somatic reflexes - lecture
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what are the features of a reflex?
- requires stimulation
- rapid processing
- involuntary
- stereotyped action (same response every time)
what do spinal reflexes involve?
somatic nervous system
can you have visceral (autonomic) reflexes?
yes
what is the main mechanism of the knee jerk reflex?
tapping the patella tendon causes stimulation of the muscle spindles which causes contraction of the quadriceps and relaxation of the hamstrings
what type of reflex is the knee jerk reflex?
monosynaptic stretch
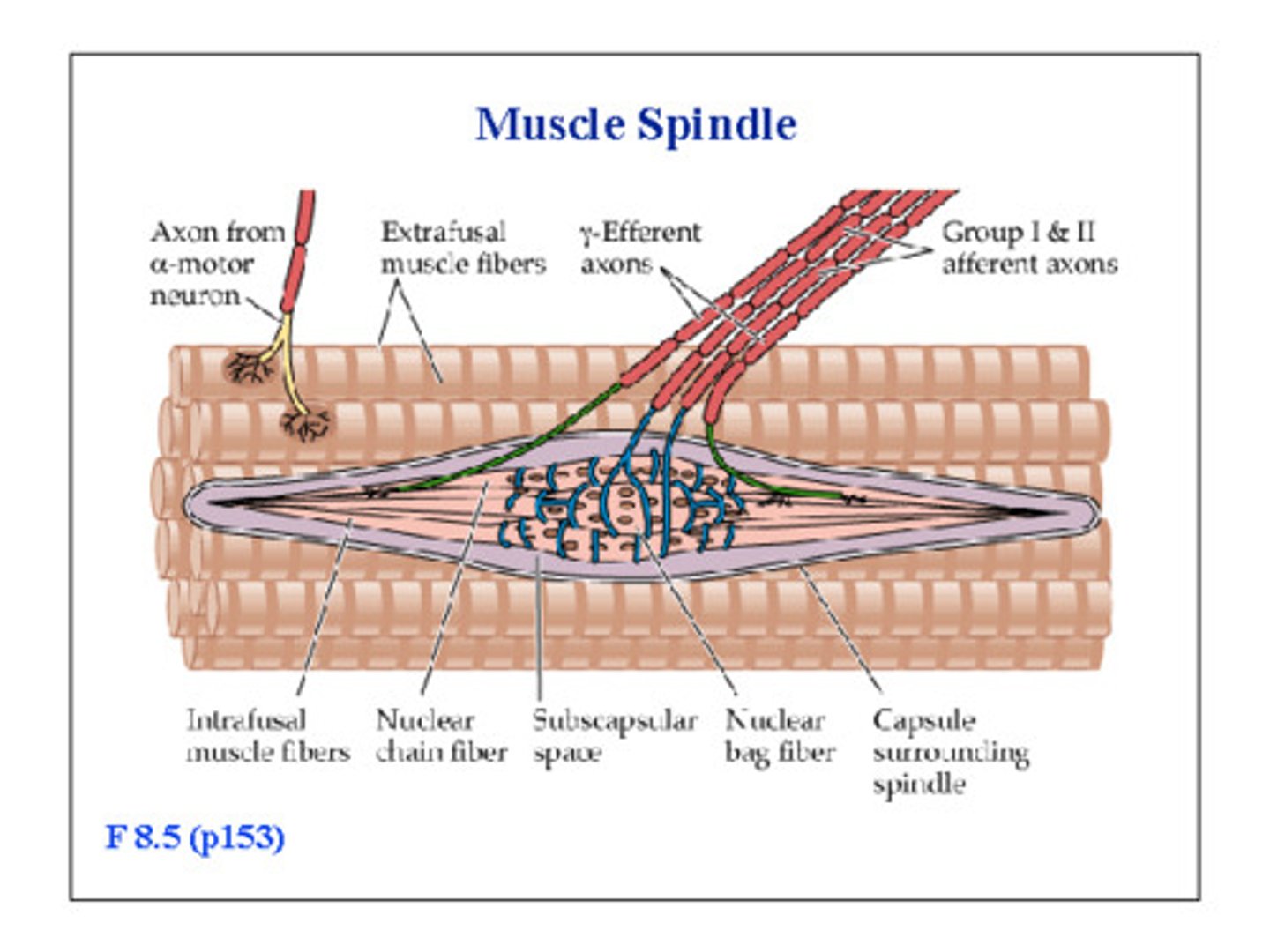
what are muscle spindles?
sensory receptors within muscles
what are the differences between muscle spindles and normal muscle cells?
muscle spindles have...
- nuclei that can be in a chain (spread out) or bag (all in the middle)
- sarcomeres only at the ends so have contractile outer portions and a non-contractile inner portion
- motor innervation by gamma motor neurones instead of alpha
- named intrafusal fibres rather than extrafusal
why do muscle spindles need a non-contractile portion?
to only send signals when the muscle actually contracts
what is wrapped around the non-contractile portion of the muscle spindles?
type Ia primary afferent fibres (in blue)
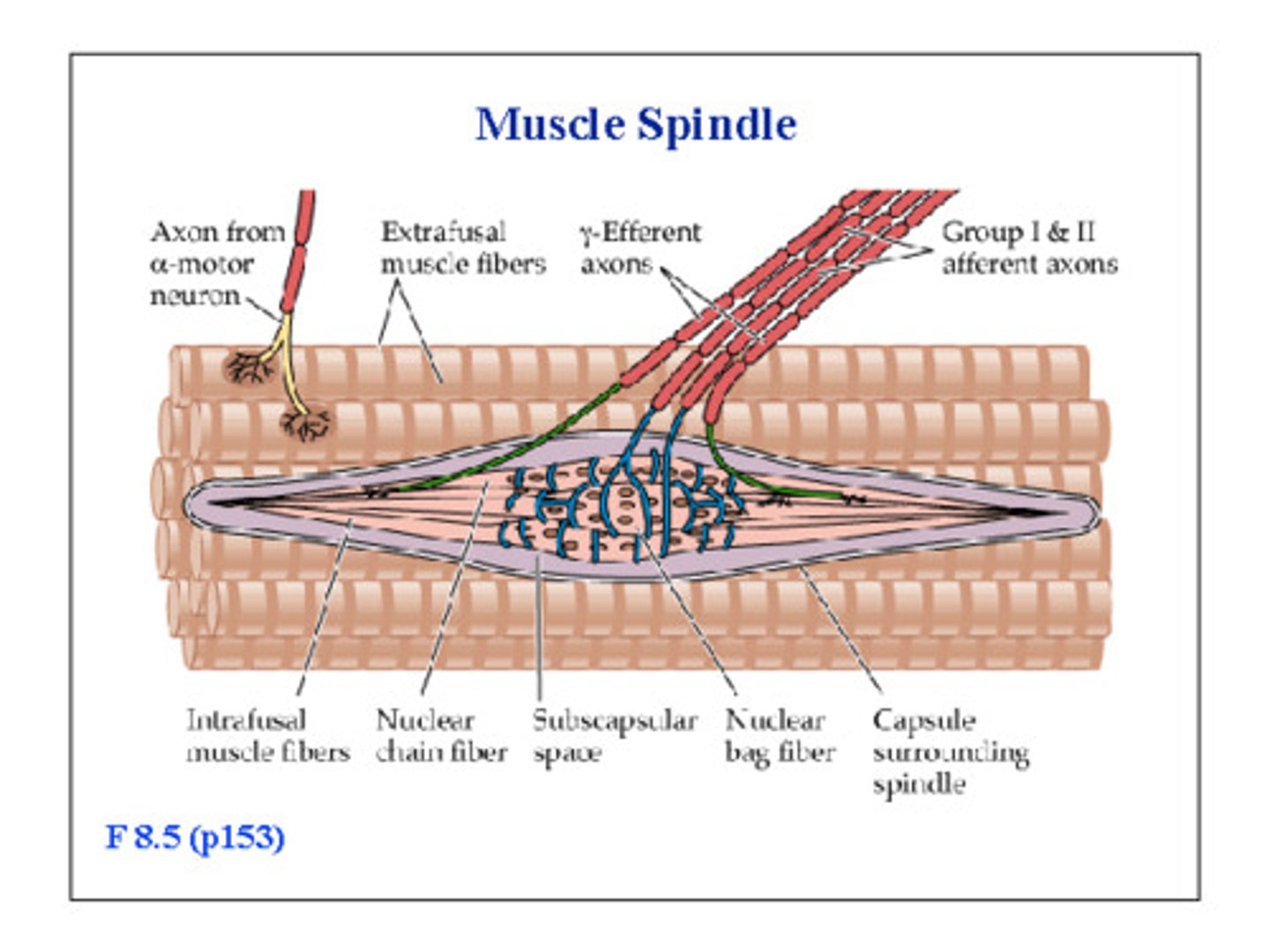
what is located in the contractile portion of the muscle spindles?
type IIa secondary afferent fibres (in green)
what are the functions of type Ia and IIa afferent fibres?
detect changes in the length of the muscle - stimulated by stretching of the mid-portion of the muscle spindle
what happens to type Ia and IIa afferent fibres when they are stimulated?
increase firing
what is the motor innervation of the muscle spindle?
gamma motor neurones in the contractile portions (red)
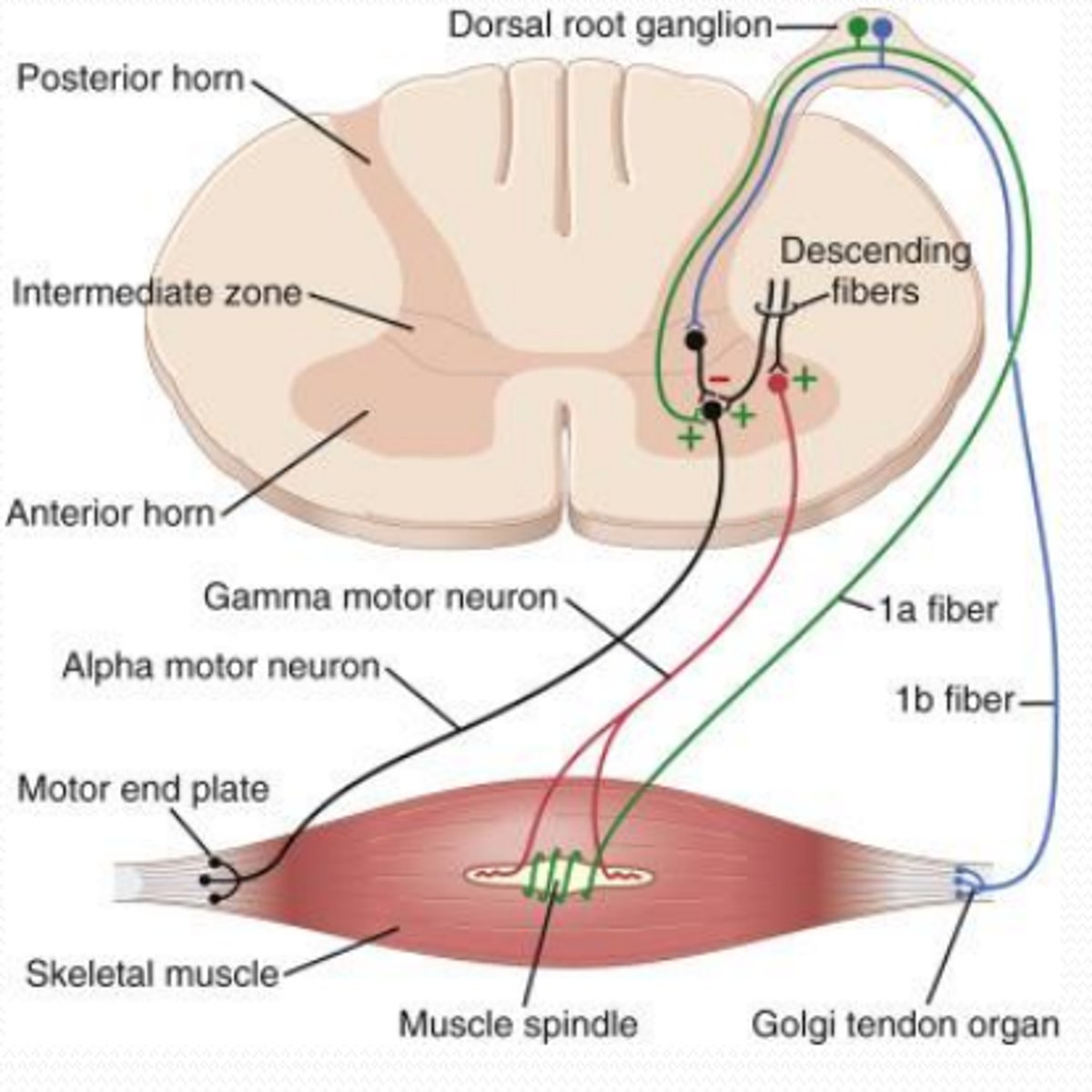
what happens in the monosynaptic stretch reflex?
- stretching of the muscle stimulates the muscle spindles
- sends signals from type Ia afferent fibres to dorsal horn
- synapses with alpha motor neurone of same muscle
- stimulates muscle to contract
what else needs to happen alongside contraction of the muscle group?
relaxation of the opposite muscle group
is the relaxation pathway monosynaptic?
no, it is polysynaptic, including an inhibitory interneurone
what is the relaxation pathway for the stretch reflex?
- stretching of muscle stimulates muscle spindles
- sends signals to dorsal horn of spinal cord
- synapses with inhibitory interneurone
- synapses with motor neurone and stimulates the relaxation of muscle group
why is a distraction sometimes needed when trying to initiate a reflex?
to override conscious awareness - Jendrassik manouevre
what can cause hyperreflexia? (4)
upper motor neurone problems:
- spinal cord injury
- brain injury
- MS
- pre-eclampsia (causes cerebral oedema)
what causes hyporeflexia?
lower motor neurone problems:
- peripheral neuropathy (diabetes, alcohol etc)
- trauma
- guillian barre syndrome
what is the golgi tendon relfex also called?
reverse stretch reflex
what is the function of the golgi tendon relfex?
protective reflex to stop muscles from damaging themselves from too much tension
what is a golgi tendon organ?
sensory receptor located at the junction between a muscle and its tendon
what stimulates the golgi tendon body?
muscle tension stimulates type II B fibres
what happens in the golgi tendon reflex?
- muscle tension stimulates type II B fibres
- type II B fibres synapse with inhibitory interneurones in the dorsal root
- inhibitory interneurones synapse with alpha motor neurones
- inhibition of alpha motor neurones causes muscle to relax