EOY BIOLOGY
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
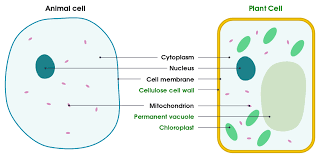
Nucleus
membrane bound organelle that contains (DNA) genetic information, produces ribosomes and regulates/controls the cell
Ribosomes
Site of protein synthesis
Mitochondria’s
Site of respiration
Cell membrane vs Cell wall
Cell membrane - outside barrier that protects / separates the inside of the cell from outside. Semipermeable so controls what enters and exits the cell.
Cell Wall - provides support and gives the PLANT cell a rigid structure (made of cellulose)
Cytoplasm
A gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of the cell that helps with shape and structure where organelles are suspended - site of most chemical reactions
Chloroplasts
Photosynthesize and convert light energy into chemical energy. They contain chlorophyll (pigment that is green and absorbs light. SITE OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
Permanent Vacuole
Stores cell sap, maintains turgidity and helps isolate waste
Plant cell vs animal cell
Plant have cell wall, chloroplast, vacuole and are rectangular due to cell wall
Tissues And Organs
Tissues - A group of similar cells working together to perform a specific task (e.g. muscle or nerve)
Organs - A group of similar tissues working together to perform a more complex function (e.g. heart)
Levels of organization in organisms
Organelles → cells → tissues → organs → systems
Population vs community vs habitat vs ecosystem
Population – all the organisms of one species in a habitat
Ecosystem – all of the living organisms in an area and all the non-living (abiotic) conditions.
Community - all the different species in a habitat
Habitat – the place an organism lives
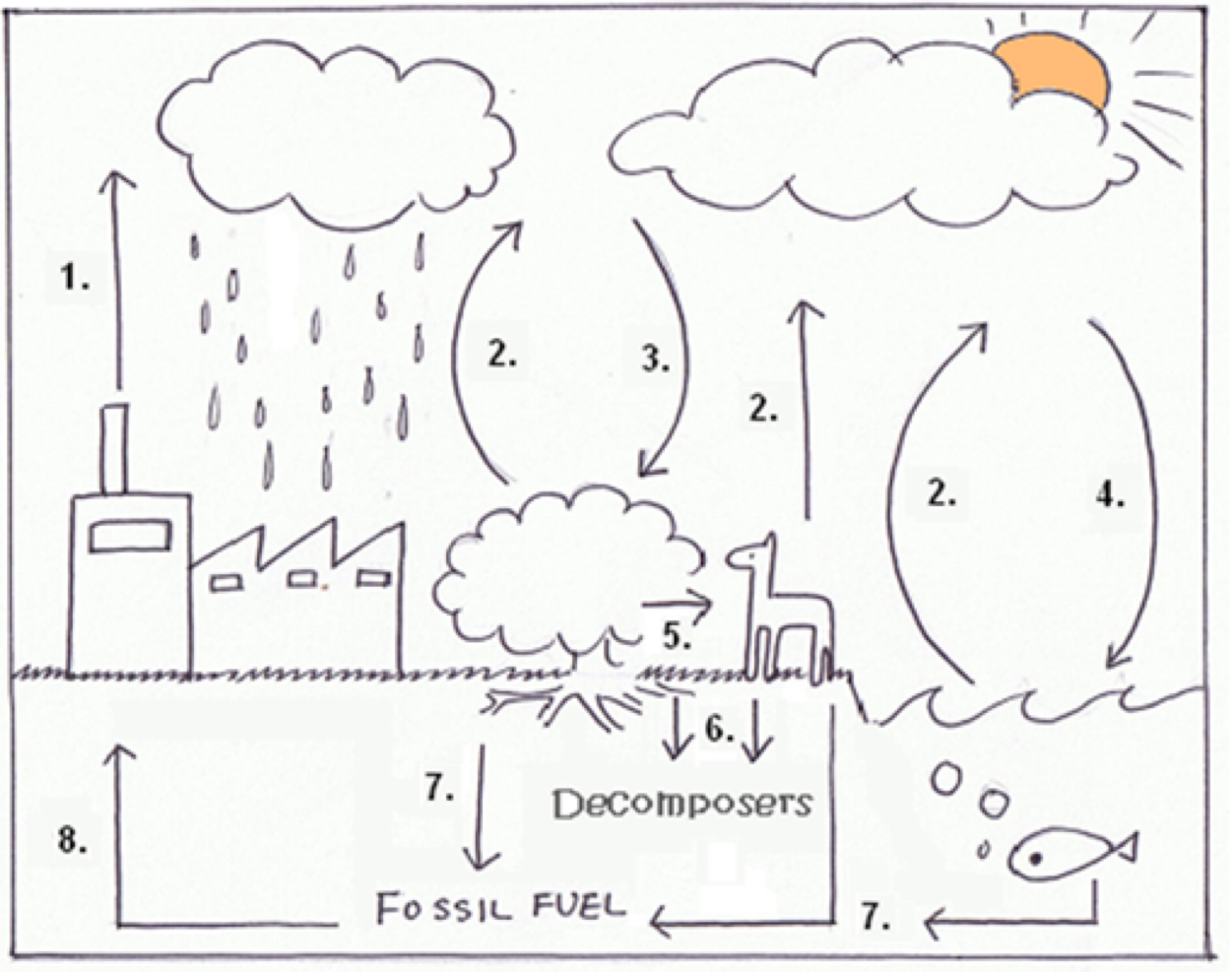
Number the carbon cycle and explain it
Combustion releases carbon dioxide from the fossil fuels
Respiration in all living things releases carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere
Photosynthesis ‘Fixes’ carbon atoms from carbon dioxide in organic compounds
Carbon dioxide from atmosphere naturally dissolves in the ocean - eventually becomes limestone
Feeding - These get passed along a food chain by feeding
Death of organisms and the decomposition (of organic carbon compounds broken down to carbon in soil) - e.g. organisms or their waste products
Fossilization can occur and carbon can get stored as fossil fuels like coal and natural gas
Extraction of fossil fuels stored in the ground to them in the surface
Name the greenhouse gases and how human activity impacts them (5)
Water vapor → not much
Carbon dioxide → burning fossil fuels in factories, cars, etc.
Nitrous oxide → car fumes, more fertilizers (denitrifying bacteria makes nitrous oxide)
Methane → cows, decay in landfill, more rice
CFCs → aerosols , damage ozone layer
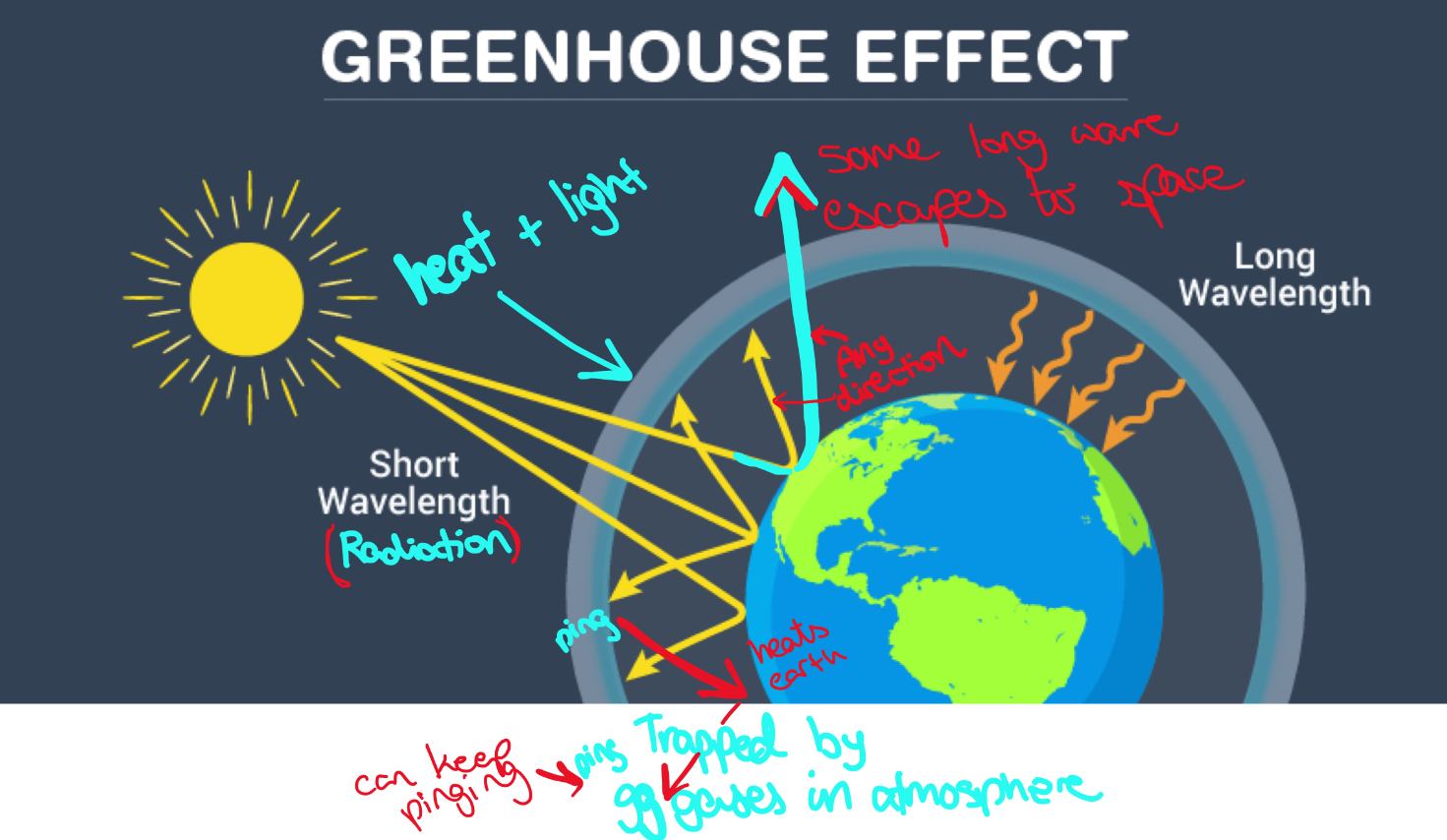
Explain the greenhouse effect
Some of the infrared radiation from the Sun passes through the atmosphere, but most is absorbed and re-emitted in all directions by greenhouse gas molecules and clouds. The effect of this is to warm the Earth's surface and the lower atmosphere
Why is pollution of water by sewage bad? (What is Eutrophication?)
→ Sewage (rich in minerals + nutrients) provides lots of energy for decomposers, or fertilizers run off due to rainfall
→ this goes into water and also encourages algae growth on the surface of rivers and lakes
→ as algae blooms form, they block sunlight and prevents aquatic plants from photosynthesizing (die)
→ decomposers break down sewage + plants (aerobic respiration) and deplete oxygen reserves in water
Diffusion vs Osmosis vs Active Transport
Diffusion → movement of particles from a high to lower concentration
Osmosis → diffusion of water across a membrane from high to low concentration
Active transport → moves particles from low to higher concentration
Why is diffusion reliable for single celled organisms
→ 1 cell so larger SA:V → efficient rate of diffusion and they can rely solely on it as distances are often short
Common features of diffusion or exchange surfaces:
Thin Cell Walls (1 cell thick) → minimize distance
Large Surface Area to Volume Ratio → long, thin or flat or folded to increase ratio
Moist → dissolves gases or substances to make them move through easier
High/Steep Concentration Gradient → to make sure they get exchanged faster
Fungi + Protists
FUNGI: Eukaryotic, usually multicellular (not yeast), reproduce asexually or sexually,
PROTOCTISTS: eukaryotic, mainly single celled, asexually or sexually
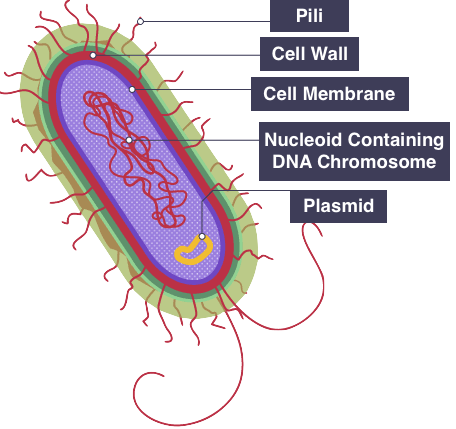
Common features in bacteria:
Unicellular, feeds on organisms, asexual reproduction
How are Bacteria, Fungi, Protoctists and Viruses pathogens?
Bacteria: Prokaryotic, not always bad, E-COLI or SAMONELLA
Protoctist: Eukaryotic, requires vector (has to be carried), MALARIA or POTATO BLIGHT
Fungi: Eukaryotic, more deadly to plants (block sunlight by taking over large spaces), ATHLETES FOOT, RINGWORM
Virus: Dead, needs a host to survive, always bad, lacks organelles, HIV or INFLUENZA
What is a pathogen?
A bacterium, virus or other microorganism that can cause disease
How do Sulfur Dioxide create consequences biologically?
SO2 → combustion of fossil fuels → dissolves in clouds to make Sulfuric acid (ACID RAIN) which corrodes metals, acidifies rivers and leaches minerals out of the soil
Who do multicellular organisms need a transport system / features? (2)
→ Small SA:V ratio, so inefficient rate of diffusion
Use tubes or vessels to carry substances
Pumps to ensure constant supply
Name the tropic levels + define them
Producer → plants that photosynthesize and get energy from the sun, they supply energy to the ecosystem
Primary / Secondary / Consumer → Animals that eat the plants or other animals (or top predator)
Decomposers → bacteria or fungi that decay dead material to recycle nutrients
Pyramid of numbers vs biomass vs energy transfer
NUMBERS: just how many there are
BIOMASS: total amount of living material (dry mass x organism) - plants usually have lots of dry mass
ENERGY TRANSFER: 10% passed on (JOULES)
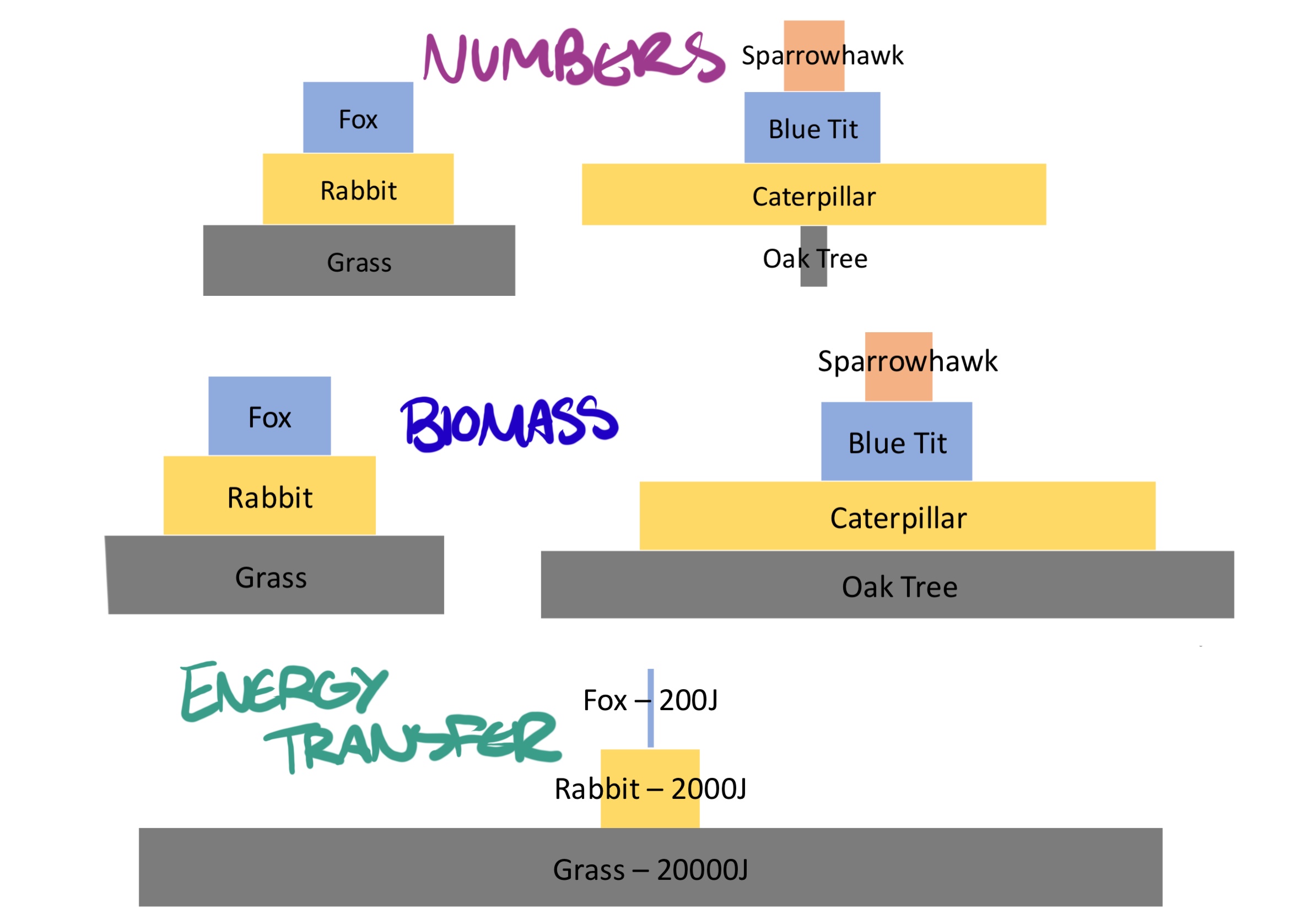
Why is energy transfer in a food chain only 10%?
→ animal doesnt eat all of the grasshopper
→ uses some of the energy for movement, respiration, reproduction
→ some materials aren’t absorbed and are egested
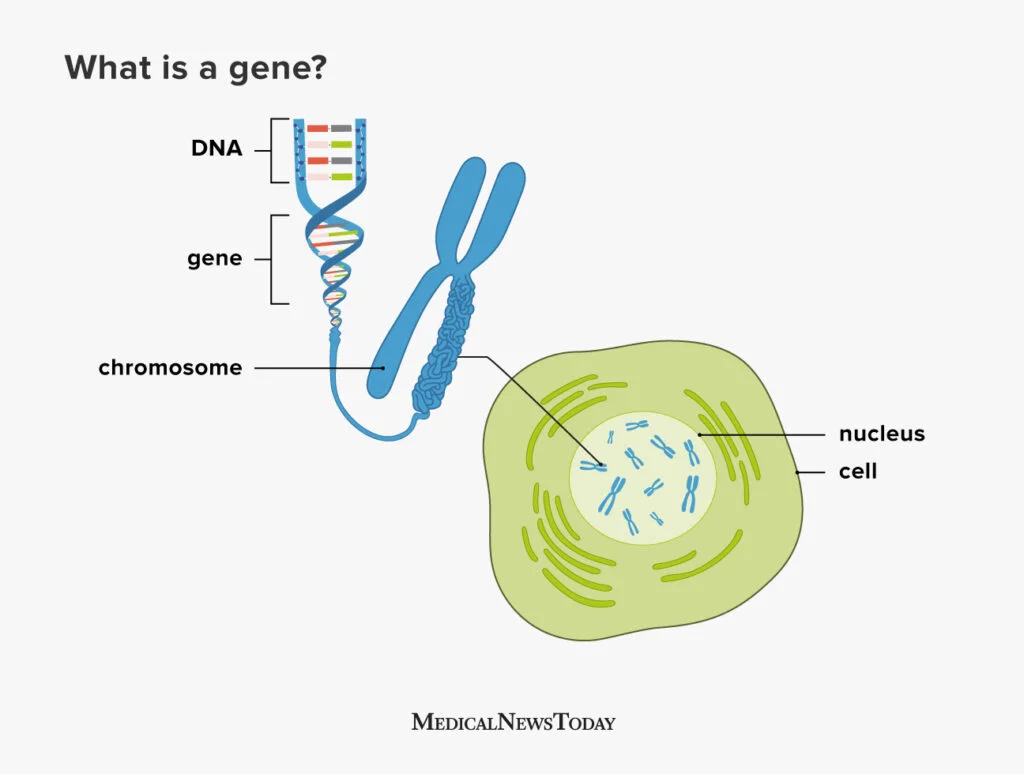
Genome vs gene vs allele
Genome: ENTIRE DNA of an organism
Gene: a section of a molecule of DNA that codes for a specific protein
Allele: alternate form of a gene
Polygenic (what does it control, give and example of monogenic and polygenic)
Polygenic: controlled by many genes (controls most phenotypes (eye, hair)). Monogenic = sickle cell anemia
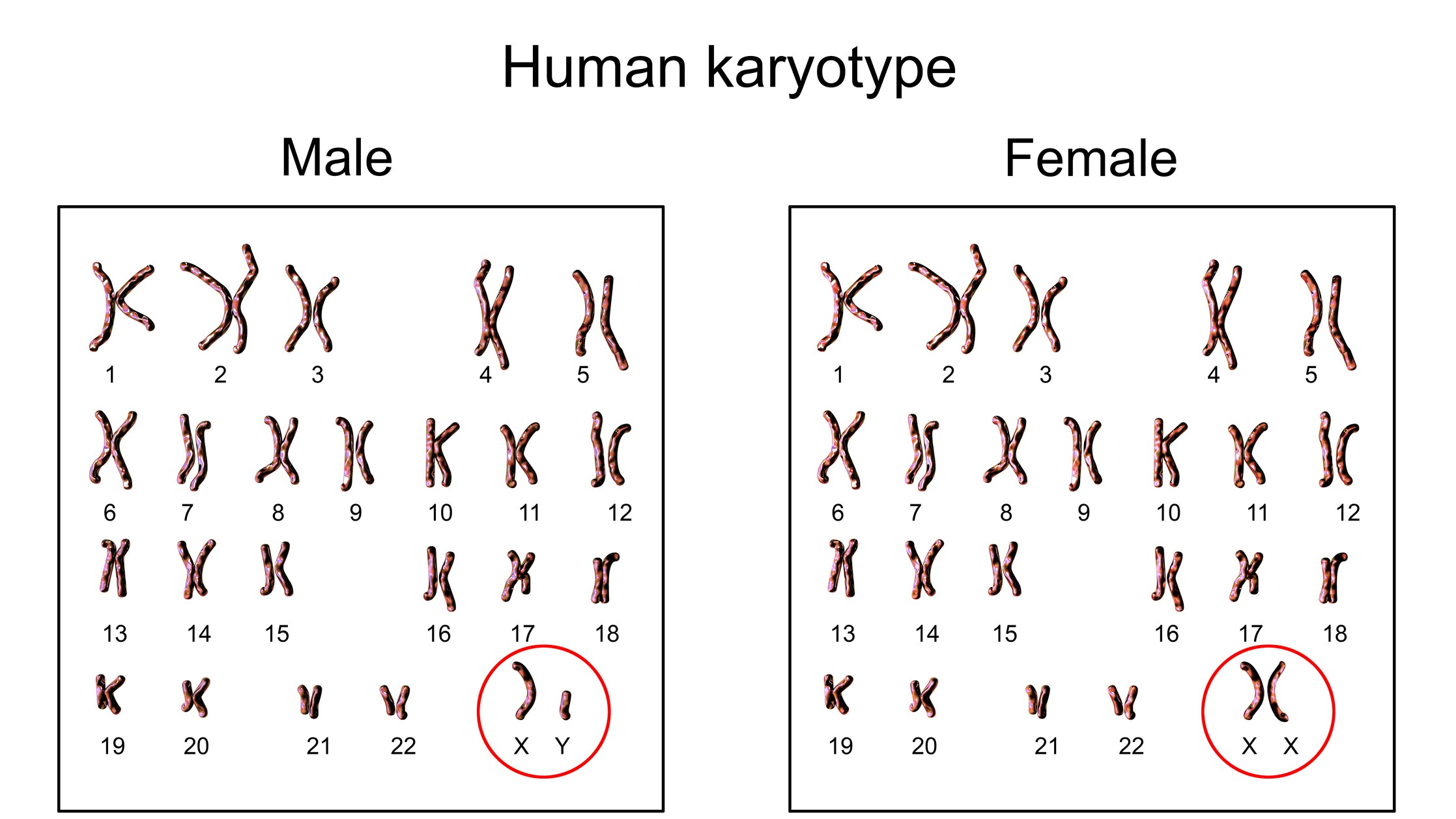
How many chromosomes normal human cells have? (And which pair codes for sex)
46 (23 pairs - the 23rd PAIR codes for sex)
What is a chromosome and where is it found, what does it carry?
a thread-like structure composed of DNA, found in the nucleus of a cell. It carries genetic information in the form of genes, which are specific lengths of DNA that code for proteins
Dominant vs recessive, homozygous vs heterozygous, phenotype vs genotype :3
Dominant → allele always expressed—————Recessive → allele only expressed if paired with another recessive
Homozygous → two identical alleles ————-Heterozygous → two different alleles
Phenotype → the physical characteristics expressed———————-Genotype → just the allele combination
Monohybrid inheritance
Study of inheritance of one characteristic (Gene) shown Using a Punnett Square

Haploid cells vs diploid cells definition + example of each (IN HUMANS)
Haploid (sperm or egg) have only 23 chromosomes, Diploid have 46 chromosomes (most cells like blood or nerve cells)
What is a genetic mutation?
A rare, random change in genetic material that can be inherited
Mitosis vs meiosis (What’s produced, are they genetically identical?, how many cell divisions)
Mitosis → produces two diploid daughter cells that are genetically identical, only 1 cell division
Meiosis → produces four haploid daughter cells that are genetically different, 2 cell divisions occur
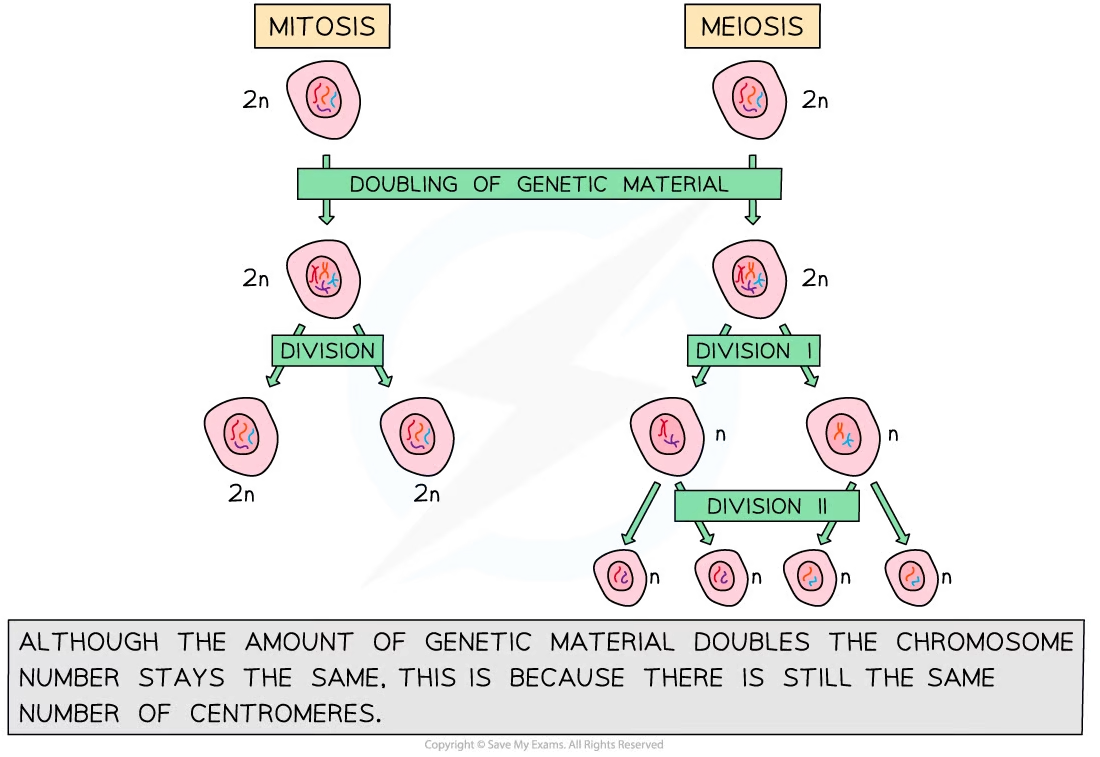
When is mitosis (4) used vs meiosis (1)?
Mitosis → growth, repair, cloning, asexual reproduction
Meiosis → production of gametes (sperm and egg)
What is genetic variation and Why does it happen (4)
GENETIC VARIATION: Difference in DNA Sequence of Individual offsprings from the same parent or species
→ result of random fertilization, meiosis or mutations → each different sperm produces a genetically distinct zygote
What is random fertilization?
during sexual reproduction, the male gamete and female gamete that fuse to produce an offspring are selected randomly from the pool of male and female gametes
What are catalysts + example?
a substance that increases the rate of a reaction without itself undergoing any chemical change or being used up (e.g. enzymes like Amylase)
What is ATP (ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE)?
High energy molecule thats an immediate source of power for cell processes and is produced in cellular respiration
What is cellular respiration? (Mitochondria)
The process that converts the energy stored in glucose into a usable form of energy, ATP
What is CHO CHO CHON for
CHILDE LOVES PAIMON (acronym)
How are vitamin D, C and A important for the body and what are the sources?
Vitamin D→ the sun, eggs, fish → good for absorbing calcium and bone health
Vitamin C→ citris fruits, tomatoes → teeth/bone repair and making collagen
Vitamin A → leafy greens, carrots → vision in dim light and immune system
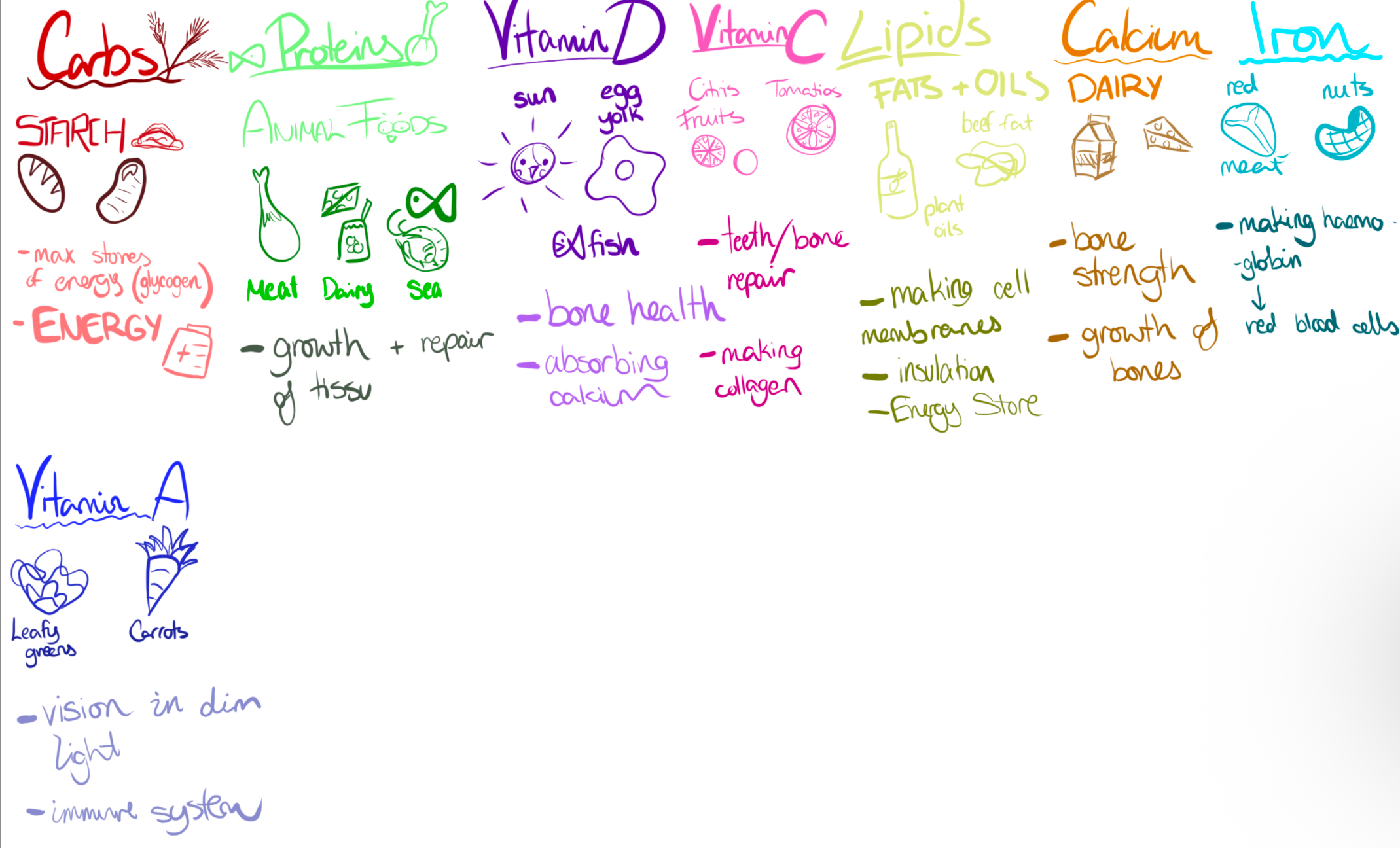
Carbs, Proteins, Iron uses and where found
Carbs→ starch (bread / potatoes) → gives energy for muscles
Protein → Animal foods (meat / dairy) → growth and tissue repair
Iron → red meat / nuts → making haemoglobin (for red blood cells)
Lipids and Calcium, Fiber, where found, what function?
Lipids: Fats and Oils (olive oil and beef fat) → making cell membranes → insulation and energy store
Calcium: Dairy → bone strength and growth
Fiber: beans / whole grains → relieves constipation and lowers blood cholesterol
Bile: where made, where stored, what are it’s roles in digestion?
Made in the liver, stored in the gall bladder. It’s an alkali so it neutralizes food covered in stomach acid and emulsifies (mix) large liquids