Lecture 1: Cranium
1/224
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
225 Terms
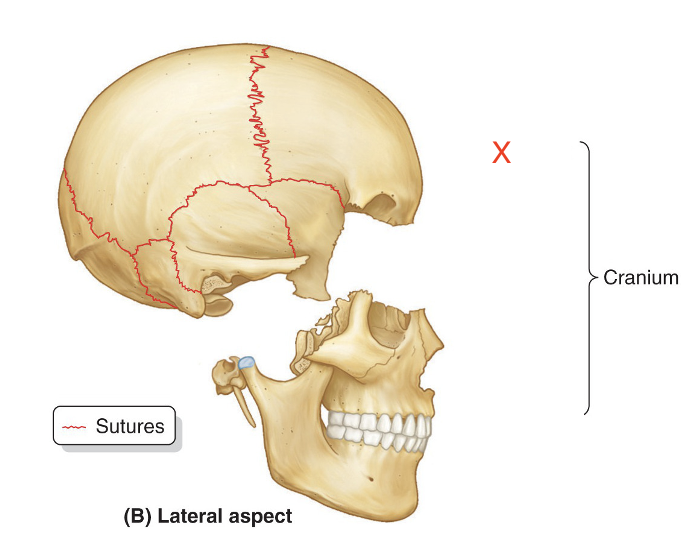
Name the area marked “X”
Neurocranium
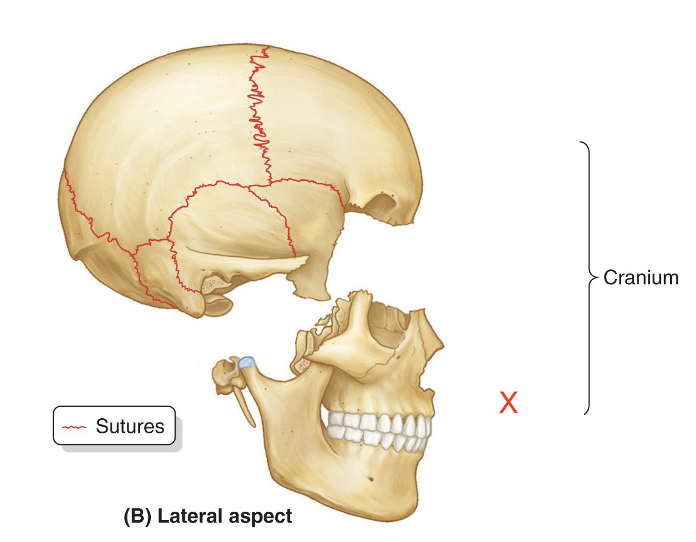
Name the area marked “X”
Viscerocranium
Name the cranial nerves that supply ONLY efferent (motor) fibers
Oculomotor (CN III), Trochlear (CN IV), Abducens (CN VI), Spinal Accessory (CN XI), and Hypoglossal (CN XII)
Name the cranial nerves that supply ONLY afferent (sensory) fibers
Olfactory (CN I), Optic (CN II), and Vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)
What nerve is CN I?
Olfactory
What nerve is CN II?
Optic
What nerve is CN III?
Oculomotor
What nerve is CN IV?
Trochlear
What nerve is CN V?
Trigeminal
What nerve is CN VI?
Abducent
What nerve is CN VII?
Facial
What nerve is CN VIII
Vestibulocochlear
What nerve is CN IX?
Glossopharyngeal
What nerve is CN X?
Vagus
What nerve is CN XI?
Spinal accessory
What nerve is CN XII?
Hypoglossal
What does the olfactory nerve (CN I) do?
Give sense of smell
What does the optic nerve (CN II) do?
Give sight
What does the oculomotor nerve (CN III) do?
Moves all extrinsic eye muscles EXCEPT superior oblique (CN IV) and lateral rectus (VI)
What does the trochlear nerve (CN IV) do?
Moves the superior oblique muscle of the eye
What does the abducent nerve (CN VI) do?
Moves the lateral rectus muscle of the eye
What does the trigeminal nerve (CN V) do? (Motor)
Moves muscles of mastication
What does the trigeminal nerve (CN V) do? (Sensory)
Gives sense of feeling to the face, nose, mouth, teeth, and anterior 2/3 of the tongue
What does the facial nerve (CN VII) do? (Motor)
Moves facial expression muscles and stimulates submandibular, sublingual, lacrimal, nasal, and palatine glands
What does the facial nerve (CN VII) do? (Sensory)
Senses taste from the anterior 2/3 of the tongue and soft palate
What does the vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII) do?
Maintains equilibrium and motion; senses hearing
What does the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) do? (Motor)
Moves stylopharyngeous and stimulates parotid gland
What does the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) do? (Sensory)
Senses taste from the posterior 1/3 of tongue and general sensation of the throat
What does the vagus nerve (CN X) do? (Motor)
Moves palate, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, heart, and GI tract to the left colic flexure
What does the vagus nerve (CN X) do? (Sensory)
Reflex from trachiobronchial tree, lungs, heart and GI tract to left colic flexture
What does the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) do?
Moves the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles
What does the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII) do?
Moves all intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue NOT INCLUDING the palatoglosus and palatine muscles
If CN I were damaged, what would happen?
Loss of smell and cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea
If CN II were damaged, what would happen? (two things)
Loss of pupillary constriction or visual field defects
If CN III were damaged, what would happen?
Dilated pupil, eye turns in and out, pupillary reflex is gone
If CN IV were damaged, what would happen?
Inability to look down the eye is adducted
If CN V were damaged, what would happen?
Loss of pain and touch
If CN VI were damaged, what would happen?
Eye fails to move laterally; diplopia on lateral gaze
If CN VII were damaged, what would happen?
Paralysis of facial muscles; eyes stay open and angle of mouth droops
If CN VIII were damaged, what would happen?
Progressive unilateral hearing loss and tinnitus
If CN IX were damaged, what would happen?
Loss of taste on posterior 1/3 of tongue and loss of sensation on soft palate
If CN X were damaged, what would happen?
Sagging of soft palate, paralysis of vocal chord, deviation of uvula
If CN XI were damaged, what would happen?
Paralysis of sternocleiodomastoid and descending fibers of trapezius; drooping of shoulder
If CN XII were damaged, what would happen?
Protruded tongue deviates towards affected side; moderate dysarthria
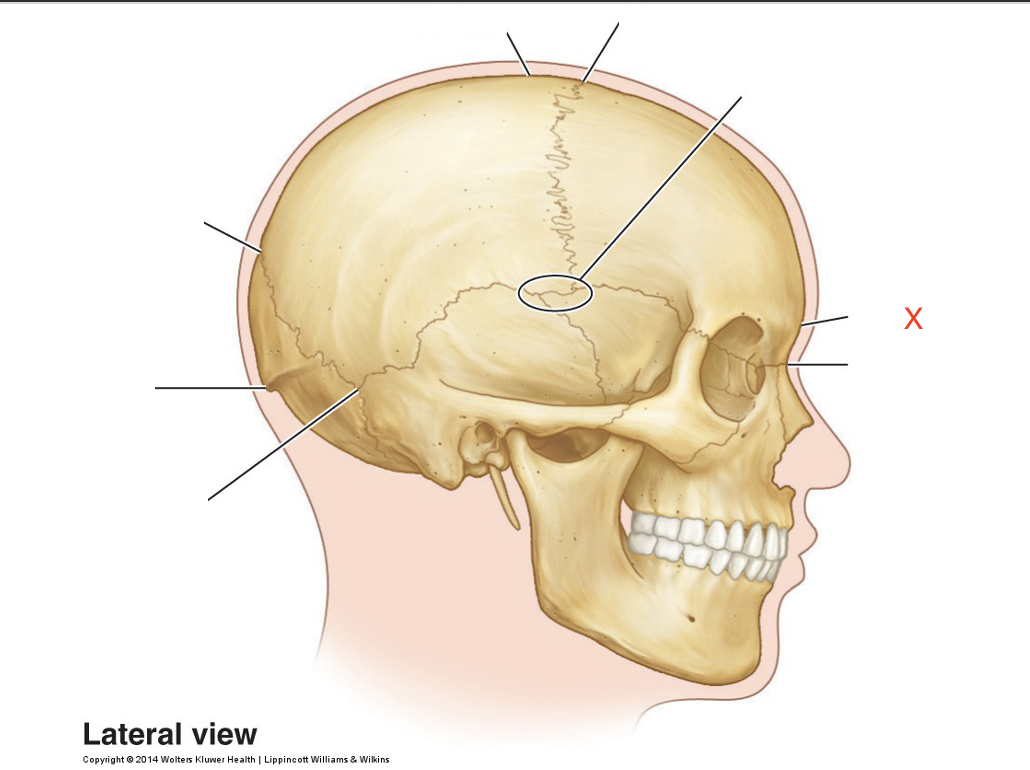
Name the area marked “X”
Glabella
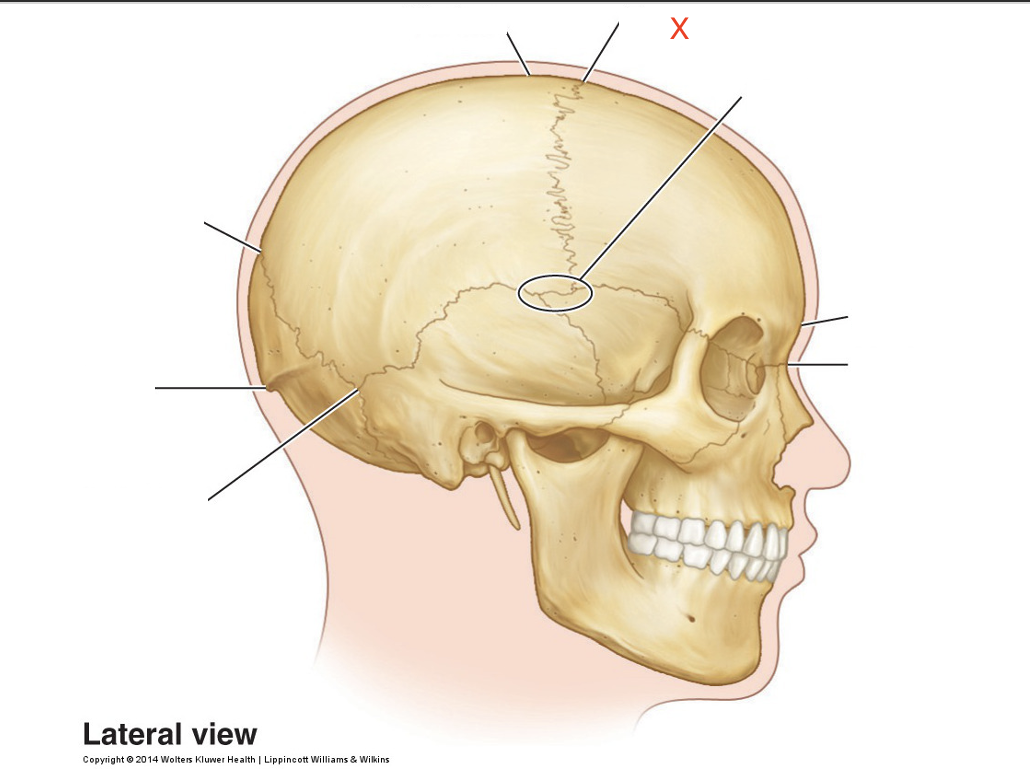
Name the area marked “X”
Bregma
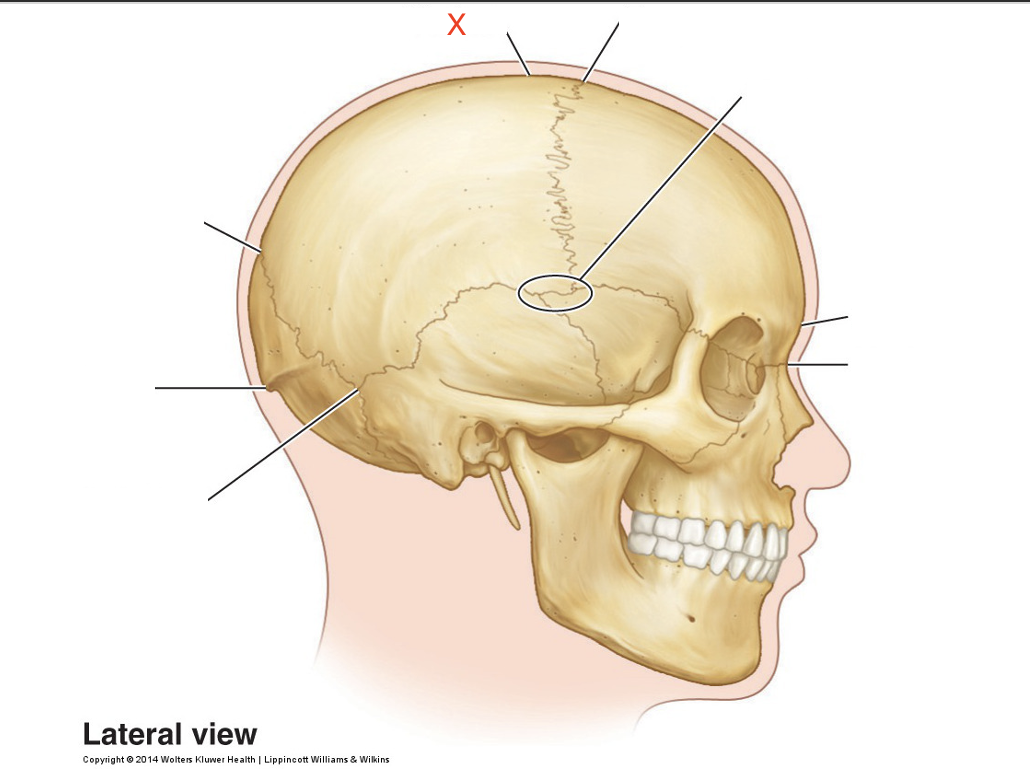
Name the area marked “X”
Vertex
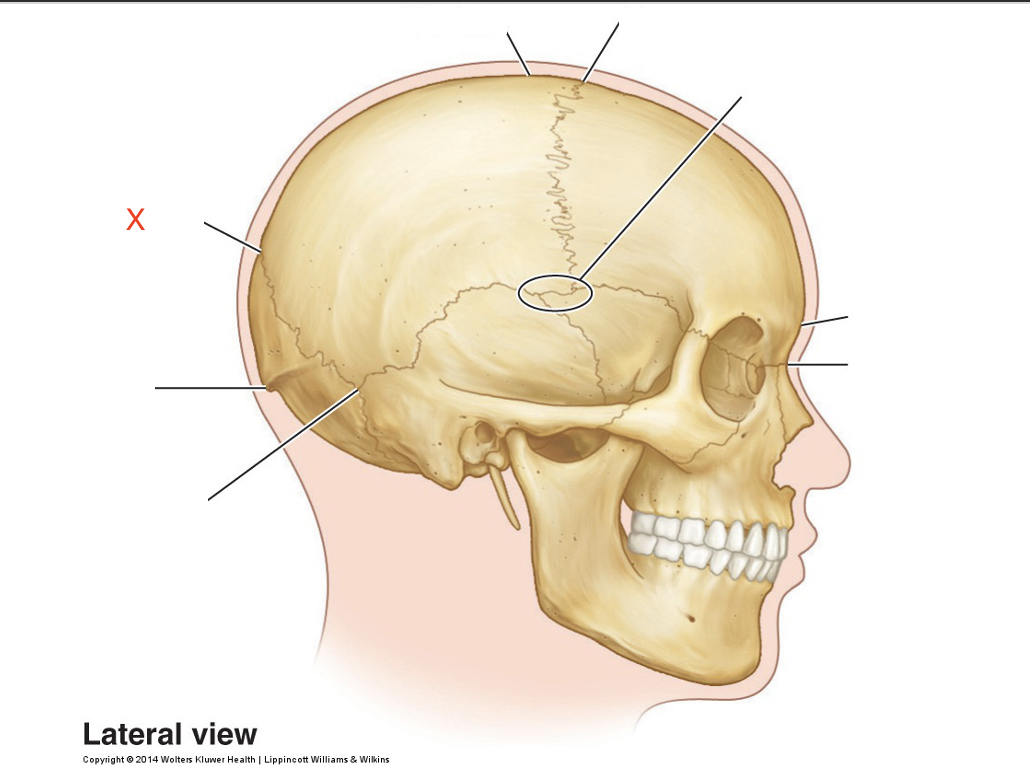
Name the area marked “X”
Lambda
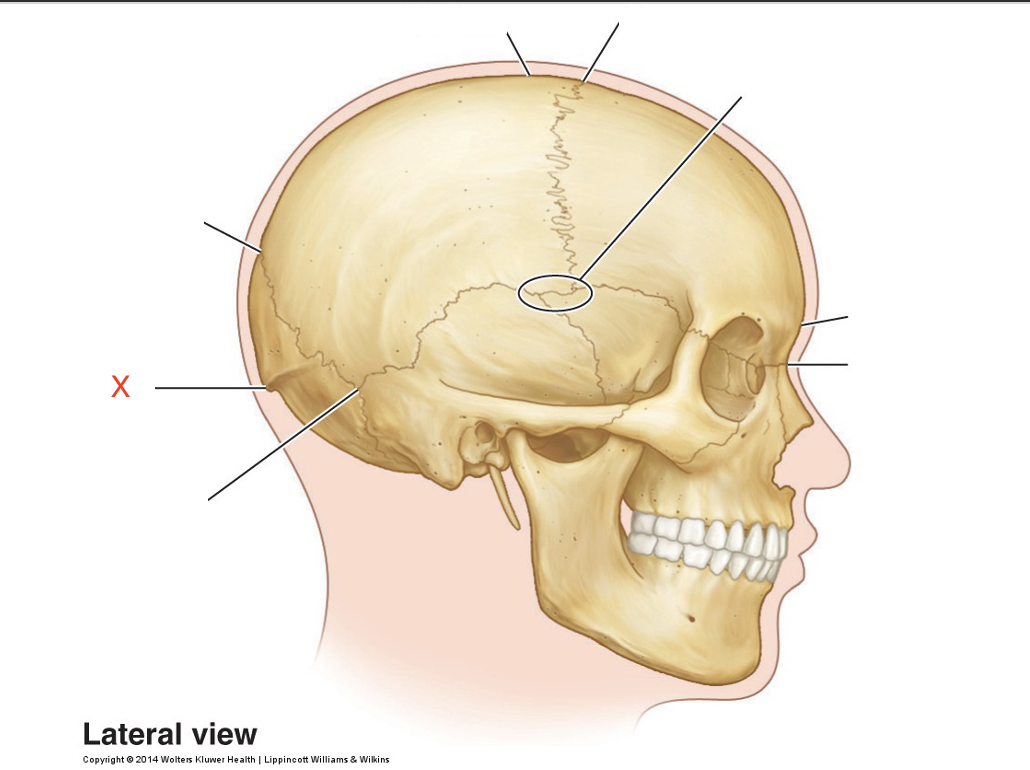
Name the area marked “X”
Inion
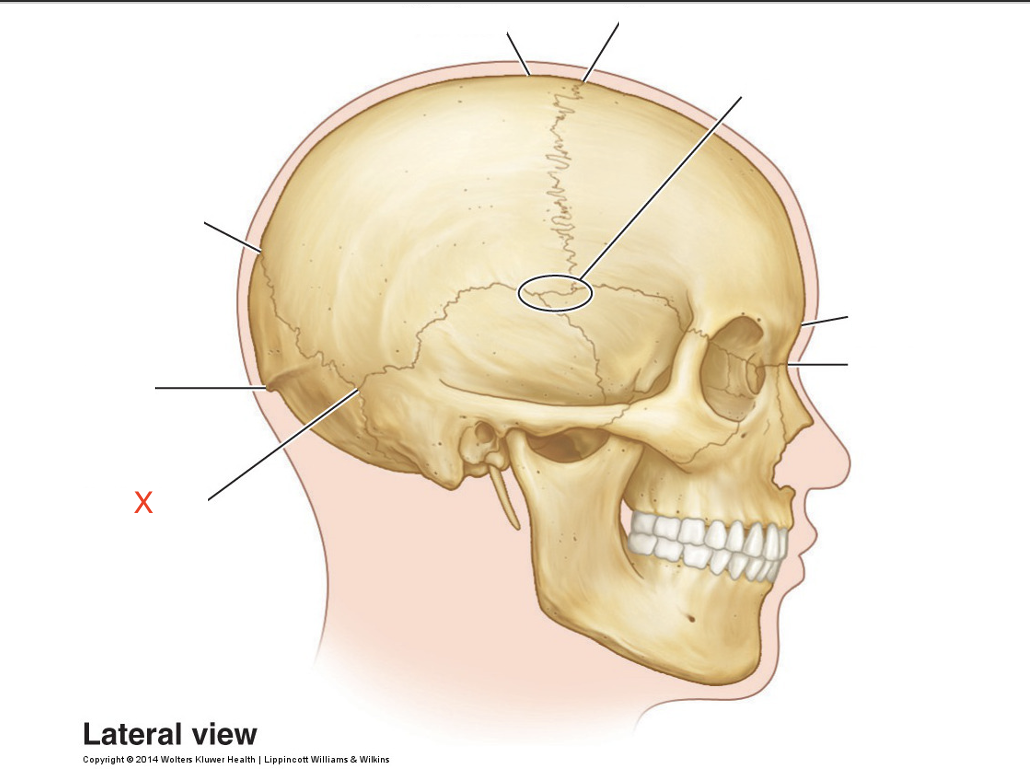
Name the area marked “X”
Asterion
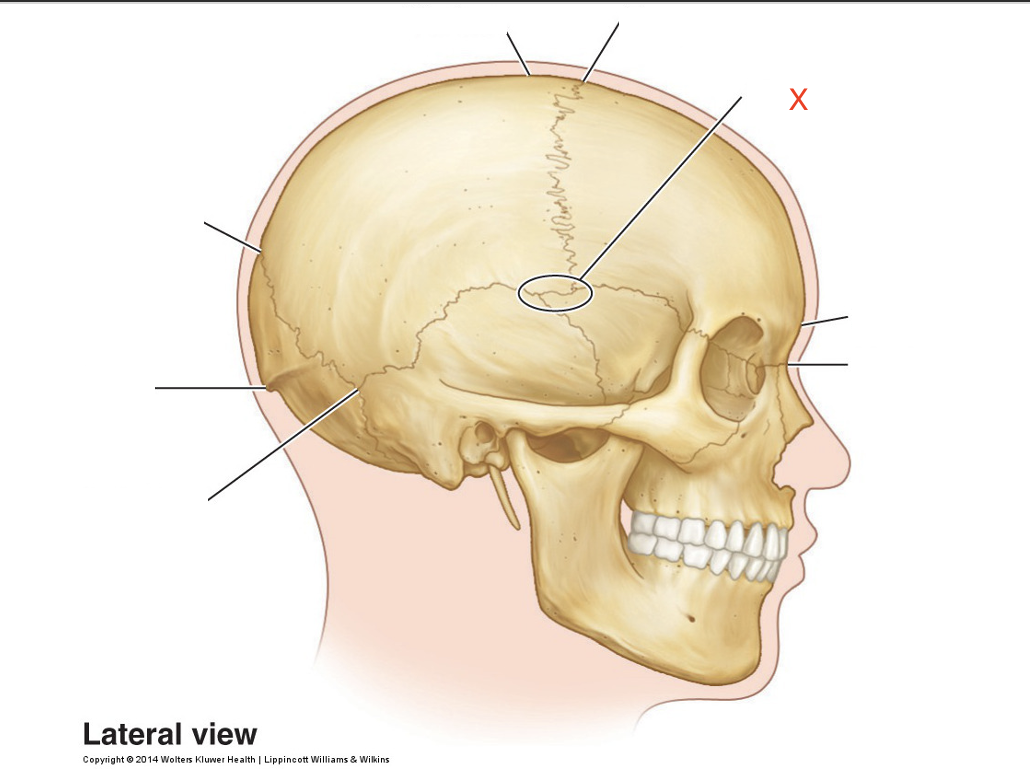
Name the area marked “X”
Pterion
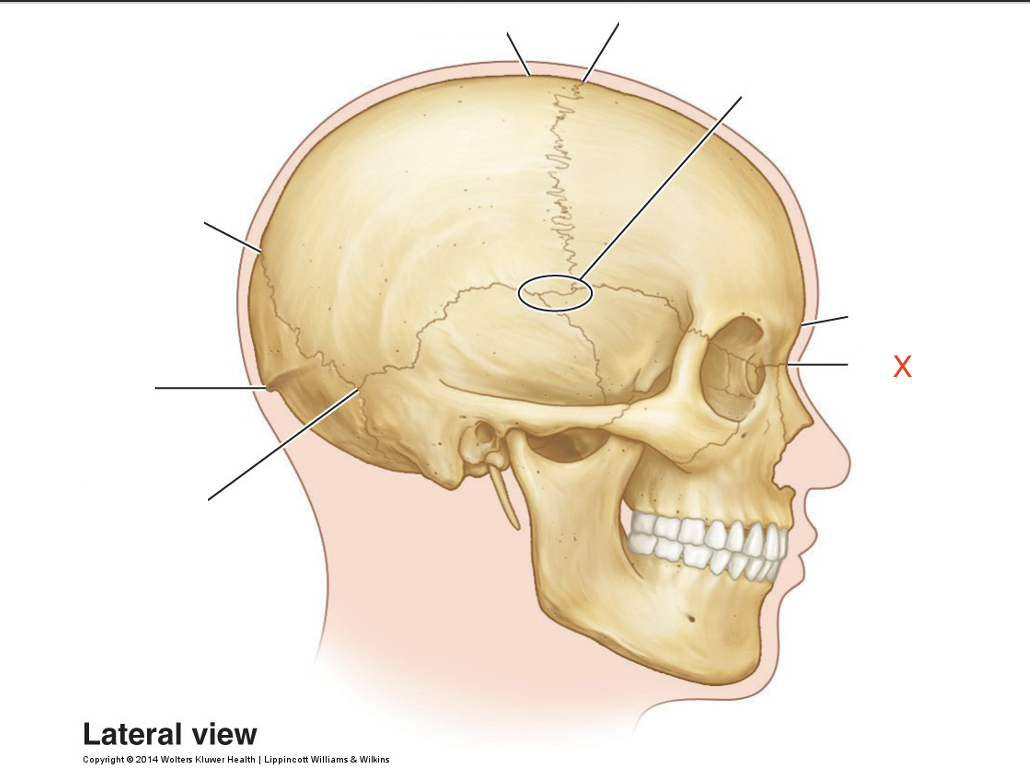
Name the area marked “X”
Nasion
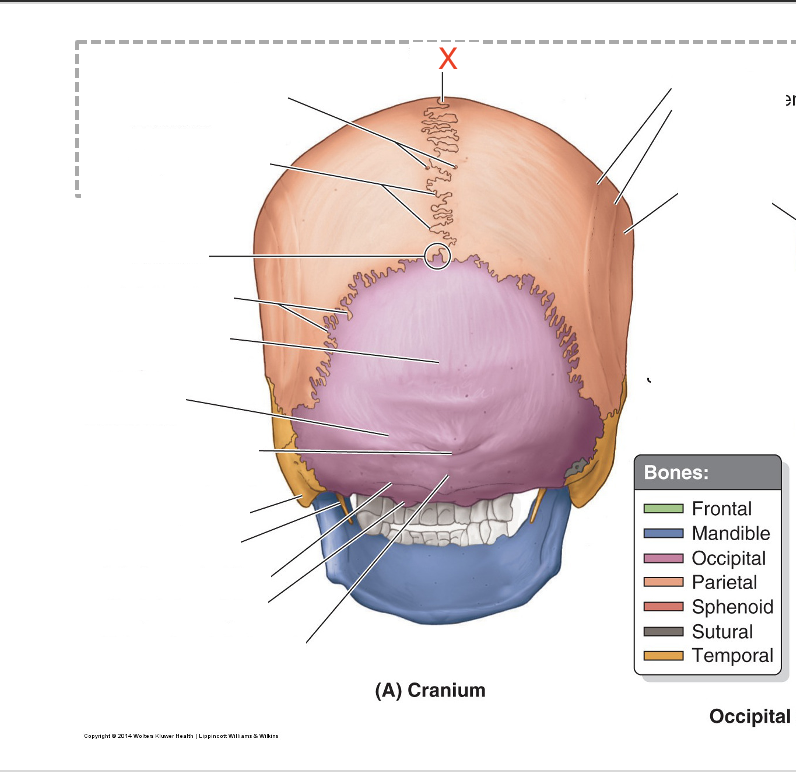
Name the area marked “X”
Vertex
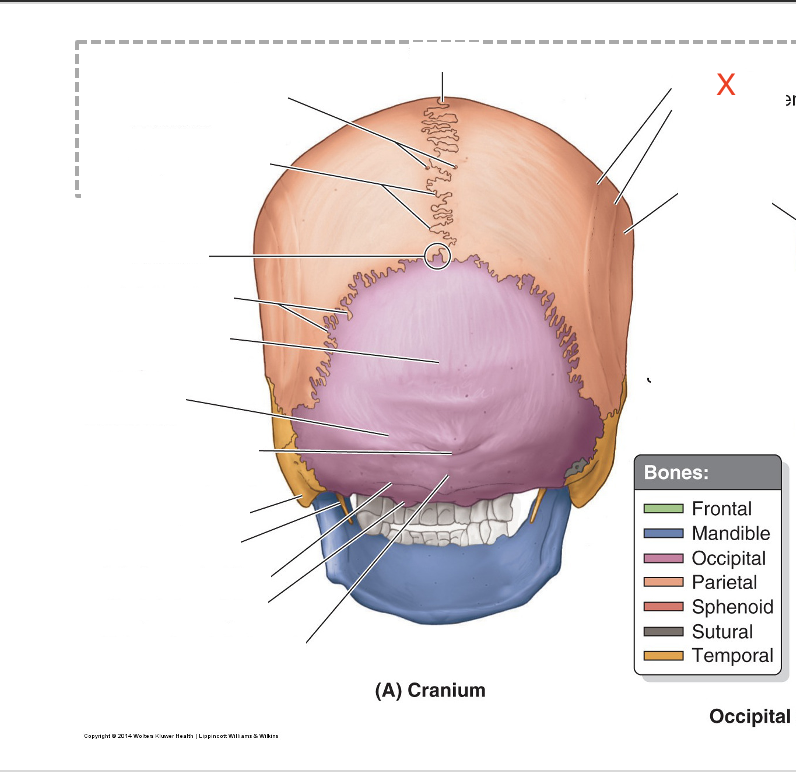
Name the area marked “X”
Superior temporal line
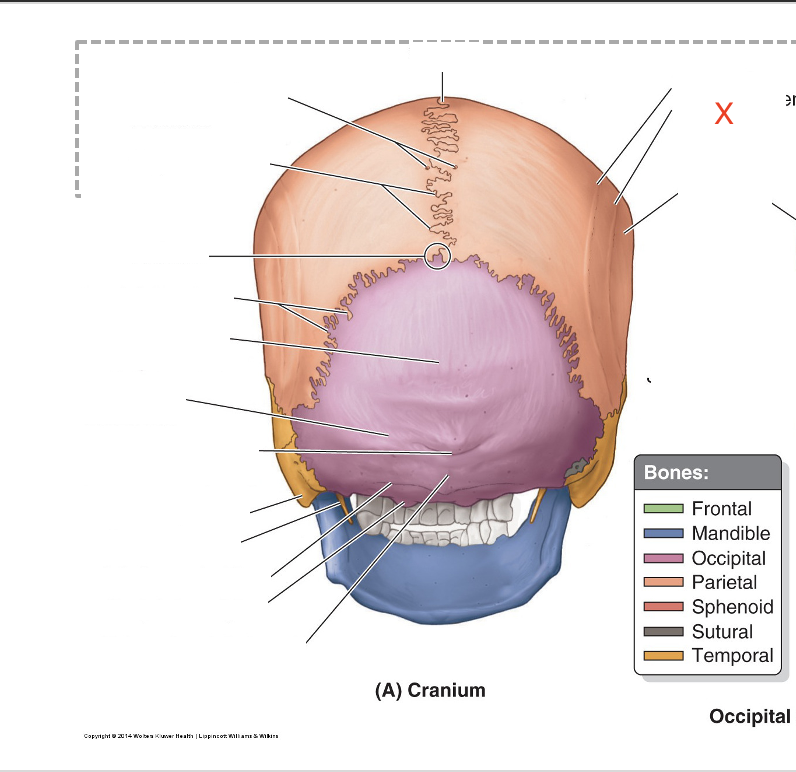
Name the area marked “X”
Inferior temporal line
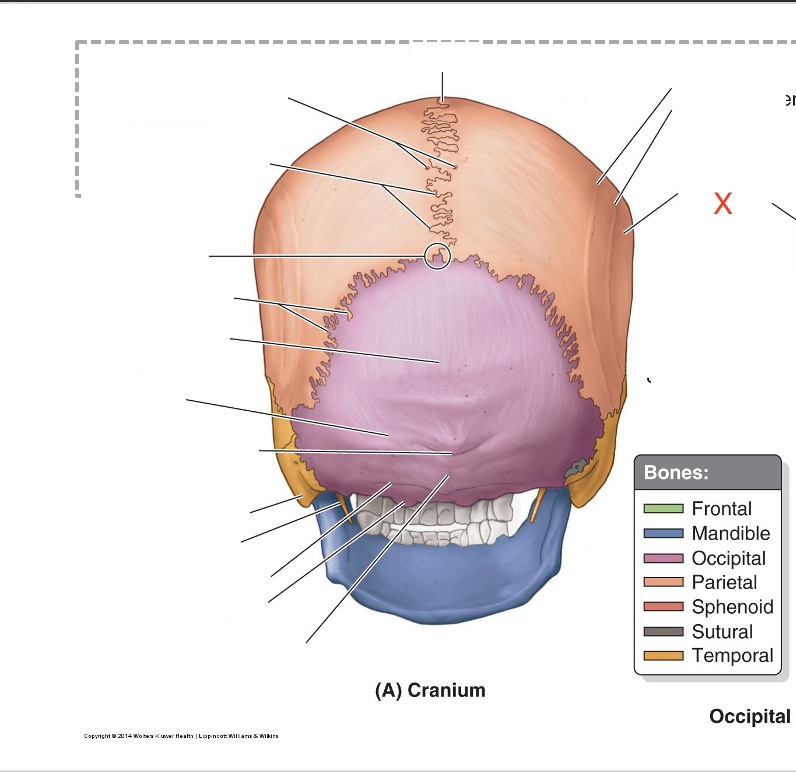
Name the area marked “X”
Parietal eminence
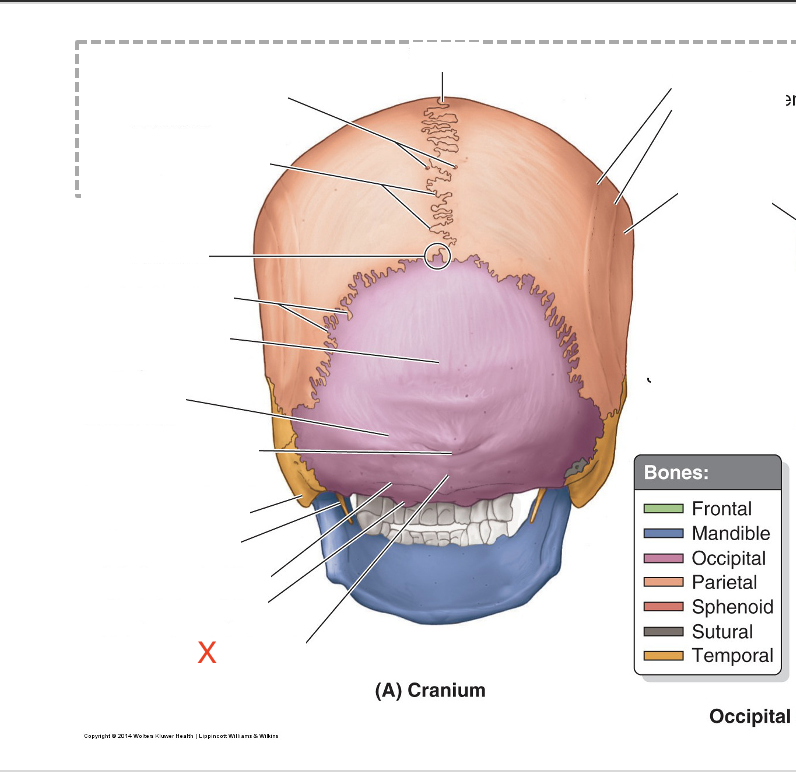
Name the area marked “X”
External occipital crest
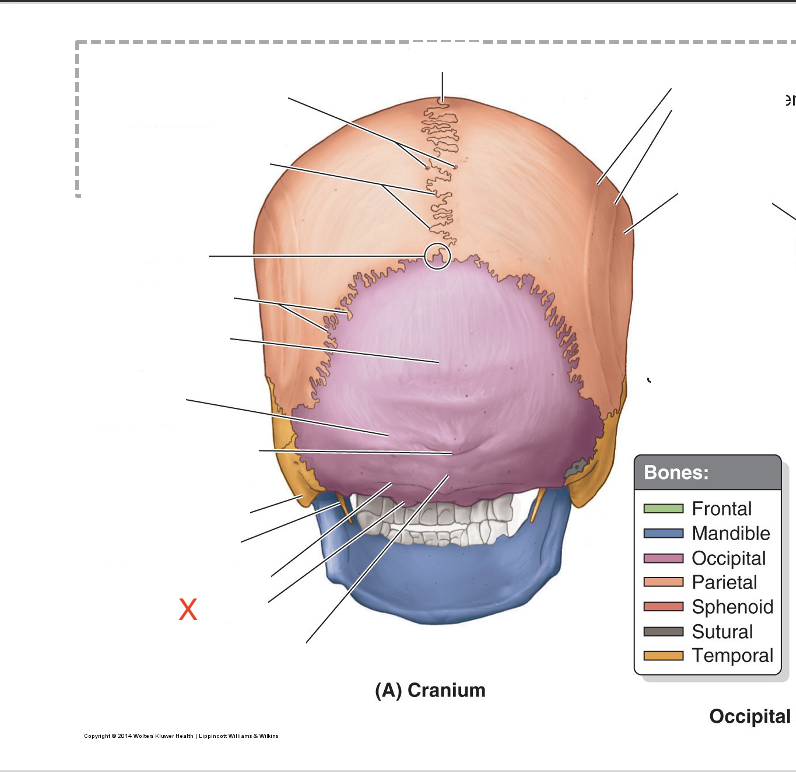
Name the area marked “X”
Occipital condyle
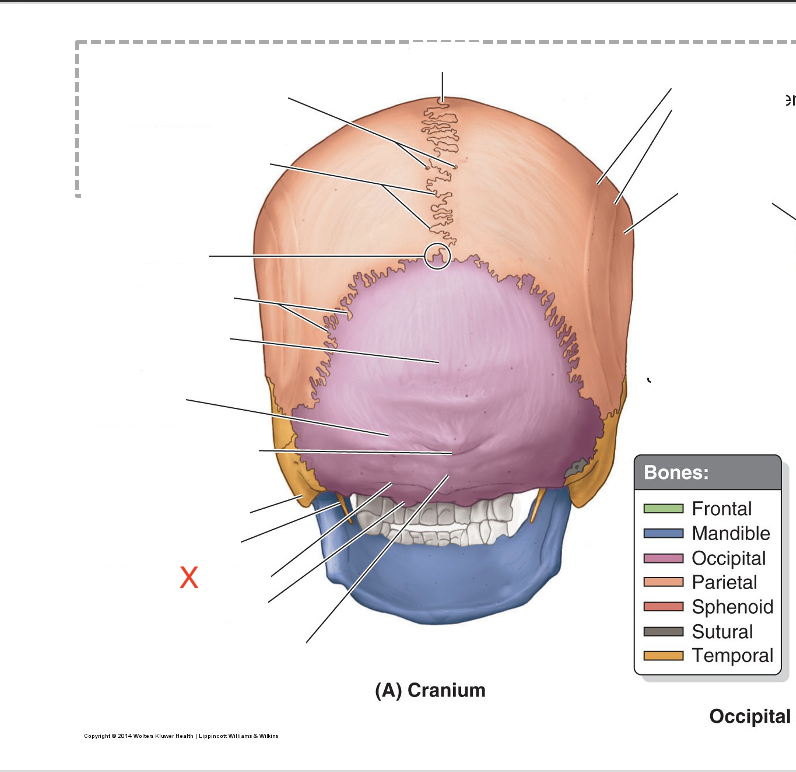
Name the area marked “X”
Inferior nuchal line
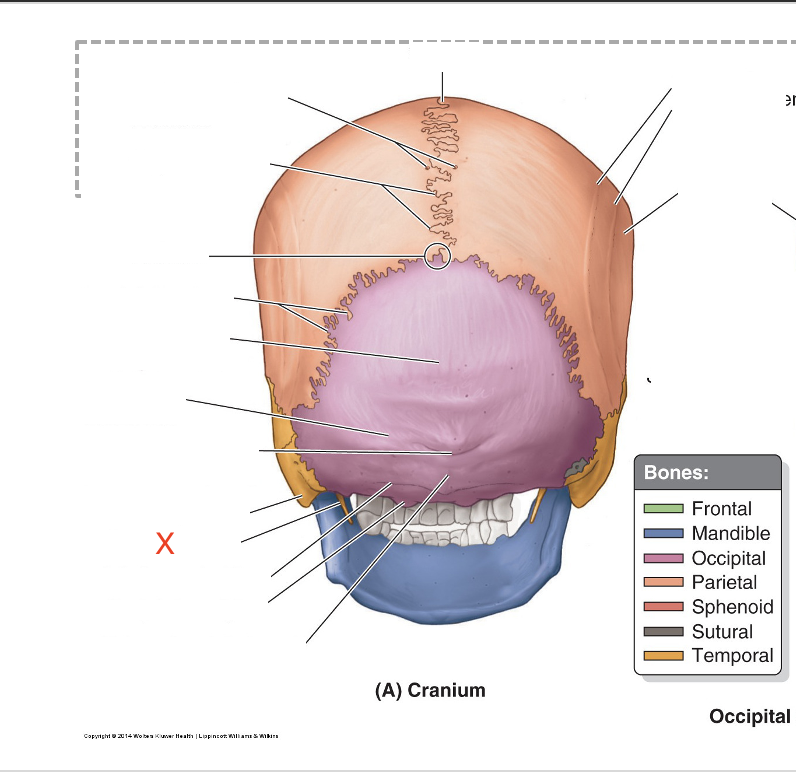
Name the area marked “X”
Styloid process
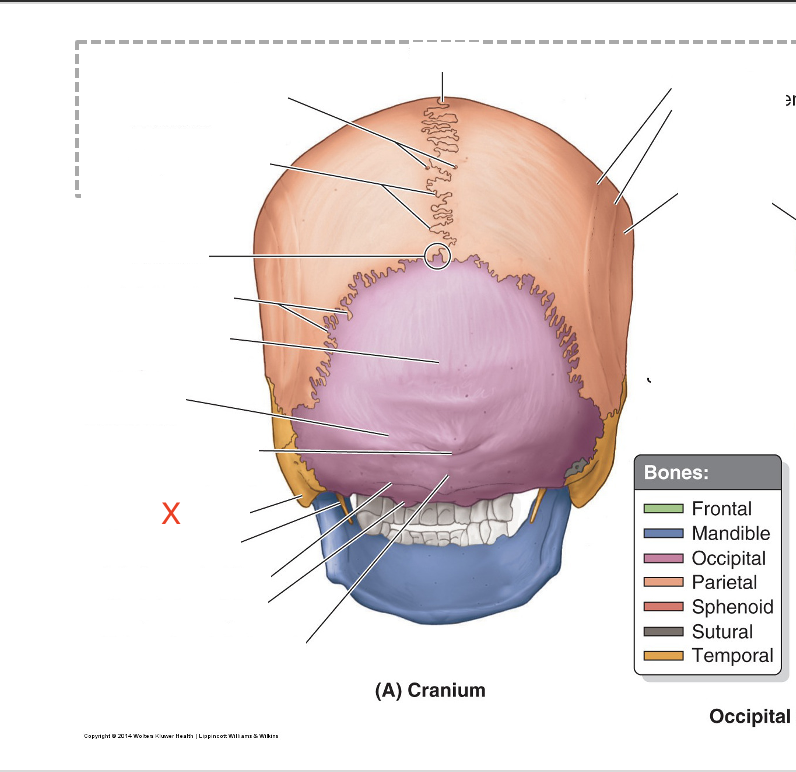
Name the area marked “X”
Mastoid process
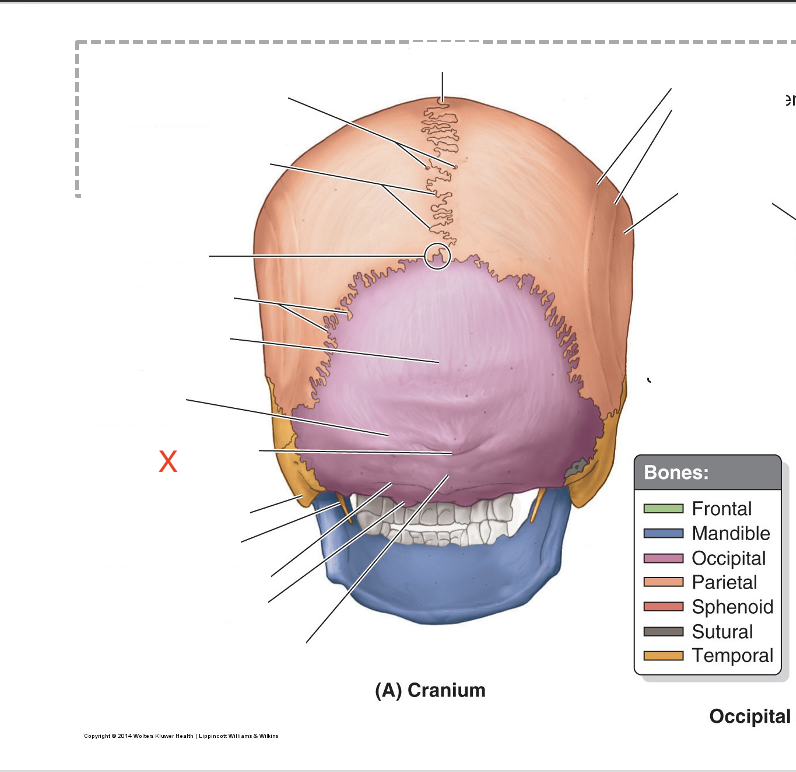
Name the area marked “X”
External occipital protuberance (inion)
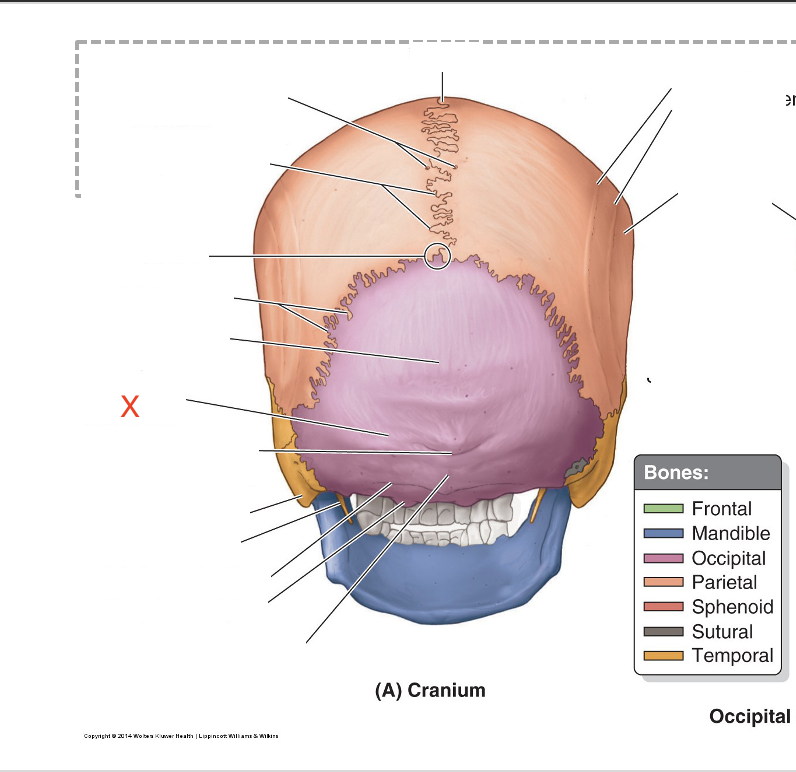
Name the area marked “X”
Superior nuchal line
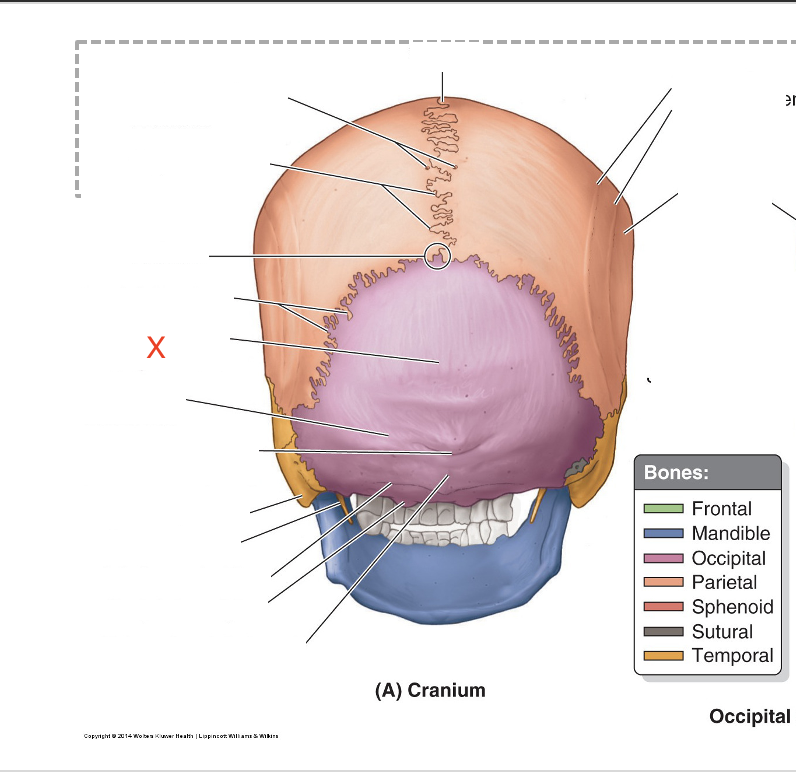
Name the area marked “X”
Squamous part of occipital bone
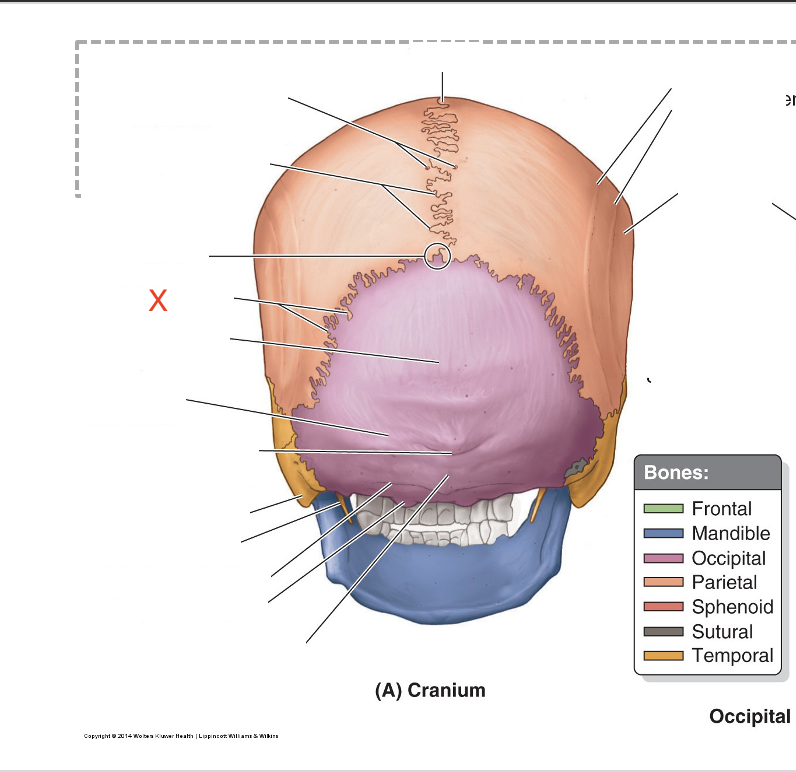
Name the area marked “X”
Lambdoid suture
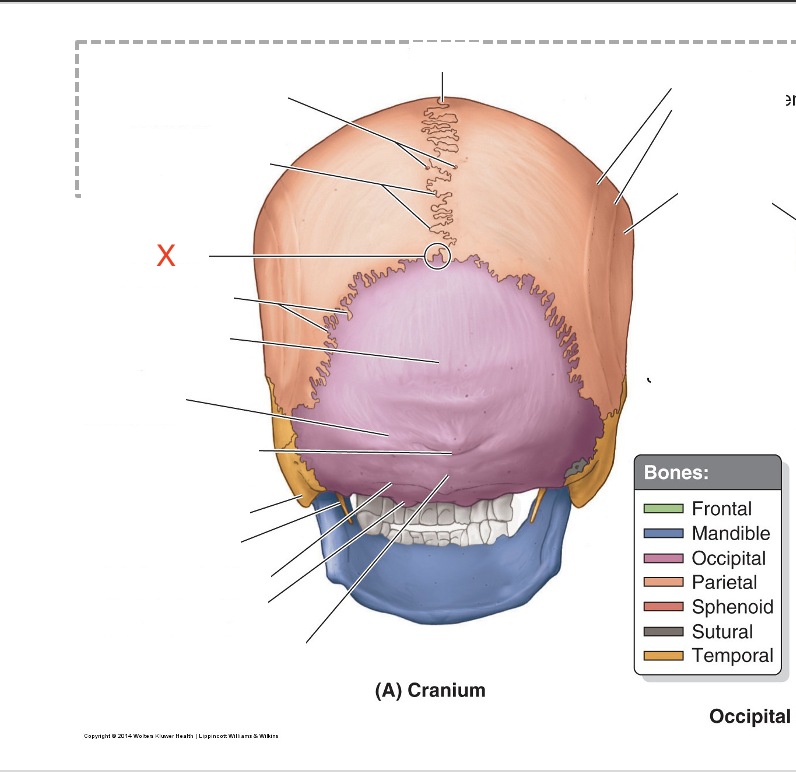
Name the area marked “X”
Lambda
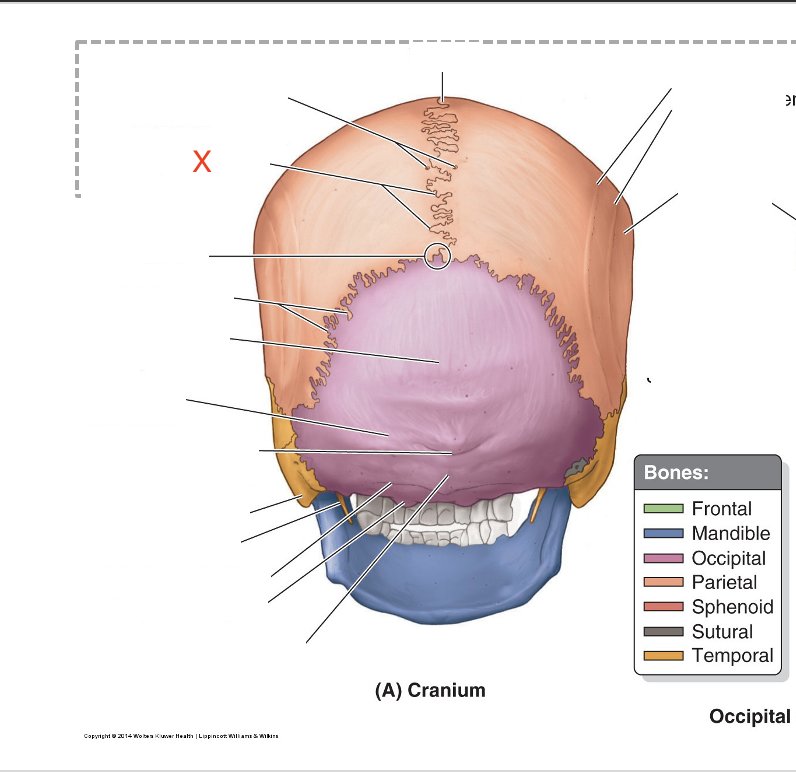
Name the area marked “X”
Sagittal suture
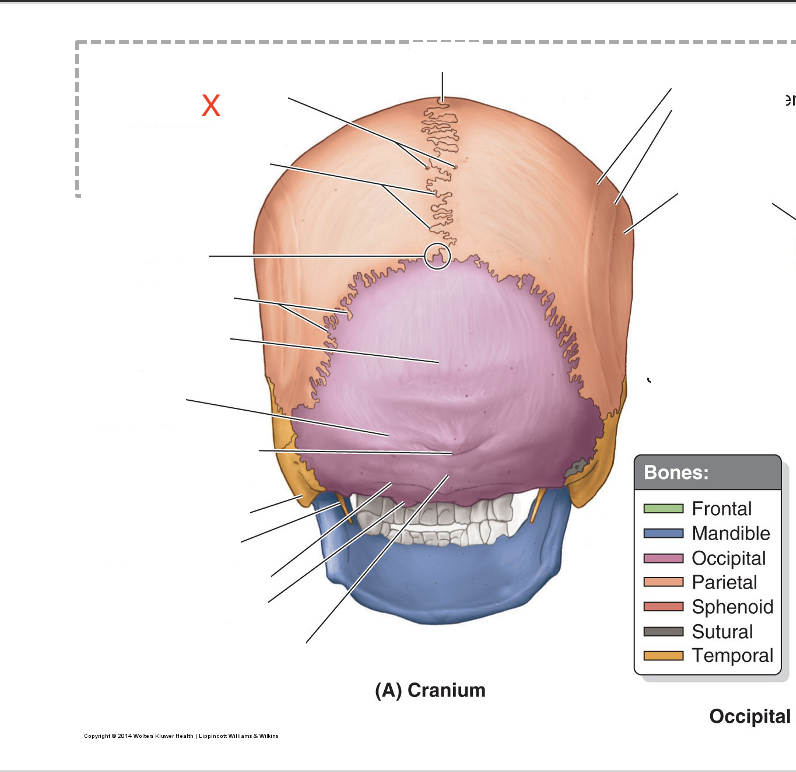
Name the area marked “X”
Parietal emissary foramina
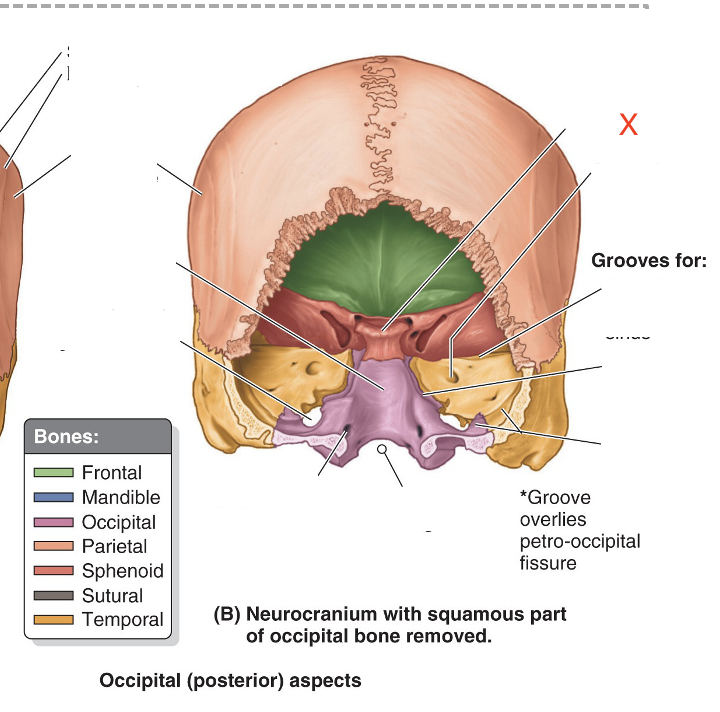
Name the area marked “X”
Dorsum sellae
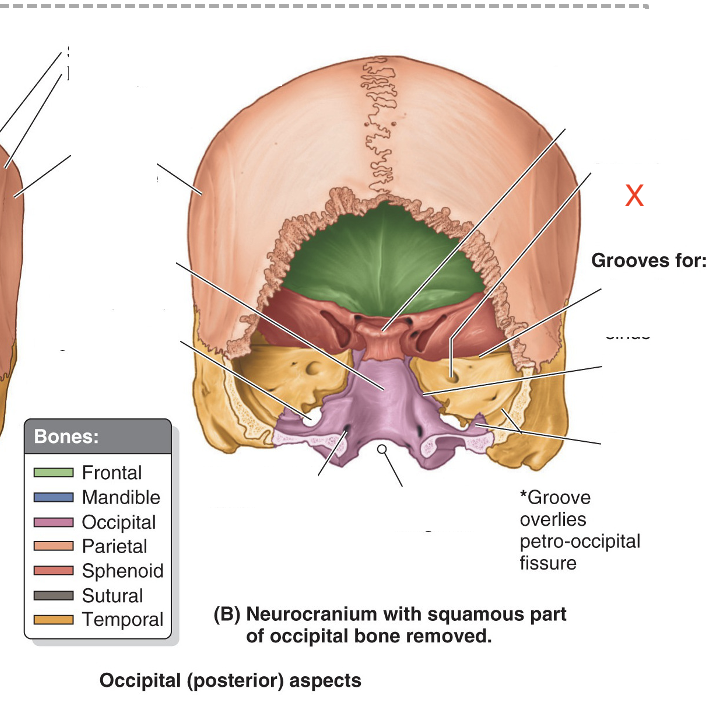
Name the area marked “X”
Internal acoustic meatus
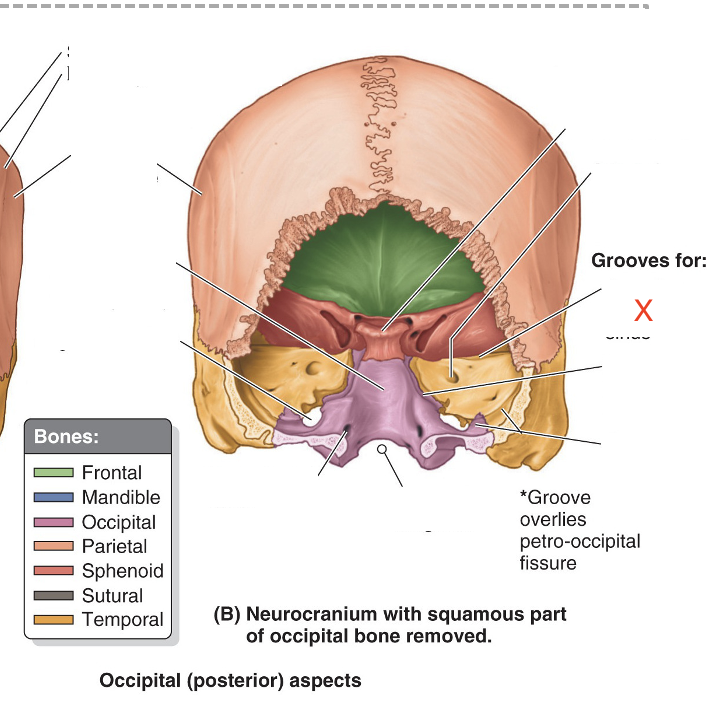
Name the area marked “X”
Superior petrosal sinus groove
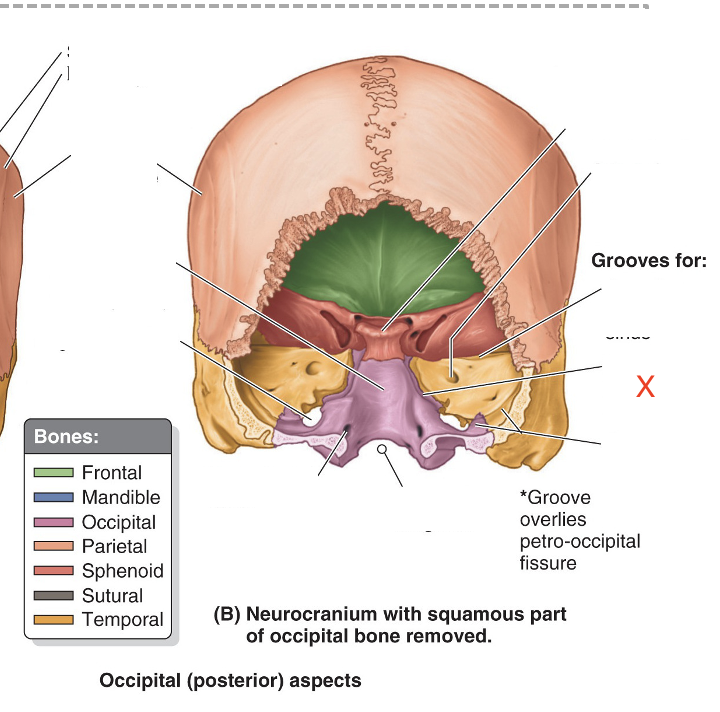
Name the area marked “X”
Inferior petrosal sinus groove
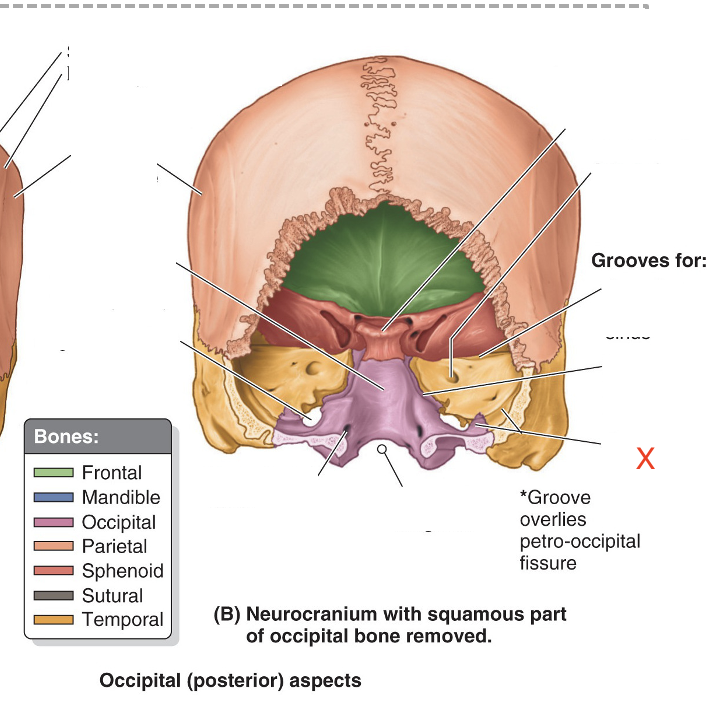
Name the area marked “X”
Sigmoid sinus groove
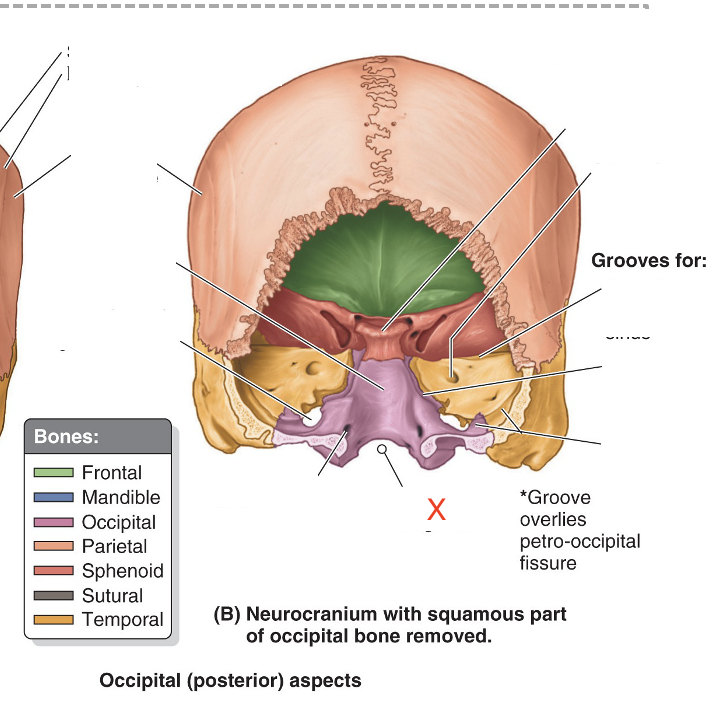
Name the area marked “X”
Foramen magnum
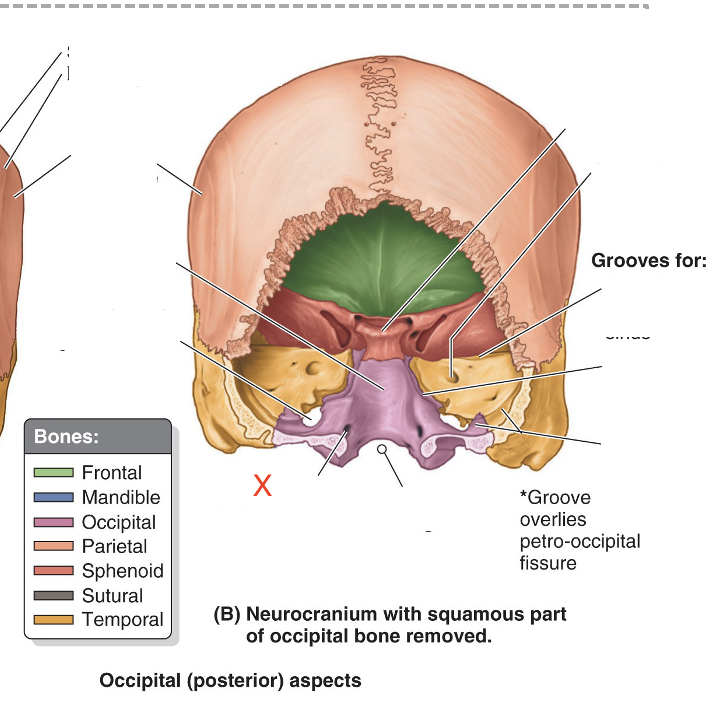
Name the area marked “X”
Hypoglossal canal
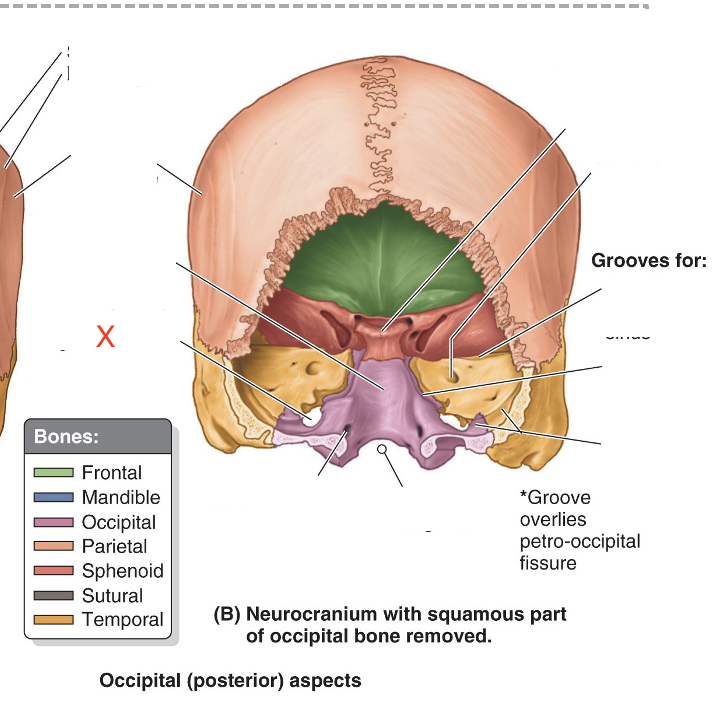
Name the area marked “X”
Jugular foramen
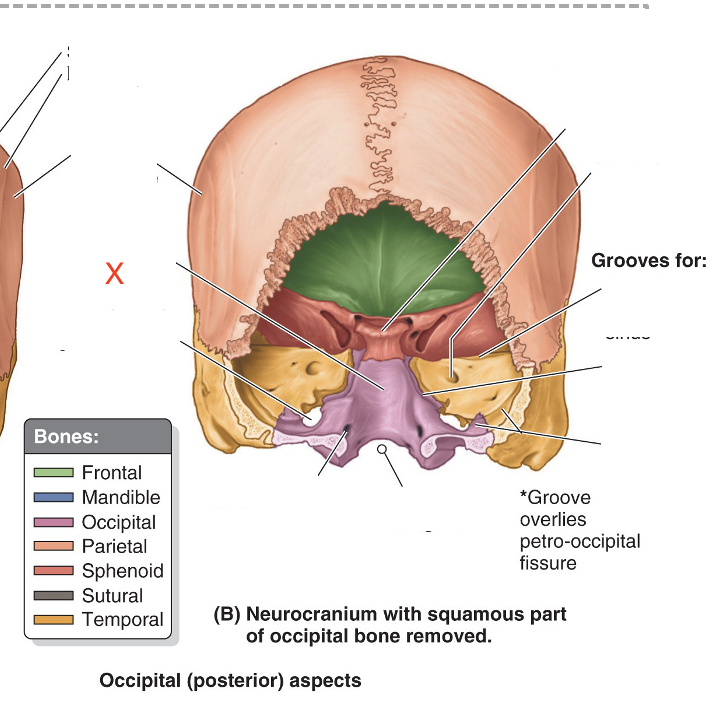
Name the area marked “X”
Basilar part of occipital bone (clivus)
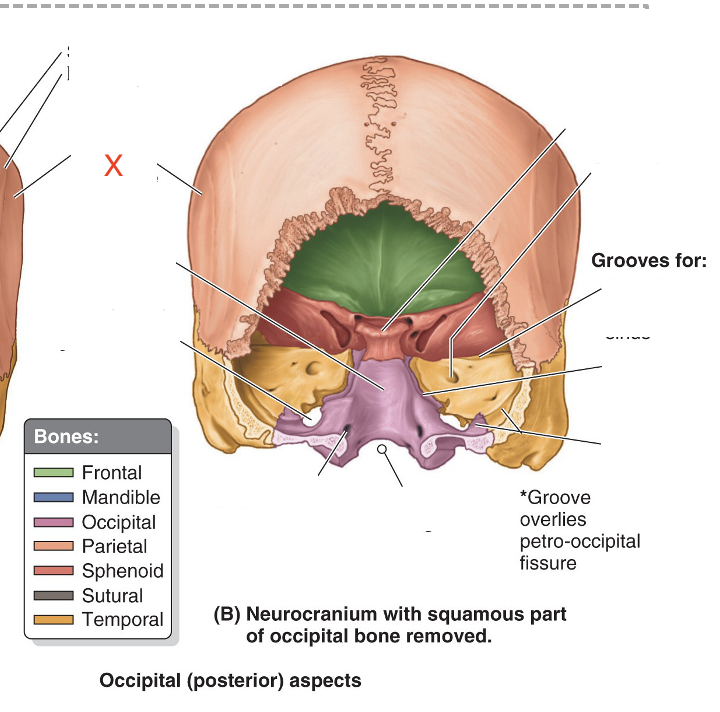
Name the area marked “X”
Parietal eminence
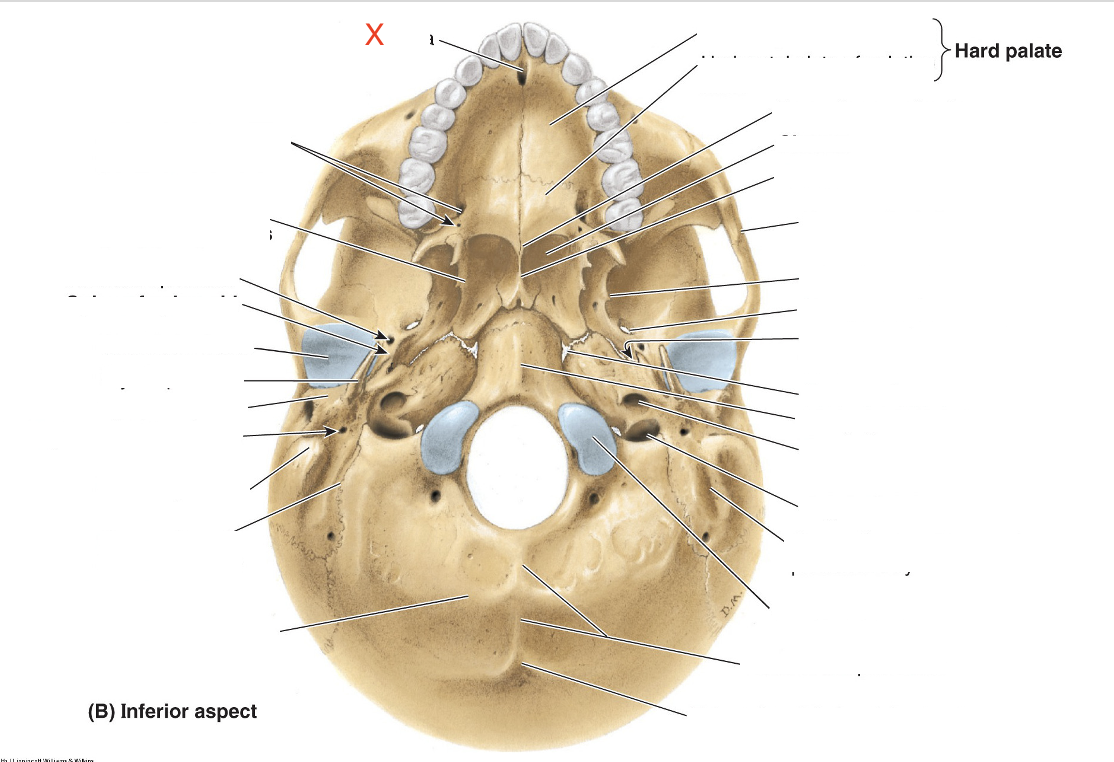
Name the area marked “X”
Incisive fossa
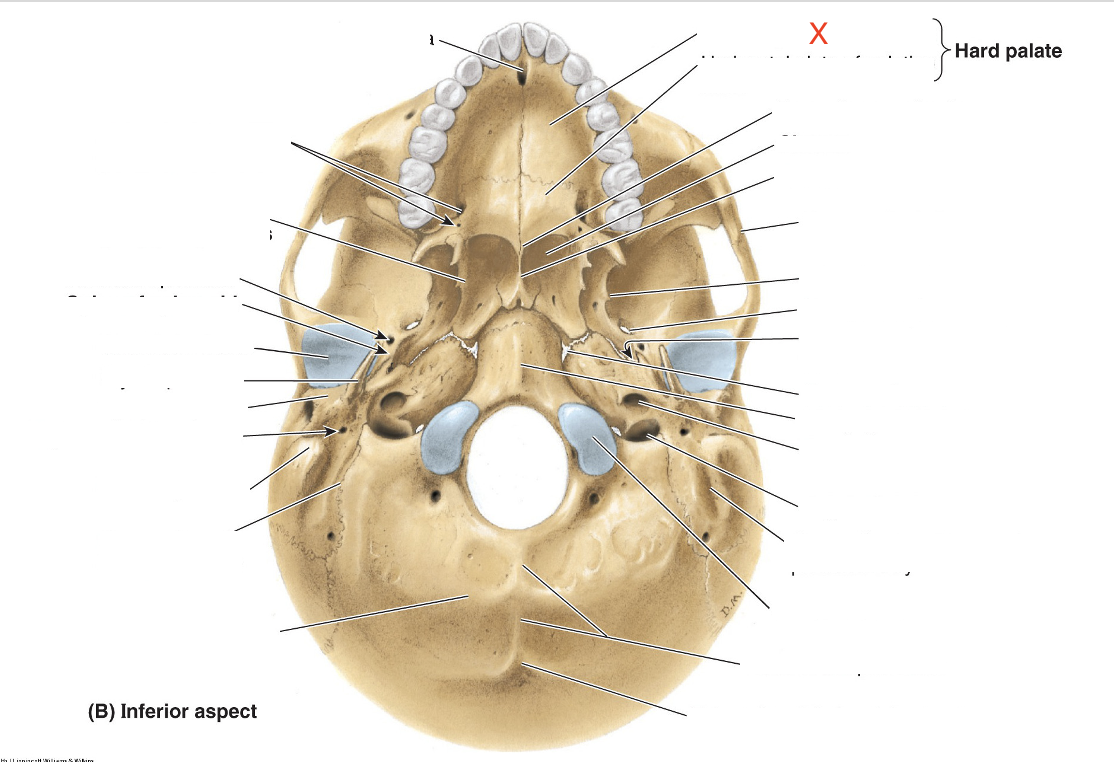
Name the area marked “X”
Palatine process of maxilla
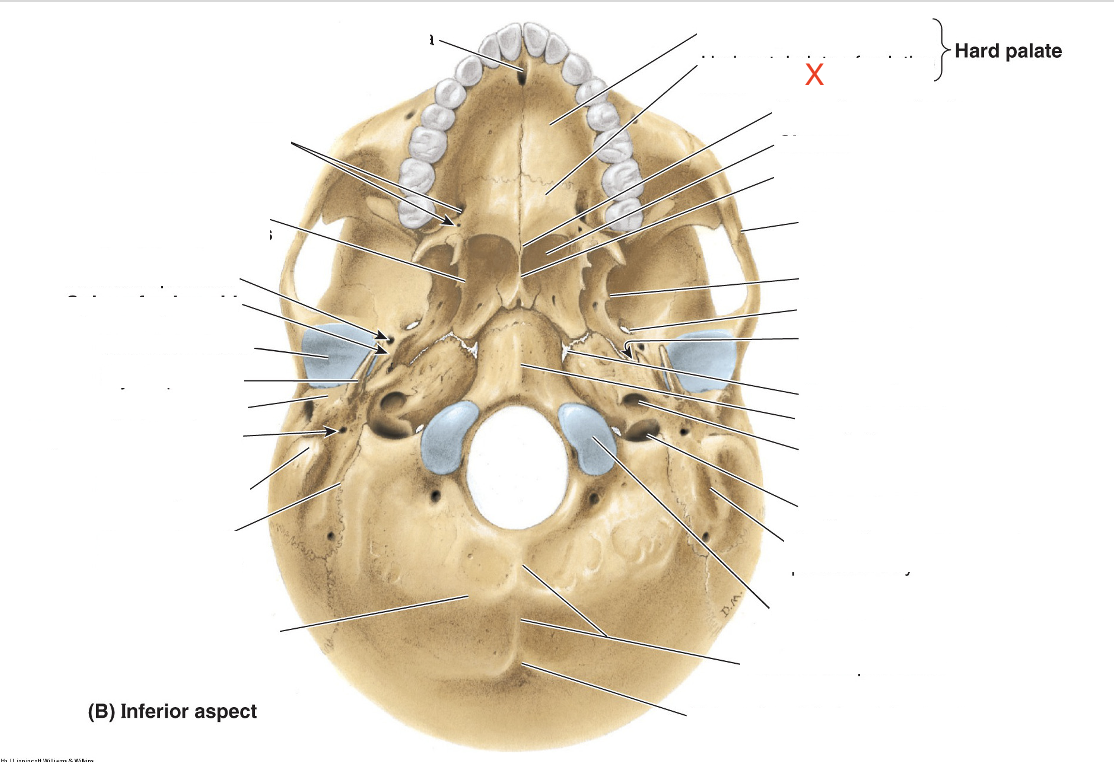
Name the area marked “X”
Horizontal plate of palatine bone
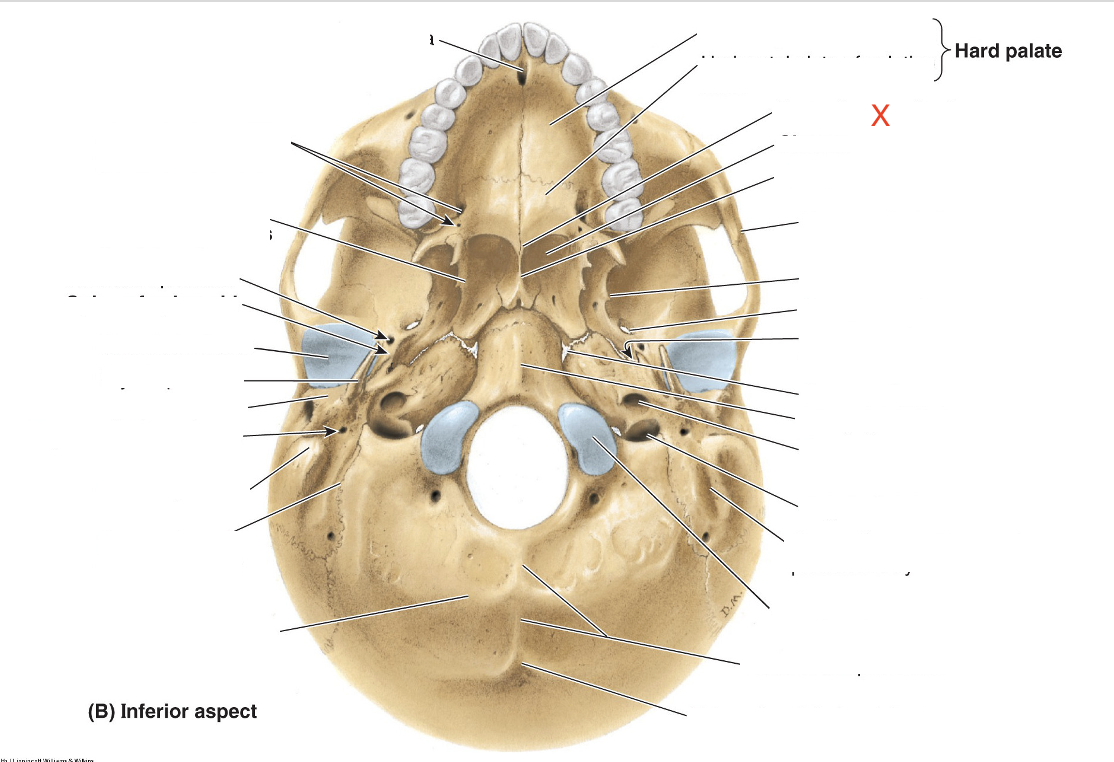
Name the area marked “X”
Posterior nasal spine
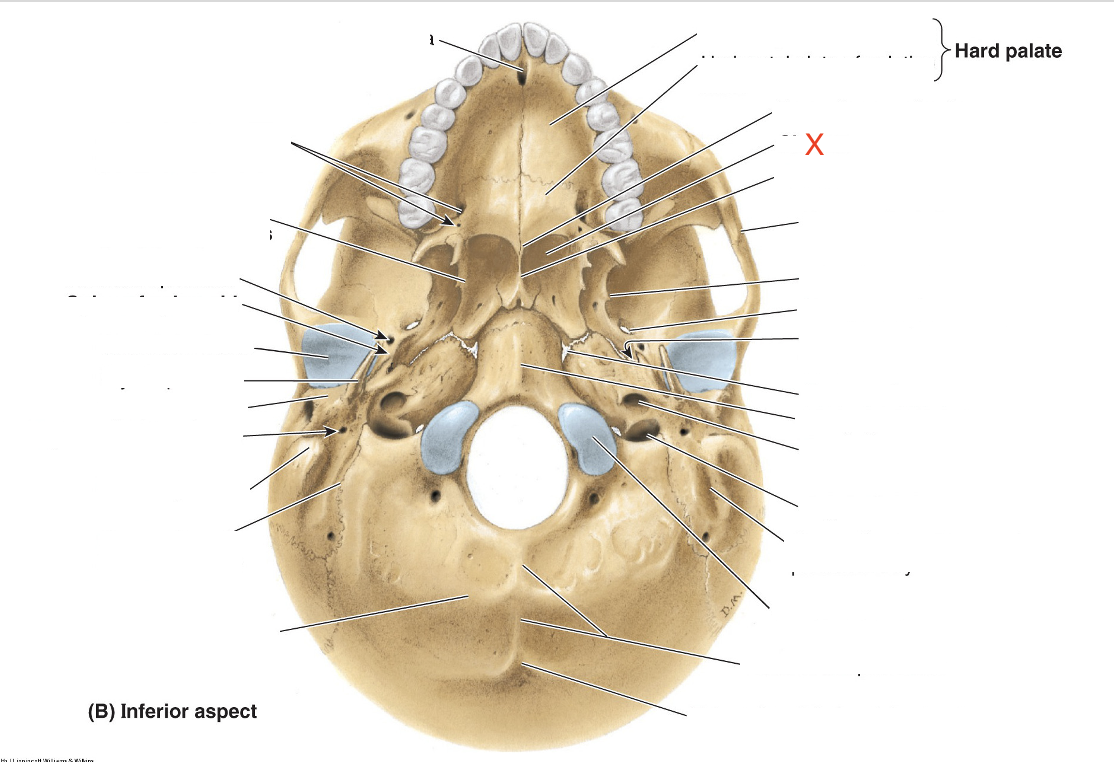
Name the area marked “X”
Choana
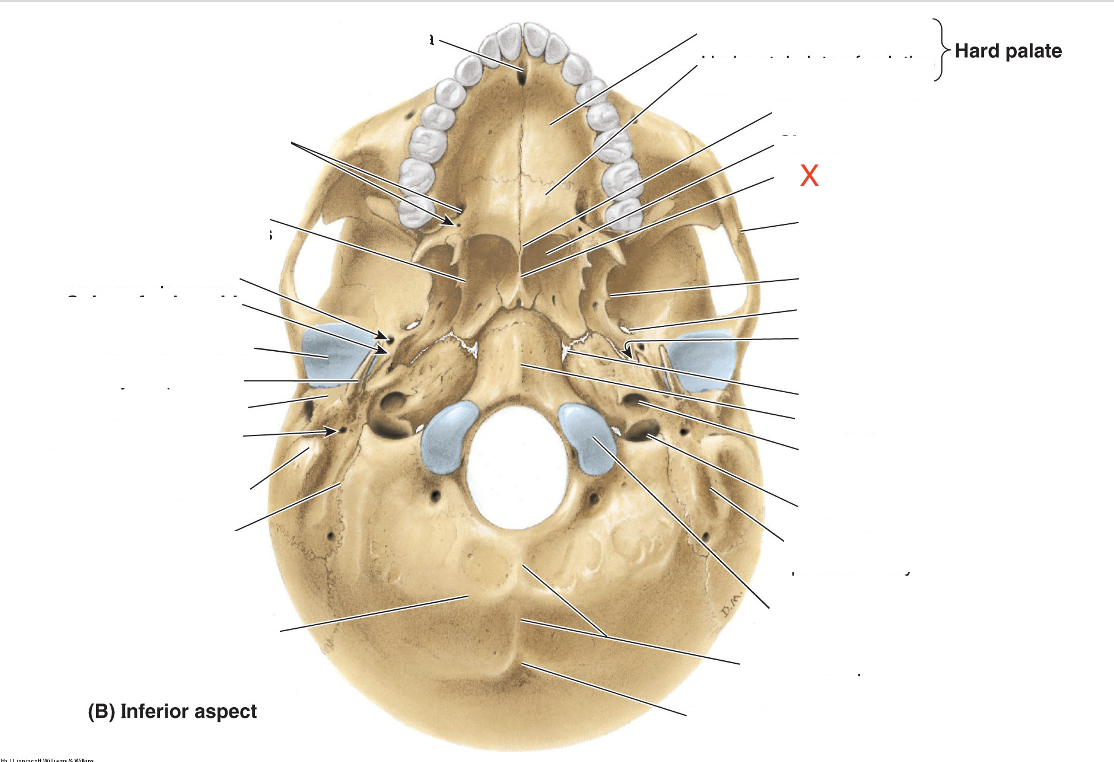
Name the area marked “X”
Vomer
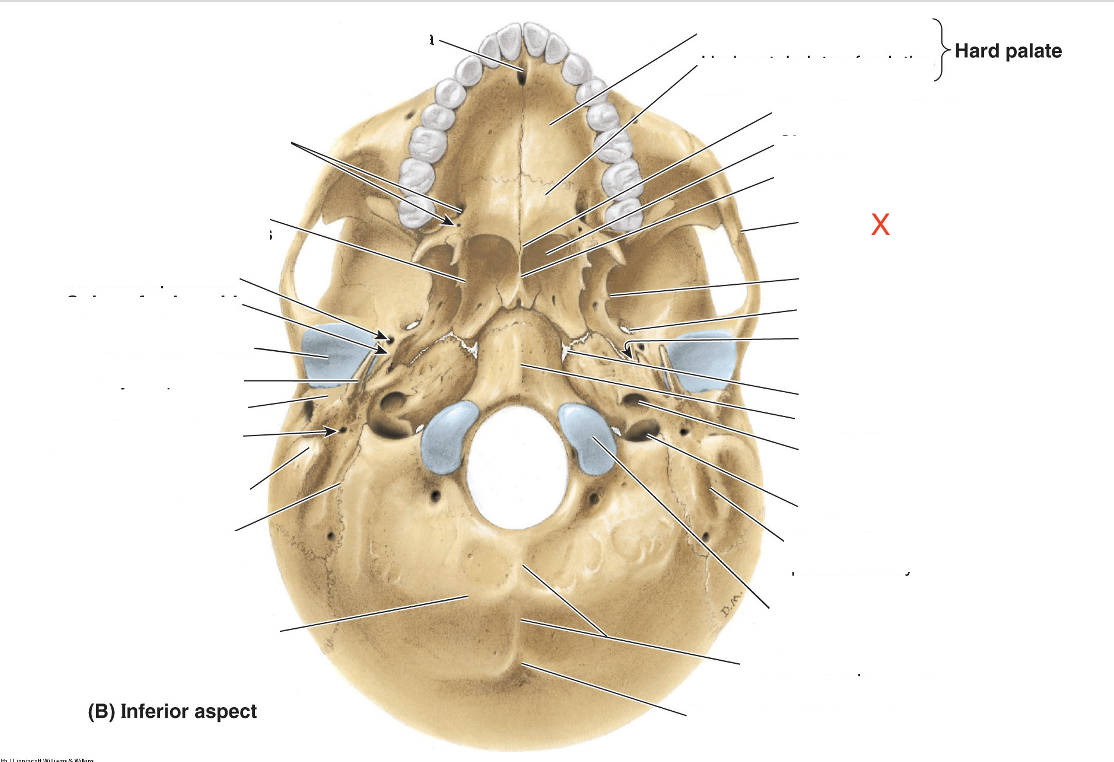
Name the area marked “X”
Zygomatic arch
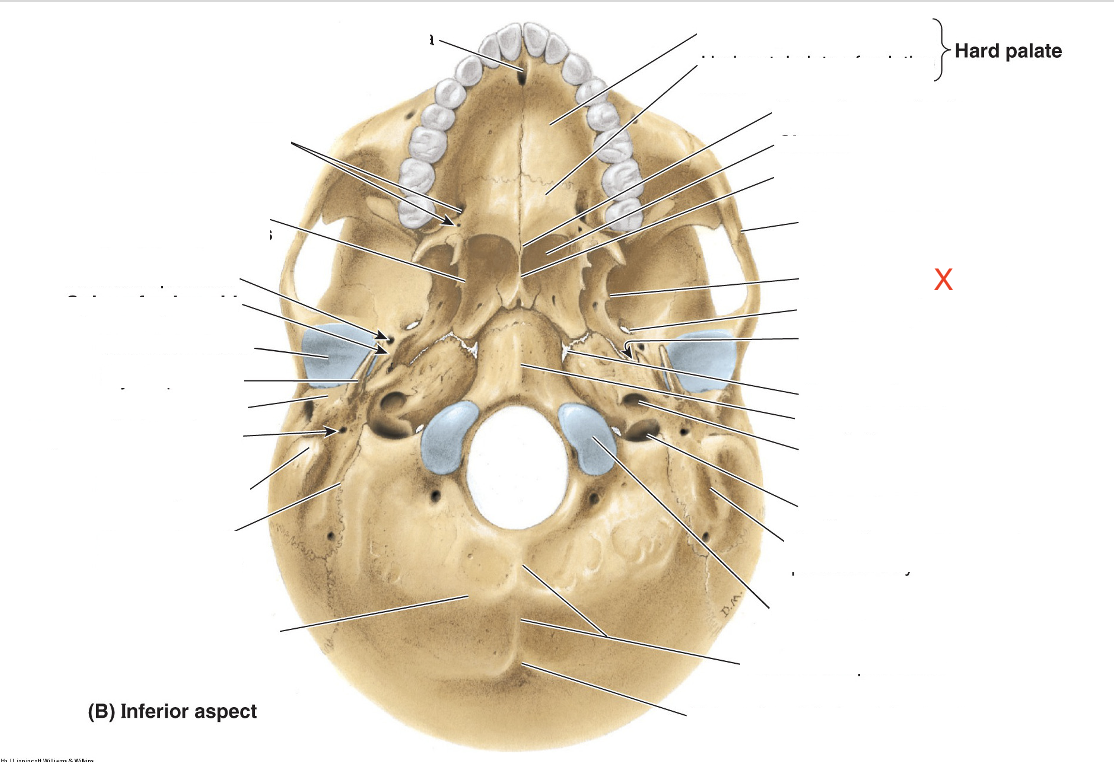
Name the area marked “X”
Lateral plate of pterygoid process
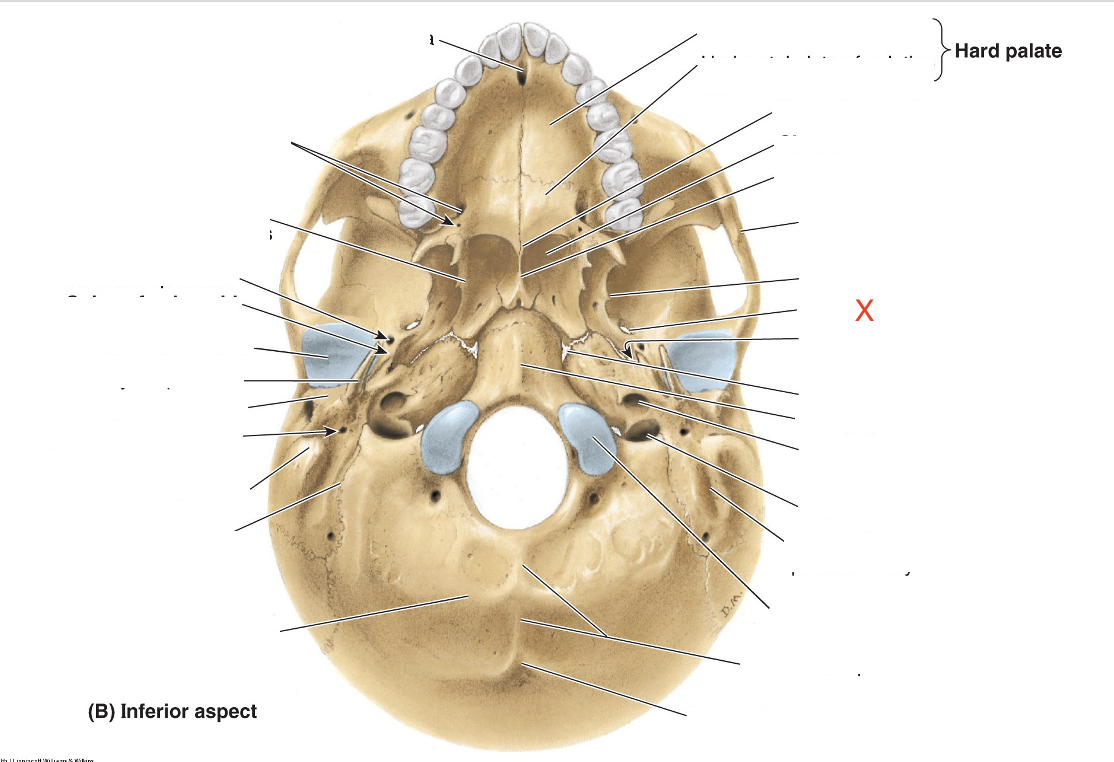
Name the area marked “X”
Foramen ovale
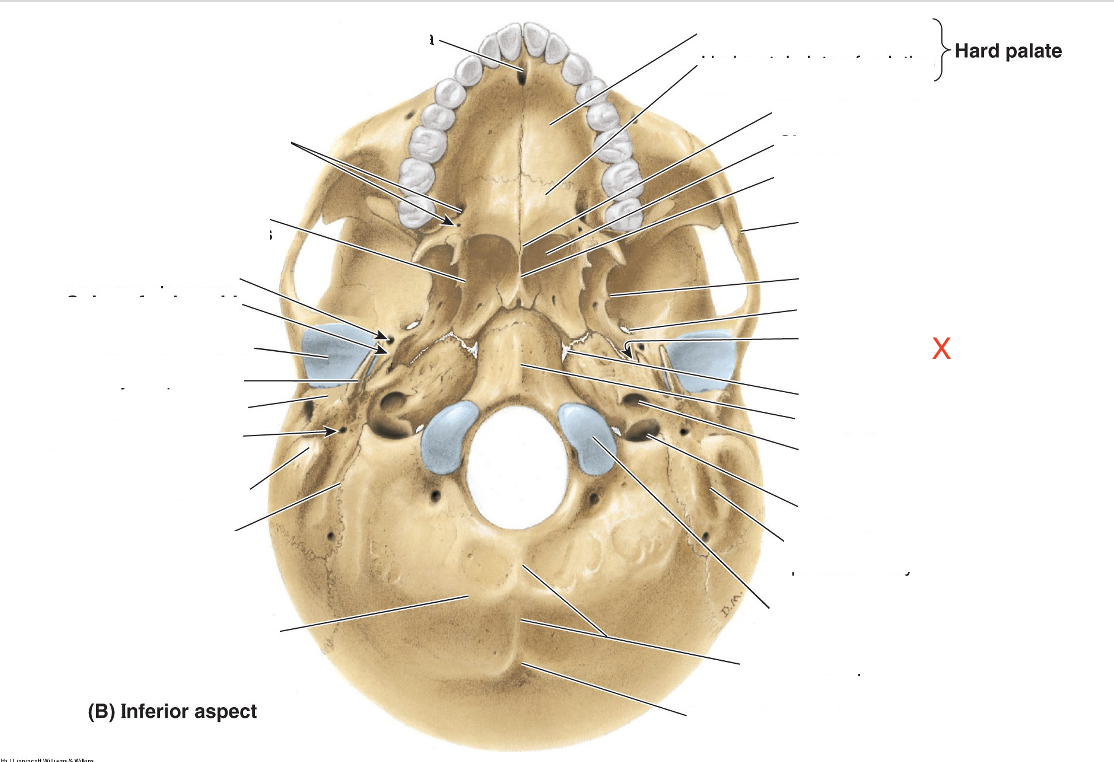
Name the area marked “X”
Bony part of pharyngolympanic tube
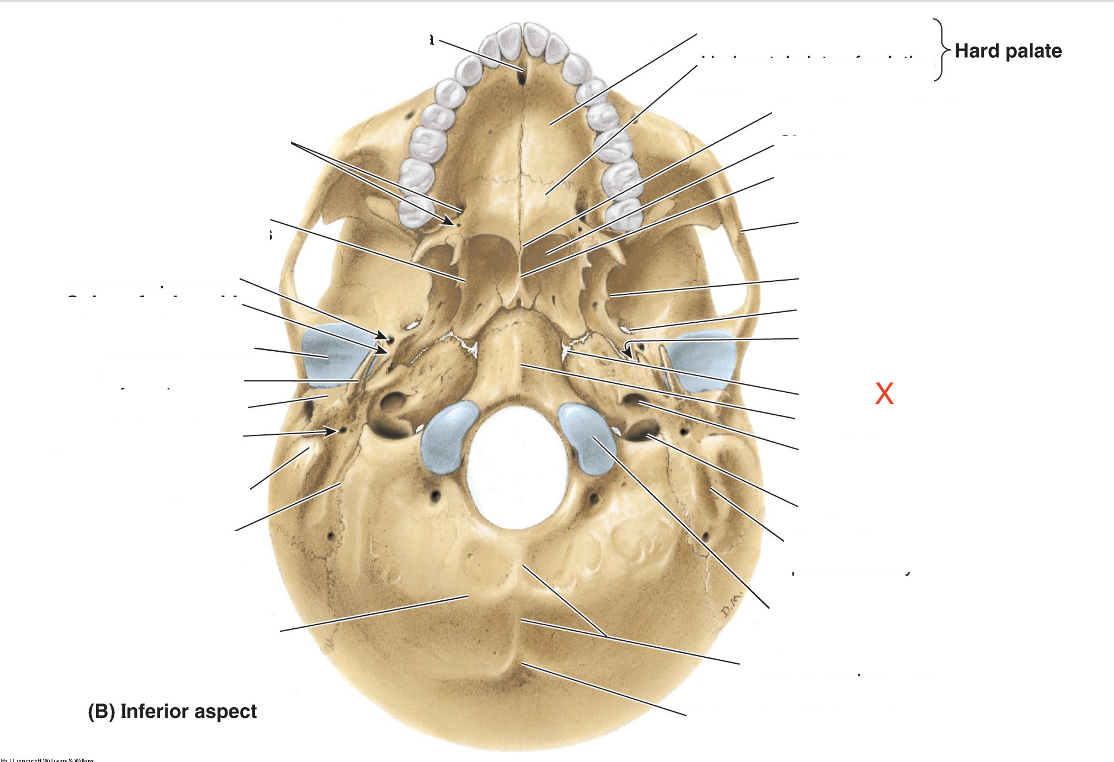
Name the area marked “X”
Foramen lacerum
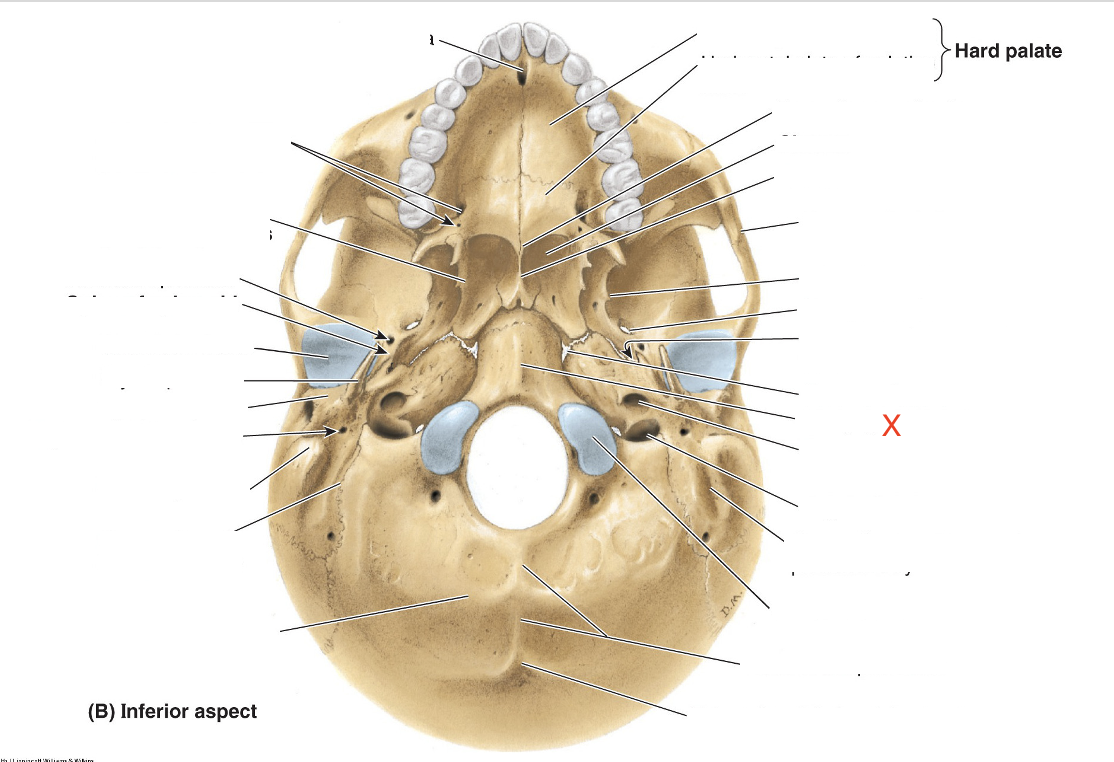
Name the area marked “X”
Pharyngeal tubercle
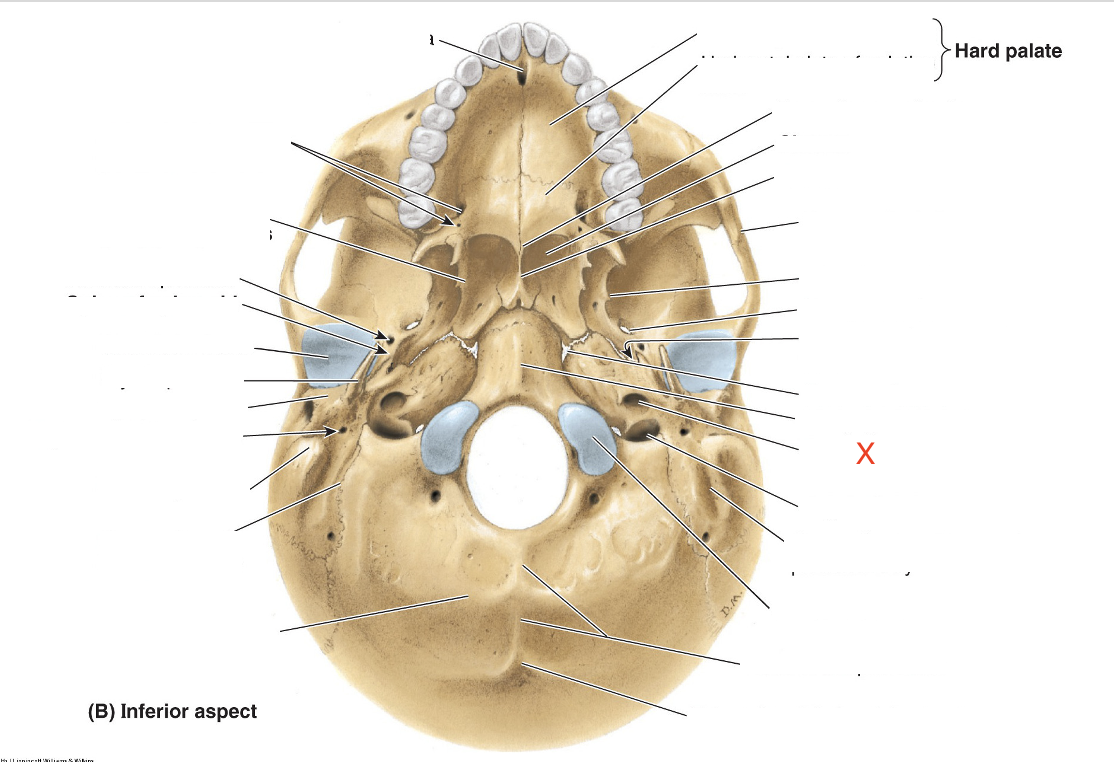
Name the area marked “X”
Carotid canal
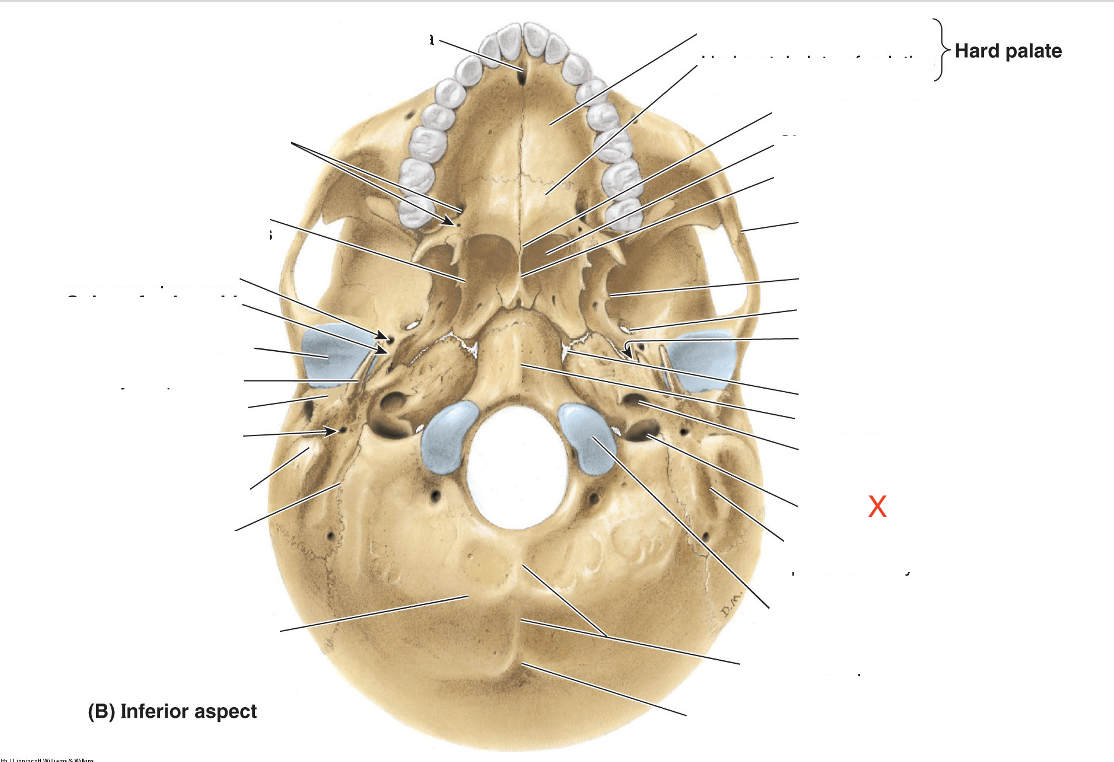
Name the area marked “X”
Jugular foramen
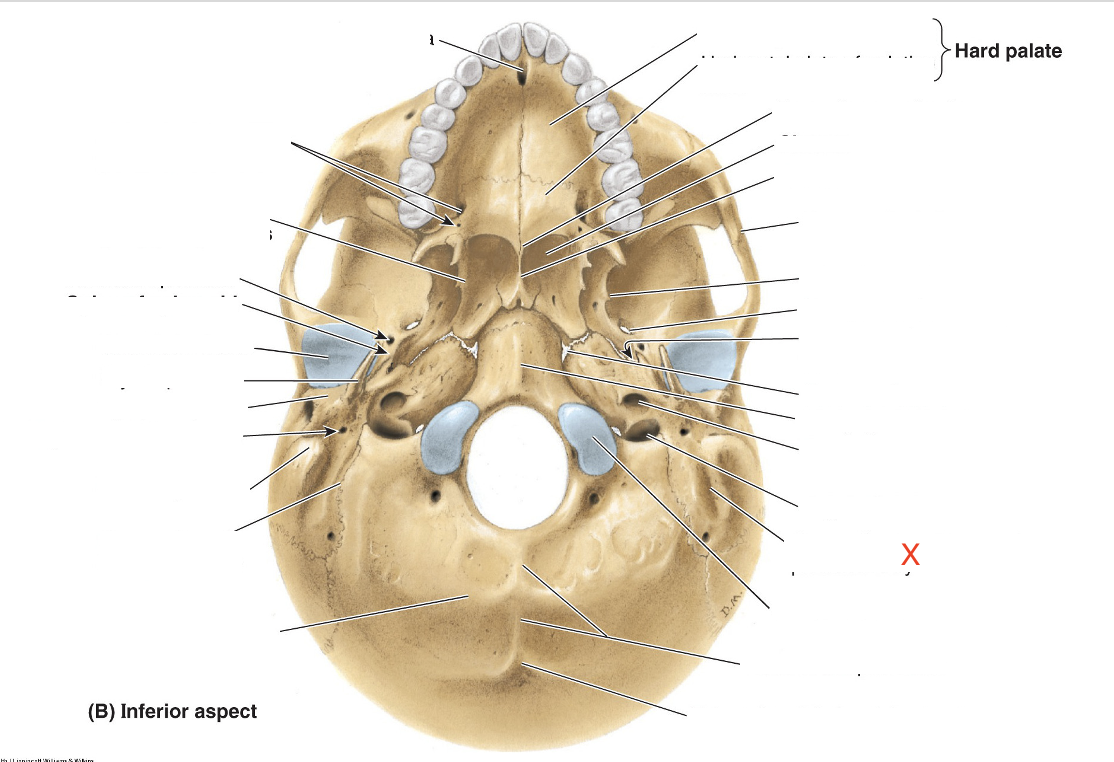
Name the area marked “X”
Groove for digastric muscle’s posterior belly
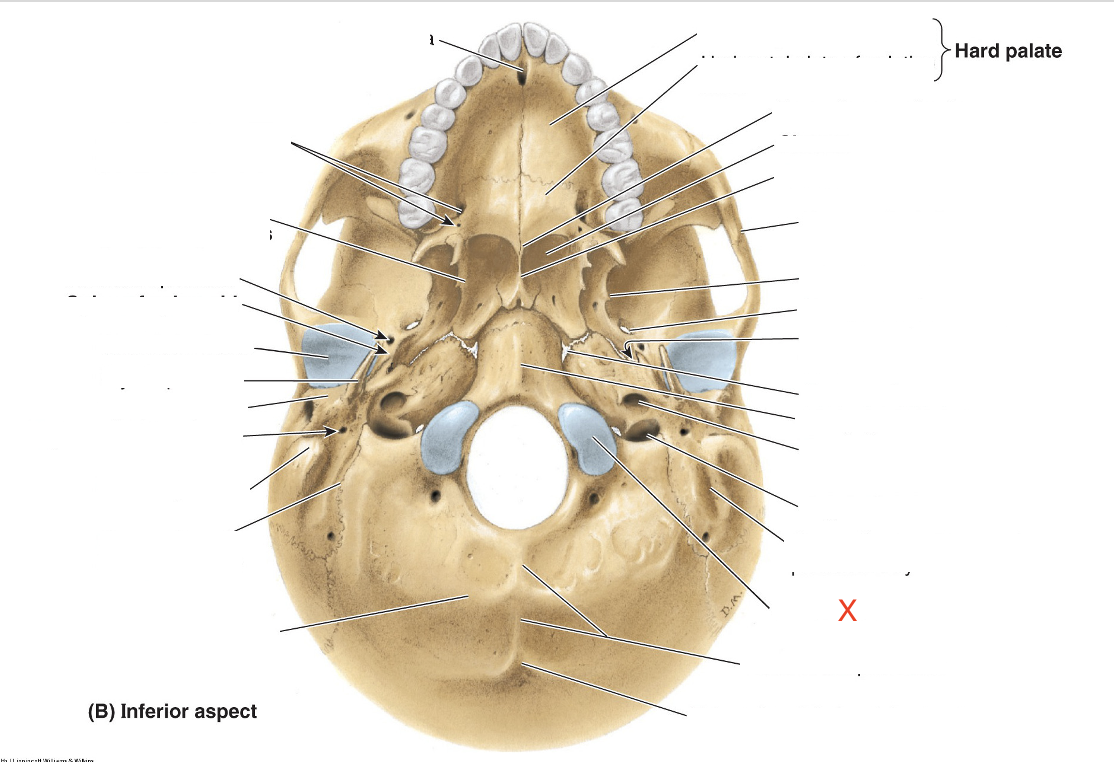
Name the area marked “X”
Occipital condyle
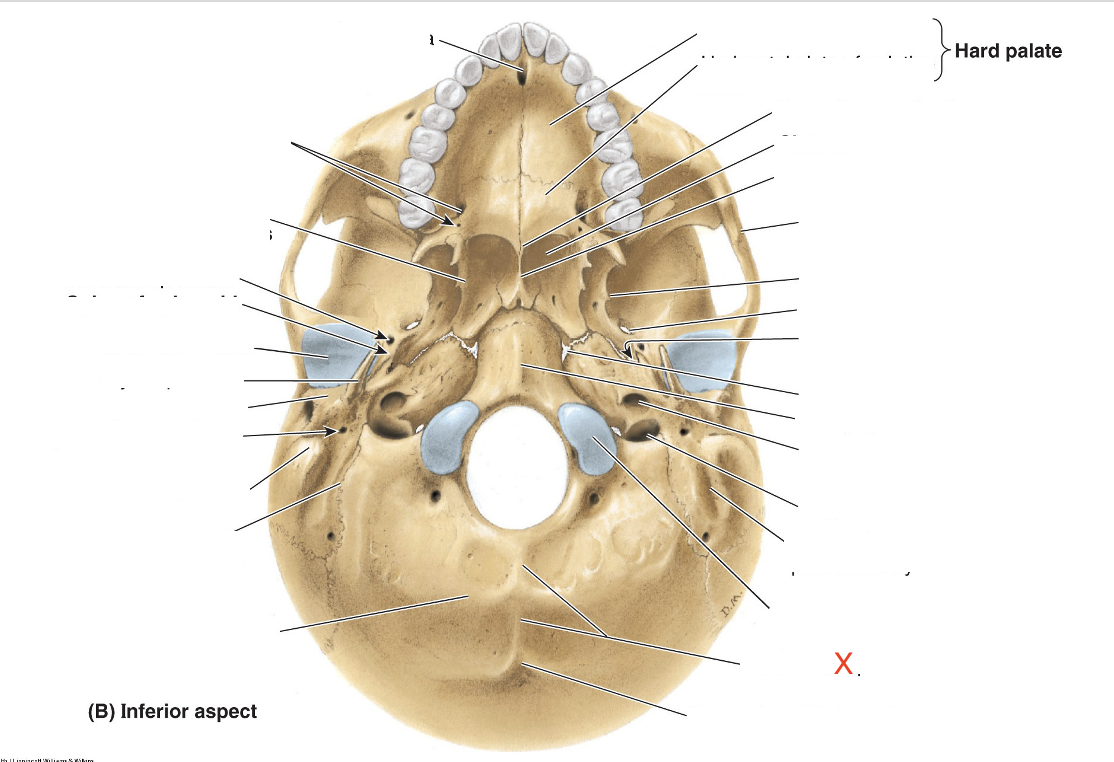
Name the area marked “X”
External occipital crest
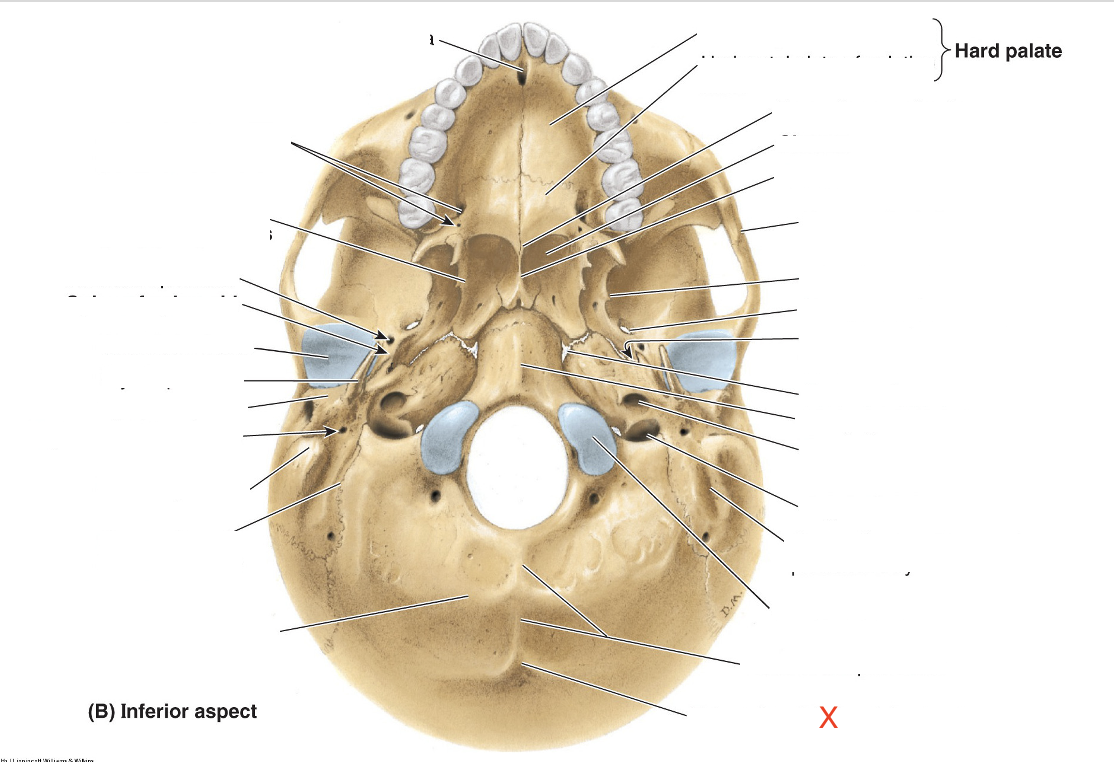
Name the area marked “X”
External occipital protuberance
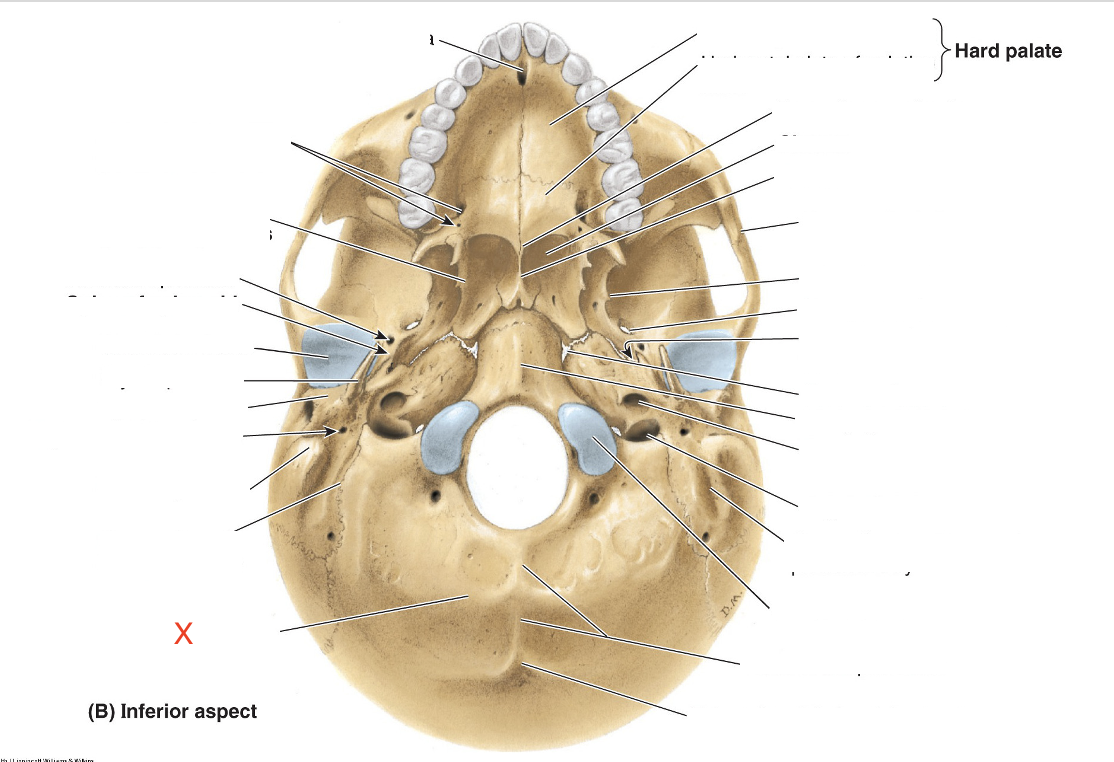
Name the area marked “X”
Inferior nuchal line
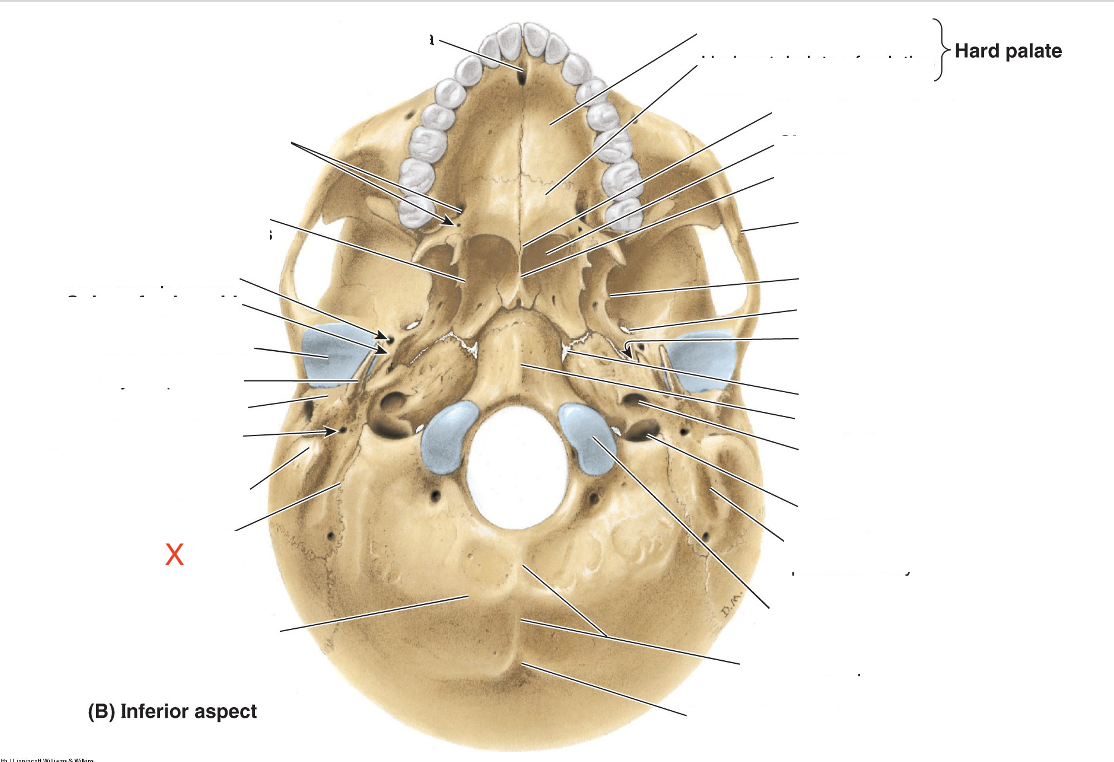
Name the area marked “X”
Groove for occipital artery
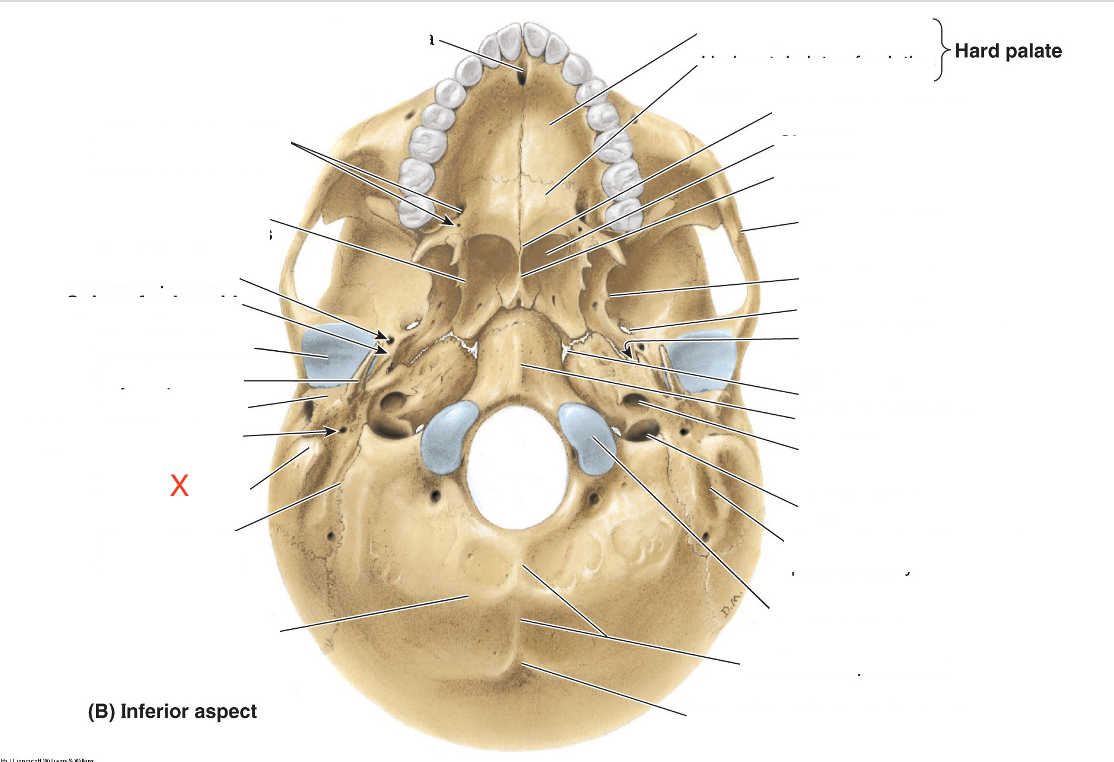
Name the area marked “X”
Mastoid process
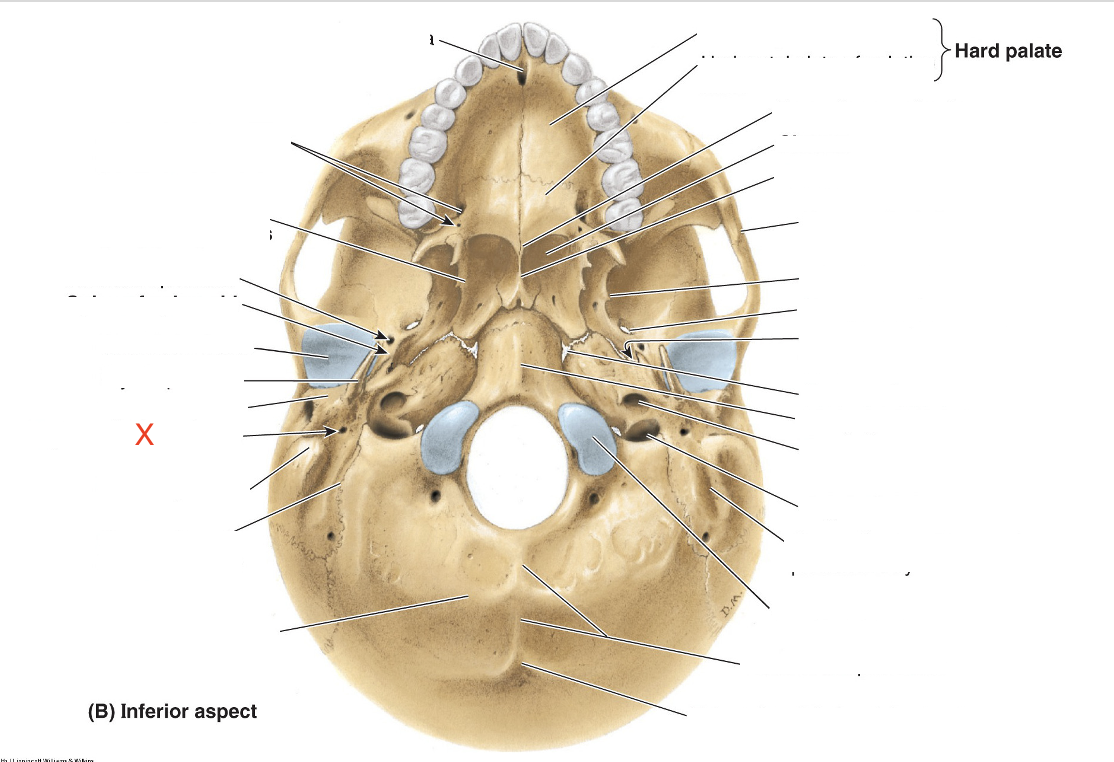
Name the area marked “X”
Stylomastoid foramen