Rewards
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
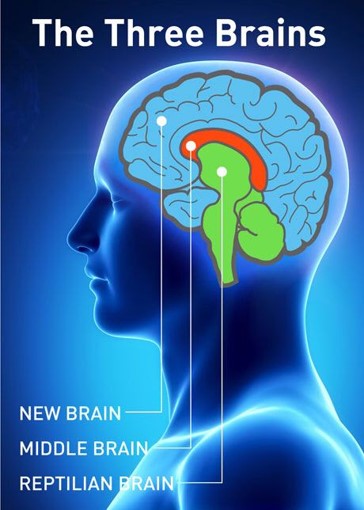
Primitive Brain
Avoid harm, satisfy essential needs (food, water, sex, safety), fight/flight/freeze, survival
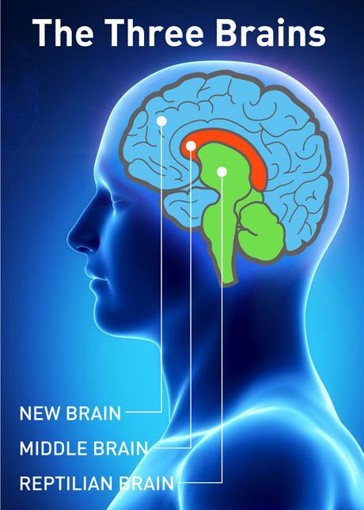
New Brain
Imagine, plan, self-monitor, rationalize, create, decision making
Striatum
Part of the brain responsible for motivation, reward, and it has a faster trajectory of development than the PFC.
Dreher and Sescousse
The more abstract and complex the reward, the more its representation stimulates the anterior regions of the orbitofrontal cortex.
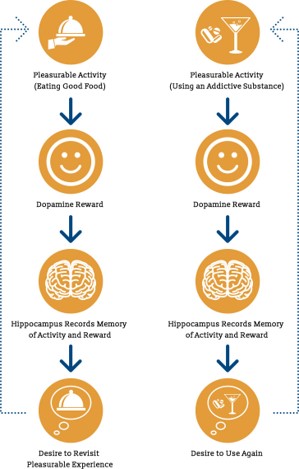
Reward-based learning
Typically there is some sort of behavior that we associate with a reward makes us feel less “bored”. The behavior to the trigger, then the reward, and then you’re going to want to repeat it.
Stress
Huge disruptor to the communication between striatum and PFC
Medial forebrain bundle
The basis of the reward circuit as it encompasses the dopaminergic axons projecting from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and prefrontal cortex
Dopamine
Amine neurotransmitter involved in coordinating movement, attention, learning, and in reinforcing behaviors.
Intracranial self stimulation (ISS)
Certain brain regions will keep an animal pressing a button or performing a behavior to get the stimulation.
Olds and Milner
Discovered intracranial self stimulation (ISS) of the brain in 1954
Orbitofrontal Cortex (OFC)
Receives direct inputs from primary taste and olfactory cortices as well as from higher order visual and somatosensory areas, thus storing reward value of all sensory stimuli. Also responds in conditions that require both approach behaviour (medial) and response inhibition (lateral).
Amygdala
Activated when positive or negative reinforcers are presented – the stronger the reinforcer the more activity there is in this region.
Ventral striatum
Stimulation is highly rewarding and plays a role in predicting rewards and biasing actions that seek rewards. Related to dopamine release and, ultimately, reward
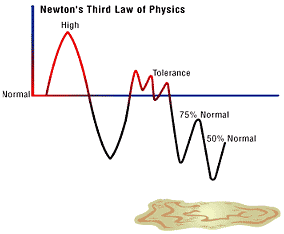
Newton’s 3rd Law of Physics
The high transforms into a corresponding low…and with each succeeding drug or alcohol event, tolerance is built up and one needs more and more to get less and less of an effect.
Endogenous Opiates
Endorphins in the VTA act on mu receptors on the dendrites of GABAergic interneurons, which increases dopamine.
Adenosine
Neuromodulator found in caffeine that reduces neural activity.
Attention and energy burst
Speeding up neural activity causing the pituitary gland to secrete hormones that increase adrenaline
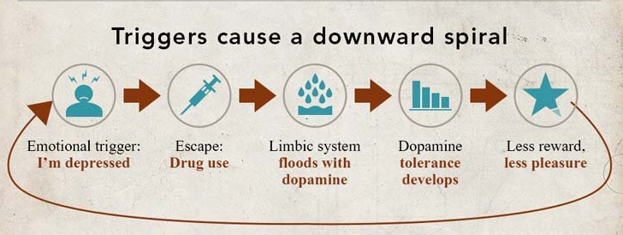
Addiction
Judgment becomes distorted and the brain starts to treat the substance as necessary for survival.
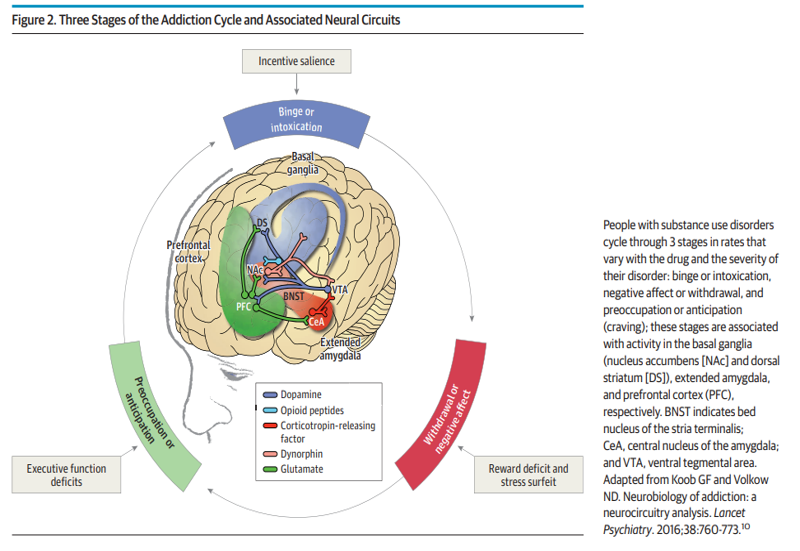
Binge/Intoxication
A phase in the model of addiction that elicits reward and incentive salience. This involves the VTA, Nucleus Accumbens, striatum, and basal ganglia.
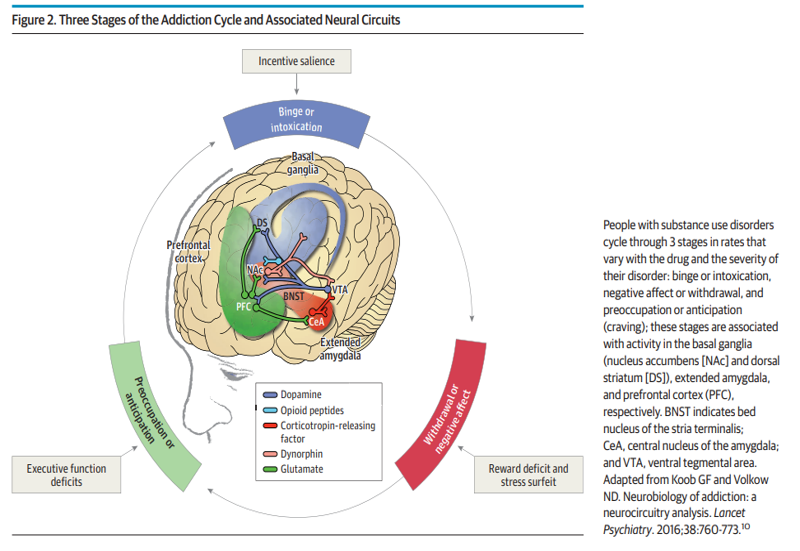
Withdrawal/Negative Affect
A phase in the model of addiction that elicits negative emotional states and stress. This involves the amygdala.
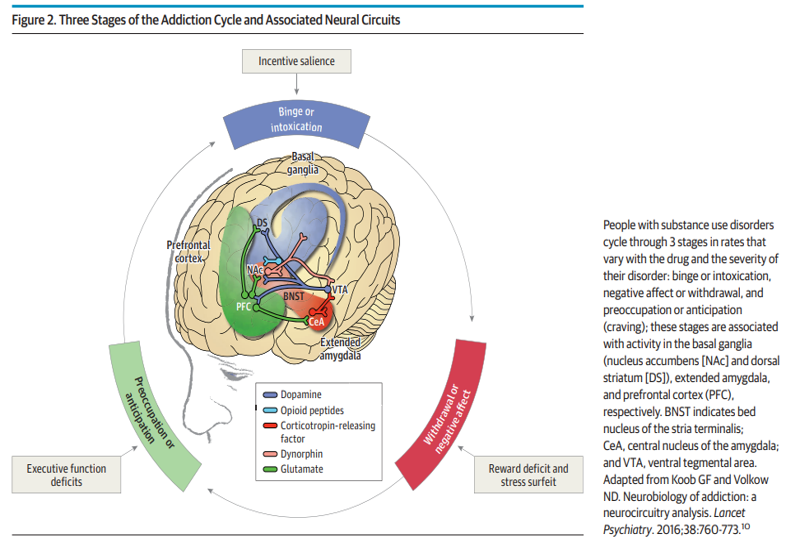
Preoccupation/Anticipation
A phase in the model of addiction that elicits craving, impulsivity, and EF dysfunction. This involves the PFC, insula, anterior cingulate
Posterior
Region of the brain where primary rewards are stimulated (ex. erotic images)
Anterior
Region of the brain where secondary rewards are stimulated (ex. money)
Mesolimbic reward pathway
Dopaminergic axons projecting from the VTA to the nucleus accumbens and amygdala
Mesocortical reward pathway
Dopaminergic axons projecting from the VTA to the prefrontal cortex
Drug dependency
In response to an artificial surplus, the endorphin/enkephalin-producing neurons reduce their activity and with no more drug, a person with a substance use disorder experiences displeasure and physical distress
Caffeine
Acts as an adenosine antagonist