IB Biology HL - A2.2: Cell Structure
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Cell Theory
All organisms consist of one or more cells.
Basic Unit of Life
Cell is fundamental structure and function unit.
Pre-existing Cells
All cells originate from existing cells.
Scientific Theory
Well-supported explanation of natural world phenomena.
Inductive Reasoning
General conclusions from specific observations or patterns.
Deductive Reasoning
Specific predictions based on general principles.
Plasma Membrane
Controls substance movement; maintains cellular homeostasis.
Cytoplasm
Site of biochemical reactions; contains organelles.
Ribosomes
Synthesize proteins using genetic instructions.
DNA
Stores genetic information for cell function.
Prokaryotes
Unicellular organisms without membrane-bound organelles.
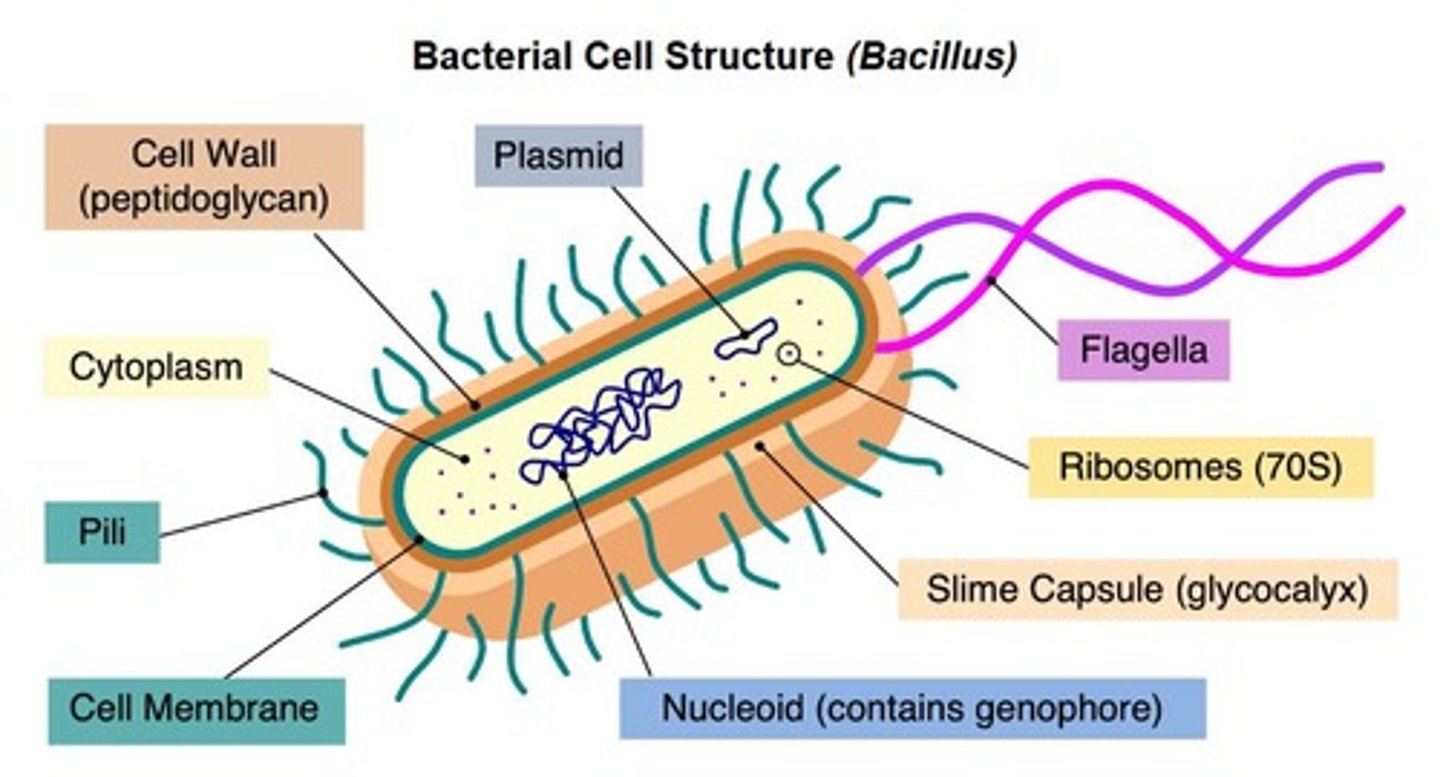
Cell Wall
Provides structural support; made of peptidoglycan.
70S Ribosomes
Smaller ribosomes found in prokaryotic cells.
Nucleoid
Region containing circular DNA in prokaryotes.
Eukaryotes
Complex cells with membrane-bound organelles.
Compartmentalization
Organelles allow specialized cellular functions.
80S Ribosomes
Larger ribosomes found in eukaryotic cells.
Nucleus
Stores DNA; controls cell activities.
Cytoskeleton
Provides structural support and facilitates transport.
Mitochondria
Powerhouse of the cell; site of ATP production.
Rough ER
Synthesizes and modifies proteins for export.
Smooth ER
Synthesizes lipids; detoxifies harmful substances.
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids.
Lysosomes
Digestive vesicles that break down waste.
Vesicles
Small sacs for transporting materials within cells.
Vacuoles
Storage organelles; large in plant cells.
Animal Cells
Lack cell walls; contain centrioles.
Plant Cells
Have cell walls made of cellulose.
Fungal Cells
Contain chitin in cell walls.
Endosymbiosis
Theory explaining origin of eukaryotic organelles.
Evidence for Endosymbiosis
Structural, genetic, and behavioral similarities to prokaryotes.
Multicellular Organisms
Organisms composed of multiple specialized cells.
Evolution of Multicellularity
Involves cell clusters and specialization.