Wave Theory of Light Chapter 9 SPH4U1
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
ray approximation
pretending that light moves in straight parallel lines
law of reflection
angle of incidence = angle of reflection
refraction
the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another
principle of reversibility
a path a light ray follows remains the same if its direction of travel is reversed
optical density
tendency to absorb energy of electromagnetic waves
higher optical density = slower speed of wavelength
index of refraction
ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium.
n = c/v
what is the index of refraction affected by
different substances and different wavelengths
snells law
n1sin01 = n2sin02
formula for wavelength from snells law
n2/n1 = λ1/λ2
dispersion
is the separation of light into its component colors due to varying indices of refraction for different wavelengths.
total internal reflection
angle of incidence surpasses critical angle resulting in no refracted ray and the ray is totally reflected at the boundary
critical angle
smallest angle where light stops refracting and begins to reflect. when the angle of refraction, or 02, is 90 degrees
equation to find critical angle
sin0c = n2/n1
diffraction
bending of a wave as the wave passes through an opening or by an obstacle
what does diffraction depend on
size of opening and wavelength of wave
diffraction analysis equation
in order for noticeable diffraction…
λ >= w or
λ/w >= 1
relationship between λ and diffraction
as wavelength increases, diffraction increases
relationship between size of slit and diffraction
as size of slit decreases, diffraction increases
*if λ remains constant
interference
two waves in the same medium interacting
constructive interference
two waves adding together to create a wavelength with greater amplitude
crest to crest or trough to trough
destructive interference
who waves subtract to create wave w smaller amplitude or cancel out
crest to trough
node
point where destructive interference occurs ersulting in 0 amplitude and 0 displacement
nodal lines
lines of 0 displacement
coherent waves
same frequency and fixed phases
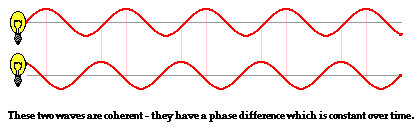
conditions for interference
Must be coherent, come from common area, two or more waves
huygens’ principle
alll points on a wave front can be through of as new sources of spherical waves
drawbacks of wave theory of light
requires invisible ether to travel through
waves spread out, while light moves in a straight line