Fungal Physiology
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
Outline the structure of fungi
eukaryotic micro-organisms
cytoplasm enclosed in cell wall
chitin cell wall
What is the cell wall of fungi made of?
chitin
How do fungi get nutrition?
absorption of organic molecules from immediate surroundings
How do fungi reproduce?
sexual and asexual spores
What are the 2 main morphological forms of fungi?
moulds and yeasts
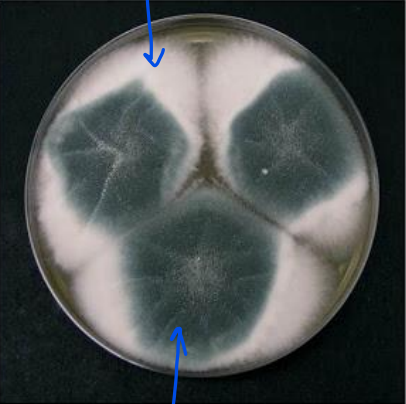
What does this image show?
mould
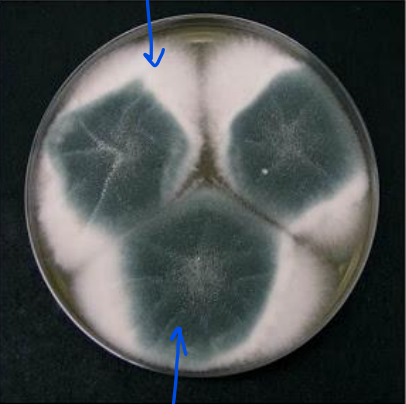
What are the white fluffy areas?
hypha
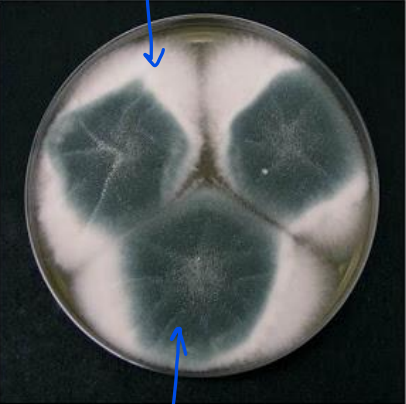
What are the blue/green areas?
spores being produced by fungus
What are hyphae?
basic cell unit of the moulds
What is the typical structure of hyphae?
apically elongating cylinder capable of branching
cross walls
What is the role of the cross walls/septa in hyphae?
strengthen tubular wall
have a central pore where the cytoplasm can stream through
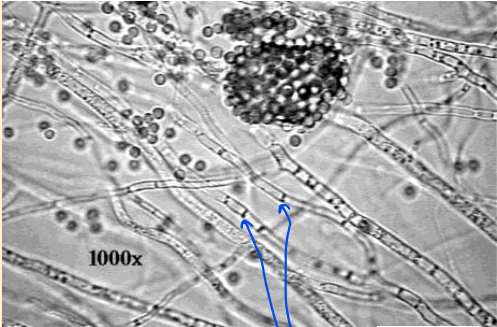
What does this image show?
hyphae
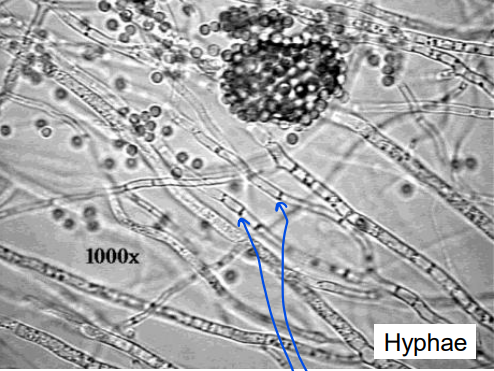
What are the blue arrows pointing to?
cross walls
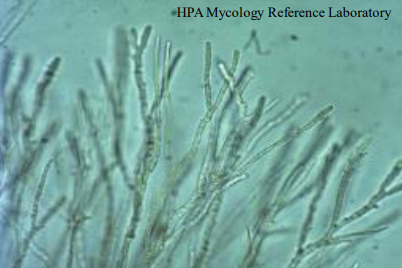
What are mycelium?
network of hyphae forming the body of the mould
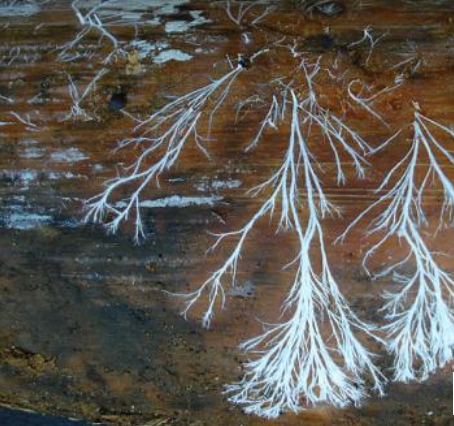
What can mycelium consist of?
submerged vegetative mycelium
aerial mycelium
bearing asexual spores

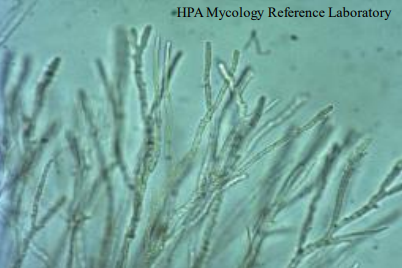
What does this image show?
mycelia
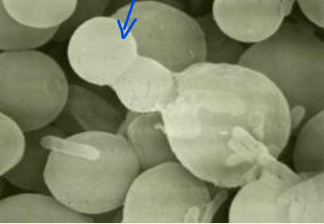
What are yeasts?
alternative growth form to the hypha
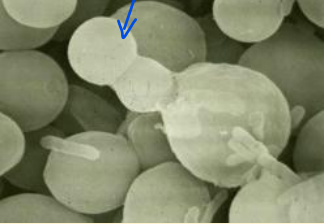
What cells do yeasts consist of?
discrete, often ovoid cells
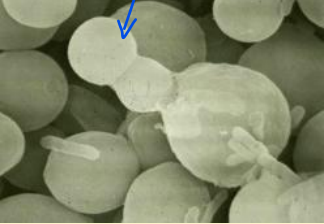
How do yeasts reproduce?
budding
What are dimorphic fungi?
produce both yeasts and hyphae depending on environmental conditions
What are fungi that produce both yeasts and hyphae depending on environmental conditions?
dimorphic
What are pseudo-mycelium?
intermediate form of growth between hyphae and yeasts in which elongated budding cells form pseudohyphae
What is a ‘colony’?
in culture, a mycelium/mass of yeast cells, usually grown from a single hyphal fragment/yeast cell
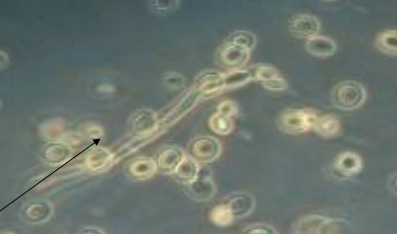
What does this image show?
pseudo-mycelium
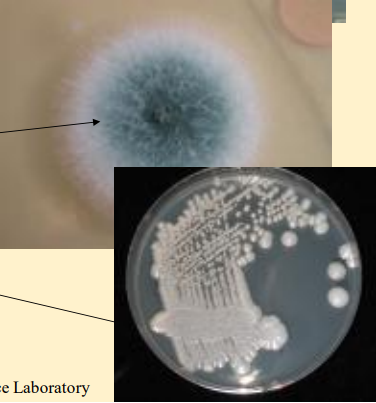
What do these images show?
colony
Name the 4 phyla of fungi
zygomycota
ascomycota
basidiomycota
deuteromycota (fungi imperfecti)
Are the fungi that are “yeasts” a taxonomic group?
NO (they represent unicellular fungi which may be members of any of the other phyla)
What are deuteromycota (fungi imperfecti)?
artificial assemblage of fungi which only produce conidia, there being no sexual reproductive state
What phyla do most pathogenic fungi species fit in?
deuteromycota (fungi imperfecti)
What have many dueteromycota evolved from?
ascomycota or basidiomycota

What does this image show?
aspergillus fumigatus
Where are aspergillus fumigatus common?
decaying vegetation

What do aspergillus fumigatus produce?
spores (so cause respiratory diseases)
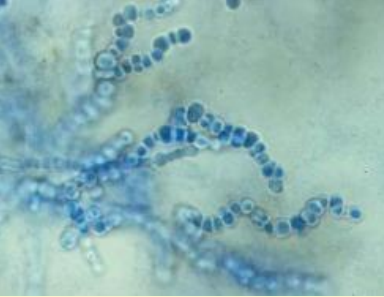
What are arthrospores?
conidia formed by simple fragmentation of hyphae in dermatophytes
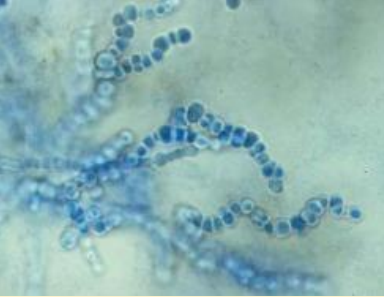
What spreads arthrospores?
itching
In what ways can fungi act as pathogens?
mycosis (infection)
allergy (inhaled spores)
toxicosis (ingesting)
What are the 2 ways toxicosis can occur?
mycotoxicosis (spoiled feed)
mycetism (ingesting poisonous fungi)
What is the main way fungi can be pathogens?
mycosis (fungus grown in/on the individual)
What are the 2 types of sources of fungal infection?
endogenous
exogenous
Endogenous sources of fungal infection
commensal flora (e.g. candida in GI tract)
Exogenous sources of fungal infection
free living saprophytes (e.g. aspergillus in hay)
parasitic on another animal host (e.g. microsporum causing ringworm)
What are the different types of infections (mycoses)?
superficial
subcutaneous
deep
What are superficial mycoses?
epidermis, nail/hair/claws/spines/feathers
What are subcutaneous mycoses?
traumatic inoculation through skin
What are deep mycoses?
inhaled, deep wound or endogenous
What are the most common type of fungal infection?
superficial mycoses
Why are we seeing more deep mycoses?
due to increased animal age so more immunosuppressed
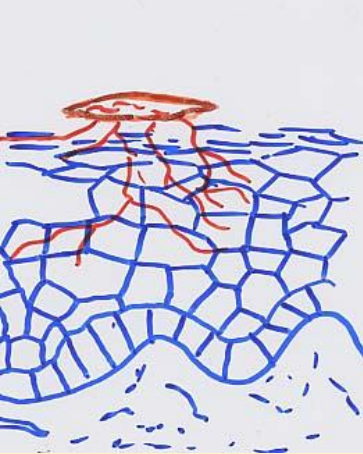
What does this image illustrate?
spore/fragments land on skin
hyphae bud/germinate into skin
skin reacts by multiplying faster → inflammation
can get deep into body
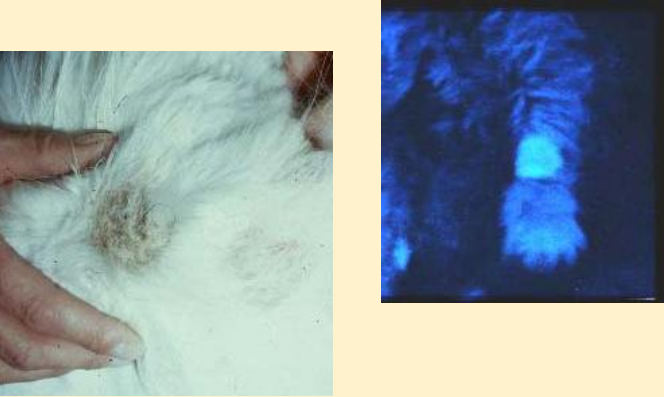
What does this image show?
microsporum canis
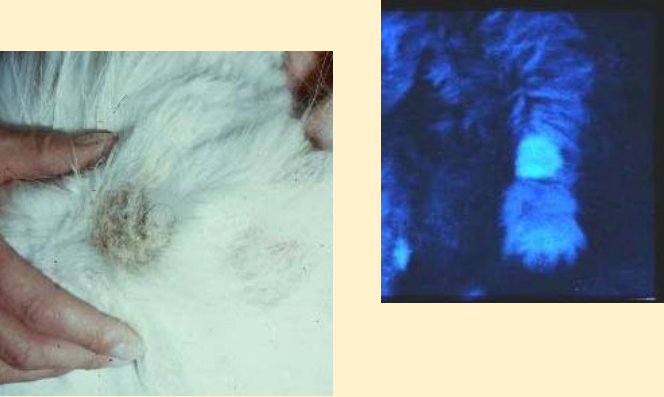
How can you identify microsporum canis infection?
UV
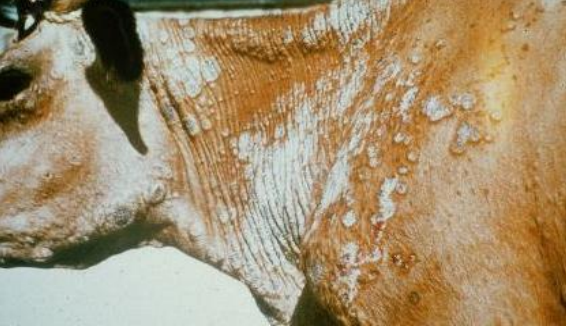
What does this image show?
trichophyton verrucosum (cattle ringworm)
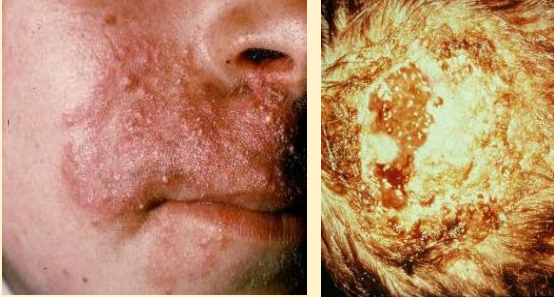
What does this image show?
trichophyton verrucosum
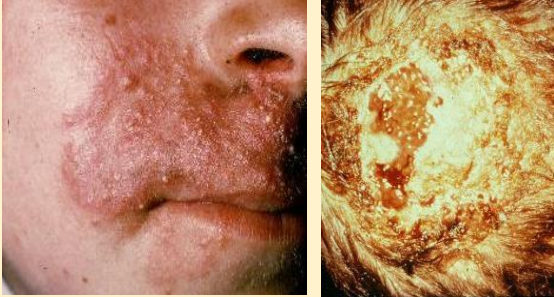
What should you avoid doing to the bubbly pustules of trichophyton verrucosum?
DON’T SCRATCH
What are the disadvantages of cattle ringworm?
loss in growth rate
lower milk yield
scarring affects hide value and stock sales
contamination persists for years
In what ways can you treat ringworm?
topical
systemic
environmental decontamination
What can you use to treat ringworm TOPICALLY?
miconazole
enilconazole
What systemic treatments can you treat ringworm with?
griseofulvin
terbinafine and itraconazole (not licenced)
How can you do environmental decontamination?
restrict movements of animals
burn bedding, collars, grooming tools
fog spray/wash other surfaces (e.g. eniconazole (bleach) persulphate)
What temperature do deep mycoses grow well at?
blood temperature
What are general characteristics of deep mycoses?
not contagious
opportunistic (attack when host has a predisposition)
What causes predisposition to fungal infection?
immune suppression
age (young and old)
trauma
exposure to heavy spore loads
What are examples of deep mycoses that are mould infections?
aspergillosis
mucoromycosis
mycotic abortion
What are examples of deep mycoses that are yeast infections?
candidosis
cryptococcosis
What is the main source of aspergillosis?
hay, straw
How big are aspergillosis spores?
2-3um
What do aspergillosis spores impact on?
alveolar wall
What does aspergillosis do in tissues?
septate hyphae in tissues
What are the 2 types of aspergillosis?
avian
mammalian
What are the 2 types of avian aspergillosis?
young chicks (acute)
mature birds (chronic)
What are the 2 types of mammalian aspergillosis?
neonatal (acute)
mature (chronic)
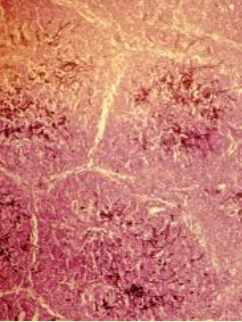
What does this image show?
acute aspergillosis in a young chick lung
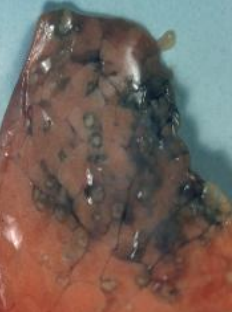
What does this image show?
acute aspergillosis in a piglet lung
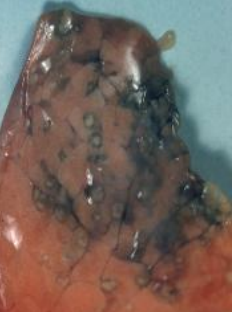
Why is there necrosis due to acute aspergillosis?
acid and alcohol produced that break down tissues
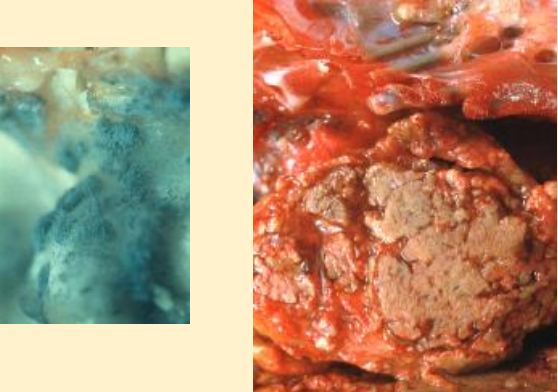
What does this image show?
chronic aspergillosis in avian air sac
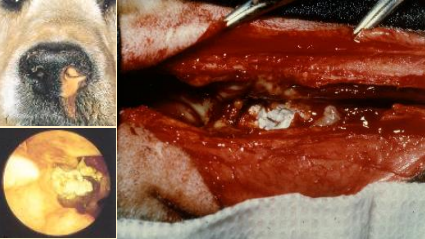
What does this image show?
chronic aspergillosis - nasal lesion of dog
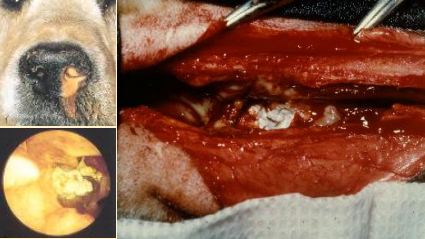
Can you do topical treatments for chronic aspergillosis (nasal lesion of dog)
Not really
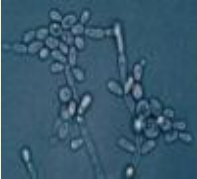
What does this image show?
candidosis

What does this image show?
cryptococcosis
What are general facts about candidosis?
yeasts of normal gut flora
opportunistic infections
What does candidosis cause?
mucosal lesions
thrush
gut ulcers
mastitis
deep systemic
What is cryptococcosis found in?
saprophytic in bird guano
What does cryptococcosis cause?
nasal granuloma
skin ulcers
deep localised
brain
mastitis
Is cryptococcosis opportunistic?
yes - goes dormant in brain then infection emerges when stressed/immunosuppressed
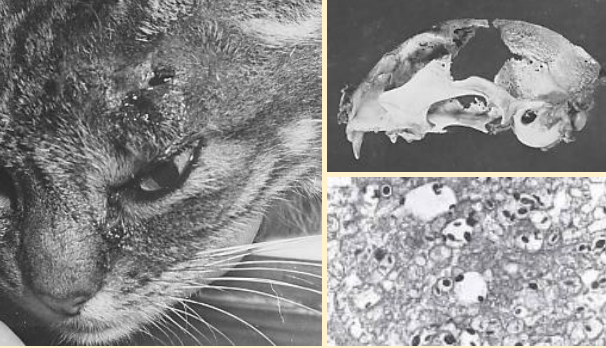
What does this image show?
cryptococcosis
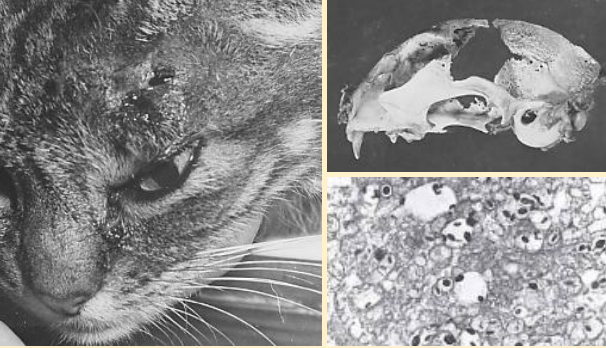
In this image, what does cryptococcosis manifest as?
skin lesions
How can you diagnose fungal infections?
direct microscopy
culture & ID
PCR
ELISA
What characteristic look do cryptococcosis infections have?
creamy goo