Chapter 14 - Mass Spectrometry
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio (m/z) of ions. In simpler terms, it allows scientists to figure out the masses of molecules or atoms in a sample and sometimes their structure.
Easier analogy
It’s a machine that weighs tiny particles like atoms or molecules and helps figure out what they are made of.
can detect from parts to billion to parts per trillion
Mass Spectrometer (Insert Visual)
What is m/z
Mass-charge ration
Charge - can be +1,+2
If there is a low m/z - there is more deflection at the magnetic field
If there is a high m/z - there is less deflection in the magnetic field
Relative intesnity
The mass of abundance within the sample
How much of a specific type (mz) is measured
👉 Abundance = how many ions of that mass and charge reach the detector
Molecular ion
The main ion (parent ion), off which little fragments occur
Is formed when an entire molecule looses an electron and becomes positively charged
when z = 1 (charge = +1), then it is a parent molecule (because all of them have the same mass anyway - as it stems from the same sample - not fragments)
Fragment ions
Are formed when the molecular ion is broken as it is in an unstable state
when the high-energy electrons in the ionization chamber cause the bonds to break - causes the molecule to break into pieces
Base peak
The most abundant and stable fragment ion (typically a fragment ion)
Is assigned intensity of 100%
All other fragments are assigned their abundance in accordance to it
Why base peak is not always the largest fragment
Is measured in respect to abundance and stability
A smaller fragment could be more stable and be more abundant than something that is larger
Abundance - Stability
If something is of a higher stability, it is able to surpass the magnetic field and stay intact all throughout the process - more that isotope is identified - leads to higher abundance
ChatGPT Outline (Easy To Understand)
Stable fragment → survives → many ions → tall peak → base peak
Unstable fragment → quickly breaks → few ions → short peak
Fragmentation
Within the ionization chamber
Electrons are bombarded
Makes the molecule electron deficient (especially in covalent bonds - shared electrons - is a big problem for stability)
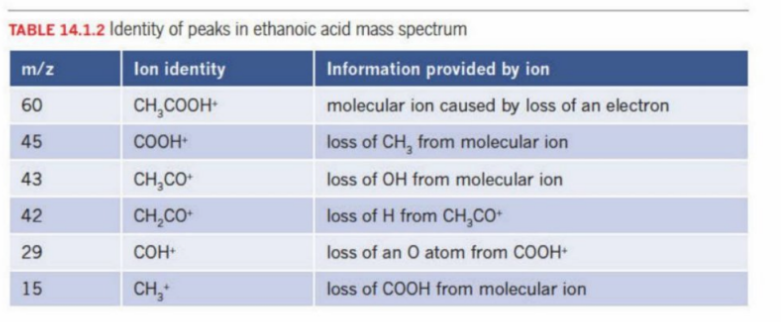
Insert Visual - Interpreting Mass Spectra
Identity Peaks of the graph above
Unclear
