Concept 2-Cell Transport
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Dynamic equilibrium
Maintained within a range, not constant
Static equilibrium
State of rest in the body
Response
Organism's reaction to environmental changes
Positive feedback loop
Intensifies a response (ex human childbirth)
Negative feedback loop
Causes a counter response to maintain stability (ex sweating, controlling blood sugar)
Cell membrane
Controls substance movement in/out of cell
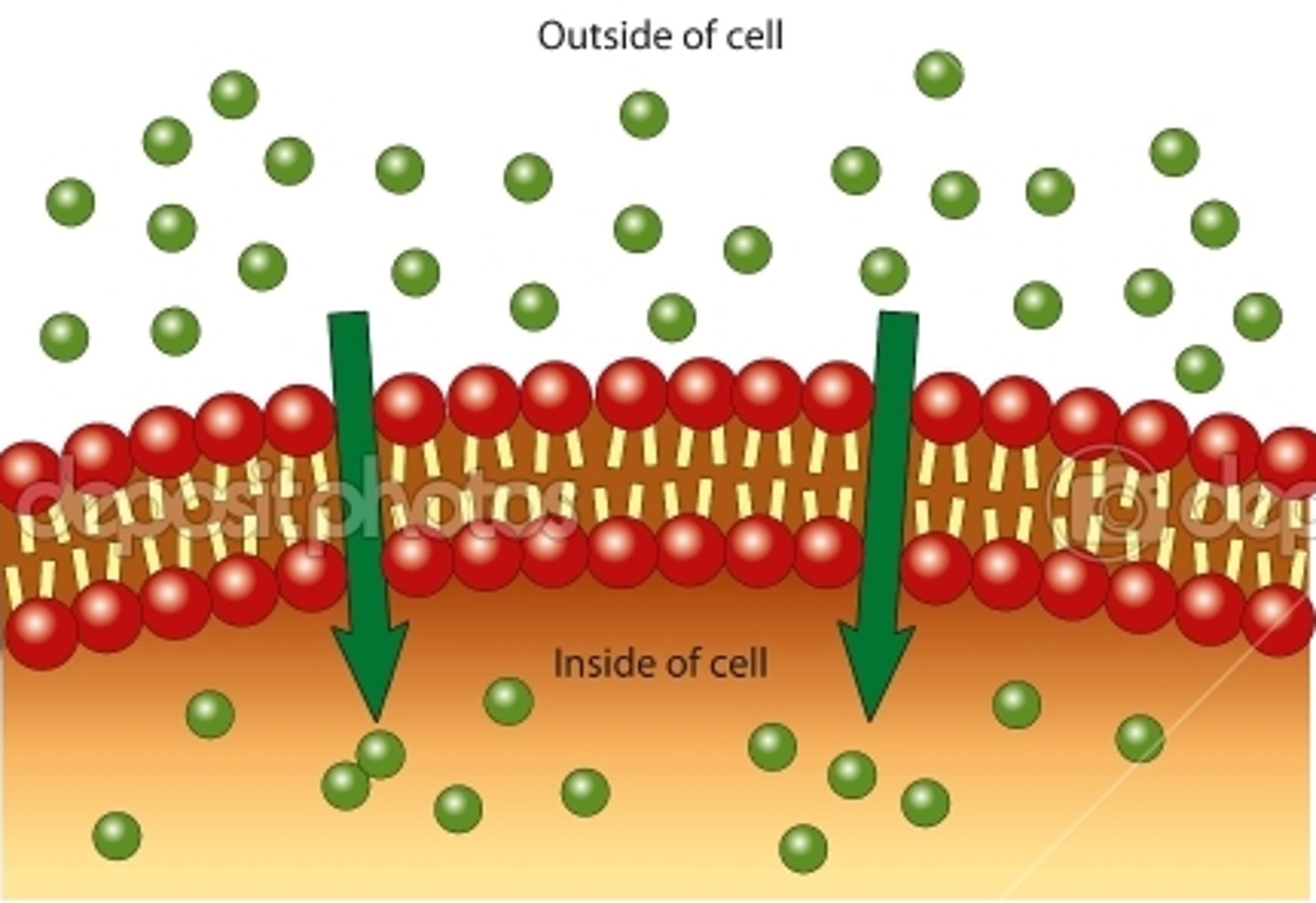
Passive transport
Molecules move from high to low concentration gradient
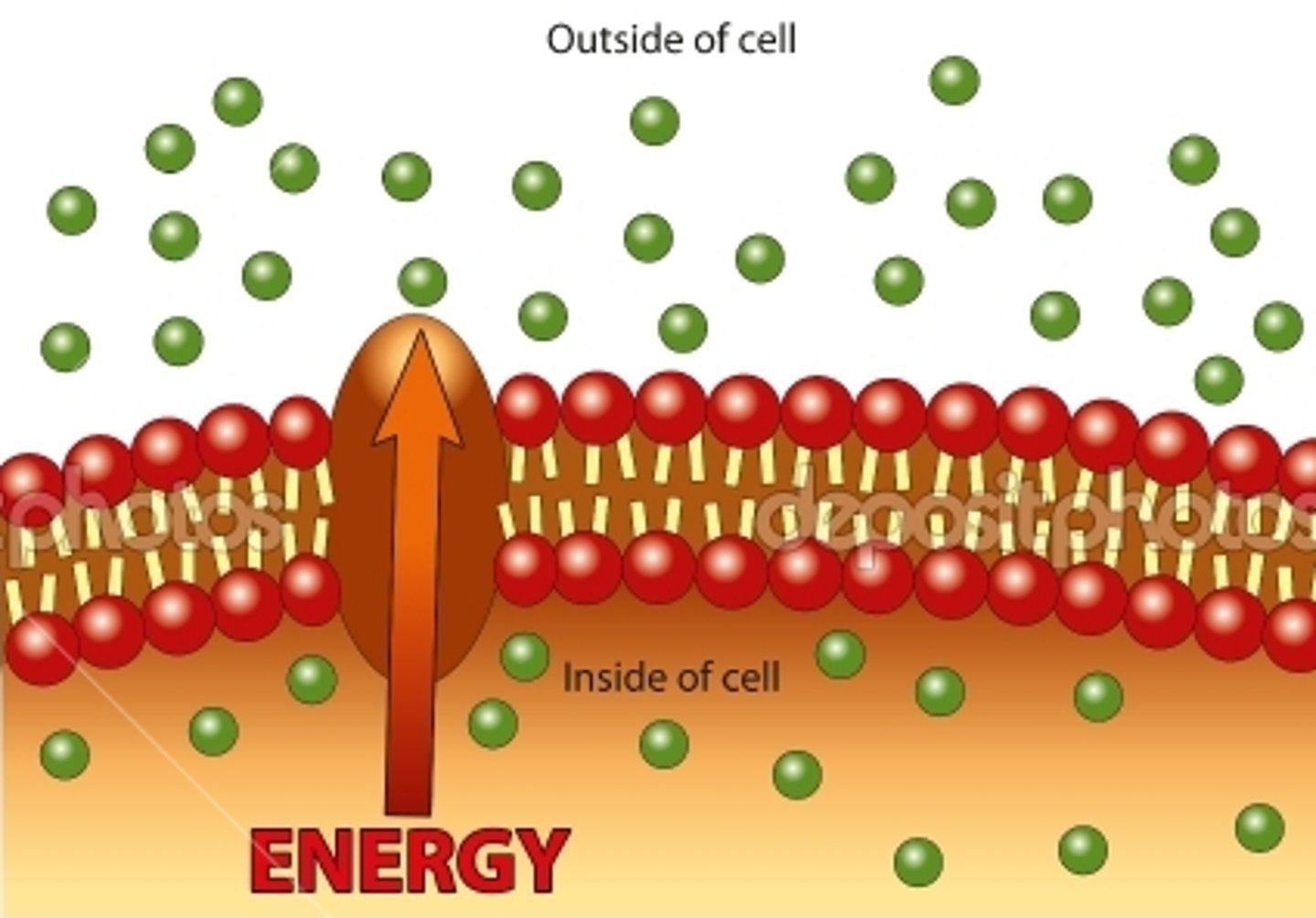
Active transport
Requires energy to move from low to high concentration gradient
Simple diffusion
(passive transport) Molecules spread across the membrane until equilibrium is reached; molecules run down the concentration gradient (high to low []) EX: for small molecules like oxygen and CO2, other small nonpolar molecules
![<p>(<span style="color: rgb(183, 161, 205)"><strong>passive transport</strong>)</span> Molecules spread across the membrane until equilibrium is reached; molecules run <strong>down</strong> the concentration gradient (high to low []) EX: for small molecules like oxygen and CO2, other small nonpolar molecules</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1525b22e-caf6-4f22-87af-ab0762cc66af.png)
Ensures that cells are oxygenated by removing CO₂
Simple diffusion Homeostasis connection
Facilitated diffusion
(passive transport) Transport protein aids in molecule diffusion from (down) high to low concentration gradient (acting as a protein channel). Large molecules like sugar, glucose and calcium
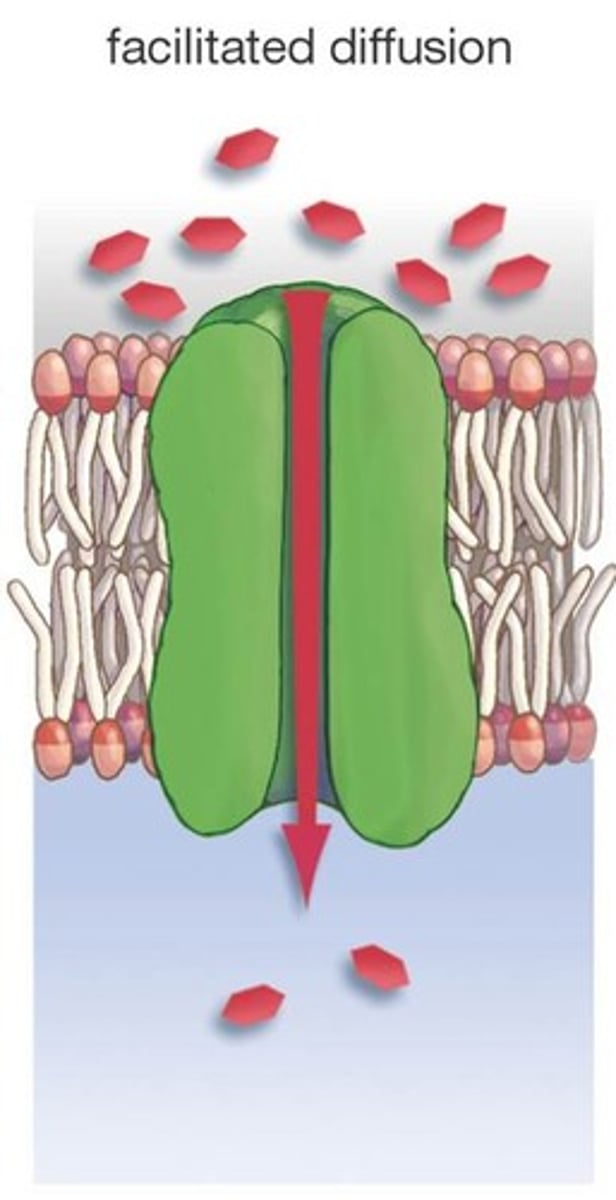
regulates blood sugar by transporting glucose into the cell (transport protein is used)
Facilitated diffusion Homeostasis connection
Osmosis
(passive transport) Simple diffusion of water across cell membrane from (down) high to low concentration gradient until equilibrium is reached
changes water volume in the body (↑ or↓ blood pressure)
Osmosis Homeostasis connection
Molecular Pumps
(active transport) Cell uses energy to move molecules across membrane against the concentration gradient through a protein channel
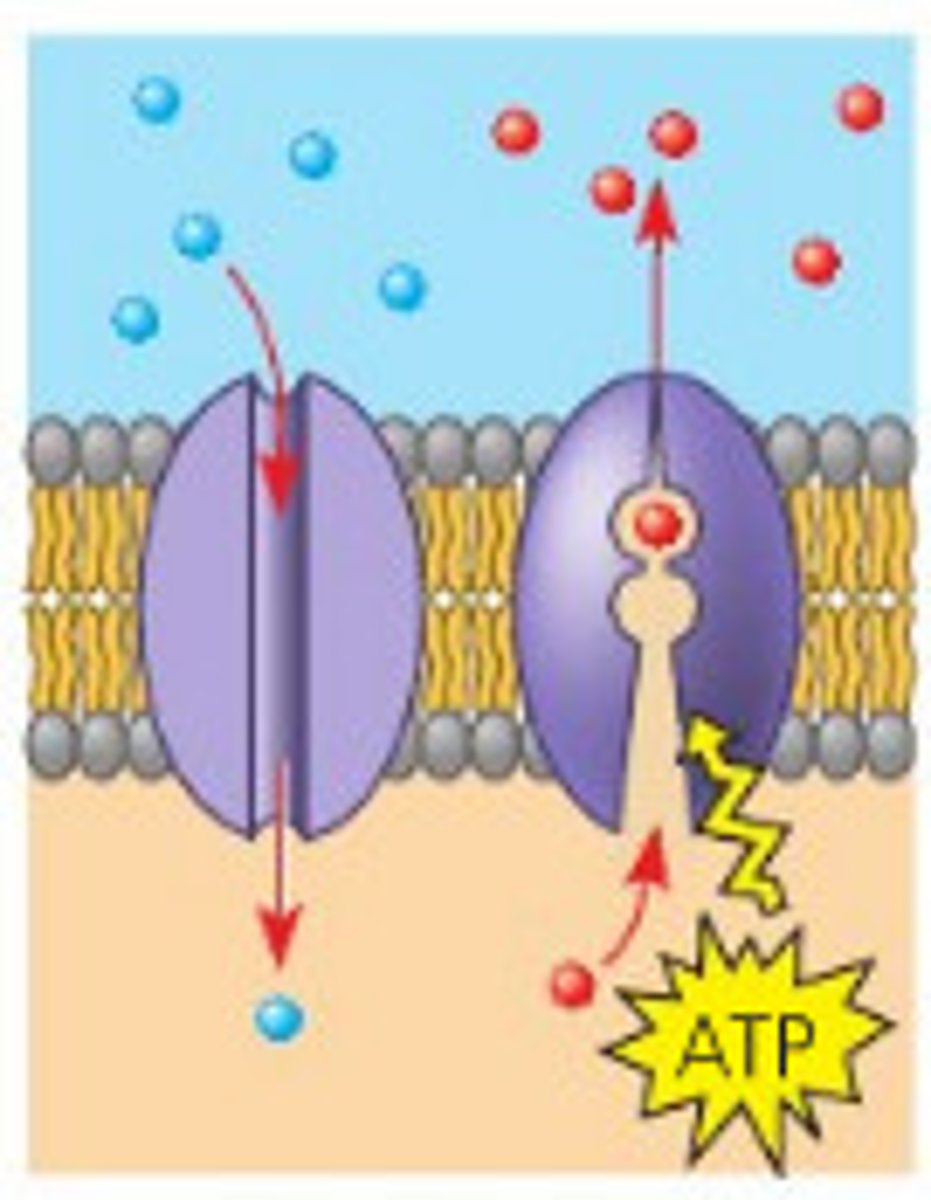
calcium ions released contract and relax muscles
Molecular Pumps Homeostasis connection
Endocytosis
(active transport) Vesicles move large particles INTO the cell (blood cell engulfs bacteria)
Phagocytosis
Endocytosis: cell eating: Cell engulfs solids into vesicle and “digests” them
Pinocytosis
Endocytosis: cell drinking: Cell engulfs liquids into vesicle and “digests them
Exocytosis
(active transport) Vesicles export materials OUT of the cell (nerve cells secrete neurotransmitters)
Types of Passive Transport
Simple diffusion
Fascilitated diffusion
Osmosis
Types of Active Transport
Molecular pump
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Hypertonic solution
Water [ ] is lower than the cells’ cytoplasm; Net movement of water OUT of the cell → cell shrivels
Hypotonic solution
Water [ ] is higher than the cell’s cytoplasm; Net movement of water INTO the cell → cell swells
Isotonic solution
Equal solute concentration to cell cytoplasm (same size cell)
Homeostasis
Organism's need to regulate internal conditions
Solute
Substance that gets dissolved (lemonade powder)
Solvent
Substance that does the dissolving (water)
Solution
Uniform mixture of two or more substances
Concentration
Amount of solute dissolved in solvent
Concentration Gradient
Difference in concentration of a substance from on location to another