Endocrinology CT Overview
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
thyroid nodule tx
Nonpharm
-smoking cessation, weight management
-adequate iodine intake
-small benign nodule = observe and follow up with repeat US
Pharm
-tx of hyper or hypothyroidism
Surgery
-lobectomy or total thyroidectomy indicated for large benign nodules and malignant
-radiofrequency ablation
thyroid cancer tx
Surgery = first line
-lobectomy
-total thyroidectomy
Pharm
-if thyroid is taken out will need levothyroxine due to hypothyroidism
-radioiodine is administered after thyroidectomy in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer to able residual normal thyroid tissue
MEN syndrome tx
-regular surveillance and screening
-surgical removal of tumors where indicated
-children harboring MEN2 mutation are advised to have prophylactic total thyroidectomy by age 6
-no age with MEN2 should receive GLP1 agonist bc it may increase for medullary thyroid cancer
pheochromocytoma tx
Pharm
-alpha blockers (doxazosin), CCB are used to manage HTN
-surgical removal
parathyroid carcinoma tx
-first line = surgery
-management of hypercalcemia: IV fluids, loop diuretics, bisphosphonates, cinacalcet
adrenal adenomas tx
-observation for non functioning adenomas <4cm
Surgery
-functioning
->4cm with suspicious features
Pharm
-cortisol producing: ketoconazole
-aldosterone producing: spironolactone
paraneoplastic syndrome tx
-treat underlying malignancy
Hypercalcemia management
-normal saline, loop diuretics, calcitonin
Cushing syndrome tx
Surgery = First line
-primary Cushing disease = transsphenoidal selective resection of pituitary adenoma
-ectopic ACTH secreting tumor = resection
-adrenal cushing syndrome = adrenalectomy
Pharm
-if surgical tx is delayed or contraindicated
-ketoconazole, metyrapone
primary adrenal insufficiency tx
Non-pharm
-manage stress and emergency
-high sodium and adequate protein intake
Pharm
-hydrocortisone + fludrocortisone for life
-increase maintenance dose during stress for glucocorticoids (3x normal)
secondary adrenal insufficiency tx
-hydrocortisone ONLY
-mineralocorticoid production preserved since problem is with pituitary not adrenal gland
acute adrenal crisis tx
-begin therapy immediately
-IV fluids and IV hydrocortisone
congenital adrenal hyperplasia tx
Tx of crisis
-IV fluids, steriods, ICU
Long term
-hydrocortisone and fludrocortisone
Surgical
-genital reconstruction if severe virilized females
hyperaldosteronism tx
Surgery
-curative for adrenal adenoma
Primary
-spironolactone, eplerenone, amiloride
Secondary
-salt restriction and correction of underlying cause
-most often discontinue diuretic
type 1 DM tx
Non-pharm
-education, carbohydrate counting and insulin to carb ratio
-monitoring, sick day management, exercise
-no smoking or alcohol, regular foot care inspection
Pharm: INSULIN
Bolus: short acting
-aspart, lispro, glulisine
-at mealtime: 1 unit per 10-15g of carbs
Basal: long acting
-glargine, detemir, degludec
-0.1-.02 units/day
how to calculate short acting insulin
Carb calucation
-1-60 ratio
-23 for yogurt: 23/60= 0.38 ~0.5
Insulin calculation
Carb ratio: count carbs 45g, your ratio 1:15 = 45/15 = 3 units
Correction factor: blood sugar 200, target is 100
-200-100= 100
-correction 1:50 ratio
-100/50 = 2 units
Total insulin = 3+2= 5 units
-1 unit of insulin will drop blood glucose 30-50mg/dL
simple formula
(Total Carbs ÷ Carb Ratio) + (Current BG Target BG ÷ Correction Factor) = Total Insulin
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) tx
Non-pharm
-ICU monitoring, strict I&O, hourly glucose and ketone
-NPO, foley cath, DVT prophylaxis
-review factors, sick day management
Pharm
Fluid resuscitation: 0.9 NaCl in first hour
-0.45 NaCl 250-500 if corrected Na normal/high
-switch D5W + 0.4 NaCl when glucose <250
-replace 50% of fluid in first 12-24 hrs
Insulin: IV/IM regular 0.1 continuous infusion
-decrease glucose by 50-75
-when glucose <250 reduce insulin 0.05 until anion gap normalizes
Electrolyte replacement: potassium make sure >3 before giving insulin
Transition to sub Q insulin 1-2 hrs before stopping IV
Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS) tx
Non-pharm
-ICU, foley cath
-hourly vitals and neuro assessment
-electrolytes every 2-4 hours
Pharm
-Fluid resuscitation: 0.9 NaCl in first hour
-0.45 NaCl 250-500 if corrected Na normal/high
-switch D5W + 0.4 NaCl when glucose <250
-avoid rapid correction
Insulin only after adequate hydration : IV/IM regular 0.05-0.1 continuous infusion
-decrease glucose by 50-75
Electrolyte replacement: potassium make sure >3 before giving insulin
hypoglycemia tx
-15-15 rule: give 15g fast acting carbs wait 15 min and recheck
-repeat if glucose <70
Conscious mild-mod hypoglycemia
-oral glucose 15-20g
Severe hypoglycemia
-glucagon 1mg IM/SC (adults), 0,5mg (kids)
-hospital: D10W infusion to maintain glucose 100-150
-glucagon ineffective in alcohol induced
dawn phenomenon tx
increase morning intermediate or long acting insulin
-consider insulin pump
-adjust timing of insulin
Somogyi effect tx
-reduce evening insulin
-change timing of evening snack
-adjust bedtime snack
-consider switching insulin types
latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) tx
Non-pharm
-education, nutritional therapy, weight management, exercise
-self monitoring
Pharm
-first line: insulin
-metformin
-insulin typically increase over 2-4 years
-regular C peptide to asses beta cell function
metabolic syndrome tx
Non-pharm
-weight loss 5-10%, exercise, diet, smoking cessation, stress management
Pharm
-HTN: ACE/ARB
-dyslipidemia: statins
-insulin resistance: metformin
-obesity: weight loss meds (orlistat)
obesity management
Recommended for BMI >27 if lifestyle therapy fails
-orlistat: lipase inhibitor
-phentermine + topiramate: sympathomimetic + AED
-naltrexone + bupropion: opioid antagonist + antidepressant
-liraglutide, semaglutide: GLP1
gestational diabetes tx
-nutrition counseling + meds
-insulin = gold standard
Complication
-excessive fetal growth can cause maternal and perinatal morbidity
-increased risk in future pregnancy
-increase risk of T2DM in future
prediabetes tx
Non-pharm
-behavior mods + dietary therapy + 5-7% weight loss
-smoking cessation
Pharm
-first line = metformin
type 2 DM tx
Goal = A1c: <7
-checked every 3-4 months until target then 2x per year
Step 1
-first line = metformin + comprehensive lifestyle
-engage in 150 min or more of exercise that breaks a sweat per week spread over 3 days with no more than 2 consecutive days without activity
Step 2/3: T2DM + artherosclerotic or CV risk, CKD, HR
-SGLT2i or GLP1
-pick whichever one you didn't before
Step 4: Insulin initiation
-A1c uncontrolled >3 mon
-Alc >10%
-blood glucose >300
-symptomatic for hyperglycemia
1. long acting insulin: glargine
-10 units or 0.1-0.2 units/kg
-target fasting plasma of 80-130
2. short or rapid acting: lispro
-added if not enough glycemic control with basal insulin alone
-10% of basal dose or 5 units before largest meal
-or basal +1, +2, +3 respectively
diabetic retinopathy tx
Tx
-glycemic and BP control
-regular screening
-lazer photocoagulation or anti-VEGF
diabetic nephropathy tx
Tx
-ACE/Arb
-SLGLTi = preferred initial therapy for T2D< with CKD
diabetic neuropathy tx
Tx
-pain management: gabapentin and pregabalin
cardiovascular complication tx
Tx
-ACE/ARB
-statin for all >40
-consider 81mg of ASA in high ASCVD score
-hypertriglyceridemia: icosapent ethyl
-GLP1 for pts for T2DM with high ASCVD
-SGLT2 for CV and T2DM
peripheral artery disease tx
Tx
-smoking cessation, exercise therapy, antiplatelet therapy, revascularization
diabetic foot ulcer tx
Tx
-wound care, offloading, infection
-revascularization
infections with diabetes
-increased susceptibility to infection
Common
-UTI, skin infection, periodontal disease
Tx
-glycemic control
-tx of infection
Prevention
-appropriate vaccination
hyperparathyroidism tx
-manage acute hypercalcemia: normal saline + free water
-prevention of complication
-specific management of underlying
Primary hyperparathyroidism tx
Active surveillance
-monitor serum calcium, renal function
-osteoporosis, nephrolithiasis
Pharm
-adequate calcium intake
-Bisphosphonates: maintain bone density
-cinacalcet: help decreased PTH and calcium levels
Surgery
-parathyroidectomy = definitive
-indications: symptomatic, calcium >1 above normal, <60 creatinine, nephrolithiasis, osteoporosis
secondary and tertiary hyperparathyroidism tx
Secondary
-referral
-phosphate binder, calcium, vti D analogs
-control of PTH, calcium, phosphate
Tertiary
-parathyroidectomy
hypoparathyroidism tx
Non-pharm
-high calcium, low phosphorus diet
-monitor and maintain serum calcium levels every 3 months
Pharm
-acute/severe hypocalcemia: IV calcium gluconate
-chronic: calcium carbonate QD, calcitriol BID
-thiazide diuretics, magnesium
-recombinant PTH
Surgery
-transplantation of preserved parathyroid tissue
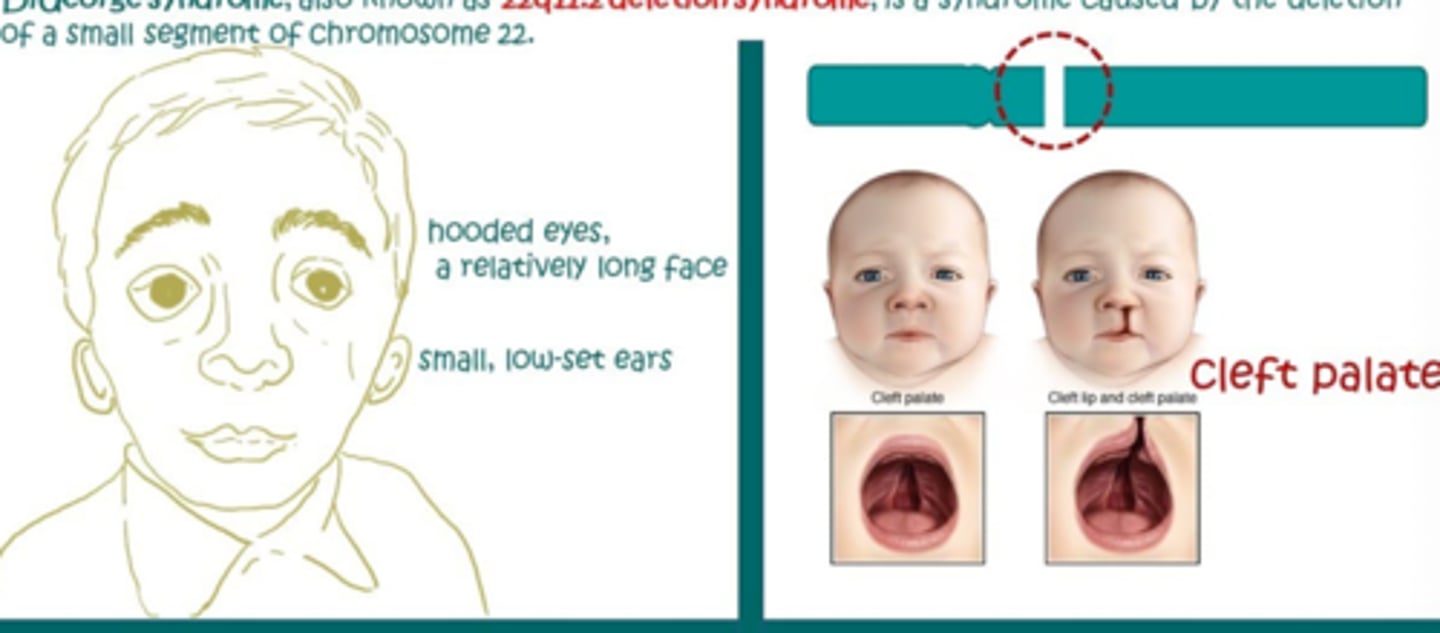
DiGeorge Syndrome
-22q11.2 deletion syndrome
-parathyroid glands fail to develop properly or absent
Sx
-cardiac anomalies, abnormal facies, thymic hypoplasia, cleft palate, hypocalcemia
-CATCH-22
Tx
-lifelong calcium and Vit D
-regular monitoring of calcium
-thymic transplant
hypothyroidism tx
First line:
-levothyroxine 1.6 mcg/kg/day PO
-recheck TSH 6-8 weeks
Other:
-liothyronine if levo isn't working or as add on for sx relief
-armour thyroid
-follow up annually TSH level
Pregnant
-monitor TSH every 4 weeks in first half of pregnancy
-immediately after pregnancy
congenital hypothyroidism tx
-levothyroxine
autoimmune Hashimoto thyroiditis
-cell mediated and antibody mediated destruction of thyroid gland
-autoantibodies against thyroid peroxidase, thyroglobulin, TSH receptor
Subclinical hypothyroidism
-compensation phase: normal thyroid hormones are maintained to rise TSH
-later unbound T4 levels fall and TSH level rise further > sx become apparent
hyperthyroidism tx
First line
-methimazole
-propylthiouracil: used in first trimester for pregnancy then switch
-symptomatic relief: propranolol
Other
-Radioactive Iodine: releases iodine that is absorbed by thyroid gland which destroys thyroid cells
-surgery: results in permanent hypoparathyroidism
Both require lifelong thyroid hormone replacement
thyroiditis
-most common: chronic Hashimoto thyroiditis
-postpartum thyroiditis and subacute lymphocytic thyroiditis > transient hyperthyroidism
-TPO antibodies or Tg antibodies = high
painful subacute thyroiditis tx
Tx
-conservative
- NSAIDs
infectious suppurative thyroiditis tx
Tx
-abx
I&D
IgA related thyroiditis
-replacement of thyroid tissue with fibrosis tissue > thyroid gland become form and fixed
Sx
-hypothyroidism
-difficulty swallowing
-hard woody thyroid gland
Tx
-thyroid hormone replacement
-surgery for severe cases
acromegaly tx
Non-pharm
-education
-sleep study and CPAP
-colonoscopy screening, cardiac eval, DM management, PT, weight management
Pharm
-first line: somatostatin receptor ligands (octreotide, lanreotide)
-GH receptor antagonist
-dopamine agonist (cabergoline)
Surgery
-transsphenoidal adenomectomy = preferred initial
gigantism tx
Non-pharm
-genetic counseling, monitoring of growth
-psychological support
-management of complication, nutrition
Pharm
-octreotide, pegvisomant, cabergoline
Surgery
-first line: transsphenoidal adenomectomy
dwarfism tx
Non-pharm
-nutrition, counseling, PT, support groups
-monitoring of growth
Pharm
-GH therapy: somatropin
-treat endocrine disorder
pituitary adenoma tx
Non-pharm
-observation for small nonfunctioning
-regular monitoring with MRI and hormone levels
Pharm
-first line for prolactinomas: cabergoline
Surgery
-transsphenoidal resection if visual defects, hormone hypersecretion, pituitary apoplexy
Radiation
-reserved for recurrent disease after surgery
-stereotactic radiosurgery for small residual tumor
hypopituitarism tx
Non-pharm
-education, medical alert bracelet
-stress dose steroids
Pharm
-ACTH deficiency (most urgent): hydrocortisone
-TSH deficiency: levothyroxine
-gonadotropin deficiency: testosterone, estrogen/progesterone
-GH deficiency: somatropin
-ADH deficiency: desmopressin
hyperpituitarism tx
Non-pharm
-monitor is small
-manage complication, education
Pharm
-prolactinomas = cabergoline
-GH = somatostatin
-ACTH = surgical resection, ketoconazole
-TSH = somatostatin, surgical resection
-non prolactin adenomas = transsphenoidal adenomectomy
prolactinomas tx
Non-pharm
-observation for small
-calcium and vit D supplement
-bone density monitoring
Pharm
-first line: cabergoline, bromocriptine
Surgery
-reserved for drug intolerance, large adenomas, patient preference
diabetes insipidus tx
Non-pharm
-ensure enough water, monitor fluids
-dietary mods
-check medications
Pharm
-Central = desmopressin
-nephrogenic = thiazide diuretics, amiloride, NSAIDs, low sodium diet
SIADH tx
Non-pharm
-education, fluid restriction, dietary mods
Pharm
-acute severe hyponatremia <125 = 3% hypertonic saline
-chronic asymptomatic = demeclocycline
-alternative: tolvaptan, conivaptan
male primary hypogonadism tx
Testosterone replacement therapy
-boys who have no yet entered puberty by age 14
-men with primary testicular failure
male secondary hypogonadism tx
-significant weight loss
Testosterone replacement therapy
-mainstay
-indications: serum testosterone <150
-men without elevated LH and average of 2 morning serum total testosterone <275
-applied to upper arms, shoulders, abdomen
females hypogonadism tx
Hormone replacement therapy with estrogen
-oral estrogen, transdermal estrogen, vaginal estrogen, injectable estrogen
-progesterone and estrogen combined for postmenopausal women to mimic natural menstrual cycle
-risk: breast cancer, CV risk, VTE. endometrial cancer, gallbladder disease, bone health