P4 - Atomic Structure / Nuclear Physics
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Nuclear decay
Unstable nuclei will decay to become more stable, emitting radiation in the process. These ionise other atoms/molecules which can be dangerous
Alpha decay
Nucleus ejects a helium nucleus (2 protons + 2 neutrons), an alpha particle
What happens in an alpha decay equation?
Mass number - -4
Atomic number - -2
+ a helium nucleus 4 / 2 He
Beta decay
A neutron decays into a proton and an electron
A high speed electron is emitted
This is a beta particle
What happens in an beta decay equation?
The mass number stays the same
Atomic number - +1
+ 0 / -1 e-
Gamma Radiation
A high energy electromagnetic wave that can be emitted by a nucleus, but is not due to decay, it is due to the nucleus having excess energy

What is this the symbol for?
Gamma radiation
What happens in an gamma radiation equation?
Both the atomic and mass number stay the same
+ symbol for gamma radiation
What do the types of radiation do to other atoms?
Ionise them
With what piece of equipment can be used to detect radiation?
Geiger-Muller tube
What should be taken before a count with a source of radiation?
Background radiation count, then this number can be subtracted from count with source
Examples of background radiation
Cosmic rays, radon gas (rocks), nuclear weapons, medical equipment
Neutrons can also be ejected by unstable nuclei, why is this dangerous?
They can be absorbed by other nuclei to make them unstable, they’re now radioactive
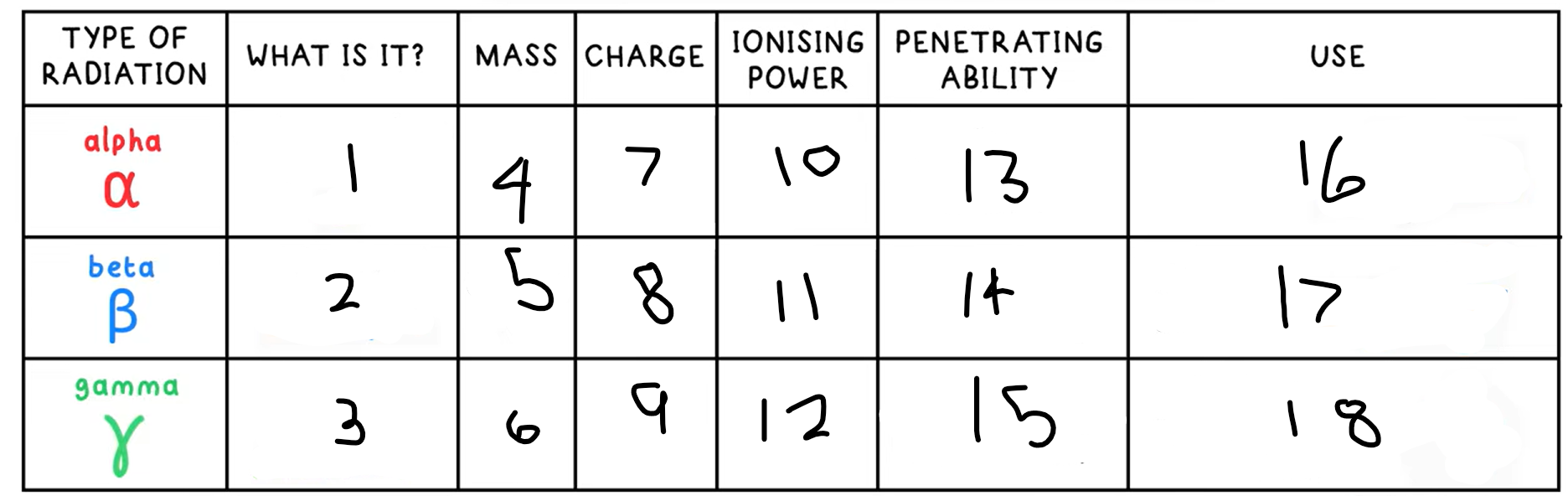
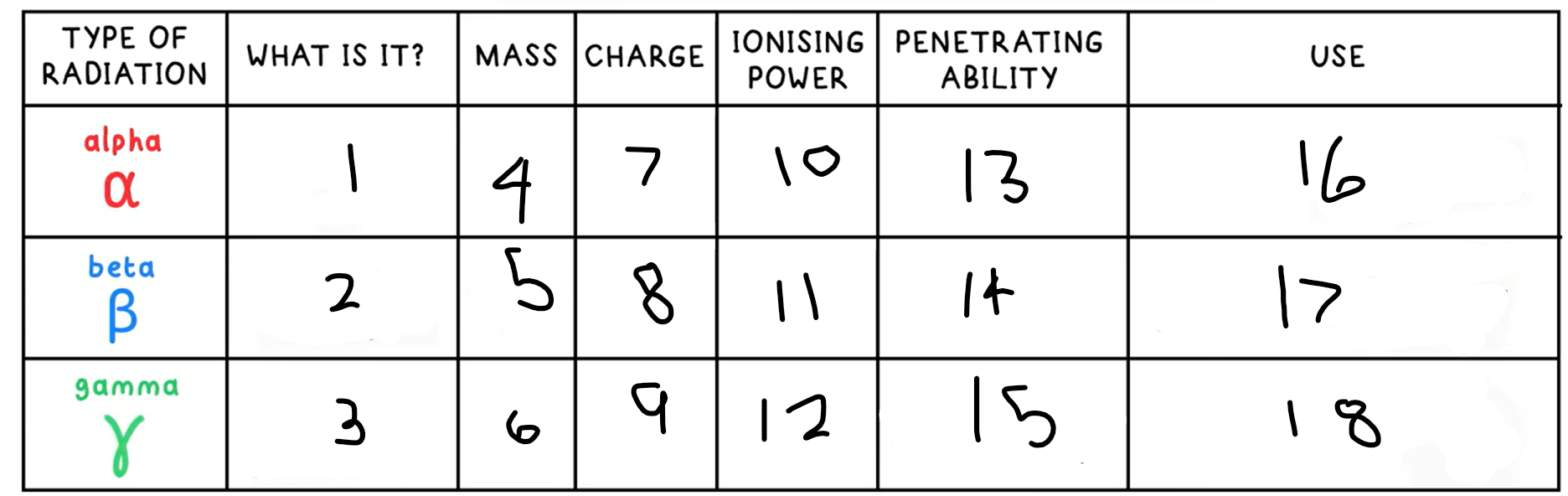
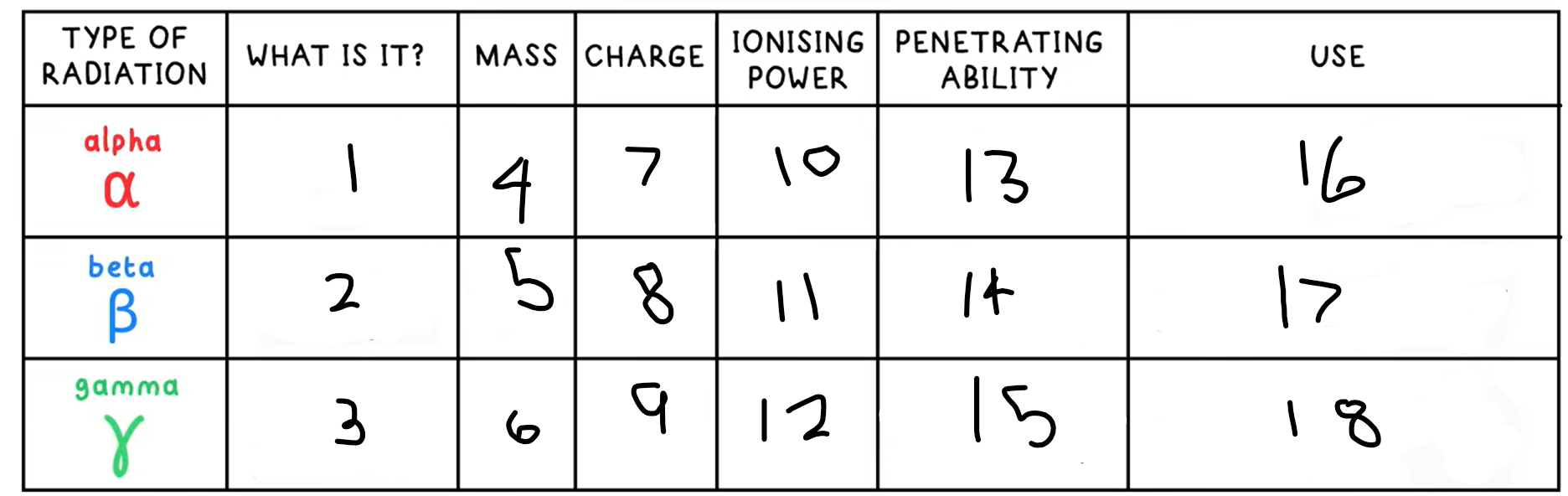
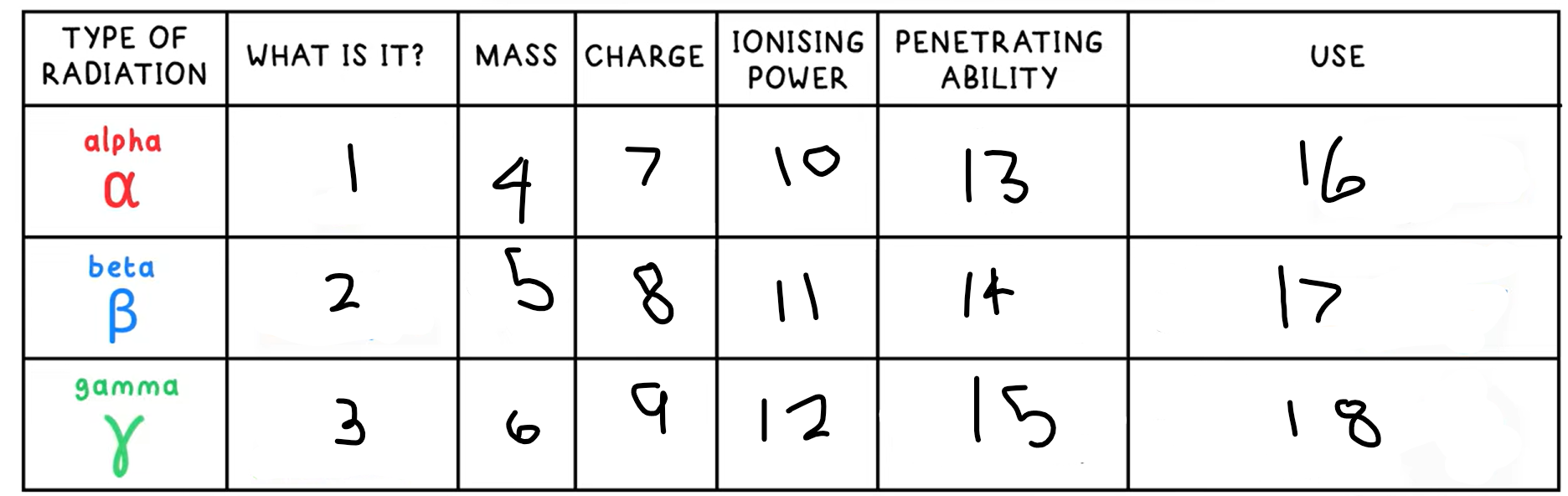
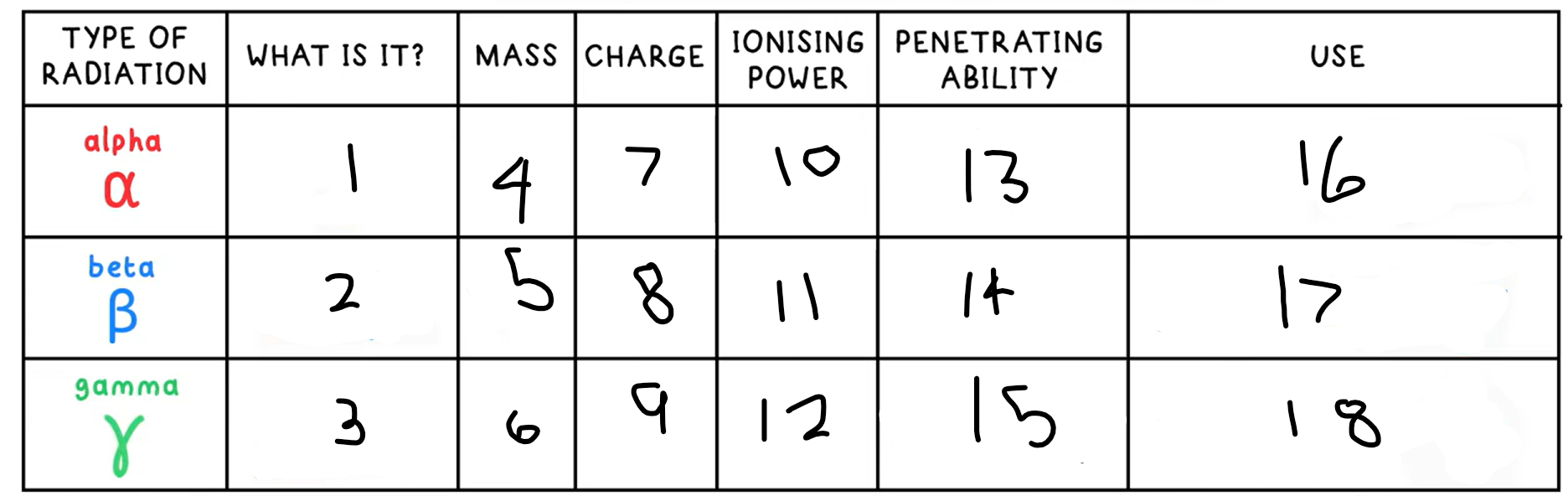
1?
Helium nucleus - 2 protons + 2 neutrons

2?
Fast moving electron
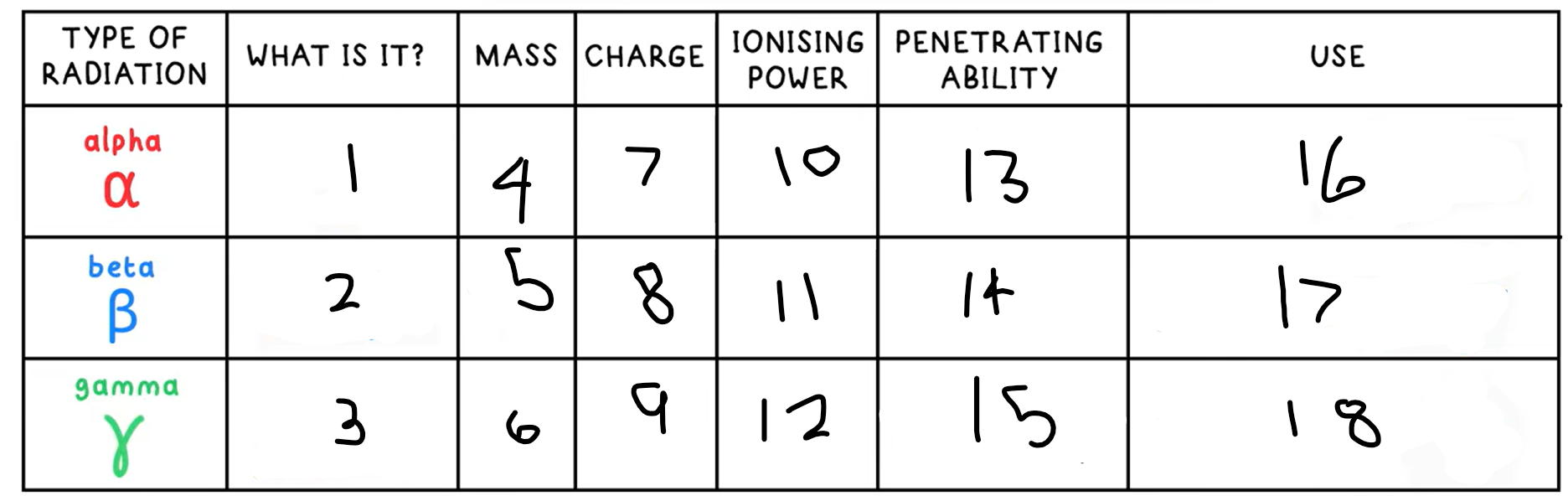
3?
High energy electromagnetic wave
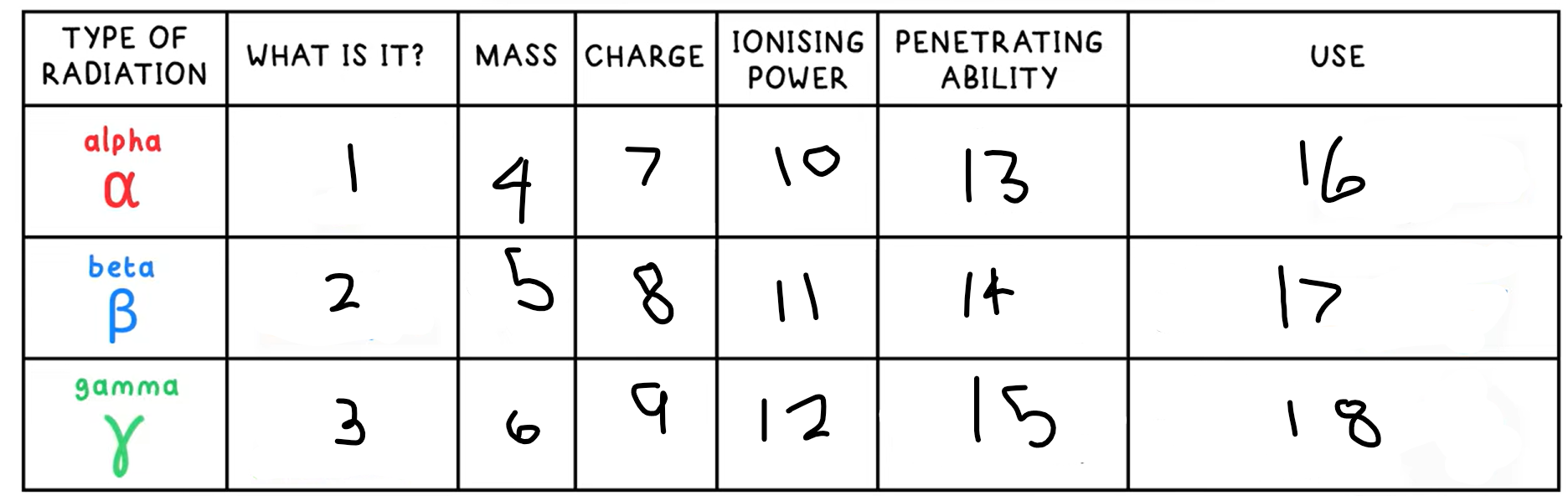
4?
4
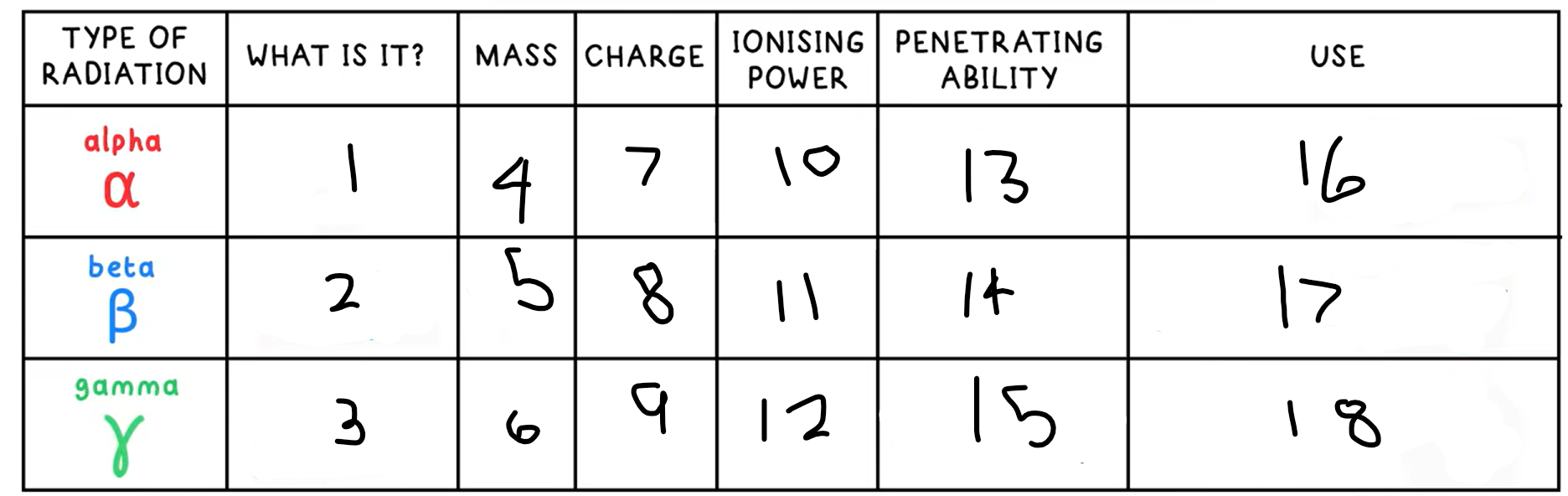
5?
(basically) 0
6?
0
7?
+2
8?
-1
9?
0
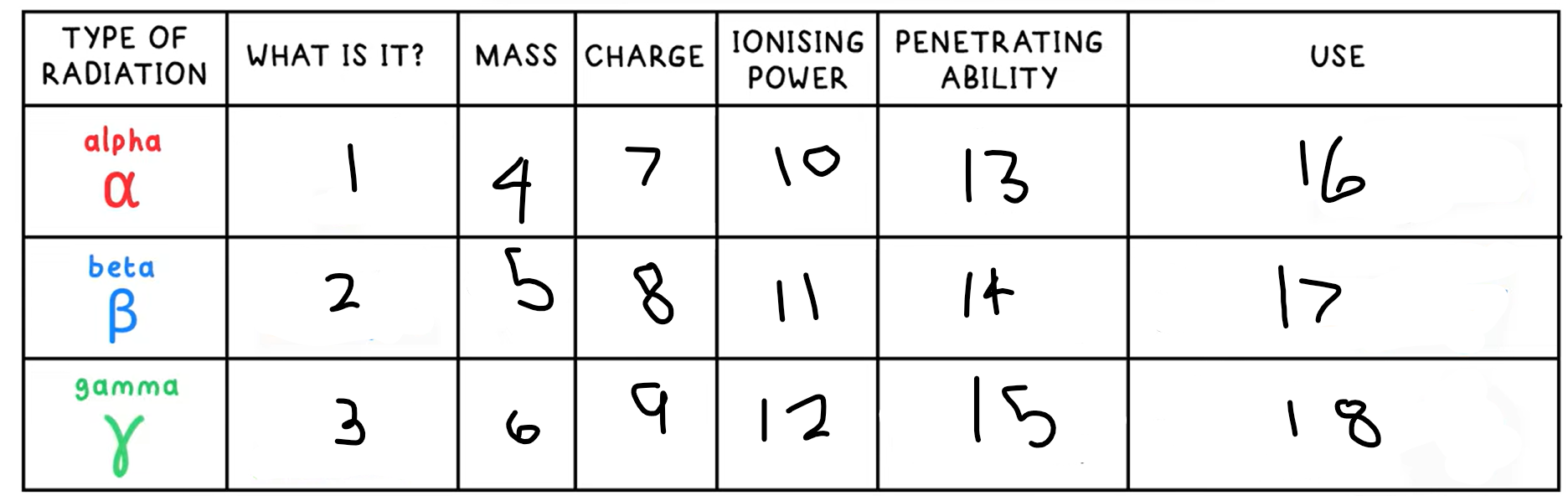
10?
High
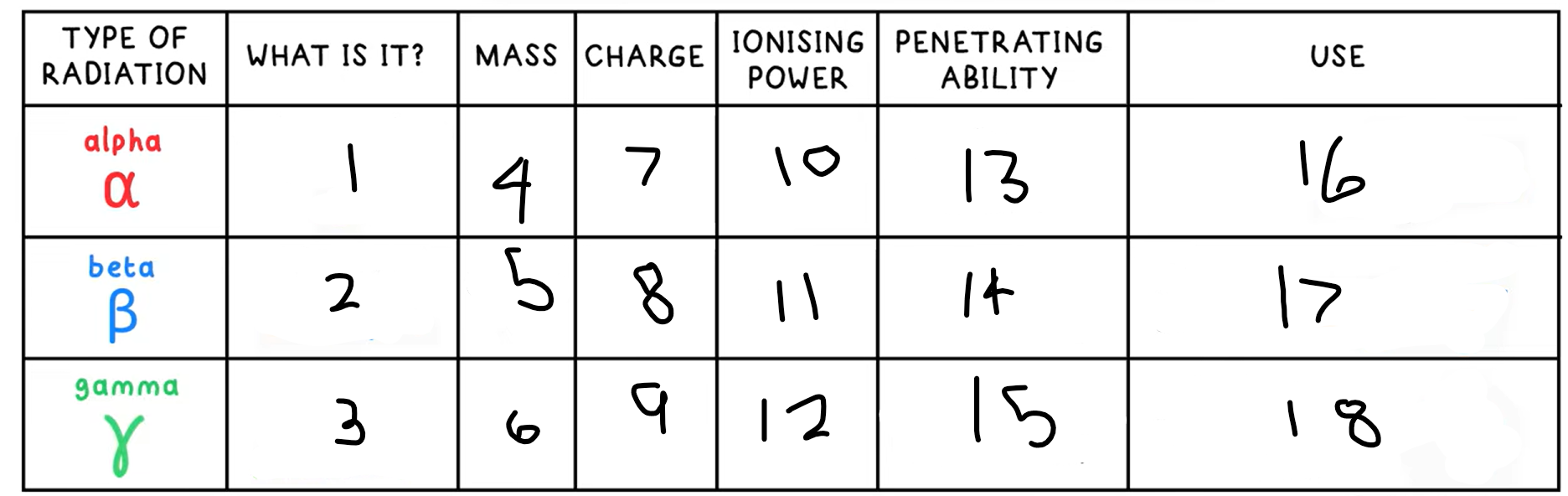
11?
Medium
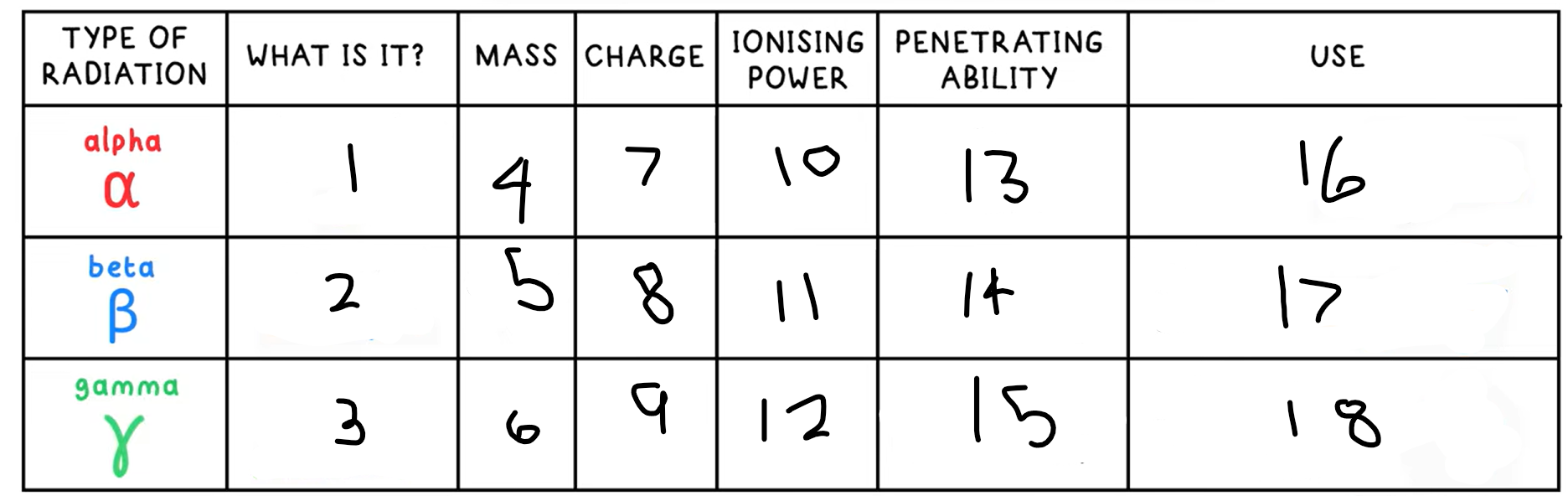
12?
Low
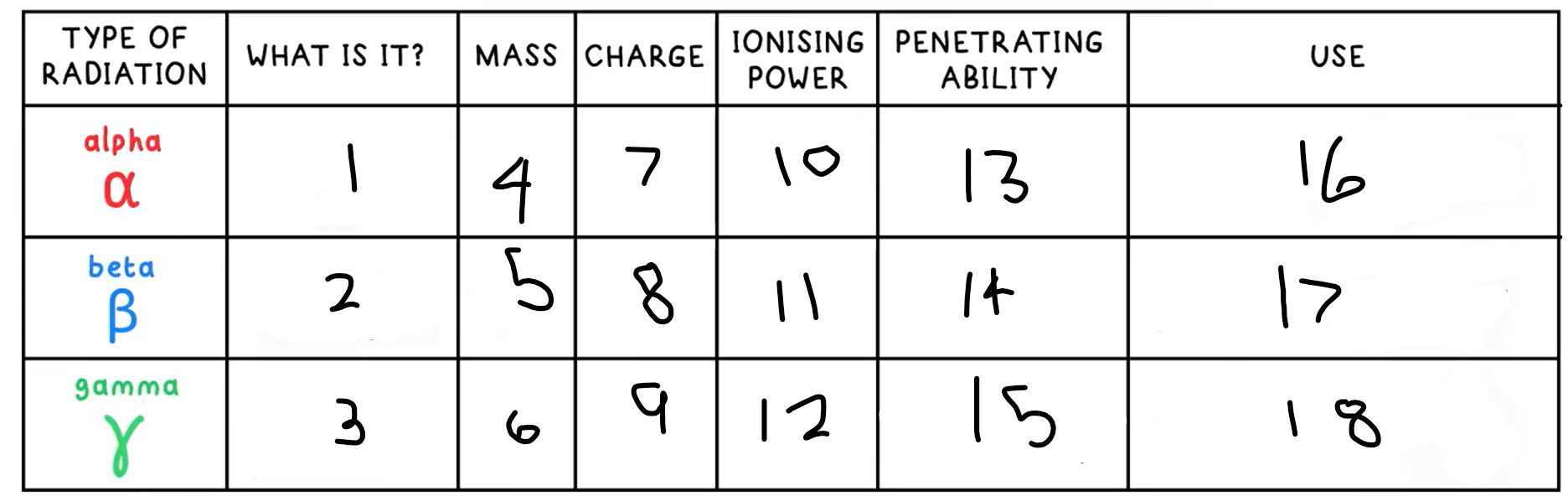
13?
Low - absorbed by paper / few cm of air
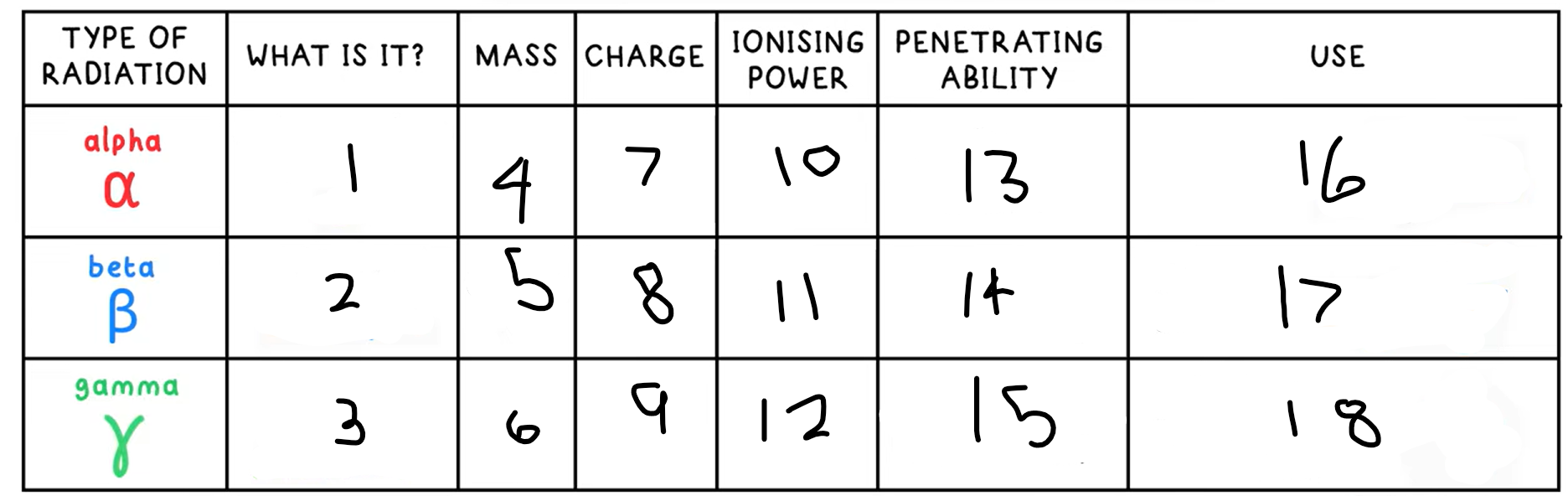
14?
Medium - absorbed by a few mm of aluminium
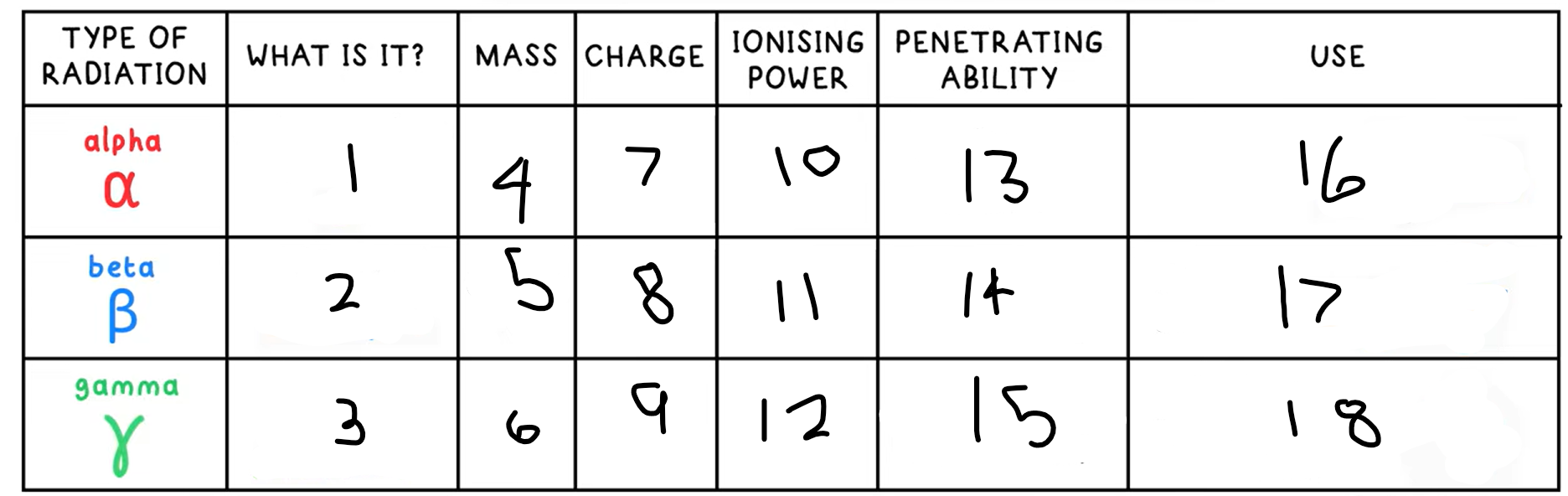
15?
High - intensity reduced by lead and concrete
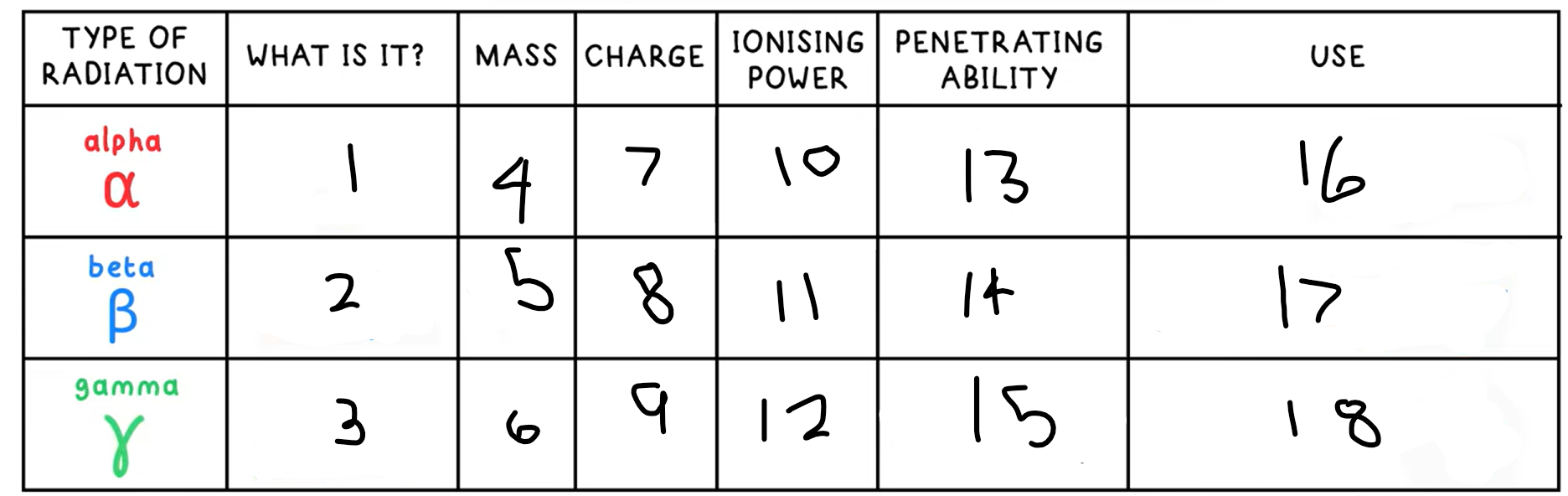
16?
Smoke detectors
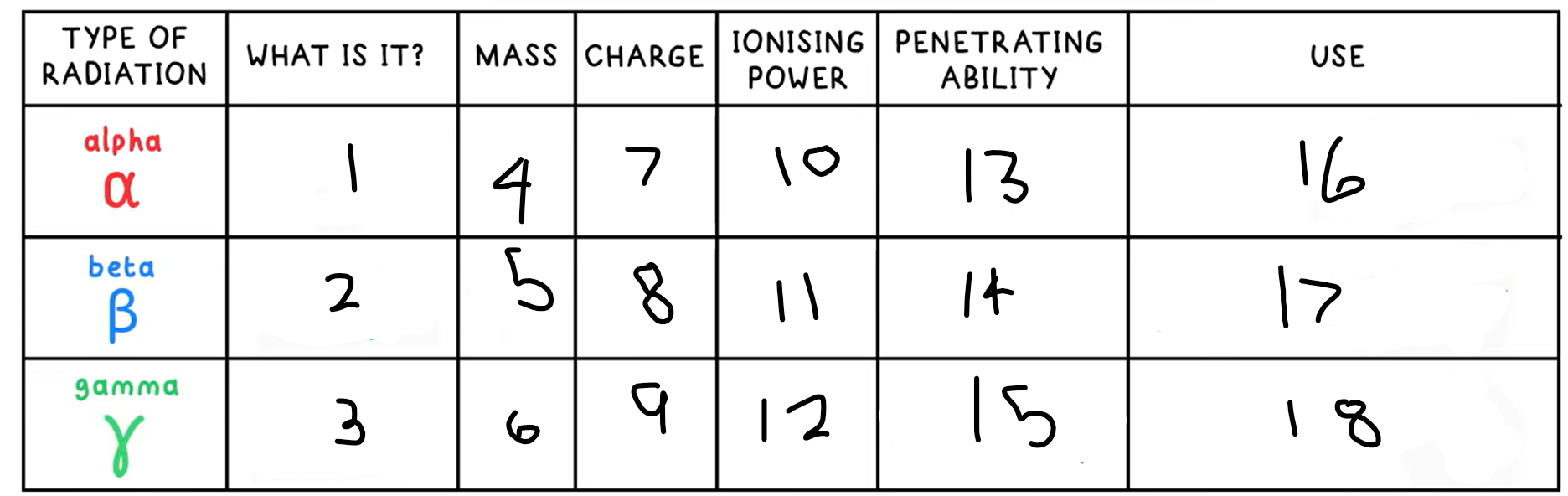
17?
Thickness gauge
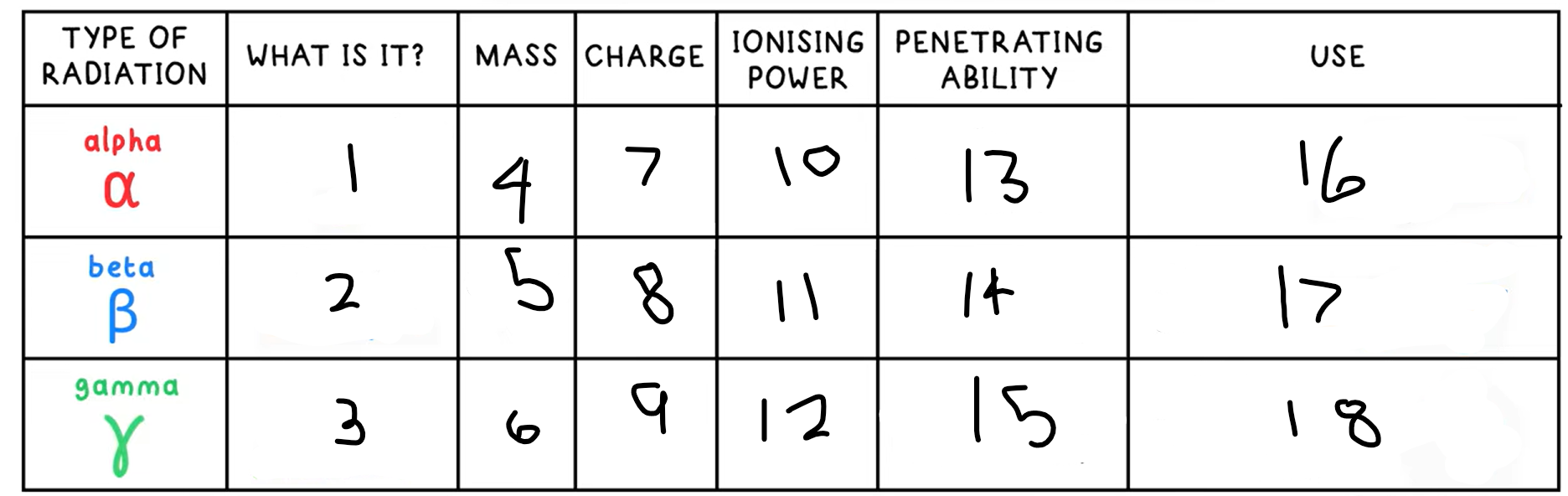
18?
Radiotherapy / sterilisation
Radioactivity
The rate of decay in a sample of radioactive material, this is equal to the rate of radiation emitted
What is the unit for radioactivity?
Becquerel (Bq)
Half life
The time taken for the activity to half