WEEK 1 CO2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
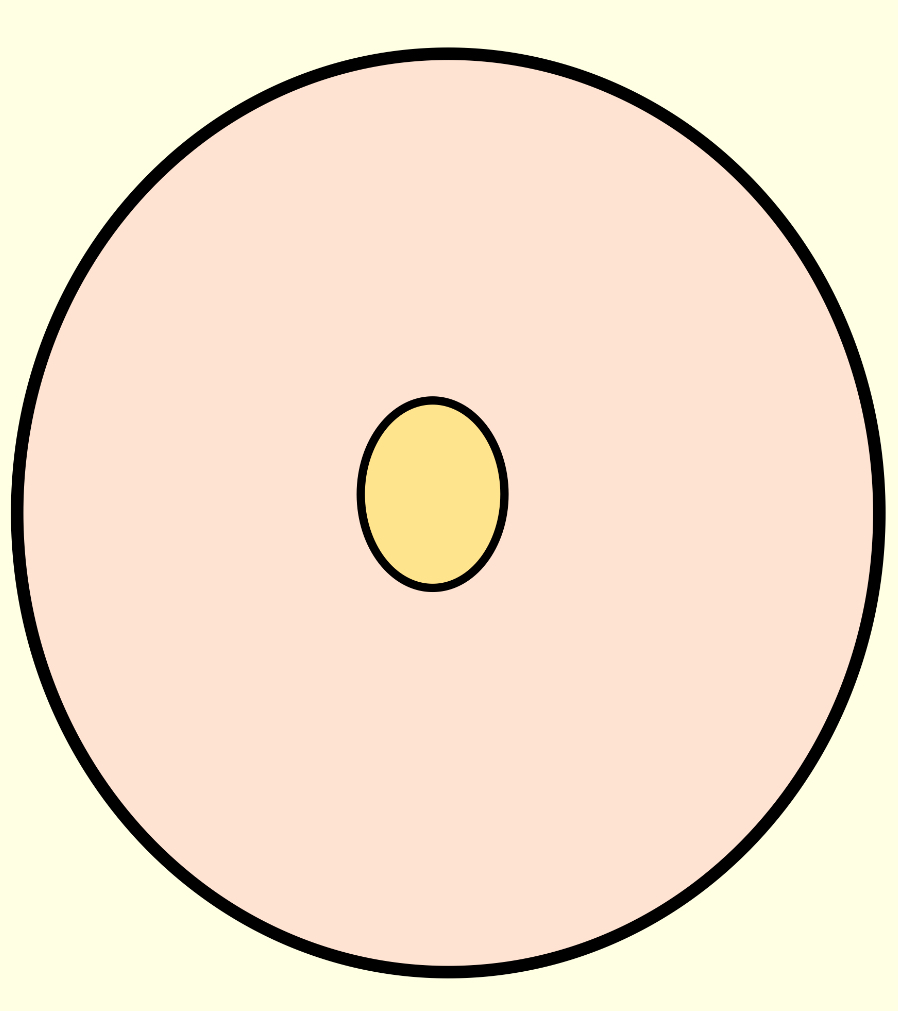
What is the C:D ratio of this?
0.2
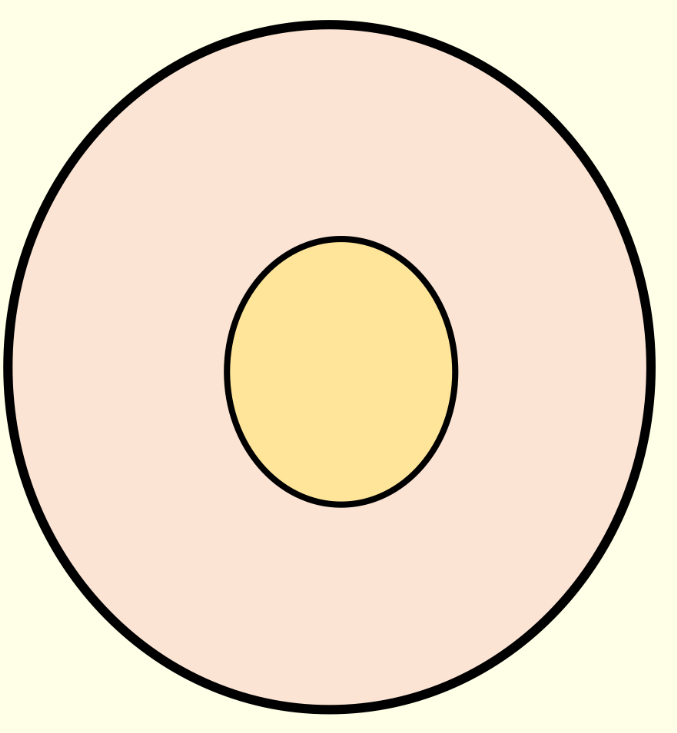
What is the C:D ratio of this?
0.4
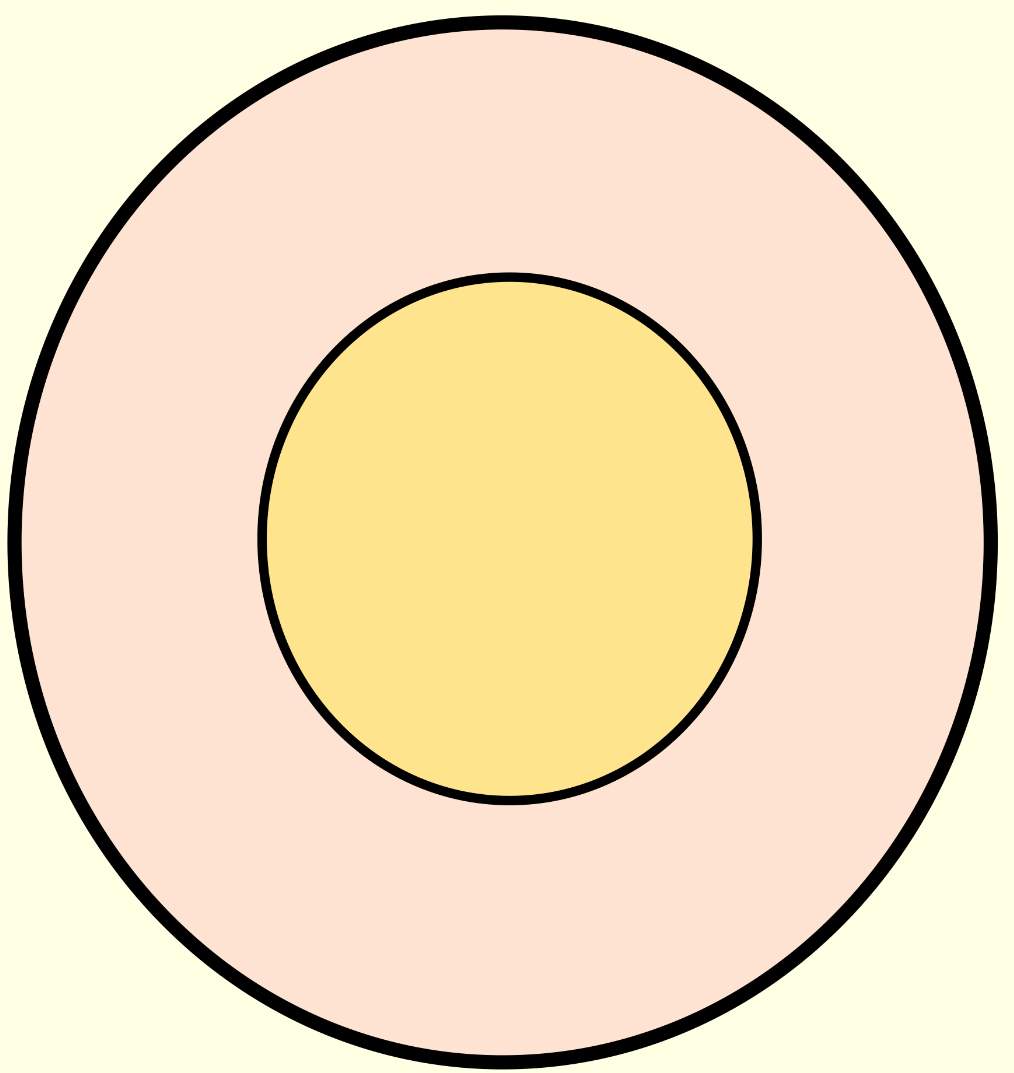
What is the C:D ratio of this?
0.6
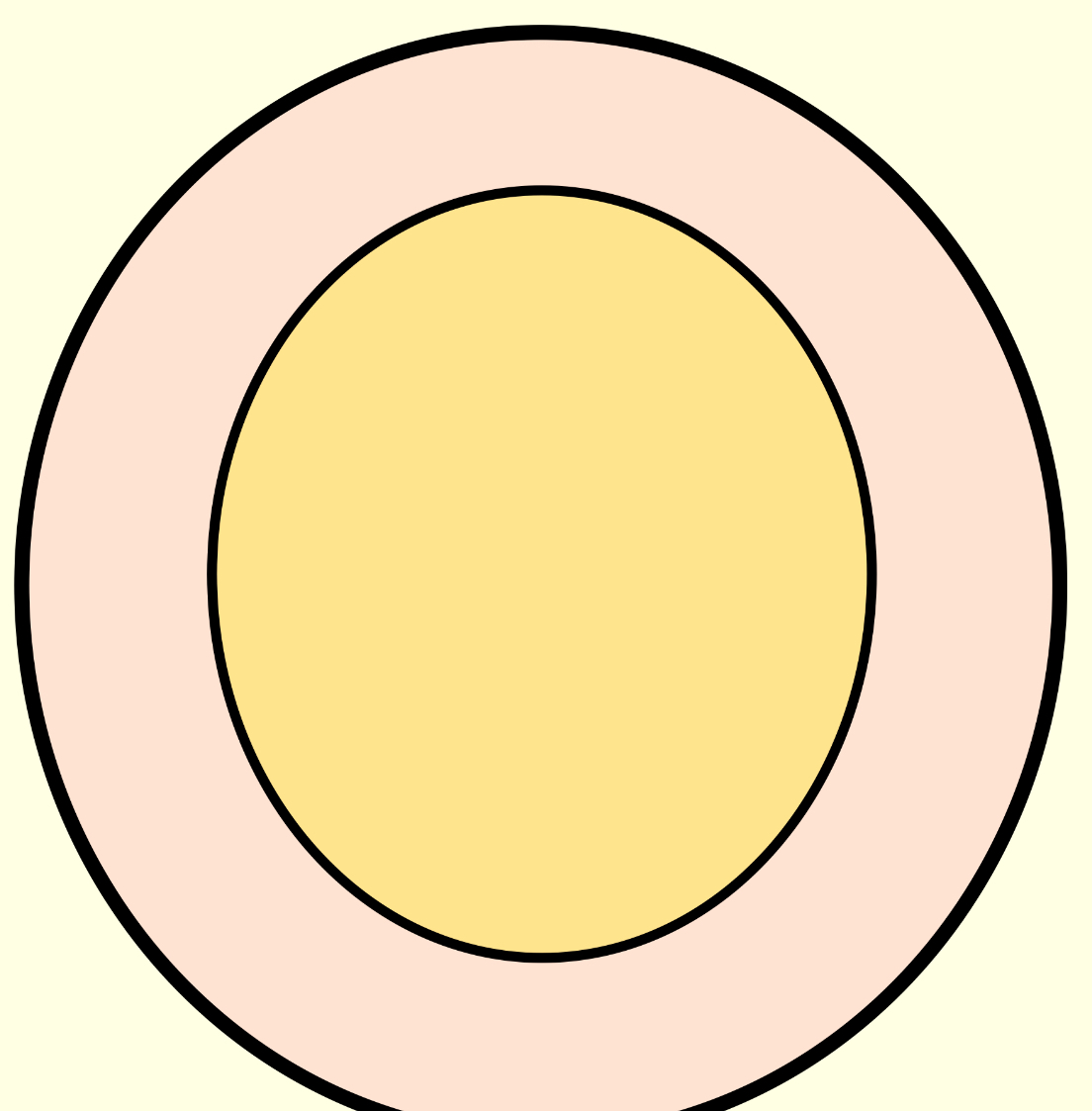
What is the C:D ratio of this?
0.8
What are the 4 bad signs when looking at the optic disc?
eccentric cup (not placed centrally)
Notch in rim
Asymmetry between the 2 eyes
Pale colour
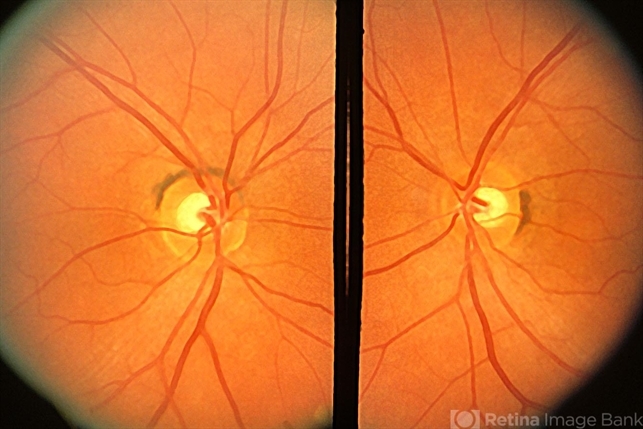
What is this and should we be worried?
Choroidal crescent, it’s normal
choroidal pigment visible because retinal tissue does not abut the optic nerve
How does a normal AV crossing look like?
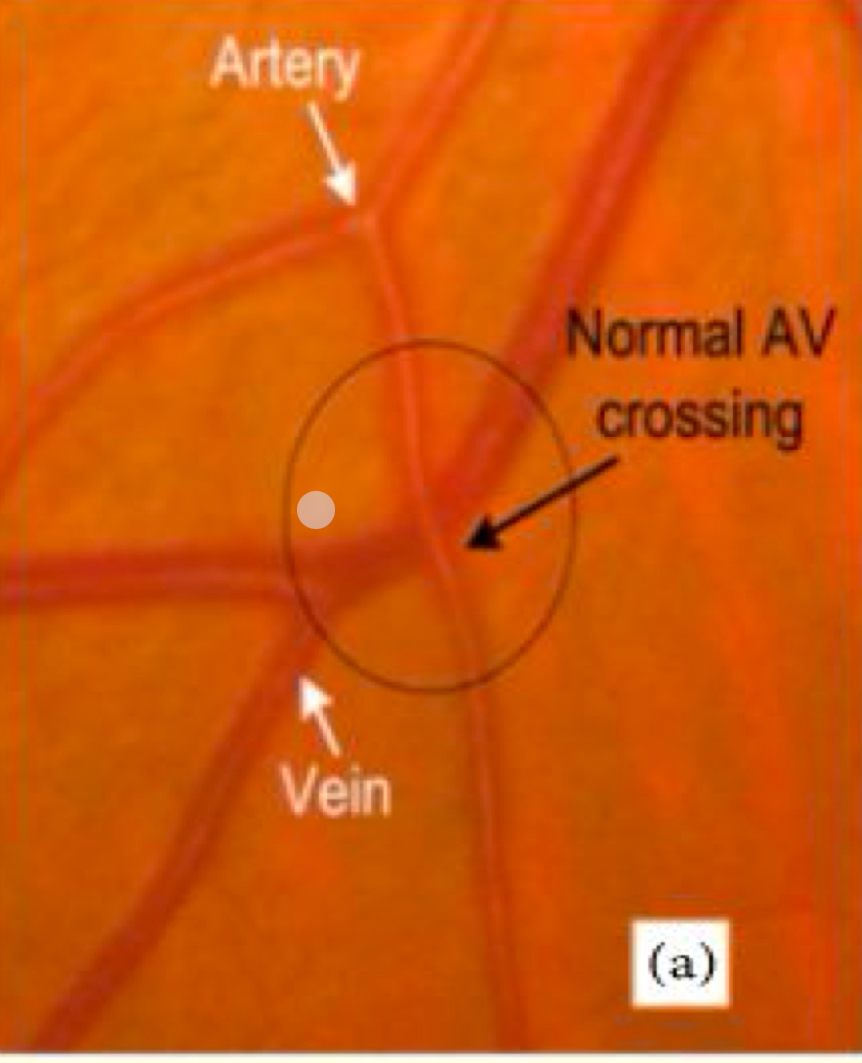
Can you explain an AV crossing?
The artery overlaps on the vein
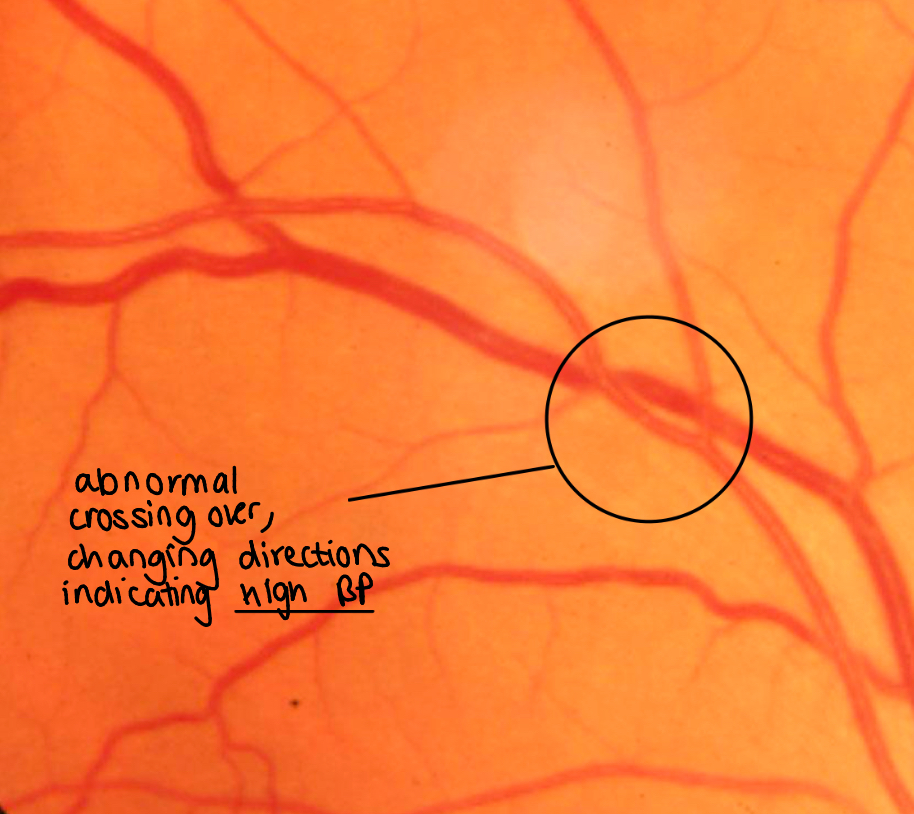
Can you describe an abnormal AV crossing and how it might occour?
AV nicking - The artery presses in the vein at the crossing causing constriction
Hypertension
What scenario would you use retinoscopy?
new px
Children
Poor subjective responses
Non-English speaking
Learning difficulties
Young hyperope (accommodate a lot)
During retinoscopy, which meridian do you neutralise first and why?
positive/with meridian
The other meridian will show an against movement, so we end up using minus cyl
How do you check your final rx is accurate with ret?
move forward - with movement
Moving back - against movement

When can the scissors reflex be seen?
spherical aberration
Distorted cornea
Tilted crystalline lens
Large pupil
Astigmatism
Kerataconus
What would you do if you saw the scissors reflex?
increase room lighting to reduce pupil size to cut out peripheral aberrations
Use bigger steps than 0.25D
What causes a dim reflex during ret?
high rx (espc in young patients)
Cataracts
Small pupils
What would you do if you saw a dim reflex?
Move closer to increase brightness of reflex, adjust WD accordingly
Start with higher powered lens (+5/-5 and check what direction)
How does an amblyopic optometrist perform ret if they can’t use one eye?
use good eye for both px eyes
Px fixates on ret light
Repeat with distance target using good eye on equivalent px’s eye
Apply difference in sphere found at distance to other eye’s ret result
What are common errors of ret?
wrong WD
Performing off-axis
Smudged lenses
Not focusing on centre of pupils
Blocking patients view, stimulating accommodation
What is an auto-refractor?
measures refractive state of the eye
No px or examiner judgement required
What are the advantages of auto refractors?
quick and convenient
Usually accurate and repeatable
Good for astigmatism
Useful for children, nonverbals
Provides 2nd objective measure
Reliable, valid
faster than ret
Can be delegated
Accommodation reduced with IR light
Accurate with cycloplegia (paralysis of eye muscle)
What are auto aspects of auto refractors?
auto centration
Auto firing
Auto fogging
What are the main principles of an autorefractor?
fundus is illuminated
Light is scattered and reflected
Reflected light is analysed
Scheiner principle
What principle do most auto refractors use?
Scheiner principle - two small bundles of light are imaged at the pupil, separation depends on refractive error
What image will an emmetrope produce as a result of the Scheiner principle?
Single image
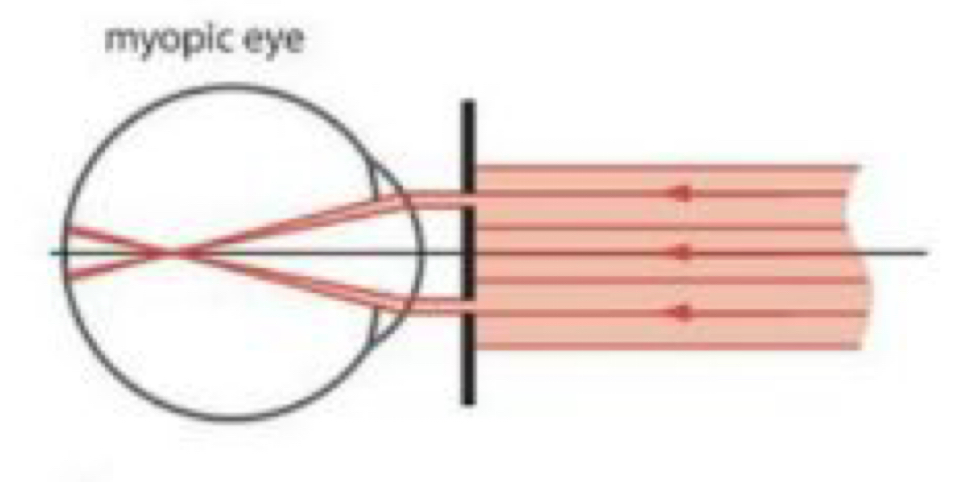
What image will an myope produce as a result of the Scheiner principle?
Double crossed
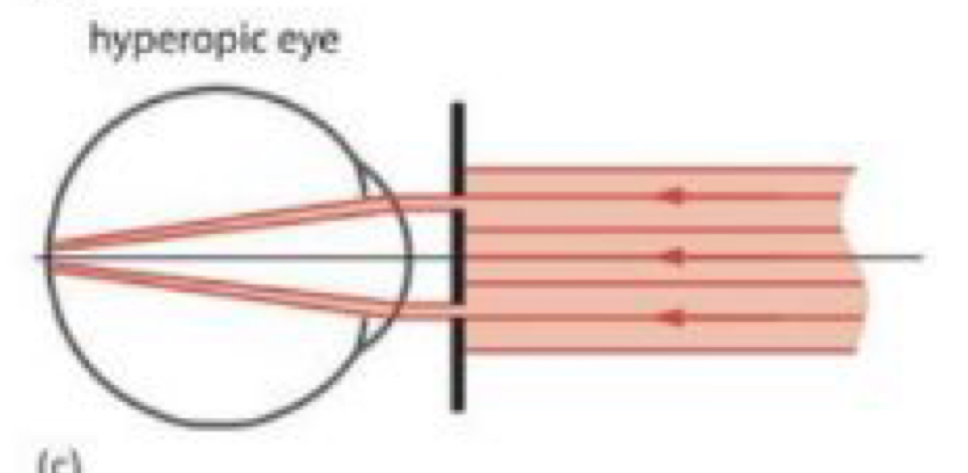
What image will an hyperope produce as a result of the Scheiner principle?
Double uncrossed
How does the Scheiner principle work for astigmatism?
2 IR LED’s imaged at pupil, separation depends on refractive error
For astigmatism, 4 LED’s used, 1 for each meridian
System moves back and forth until the diplopic images merge to give the refractive power for each meridian
What are some other autorefractor principles?
retinoscopic - observes direction and motion of light reflex
Basal optometry - uses a condensing lens and a moving target to form a sharp image on retina
What are the common characteristics of an autorefractor?
Near IR radiation
Pupil size dependant
Vertex distance must be accounted for
Accommodation needs to be controlled
Fixation target
What are the advantages of IR radiation?
Higher light yield
Effectively reflected from fundus
Invisible
Doesn’t stimulate accommodation or pupil reflex
What are the disadvantages of near IR radiation?
fundus reflects IR more diffusely than visible light
More light used
Unsure of surface of reflection
-0.50/-0.75 must be added to compensate for refraction with visible light
What are the two types of end point auto refractors?
nulling principle - instrument changes the optical system until refractive error is neutralised
Non-nulling - measurement is made by analysing the characteristics of the radiation exiting the eye
For autorefractor to work, what size should they be bigger than?
More than 2.5-3.00 mm
Why is vertex distance important in autorefractors?
Autorefractors measure refraction at corneal plane but converted to spectacle plane at a choice of distances
Why are fixation targets important in autorefractors?
helps control gaze and accommodation
Px must fixate properly = accurate = reliable
How do autorefractors control accommodation?
distant fixation targets (optically distance, subjectively near)
Auto-fogging - blurring image to relax accommodation
Near IR is used to prevent accommodation being triggered
What are uses of autorefractors?
preliminary refraction
Screening of children
Confirmation of difficult/unusual refractions
Refraction of non-verbal px
Research
What are the main sources of error in autorefractors?
changes in accommodation, pupil diameter and fixation
Diurnal variation
Media opacities
Keratoconus
Refractive surgery
Unstable tear film
Ptosis/long lashes
Intrinsic inaccuracy of instrument
What are the disadvantages of autorefractors?
expensive
May be unreliable with patients w: Aphakia, cataracts, IOL implants, poor fixation, small pupils, media opacities
Accommodation (proximal)
range limitation (+15 to +23D, -12 to -20D)
No qualitative info eg keratoconus, cataract
What is photorefraction?
uses camera and infrared LED’s place eccentrically to visual axis
Eye is focused = uniform brightness at pupil
Defocused = light forms a gradient which is used to calculate rx
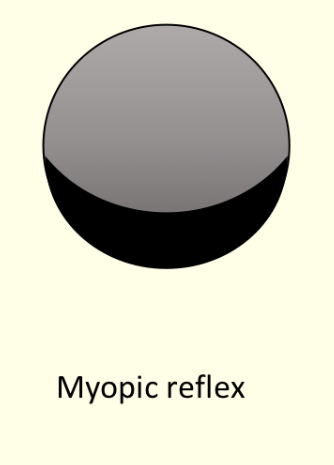
What does a myope look like during photorefraction?
Ilumiance at top, black at bottom
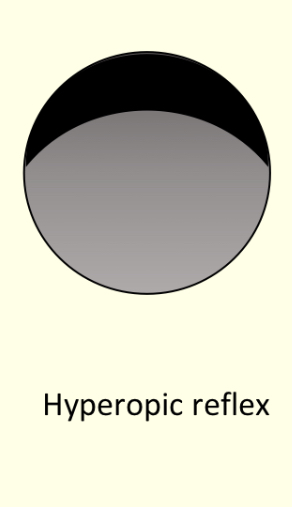
What does a hypermyope look like during photorefraction?
Illuminance at bottom, black on top
What are advantages of photorefraction?
binocular - test both eyes simultaneously
Good with young children and uncooperative px
Screening tool
iPhone attachment
What are disadvantages of photorefraction?
calibration must be accurate
Depend on ethnicity
Calibration error increases with refractive error