Ch 1 - A&P Intro
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
74 Terms
Define human anatomy
the study of internal and external structures of the body
Define human physiology
the study of the function of the structures in the body
What are the levels of structural organization and body systems in order?
chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organ systems level, and organism level
Describe the chemical level of organization
it’s the smallest level of organization and includes atoms and molecules
Describe the cellular level of organization
several molecules combine to form functional components that will work together as cells and form organelles
Describe the tissue level of organization
two or more cells that come together to perform a common function as a tissue. They are made up of two components: cells and extracellular matric (ECM)
Describe the organ level of organization
tissues that work together to form an organ, which also gives an identifiable structure and performs specialized tasks.
ex: heart, skin, bones of the skeleton, etc.
Describe the organ system level of organization
the body’s organs are grouped into organ systems and they consist of two or more organs that carry out a broad function in the body
ex: the cardiovascular system, where the heart and blood vessels work together to transport and deliver blood throughout the body
Describe the organism level of organization
the organ systems function together to make up a working human body (AKA organism)
Define histology
histology is the science that studies the microscopic structure of tissues
Define cytology
the study of structure & function of cells
What are the different types of anatomy?
systemic anatomy, regional anatomy, surface anatomy, gross anatomy, and microscopic anatomy
Describe systemic anatomy
the study of the body’s organ systems and their functions
ex: skeletal system, muscular system, nervous system, etc.
Describe regional anatomy
the study of the body by specific areas (regions)
head and neck, thorax (chest), abdomen, pelvis, upper limbs (shoulder→ head), lower limbs (hip → feet)
Describe surface anatomy
the study of external features on the surface of the body to locate internal structures
Describe gross anatomy
the study of structures that can be seen with the unaided eye - organs and organ systems
Describe microscopic anatomy
the study of structures that can only be seen with the aid of a microscope
has specialized fields: histology and cytology
What are the planes of section and what are the 3 primary planes of section?
the standard ways of dividing a body or body part to examine its internal structure
the sagittal plane, frontal plane, and transverse plane
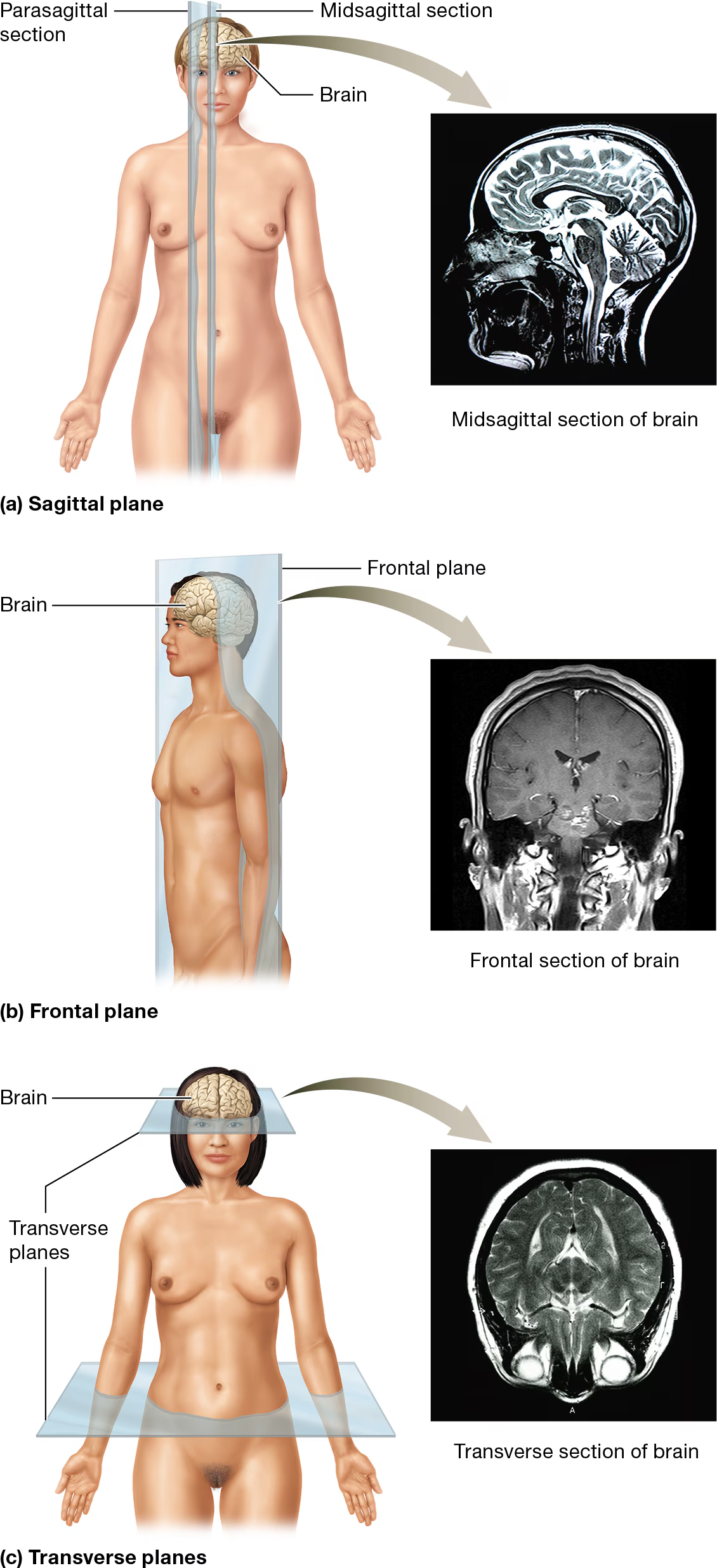
Describe the Sagittal plane
it divides the body/body part into right and left sections and has two variations:
midsagittal plane (median plane, not the same as medial): divides the body/body part into equal right and left halves
parasagittal plane: divides the body/body part into unequal right and left halves
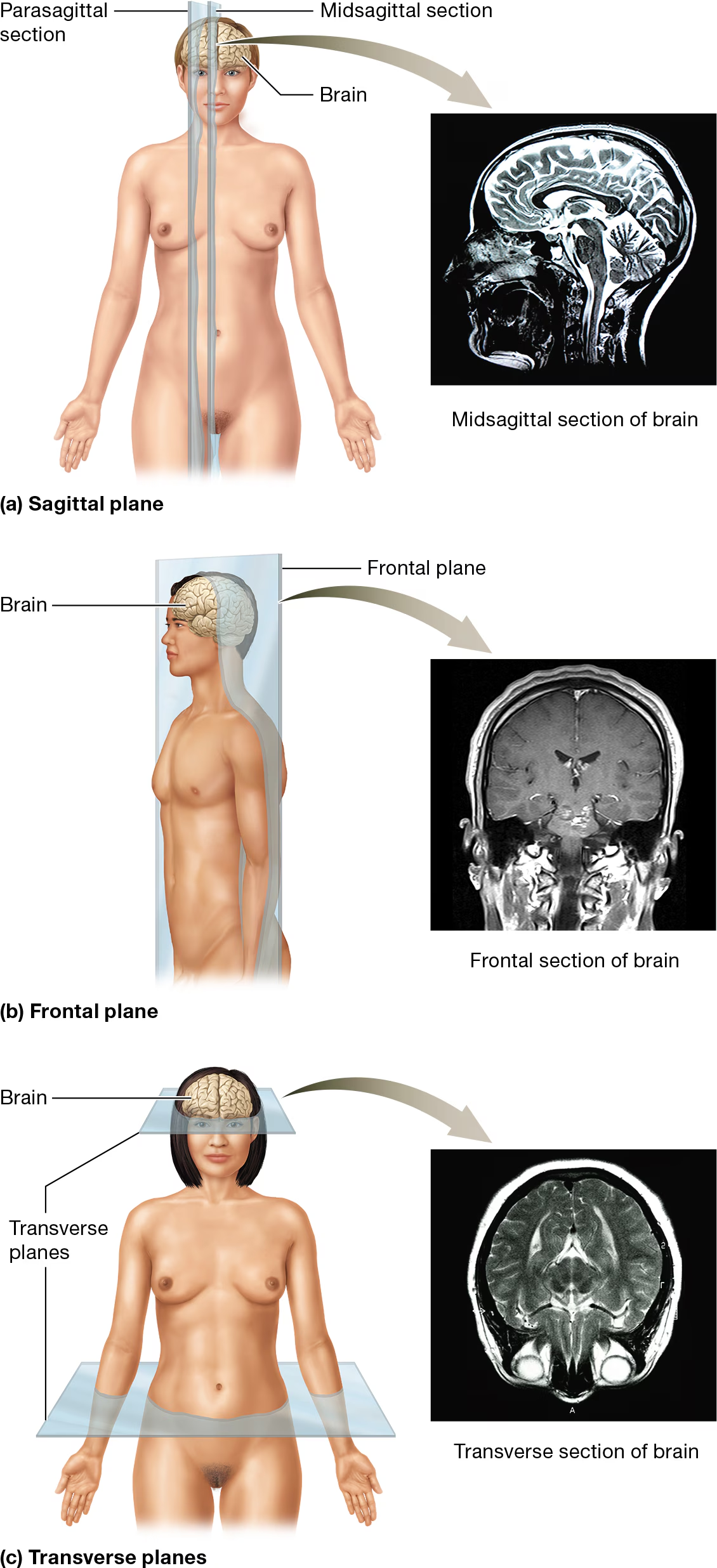
Describe the frontal plane
AKA the coronal plane and it divides the body/body part into anterior and posterior sections
easy to remember because the frontal plane gives a front section and back section
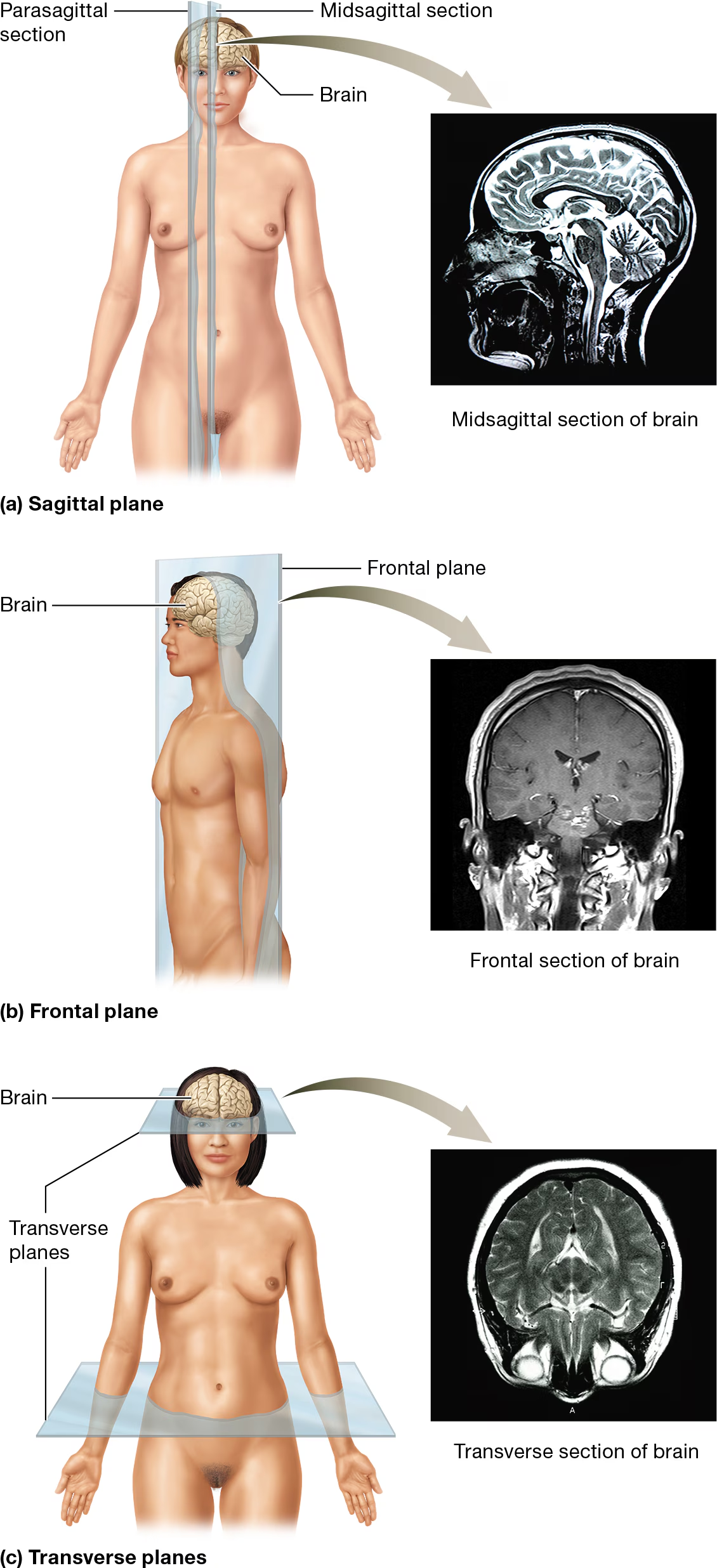
Describe the transverse plane
AKA the horizontal plane or cross section and it divides the body/body part into superior and inferior parts. it also divides the appendicular region into proximal and distal parts
What is an oblique plane?
a less standardized plane, is taken at an angle and is useful for examining structures that aren’t easy to study with the standard planes of section
What are cavities?
a cavity is any fluid-filled space within the body
body cavities both protect internal organs and allow them to move/expand when necessary
What are the two major cavities?
posterior body cavity and anterior body cavity
What two subcavities lie within the posterior body cavity?
Cranial cavity and the Vertebral/Spinal cavity
Where and what is the function of the cranial cavity
located within the skull and protects the brain
Where and what is the function of the vertebral/spinal cavity?
located within the vertebral column and protects the spinal cord
What fluid does the cranial cavity and vertebral/spinal cavity contain?
both have a fluid called “cerebrospinal fluid” (CSF)
it bathes both organs and keeps the brain buoyant within the skull
The anterior body cavity’s two main divisions are separated by,,?
the diaphragm
What is superior to the diaphragm?
the thorax; which is known as the thoracic cavity
What is inferior to the diaphragm?
the abdomen pelvis; which is known as the abdominopelvic cavity
What are the 3 subcavities of the thoracic cavity?
pleural cavity
mediastinum
pericardial cavity
What are pleural cavities?
there’s right and left PC and they each surround one lung and they’re located within serous membranes
What are mediastinum?
they are between the pleural cavities and it houses the heart, great blood vessels, trachea, and esophagus
NOT located within a serous membrane
What is the pericardial cavity?
it’s inferior to the mediastinum and within a serous membrane; it also surrounds the heart
What are the two subcavities of the Abdominopelvic cavity?
abdominal cavity
pelvic cavity
what organs does the abdominopelvic cavity contain?
it contains organs of multiple systems, including the digestive, lymphatic, reproductive, and urinary system
below the diaphragm
what subcavity can the organs of the abdominopelvic cavity also be in?
the peritoneal cavity, which is a abdominal subcavity and found within a serous membrane
What organs does the pelvic cavity contain?
organs of several systems, including the reproductive, digestive, and urinary systems
contains reproductive organs
What are the 4 quadrants of the abdominopelvic cavity and where do they cross?
Right Upper Quadrant (RUQ)
Left Upper Quadrant (LUQ)
Right Lower Quadrant (RLQ)
Left Lower Quadrant (LLQ)
they cross at the umbilical region/umbilicus
What are the 9 segments of the abdomonipelvic cavity? (upper region)
Right and Left hypochondriac region
epigastric region
Where is the right/left hypochondriac region located?
they lie below the cartilage of the ribs
Where is the epigastric region located?
in between the right/left hypochondriac region and superior to the stomach
What are the 9 segments of the abdominopelvic cavity? (middle region)
Right and Left lumbar region
Umbilical region
Where is the right/left lumbar region located?
approximately the same region as the lumbar vertebrae
Where is the umbilical region located?
in the center of the abdomen, between the right/left lumbar region and contains the umbilicus
What are the 9 segments of the abdomonipelvic cavity? (lower region)
Right and Left iliac region
Hypogastric region
Where are the right/left iliac region located?
named for the anatomical regions over which they lie, the lower abdomen
Where is the hypogastric region located?
it’s between the right/left iliac region and inferior to the stomach
What are serous membranes and what organs do they contain?
they are formed by thin sheets of tissue within the anterior body cavity and they fold themselves to to make a continuous double-layer structure with space between their layers
contains the heart, lungs, and many abdominal organs
What are serous fluids and what is their function?
they are within the layers of serous membranes and it’s a water, slippery liquid produced by the cells within the serous membrane
they function to lubricate organs in the cavity to prevent friction as the organs move against adjacent structures
What are the 2 layers of serous membranes?
Visceral layer (inner layer)
Parietal layer (outer layer)
What are the 3 main serous membranes?
pleural membranes
pericardial membranes
peritoneal membranes
What is homeostasis?
the body’s ability to maintain a relatively stable internal environment
What are feedback loops?
a change in a regulated variable causes effects that feed back and in turn affect that same variable
What is negative feedback?
one of the primary mechanisms for the maintenance of homeostasis and it opposes the initial change in a regulated variable and reduces the output
negates any stimulus that moves a variable away from homeostasis
What is a positive feedback?
less common than negative feedback loops. the effector activity increases and reinforces the initial stimulus and shuts off when conditions return to the normal range
a continuous loop - increases the response to a stimulus
What is a set point in feedback loops?
it’s basically the normal value. how normal body temps are 37 degrees C or normal BP is 110/70
in reality, it’s a normal range around that certain set point
set point → the target value a system aims to maintain
normal range → the safe fluctuation zone around that target
What are receptors (sensors) in feedback loops?
when a regulated variable is outside its normal range, the information is picked up by the stimulus is picked up by the receptor (sensor)
What is the control (integrating) center in feedback loops?
where it processes the information sent from receptors and determines the appropriate response to restore balance in the system
What is the effector in feedback loops?
the organ that causes the physiological responses that returns the variable to the normal/stable range
where the control center sends the message to
Variables in feedback loops are…
anything that can change and affect the system
What are the 4 core principles of anatomy?
feedback loops
relationship between structure and function
gradients
intercellular (cell-cell) communication
What is a gradient?
It’s when more of something exists in one area than another and the two areas are connected; they drive many psychological processes
What are the different examples of gradients?
temperature gradient
concentration gradient
pressure gradient
How do cells communicate with one another and explain why it’s necessary for multicellular organisms
They communicate through electrical signals or chemical signals and it’s necessary to coordinate activities, maintain homeostasis, and facilitate responses to changes in their environment
What is electrical signals?
typically transmitted directly between neighboring cells
What is chemical messages?
they are released from one cell directly onto another cell or into the fluid surrounding another cell, or they can reach another cell through the blood
What are the 5 types of communication?
direct communication
autocrine communication
paracrine communication
endocrine communication
synaptic communication
Describe direct communication
signals are transmitted through gap junctions
chemical mediators are ions, small solutes, lipid soluble materials
distribution effects are usually limited to adjacent cells of the same type that are interconnected by connexons
Describe autocrine communication
transmitted through ECF
chemical mediators are autocrines
distribution effects are limited to the cell that secretes the chemical mediator
Describe paracrine communication
transmitted through ECF
chemical mediators are paracrines
dnearly cells with receptor binds to chemical and changes activity
Describe endocrine communication
transmitted through the bloodstream
chemical mediators are hormones
distribution effects can be widespread (tissues/organs) and needs a receptor for the hormone
Describe synaptic communication
transmitted across synapses via neurotransmitters
chemical mediators are neurotransmitters
distribution effects are limited to a single synapse. the target cell must have an appropriate receptor