Exam prep
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
An excipient is:
A dosage form designed for a route of administration and in some cases with specific administration devices to facilitate the desired effect.
The active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or pure drug substance exhibiting a pharmacological effect.
An inert ingredient that is combined with the drug to form the dosage form.
The rate and extent of drug absorption
An inert ingredient that is combined with the drug to form the dosage form
All the following are benefits of developing a controlled release formulation to deliver the active pharmaceutical ingredient, except:
To reduce the frequency of drug administration, thus improving the patient’s compliance.
To ensure that the drug effect does not decline rapidly, which provides. continued absorption for a longer period
To produce the desired effect without the intense side effects that may be caused by rapidly rising high drug levels in the body.
To enable the rapid dissolution of the active ingredient in the buccal cavity to avoid the first-pass metabolism.
To enable the rapid dissolution of the active ingredient in the buccal cavity to avoid the first-pass metabolism
Which of the following dosage forms can avoid first-pass metabolism?
Orally disintegrating tablets.
Oral solution.
Delayed-release tablets.
Sublingual tablets.
sublingual tablets
Disintegration of the tablet is a crucial step that must take place:
Before dissolution and absorption.
After dissolution but before absorption.
After dissolution and absorption.
Before administration.
before dissolution and absorption
Which of the following statements about suspensions is false?
They are preparations of finely divided drugs (solids) in a suitable fluid vehicle, in which they are insoluble, with the help of a suspending agent.
Suspensions have the advantage over solid dosage forms in that they are presented to the body in fine particle size, ready for dissolution immediately upon administration.
Not all oral suspensions are intended to be dissolved and absorbed by the body. For instance, the suspended kaolin or attapulgite acts locally in the intestinal tract without being absorbed.
Drugs administered in aqueous suspensions are absorbed much more rapidly than those administered in solutions.
Drugs administered in aqueous suspensions are absorbed much more rapidly than those administered in solutions
Which one of the following statements is false concerning suppositories?
They are solid bodies of various weights and shapes intended for introduction into a body orifice where they soften, melt, or dissolve; release their medication; and exert their effects.
They can be used when the oral route is precluded because of vomiting or to avoid extensive first-pass metabolism.
They can be solid, liquid, or semisolid.
Their systemic absorption can be unpredicted, due to the anatomy of the hemorrhoidal veins.
They can be solid, liquid, or semisolid
Which one of the following is a true disadvantage of the parenteral route?
Parenteral route is not ideal for emergencies due to erratic absorption.
Drugs administered parenterally experience extensive first-pass metabolism.
Once the drug is injected, there is no retreat, i.e., once the substance is in the tissues or bloodstream, removal of the drug due to an overdose is most difficult.
It cannot be used when patients are uncooperative, unconscious, or otherwise unable to accept oral medication
Once the drug is injected, there is no retreat, i.e., once the substance is in the tissues or bloodstream, removal of the drug due to an overdose is most difficult
Which statement is false concerning subcutaneous injection?
SC injection entails injection through the skin into the loose subcutaneous tissue
They are prepared as aqueous solutions or suspensions, and given in relatively small volumes, 2 mL or less.
If the patient is to receive frequent injections, it is best to alternate injection sites to reduce tissue irritation.
SC injection can be given as a large volume (e.g., 500 ml) slow drip infusion.
SC injection can be given as a large volume (e.g., 500 ml) slow drip infusion
Diabetic patients who switched the subcutaneous insulin injection site from abdominal to the thigh, and then performed physical exercise such as jogging, should expect:
Faster insulin absorption.
Slower insulin absorption.
No noticeable effect on insulin absorption.
Hypotension.
Faster insulin absorption
Which of the following dosage forms is completely unable to avoid first pass metabolism?
Rectal suppository.
Sublingual tablets for buccal cavity/sublingual absorption.
Orally disintegrating tablets (ODT) for intestinal absorption.
Transdermal patches.
Orally disintegrating tablets (ODT) for intestinal absorption
Choose the correct statement concerning epicutaneous delivery systems
If the medication is intended for topical effect, systemic absorption will probably be considered as an added benefit.
Transdermal dosage forms aim to provide local effect.
Nitroglycerin transdermal patches are intended for local (topical) drug delivery.
Ointments are usually more greasy and contain less water content compared to creams
Ointments are usually more greasy and contain less water content compared to creams
Which statement is true concerning the chelating agent?
It is a substance that forms stable water-soluble complexes with metals; and it is used as stabilizers to complex heavy metals that might promote instability.
It decreases or increases pH in preparations or protects compounds from rapid change in pH.
It prevents growth of microorganisms in liquid and semisolid preparations.
It makes a solution similar in osmotic characteristics to physiologic fluids, such as ophthalmic, and parenteral fluids.
It is a substance that forms stable water-soluble complexes with metals; and it is used as stabilizers to complex heavy metals that might promote instability
Choose the correct statement concerning tablet excipients.
Antidiarrheal agents are considered tablet excipients.
They serve many functions including protecting the API from low gastric pH.
They tend to lower the API dissolution rate.
Disintegrants are no longer needed as they may result in tablet coat cracking.
They serve many functions including protecting the API from low gastric pH
Which of the following accurately defines the shelf-life:
It is the time required for 10% of the initial concentration to disappear.
It is the reduced life assigned to a drug product by a pharmacist as the product has been repackaged/reconstituted using a manufactured product or compounded from a manufactured product.
It is the time required for 50% of the initial concentration to disappear.
It is the change in drug or excipient concentration as a function of time
It is the time required for 10% of the initial concentration to disappear
What is defined as “the breaking of a molecular bond by reaction with water”?
Photochemical degradation.
Hydrolysis.
Isomerization.
Polymerization.
Hydrolysis
What is defined as “it is the process by which an optically active molecule with one chiral center is converted to its mirror image”?
Photochemical degradation.
Hydrolysis.
Isomerization.
Polymerization.
Isomerization
The T90 of a drug solution is 60 days in the refrigerator (5 ˚ C). What would the T90 be at room temp (25 ˚ C), assuming Q10 = 2?
1 day.
5 days.
10 days
15 days
15 days
To know the reaction order of the degradation of VX-870 in acidic solutions, a chemist plotted the drug concentrations (Y-axis) over time (X-axis). The chemist found that when Ln of the drug concentration (Ln C) is plotted against time, a straight line (R2 = 1) will be obtained. The reaction order is therefore:
Zero order
First order
Second order
Third order
First order
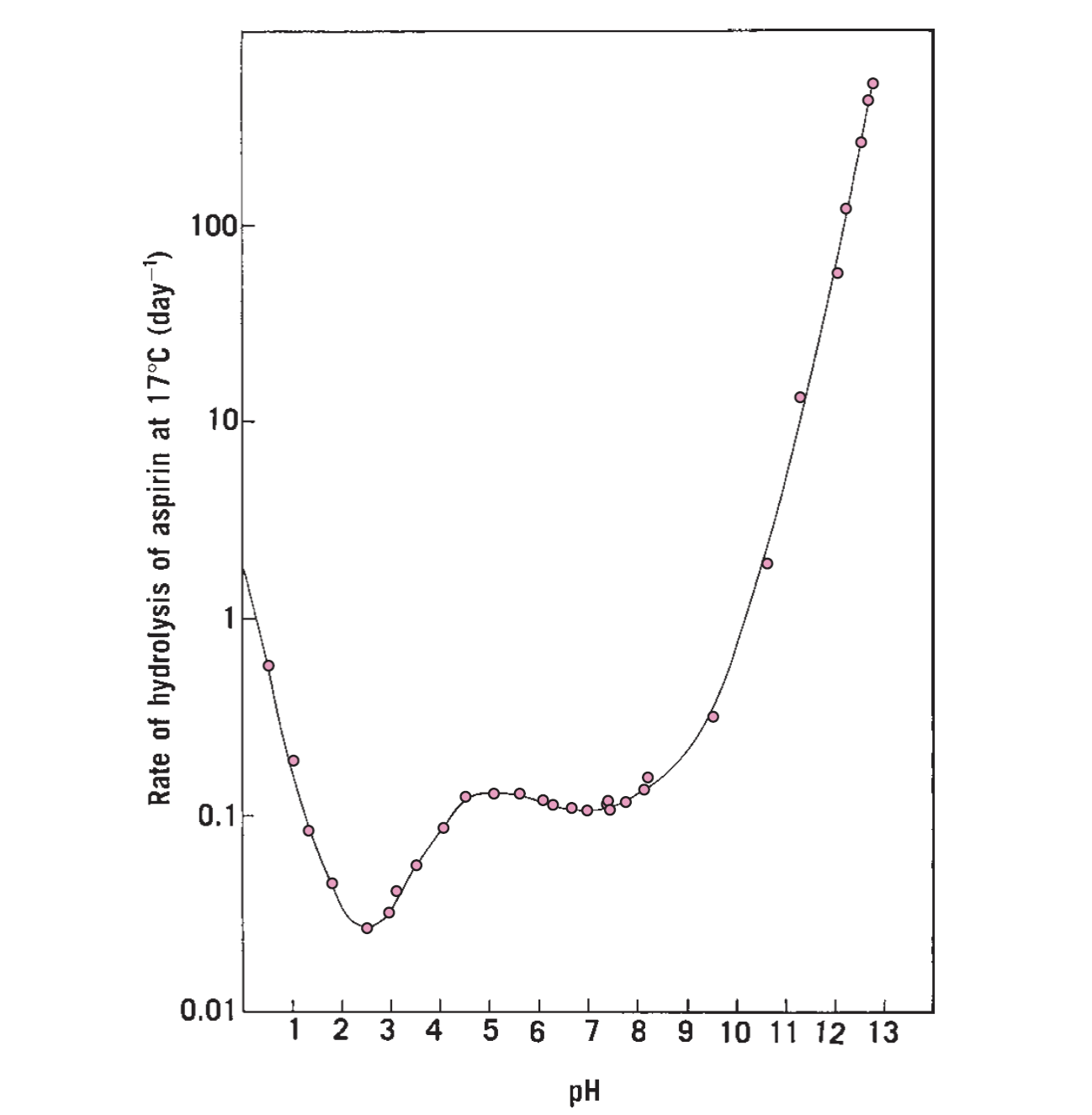
Based on the aspirin pH-stability profile in the figure attached, what should the storage pH of aspirin suspension that maintains the highest degree of stability?
pH 2.5
pH 5
pH 10
pH 13
pH 2.5
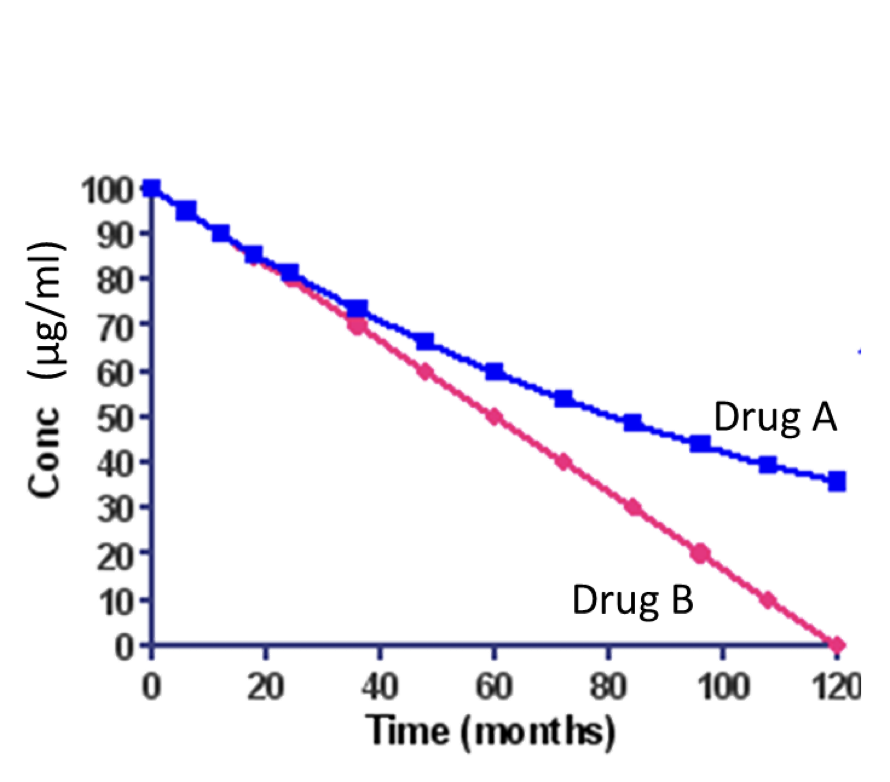
In the graph, which drug degrades following a zero-order reaction?
Drug A (blue)
Drug B (red)
Drug A and B
None of these drugs degrades following zero order reaction.
Drug B
All the following statements about weak electrolytes are true, except:
If a drug is a weak electrolyte, it should partially dissociate in water and will conduct electricity.
Most drugs are weak electrolytes and can be further classified as weak acids or weak bases.
Pseudoephedrine HCl is a salt of a weak electrolyte, as HCl is the acid and pseudoephedrine is the conjugate weak base.
Weak electrolytes fully dissociate in aqueous solutions.
Weak electrolytes fully dissociate in aqueous solutions
Colligative properties include all the following, except:
Lowering of vapor pressure.
Increasing of boiling point.
Decreasing of freezing point.
Change in the refraction of light
Change in the refraction of light
The Osmolarity of 5 M HCl (strong acid) after ionization in water is:
1 Osmol
2 Osmol
5 Osmol
10 Osmol
10 Osmol
If we add a mixture of urea and NaCl solutions, both isosmotic to the RBCs. Urea can cross the RBC membrane, while NaCl cannot. All the following statement are true about this situation, except:
RBCs will burst.
Urea will diffuse into the RBCs, due to its membrane permeability, and thus the urea solution will be considered hypotonic.
The isosmotic NaCl solution will also be considered isotonic.
An isosmotic solution can also be considered isotonic regardless of RBCs membrane permeability.
An isosmotic solution can also be considered isotonic regardless of RBCs membrane permeability
The small increment in gram equivalents (gEq) of the strong acid or base per liter added to the buffer solution to produce a pH change of pH is defined as:
The buffer capacity.
pKa of the weak acid in the buffer.
pH at which the weak acid of the buffer is 50% ionized.
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
The buffer capacity
The following approaches are used to prepare ophthalmic solutions with minimum tissue irritation, except:
Ophthalmic solutions should be prepared at the physiological pH.
The buffer capacity of ophthalmic solutions should be kept low.
The volumes of the ophthalmic solutions used should be small.
Ophthalmic solutions should be hypertonic to avoid irritation.
Ophthalmic solutions should be hypertonic to avoid irritation
If you want to prepare a solution of a weakly acidic drug (pKa 5.2). What is the recommended pH of the solution?
3.5
4.8
5.2
7.8
7.8
Which statement is true concerning miscibility of aliphatic alcohols in water?
Increasing the number of polar groups increases their miscibility in water.
Increasing the chain length will increase their miscibility in water.
Branching of the carbon chain will decrease their miscibility in water.
N-butyl alcohol is more miscible in water comparted to tertiary butyl alcohol despite even though they both have a 4-carbon chain.
Increasing the number of polar groups increases their miscibility in water
Partition coefficient:
Is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium, usually octanol and water.
Usually has negative values in case of lipophilic compounds.
Is usually high in freely water-soluble compounds.
Is usually low in BCS class II drugs.
Is the ratio of concentrations of a compound in a mixture of two immiscible solvents at equilibrium, usually octanol and water
Reducing the solubility of some drugs via the development of less soluble esters can be useful for the following purposes, except:
Protecting parent drug from excessive degradation (e.g. clarithromycin stearate)
Masking bitter taste of the parent drug.
Provide prolonged action of the drug.
Providing immediate fast action of some medications like pain killers.
Providing immediate fast action of some medications like pain killers
Which of the following is not true concerning Cmax:
It represents the peak plasma concentration.
It can be achieved when time = 0 following extravascular administration.
It is achieved at Tmax
It is equal to C0 following IV administration.
It can be achieved when time = 0 following extravascular administration
Which of the following statements accurately defines the onset time?
It is the time during which the plasma concentration is above the MEC.
It is the time at which plasma concentration intersects with the MEC during elimination following extravascular administration.
It is the time at which plasma concentration intersects with the MEC during absorption following extravascular administration.
None of these statements is true.
It is the time at which plasma concentration intersects with the MEC during absorption following extravascular administration
Disintegration testing can be used instead of dissolution testing in the following cases, except:
The product under consideration is rapidly dissolving (dissolution >80% in 15 minutes at pH 1.2, 4.0, and 6.8).
The drug product contains drugs that are highly soluble throughout the physiological range (dose/solubility volume <250 mL from pH 1.2 to 6.8).
The product is intended for the sublingual route of administration.
A relationship to dissolution has been established or when disintegration is shown to be more discriminating than dissolution and dissolution characteristics do not change on stability.
The product is intended for the sublingual route of administration
Reduction of the particle size of drug particles can enhance dissolution rate of which of the following drugs?
Ibuprofen (BCS class II drug).
Paracetamol (BCS class I drug).
Cimetidine (BCS class III drug).
Caffeine (octanol/water partition coefficient -0.07)
Ibuprofen (BCS class II drug)
After the tablet is administered orally, the correct order of the rate processes is as follows:
Disintegration of the drug product into small fragments, dissolution of the drug in an aqueous environment, and permeation across cell membranes into the systemic circulation.
Dissolution of the drug in an aqueous environment, disintegration of the drug product, and finally permeation across cell membranes into the systemic circulation.
Dissolution of the drug in an aqueous environment, degradation of the active ingredients into degradation products, and release of the drug,
Disintegration of the drug product, degradation of the active ingredient into degradation product, release of the drug, and permeation across cell membranes into the systemic circulation.
Disintegration of the drug product into small fragments, dissolution of the drug in an aqueous environment, and permeation across cell membranes into the systemic circulation
Which of the following is false concerning the duodenum and drug absorption?
The duodenum is the major site for passive drug absorption due to high surface area, and high blood flow.
The duodenum is a site where many ester prodrugs are hydrolyzed during absorption.
Duodenum is the favorable site for the absorption of many protein drugs due to the presence of the many proteolytic enzymes.
The presence of bile secreted in the duodenum from the common bile duct helps dissolve many drugs with limited aqueous solubility
Duodenum is the favorable site for the absorption of many protein drugs due to the presence of the many proteolytic enzymes
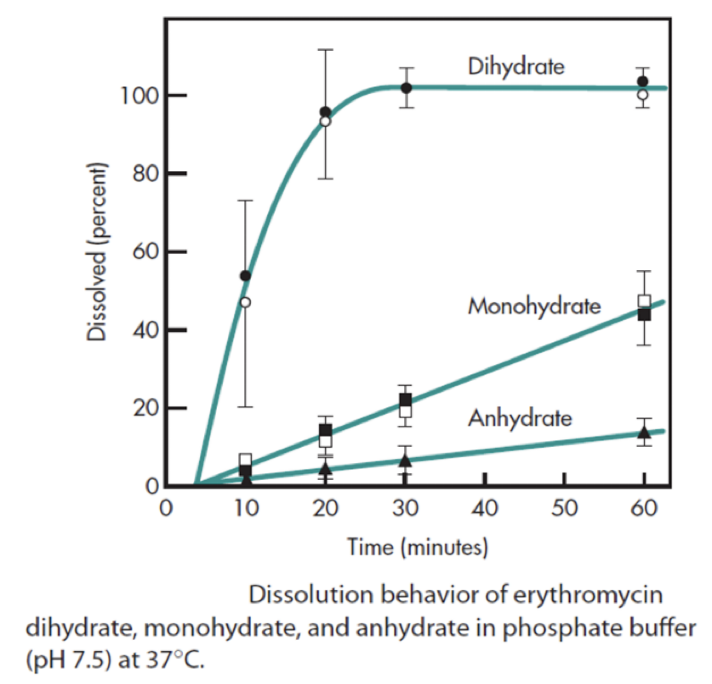
The graph shows the percent dissolved per time of erythromycin dihydrate, monohydrate, and anhydrous. Which of the following statements is false?
a. Dissolution rate of the dihydrate form is the highest.
b. The bioavailability of the anhydrous form is not expected to be higher than the dehydrate form.
c. Half of the dihydrate form is dissolved after 30 minutes.
d. Almost half of the monohydrate form is dissolved after one hour.
Half of the dihydrate form is dissolved after 30 minutes
How does achlorhydria affect the performance of enteric coated tablets?
High gastric pH associated with achlorhydria dissolves the enteric coat before reaching the intestine.
Short gastric emptying time associated with achlorhydria disrupts the composition of the enteric coat.
Shorter gastric residence time associated with achlorhydria results in poor bioavailability.
Enteric coat becomes harder and impossible to dissolve once it is exposed to high pH in achlorhydric patients.
High gastric pH associated with achlorhydria dissolves the enteric coat before reaching the intestine
How would a decrease in blood flow, like in the case of congestive heart failure, result in decreased oral drug absorption?
Congestive heart failure will decrease the rate of drug absorption from the intestinal tract via the mesenteric blood vessels, thus reducing bioavailability.
Congestive heart failure will result in increased portal circulation, thus increasing the rate of drug elimination by the liver through first pass effect.
Congestive heart failure will increase the activity of the microsomal liver enzymes.
Congestive heart failure will result in delayed gastric emptying, delaying intestinal absorption.
Congestive heart failure will decrease the rate of drug absorption from the intestinal tract via the mesenteric blood vessels, thus reducing bioavailability
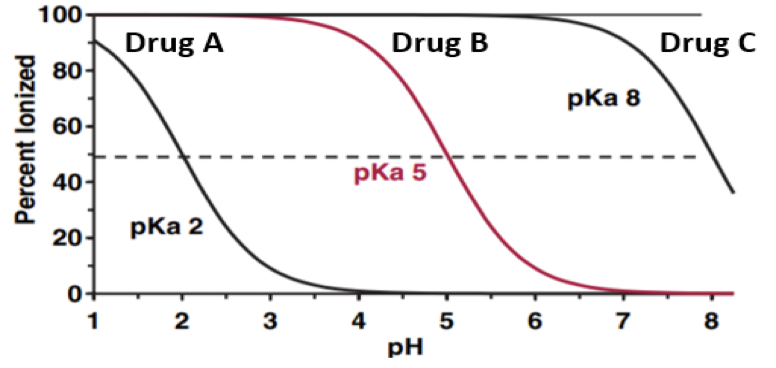
Which drug is mostly ionized at all physiological pH conditions?
Drug A
Drug B
Drug C
None of them.
Drug C
All the following statements are true concerning drug TR-598 (molecular weight 367 g/mole, weakly basic, pKa = 5), except one. Choose the false statement:
The percent ionized and percent unionized are equal at a physiological pH equal to 5
The colon comprises a relatively more favorable environment for the absorption of this drug, compared to the stomach.
acidification of urine is a correct approach to facilitate excretion of this drug.
At acidic pH lower than 5, this drug is more likely to cross membranes.
At acidic pH lower than 5, this drug is more likely to cross membranes
Based on PH partition hypothesis, what of the following is the preferred site of absorption of a weakly basic drug with pKa of 5.3?
Fed stomach (pH 1.5).
Fasted stomach (pH 2.5-3.0)
Duodenum (pH 6.5-7.0).
Buccal mucosa (pH 6.2)
Duodenum (pH 6.5-7.0)
A method by which a molecule gets inside the cell by moving in the narrow channels between cells, instead of moving through the cells.
Paracellular transport.
Transcellular transport.
Active transport.
Passive facilitated diffusion.
Paracellular transport
The major difference between facilitated diffusion transporters and active transporter is:
Only active transporters are saturable.
Facilitated diffusion transporters require energy, while active transporters don’t.
Active transporters concentrate the substrate against concentration gradient, while facilitated diffusion transporters work with concentration gradient.
Active transporters can be inhibited by inhibitors, while facilitated diffusion transporters can’t be inhibited by inhibitors.
Active transporters concentrate the substrate against concentration gradient, while facilitated diffusion transporters work with concentration gradient
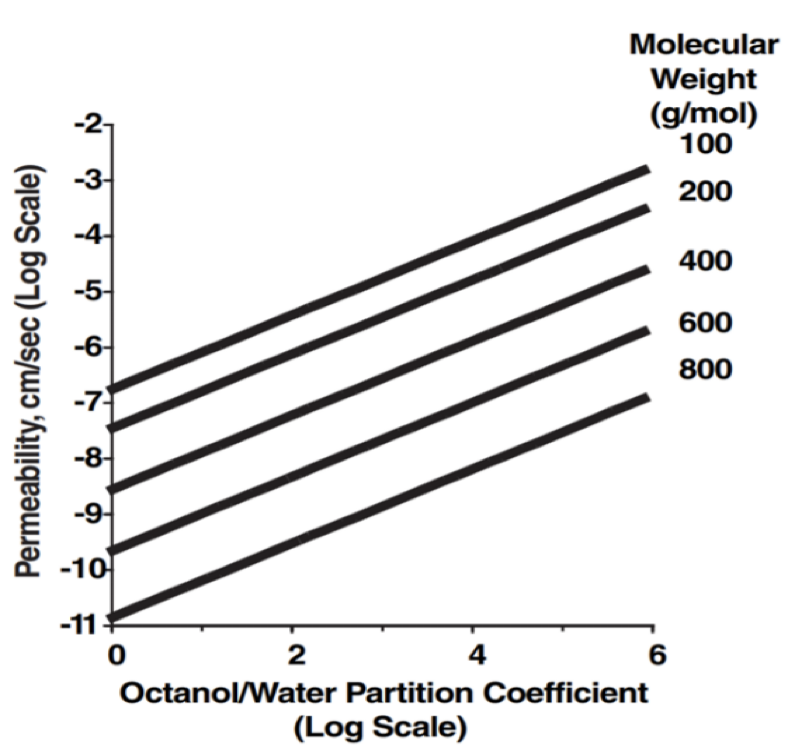
The following figure represents the relationship between permeability and partition coefficient. Which of the following is true?
Permeability increases as the molecular weight increases, regardless of the partition coefficient.
Permeability increases as the molecular weight increases while the partition coefficient is kept the same.
Permeability decreases as the molecular weight increases while the partition coefficient is kept the same.
Permeability increases as the partition coefficient decreases and the molecular weight decreases as well.
Permeability decreases as the molecular weight increases while the partition coefficient is kept the same
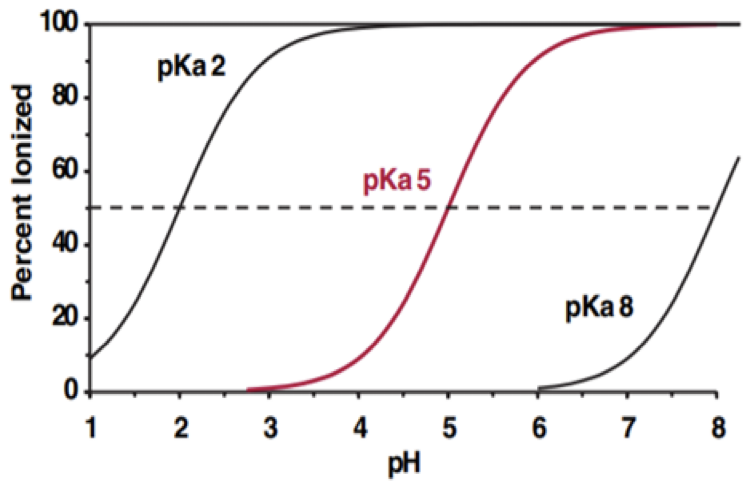
At which pH the drug with pKa 5 is 25% ionized?
1.72
4.52
5.53
7.61
4.52