Pitt AOC exam 1
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms

Blue marble
Fully Illuminated Earth
Able to see Antarctica, Madagascar, Coast of Africa, Arabian Peninsula
Highly produced
No other image like this has been taken by humans
Overview effect
Reported by almost all astronauts while Earth gazing
Reported a feeling of profound (spiritual) change
Saw the earth as an organism
Weather Vs. Climate
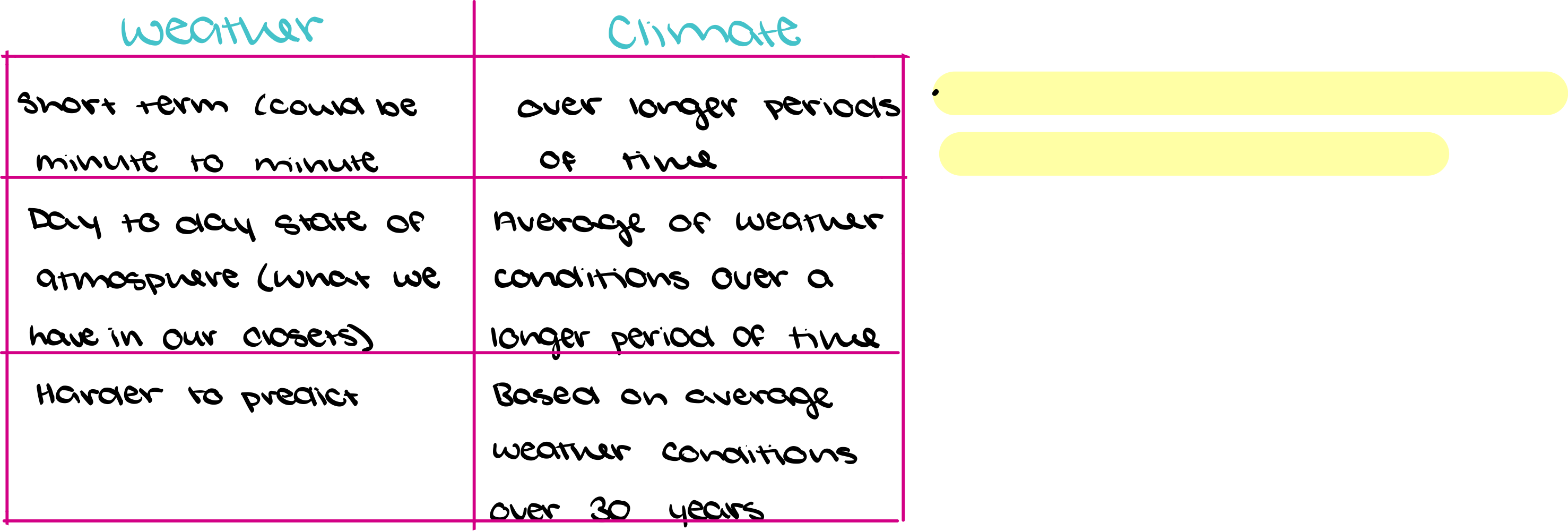
Climate is what you expect
Earth system Web diagram
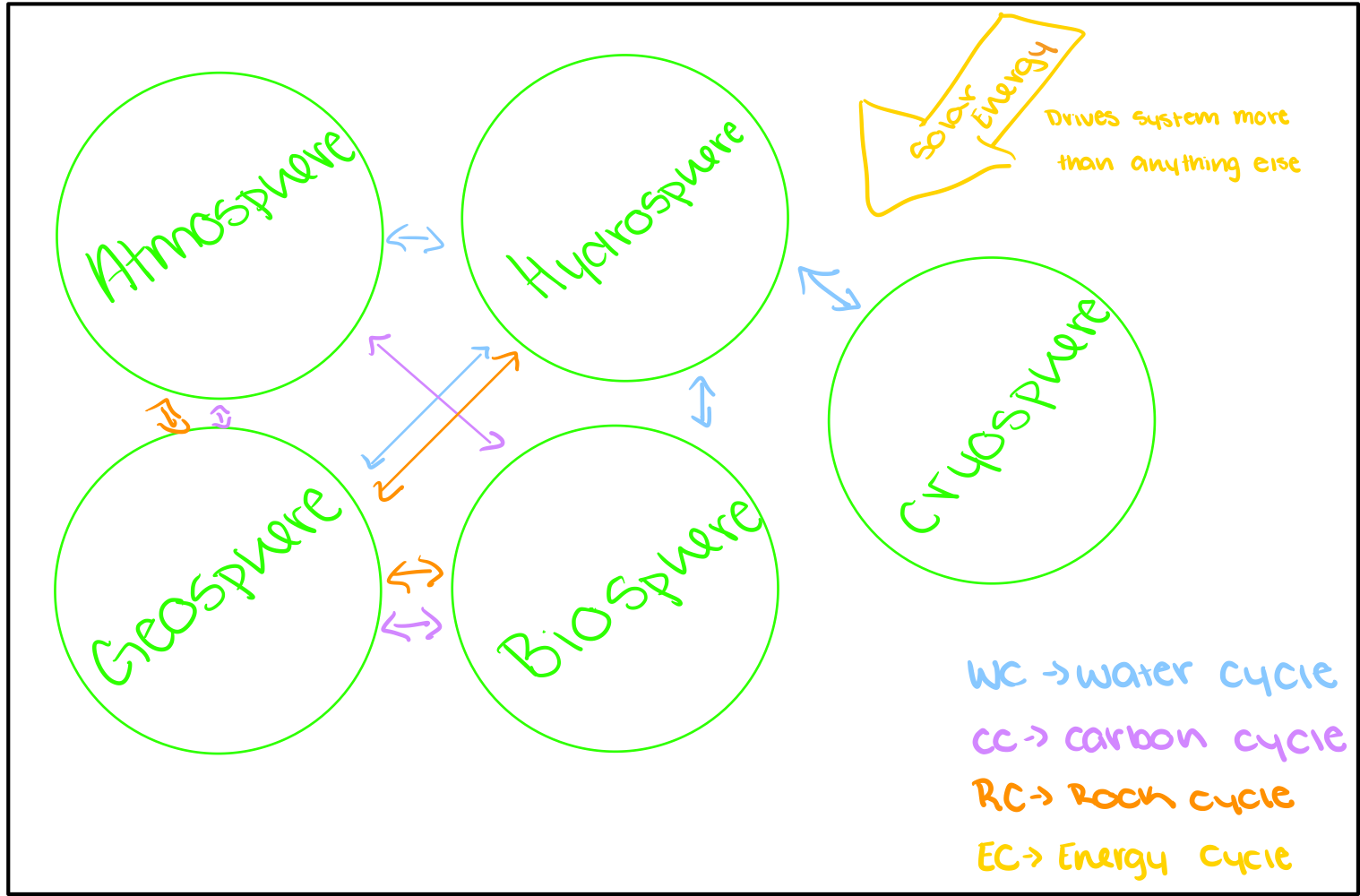
Not consistent
Not predictable
Not 1:1
System
A set of connected things or parts forming a complex whole in particular.
Set of things working together as parts of a mechanism, or an interconnecting network.
University
Government
Human body
Definition of Earth system
The unified set of chemical, physical, biological, and social components, processes, and interactions that determine the state and dynamics of Earth. Including her biota and human components
Stock
The amount of the item in interest (volume of glacier studied)
Reservoir
Where the stock sits (glacier in the side of a mountain)
Flux
Movement of flow of a quantity (water melting off of glacier)
Equilibrium
Flux in = Flux out
Residence time
Stock / flow
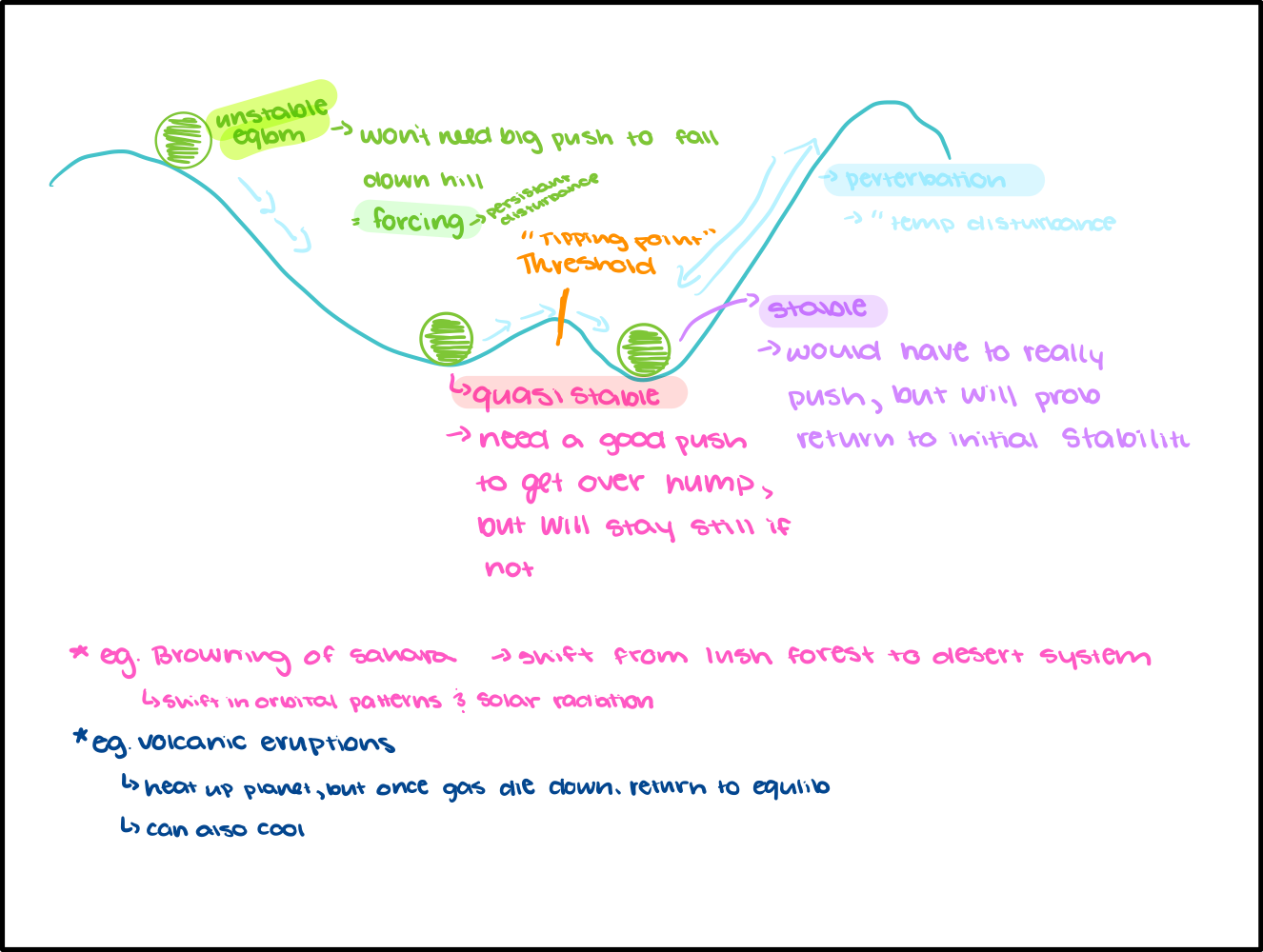
Stability
Tendency to return to equilibrium
Equilibrium Diagram
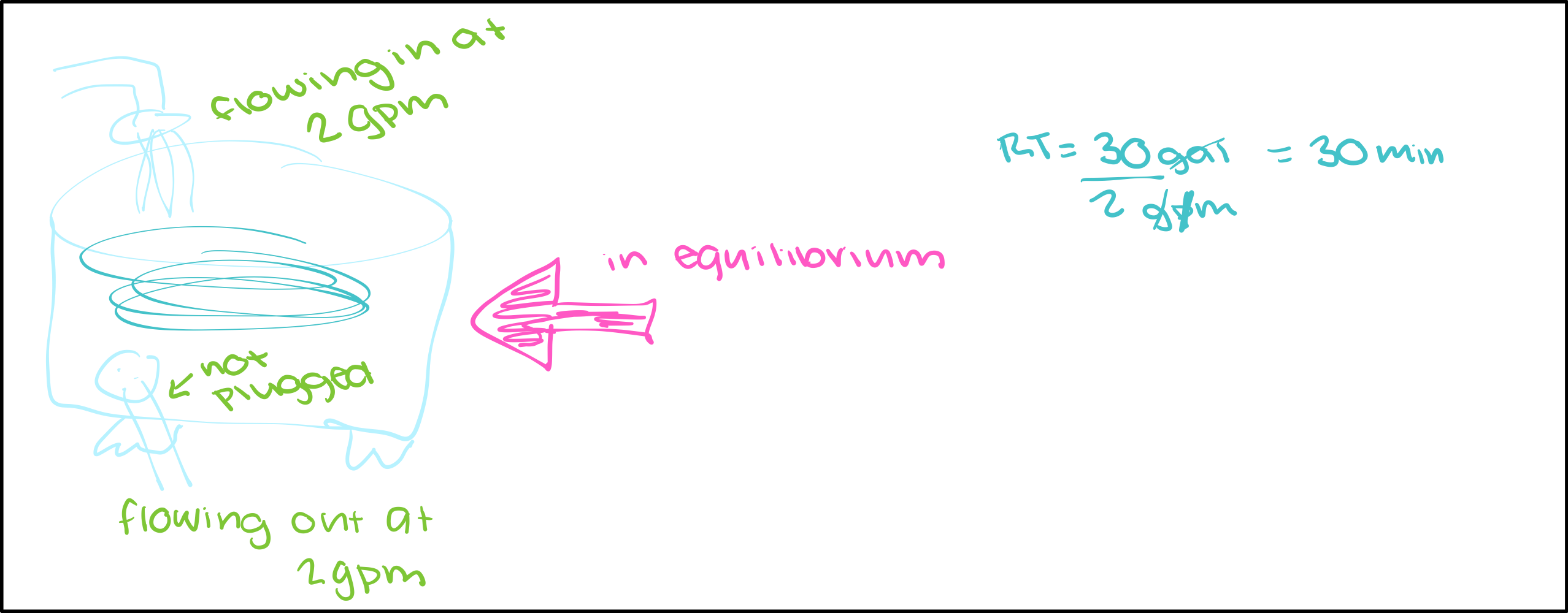
When a system is in equilibrium, only have to pick one flux to find residence time
Stability (ball) diagram
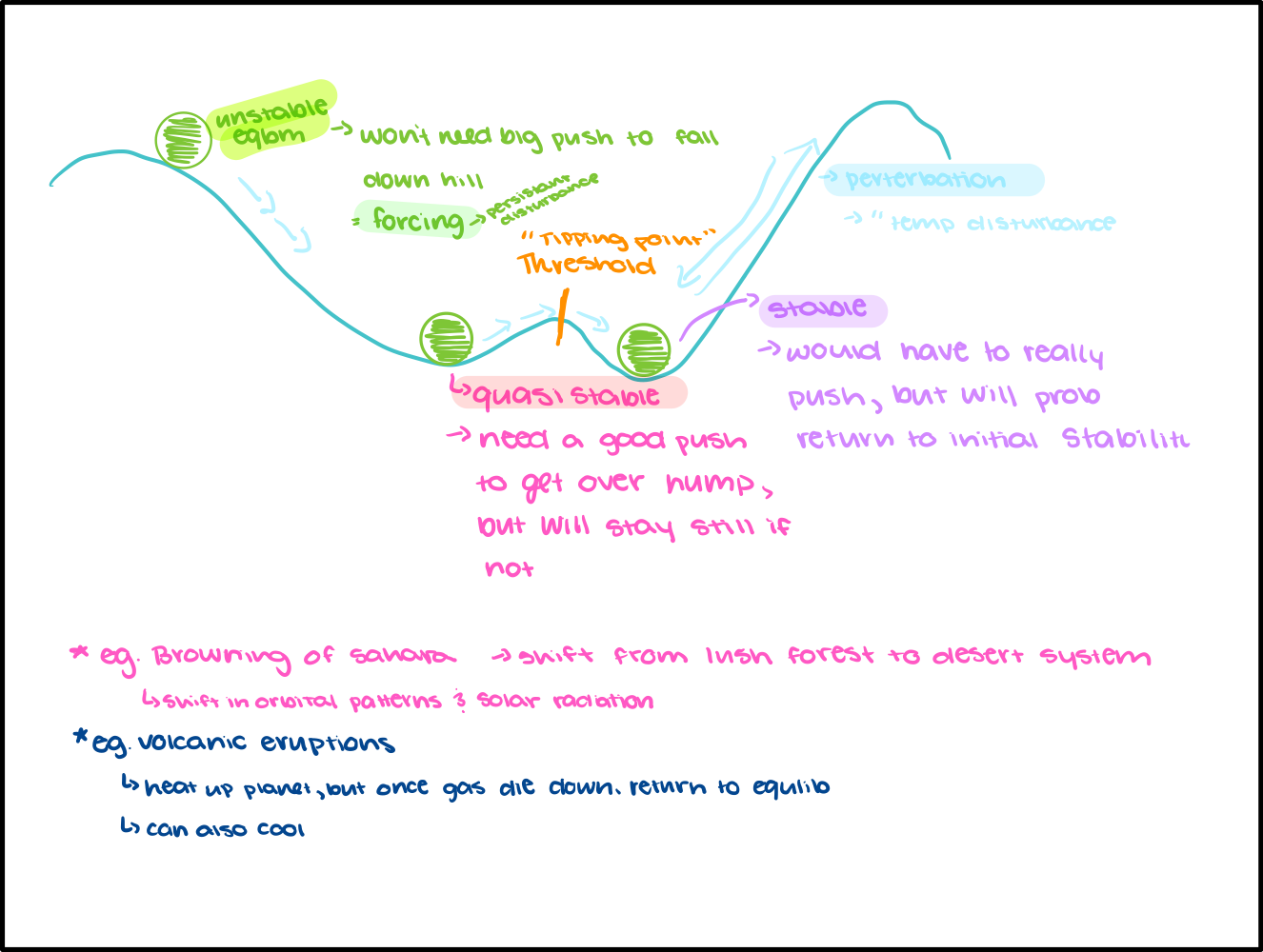

Feedback Loops
Self perpetuating mechanisms of change and response to that change
Positive Feedback
Causes system to change (and amplifies those changes)
Doesn’t mean good
Negative
Keeps system from changing (eg. diminishes the effects of a disturbance)
Doesn’t mean bad
Feedback loop diagram
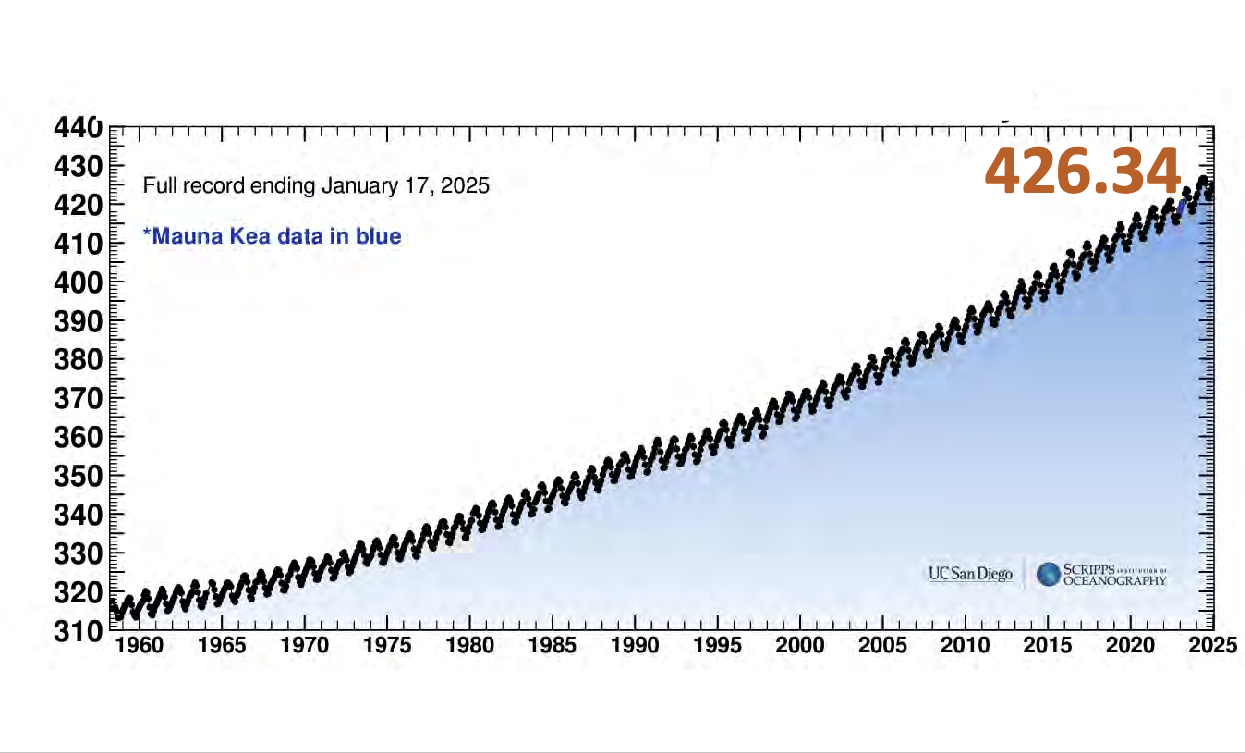
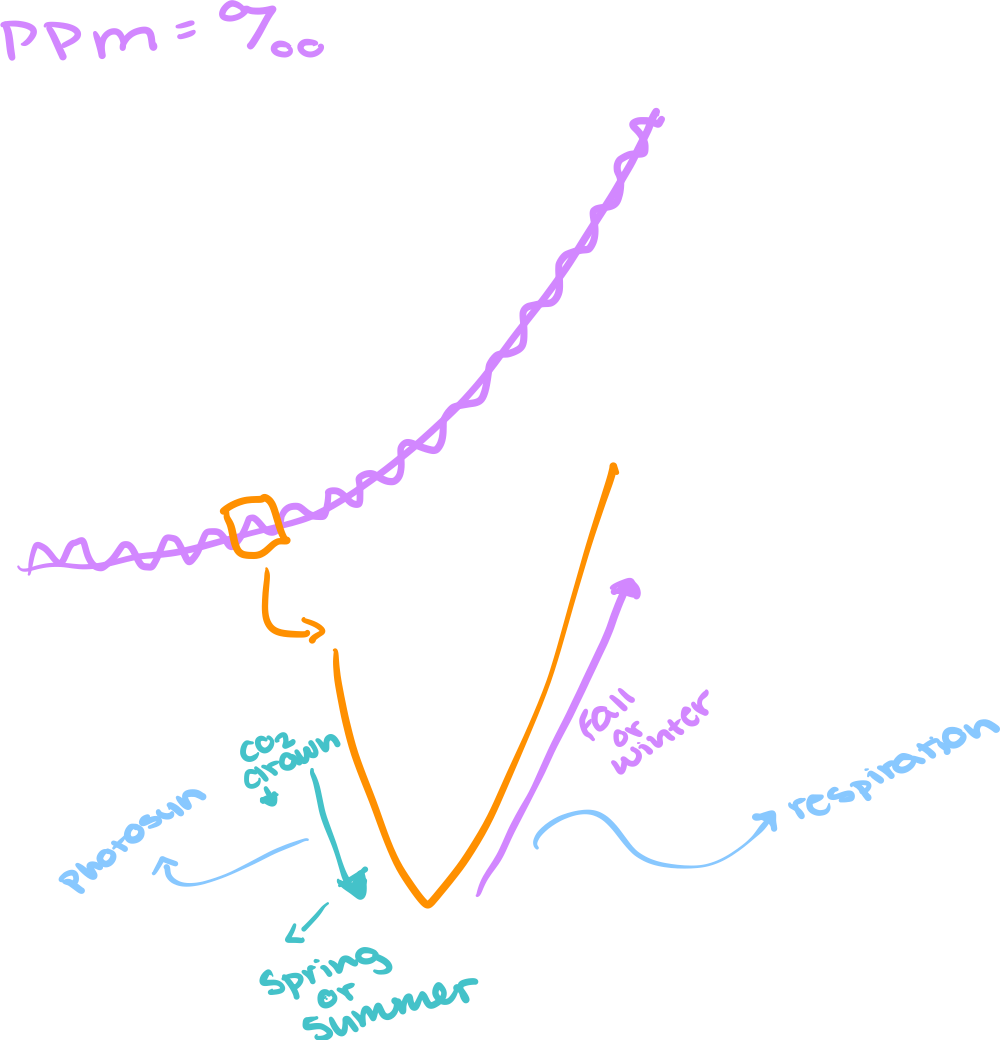
Changes in seasons change the CO2 level
As of jan 17 we are at 426.34ppm
There is typically a certain range that these fluctuations stay within (even during ice ages), but we are way above the highest level now
Fluctuation diagram
Why is the pliocene relevant in this situation
Earth’s CO2 has not been this high since that period
Global and land temps were 5-7 degrees cooler
sea levels were 100 ft higher (all the ice melted)
We know it was hot, but we don’t know why. We can assume that it was because of the higher CO2 levels, but we don’t know why they were higher
What is the atmosphere thinner than
The skin of an apple
What is so important about water vapor?
It is an important greenhouse gas
It is concentrated differently in different areas
It is very powerful
It has a short residence time in the atmosphere
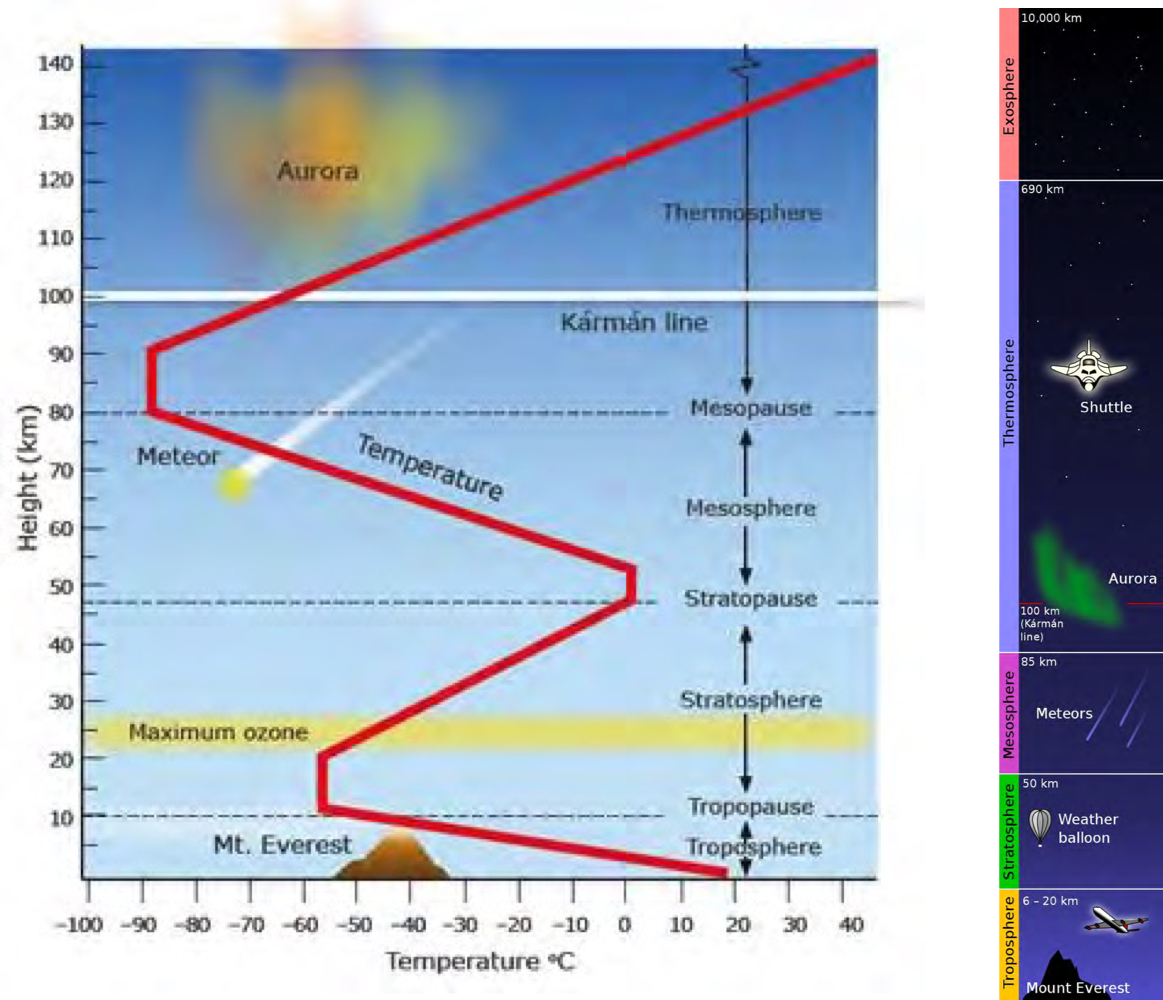
Atmospheric thermal structure
Troposphere: there is a drop in temp as there is an increase in elevation
Instability and that is why we have weather (heating and cooling of air)
Ozone in the stratosphere
How does atmospheric pressure changer with altitude
susceptible to gravity
Everything settles near Earths surface, so there is more pressure
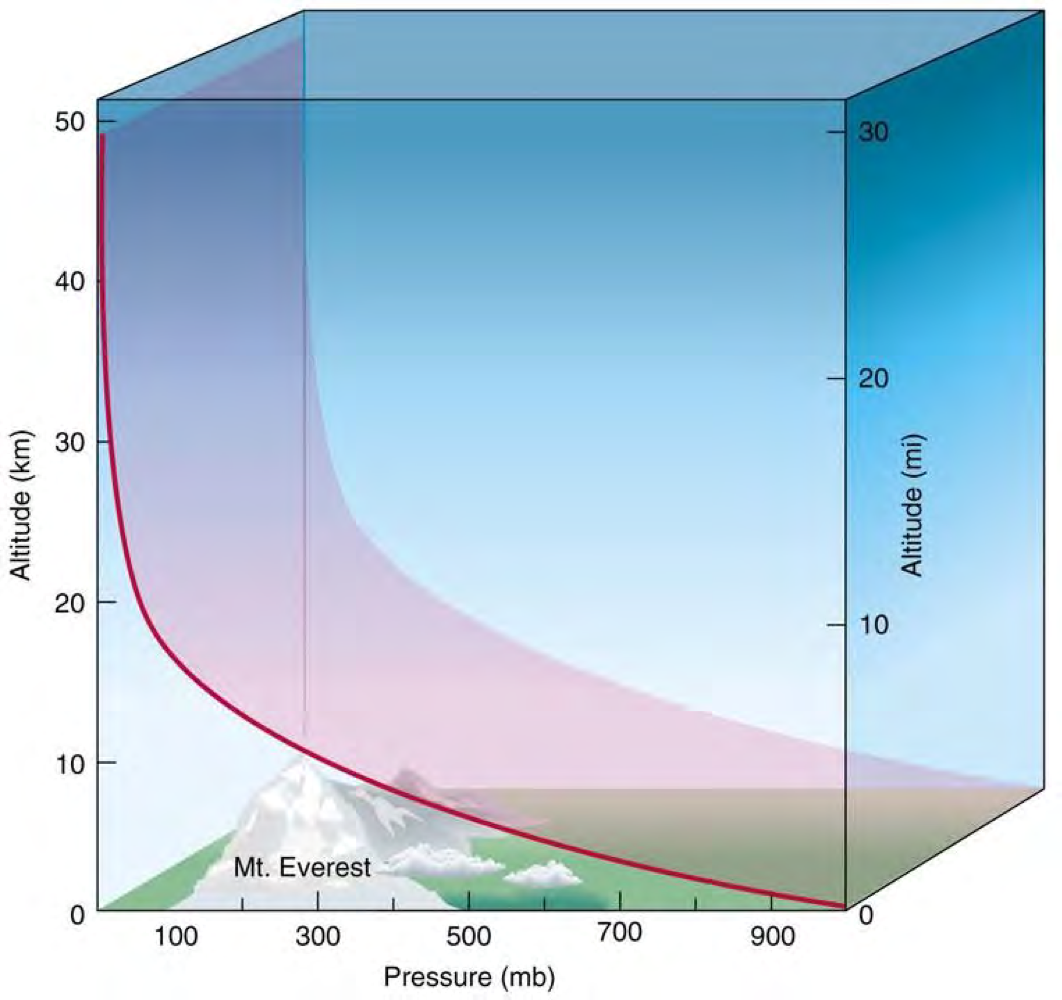
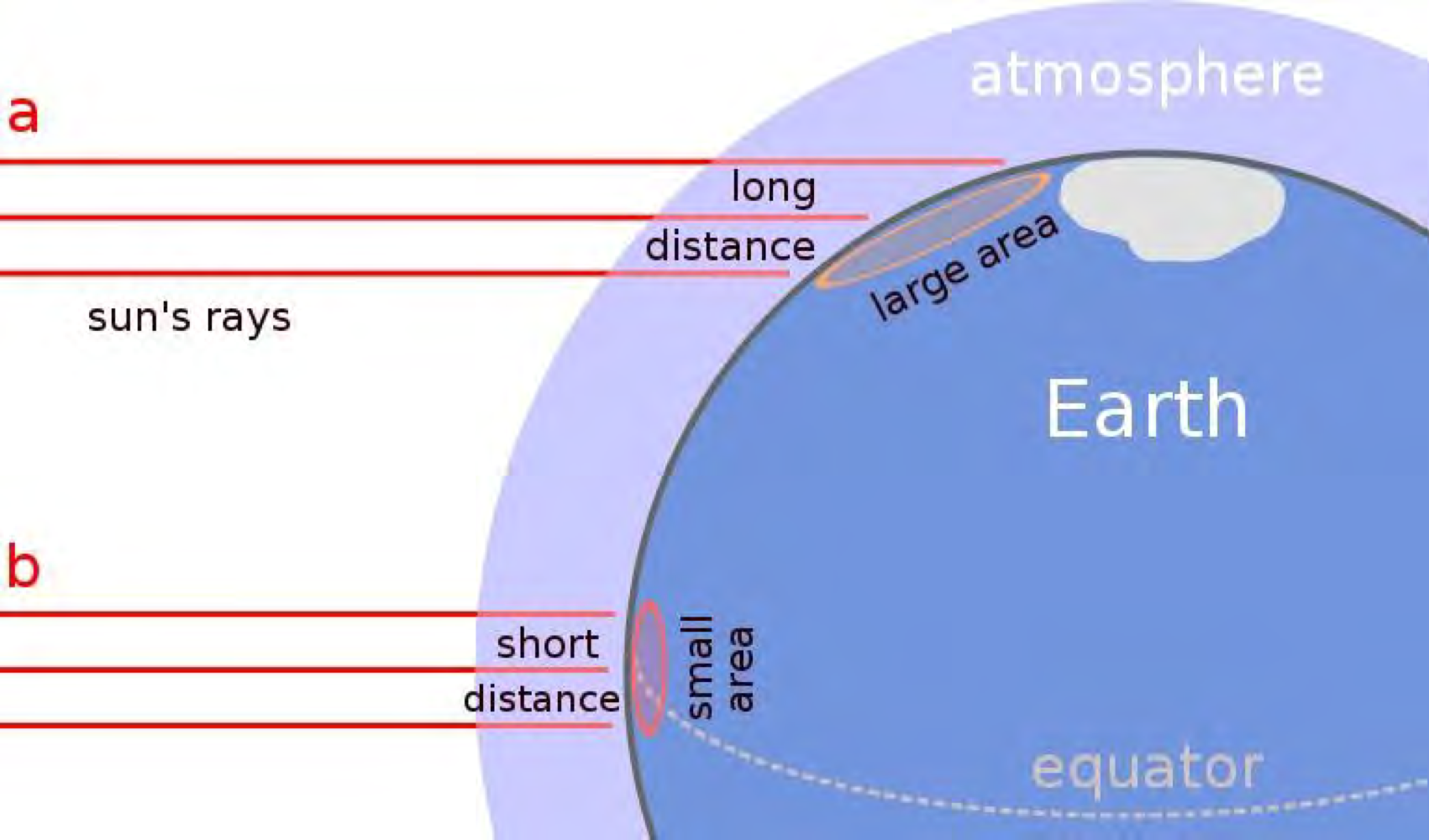
How does energy, from the sun, change at different altitudes?
Higher concentration of solar rays at the equator than at the poles
Same amount of rays at equator as at the poles, but the concentration differs due to Earth’s curvature
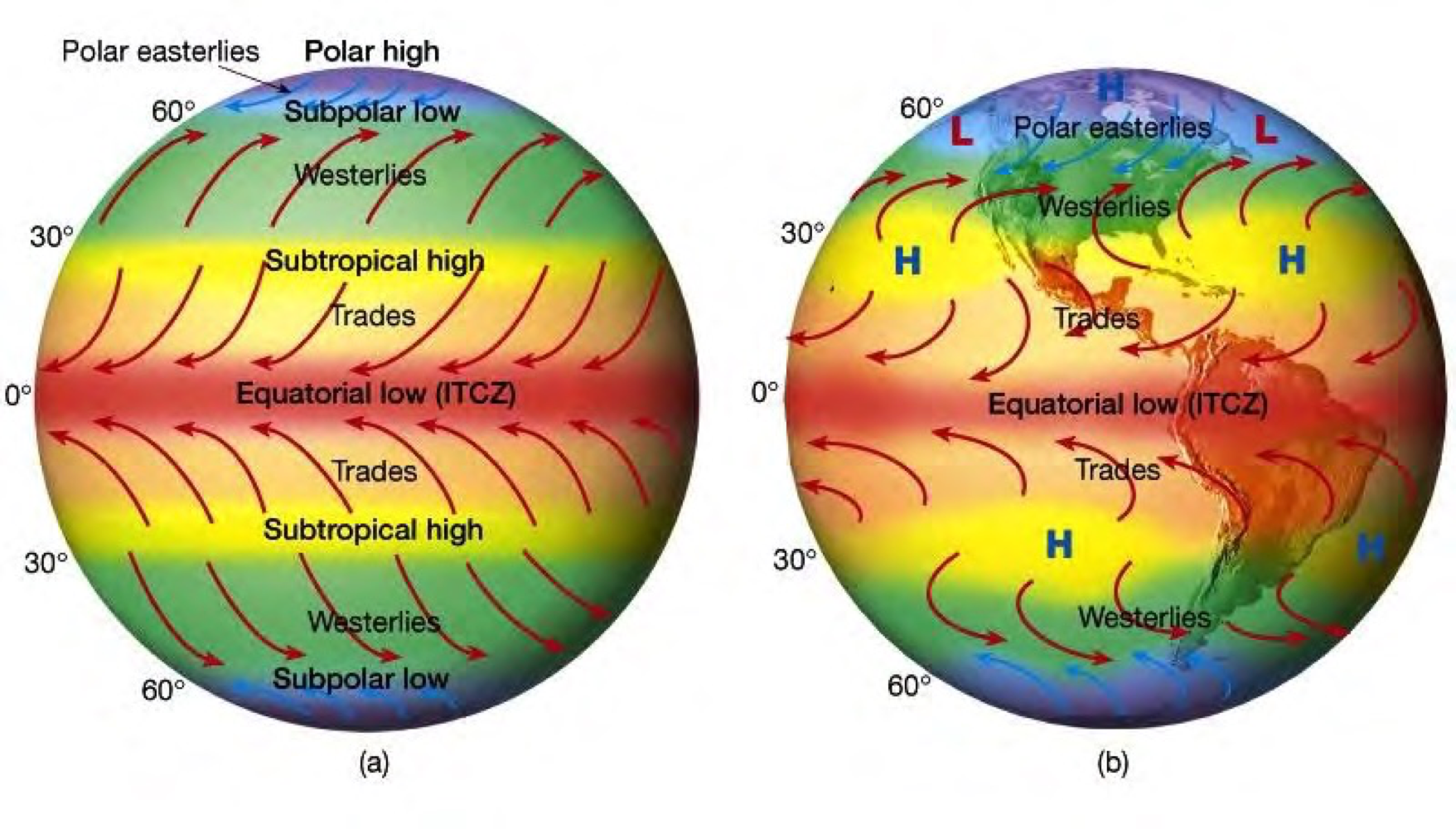
Atmospheric patters and energy distribution
Main curve:
Incoming solar radiation
Shows concentration of radiation
Flat curve:
Amount of energy going back into atmosphere
Fairly consistent
earth heats as a whole and there is radiation back
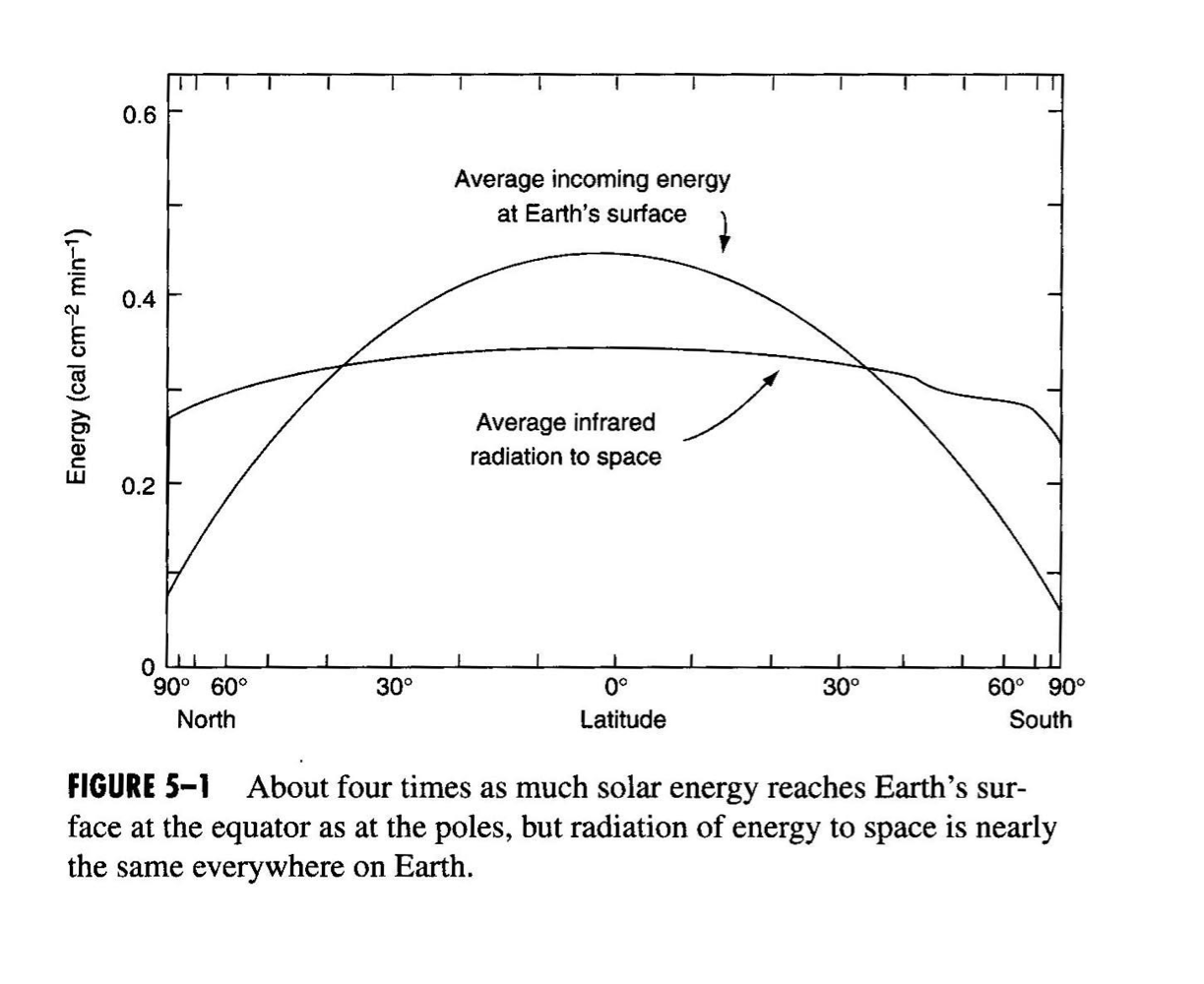
Changes in climate at different altitudes
Imbalance:
there is a net radiation deficit at higher altitudes
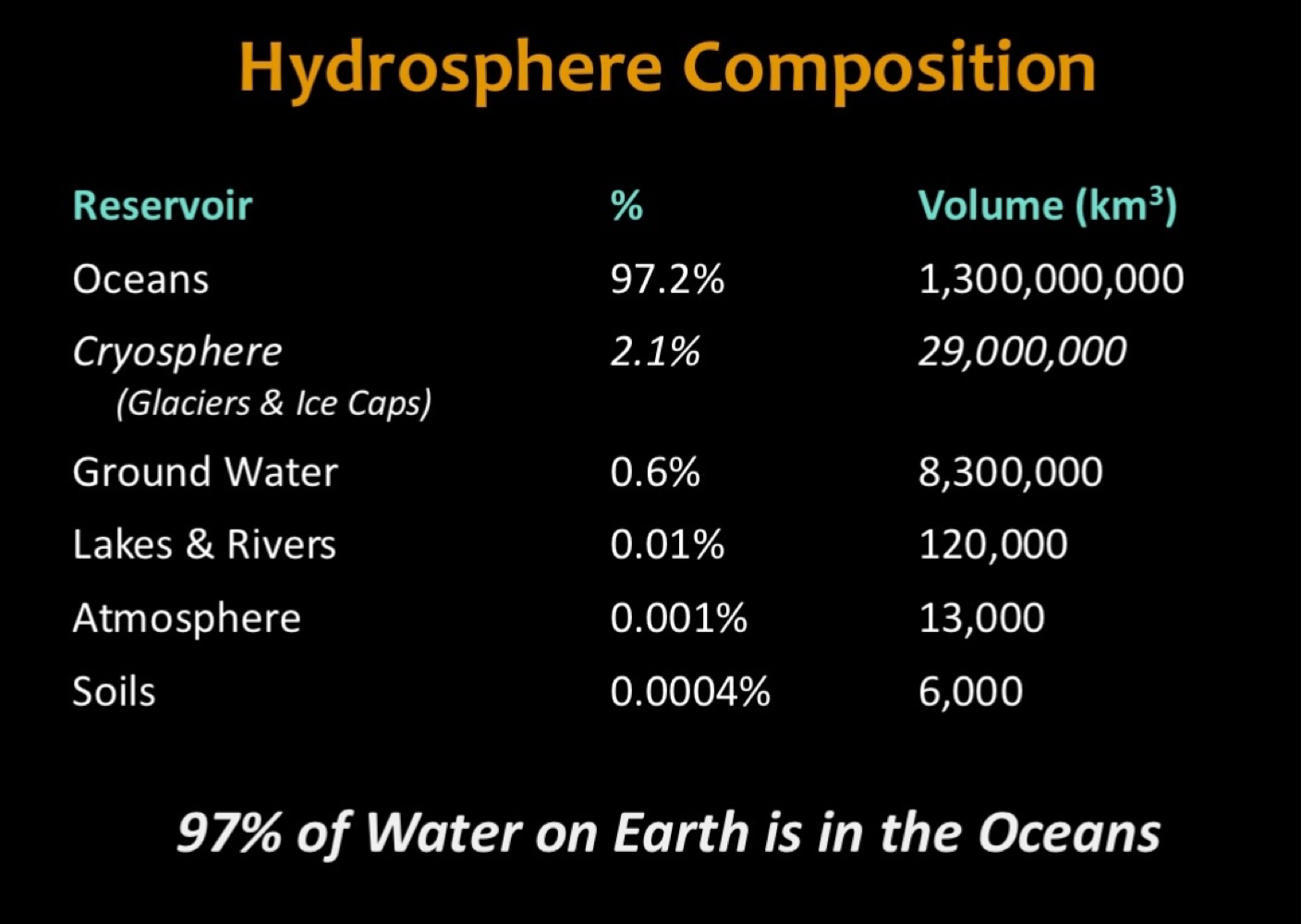
Composition of Hydrosphere
Don’t have to memorize. Just understand
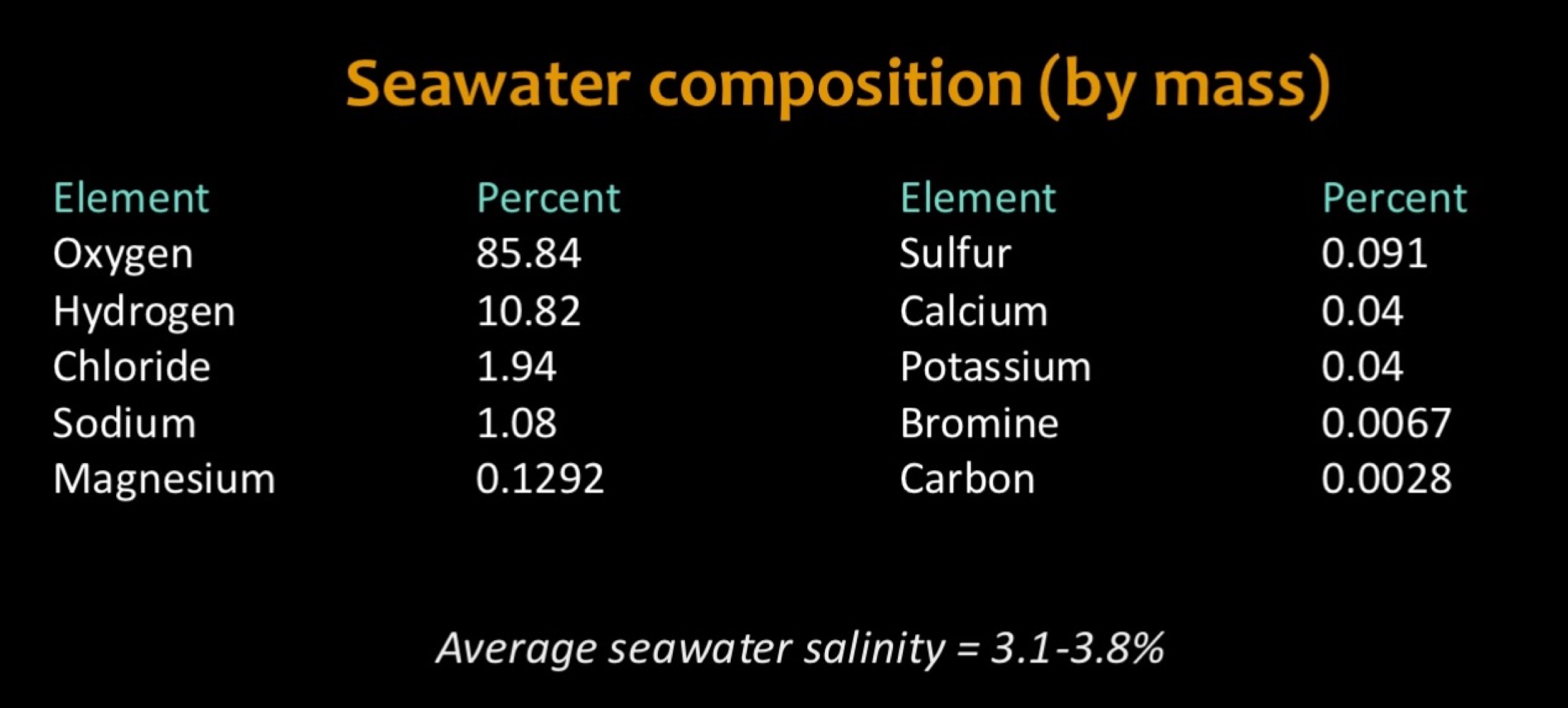
Sea Water composition
Don’t have to memorize. Just understand
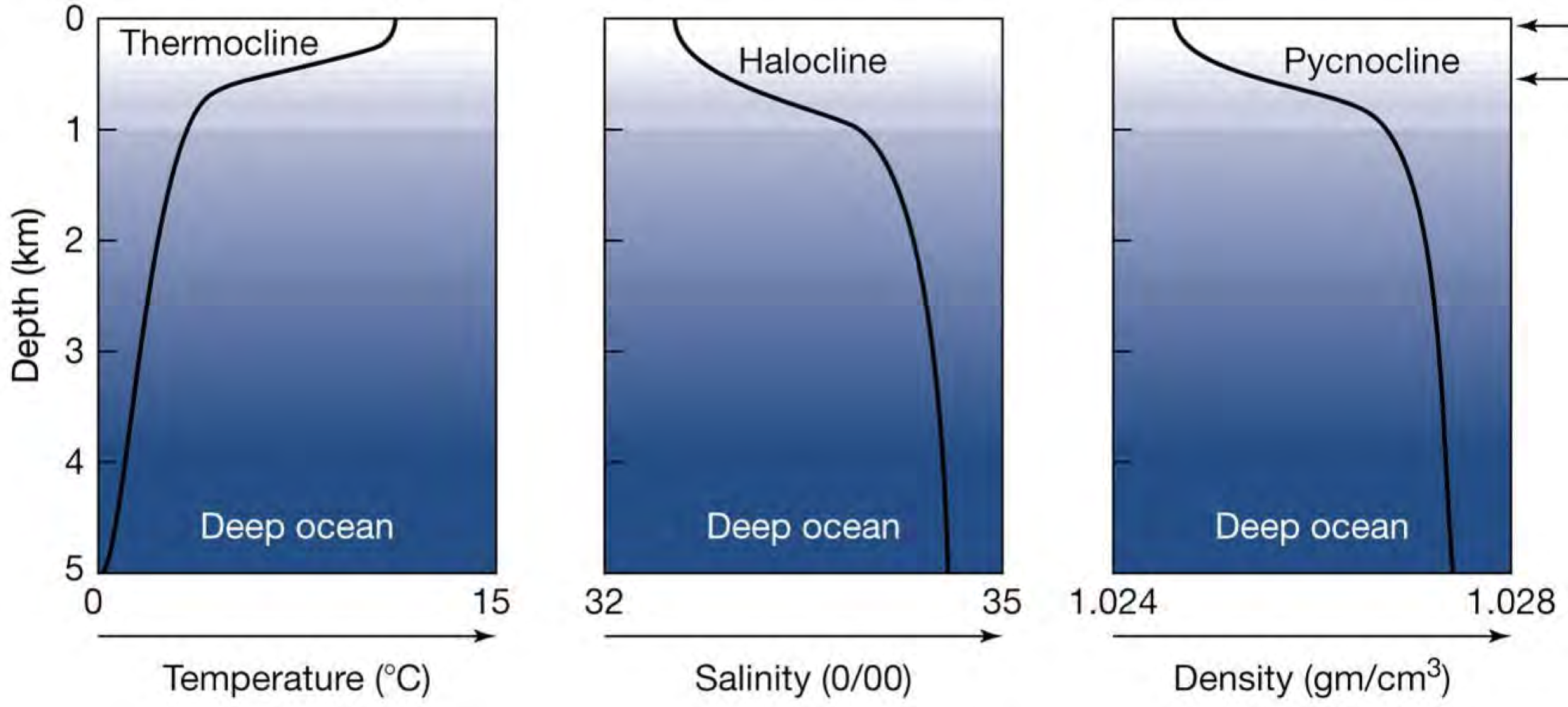
Ocean basin profiles
Thermocline drops around 1m
Increased salt content = more dense = will sink
Oceanic Conveyer belt —> Thermohaline circulation
water that is driven up the north Atlantic cools and gets more salty
When sea water freezes, salt gets left behind (as water freezes, it rejects salt from its molecular structure)
Stronger winds, more aired, more evaporated — leaves behind salt
The water then sinks and flows south
Becomes less slaty and warms (because it is less boyant)
Why is circulation important?
Energy (heat) flow
Gyres
Circular patterns of surface water movement
One in the northern hem and one in the southern hem
Driven by winds and Coriolis
Currents
Connections between gyres
Driven by winds and Coriolis
Colder on west coast of continent or eastern boundary currents
western boundary currents are warmer
ENSO definition
Coupled ocean atmosphere circulation system centered in the tropical pacific that is relate to changes in global atmospheric circulation and influences temp and precipitation patterns across the globe
ENSO cycle
normal conditions
“normal” arrow sizes and they indicate “normal” winds
Wind is dragging warm waters to the west
Also get tropic on western side of pacific
December - February are when ENSO conditions are most apparent
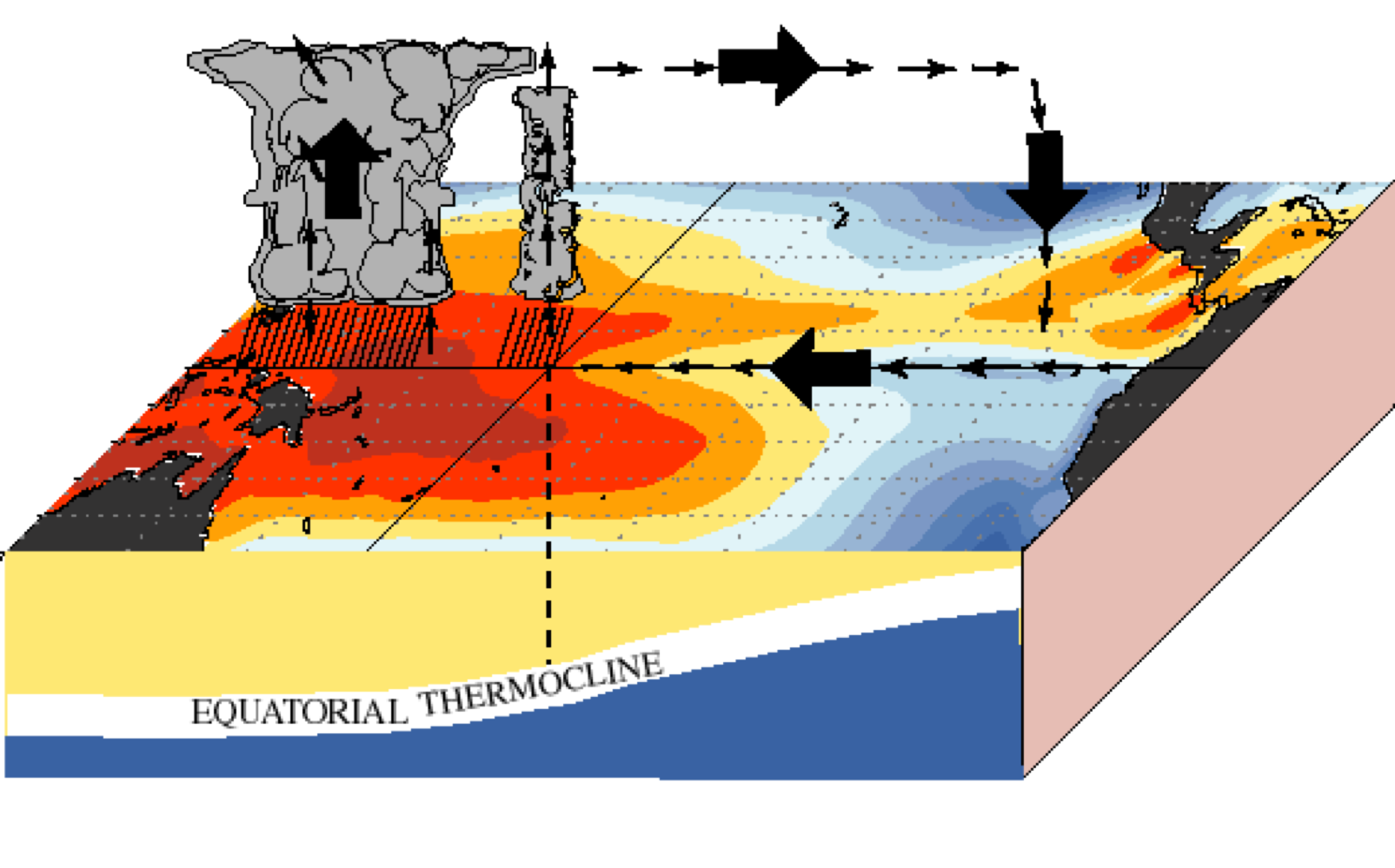
El nino
Less wind on water surface (sometimes they change directions)
Fire weather in Australia, typically very hot, but not wet
Thermocline is not allowing the cold water to circulate to the surface
Influencing fishing industry off west coast of south America
More evaporation over whole pacific because warm air is not being pushed all in one way
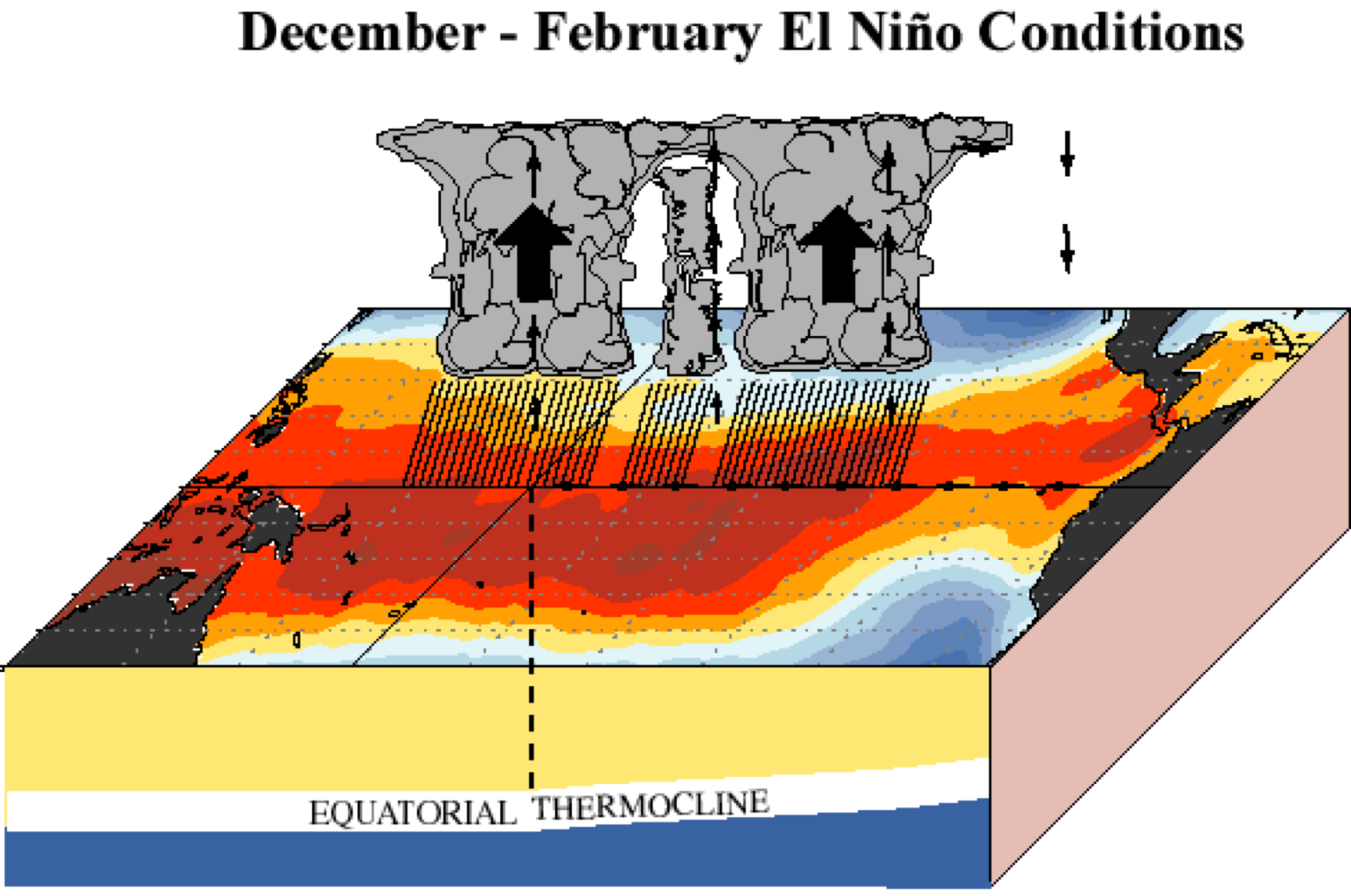
La Nina
lots of rain in wester pacific
strong winds in every direction
very steep thermocline
Deep waters are able to get closer to the surface
low pressure warm air rising (Australia and Indonesia), high pressure air sinking
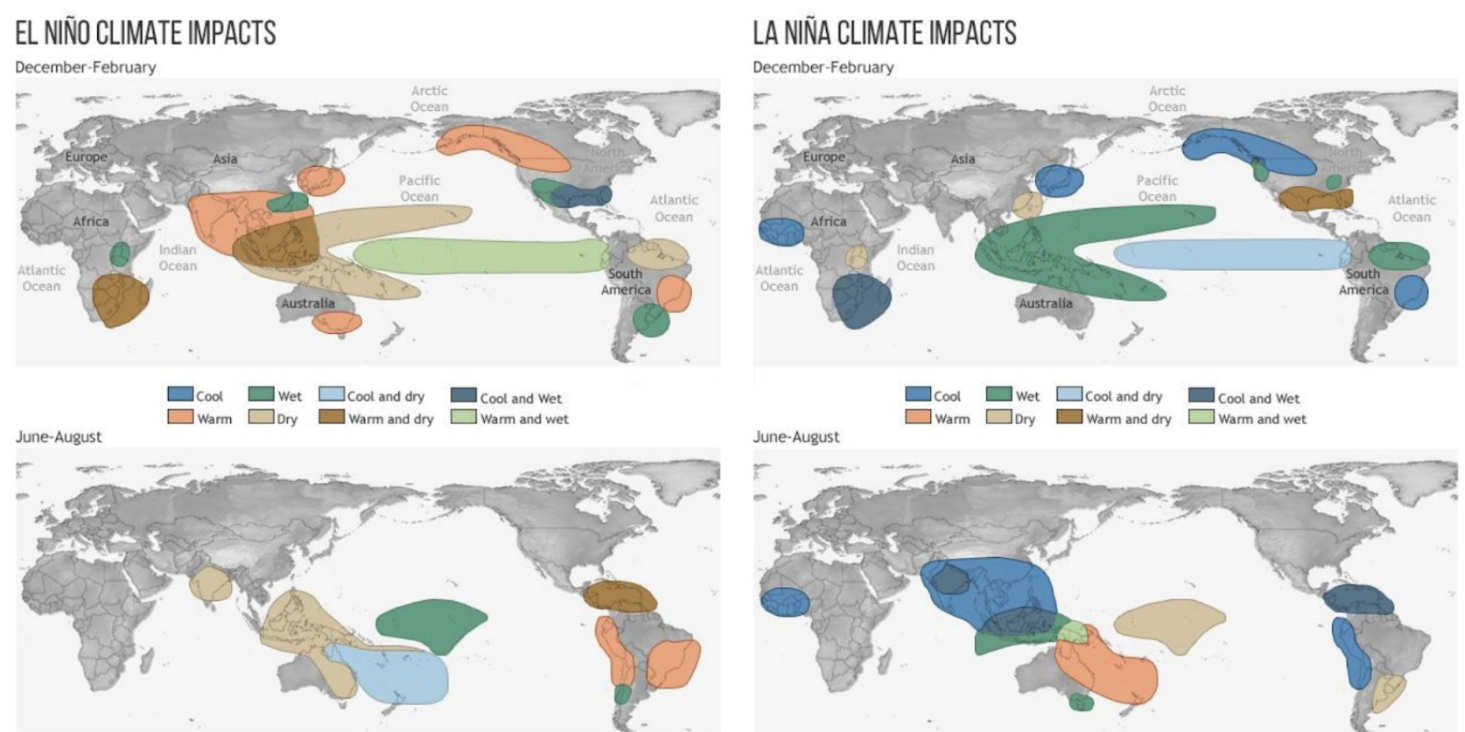
What are the effects of El Nino on Canada and Alaska?
When we have el Nino, Canada and Alaska are quite warm and there are wet conditions in southern us. ( dece- feb)
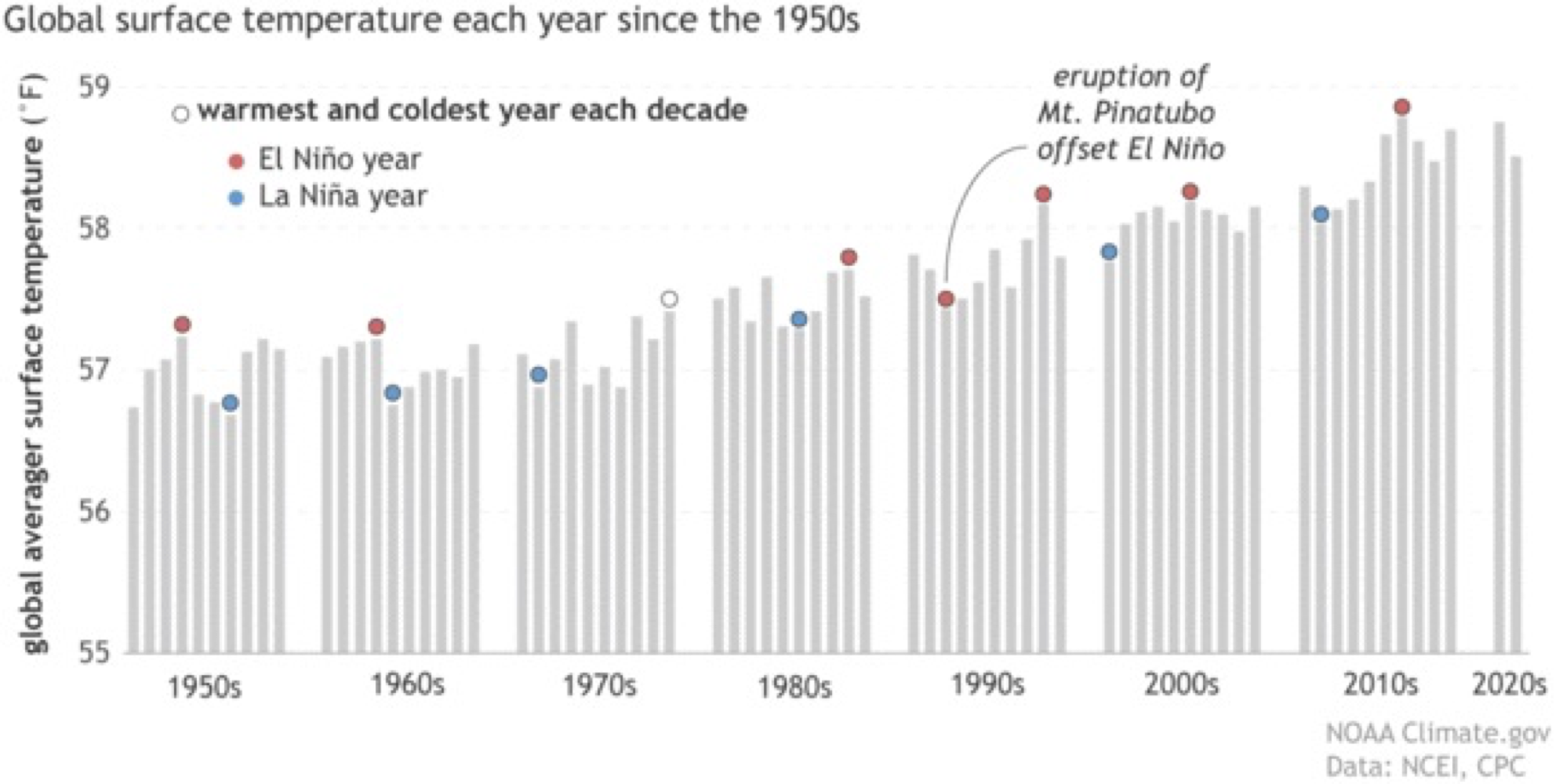
Trends in this graph
Typically warmest is el Nino and coolest is Nina
79- didn’t really classify as a Nino, but there were Nino qualities (delayed in 79)
90- Eruptions lead to cooling
Nino and Nina are hotter than they have ever been and Nina is now warmer than past Ninos
Characteristics of the Cryosphere
Land and sea cover change because if the seasons
Northern hem because we have more landmass spread across the northern hem
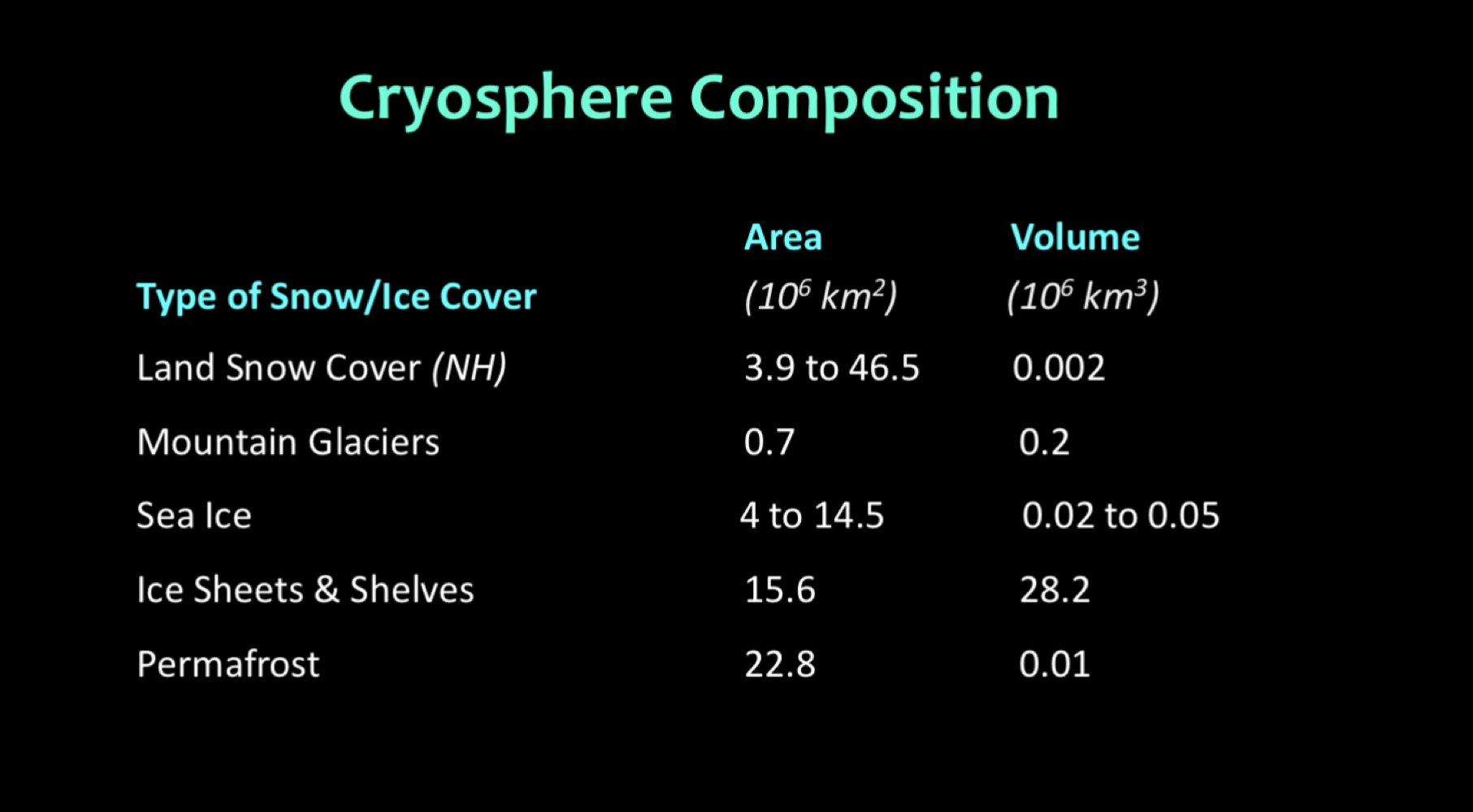
All of the elements (from cryosphere) shown in this image
Albedo feedback
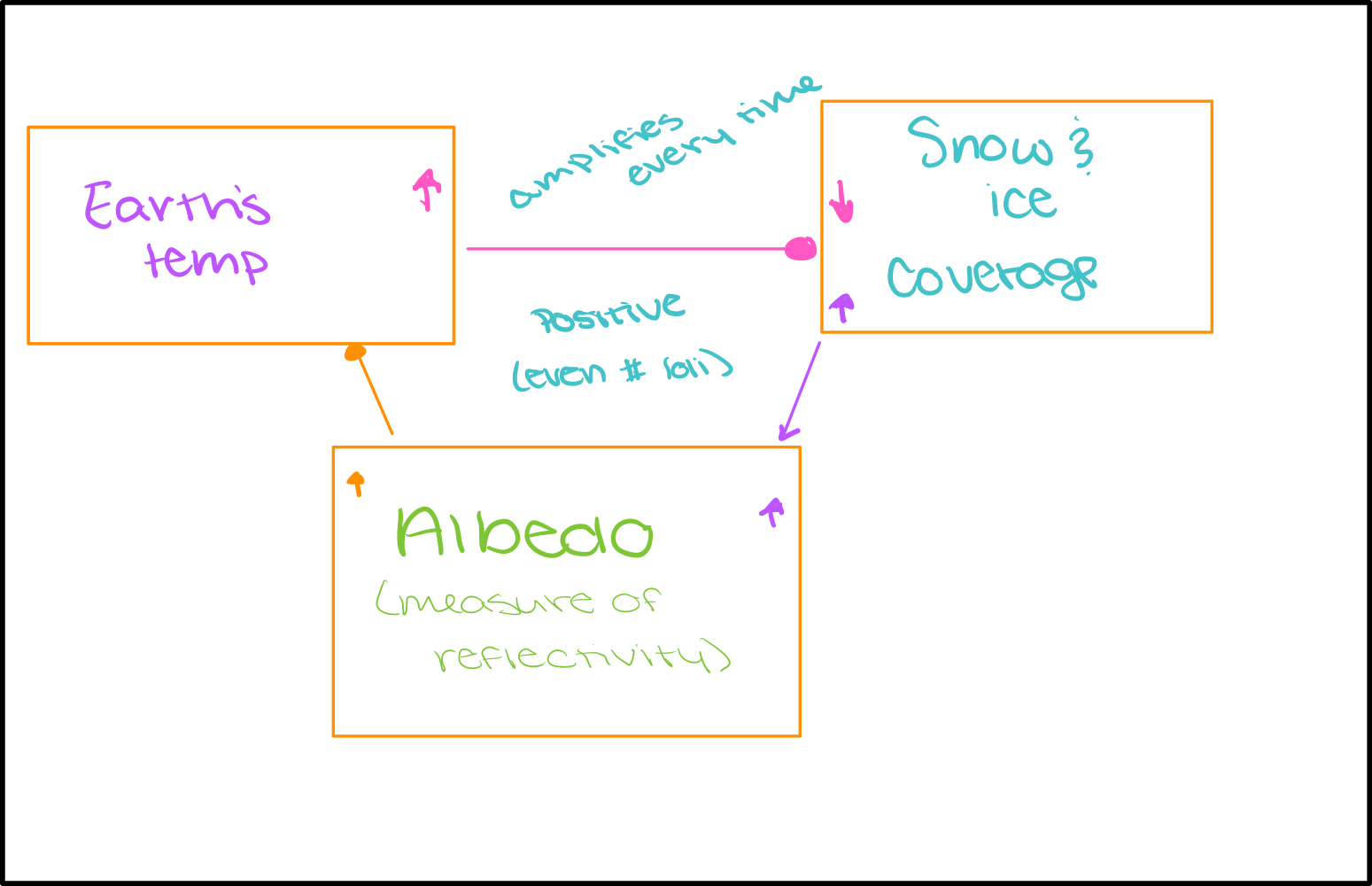
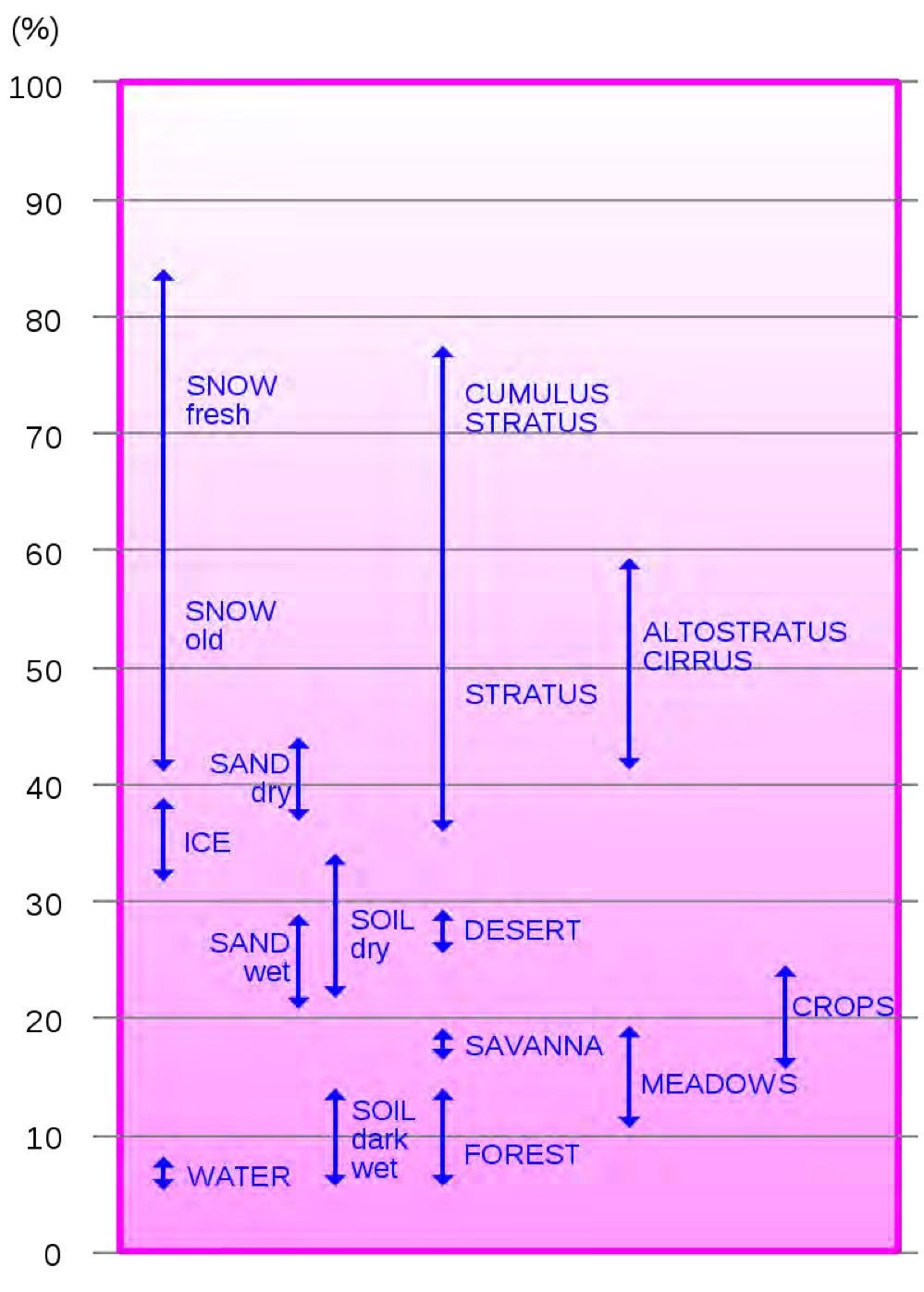
What is the average albedo of earth
The average albedo of earth is 30% (0.30)
Water cycle Diagram
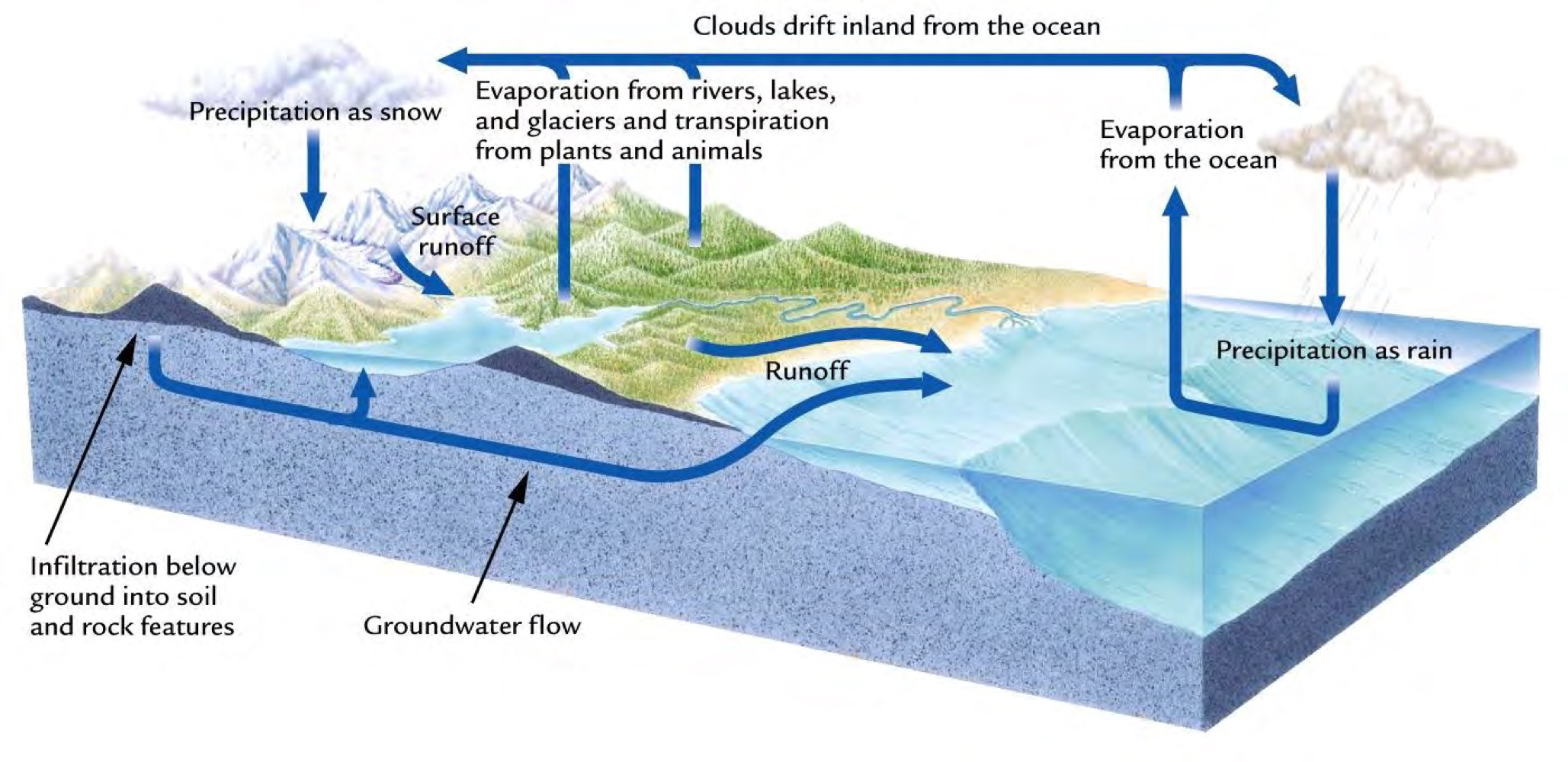
Precipitation
The change of atmospheric water vapor into a liquid or solid
Evaporation
The exchange of water from a liquid to a vapor
Transpiration
The release of water into the atmosphere by plant and animal cells
Infiltration
The movement of liquid water downward from land surface into and through soil and rock
Runoff
The total amount of water flowing into a stream
What is the residence time of water in the atmosphere?
10 days
What is the residence time of CO2 in the atmosphere?
100 - 1000 years
Biosphere range
Height of troposphere to deep in the earths crust
3.1 miles deep
7.0 miles high
Prokaryotes
No membrane bound nucleus
Where might cyanobacteria be found?
fossil material (churt)
There are some rocks from millions of years ago that have oxygen
Fossil evidence: 3.5 gya
Chemical evidence: 3.8 gya
Photosynthesis
6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
Geosphere composition
Crust varies in thickness depending on location
Continental and oceanic crust (vary in rock type and rock density)
Granite is much less dense than basalt
What is a geomagnetic dynamo?
liquid swirling around solid
Protects us from solar radiation
Mantel characteristics
like silly putty—> very slow flowing (not like liquid)
Mobile and convecting
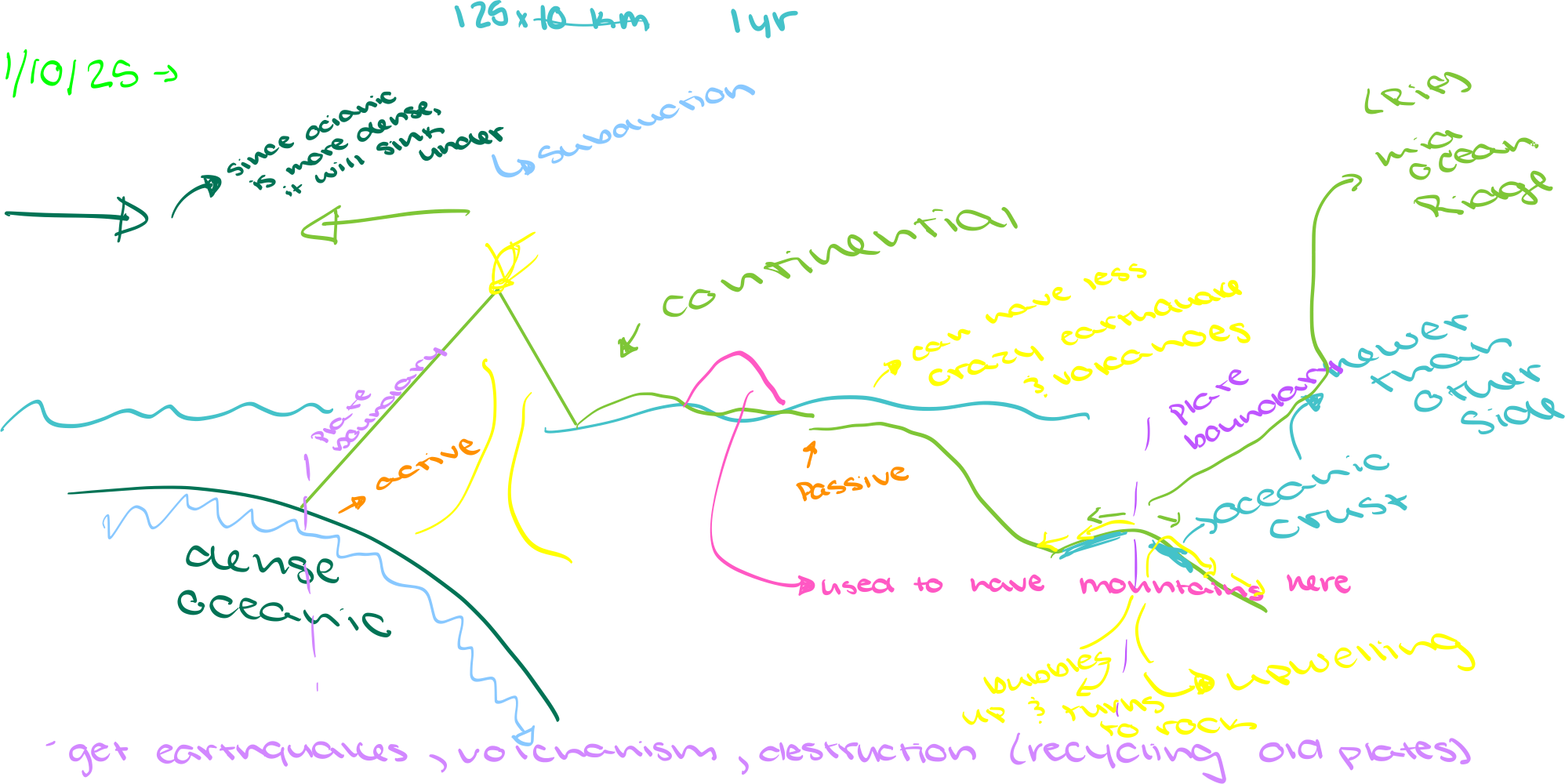
What are tectonic plates
not equivalent to the size or shape of continent
Techtonic diagram
The rock cycle
Metamorphic: heat and pressure
Igneous: formed from melted rock that has cooled
Sedimentary: accumulation of sediments that are buried and lithified
Need to break down other rocks to get the sediments
Can take any metamorphic rock and subject it to heat and pressure and it becomes another metamorphic (the same with the other types)
Recycling process