IMED1004 - How the brain works (L19)
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
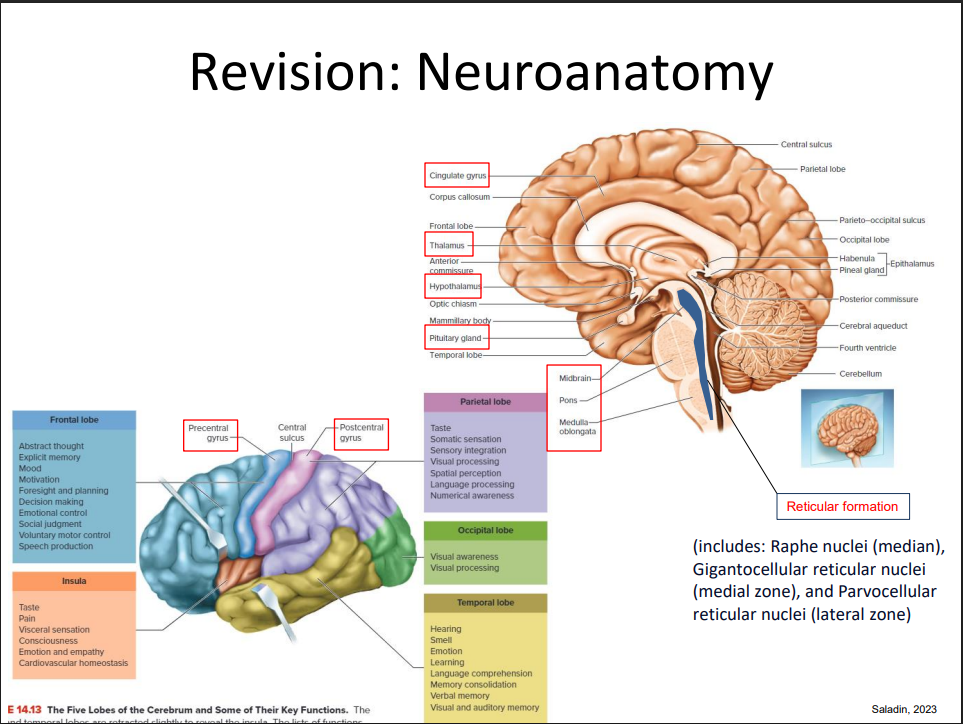
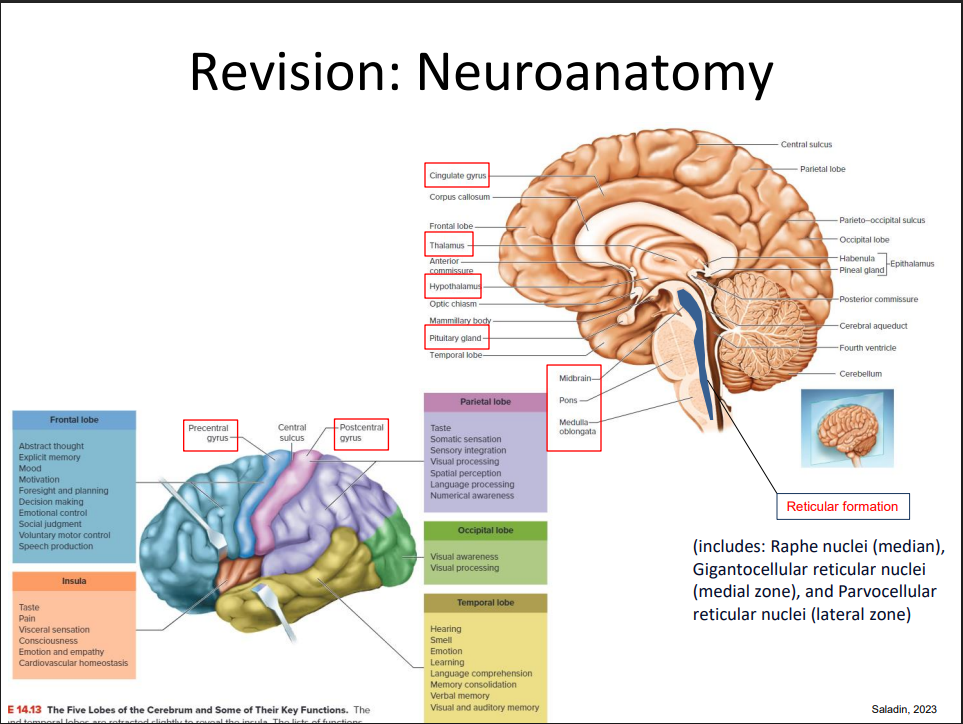
Revision of Neuroanatomy
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 3
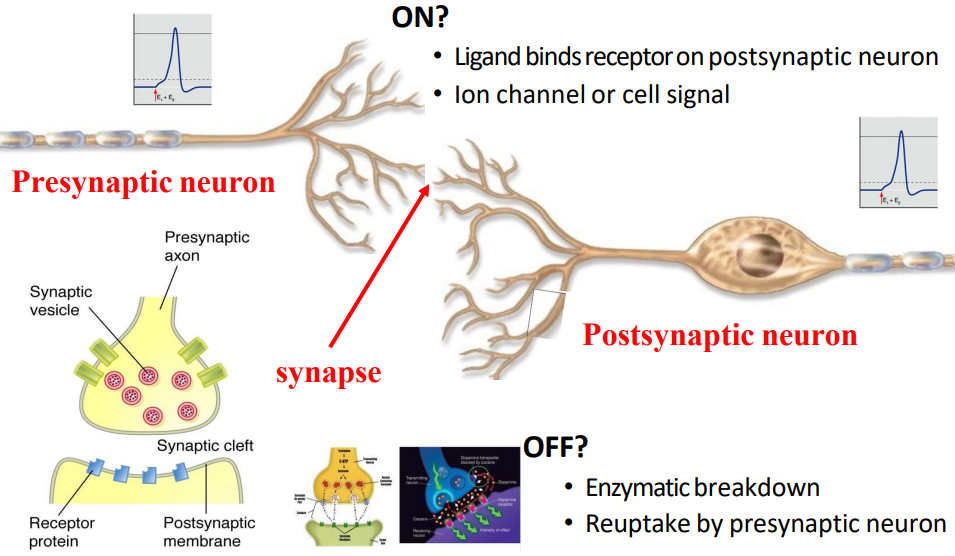
What your brain already knows about your brain
ON?
- Ligand binds receptor on postsynaptic neuron
- ion channel or cell signal
.
OFF?
- enzymatic breakdown
- reuptake of presynpatic neuron
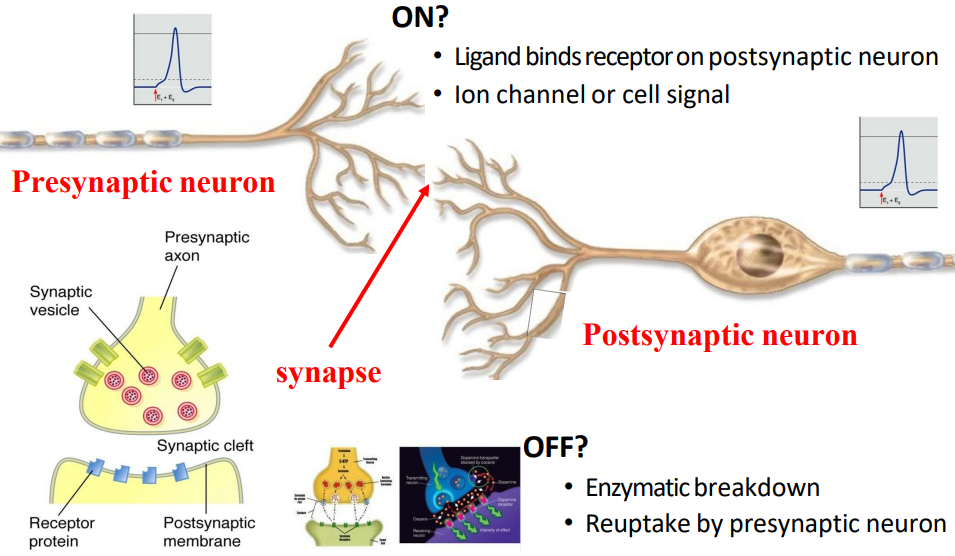
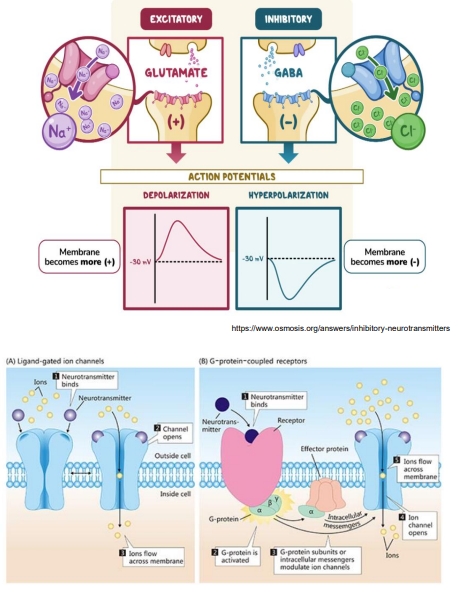
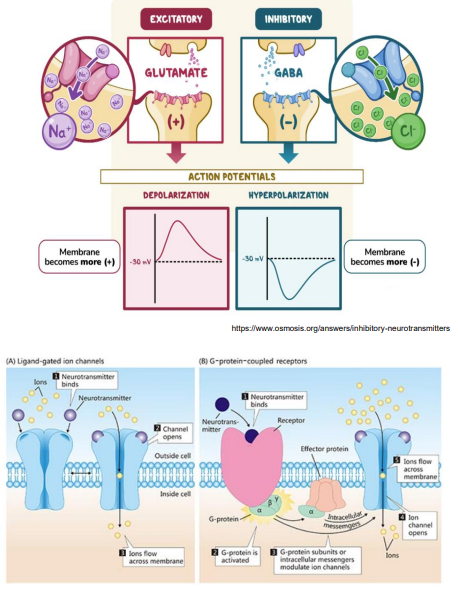
Neurotransmitters and Synaptic Transmission
A neurotransmitter can lead to synpatic transmission that is: Excitatory OR Inhibitory OR either
The post synpatic membrane may respond via:
- Ion Channels (e.g glutamate and GABA) OR
- Transmembrane proteins that signal secondary messenger systems such as cAMP via G-protein coupled receptors (GCPRs) (e.g monoamines i.e noradrenaline, dopamine, serotonin)
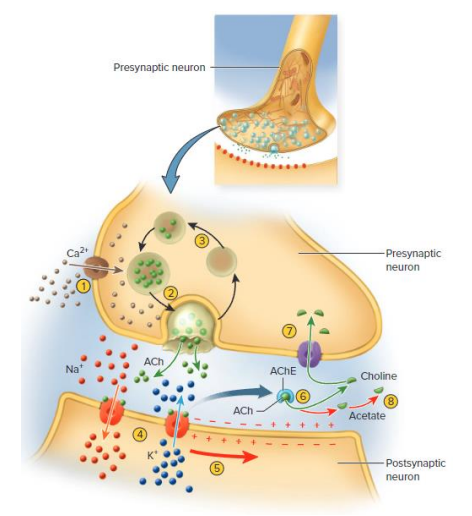
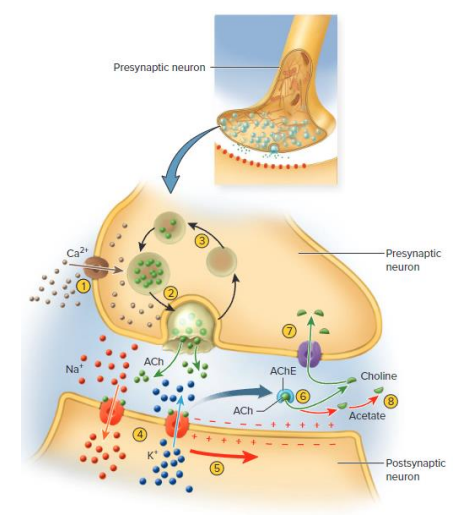
Neurotransmitters (NTs) removal
ENZYME DEGREDATION:
- neurotransmitter broken into fragments (e.g monoamine oxidase (MAO))
REUPTAKE:
- NT/broken products reabsorbed by transport proteins
DIFFUSION:
- Simple diffusion away from synapse. In CNS astrocytes absorb and return NT to presynpatic Neuron
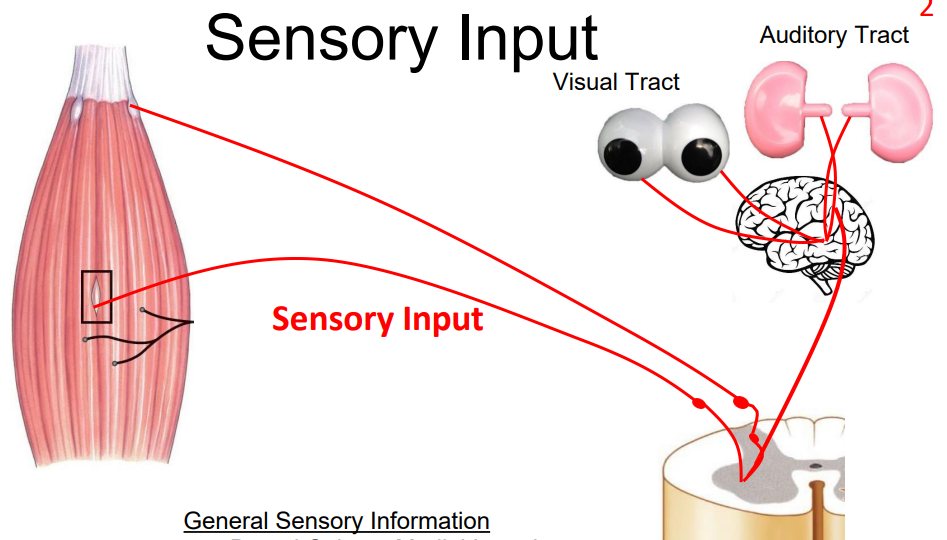
Sensory Input
- GENERAL SENSORY INFORMATION:
- e.g Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus (DCML) Tract (carries discriminative touch), OR spinocerebellar tract (proprioception)
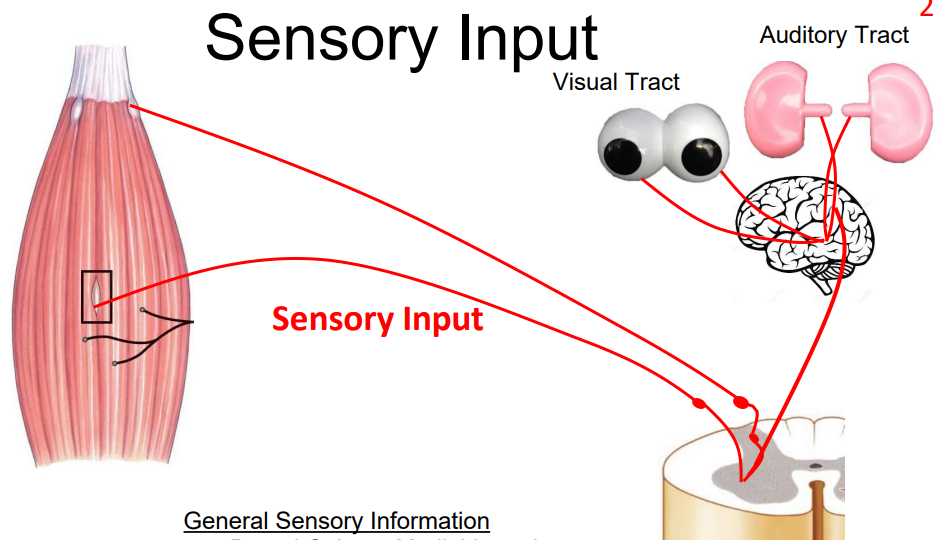
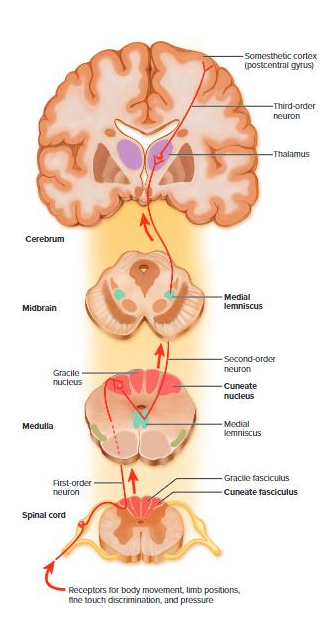
General Sensory Information
e.g Dorsal Column Medial Lemniscus (DCML) Tract (carries discriminative touch)
.
- dorsal column is telling you that it is the sensory pathway, it is moving up on the dorsal part of the spinal cord
- Medial Lemniscus is telling you that the cross over of that tract is happening within the brainstem, which is where the medial meniscus is
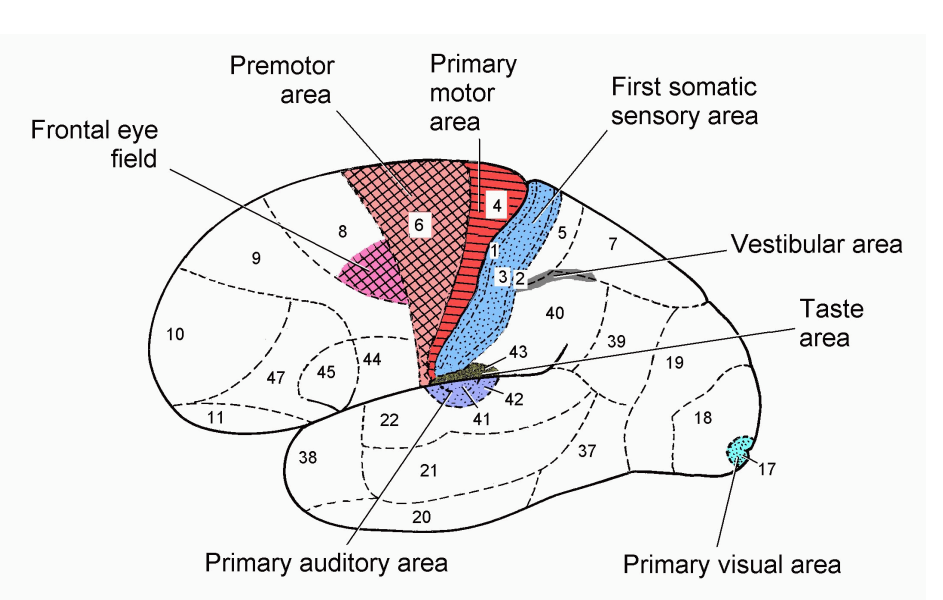
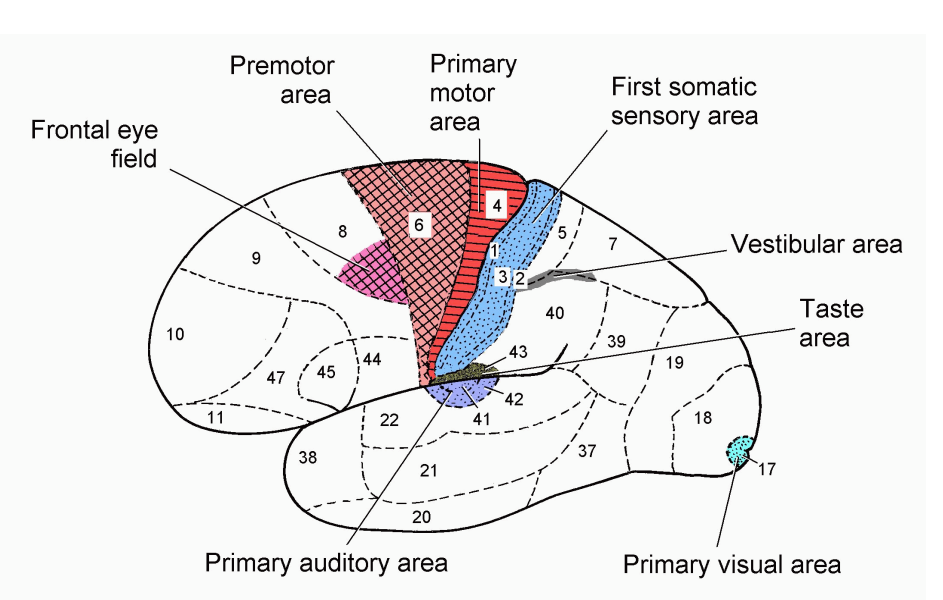
Brain Part
- we are coming back to the central sulcus
- in blue
.
- information where sensation comes from is the first somatic sensory area
- central sulcus lies between regions 4 (red) and 3 (blue)
- when you want to produce a motor command (the intiiation for the actual command) comes from the primary motor area (red) (pre-central gyrus)
- then its going to descend (next slide)
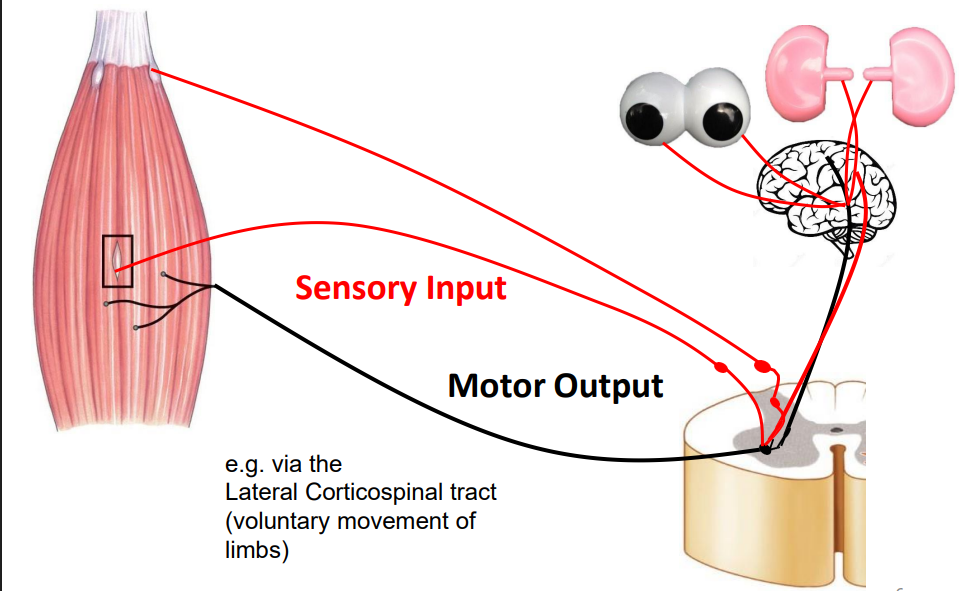
Motor Output
- the command is going to descend (from prev slide) out the black pathway to the muscle)
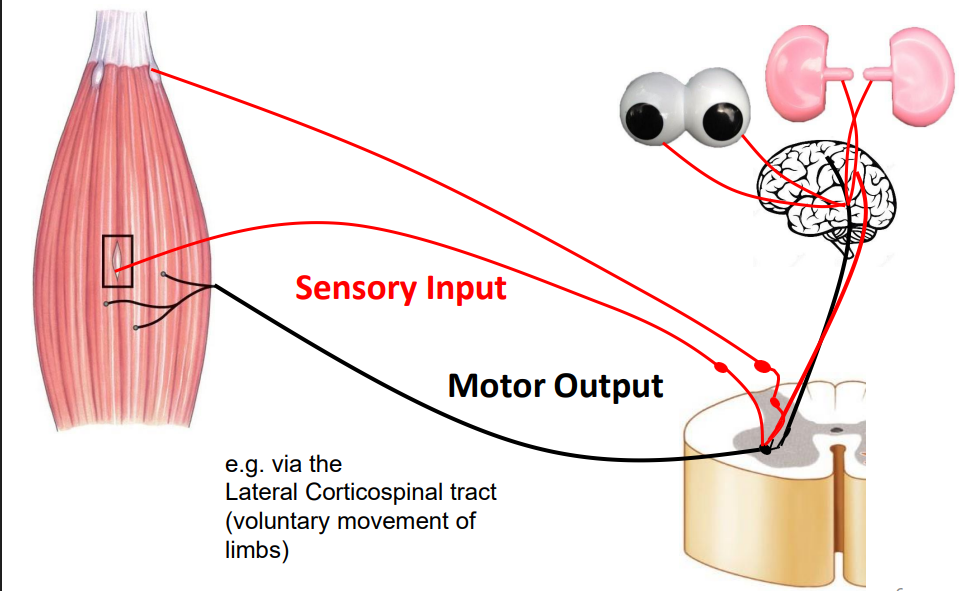
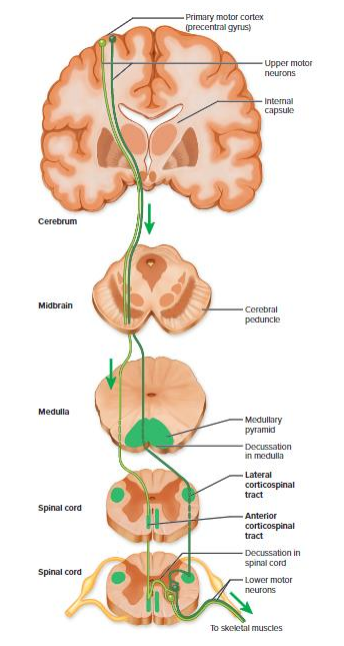
Motor Output with info
- e.g via the Lateral and Anterior Corticospinal Tract (voluntary movement of limbs)
.
- starts in pre-central gyrus (primary motor area)
- descend through midbrain
- cross at one point or the other, either at the midbrain or at thre level of the spinal cord then its going to reach the muscle on the other side
- left brain controls right side
All we need for this on/off is
neurotransmitters
- Glutamate, GABA, ACh will do that (ionotropic)
But CNS is not just a sensory and motor, theres also a bunch of other stuff
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 15
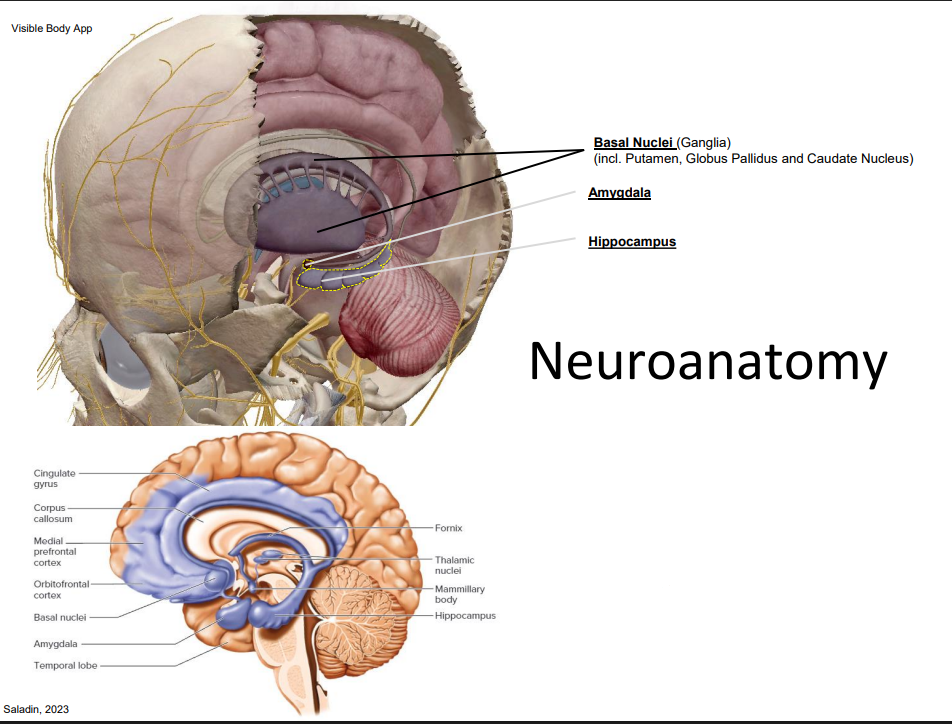
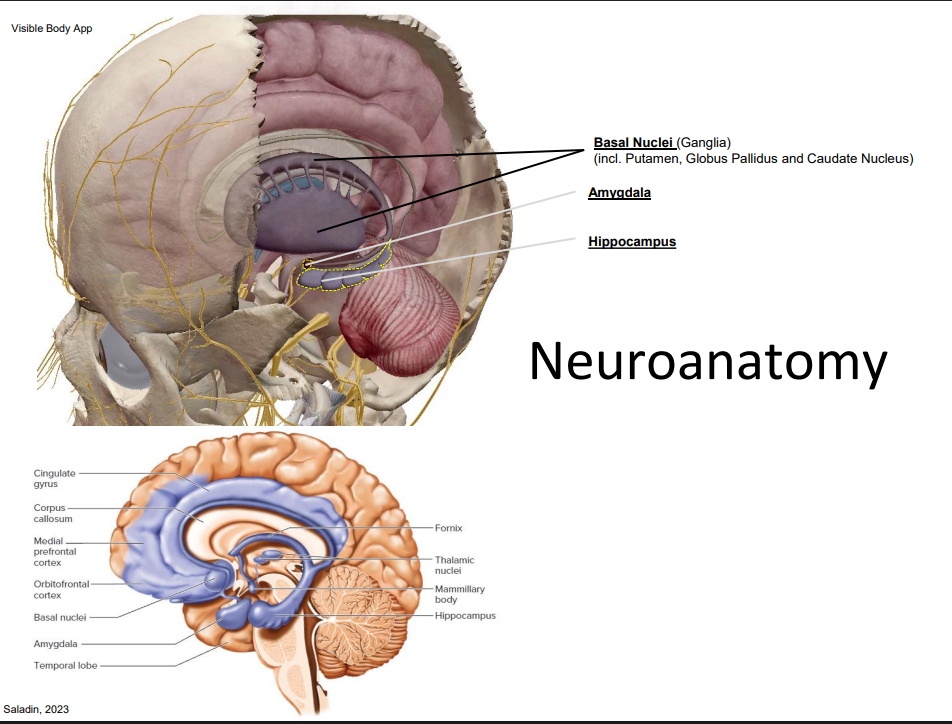
The Limbic System
- the mammilian brain for: emotions, memories, habits, attachments
- if we go back down our longitudinal fissure that separates the hemispheres, we have this cingulate gyrus
- thats at the base of the longitudinal tissue on the left and right hand sides
- so we have this little gyrus at the bottom
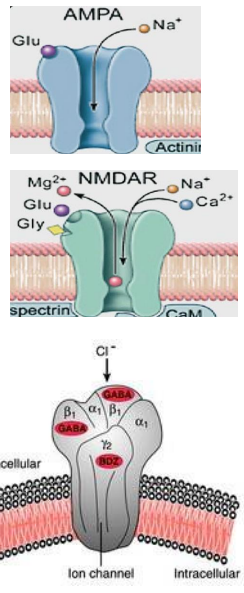
The two biggies (CNS)
GLUTAMATE:
- The dominant excitatory CNS neurotransmitter
- binds/opens iGluRs (ionotropic glutamtae receptors)
- AMPA receptor is a Na+ channel (EPSP)
- NMDA receptor is a Na+ and Ca2+ channel (EPSP)
- Also mGluRs (metabotropic glutamate receptors)
.
GABA
- the dominant inhibitory CNS neurotransmitter
Binds/opens GABA(A)Rs: Cl- channels:
- Cl- influx causing hyperpolarisation
- inhibits post-synaptic neuron (IPSP)
.
- also GABA(B)Rs: metabotropic
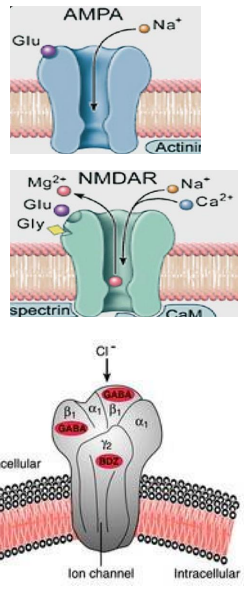
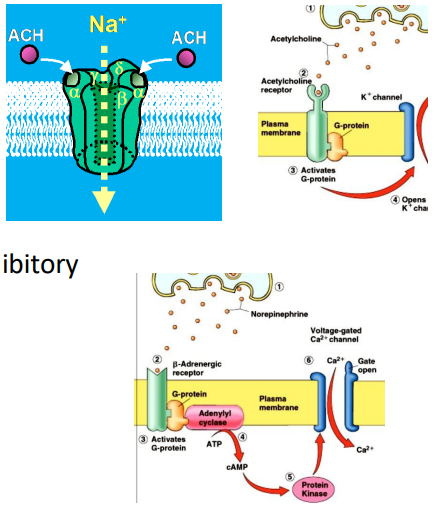
The two biggies (PNS - also in CNS)
ACETYLCHOLINE (ACh) - excitatory or inhibitory:
Nicotinic (nAChR)
- Ionotropic - ligand-gated Na+ channel
- always excitatory
Muscarinic (mAChR) - GPCRs
- metabotropic - activates enzymes
- often inhibitory (can be excitatory)
.
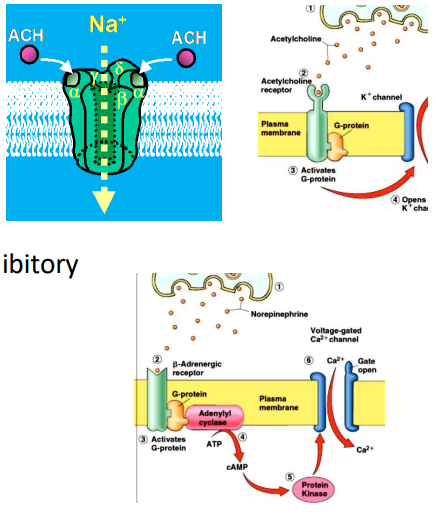
NORADRENALINE (NA) - excitatory or inhibitory
Alpha-adrenergic receptors - GPCRs
- metabotropic - activates enzymes
- excitatory or inhibitory
Beta-adrenergic receptors - GPCRs
- metabotropic - activates enzymes
- excitatory or inhibitory
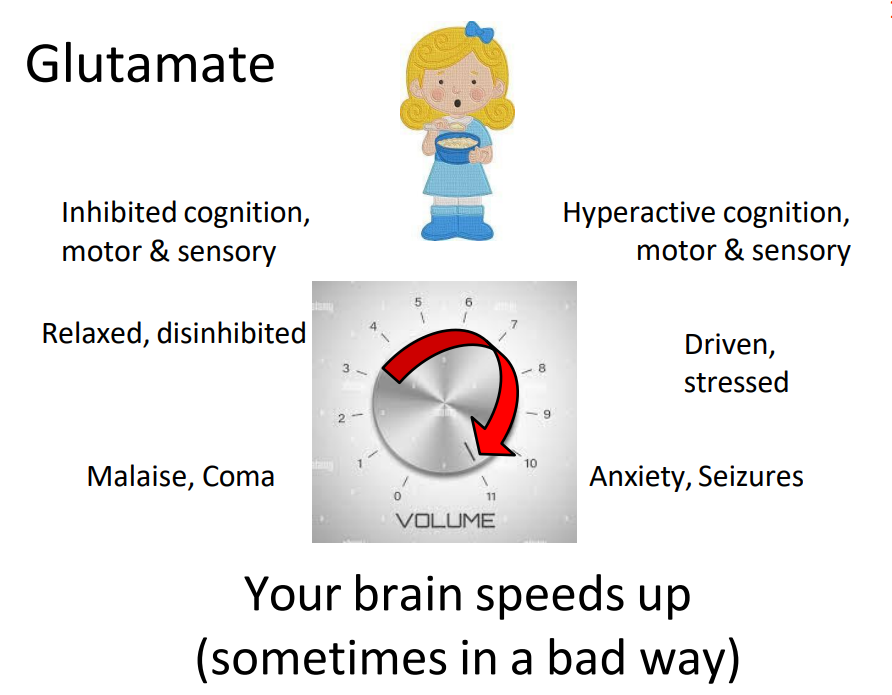
Glutamate = and GABA =
- Glutamte: excitatory
- GABA: inhibitory
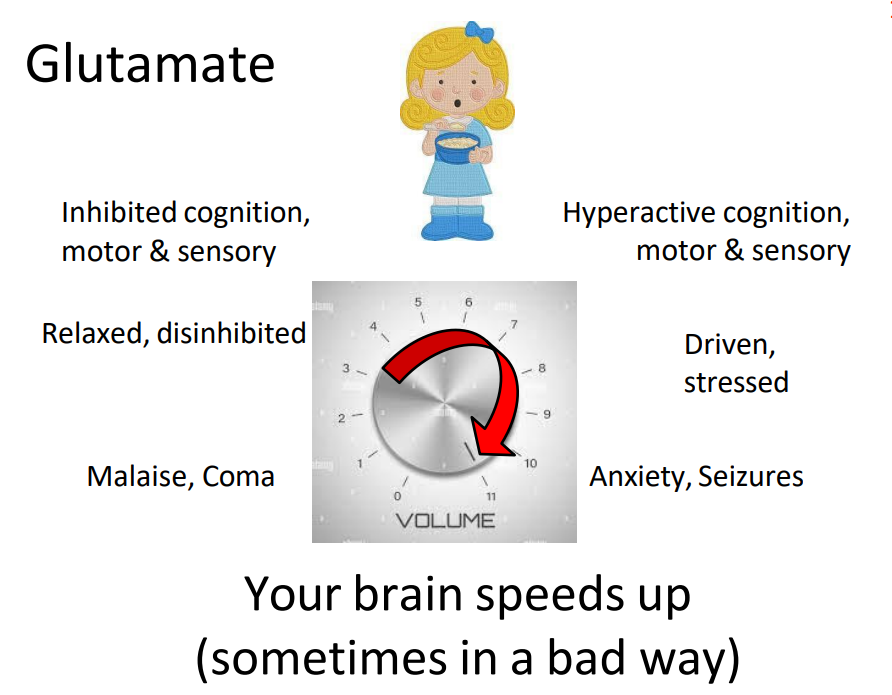
Glutamate
- diagram shows that if we have too much glutamate, we get to a point where we are overdriven:
ASSOCIATED WITH (increasingly bad):
- hyperactive cognition, motor and sensory
- driven, stressed
- anxiety, seizure
.
- your brain speeds up (sometimes in a bad way)
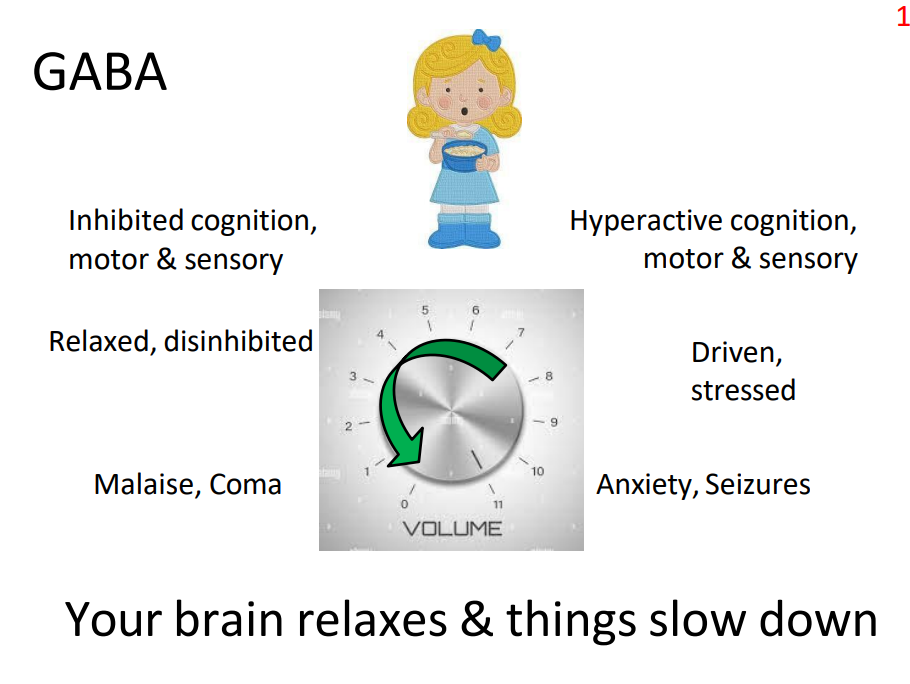
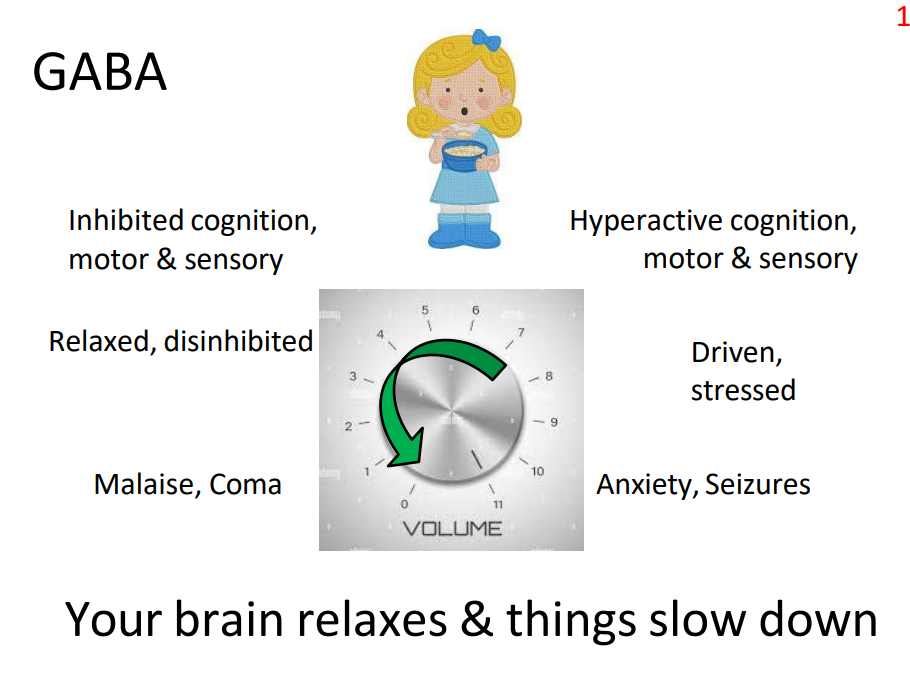
GABA
IF U HAVE TOO MUCH:
- Inhibited cognition, motor and sensory
- relaxed, disinhibited
- malaise, coma
.
- your brain relaxes and things slow down
Normal thinking depends on the balance of:
- excitatory glutamate and inhibitory GABA -> = impaired cognition
- Behaviour and emotions are even more complicated
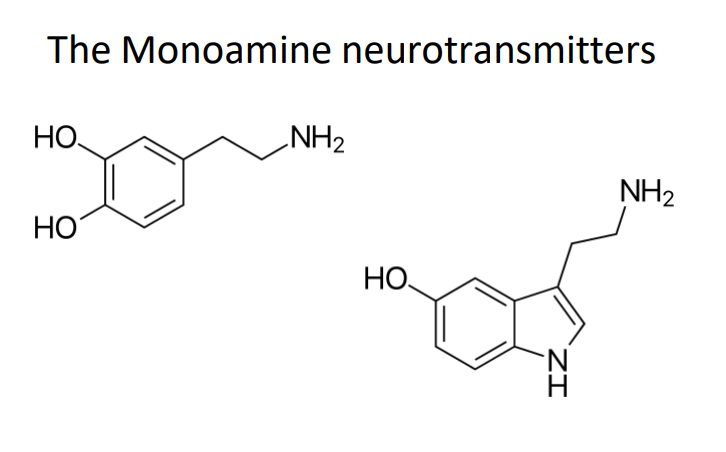
Serotonin and Dopamine are types of
monoamines
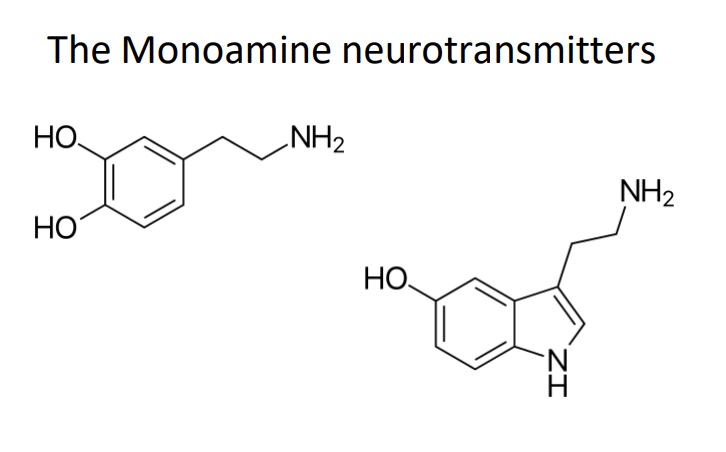
The Monoamine Neurotransmitters
- he uses can't not because they are involved in rewards, euphoria, drive, safety
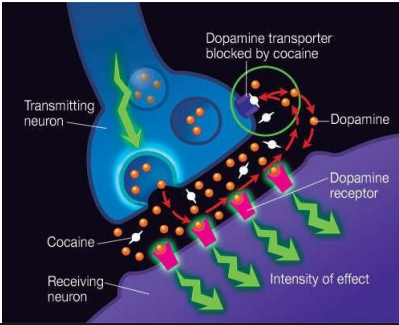
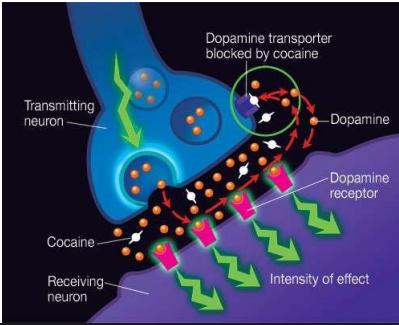
Dopamine (DA)
ON = activate DA receptors (GPCRs)
- D-1 like (increase cAMP) and D2-like (decrease cAMP) are all GPCRs but act in contradictory ways
.
OFF =
- reuptake - DA transporter (DAT), then...
- broken down by enzymes: monoamine oxidase (MAO), catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT)
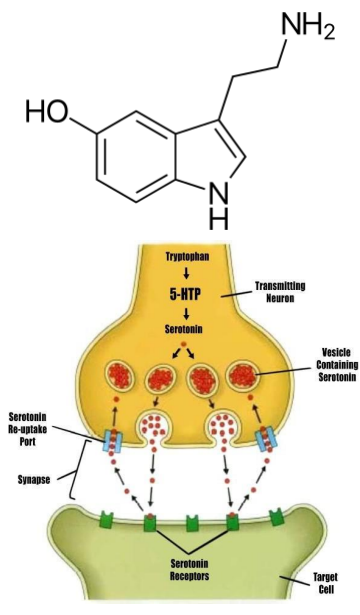
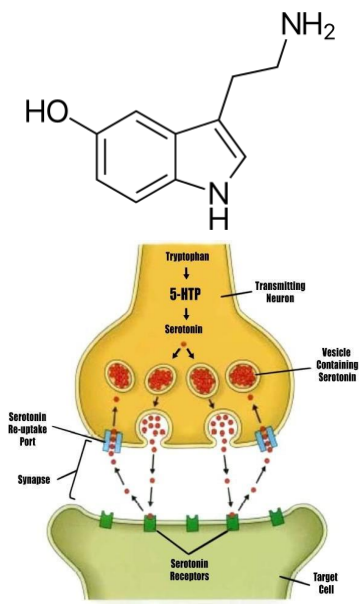
Serotonin
ON = activate 5-HT receptors
- the 5-HT receptors, are GPCRs -> signalling (except 5-HT3 receptor = ligand-gated cation channel) (its ionotropic)
.
OFF = reuptake
- monoamine transporter (SERT), on the presynaptic neuron
- various agents can inhibit 5-HT reuptake, including cocaine, tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) → increase synaptic 5-HT.
How do we use these monoamines
- Neurohormonal control systems
- the limbic system
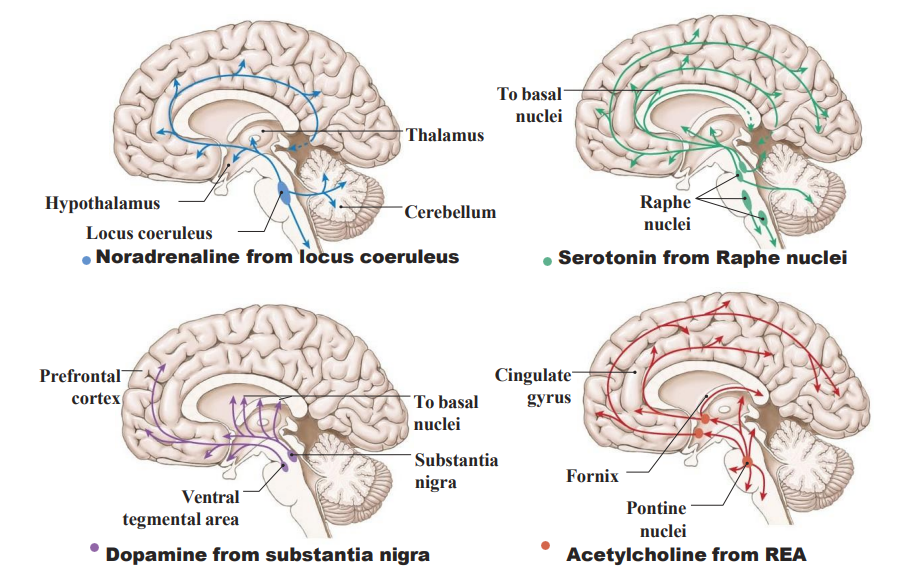
Neurohormonal Control Systems
- they have common features:
- the original nuclei/driver is located in the brain stem
- a lot of pathways go to prefrontal cortex and basal nuclei and limbic sytem
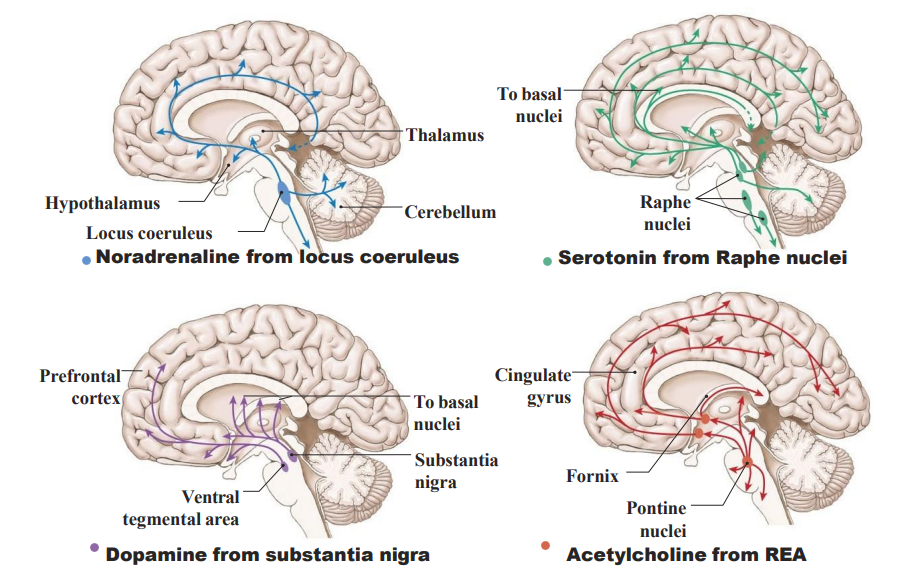
Reticular Excitatory Area (REA) - ACh system
GENERAL SYSTEM FOR CONTROL OF THE OVERALL LEVEL OF EXCITATION OF THE BRAIN:
- in reticular formation of pons and midbrain
- spreads throughout entire cortex
- causes acutely awake + excited nervous system
RAPID TRANSMISSION (ms) TO EXCITE THE CEREBELLUM:
- gigantocellular neurons: excitatory -> ACh (rapid acting, rapidly destroyed)
MAKES YOUR BRAIN ACUTELY AWAKE:
- ACh from the REA activates lots of other Glutamatergic neurons
SWITCHED FOF BY ITS OWN INHIBITORY AREA (serotonergic)
.
WAY TO RMBR: Acutely Awake and Active
.
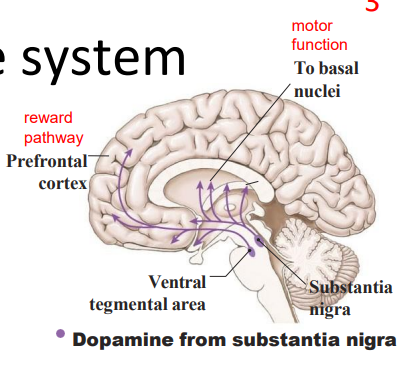
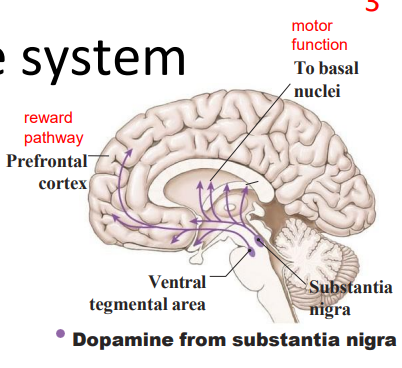
- substantia nigra means black substance
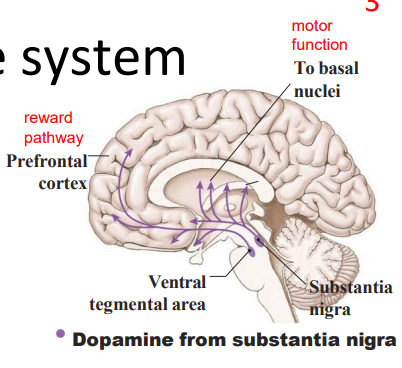
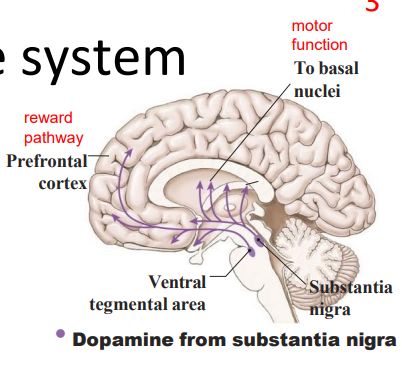
The dopamine system
- substantia nigra, ventral tegemental area - fibres spread to specific regions
- Excitatory or inhibitory (region dependent - different receptors)
Dopamine: main focus/desire neurotransmitter:
- responsible for our drive or desire to acquire (food, sex, an achievement, drug)
- makes people more talkative and excitable, often leaves them wanting more (addiction)
.
WAY TO RMBR: Drive, reward and pleasure
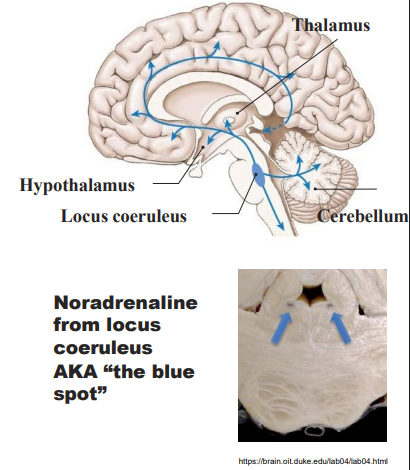
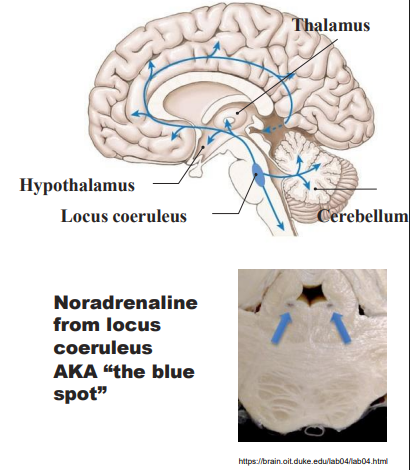
The Noradrenaline System
- from locus coeruleus (pons)
- mostly excitatory; fibres spread through cortex
- involved in numerous activites in the stress response
- the locus coereuleus is activated by stress -> NA -> alters cognitive function (through the prefrontal cortex), increaeses motivation
- pain control (anti-nociceptive)
.
WAY TO RMBR: ANxiety, arousal and pain control
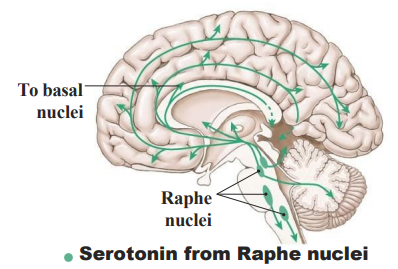
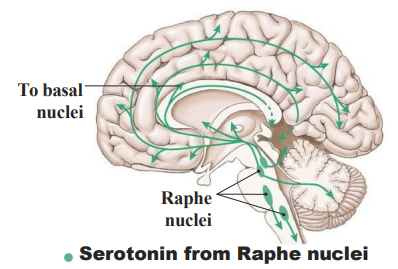
The Serotonin System
- From Raphe Nuclei (medulla, pons, midbrain)
- usually inhibitory, fibres to specific cortex regions (dense in frontal lobe and corticolimbic projections)
- Serotonin: main well-being/satisfaction neurotransmitter (it allows us to be content and happy, keeps mood under control by helping with sleep, calming anxiety and relieving depression
- pain control (anti-nociceptive)
.
WAY TO RMBR: Safe, happy, relaxed, euphoric and low-pain
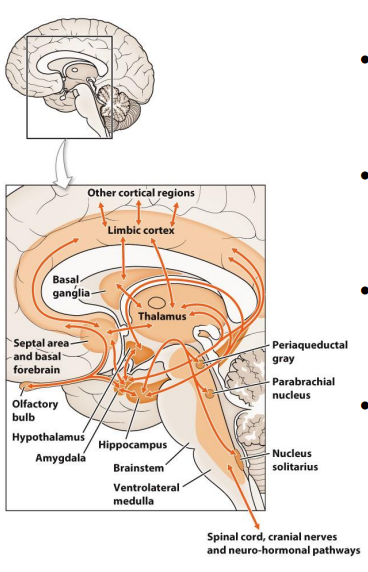
The Limbic System EXPLAINED
- a set of structures involved in the processing of emotion, motivation, learning and memory
- core structures: hypothalamus, amygdala and hippocampus (also nuclei of midbrain and brainstem)
- they also work closely with certain circuits through the basal ganglia and cortex
- integrate and involve all the neurohormonal control systems (in different ways)
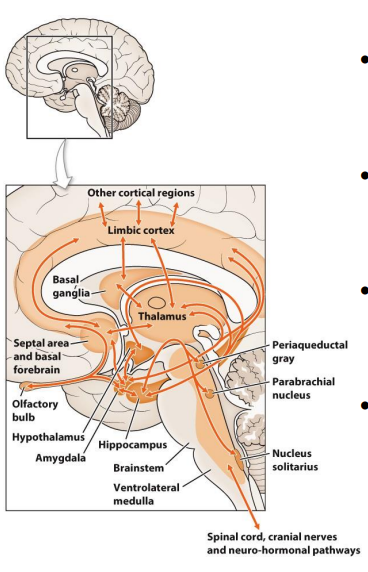
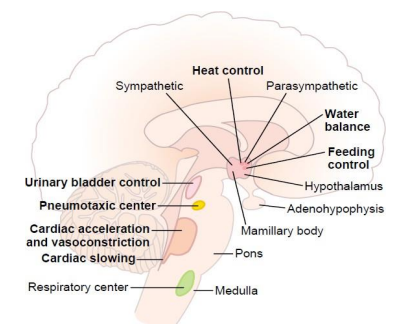
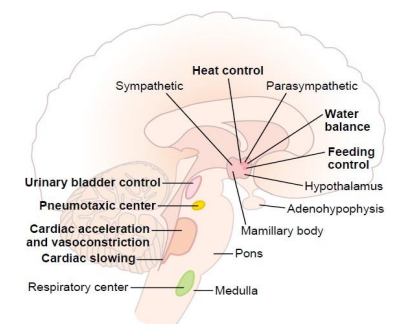
Hypothalamus - Homeostasis
- plays a role in regulating most basic physiological
- hunger, thirst, temperature, arousal, sleep etc.
- central command centre of the ANS
- receieves signals from the brainstem, (serotonin and dopamine) and integrates to influence behaviours like food intake and mood
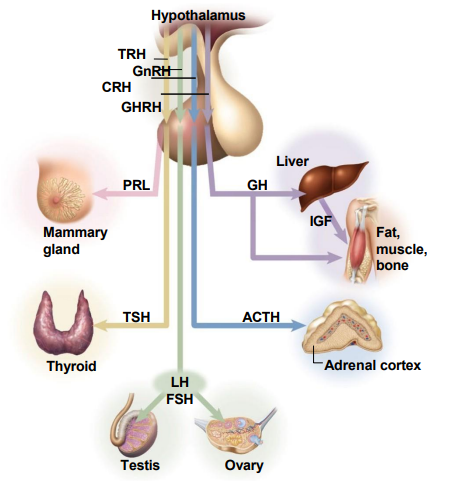
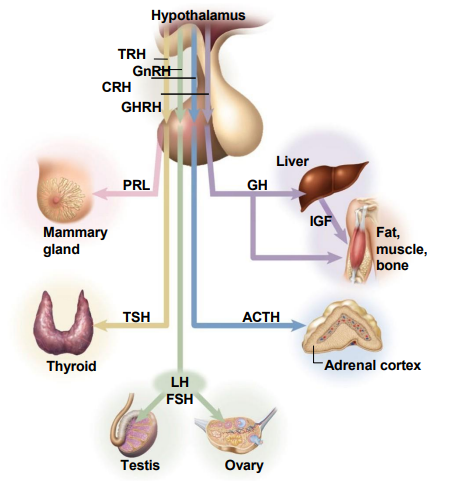
Links nervous and endocrine systems - hypothalamus controls the pituitary which controls everything
- hypothalamus produces releasing hormones
- control levels of growth hormone, thyroid hormone, adrenal cortex steroids, sex steroids
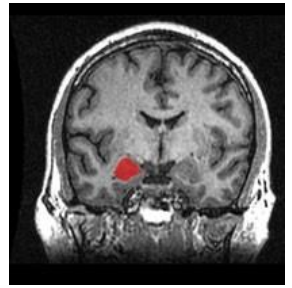
Amygdala - Fear, Focus and Reward
- decision making (drive), and emotional responses (including desire, fear, anxiety and aggression)
- emotional arousal and emotional learning (communicates with hippocampus)
- reward (dopamine) pathways too
.
- amygdala is triggered if someone has had trauma
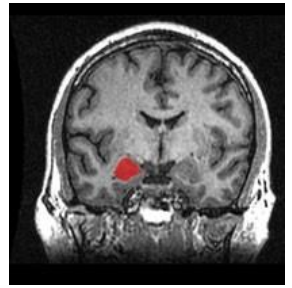
Hippocampus = Learning and memory
- regulates memory formation and storage
- regulates glutamate neurotransmission via NMDA receptors
- fed by pleasure (dopamine) and fear (amygdala) pathways
.
DONT HAVE TO MEMORISE HTE BOTTOM THING

TAKE HOME MESSAGES
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 40
