Unit 6: Gene Expression and Regulation
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Thomas Hunt Morgan
Worked with fruit flies
Did not know if the DNA or protein that make up chromosomes are the genes
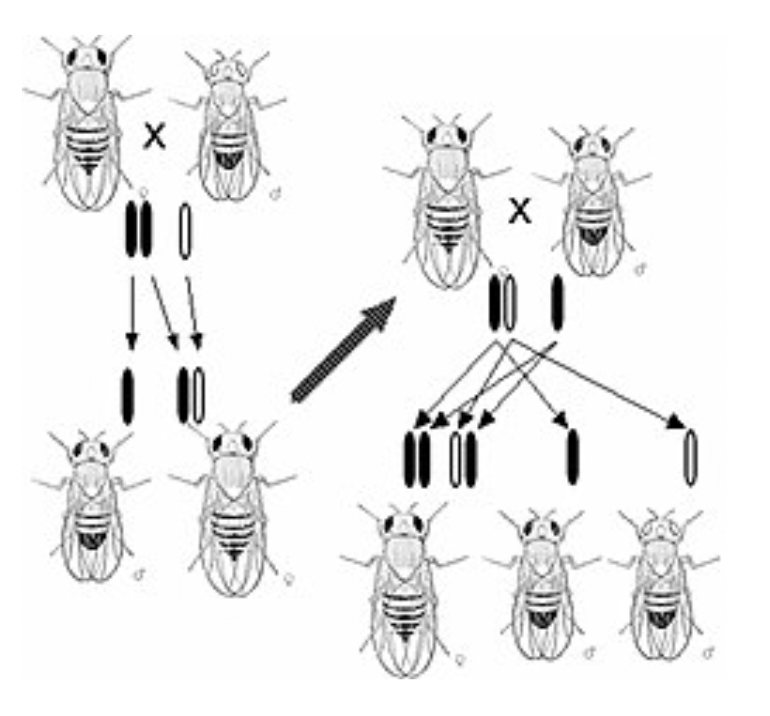
What did Thomas Hunt Morgan conclude?
Genes are on chromosomes
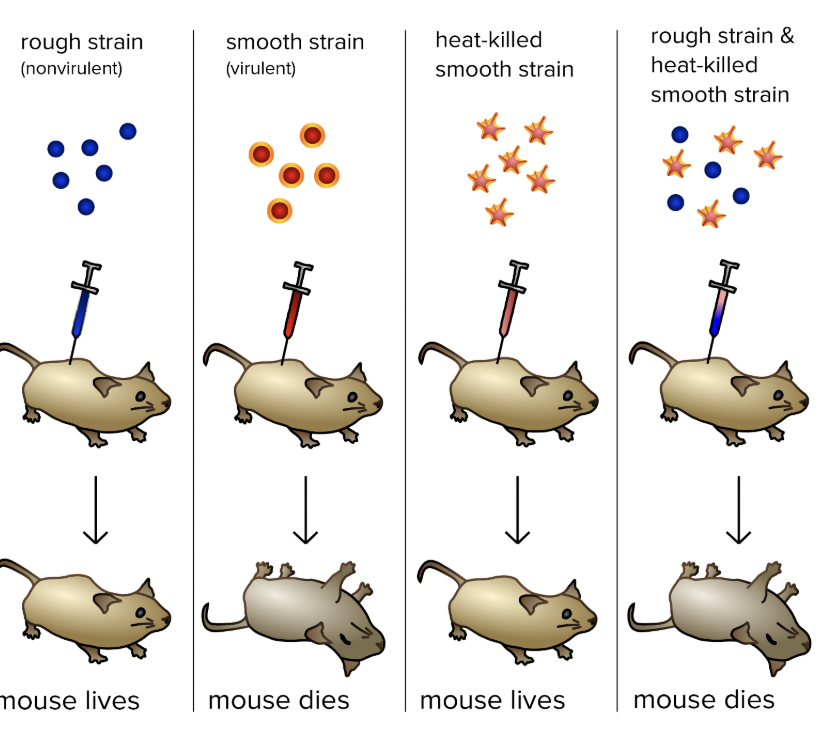
Frederick Griffith
Studied bacteria to find a cure for pneumonia
What did Griffin discover?
Harmless live bacteria mixed with heat-killed infectious bacteria caused diseases in mice
Substance passed from dead bacteria to live bacteria - “transforming factor”
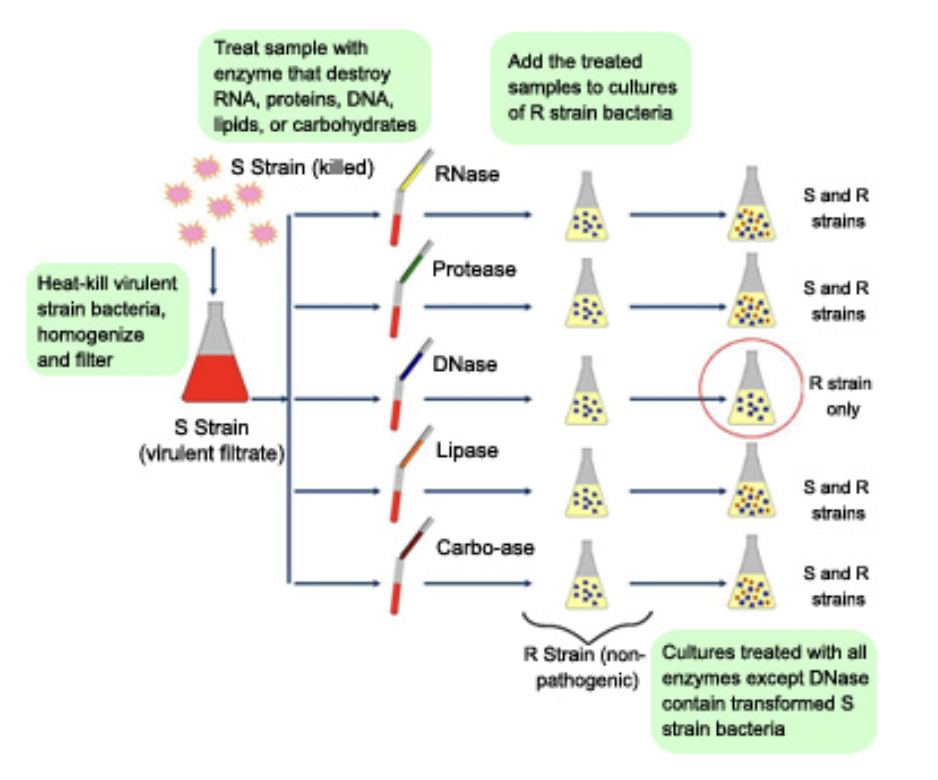
Avery, McCarty, & MacLeod
Purified both DNA and proteins from bacteria
Avery, McCarty, & MacLeod, what results did they get?
Injected protein into bacteria → no effect
Injected DNA into bacteria → transformed harmless bacteria into virulent bacteria
Hershey and Chase
Used bacteriophages (viruses that infect bacteria) with radioactive sulfur and phosphorous
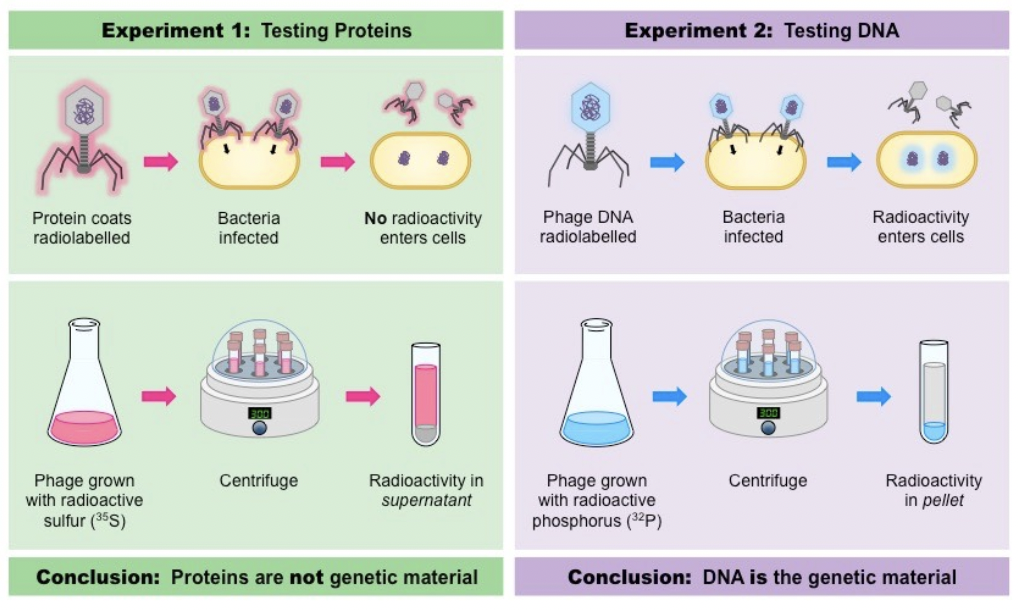
Hershey and Chase, results from sulfer and phosphorous.
Radioactive sulfur did not enter the bacteria
Radioactive phosphorus did enter the bacteria → DNA is “transforming factor”
Chargaff Discovery
DNA composition varies from species to species but the bases are present in a characteristic ratio
In humans, what are the DNA bases? What are their percentages?
A = 30.9%
T = 29.4%
G = 19.9%
C = 19.8%
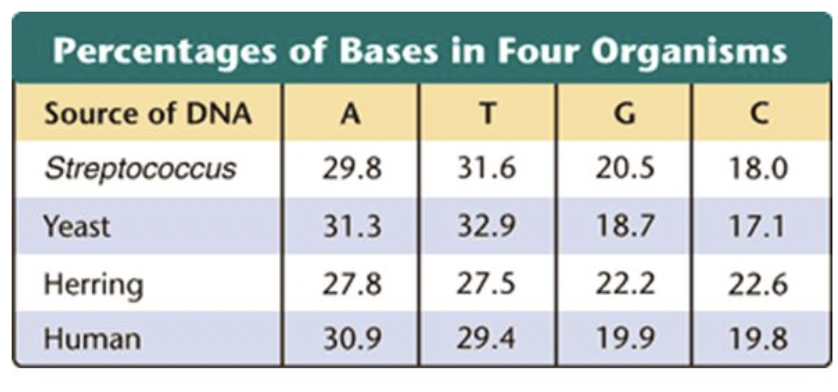
Watson and Crick
Developed the double helix model of DNA
Used a photograph taken by Rosalind Franklin
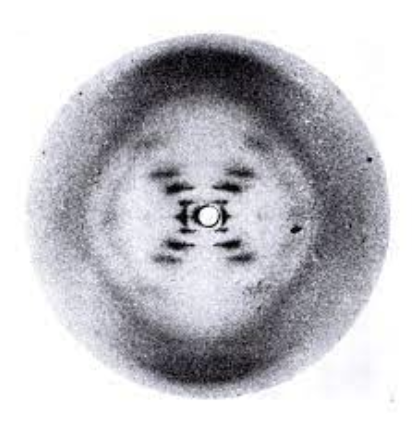
Pyramidines
Nitrogen bases with 1 ring (T & C)
Purines
Nitrogenous bases with 2 ring (A & G)
How do the DNA strands run?”
The strands are antiparallel
Which side on a strand has a phosphate and which doesn’t.
3’ = no phosphate on end
5’ = phosphate on end
What holds the strands together and how many of this thing? Which bases go together?
Hydrogen bonds hold the two strands together
2 between A & T
3 between G & C
What holds the phosphates and sugars together?
Phosphodiester bonds
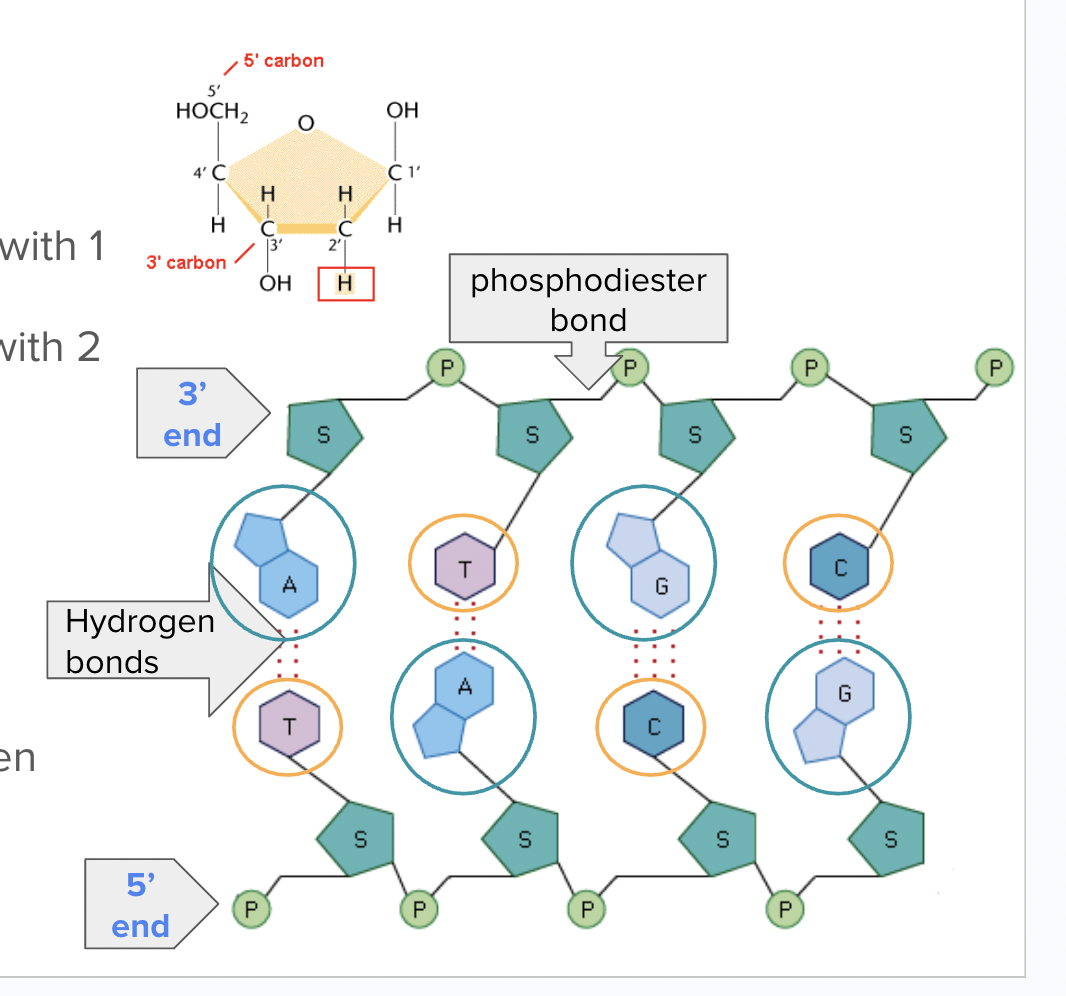
DNA in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
DNA Replication
Base pairing allows each strand to serve as a template for a new strand
How is DNA replication a semi-conservative process?
Each double helix consists of a parent/template strand and a new DNA strand
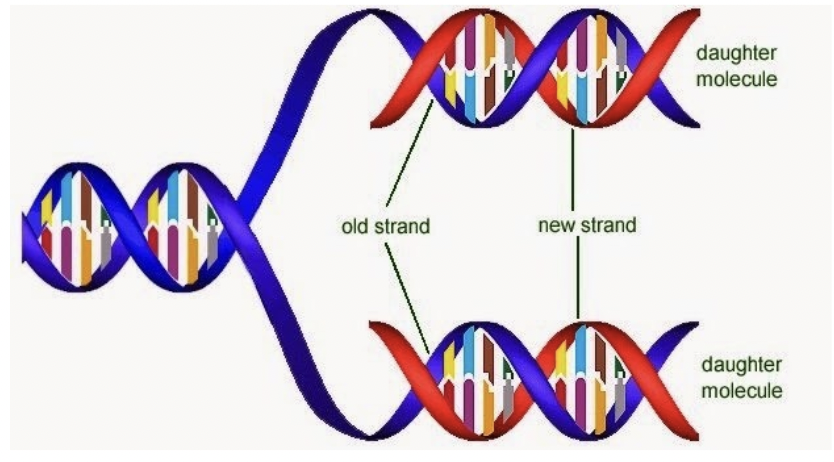
When does DNA replication occur?
S phase of the cell cycle
Enzymes involved in DNA Replication
Helicase, Topoisomerase, DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase (primase), Ligase
Helicase
unwinds part of the DNA double helix
Topoisomerase
helps relieve the strain of unwinding by breaking, swiveling, and rejoining DNA strands
DNA polymerase
Connects nucleotides together to make a strand; proofreads and edits as it builds the new strand.
There are multiple DNA polymerases;
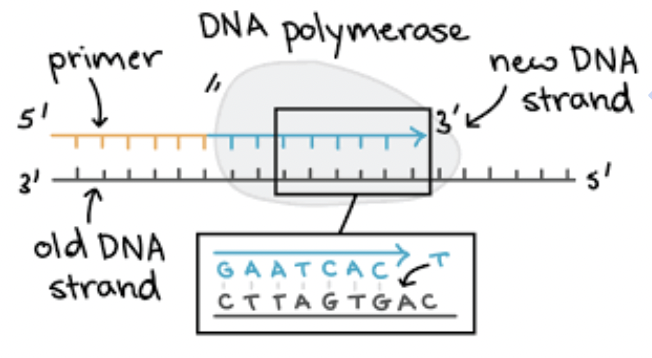
RNA polymerase (primase)
adds a few nucleotides of RNA to get the process started
Ligase
connects DNA fragments together
How does DNA replication start?
First DNA helicase unwinds the DNA strands.
Topoisomerase relaxes supercoiling in front of the replication fork.
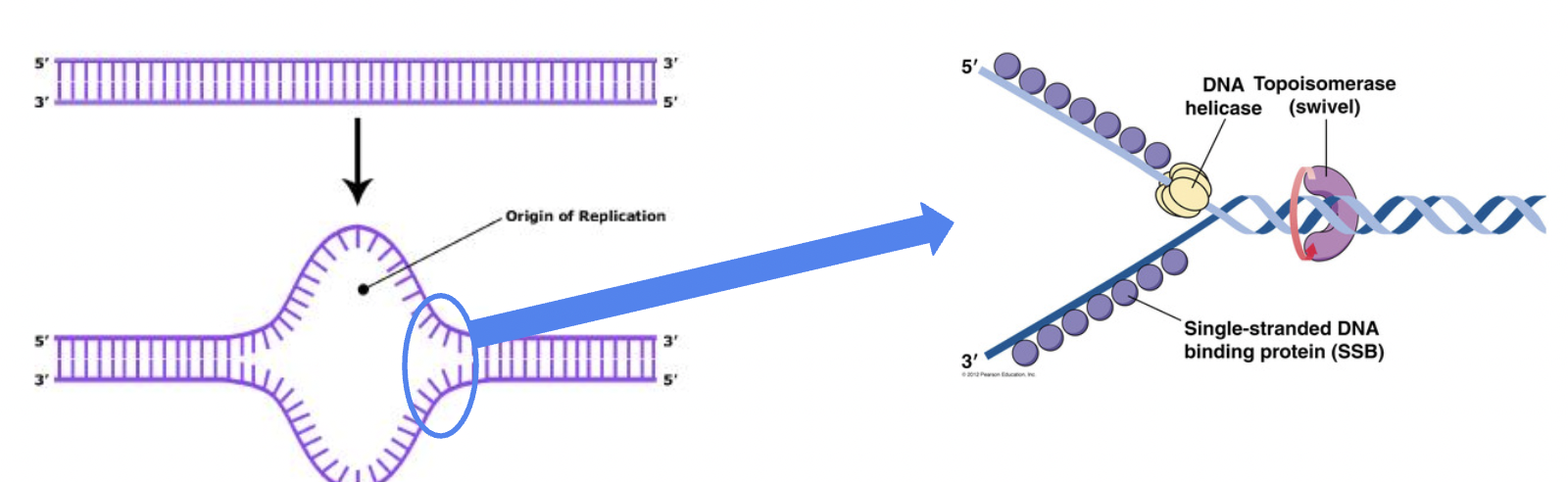
How does DNA replication continue?
Then complementary nucleotides match with the nucleotides on the original DNA molecule; the new nucleotides are connected together to make a strand
What is the difference between DNA and RNA polymerase?
DNA polymerase connects the nucleotides but can only add nucleotides to a 3’ end of a growing DNA strand
RNA polymerase (primase) adds a few nucleotides so DNA polymerase can get started; the RNA nucleotides are later replaced
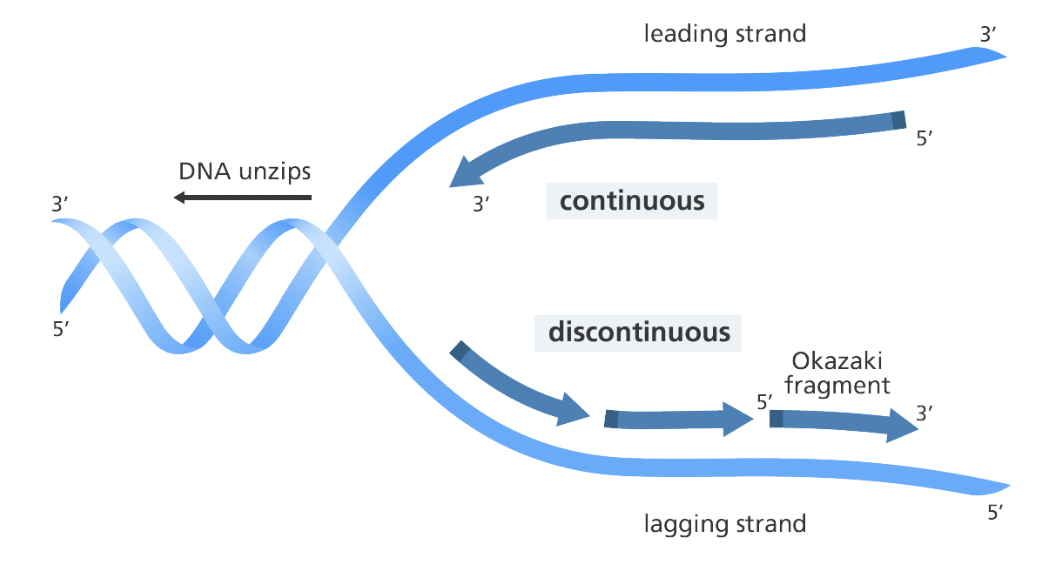
Leading strand
Made continuously in the 5’ to 3’ direction
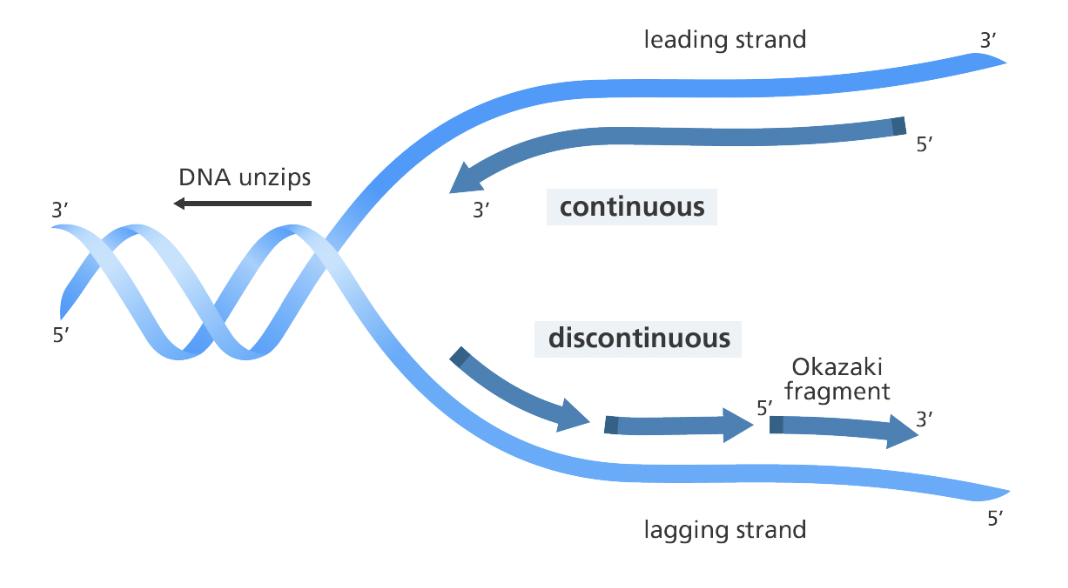
Lagging strand
Made in Okazaki fragments that are later joined together by ligase
Telomeres
The ends of chromosomes in eukaryotes that are repeating, non-coding sequences that serve as protective caps
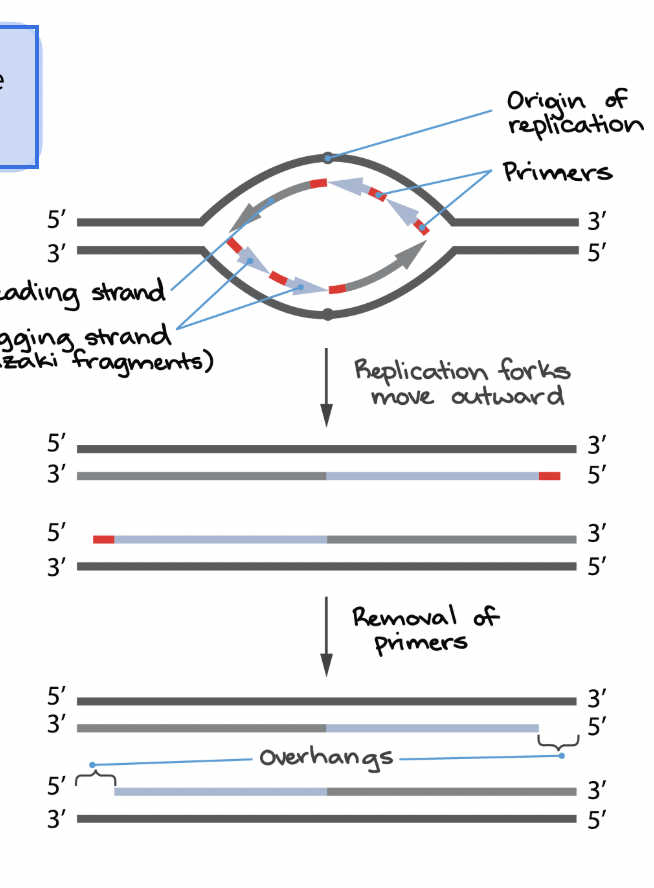
Why is there an aging process in eukaryotes?
Chromosomes get shorter with each replication (limits # of cell divisions)
Telomerase
Can add DNA bases at 5’ end; high activity in stem cells and cancers but not in most somatic cells
Do prokareyotes have telomeres?
No since their chromosomes are circular
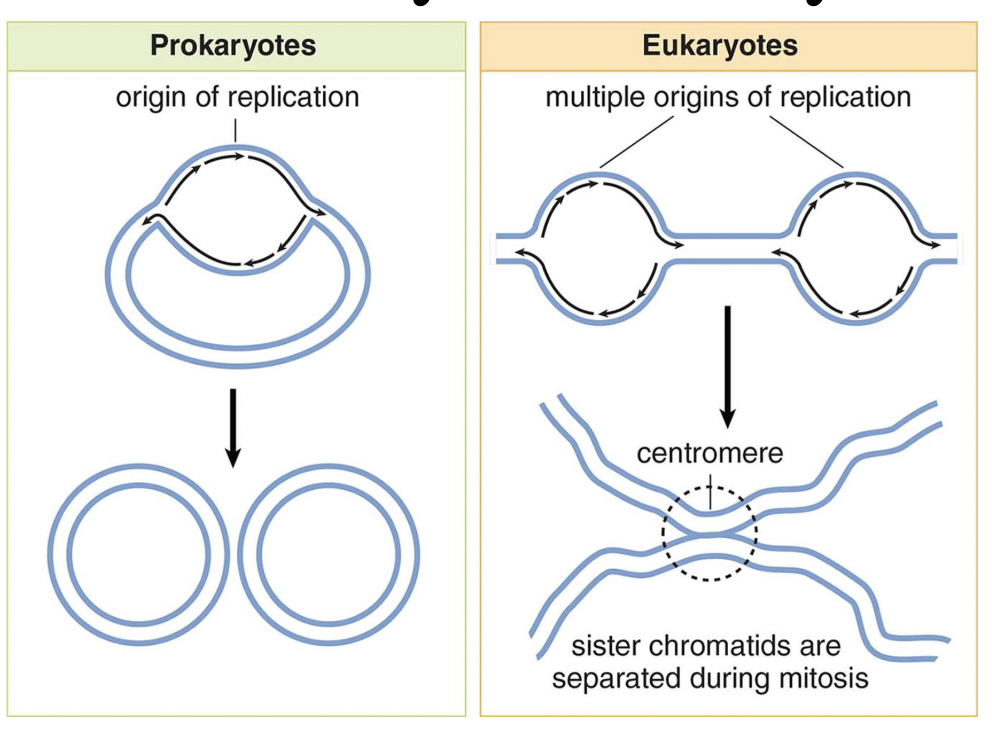
Dna Replication in Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
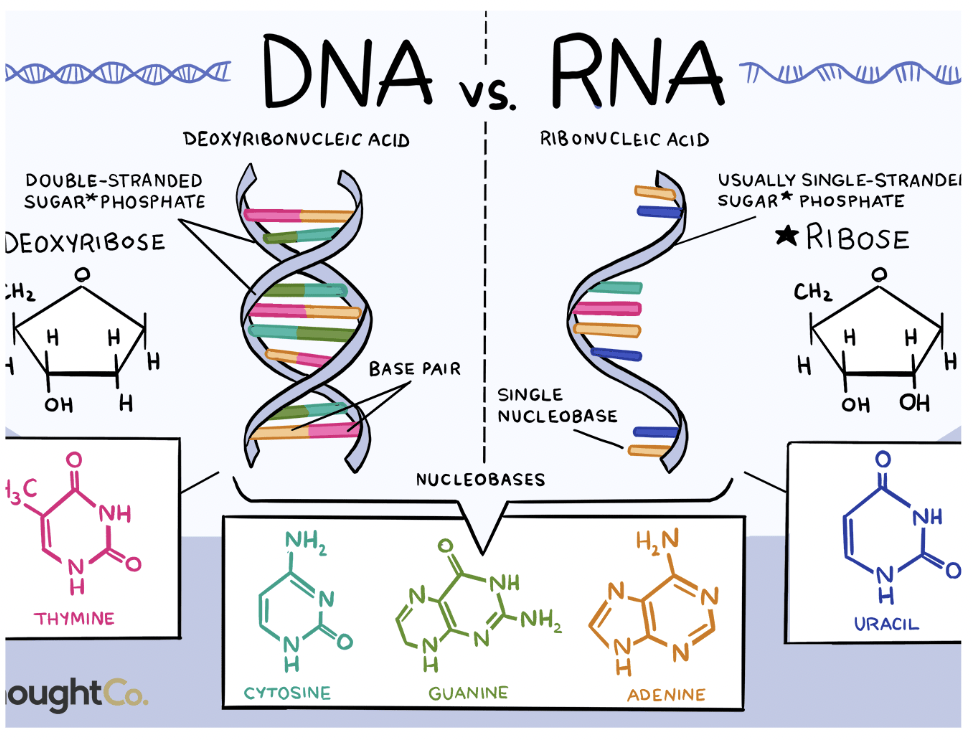
RNA
Ribose sugar
Uracil instead of thymine
Single stranded
Types of RNA
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, and microRNA
Difference in DNA and RNA
What determines RNA function?
The sequence of the RNA bases, together with the structure of the RNA molecule
mRNA
Carries information from DNA to the ribosome
tRNA
Carries amino acids to the ribosome

rRNA
Building blocks of ribosomes
microRNA
Small RNA molecules that bind to other RNA molecules to degrade them
Transcription
The nucleotide sequence in the DNA is used to make a complementary sequence in mRNA
What enzymes are used in transcription?
Uses many of the same enzymes from DNA replication - helicase, topoisomerase, RNA polymerase, etc.
How does transcription happen?
RNA polymerase uses a single strand of DNA to make mRNA; works in the 5’ to 3’ direction
It makes a mRNA strand identical to the coding DNA strand (but swap U for T).
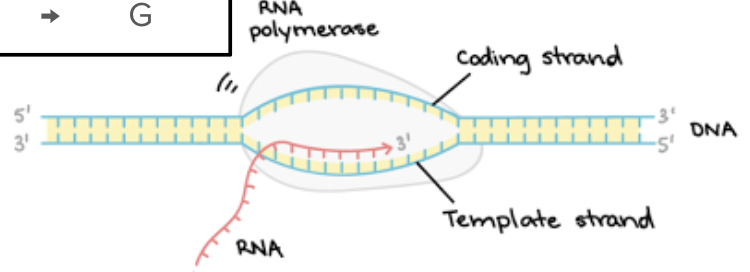
Which DNA strand is used in transcription?
The DNA strand that is used is called the template strand, noncoding strand, minus strand, or antisense strand.
Are DNA and mRNA strands different?
Yes because the strands of DNA are complementary and antiparallel, the mRNA made from the strands are not the same → code for different proteins
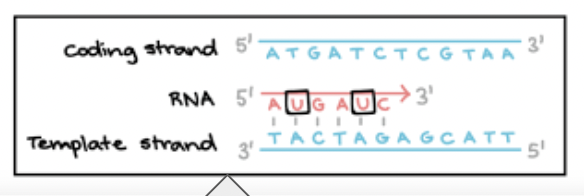
How do the bases change in DNA and RNA?
DNA RNA
A → U
T → A
G → C
C → G
Post-Transcriptional Modification
Before the mRNA leaves the nucleus -
A poly-A tail is added
A GTP cap is added
Splicing by spliceosomes

Introns
Stay in the nucleus; do not code for proteins
Exons
Exit the nucleus to go to the ribosome; do code for proteins
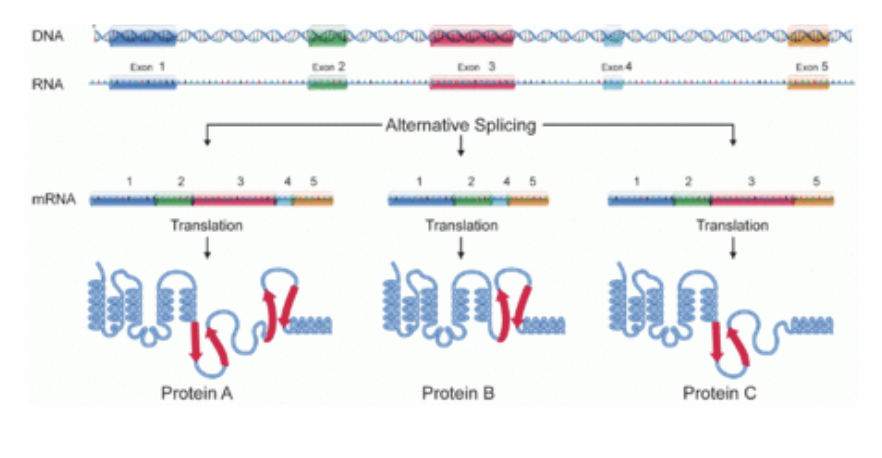
Alternative splicing
Different versions of the mRNA result from combining different exons
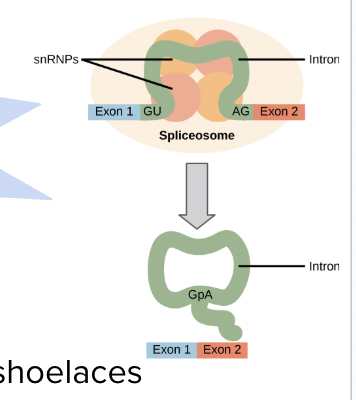
Where does post-transcirptional modification occur?
In eukaryotes only
Translation
Three steps - initiation, elongation, and termination
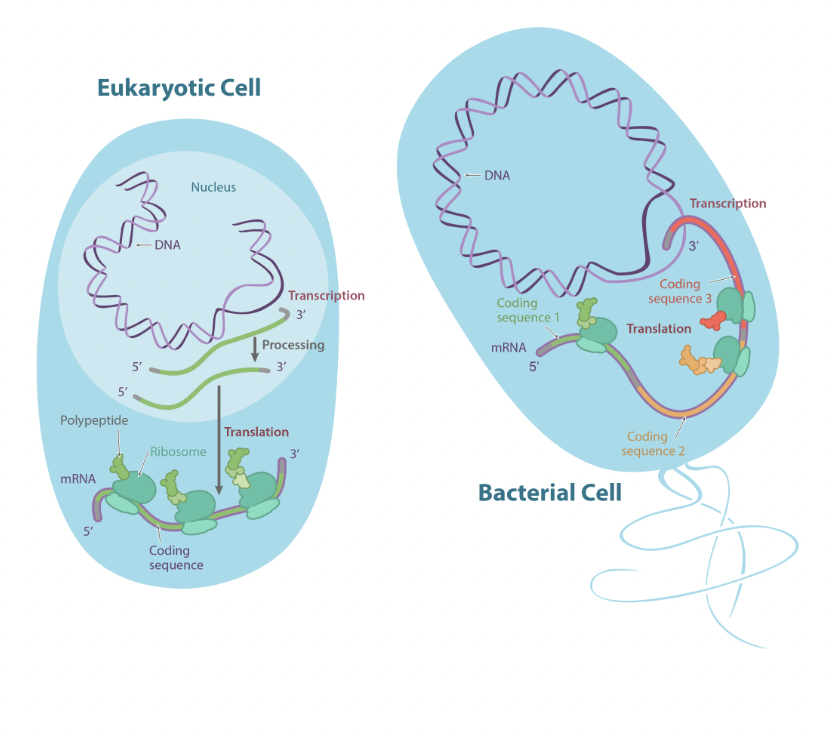
Where does translation occur?
Occurs at ribosomes
Free ribosomes in prokaryotes
Free ribosomes or bound ribosomes (to rough ER) in eukaryotes
What is the difference between when transcription occurs in prokaryotes vs eukaryotes
In prokaryotes, translation occurs as the mRNA is being transcribed
In eukaryotes it occurs after transcription
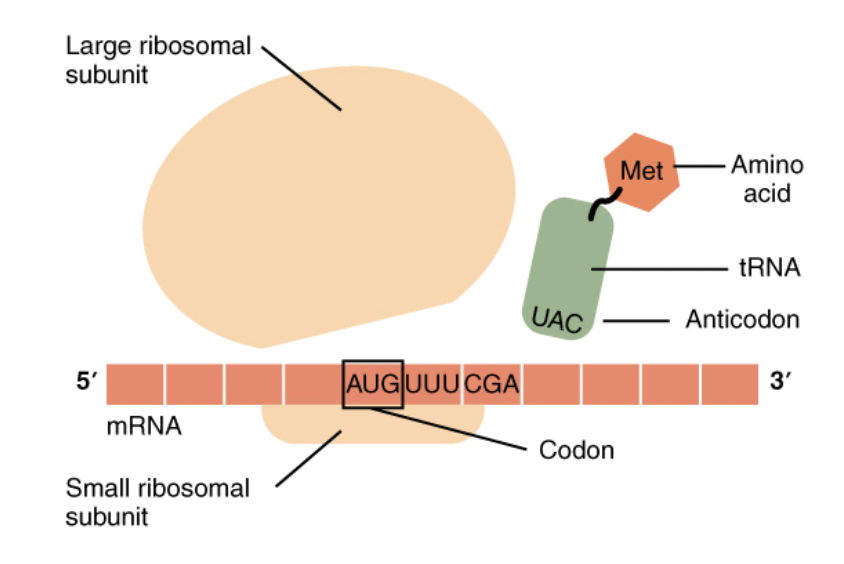
Initiation
Small ribosomal subunit binds to mRNA and an initiator tRNA
Then the large ribosomal subunit attaches
Elongation
For each codon, a tRNA with a corresponding anticodon brings an amino acid to the ribosome
The amino acid is added to the preceding one by a peptide bond
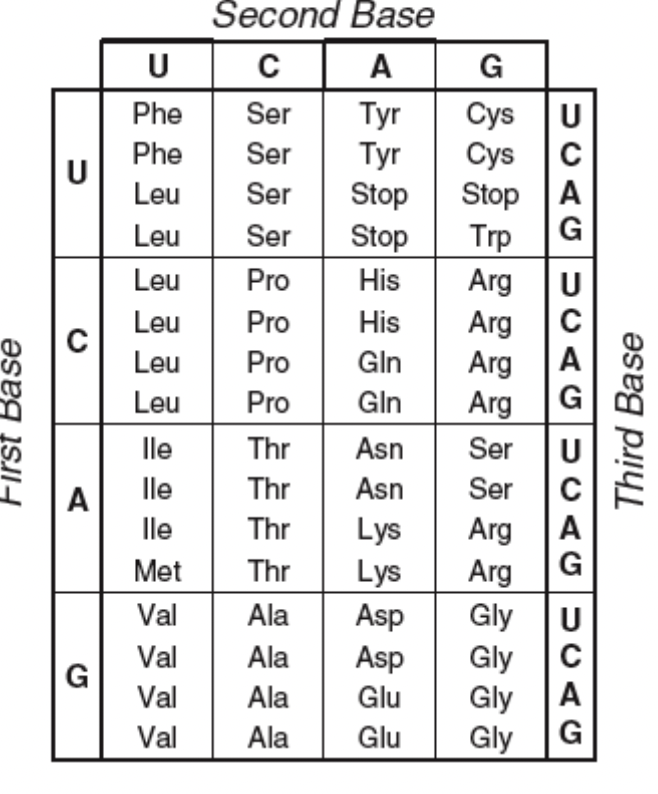
Codon
3 bases on the mRNA
In what direction does the RNA movie in translation?
The ribosome moves down the mRNA in the 5’ to 3’ direction
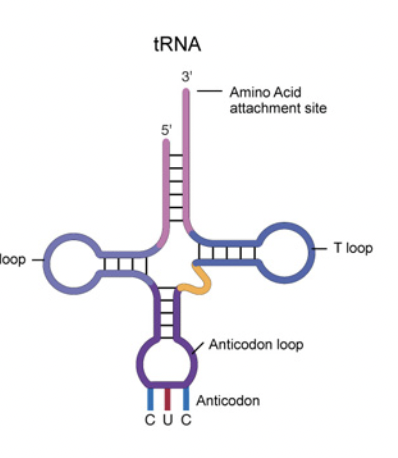
Ribosomes have three different sites for the binding of tRNA:
Think ‘Arrive, Processing and Exit’ or A,P,E.
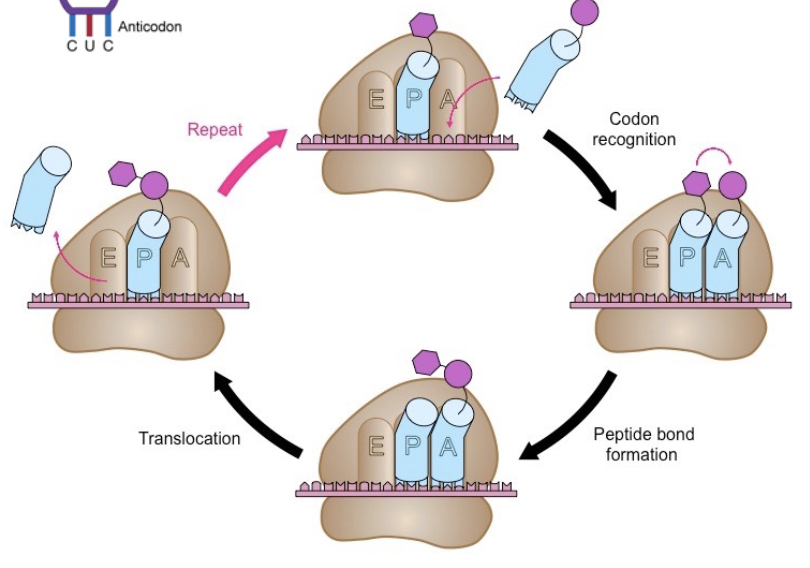
Which amino acid gets added to the polypeptide?
Each codon in the mRNA corresponds to one amino acid
If the anticodon on the tRNA is complementary to the codon on the mRNA:
The correct amino acid is at the ribosome and gets added
If the anticodon on the tRNA is not complementary to the codon on the mRNA
The correct amino acid is not at the ribosome; must wait for another tRNA with a complementary anticodon to arrive
Termination
Elongation continues until the ribosome reaches a stop codon in the mRNA
A protein called a release factor that causes the polypeptide chain to separate from the ribosome
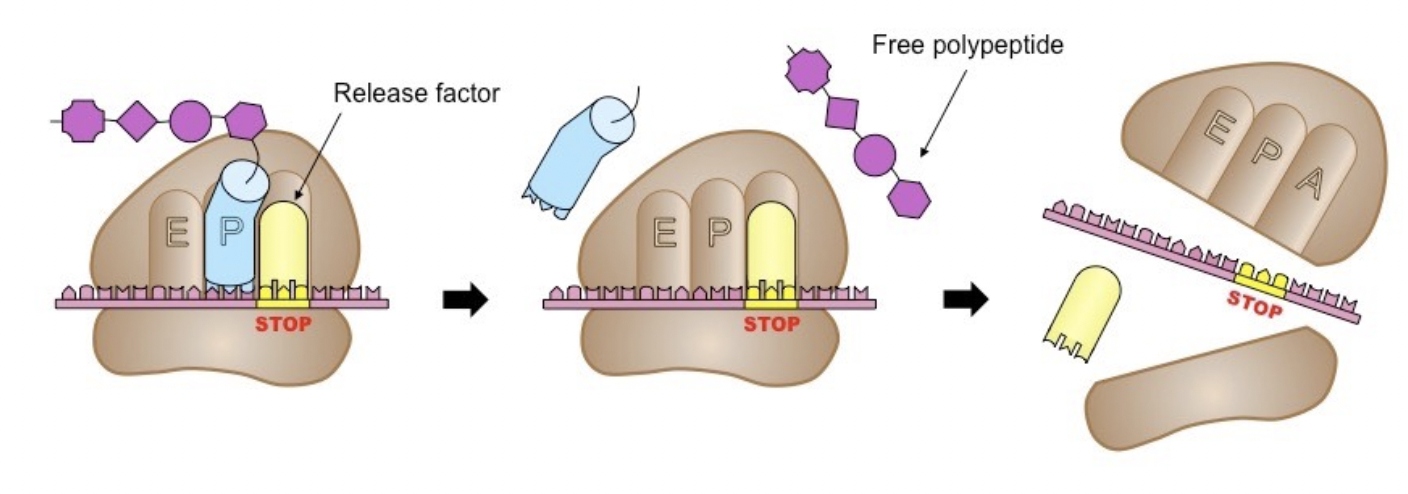
Examples of stop codons
UAG, UAA, or UGA
What happens after translation?
The polypeptide folds up based on the arrangement of its amino acids (secondary and tertiary protein structure)
Some polypeptides combine with others to make larger proteins (quaternary structure)
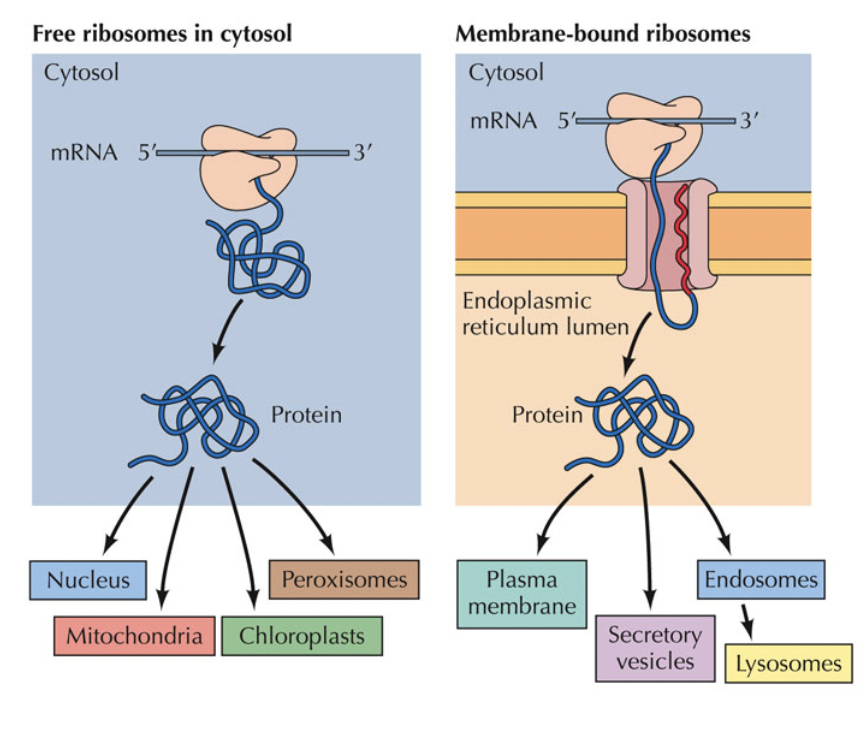
Where do the proteins go?
May be packaged at ER or modified and packaged at the Golgi
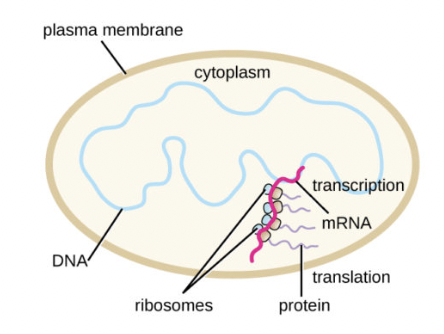
Protein Synthesis in Prokaryotes
Transcription occurs in the cytoplasm
No mRNA editing
Transcription and translation occur simultaneously
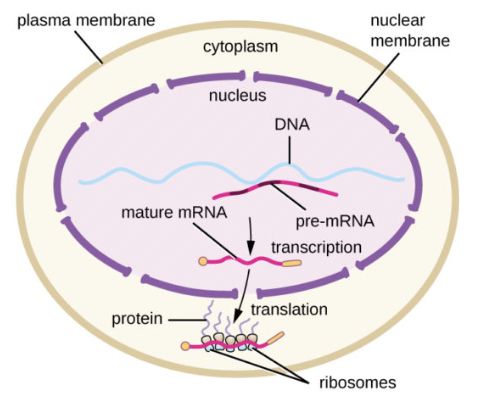
Protein Synthesis in Eukaryotes
Transcription occurs in the nucleus
mRNA is edited prior translation
Translation occurs after transcription is completed
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence
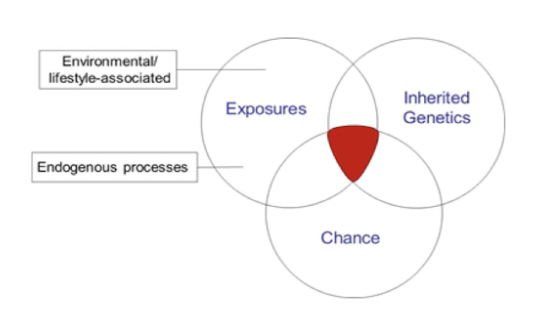
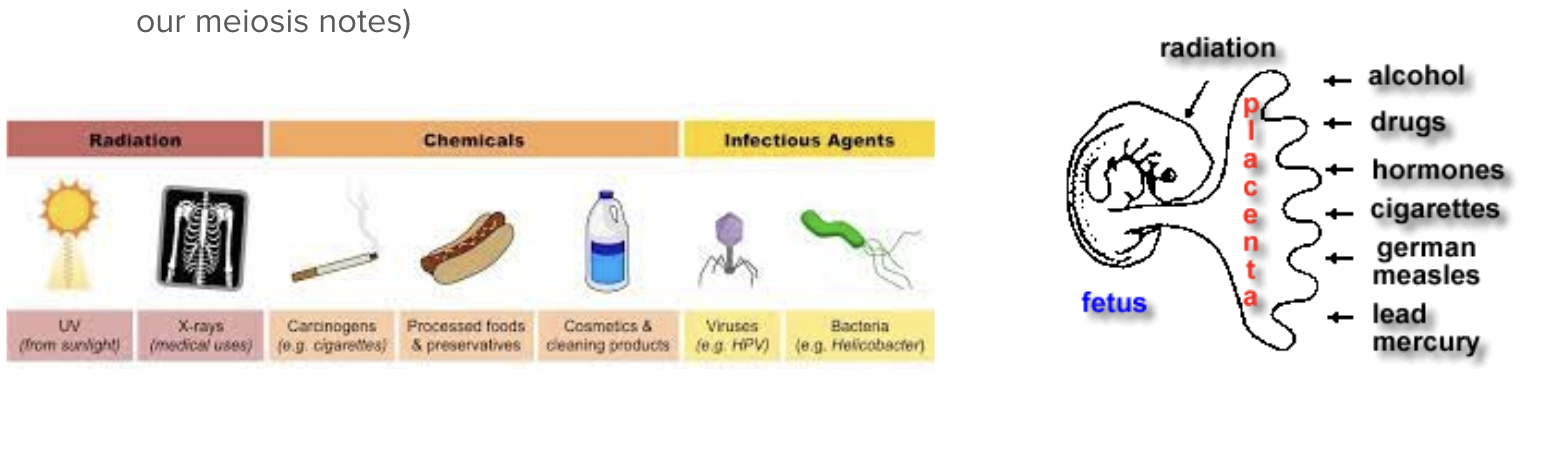
Mutations can be caused by:
Mutagens - external factors such as radiation and reactive chemicals (teratogens in a fetus)
Errors in DNA replication (random)
Errors in mitosis or meiosis (we talked about changes in chromosome number and structure in our meiosis notes)
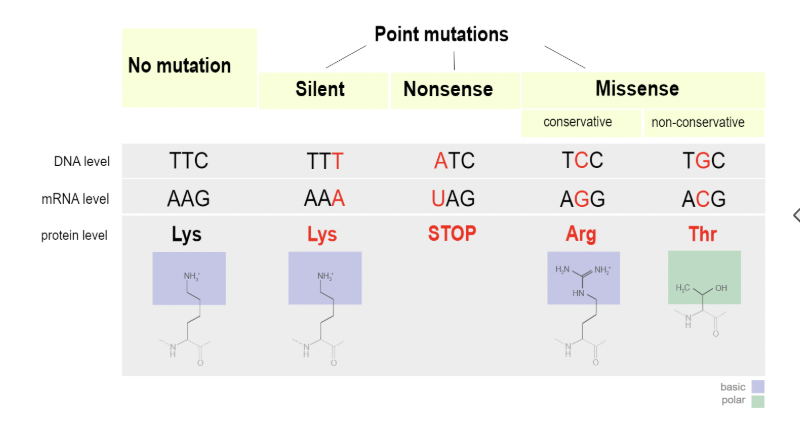
Point mutations
Also called a substitution
A base is changed but the number of bases stays the same
Types of point mutations
Nonsense - now code for a stop codon
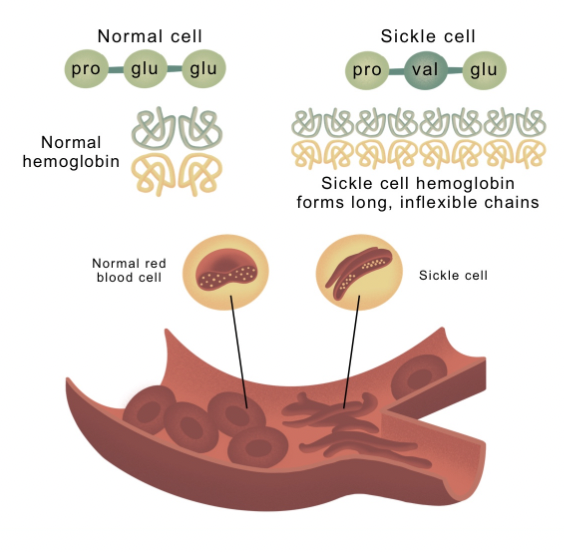
Missense - now codes for a different amino acid
Silent - still codes for the same amino acid
How do mutations affect proteins?
Proteins fold up based on the properties of their amino acids; if a mutation results in an amino acid with a different property, the protein will have a different shape & function
Frameshift Mutations
The insertion or deletion of a base shifts the reading frame, changing all the codons after mutations
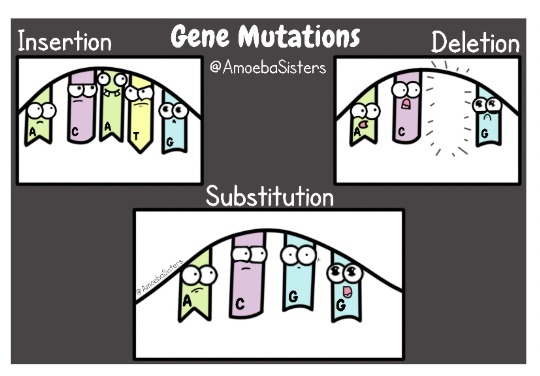
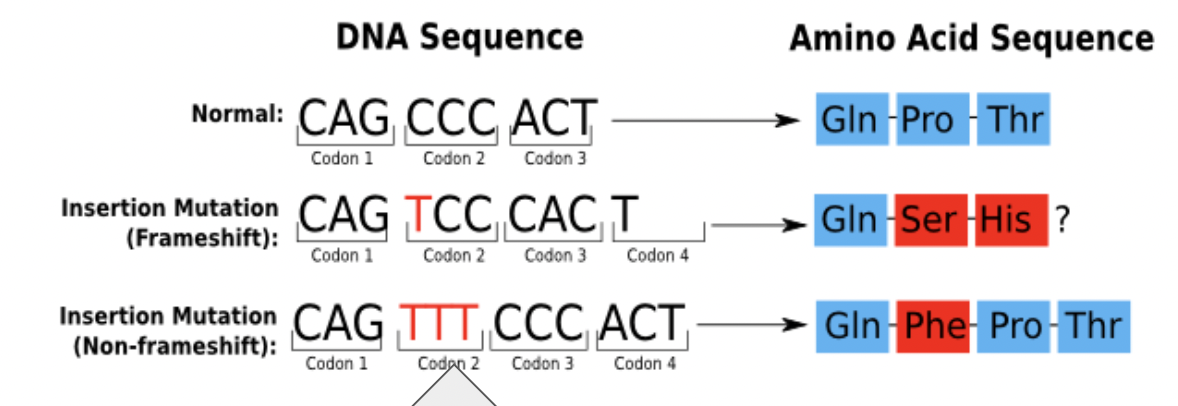
What type of mutation is this?
This is an insertion but not a frameshift because the codons were not regrouped as a result.
Are all mutations bad?
No, mutations are random and can be positive, negative, or neutral
Examples of positive, negative, and neutral mutations
Positive - lactose tolerance in humans; antibiotic resistance in bacteria
Negative - cystic fibrosis
Neutral - eye color
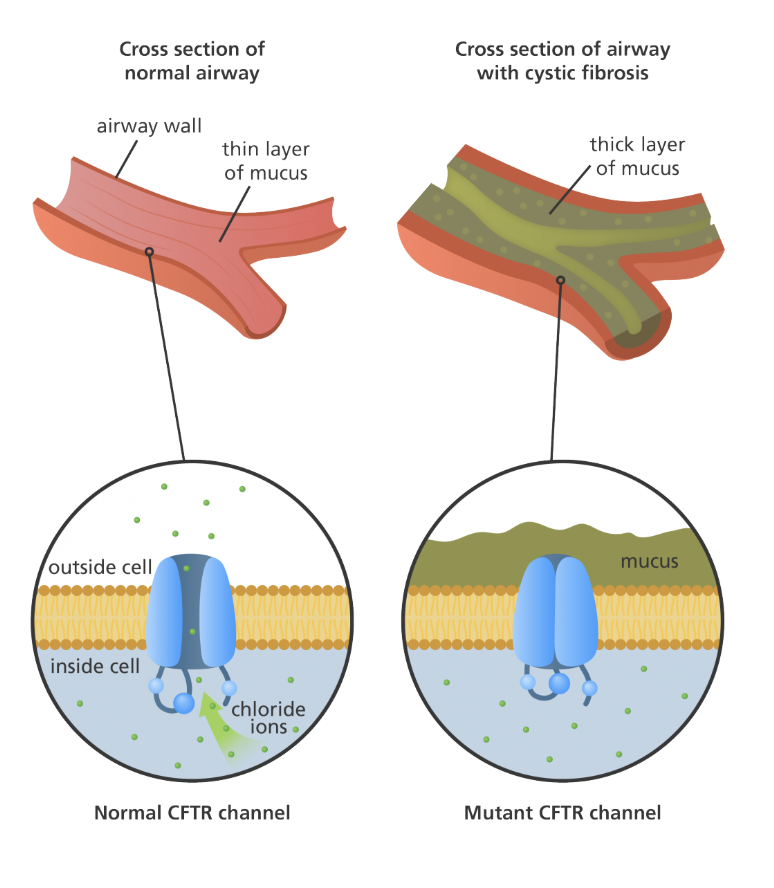
How can some mutations be neutral?
Could be silent
Could be in an intron → not used to make proteins
Regulation of Gene Expression - Eukaryotes
Even with the same DNA, not all cells in a multicellular organism look the same or do the same things (ex. Skin cells vs. stomach cells)
Cells turn on the parts of DNA they need and off those they don’t → cell differentiation
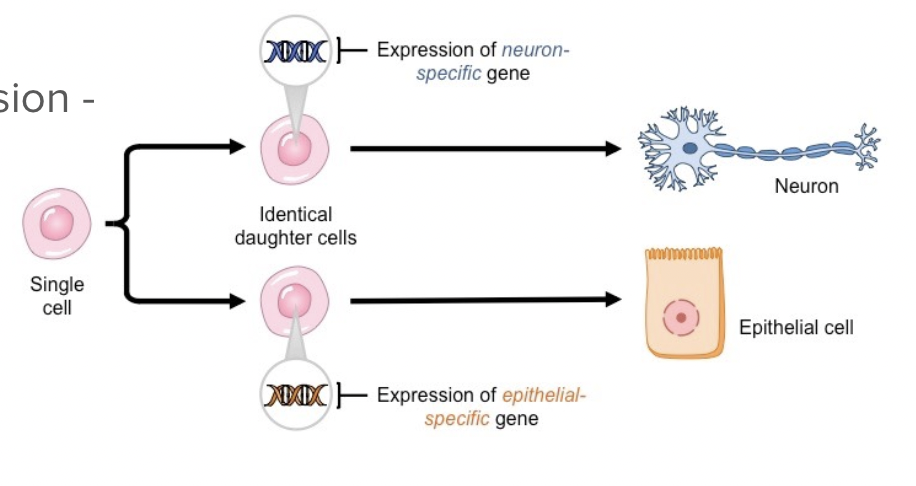
Methods to regulate gene expression
Regulate chromatin structure
Regulate transcription initiation
Post-transcriptional regulation
Regulating Chromatin Structure
DNA is wrapped around proteins called histones
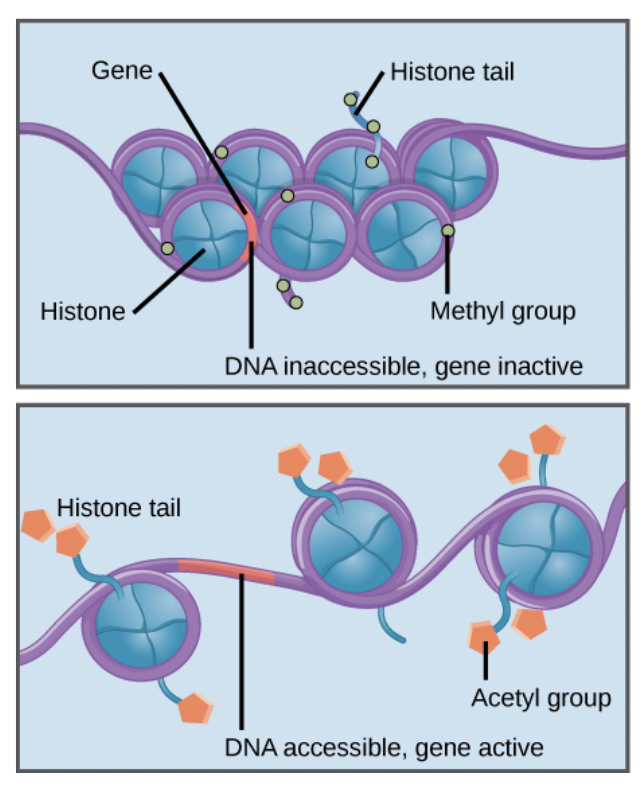
Histone acetylation
Acetyl groups are added to histones, which prevents them from binding the DNA as tightly, making room for proteins to bind for transcription
DNA methylation
Methyl groups can attach to DNA bases, preventing transcription
Exons and Introns
Introns can be considered as intervening sequences, and exons as expressed sequences. There are an average of 8.8 exons and 7.8 introns per human gene.
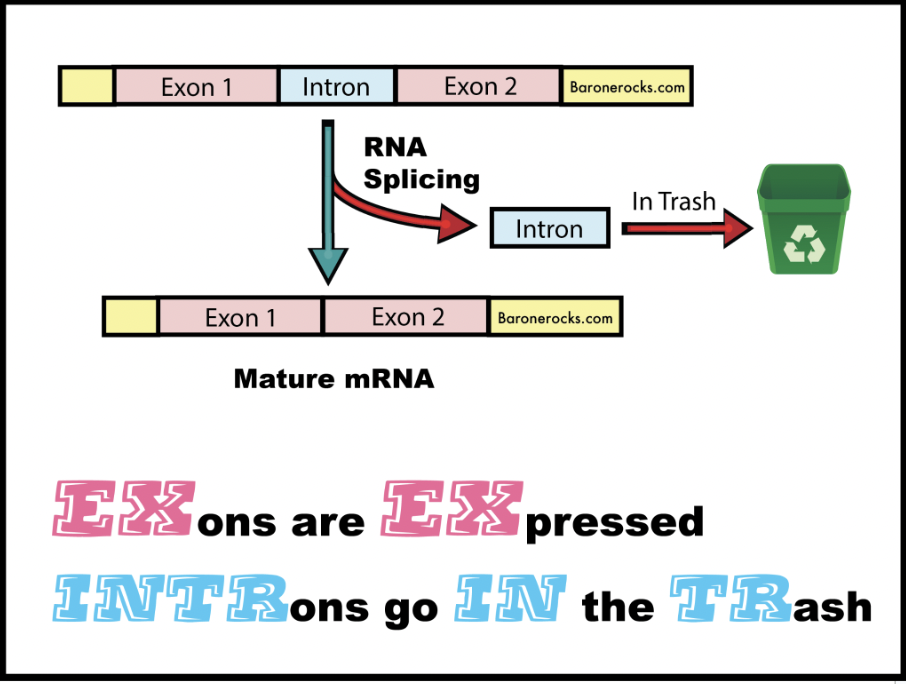
Why are introns important?
They allow for alternative splicing, which in turn allows one gene to code for multiple transcripts and therefore serve multiple complex cellular functions.
What can introns affect?
Gene expression, the rate at which genes get turned on to make proteins and other non-coding RNA
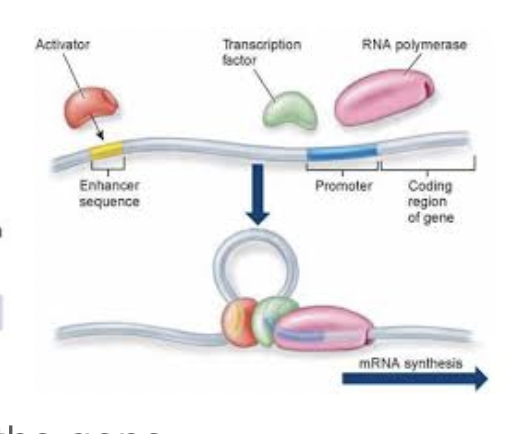
Regulating Transcription Initiation
Activators help RNA polymerase bind to the DNA, increasing transcription
Repressors prevent RNA polymerase from binding to the DNA, preventing transcription
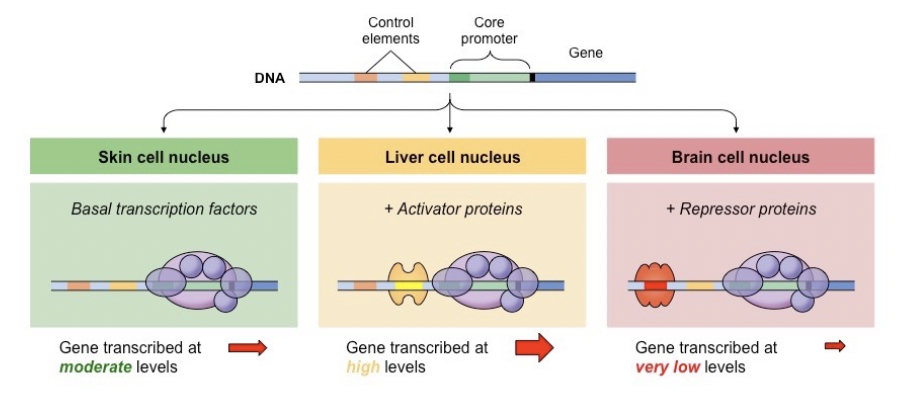
Transcription factors
Proteins that bind upstream of the gene
Post-transcriptional Regulation
RNA splicing
mRNA degradation
Initiation of translation
Protein processing and degradation
MicroRNAs
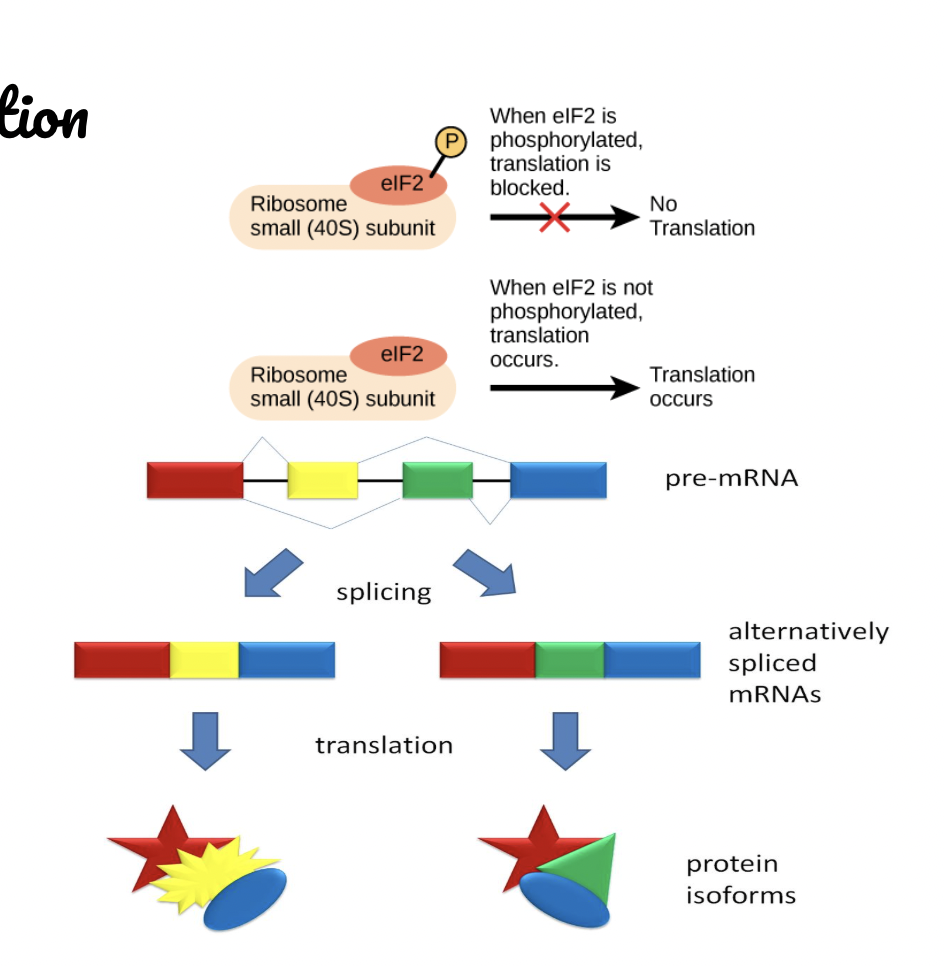
RNA Splicing
Different mRNA molecules are produced from the same primary transcript depending on which exons are used - one gene can code for more than one protein
mRNA degradation
Nuclease enzymes break down mRNA; lifespan of mRNA varies
Initiation of translation
If the ribosome does not form or mRNA cannot attach, translation does not occur
Protein processing and degradation
Many proteins need to be modified to become active usually via phosphorylation. They may be also be modified by the addition of ubiquitin, which triggers proteasomes to break down the protein
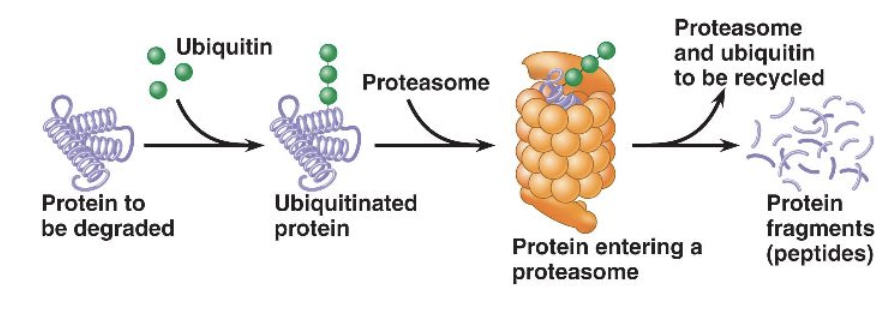
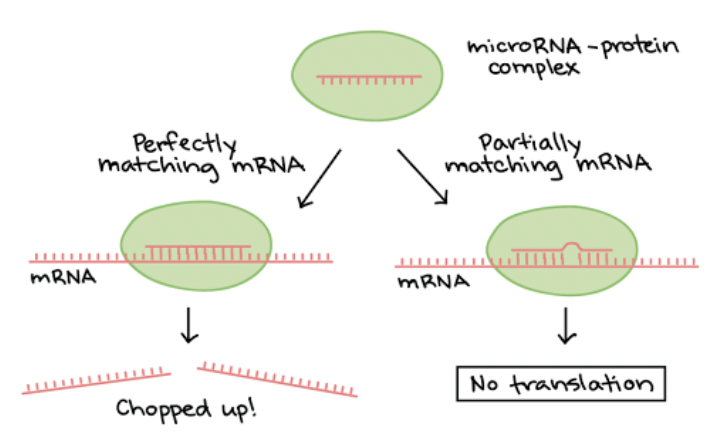
MicroRNAs
Can bind to mRNA, causing it to degrade or blocking it from being translated
Operon
A group of genes of related function