Gas exchange in plants
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
What's the formula for respiration?
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water + ATP
What's the formula for photosynthesis?
Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy → Glucose + Oxygen
What is the structure of leaves?(bottom to the top)
Waxy cuticle
Guard cells
Stoma
Lower epidermis
Air space
Mesophyll
Spongy mesophyll
Palisade mesophyll
Upper epidermis
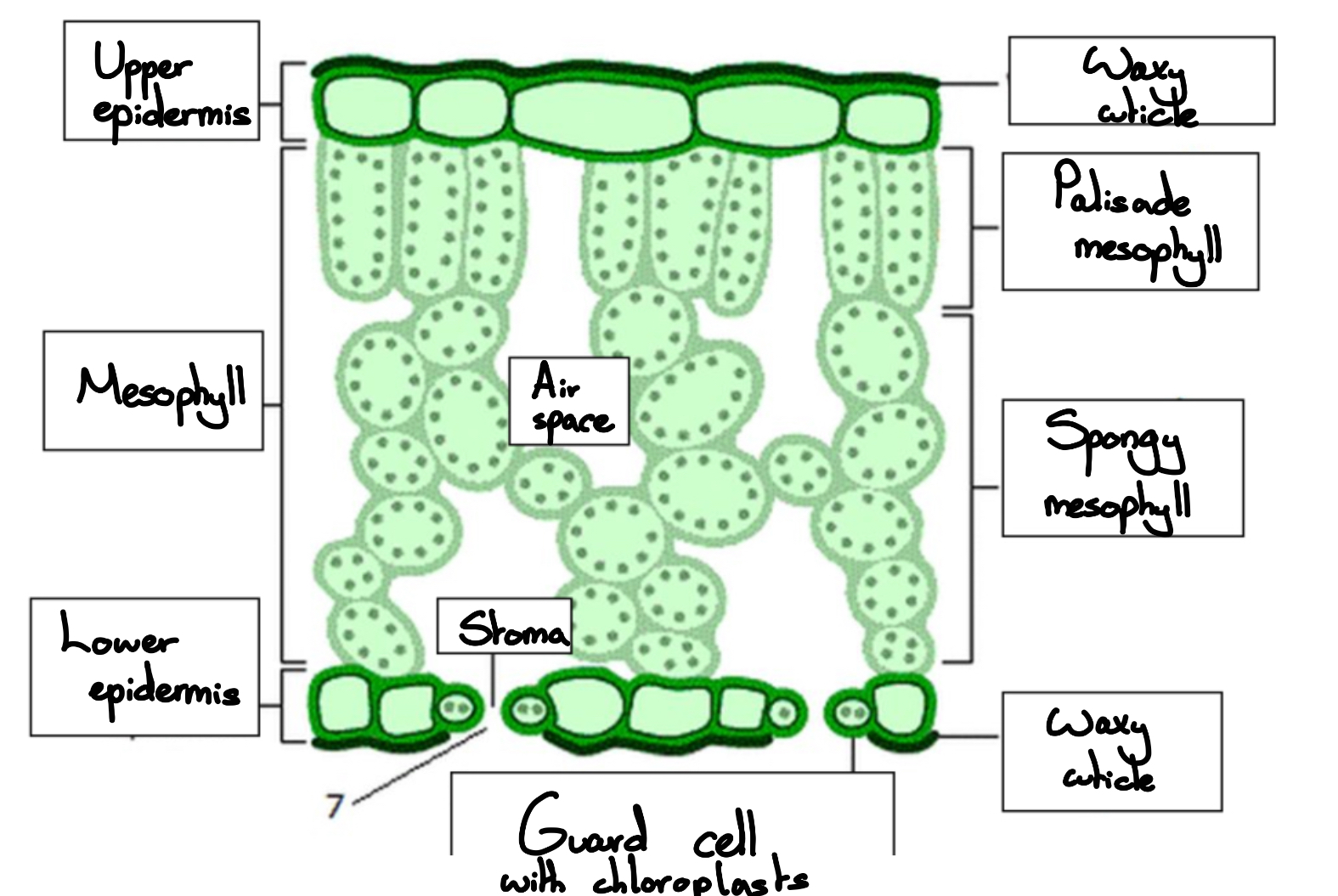
What are some adaptations of leaves?
- Leaf is thin + flat so large SA:V ratio
- Stomata mostly on lower surface so less water is lost
- Diffusion distances are short (air spaces mean no cells are far from air)
- Diffusion occurs through air spaces which is more rapid than through water
- When guard cells are turgid, stoma open, when the cells are flaccid, stoma close to prevent water loss
What are xerophytes?
Plants that are adapted to live in areas where water's limited.
Name and describe some xerophytes.
1. Holly- has a thick waxy cuticle so less water can escape
2. Pine trees- leaves are reduced to pine needles
3. Cactus- leaves are reduced to spines which reduces surface area and reduces evaporation of water
4. Marram grass- rolling up of leaves protects the lower surface of the leaf from the outside and traps a region of still air within the leaf (becomes saturated with water vapour) reduces water potential gradient so prevents water moving out.
5. Stomata sunk in pits to trap water vapour
6. Lambs ear- hairy leaves traps still moist air around the stomata (works like rolled leaves)
7. Curled leaves with stomata inside protect them from wind (windy conditions increase rate of diffusion + evaporation)
8. Reduced number of stomata, so there are fewer places for water to escape