MSE 2100
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
Ionic
Which bond type do the bonded atoms have large difference electronegativity?
True
In a neutral atom, the number of electrons and protons are equal.
Increases
As the degree of polymerization increases, the molecular weight _____.
DP=(Mn/m)
Quantum shell number
The rows in the Period Table correspond to _____.
Valence electrons
The columns (groups) in the Periodic Table correspond to ____.
Iron, Aluminum
Examples of metals
Oxygen, fluorine, selenium, neon
Examples of non-metals
smaller
What’s true about the size of Na and Na+ atoms? The radius of Na+ and Na are different, and the radius of Na+ is ____.
False
Do ceramics only contain pure ionic bonds?
BCC, FCC
Which of the following are metallic crystal structures?
K+, Ca2+ Cl-
Which elements have the same electronic configuration as Inert Gas Argon (Ar)?
Charge neutrality, ration of cation radius to anion radius
What are two factors influencing the ceramic crystal structure?
thermosets
What has a significant number of crosslinks?
Rock salt
What is the crystal structure of a material with AX structure and the coordination number of 6?
Secondary bonding
For linear polymers, what type of bonding occurs between adjacent linear chains?
Atactic structure
R groups randomly positioned (not very good for crystallization)
Syndiotactic structure
R groups alternate side of chain
isotactic
all R groups on the same side of the chain
Linear Polymers
What is it easy for to achieve crystallinity?
amorphous
Most crosslinked and network polymers are almost always ____.
Hydrogen bonding
Which type of bonding has the lowest bond energy in general?
Triple Nitrogen bonding
Which type of bonding has the highest bond energy in general?
family direction
<>
single direction
[]
single plane
()
family plane
{}
18
Max # of M shell
8
Max # L shell
2
Max # K shell
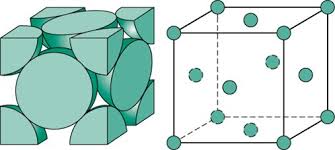
BCC
Coordination number: 8
APF: .68
Edge length: a=(4r)/sqrt3
Metals: Iron (room temp), chromium, tungsten, sodium, potassium
Atoms/Cell: 2
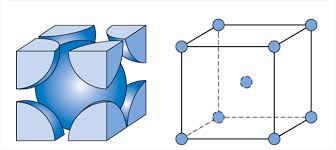
FCC
Coordination number: 12
APF: .74
Edge length: a=2sqrt2*r
Metals: Aluminum, copper, gold, silver, nickel
Other: 8 lattice points at each corner
Atoms/Cell: 4
SC
Coordination number: 6
APF: .52
Edge length: a=2r
Metals: Polonium
Atoms/Cell: 1