ECONOMICS: Topic 3 > Economic Issues
1/85
Earn XP
Description and Tags
revision for AT1 on content from topic 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
what is the main economic issue?
unlimited wants, limited resources
(land, labour, capital, enterprise)
what is economic growth?
the increase in the value of goods and services produced over time (measured by real GDP)
what is unemployment?
the proportion of the labour force that is willing and able to work but cannot find a job
what is inflation?
increase in the general price level of goods and services
what is the distribution of income & wealth?
how income and assets are shared across households
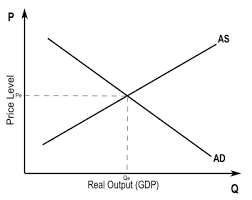
what is the law of demand?
states that as prices decrease, quantity demanded increases
what does aggregate demand refer to?
the total demand of goods & services within an economy at a certain price level
what does aggregate supply refer to?
the total amount of goods & services an economy can produce at a certain price level
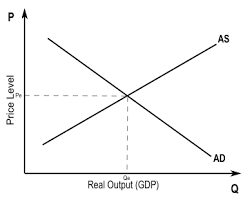
what is the memory key for remembering the set up of an AD/AS graph?
Demand - to the dirt
Supply - to the sky
what does AD/AS diagram show?
how shifts in aggregate demand & aggregate supply may impact shifts in price (inflation) and economic output (growth)
what words describe movement along the demand & supply curves?
expansion & contraction
what words describe a shift of the demand & supply curves?
increase & decrease
what is GDP?
total value of goods & services produced in an economy over a year
what is nominal GDP growth?
where GDP increases due to a change in prices (inflation), NOT an increase in output
what is real GDP growth?
increases due to a change in the output of goods and services, adjusted for changes in inflation over time.
what is more accurate for measuring GDP & why? (real or nominal)
real GDP, because increasing the volume of output is what improves living standards
what is the economic growth formula?

what is the formula to convert nominal GDP into real GDP?
removes effects of inflation
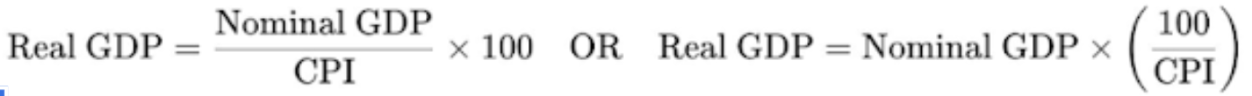
what is the formula of aggregate demand (AD)?
C + I + G (X-M)
what type of growth does demand-side (AD) growth drive?
short-term growth
what type of growth does supply-side (AS) growth drive?
long-term growth
what is aggregate supply determined by?
the quantity & quality of factors of production (land, labour, capital, entreprenurship)
what does the simple multiplier calculate?
how much additional GDP results from an additional change in expenditure
when can increased economic growth result in inflation?
when AD (inflationary pressure) outpace AS
what are some consumption factors that may contribute to economic growth?
disposable incomes, interest rates & consumer expectations
what are some investment factors that may contribute to economic growth?
business profits, business expectations & interest rates
what is the natural rate of employment?
rate of employment with no cyclical unemployment
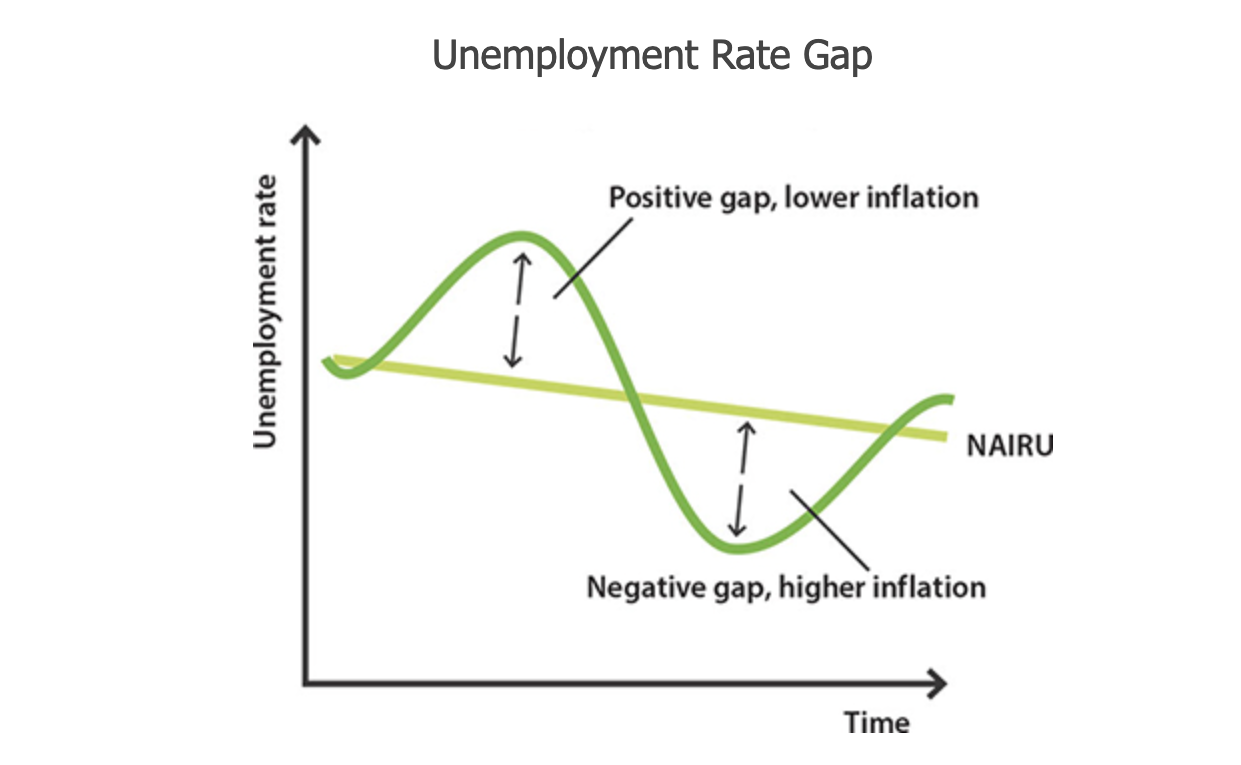
what is the NAIRU?
non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment, which is the lowest unemployment rate that can be sustained without causing wages growth and inflation to rise.
what are some examples of the main groups affected by unemployment?
Youth
Mature-age workers
Low-educated individuals
Low-skilled occupations
Industries facing structural change
First Nations Australians
Migrants
And, specific regions.
who makes up the labour force?
unemployed & employed
what is the definition of unemployment?
working age people who are actively looking for work but are currently without a job
what are two issues with the unemployment rate measurement?
excludes hidden unemployment & underemployment
what is hidden unemployment?
when people are not counted as unemployed or in labour force due to given up hope and stopped looking for work
what is underemployment?
when those who are technically employed, would like and are available to work more hours
what is an example of underemployment?
someone working part-time, but wants to work full-time
what is cyclical unemployment?
occurs with changes in the business cycle
what is structural unemployment?
occurs with a mismatch between the jobs that are available and the people looking for work
what is frictional unemployment?
occurs when people are moving between jobs in the labour market & moving in and out of labour force
what is seasonal unemployment?
occurs at different points in year because of seasonal patterns
what is hard-core unemployment?
out of work for so long that individuals are rarely employed due to personal circumstances
what is the formula for the participation rate?
% of working-age population (15+) that are in the labour force
what is the formula for the unemployment rate?
% of people in labour force who are unemployed
what does technical efficiency refer to?
producing the maximum level of output from a given quantity of inputs, shown as along the PPF
what does allocative efficiency refer to?
maximising total benefit from its scarce resources by producing a combination that best matches community preference
what does dynamic efficiency refer to?
how well resources are allocated over time to meet the preferences
what is the unemployment rate gap?
the difference between the NAIRU & the unemployment rate
when will inflation & wages growth exist in the NAIRU graph? and why?
when UE is at or below NAIRU, below there is limited spare capacity (no cyclical unemployment)
what types of policies can help reduce the NAIRU, by reducing structural unemployment?
Subsidised Training
Relocation Assistance
Funding Employment Programs
> ALL reduce skill & location mismatch
what policies could increase the participation rate?
Increasing the minimum wage
Increasing childcare access to encourage parents to re-enter the workforce
Expansionary monetary policy
Reskilling for mature-aged workers to delay retirement
what is price stickiness?
describes wage growth & tendency to remain unchanged despite shifting market conditions
what is inflation?
a sustained increase in the general price level over time
what is headline inflation?
measures items in CPI basket, which are weighted based on percentage spent on groups
what is underlying inflation?
measures inflation excluding items that have large price changes (such as assets), or one-off price changes
what are two weaknesses of headline inflation?
doesn’t include property
doesn’t include ALL items consumed
what is the headline inflation target?
2-3%
what is deflation?
when the general price level decreases
what is stagflation?
stagnant or low economic growth, high unemployment, and rising inflation.
what is demand-pull inflation?
when increases in AD exceed increases in AS, through a shortage of goods & consumer competition
what are inflationary expectations?
when consumers expect higher prices therefore ‘panic buy’, which increases demand-pull inflation
what is cost-push inflation?
when production costs rise, foricing firms to increase their prices to maintain profit margins
what is imported inflation?
when AUD is weak OR inflation is high overseas, costs of imported materials rise, rising prices of final goods & services
what is the wage price spiral?
when inflation & wages push eachother higher, as consumers desire purchasing power and businesses aim to remain profitable
what is the difference between income and wealth?
income is the amount of money that flows to individuals WHEREAS wealth is the stock of assets individuals own at a particular point in time.
what are the three negative effects of inflation on the economy?
reduced economic growth
reduced international competitiveness
reduced exchange rate
what is purchasing power?
the amount of goods or services a certain amount of money can buy
what are two groups who benefit from inflation?
1) owners of real assets - ie property & commodities
2) borrowers on fixed interest repayment plans
what are the four sources of income?
salaries, rent, interest, profit
what is the difference between gross income and disposable income?
gross is the sum of all income WHEREAS disposable is income individuals keep after tax
which type of income (nominal or real) is adjusted for inflation?
real income
what does the line of perfect equality in the lorenz curve represent?
a perfectly equal distribution of income
What represents a more unequal distribution of income? (high GINI or low GINI)
high GINI
who are the disadvantaged groups in the distribution of income in Australia?
non-english speaking migrants
youth
women
what is the two main sources of income for Australian households?
wages/salary & transfer payments
what are the two largest sources of wealth?
owner-occupied property & superannuation
what is absolute poverty?
where people don't have enough money to meet basic needs and earn below the poverty line
what is relative poverty?
where individuals have an income that is less than 50% of the median income
what does utility refer to?
satisfaction OR happiness
what is an example of a progressive tax?
income tax, the more you earn, the more you are taxed
what is an example of regressive tax?
GST (Goods & Service Tax), affects low-income earners disproportionately
what are the economic costs of income inequality?
Reduced overall utility (satisfaction).
Reduced consumption and slow economic growth.
Need for increased government expenditure.
what is the single economic benefit of income inequality?
Can create incentives that lead to an increase in potential output, and therefore long term growth
what are the social benefits of income inequality?
Sense of personal achievement
Greater role for charity, fostering positive social connections.
what are the social costs of income inequality?
Reduces social cohesion
Increased poverty
what is non-discretionary government expenditure?
automatic adjustments in government spending
what is discretionary government expenditure?
deliberate changes in government spending
what is the point on the line in the PPF (production possibility frontier) called?
allocative efficiency