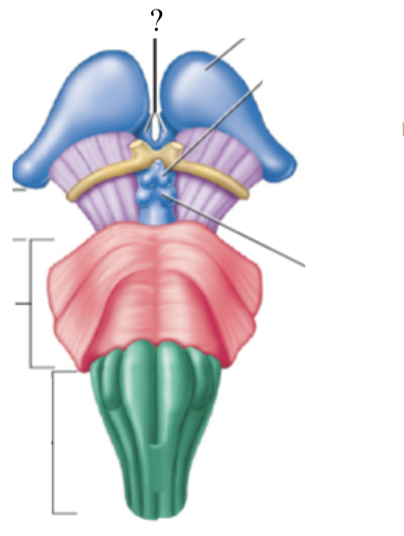
midbrain
associated with controlling our awareness of pain and collaborating in fine motor control
contains colliculi
2 cranial nerves originate here
colliculi
4 bulges in the midbrain that split into 2 superior colliculi and 2 inferior colliculi
superior colliculi: involved with control of extrinsic eye muscles
inferior colliculi: relay signals from the inner ear to the thalamus
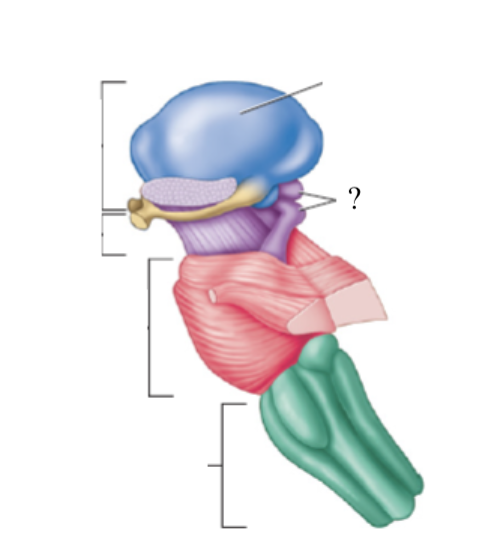
pons
responsible for relaying signals, hearing, equilibrium, taste, eye movements, swallowing, bladder control, and posture
4 cranial nerves originate here
medulla oblongata
cardiac, respiratory, and vasomotor center
once it passes through the foramen magnum it becomes the spinal cord
4 cranial nerves originate here