bar graph frq
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
5 Terms
(a) Describe the role of water in the hydrolysis of ATP.
Water breaks down/splits ATP.
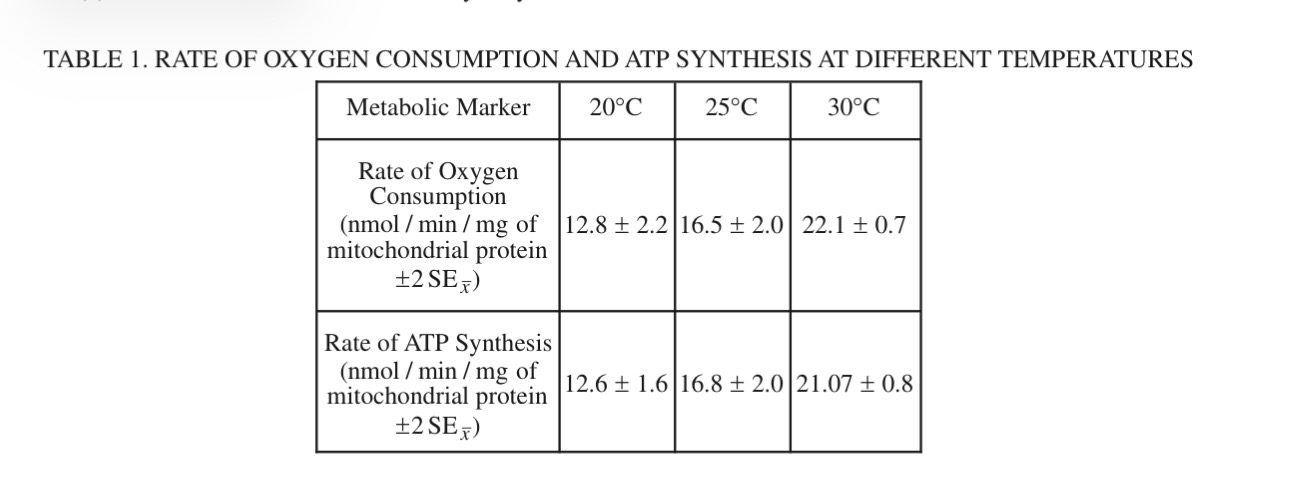
(B) Based on the data provided, determine the temperature in C ° at which the rate of oxygen consumption is different from the rate of oxygen consumption at 25 C
30
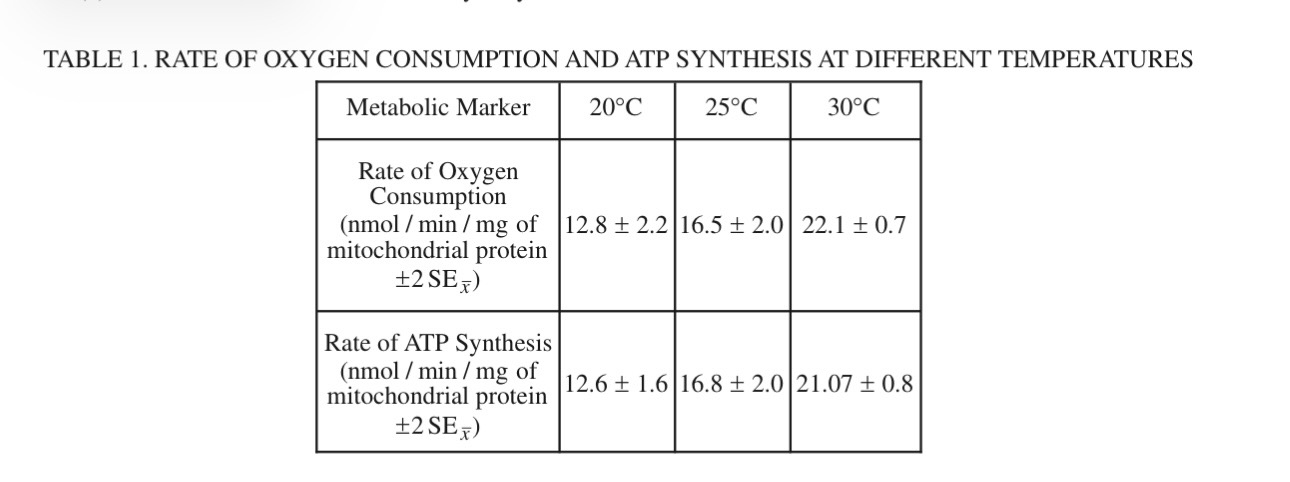
(c) Based on the data in Table 1, describe the effect of temperature on the rate of ATP synthesis in liver cells from toads.
As the temperature increases, the rate of ATP synthesis also increases.
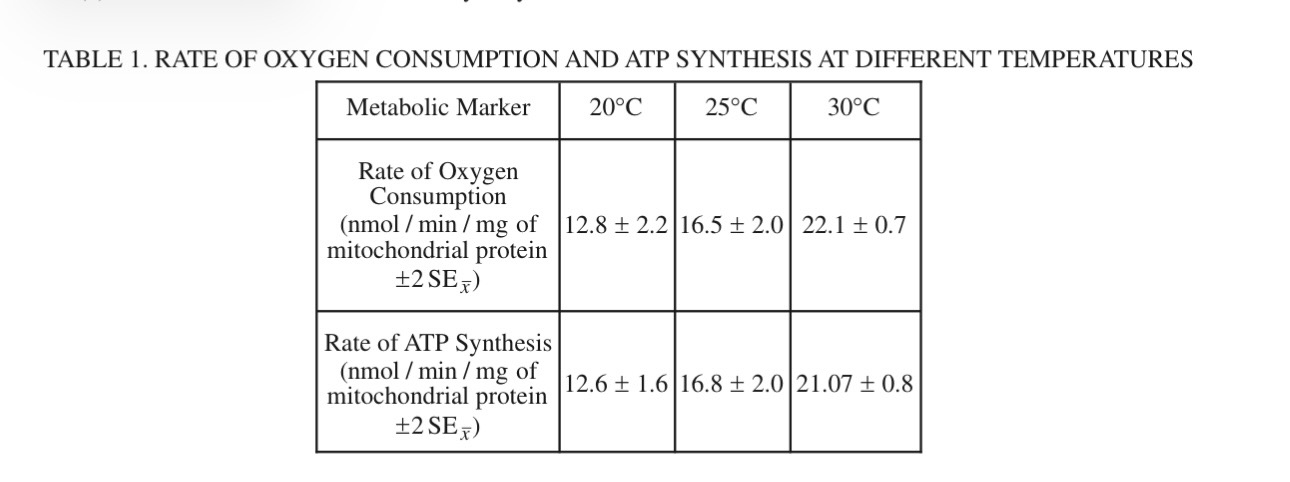
C) Based on the data in Table 1, calculate the average amount of oxygen consumed, in nmol , for 10 mg of mitochondrial protein after 10 minutes at 25 C °
1650nmol
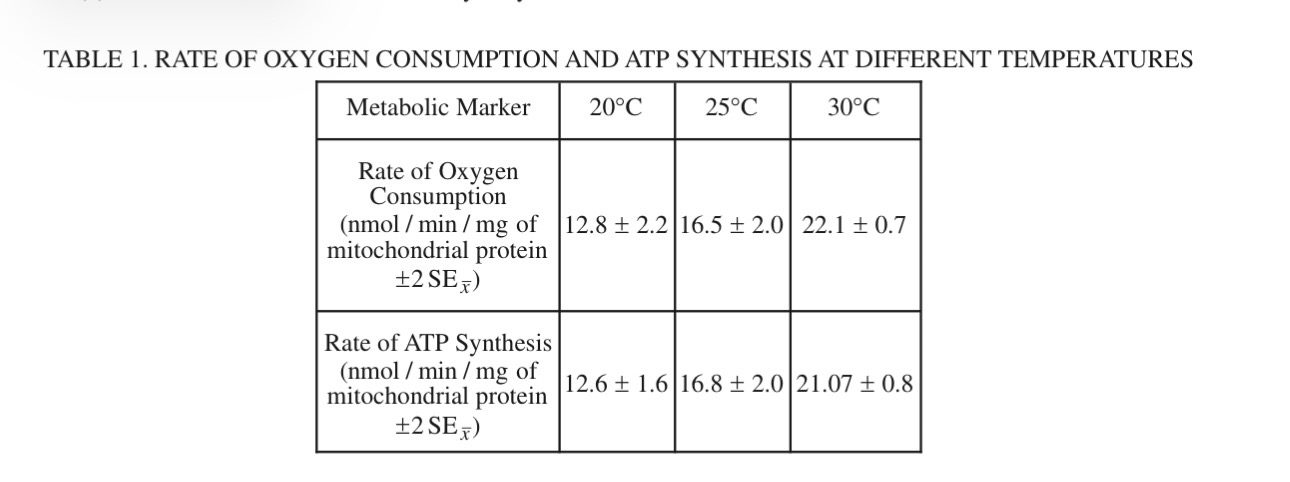
(d) Oligomycin is a compound that can block the channel protein function of ATP synthase. Predict the effects of using oligomycin on the proton gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Justify your prediction.
The proton gradient will increase because more protons will accumulate in the intermembrane space