304M: Atmospheric Pressure and the Vertical Movement of Air
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
What is the definition of Atmospheric Pressure?
The force per unit area exerted by the atmosphere due to the weight of the overlying air.
Where is atmospheric pressure the greatest?
Atmospheric pressure is greatest at the Earth's surface.
What is Station Pressure?
The actual atmospheric pressure computed at an observing station.
Why would the station pressure in Calgary be lower than in Vancouver?
Because Calgary is at a higher altitude, there is less overlying air, resulting in less weight and lower pressure.
Generally speaking, the higher the station elevation, the _____ the station pressure will be.
lower
What common reference level is used to compare pressures from stations at different elevations?
Mean sea level (MSL) is used as the standard reference datum.
How is mean sea level pressure calculated from station pressure?
The weight of an imaginary column of air extending from the station down to MSL is added to the station pressure.
Besides the weight of an imaginary air column, what other factor must be considered when calculating MSL pressure from station pressure?
The temperature of the air, as it directly impacts the air's weight and density.
What specific temperature value is used for the calculation when reducing station pressure to sea level?
A mean temperature from the previous 12-hour period is used.
In Canada, what are the primary SI units used to measure atmospheric pressure?
Pascals (Pa), Hectopascals (hPa), and Kilopascals (kPa).
What other unit of pressure measurement, besides SI units, is commonly used in Canadian aviation?
Inches of Mercury (Hg).
In the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA), what is the average MSL pressure in inches of mercury?
29.92 inches of mercury.
In the International Standard Atmosphere (ISA), what is the average MSL pressure in hectopascals?
1013.2 hPa.
When a parcel of air rises in the atmosphere, does it expand or compress?
It expands.
What happens to the temperature of a parcel of air as it rises and expands?
It cools.
When a parcel of air descends in the atmosphere, does it expand or compress?
It is compressed.
What happens to the temperature of a parcel of air as it sinks and is compressed?
It heats up.
What is the downward motion of air, such as on the leeward side of a mountain, called?
Subsidence.
What meteorological phenomenon is defined as a layer of air where temperature increases with height?
An inversion.
What are the two primary types of low-level inversions?
Nocturnal inversions and frontal inversions.
How does a nocturnal inversion form?
The Earth's surface cools rapidly at night through radiation, cooling the air in contact with it by conduction, making it colder than the air above.
How does a frontal inversion form?
It forms when warmer, less dense air is forced to rise over a cooler, denser air mass. (warm front moved over cold front)
What is the collective term for the five processes that initiate vertical motion in the atmosphere?
Lifting processes.
List the five lifting processes.
Convection,
Mechanical Turbulence,
Orographic lift,
Frontal lift,
and Convergence.
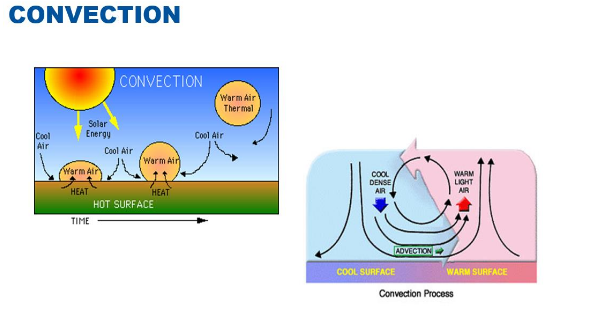
Which lifting process results from the uneven heating of the Earth's surface?
Convection.
Which lifting process is caused by friction between the air and the Earth's surface, creating eddies?
Mechanical turbulence.
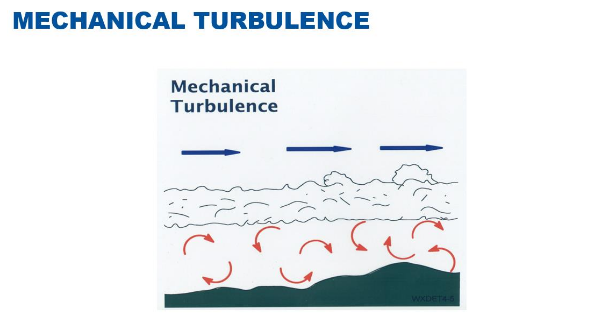
What are the three factors that influence the intensity of mechanical turbulence?
Unevenness of the ground,
speed of the wind,
and stability of the air.
The effects of mechanical turbulence are usually limited to what part of the atmosphere?
The lowest 3000 feet, also known as the boundary layer.
What is the term for the lift that occurs when an air mass is forced to move over rising terrain like mountains?
Orographic lift.

The lifting process that occurs when advancing cold air undermines warmer air is known as _.
Frontal lift
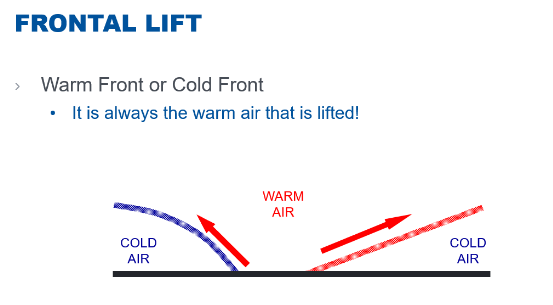
During any form of frontal lift, which air mass is always lifted?
It is always the warm air that is lifted.
What lifting process occurs when air accumulates near the surface and is forced to rise, often in low-pressure areas?
Convergence.
Which lifting process, convection or mechanical turbulence, can provide lift to much higher altitudes?
Convection (as long as the parcel of air is warmer than the
surrounding air.)
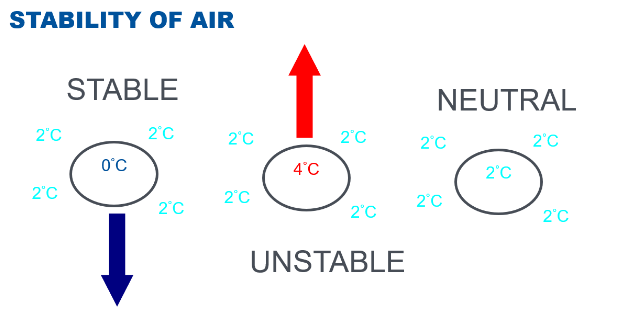
What is Atmospheric Stability
The atmospheric resistance to vertical motion.
In a stable air mass, what will a lifted parcel of air do after the lifting process is removed?
It will return to its original position.
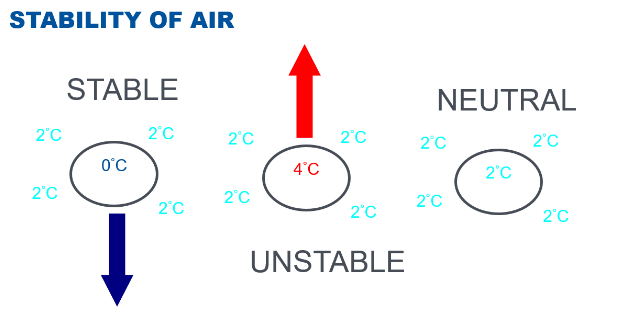
In a neutrally stable air mass, what will a lifted parcel of air do after the lifting process is removed?
It will stay in its new position.
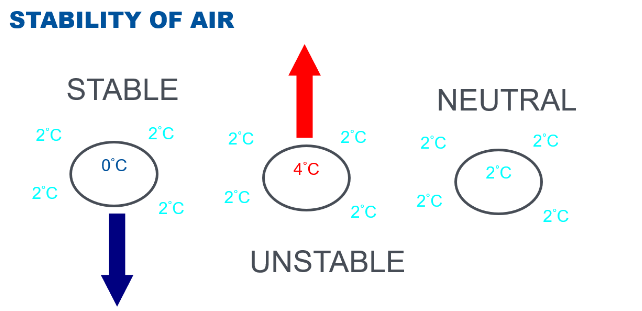
In an unstable air mass, what will a lifted parcel of air do after the lifting process is removed?
It will continue moving in the direction of the initial force (continue to rise).
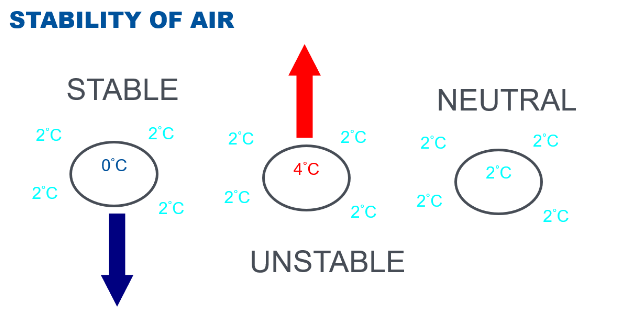
In stable air, is a lifted parcel of air colder or warmer than the surrounding air?
It becomes colder and denser than the surrounding air, causing it to sink.
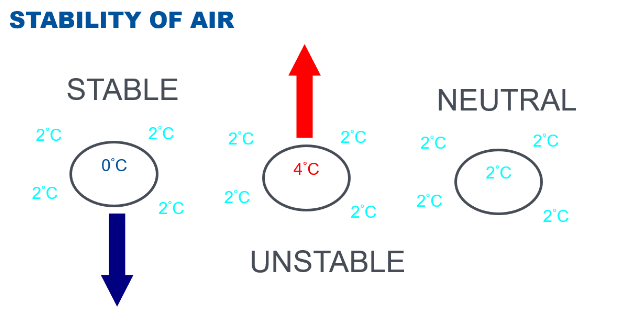
In unstable air, is a lifted parcel of air colder or warmer than the surrounding air?
It remains warmer and lighter than the surrounding air, causing it to continue rising.
What type of clouds are characteristic of unstable air?
Cumuliform clouds.
What type of clouds are characteristic of stable air?
Stratiform clouds.
What type of precipitation is associated with unstable air?
Showery precipitation.
What type of precipitation is associated with stable air?
Continuous or intermittent precipitation.
How is visibility generally affected in unstable air (outside of precipitation)?
Visibility is generally good.
How is visibility generally affected in stable air?
Visibility is often reduced due to haze, smog, or fog.
What is a steep lapse rate?
A large decrease of temperature with height.
What is a shallow lapse rate?
A small decrease of temperature with height.
What is the term for a situation where there is no change in temperature with altitude?
Isothermal.
What is the term for a situation where there is an increase in temperature with altitude?
Inversion.
A steeper atmospheric lapse rate indicates that the air is more _.
unstable
A more shallow atmospheric lapse rate indicates that the air is more _.
stable
How does an inversion layer affect upward vertical motion?
It blocks vertical motion because a rising parcel of air becomes colder than the warmer inversion layer above it.