6-Carbonate rocks
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What are non-clastic sedimentary rocks made of?
They form by chemical or biological precipitation of minerals like calcite, aragonite, dolomite, or silica, rather than by physical breakdown of older rocks.
What are the main components of a limestone?
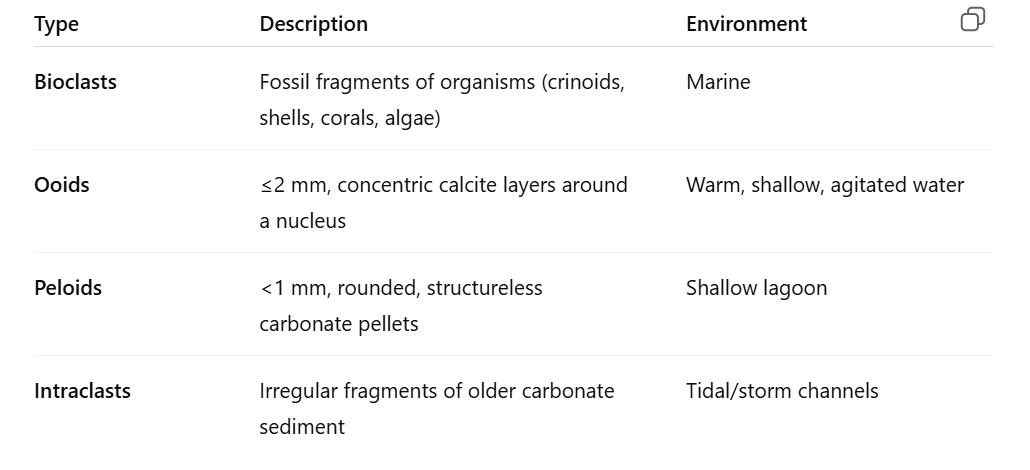
Allochems – recognizable carbonate grains (bioclasts, ooids, peloids, intraclasts)
Micrite – microcrystalline carbonate mud (matrix)
Sparite – coarse calcite cement (post-depositional)
What are the four common allochems in limestone?
How can you distinguish micrite from sparite in thin section?
Micrite – dull, fine-grained, mud-supported texture
Sparite – clear, coarse, crystalline calcite cement filling pores
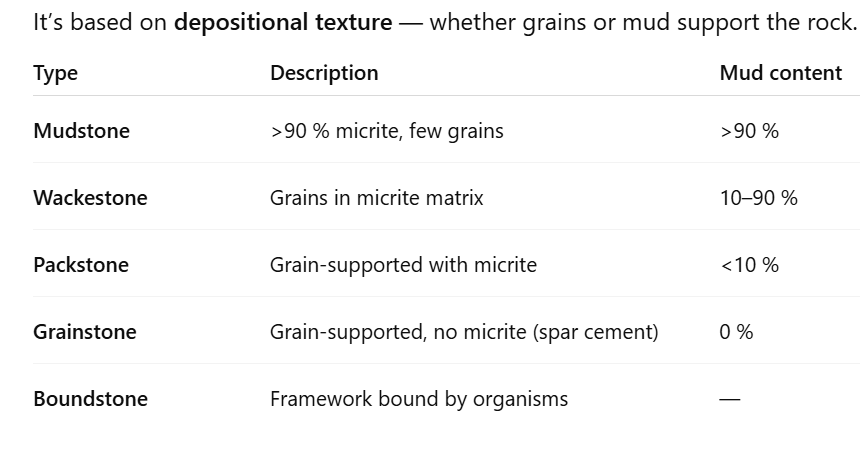
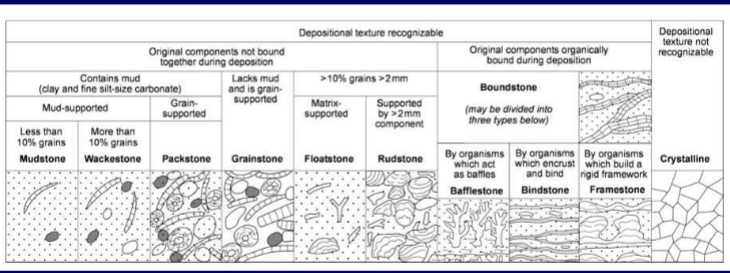
What does the Dunham classification of limestones depend on?
What is the Folk classification system for limestones?
It combines allochem type + matrix/cement type:
e.g.
Biomicrite = bioclasts + micrite
Oosparite = ooids + sparite
Intramicrite = intraclasts + micrite
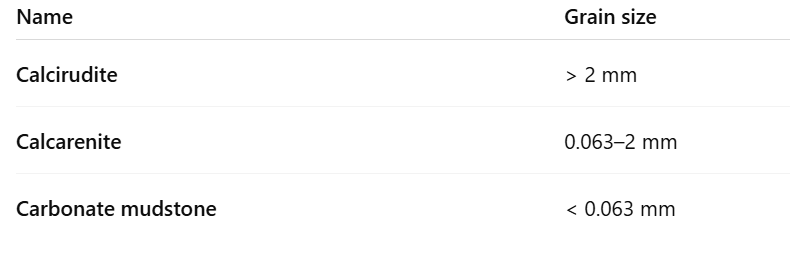
How is limestone grain size classified?
What are typical depositional mechanisms and environments for limestone?

What are carbonate mudstones and how do you identify them?
Dominated by micrite
Lack visible grains
Indicate low-energy, quiet depositional settings (e.g., lagoons, deep water)
What types of porosity occur in sedimentary rocks?
Primary porosity: formed at deposition
Intergranular (between grains)
Intragranular (within grains, e.g. shell chambers)
Secondary porosity: formed later by
Dissolution or dolomitization
Fracturing
How do you recognize dolomite?
Composition: CaMg(CO₃)₂
Crystal form: rhombohedral
Reaction: slow/weak with cold dilute HCl
Origin: replacement of calcite during diagenesis (needs Mg-rich fluids)
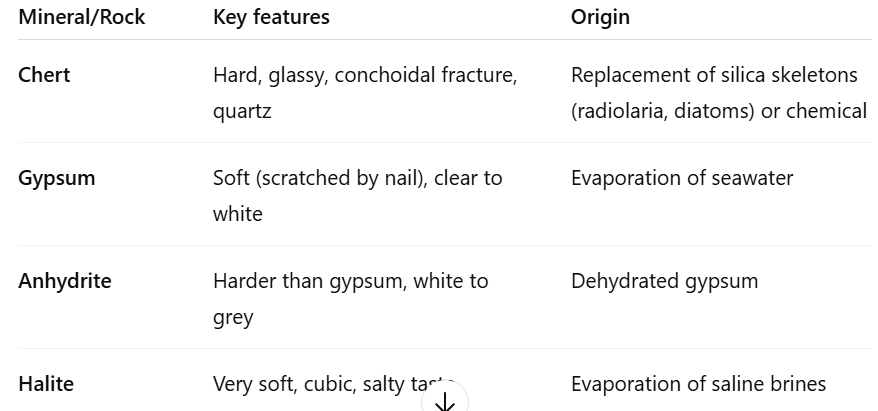
How do you recognize chert and common evaporites?
How is lithofacies defined and what does it tell you?
A lithofacies is a body of rock with a distinct set of features (grains, fossils, texture) that reflects a specific depositional environment (e.g., reef, lagoon, deep marine).
Fossil assemblages help identify these settings.
Difference between carbonates and terrigenous clastics:
Carbonate - mostly occur in shallow tropical marine environments, both chemical and biological production more rapid in warm waters.
-grain size reflects calcified organism hard parts
-sediments may be cemented on the sea floor
-sealevel fall leads to diagenesis and change to depositional texture
Terrigenous - marine, non-marine climate no constraint, just need sediment supply and hold to put it in
-grain size reflected wave and current energy
-sediments normally remain uncemented
-sea-level exposure leaves sediments unaffected
What two rock types do carbonate rocks consist of?
Dolostones - composed mostly of dolomite
Limestones - composed mostly of calcite
What controls on carbonate precipitation?
temperature - as temp increases solubility of CO2 decreases, so sea water is warmed, CO2 release back into atmosphere, and for CaCO3 to be precipitate
photosynthesis, plants take up CO2, and fix it into organic compounds, releasing oxygen
where organisms live, carbonate secreting organisms
What to look for ooids?
Nucleus, concentric layers around. <2mm
Big ooids >2mm are pisoids
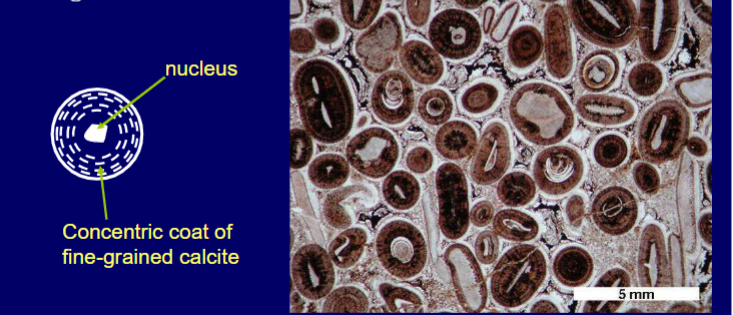
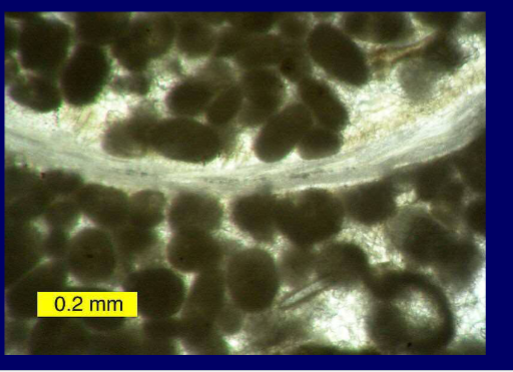
What about peloids?
No concentric structure, rounded, structureless <1mm
Faecal pellets of marine organisms e.g. gastropods
What is Dunham’s classifications scheme?
What is the relationship between porosity and permeability?
Permeable rocks must be porous.
For sandstones, permeability increases as porosity increases.