Honors Biology Unit 2
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biological Molecules and Enzymes
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
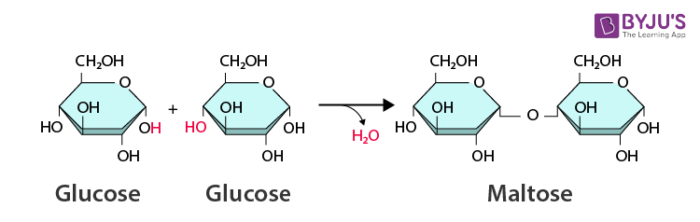
dehydration synthesis
Process that combines two molecules by removing a water molecule, forming a new bond.
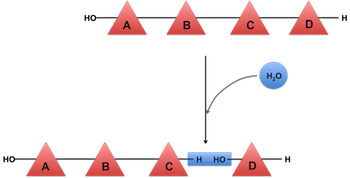
hydrolysis
Chemical breakdown of a compound by adding water.
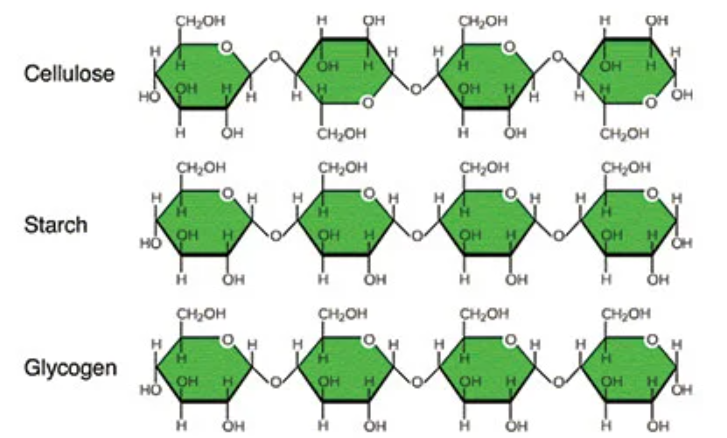
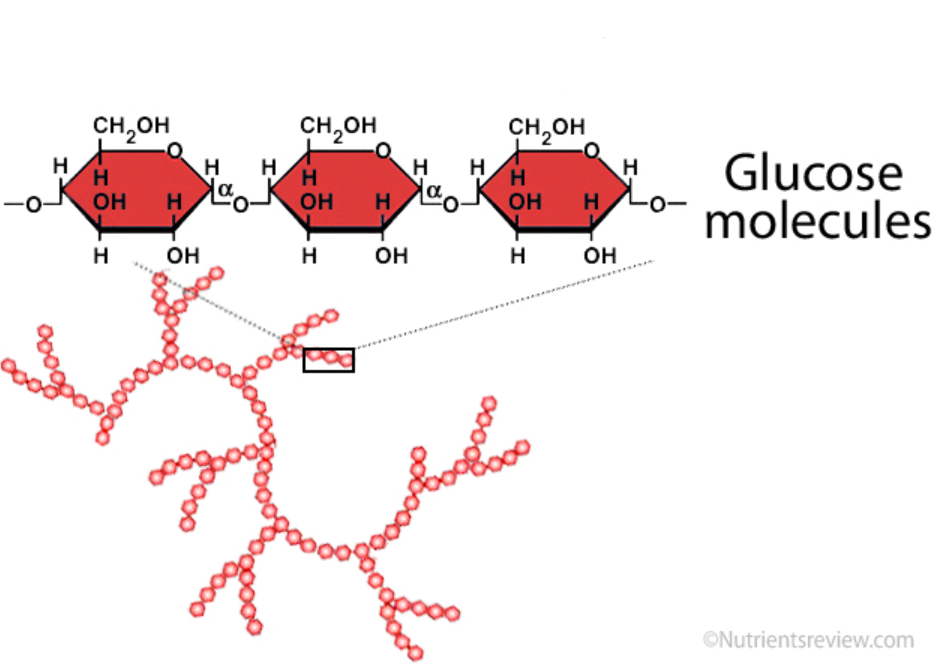
polysaccharide
A complex carbohydrate made up of multiple sugar molecules joined together.
It serves as a long-term energy storage molecule in plants and animals.
Examples include cellulose, starch, and glycogen.
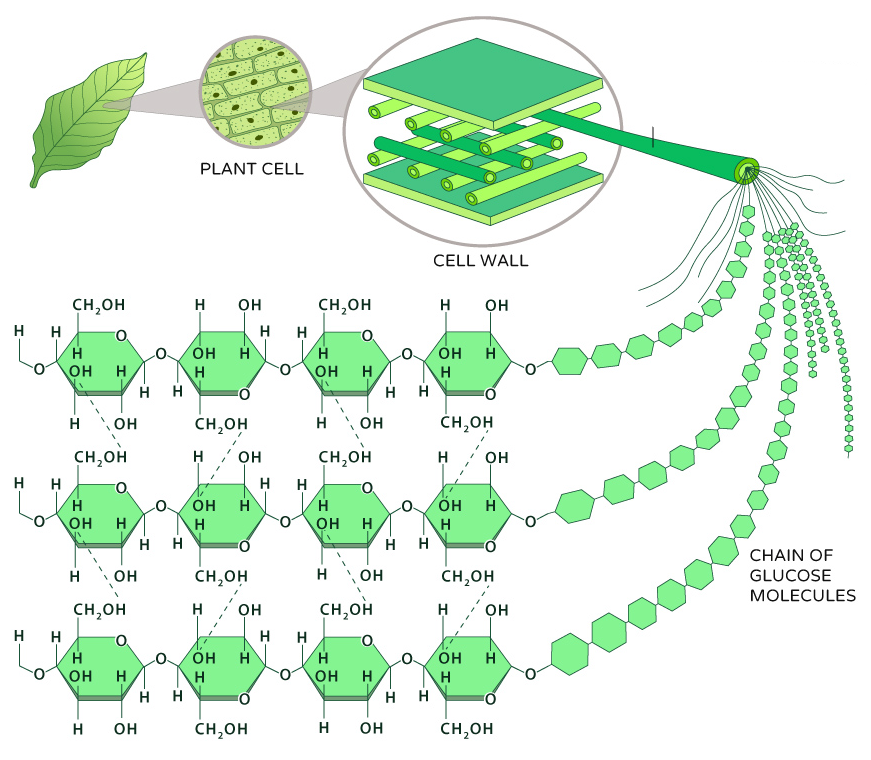
cellulose
structural polysaccharide that makes up plant cell walls
starch
storage polysaccharide found in plants
fatty acid
hydrocarbon chain with a carboxyl group at one end; majority portion in lipids
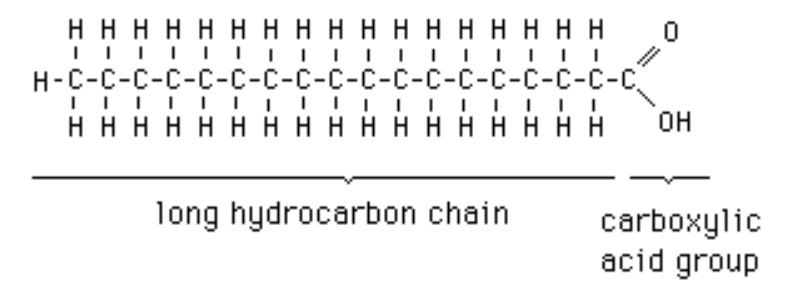
polymer
long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together
monomer
building block for polymers; only made by producers
macromolecule
giant molecule formed by the joining of smaller molecules
nucleotide
building block of a nucleic acid; five carbon sugar covalently bonded to a nitrogen base and a phosphate group
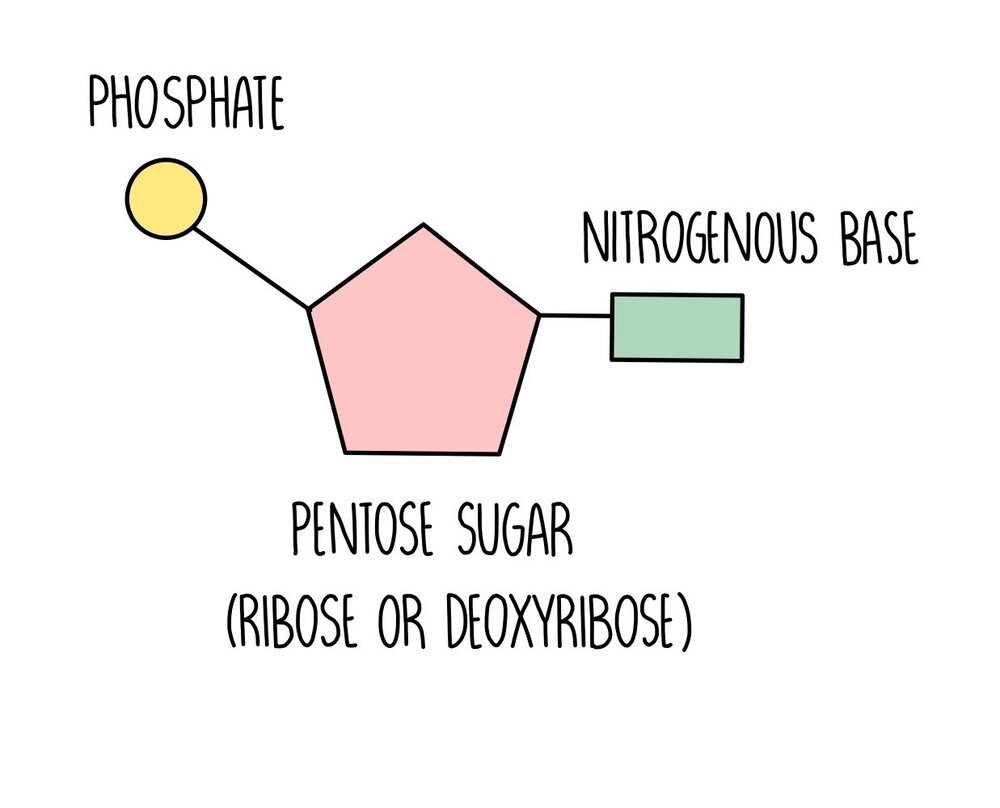
Nucleic Acid
A macromolecule composed of long chains of nucleotides, which store and transmit genetic information.
Activation Energy
The minimum energy required for a chemical reaction to occur, enabling reactants to transform into products.
Enzyme
A protein that acts as a catalyst to accelerate biochemical reactions by lowering the activation energy.
Substrate
The specific reactant molecule that an enzyme acts on during a biochemical reaction, fitting into the enzyme's active site.
Active Site
The section on an enzyme where the substrate binds (fits), speeding up the chemical reaction.
Denature
The process in which an enzyme loses its shape due to things like heat or pH changes, making it unable to bind (fit with) the substrate.