Axial and Appendicular Skeleton
1/188
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
189 Terms
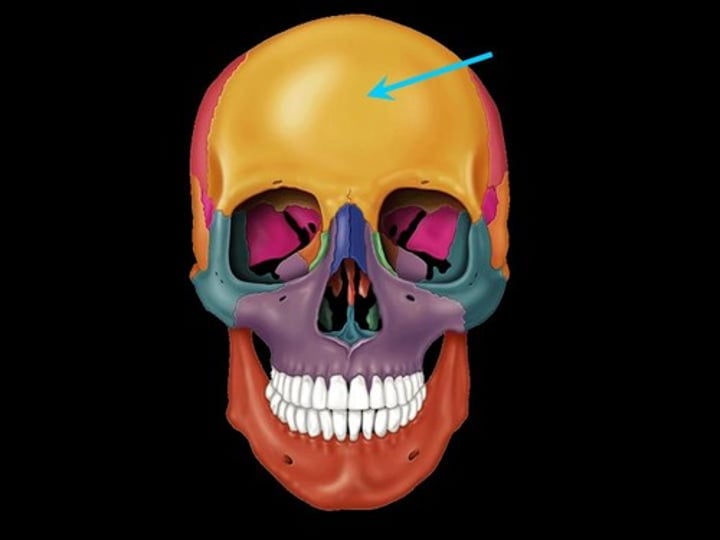
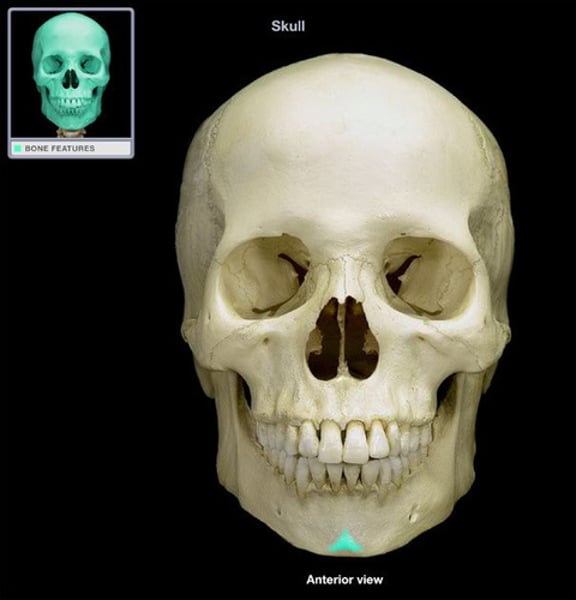
Frontal Bone (skull)
forehead bone
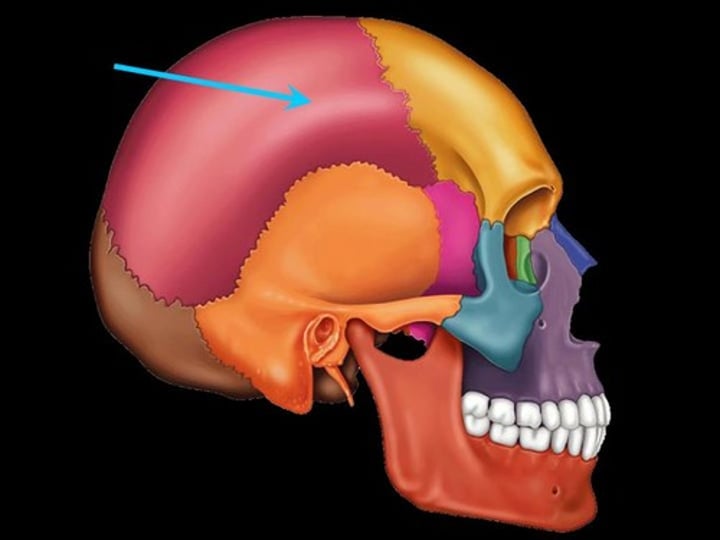
Parietal Bone (skull)
Bones that form the sides and top of the cranium.
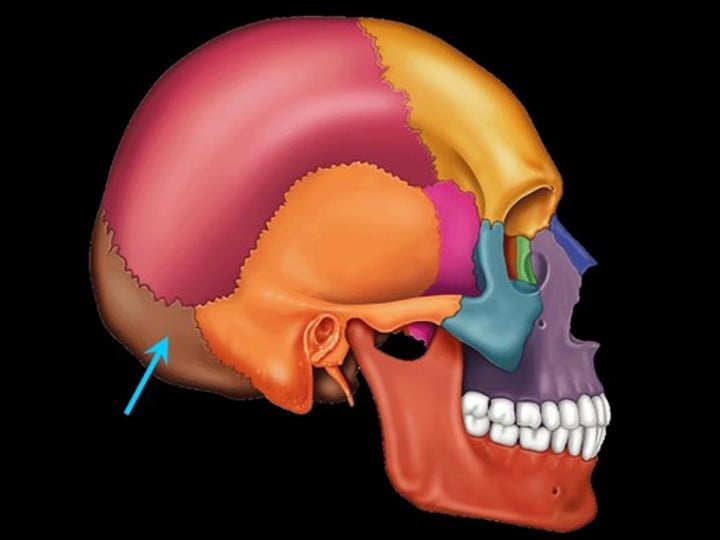
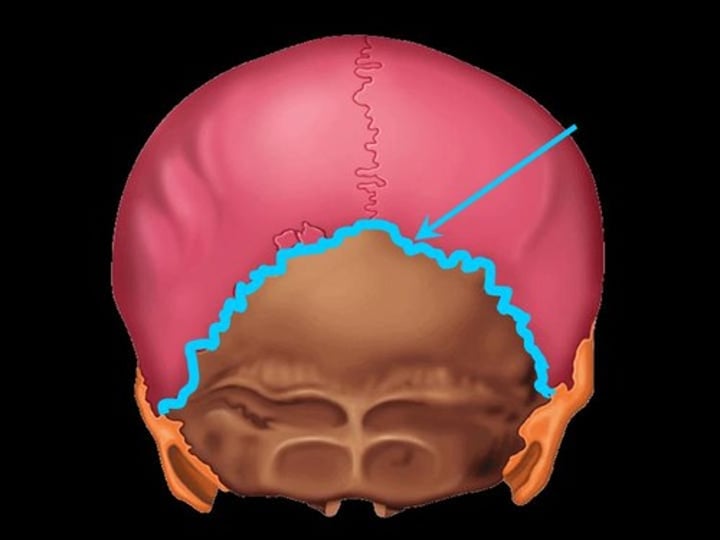
occipital bone (skull)
back of skull
Temporal Bone (skull)
Side of skull
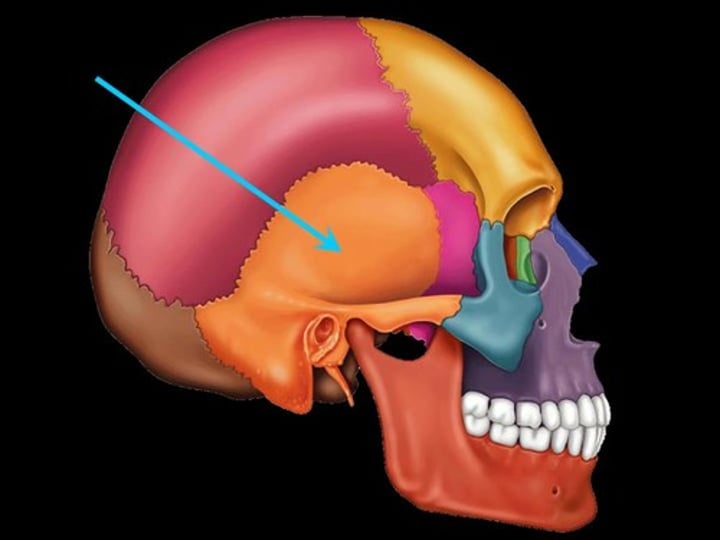
coronal suture (skull)
the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
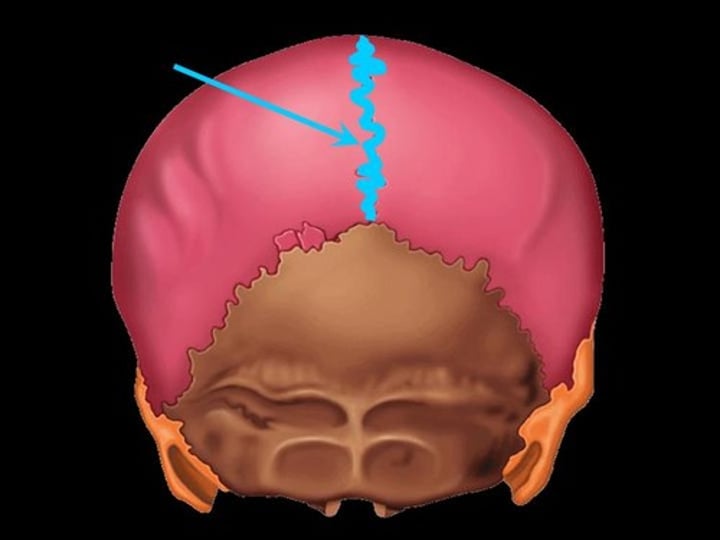
sagittal suture (skull)
the suture in middle vertical, separates parietal bones
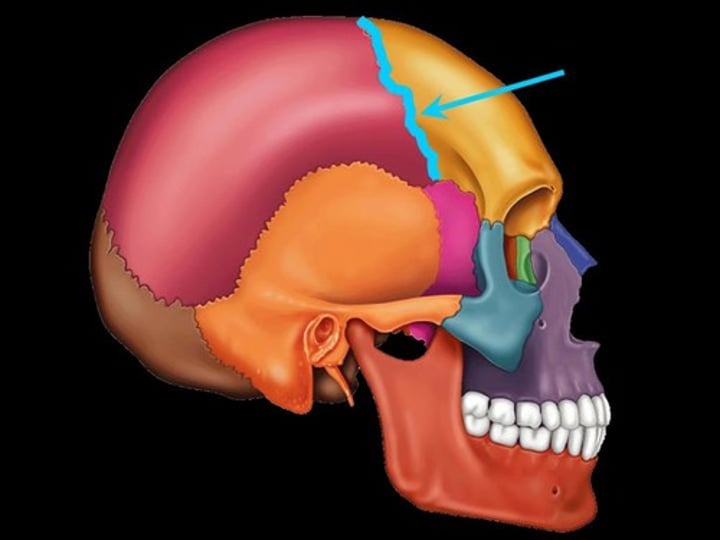
squamous suture
the suture between parietal and temporal bones
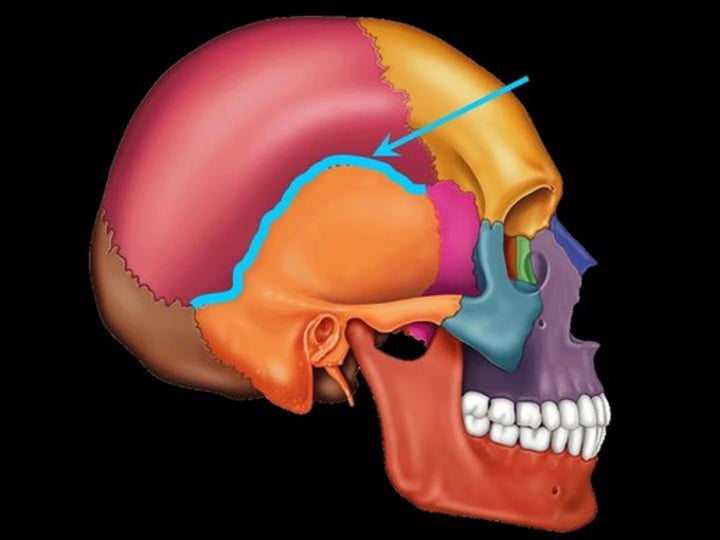
lambdoid suture
the suture between parietal bones and occipital bone
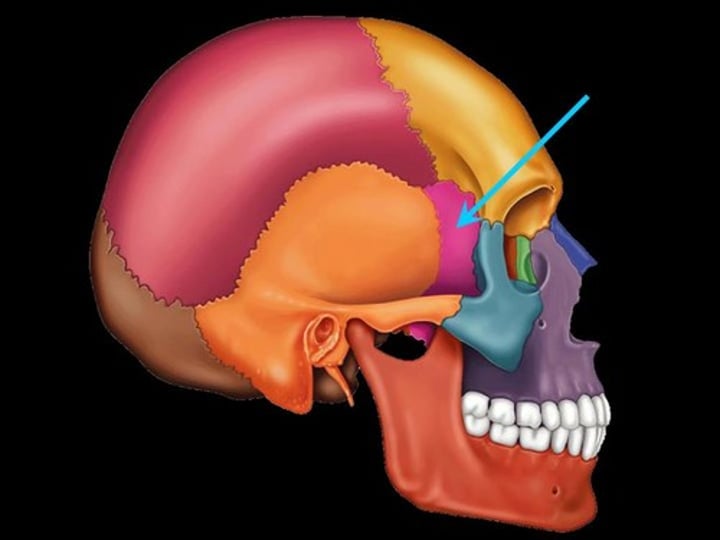
Sphenoid bone (lateral view)
forms part of the base of the skull and parts of the floor and sides of the orbit
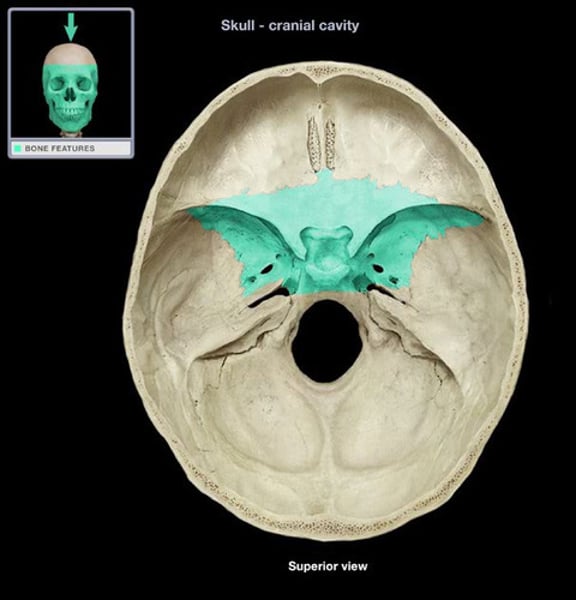
Sphenoid bone (superior view)
Butterfly shaped
-Greater wing
-Lesser wing
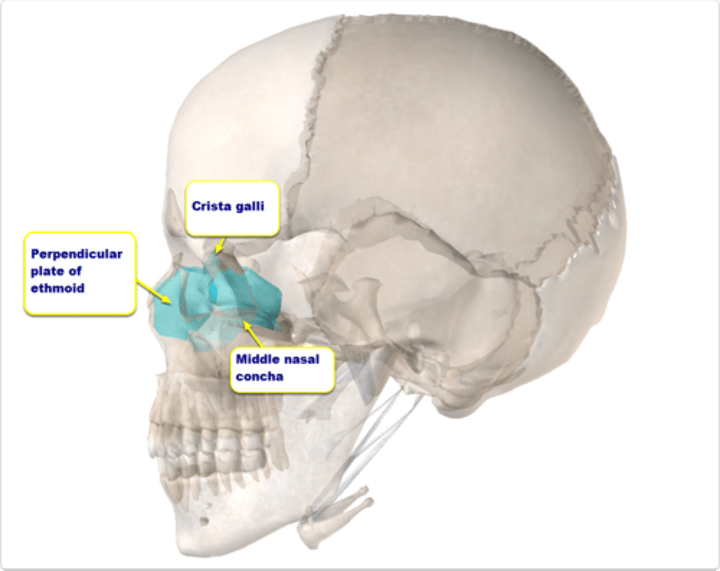
Ethmoid Bone (Medial View)
the inside portion of the eye socket, goes through behind the nose, and pops out at other inside portion of eye socket
frontal sinus
cavity within the frontal bone (swimming pool in the frontal bone)
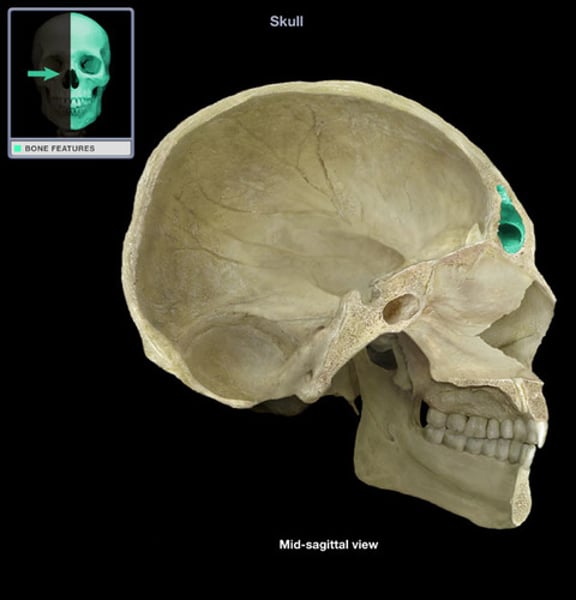
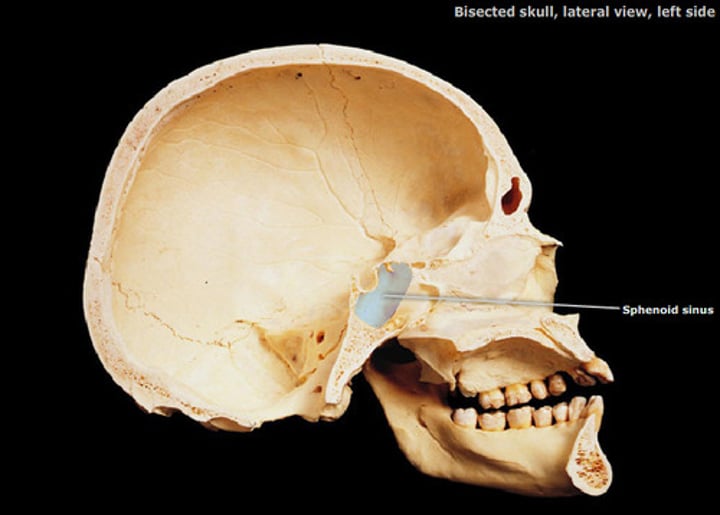
sphenoid sinus
cavity located in body of sphenoid bone
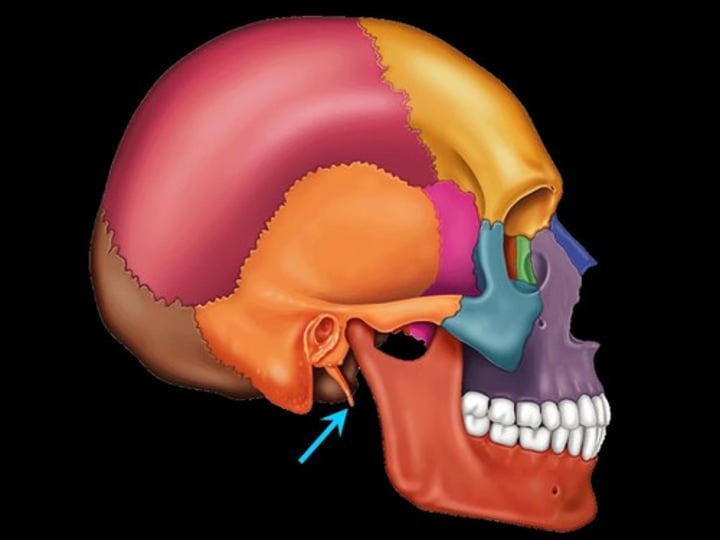
styloid process (temporal bone)
pole-like process extending downward from the temporal bone on each side of the skull
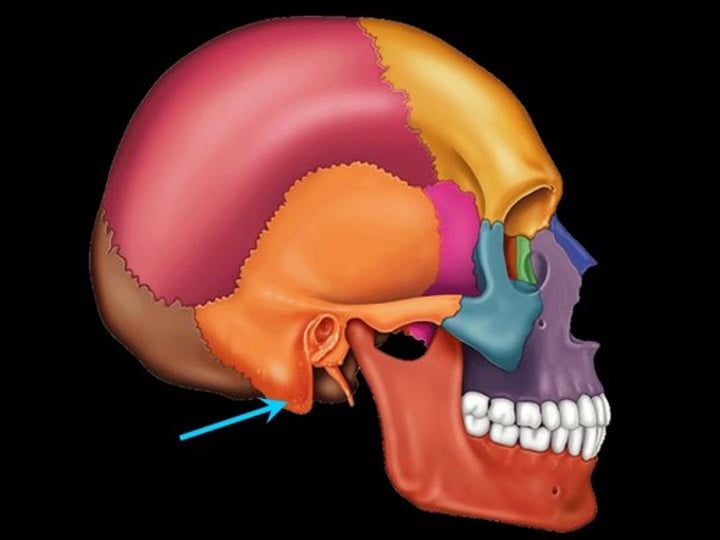
mastoid process (temporal bone)
round projection on the temporal bone behind the ear
external auditory meatus (temporal bone)
tube-like opening for ear canal in temporal bone
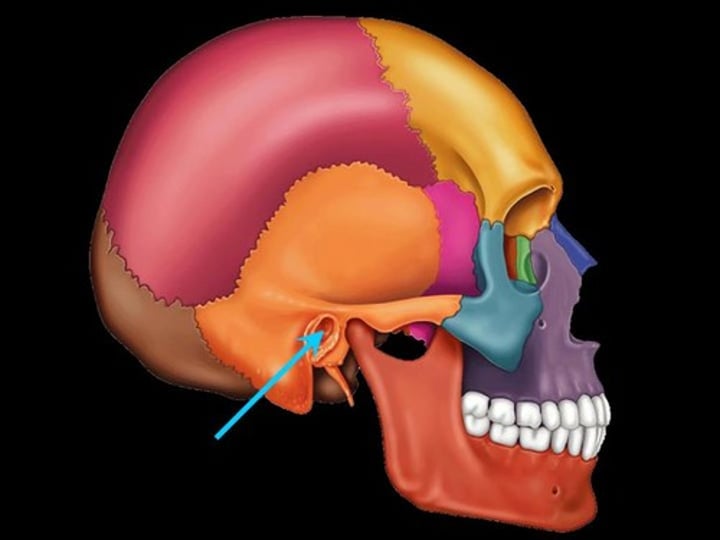
internal auditory meatus (temporal bone)
tube-like hole inside of the skull connecting to the ear canal
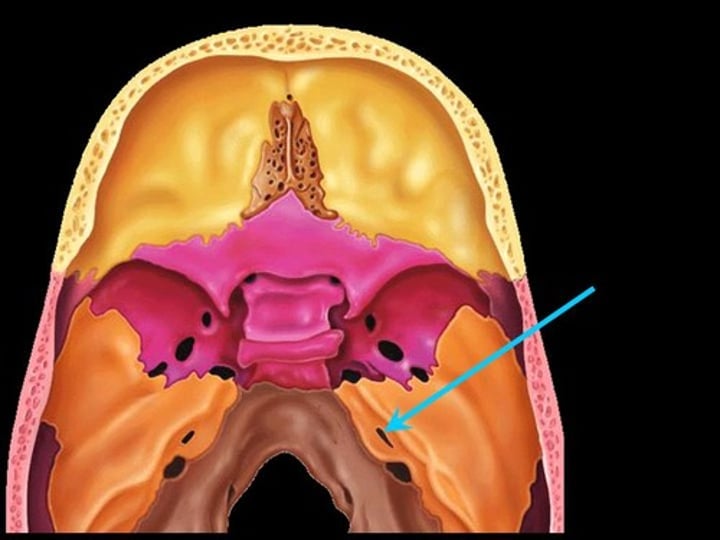
jugular foramen (temporal bone)
holes on either side of the foramen magnum (the big hole)
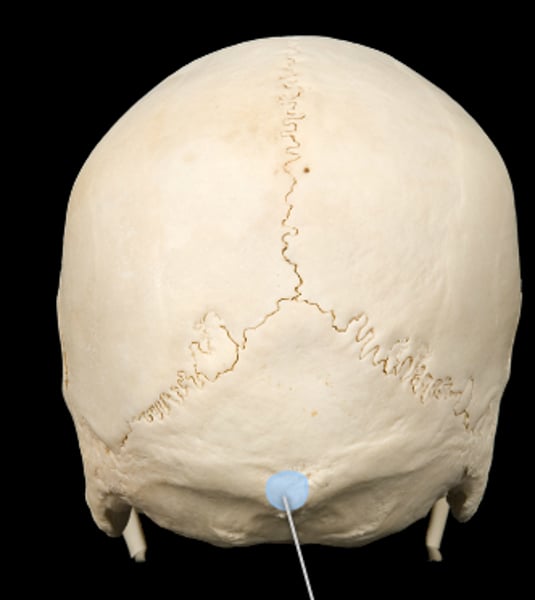
external occipital protuberance (occipital bone)
bump on back of head
foramen magnum (occipital bone)
opening of the occipital bone through which the spinal cord passes
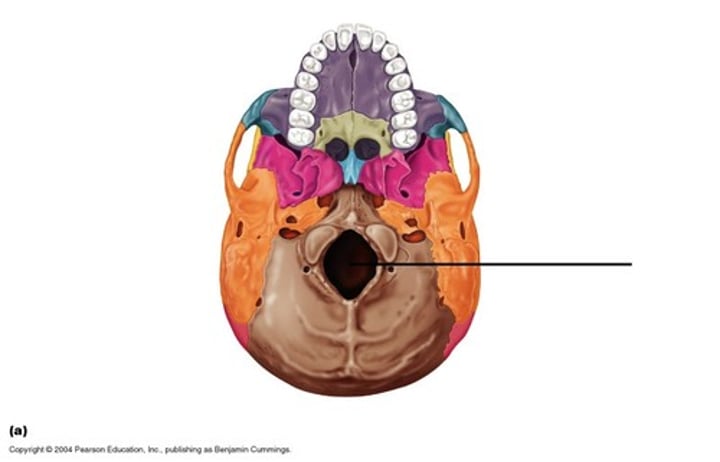
occipital condyles (occipital bone)
rounded processes that articulate with the atlas
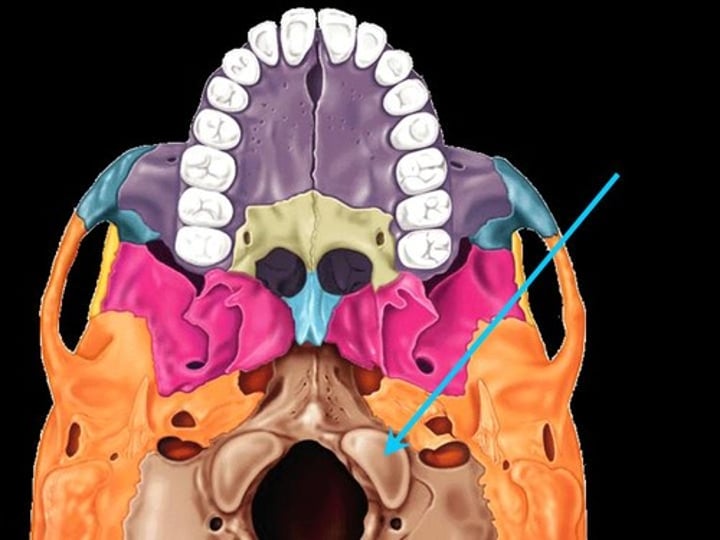
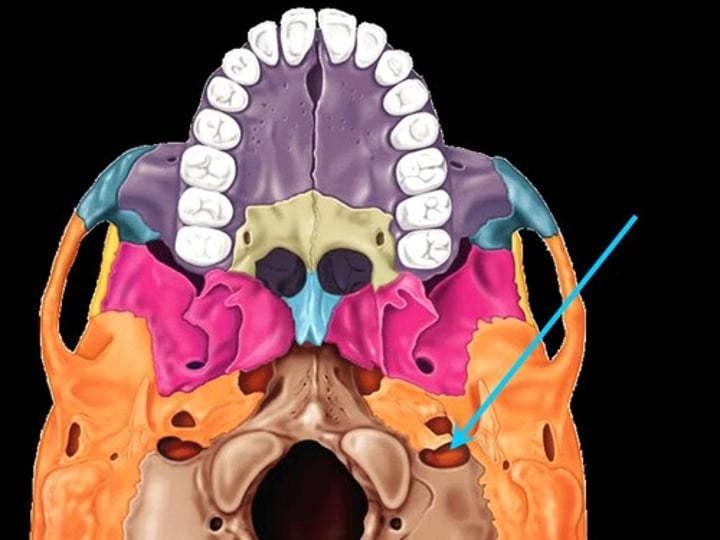
hypoglossal foramen (occipital bone)
Small hole lateral to the jugular foramen, superior to occipital condyles
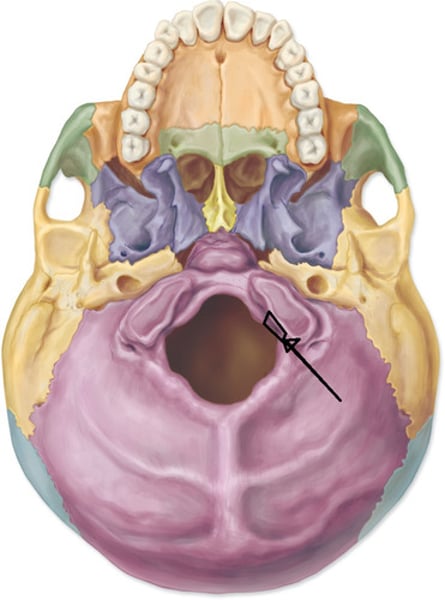
sella turcica (sphenoid bone)
houses the pituitary gland (swimming pool)
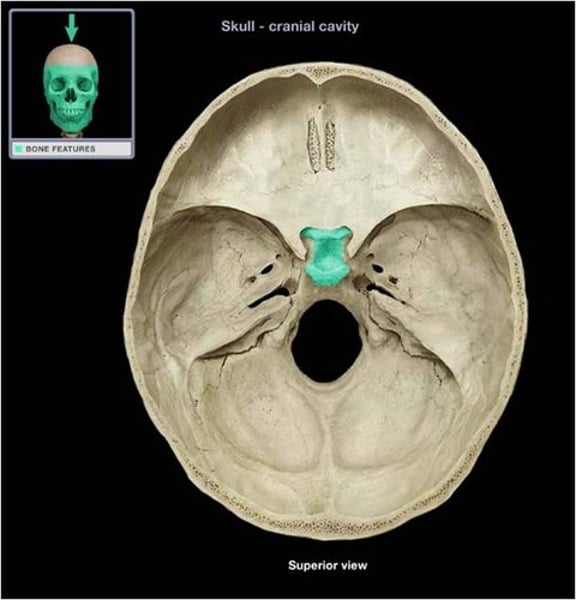
foramen ovale (sphenoid bone)
Oval shaped hole. Almost the most lateral set. at the butterfly wing
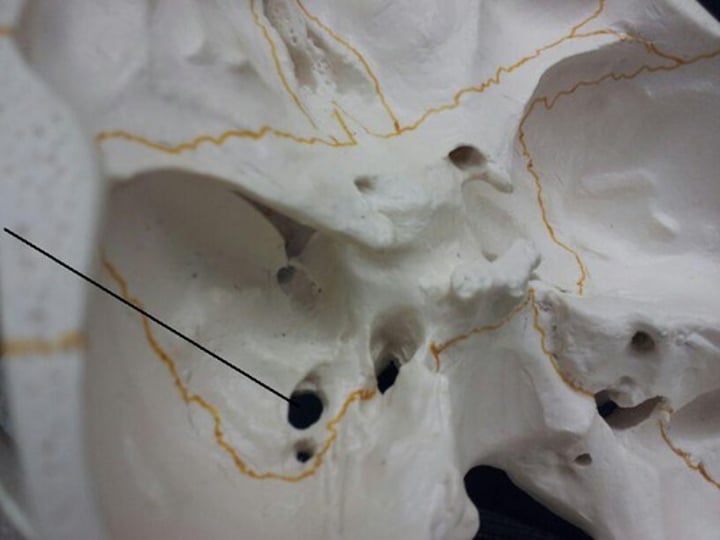
superior nasal concha (ethmoid bone)
Most cranial and posterior; harder to see.
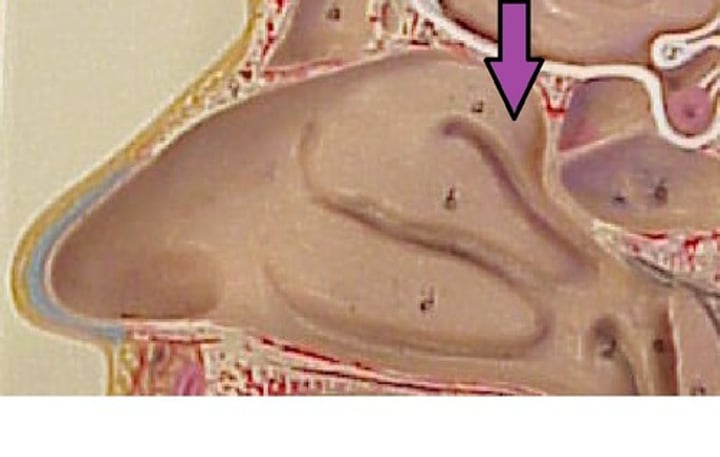
middle nasal concha (ethmoid bone)
Bone between the superior and inferior conchae
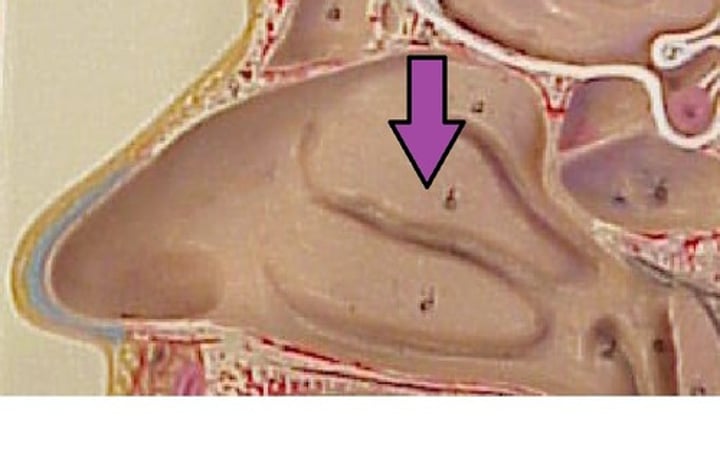
inferior nasal concha (ethmoid bone)
Below middle nasal concha
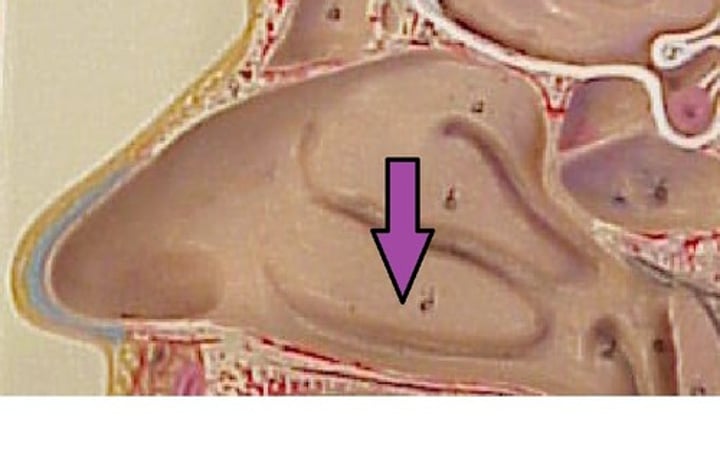
crista galli (ethmoid bone)
superior projection in the middle of the cribriform plate of the ethmoid bone; the horn
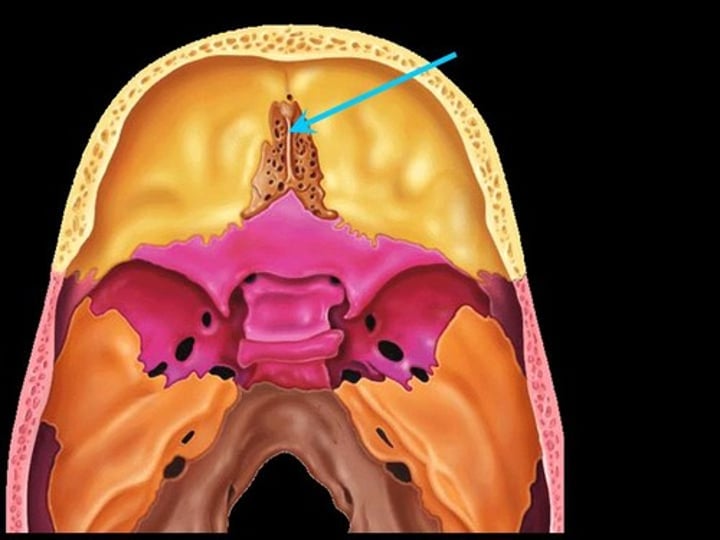
cribriform plate (ethmoid bone)
horizontal plate to crista galli that is the textured bit perpendicular to the horn
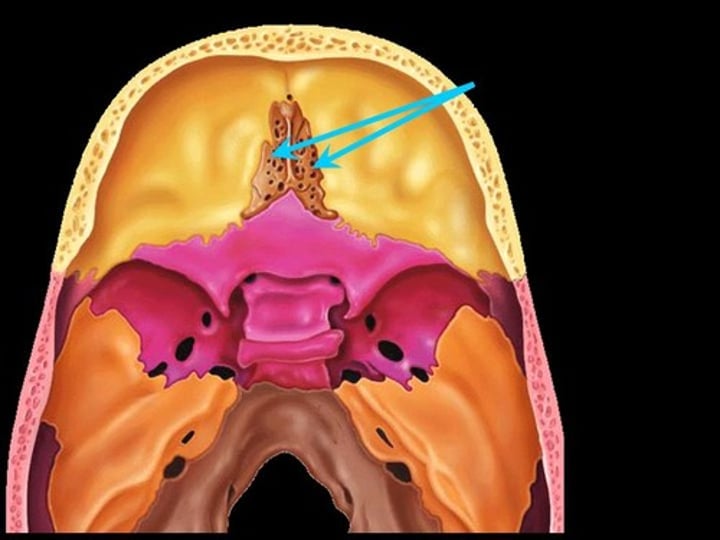
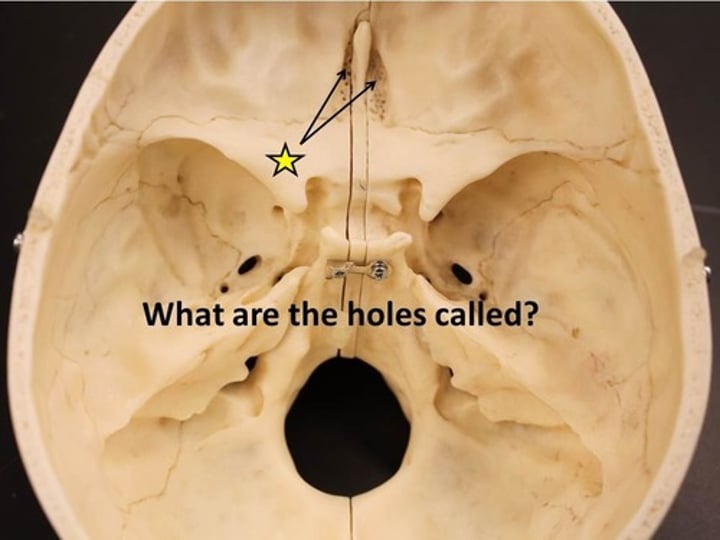
olfactory foramen (ethmoid bone)
holes on the crista galli
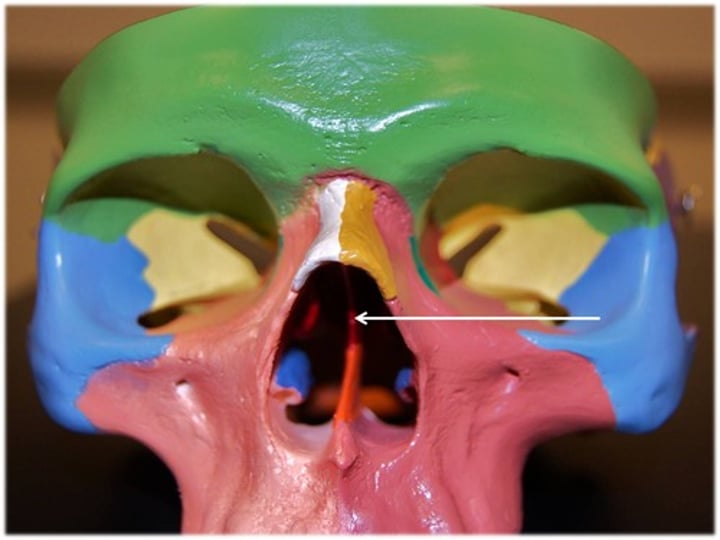
perpendicular plate of ethmoid
top portion of nasal septum
supra-orbital foramen
the hole above eye socket, at eyebrow
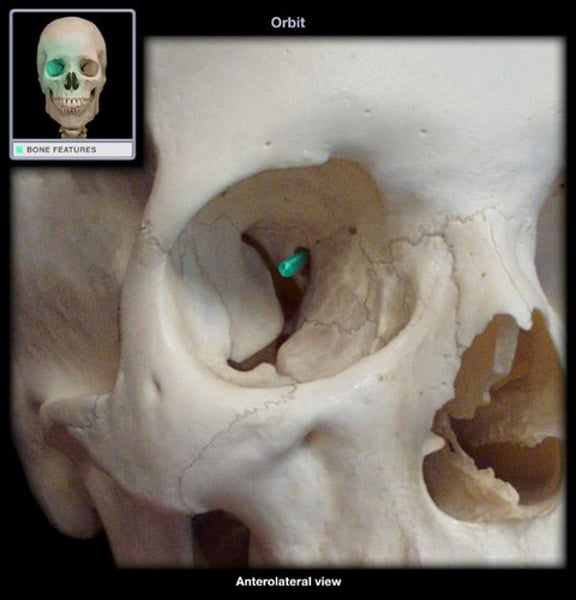
optic canal
allows the optic nerve to pass to the eye
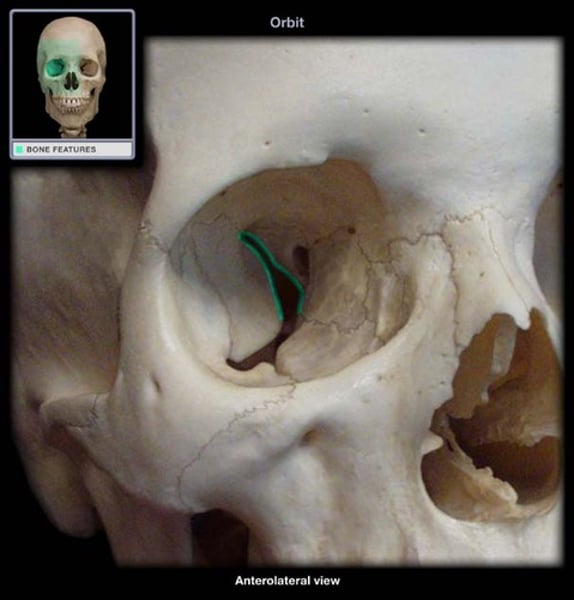
superior orbital fissure
line above the optic canal
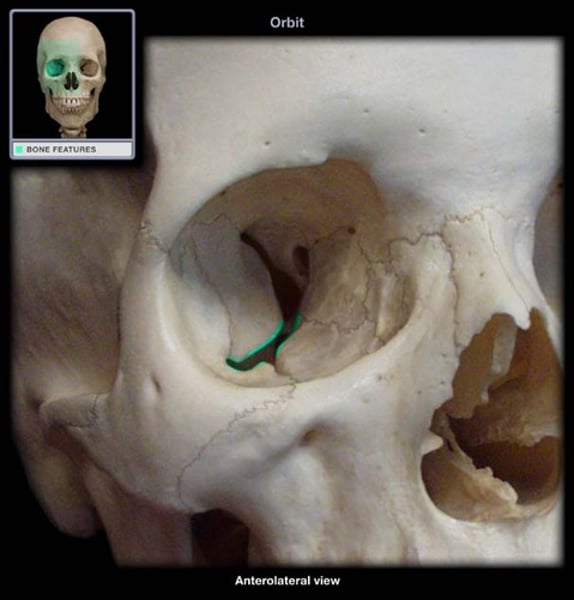
inferior orbital fissure
line below the optic canal
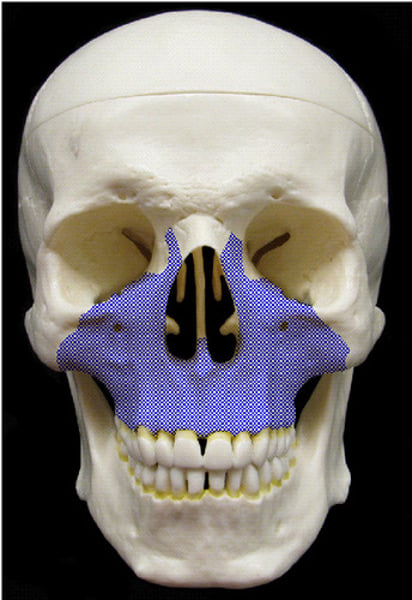
Maxilla Bone
upper jaw, where upper teeth are in
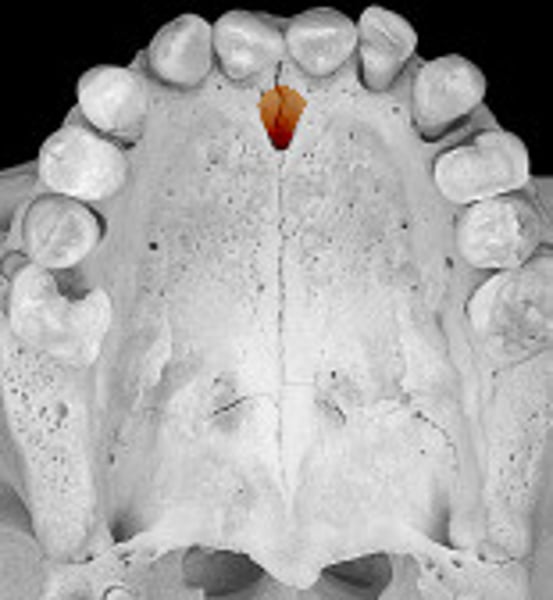
incisive fossa
Large bilateral opening located posterior to the central incisor tooth of the maxilla and piercing the hard palate
zygomatic bone
cheek bone
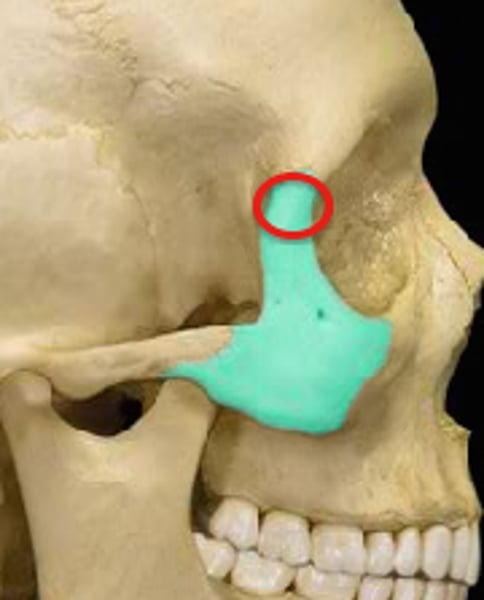
zygomatic process of temporal bone
extension from the temporal bone that forms the posterior portion of the zygomatic arch
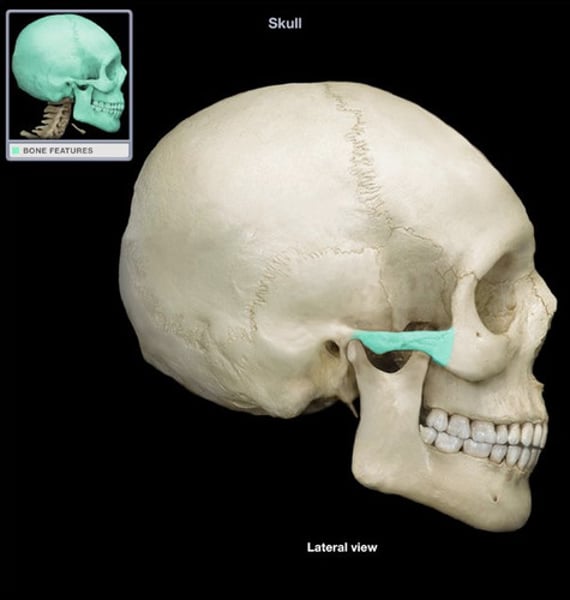
nasal bone
forms the bridge of the nose
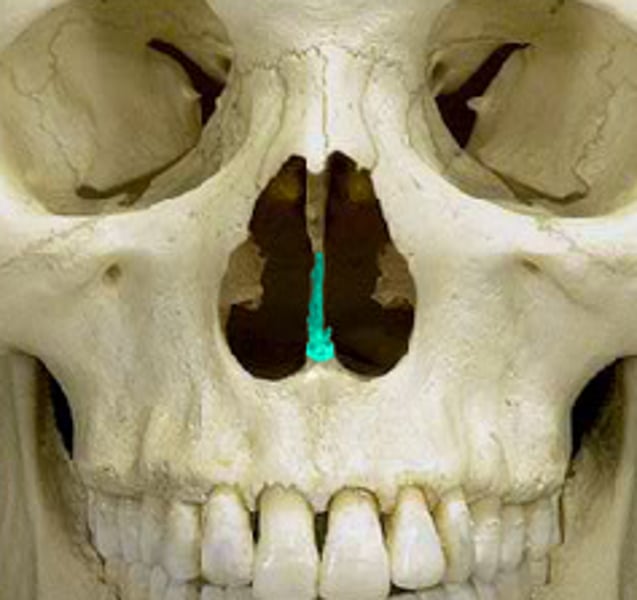
lacrimal bone
small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket (the tear drop area)
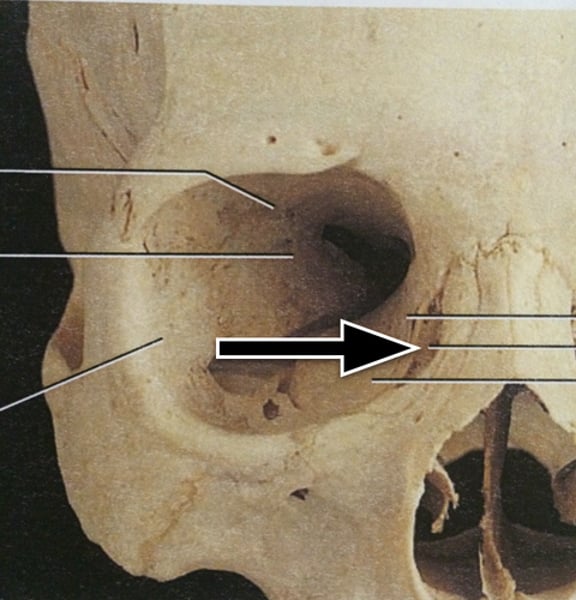
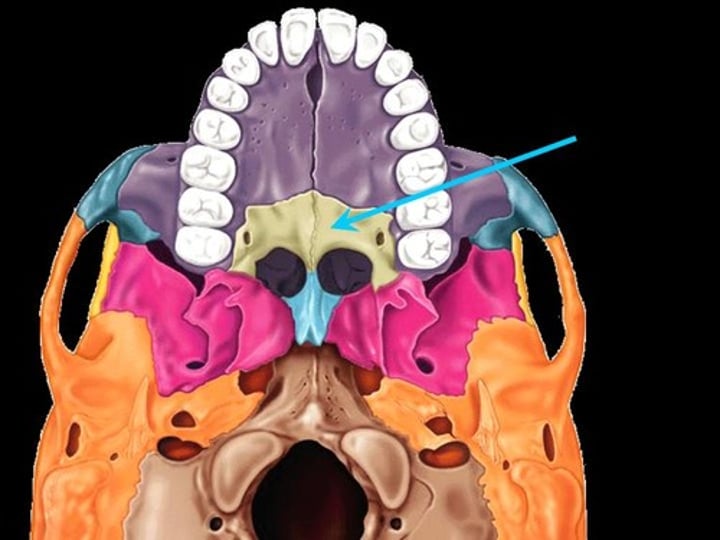
palatine bone
either of two irregularly shaped bones that form the back of the hard palate and helps to form the nasal cavity and the floor of the orbits
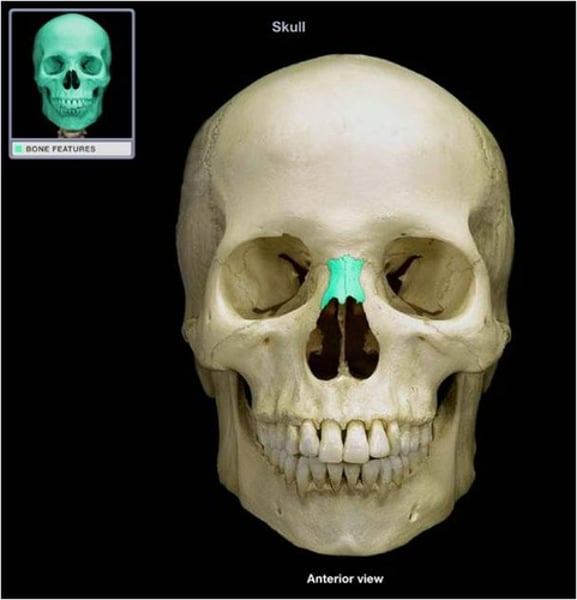
vomer bone
forms the base for the nasal septum
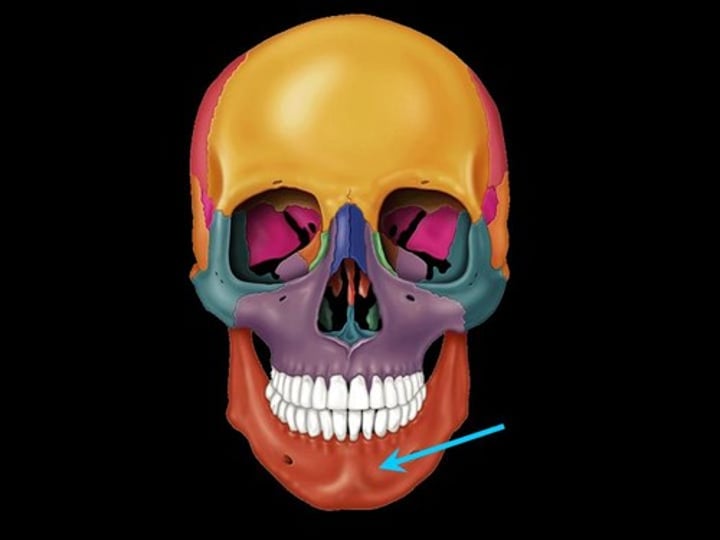
Mandible Bone
lower jaw bone
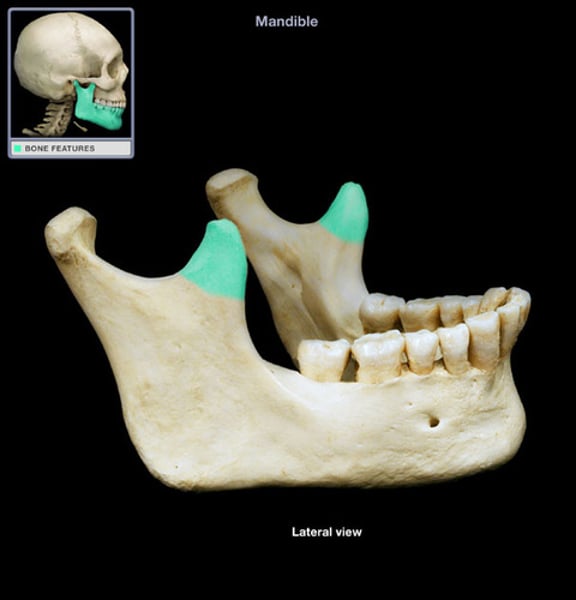
mandible condyle
articulates with temporal bone
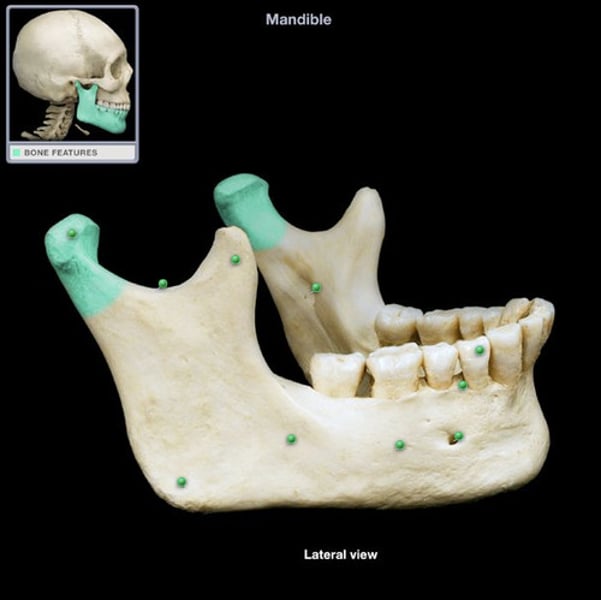
coronoid process
the shark tooth part of the mandible
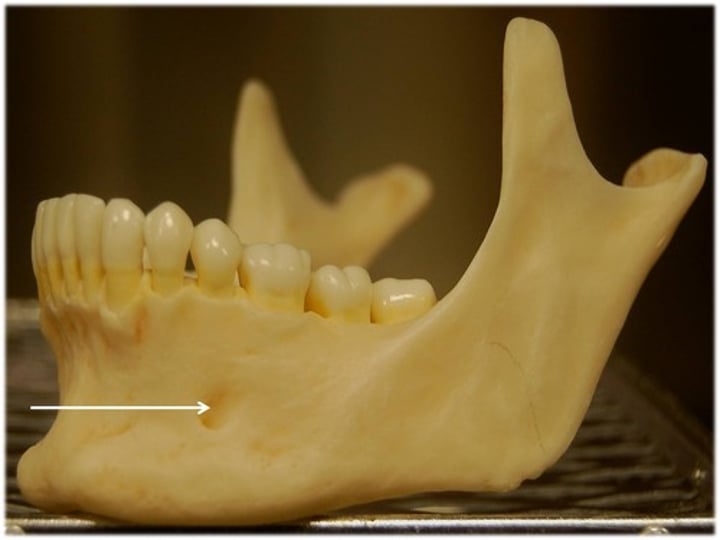
mental foramen
little holes in the mandible body
mental protuberance
Part of the mandible that forms the chin
cervical curve
neck bones supporting the head
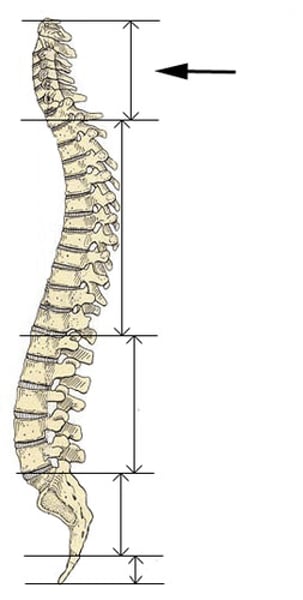
Cervical Vertebrae (C1-C7)
first set of seven bones, forming the neck
Thoracic Vertebrae (T1-T12)
second set of 12 vertebrae; they articulate with the 12 pairs of ribs to form the outward curve of the spine
thoracic curve
A primary curve, accommodates the thoracic organs
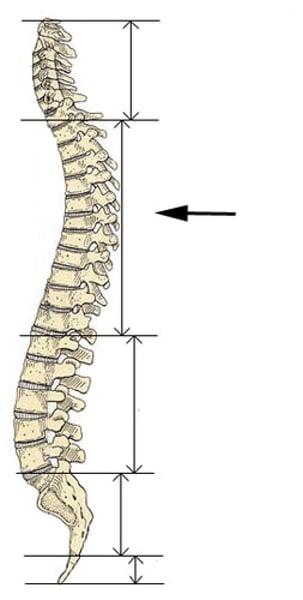
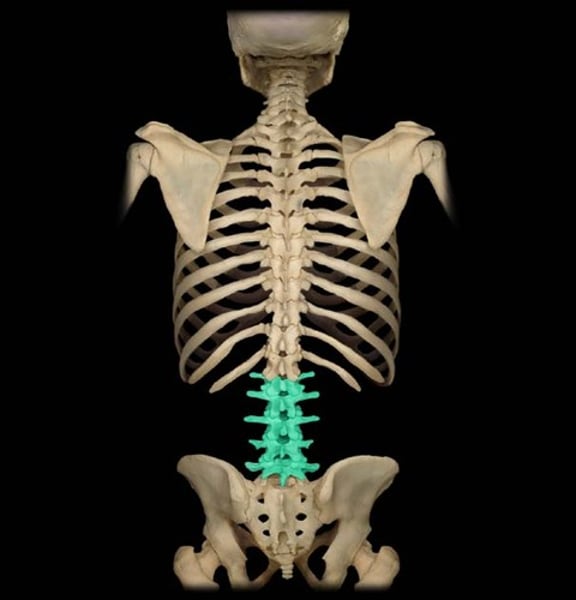
lumbar vertebrae
L1-L5 lower back
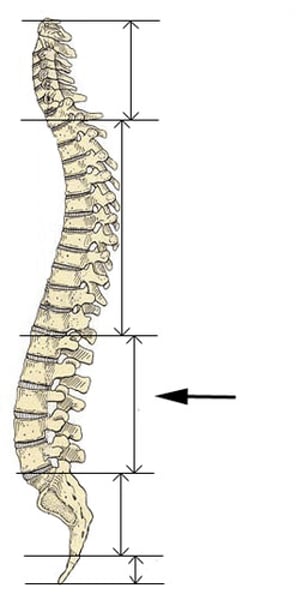
lumbar curve
a secondary curve; balances the weight of the trunk over the lower limbs; it develops with the ability to stand
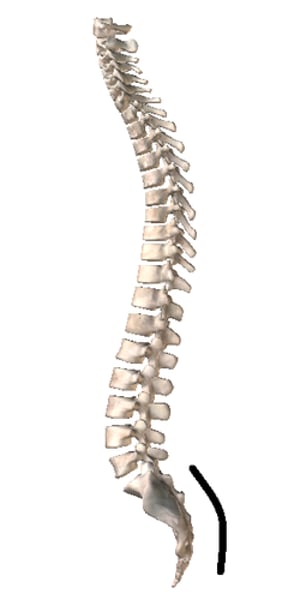
sacral curve
primary curve, accommodates the abdominopelvic organs
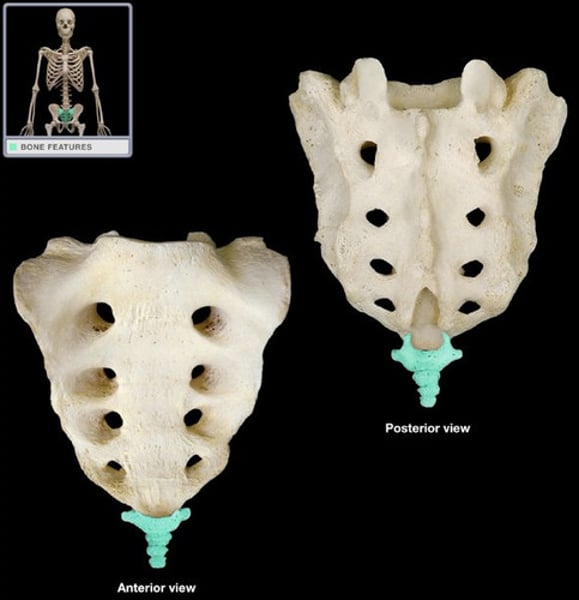
Sacrum
5 fused vertebrae at base of spine
Coccyx
tailbone
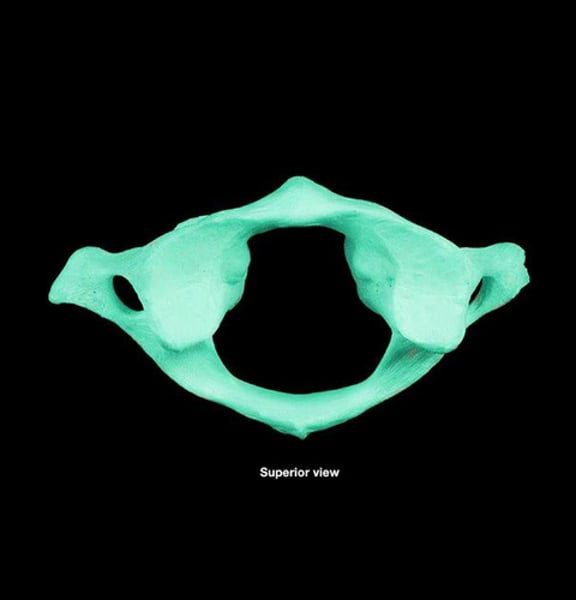
Atlas (C1)
supports the head, no body
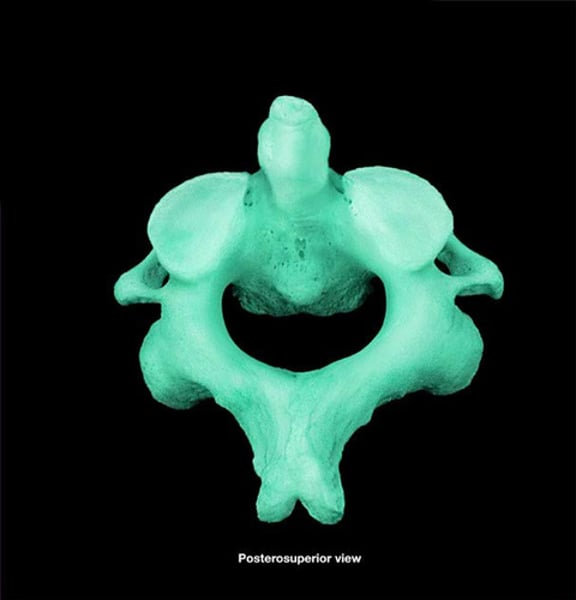
Axis (C2)
second cervical vertebrae. Allows the head to shake "no"
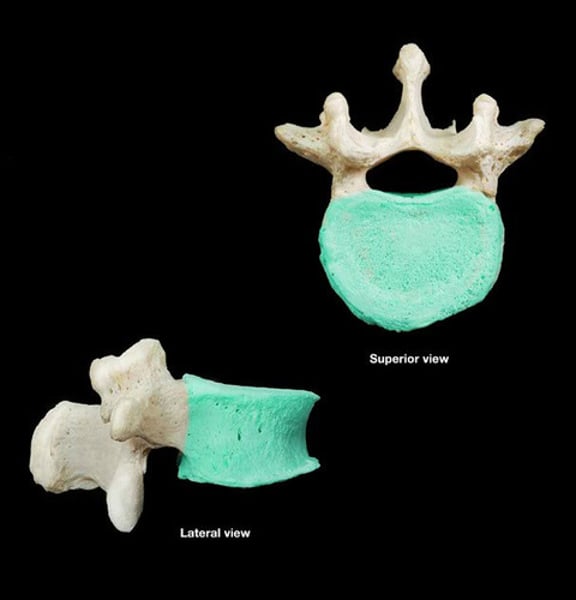
vertebral body
main portion of the vertebra, separate from the arches of the vertebra
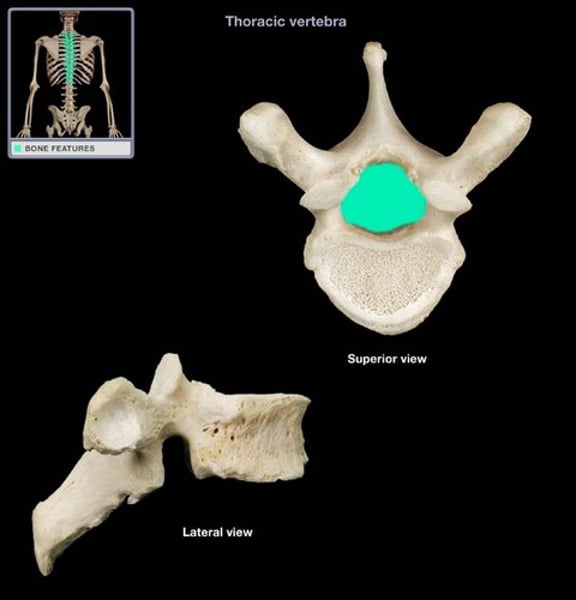
vertebral foramen
canal through which spinal cord passes
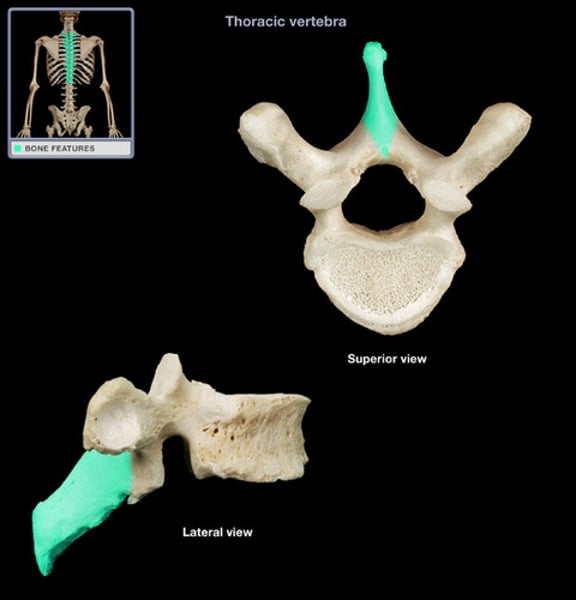
spinous process
sharp, slender projection
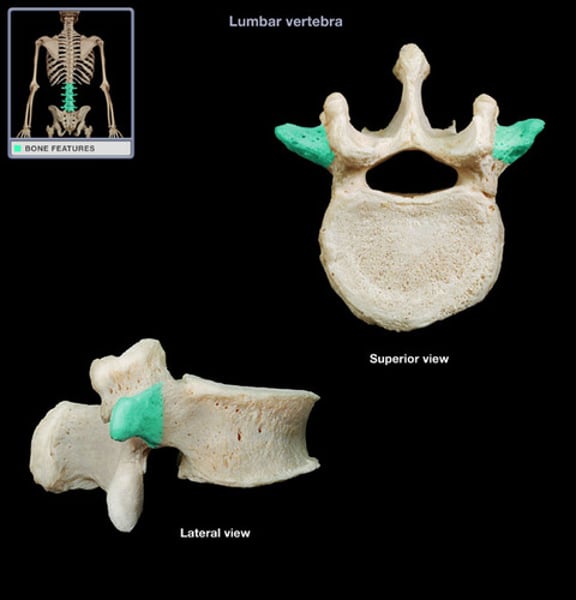
transverse process
two lateral projections from the vertebral arch
transverse foramen
only found in the cervical vertebrae and allow passage of the vertabral artery, vein, and nerve
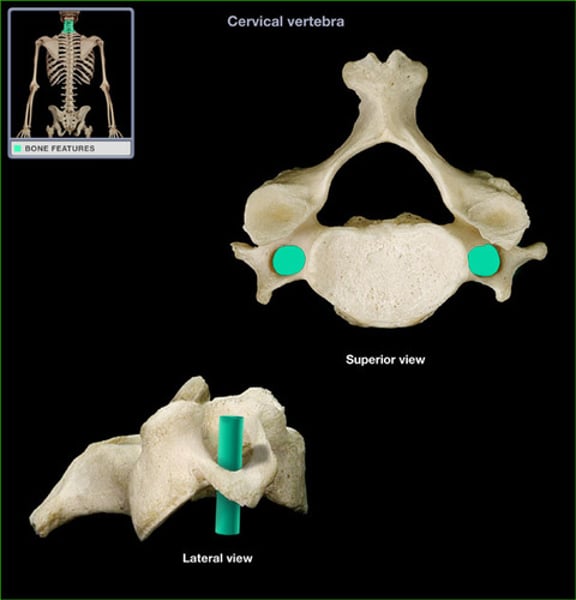
pedicles
walls of the vertebral arch
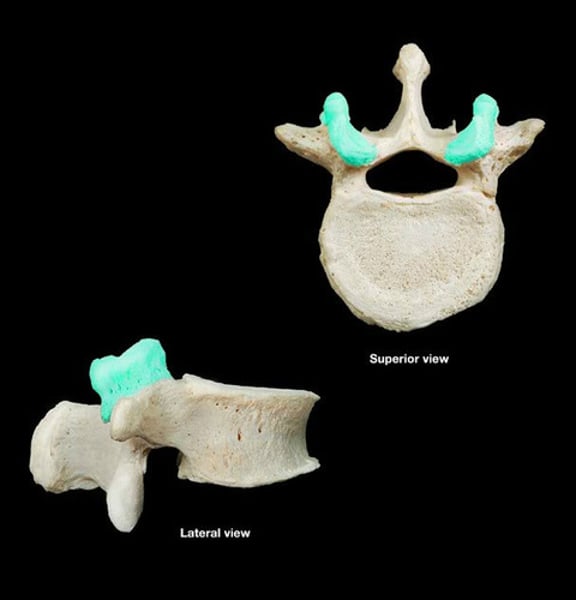
superior articular facet
contact point between the vertebrae of the veterbral column
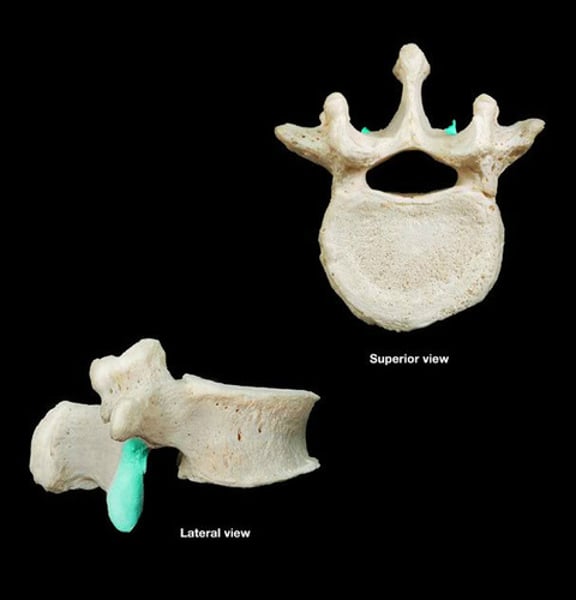
inferior articular facet
Facet on bottom process
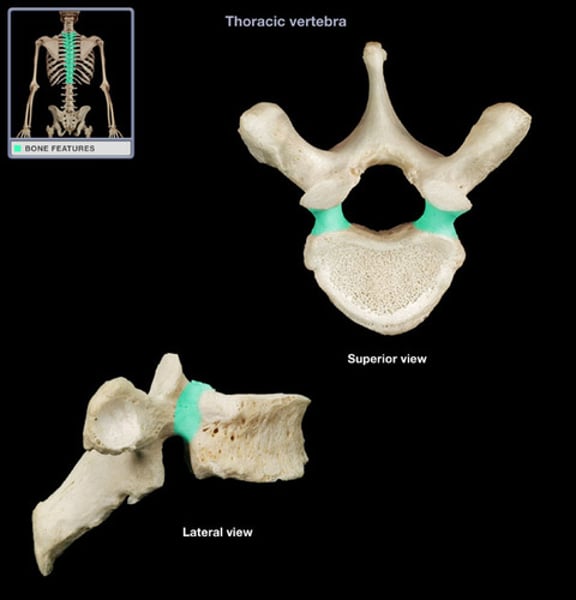
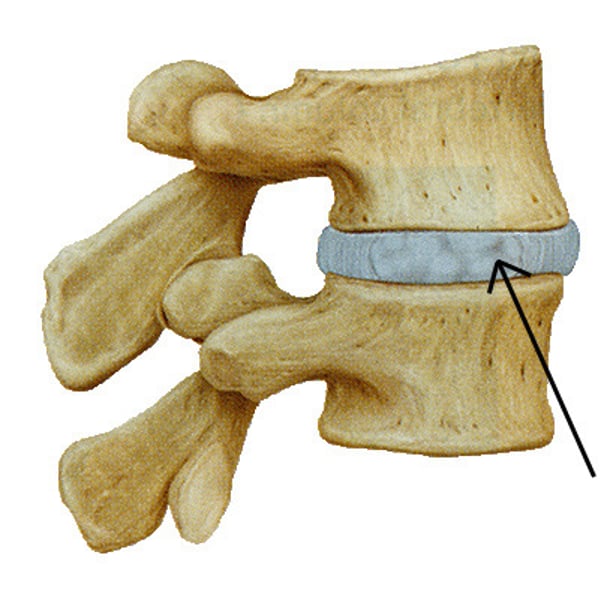
intervertebral disk
fibrocartilage pads that separate and cushion the vertebrae
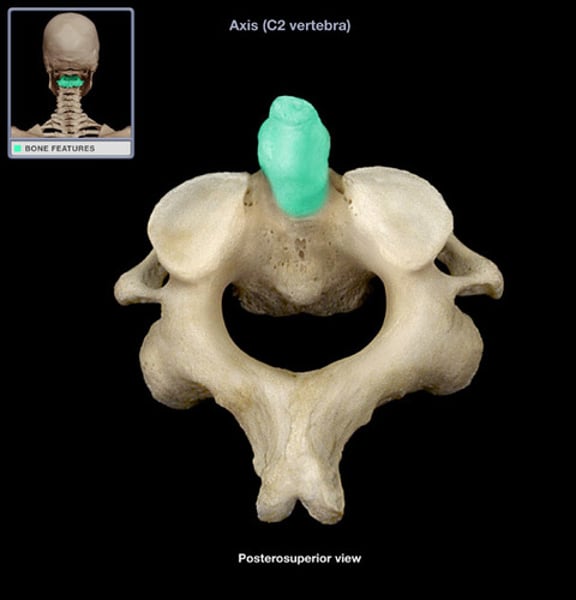
dens (odontoid process)
acts as pivot for rotation of atlas and the skull
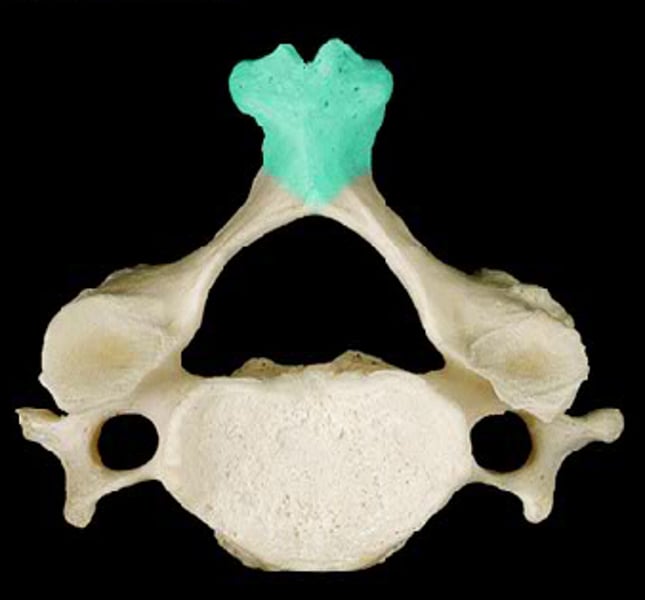
bifurcated spinous process
cervical vertebrae process
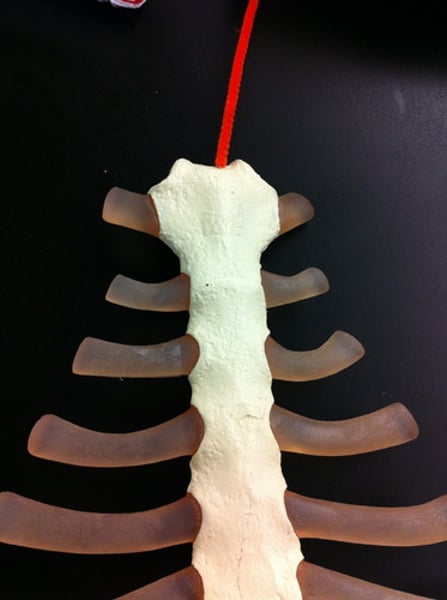
Sternum
breastbone
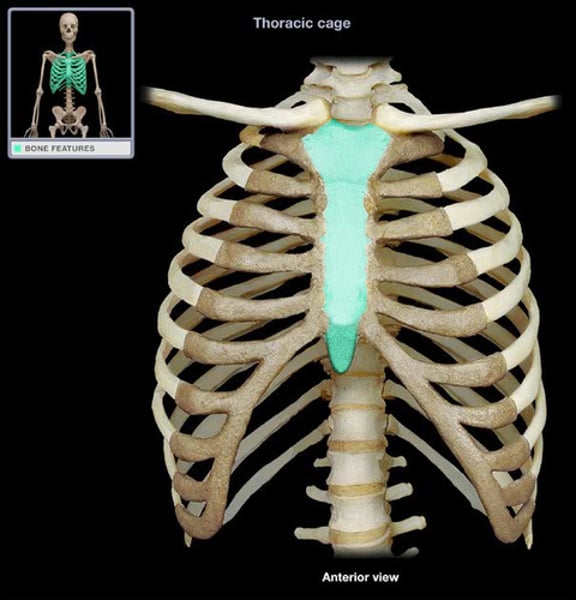
manubrium
upper portion of the sternum
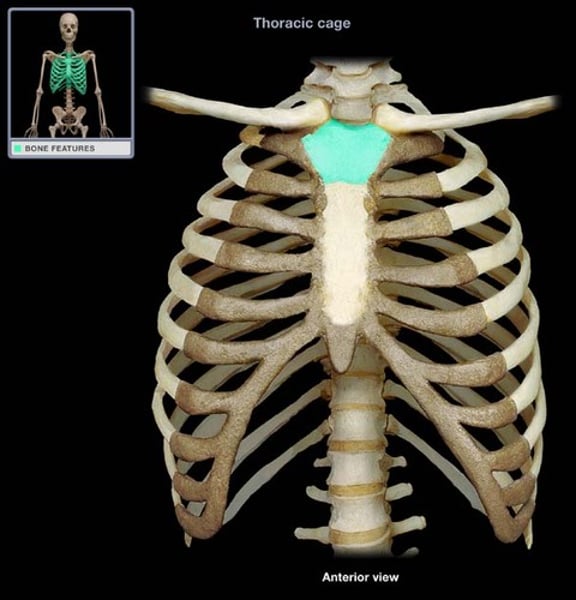
jugular notch
concave upper border of the manubrium
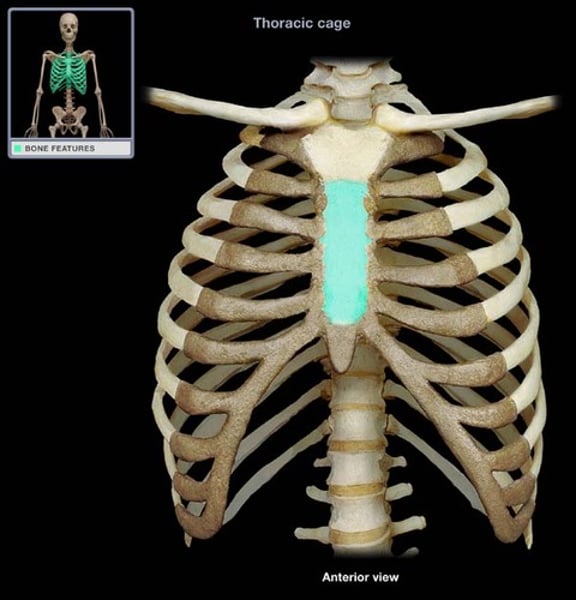
sternum body
main long part of sternum
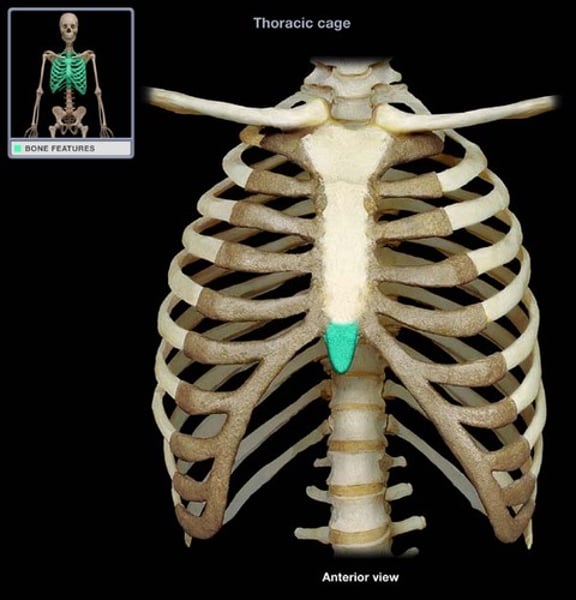
xiphoid process
lower portion of the sternum
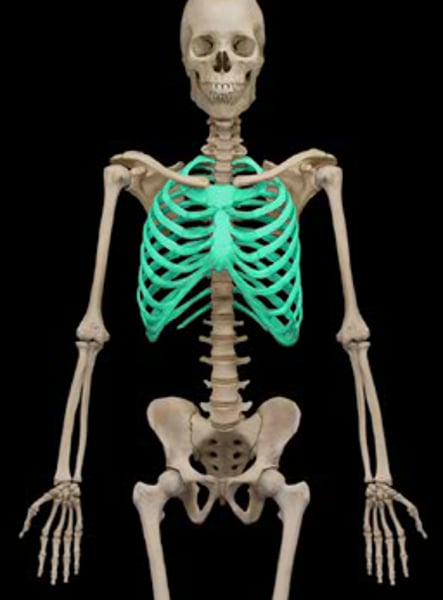
rib cage
12 pairs of ribs
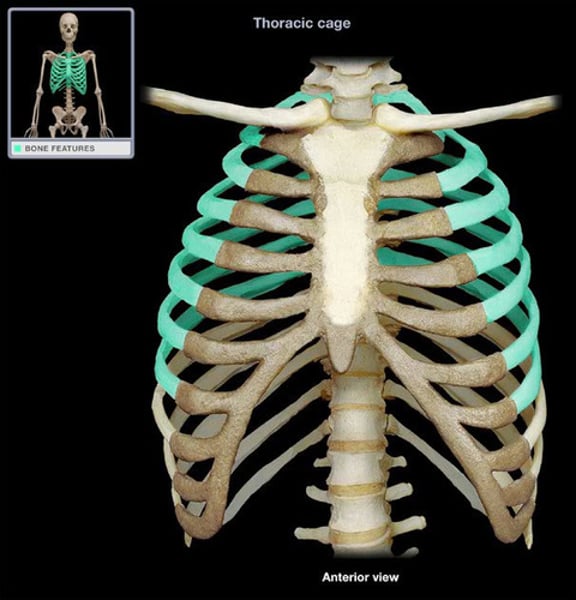
True ribs (1-7)
have a direct attachment to the sternum via cartilage
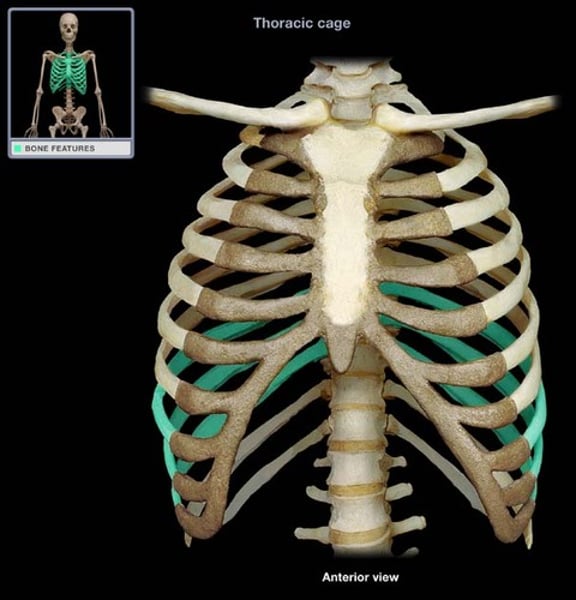
false ribs (8-12)
ribs that do not have a direct attachment to the sternum
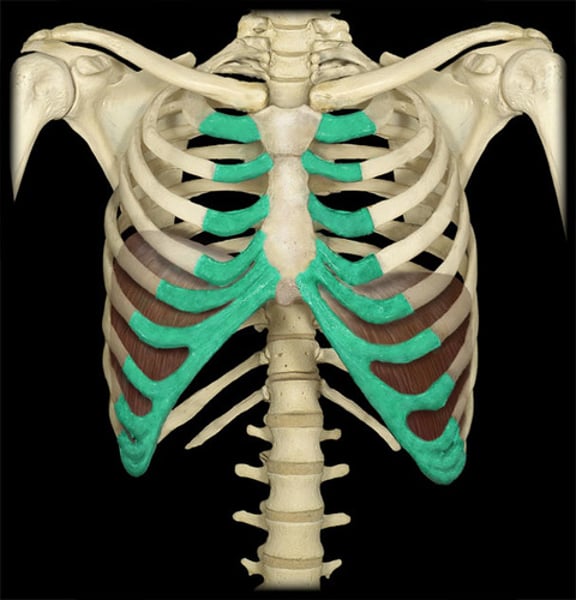
costal cartilage
connects ribs to sternum
head of rib
Articulates with the costal facet of a thoracic vertebral body.
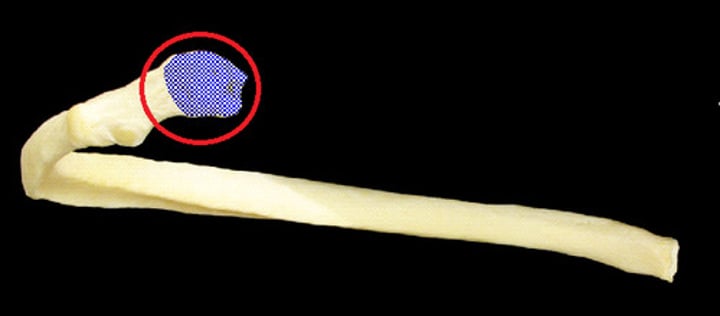
neck of rib
between head and tubercle
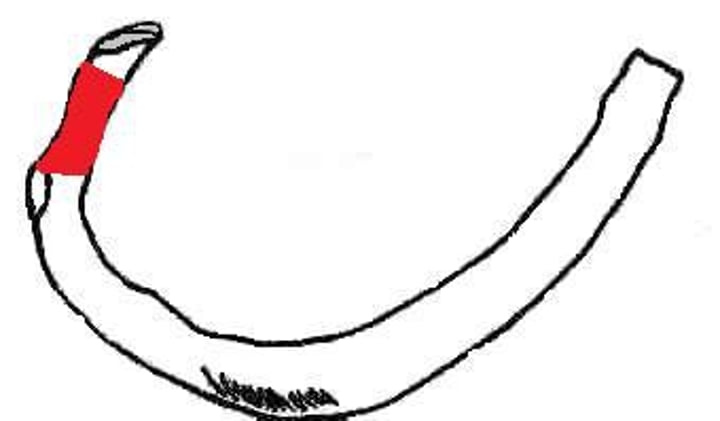
tubercle of rib
articulates with transverse process of thoracic vertebra
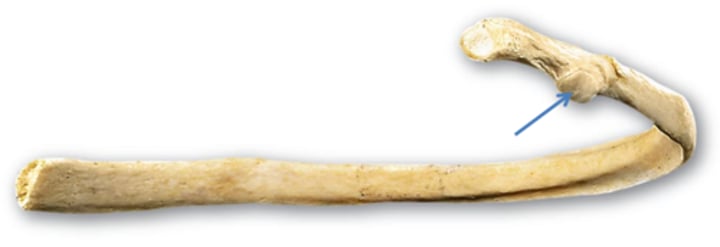
articular facet of rib
attach to thoracic bodies
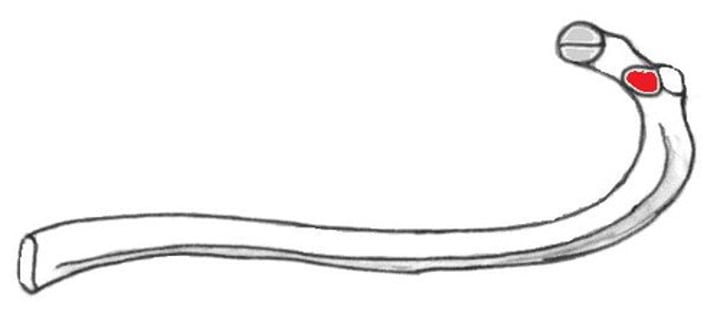
body of rib
main part of rib
hyoid bone
a U-shaped bone in the neck that supports the tongue.
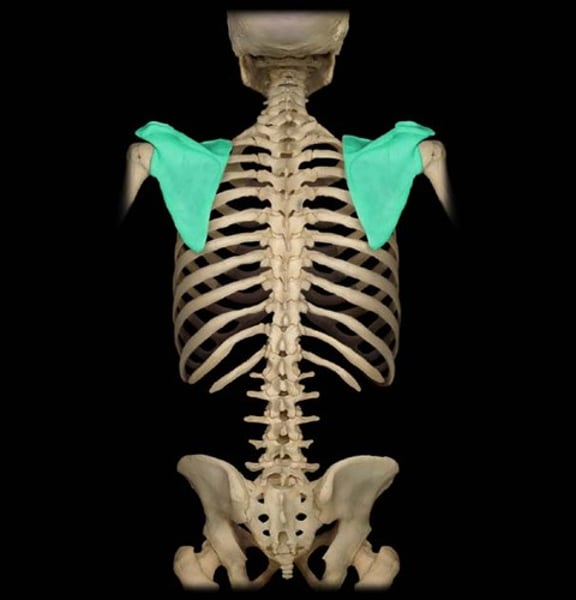
Scapula
shoulder blade
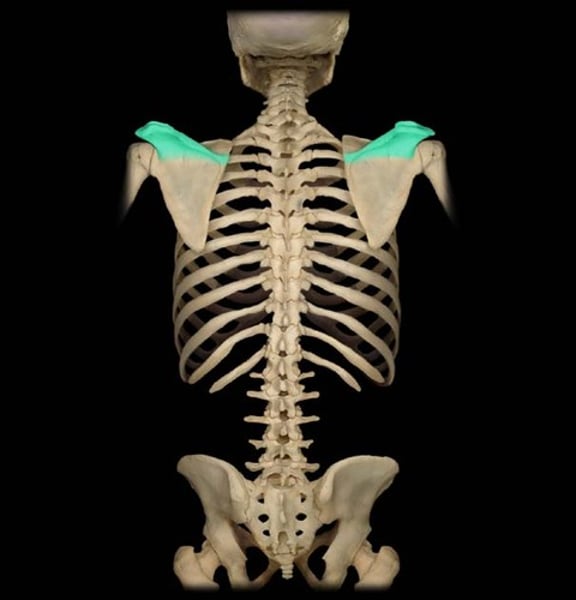
scapular spine
Divides posterior aspect of scapula into supraspinatus fossa (above) and infraspinatus fossa (below)
glenoid cavity
socket in scapular that receives head of humerus
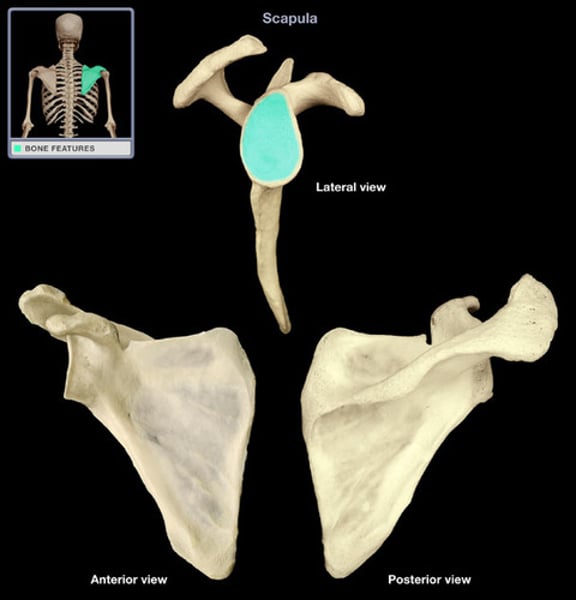
lateral border of scapula
origin of teres minor
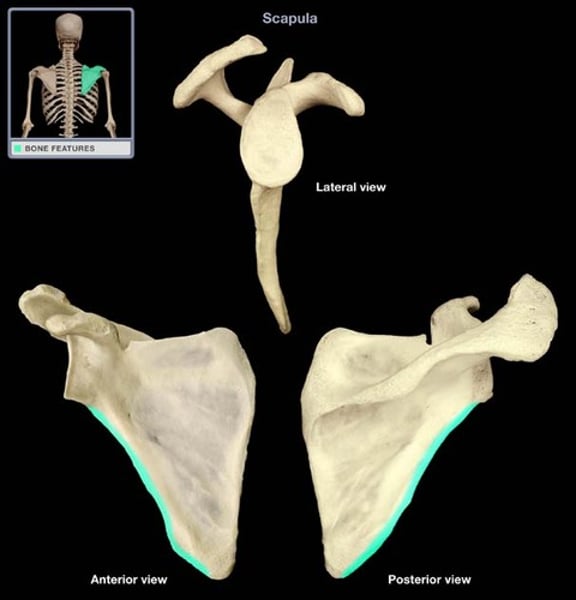
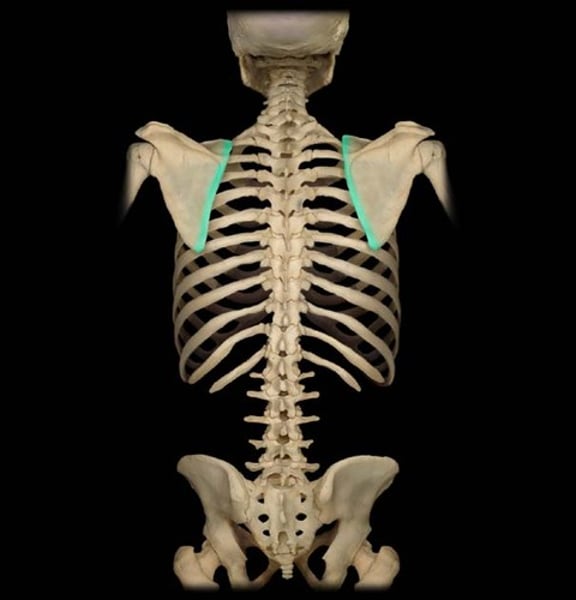
medial border of scapula
insertion of serratus anterior
acromion process
the highest portion of the shoulder
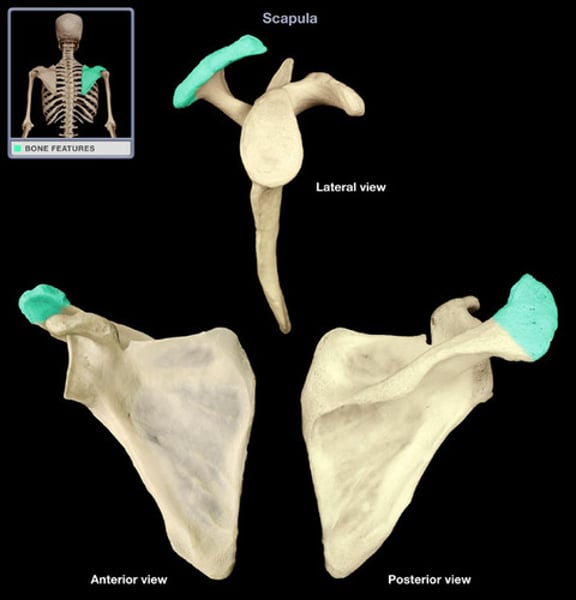
coracoid process
process above the glenoid cavity that permits muscle attachment
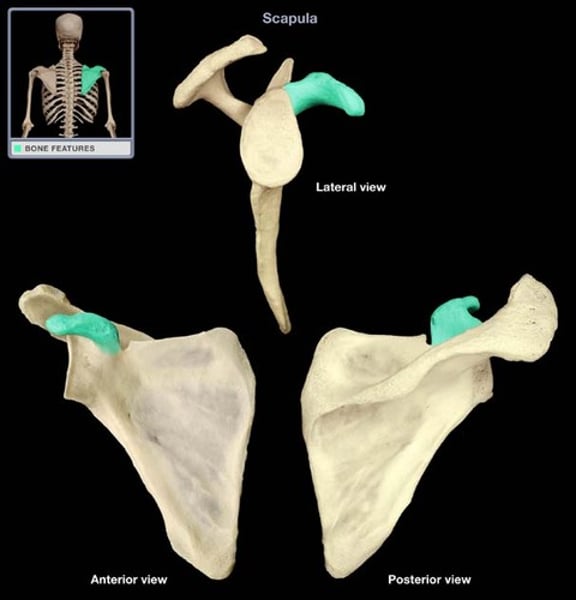
supraspinous fossa
smooth groove fossa above scapula spine
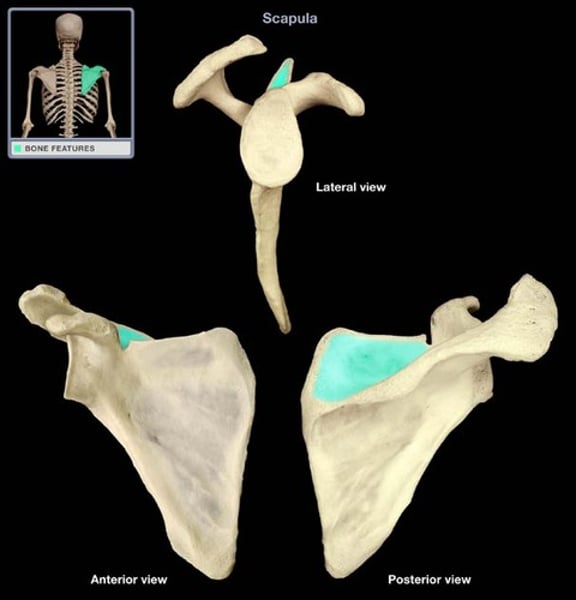
infraspinous fossa
fossa inferior to scapula spine
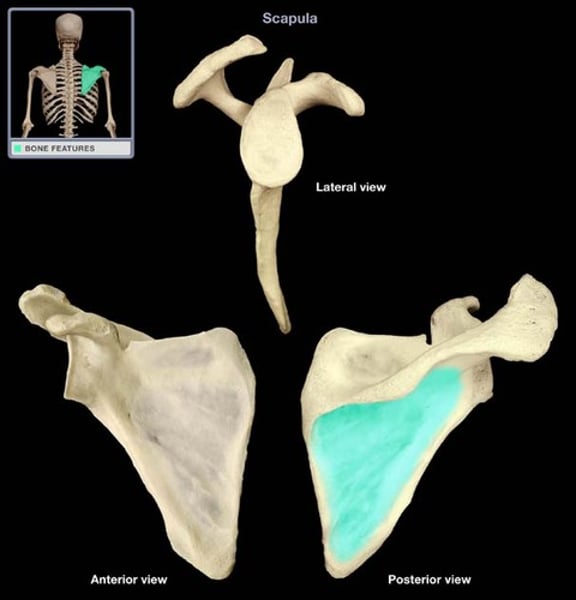
subscapular fossa
anterior surface of scapula
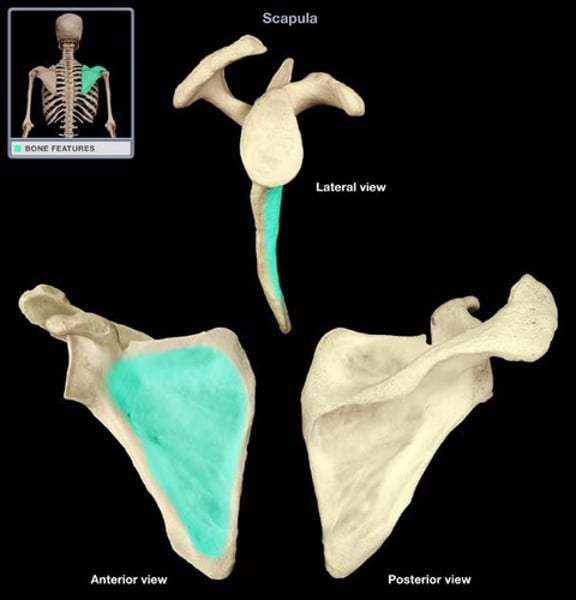
Clavicle
collar bone
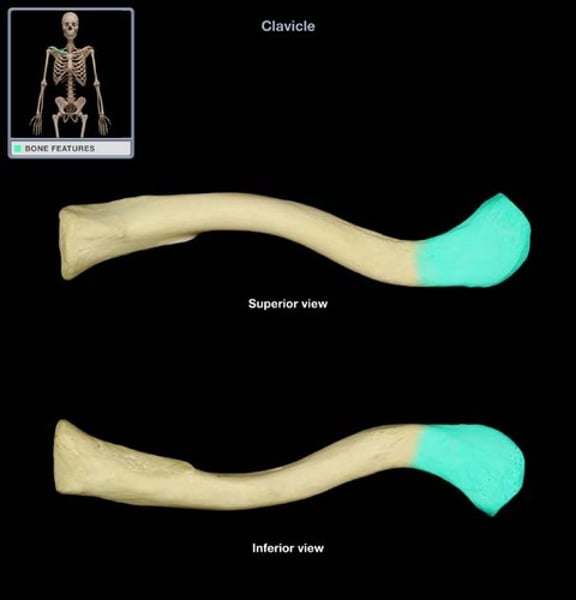
acromial end of clavicle
articulates with scapula
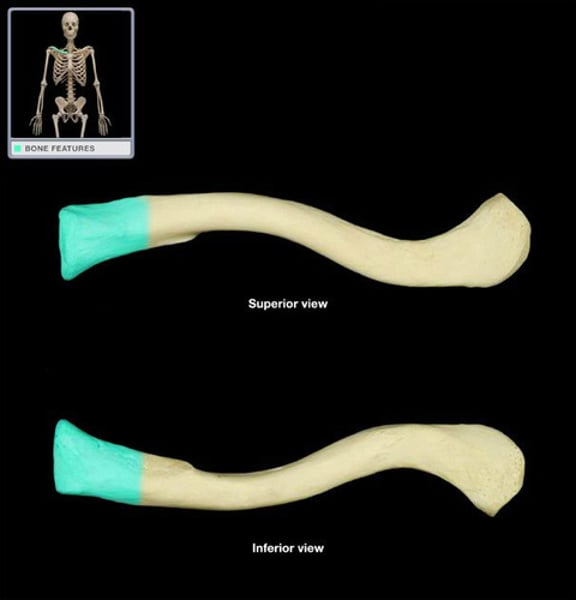
sternal end of clavicle
articulates with sternum
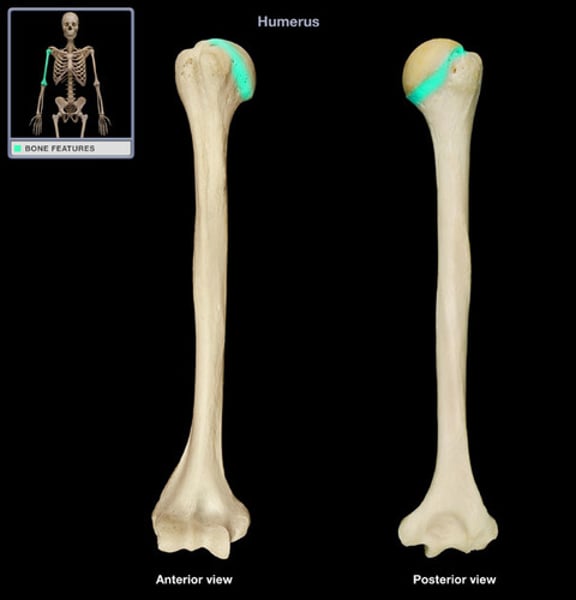
Humerus
upper arm bone
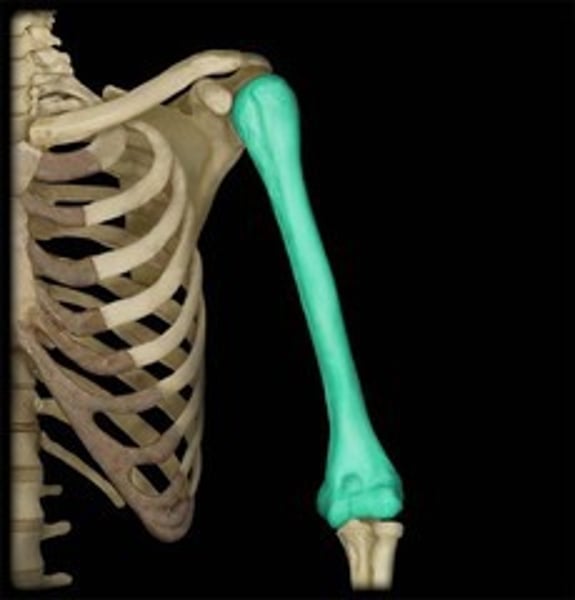
anatomical neck of humerus
margin of joint capsule