Unit 4: Cell Biology
1/62
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Characteristics of prokaryotic, eukaryotic, plant, animal, and bacteria cells as well as organelles' function
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
(1665) Hooke
first to use the term “cell” to describe the structures that make up all living things
observed cork cells (dead)
(1670’s) Leeuwenhoek
father of modern microbiology
first to observe living cells
Cell Theory
All organisms are composed of one or more cells
Cells are the basic units of structure and function for all living things
Cells arise only from other pre-existing cells
Prokaryotic cells
simplest, most ancient/oldest type of cell
Prokaryotic cells are found only in
bacteria
Two main things prokaryotic cells don’t have that eukaryotic cells do
a nucleus and “membrane-bound” organelles
Eukaryotic cells
more modern, complex cells
Eukaryotic cells are found in
plants, animals, fungi, and protists
Plant cells are what type of cell?
eukaryotic cells
Animal cells are what type of cell?
eukaryotic cells
Bacterial cells are what type of cell?
prokaryotic cells
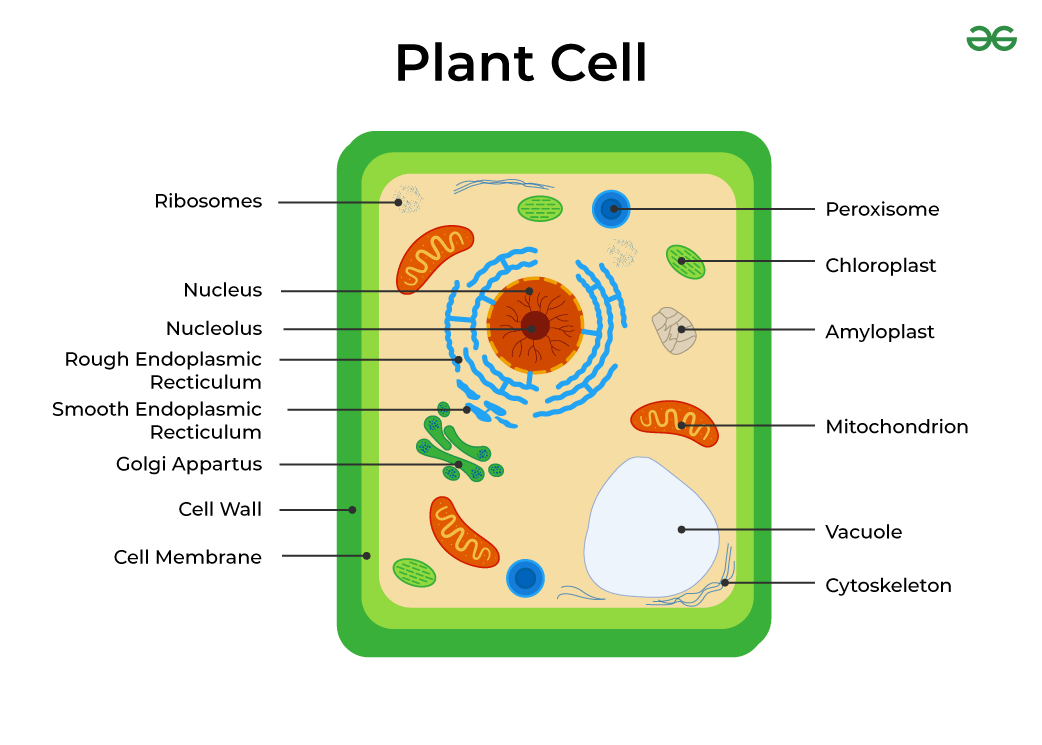
What shape is a plant cell most likely to look like in a diagram?
a rectangle
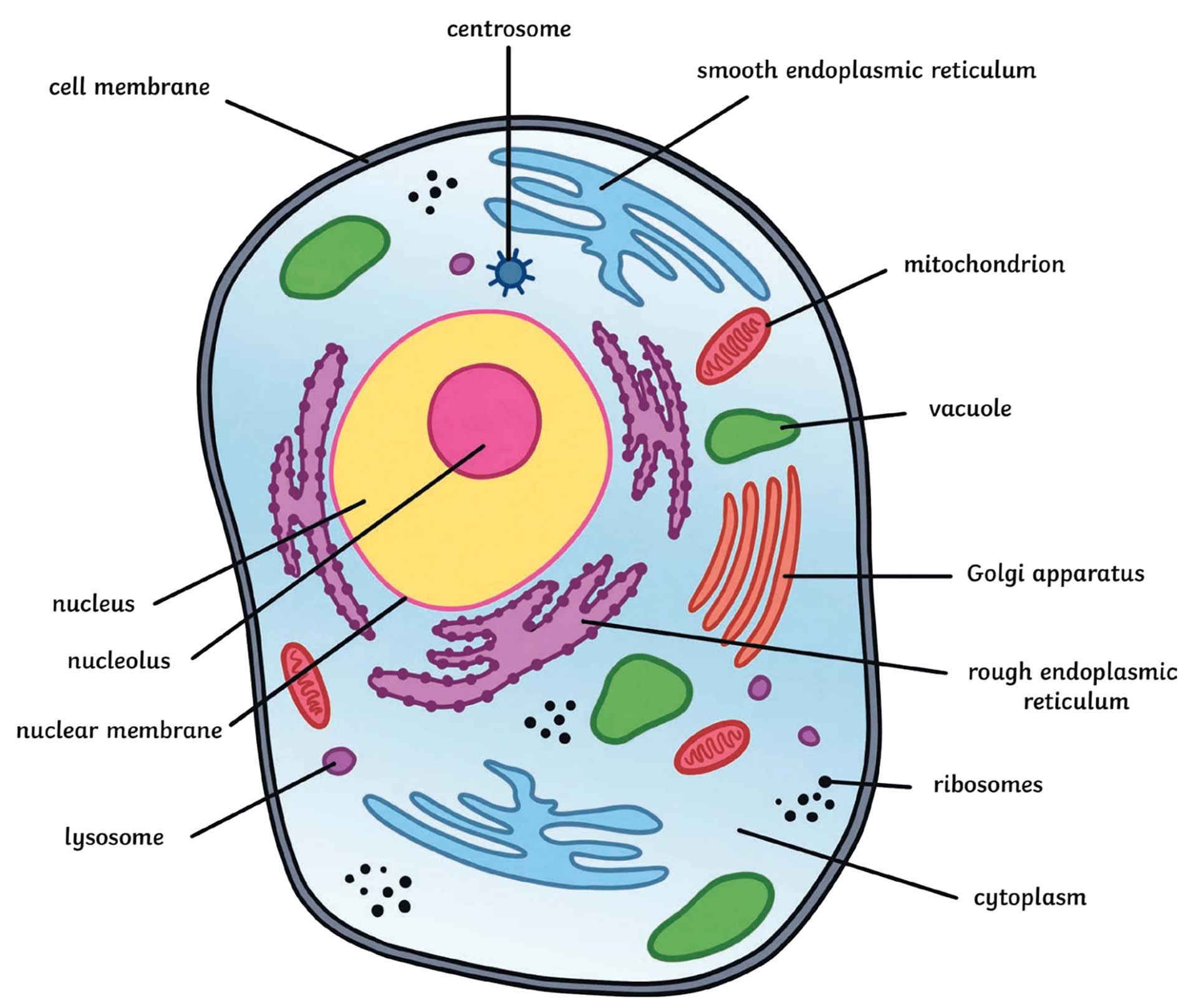
What shape is an animal cell most likely to look like in a diagram?
an irregular shape (but rounded)
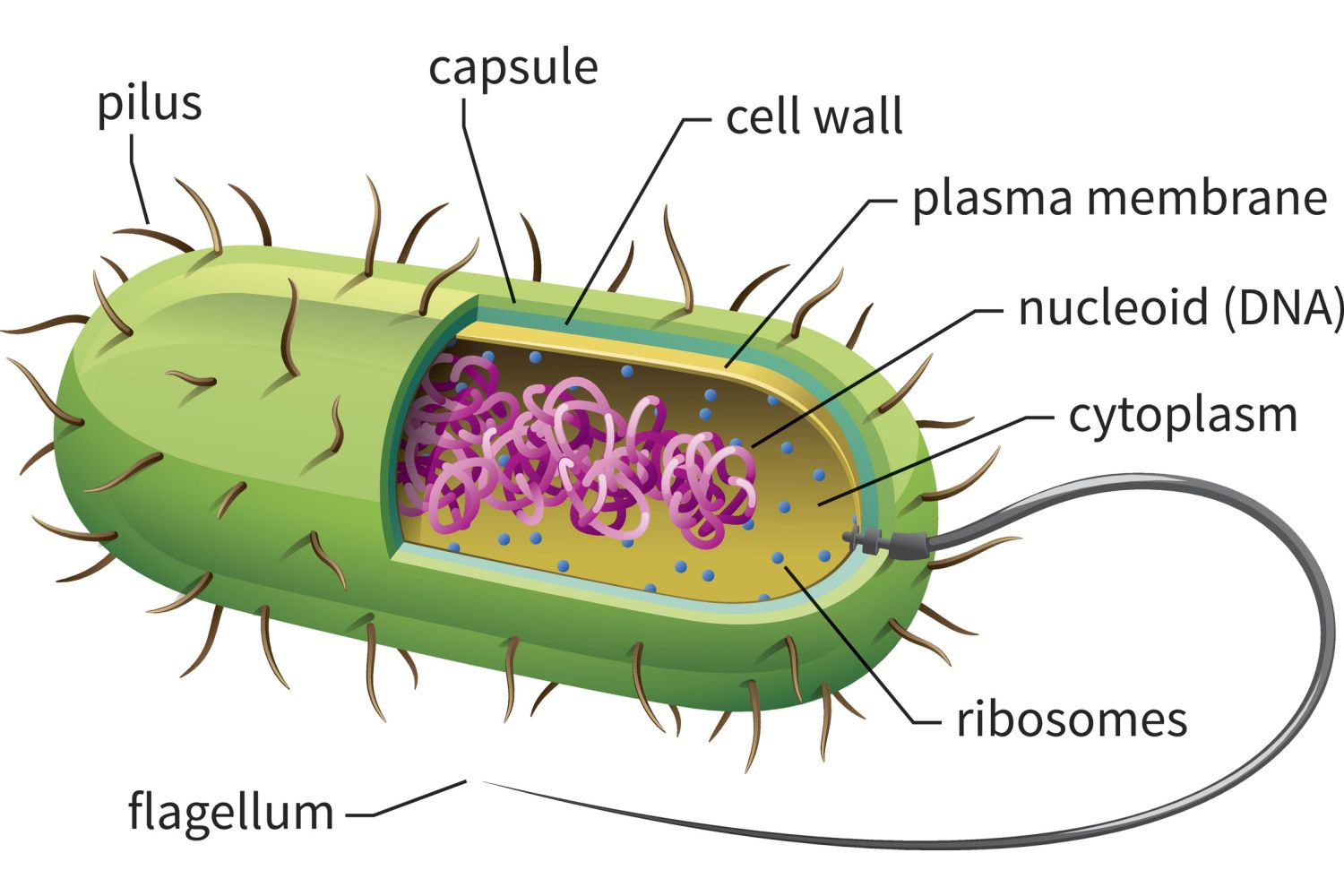
What object does a bacterial cell’s shape resemble?
a pill
Four main components needed to make a cell
cell membrane, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and DNA
Cell membrane is the same as
plasma membrane
Cytosol is the same as
cytoplasm
Function of the cell membrane
outer boundary of the cell
separates the cell from the external environment
regulates what goes in and out of the cell (maintains homeostasis)
Function of cytosol (cytoplasm)
clear fluid filling the cell in which organelles are suspended
watery environment
Function of the nucleus
contains genetic material
controls cell activity
surrounded by nuclear membrane
Function of nucleolus
found within the nucleus
site where ribosomes are made
Function of endoplasmic reticulum
“intracellular highway” - intracellular means within the cell
system of transport tubules within the cell - tubules mean small tubes
Difference in textures between endoplasmic reticulum with and without ribosomes
smooth = no ribosomes
rough = with ribosomes
Function of free-floating ribosomes
location where proteins are assembled (amino acids join to make polypeptide)
most numerous organelle
Function of golgi apparatus
packaging and processing organelle
proteins are modified and prepared for export
Analogy for golgi apparatus
a UPS store for cells
Function of mitochondria
“powerhouse” of the cell
location where ATP is made through aerobic respiration
Function of lysosome
contains digestive enzymes
breaks down food and worn-out cell parts
Analogy for lysosome
“trash disposal” + “digestion”
Function of peroxisome
small, “membrane-bound”
contains toxic peroxides that are safely broken down
Analogy for peroxisome
“nuclear waste dump” or “prison”
Function of cytoskeleton
provides shape and support for the cell
Cytoskeleton refers to which two protein strands?
microtubules and microfilaments
Function of vacuoles
storage organelle (stores material and waste)
Function of centrioles
aid in cell division
Function of the cell wall
found outside the cell membrane
usually made of cellulose (plants)
provides support
Three plastids
chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts
Function of chloroplasts
contain chlorophyll (green)
site of photosynthesis
where sunlight energy is converted to potential chemical bond energy (P.C.B.E.) in glucose
Function of chromoplasts
contain accessory pigments that aid in photosynthesis or sometimes just give color to plants
Function of leucoplasts
store starch
Cell membranes are found in
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Cytosol (cytoplasm) is found in
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Nucleus is found in
eukaryotic cells
Nucleolus is found in
eukaryotic cells
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is found in
eukaryotic cells
Free-floating ribosomes are found in
prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Golgi apparatus is found in
eukaryotic cells
Mitochondria is found in
eukaryotic cells
Lysosome is found in
eukaryotic cells
Peroxisome is found in
eukaryotic cells
Cytoskeleton is found in
eukaryotic cells
Vacuoles are found in
eukaryotic cells
Describe the vacuoles in animal cells
rare/small/several
Describe the singular vacuole in plant cells
large (holds water)
Centrioles are found specifically in
animal cells
Cell walls are found
specifically in plant cells and all prokaryotic cells
Plastids are found specifically in
plant cells
How do flagella help prokaryotic cells?
they assist in cell movement
Many prokaryotic cells have pili, which
aid in cell adhesion
The outside of a prokaryotic cell is called
a capsule
Prokaryotic cell walls are made of
peptidoglycan
Many prokaryotic cells carry DNA plasmids, which
often provide bacteria with genetic advantages, such as antibiotic resistance
Cell specialization
ex: epithelial, immune, sex, muscle, fat, bone, blood, nervous, and stem cell