Tissue Types
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Tissue
A group of cells found together in the body
Types of Tissue
Epithelial Tissue
Connective Tissue
Muscle Tissue
Nervous Tissue
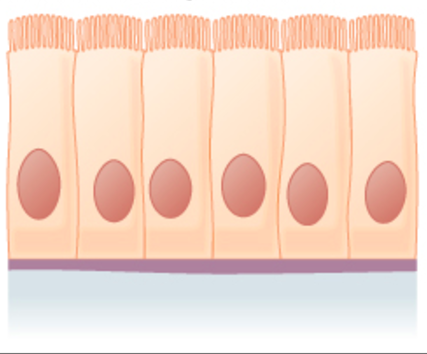
Epithelial tissue
Sheets of cells found on the outer surfaces of the body (skin) or glands
Joined by cell junctions - cells directly connected to one another
All substances must enter and exit through the epithelium
Apical-Basolateral Polarity - The cell’s top and bottom structure differ
Apical surface: ‘top’ surface facing the ‘outside’
Basolateral surface: ‘bottom’ that faces underlying tissue
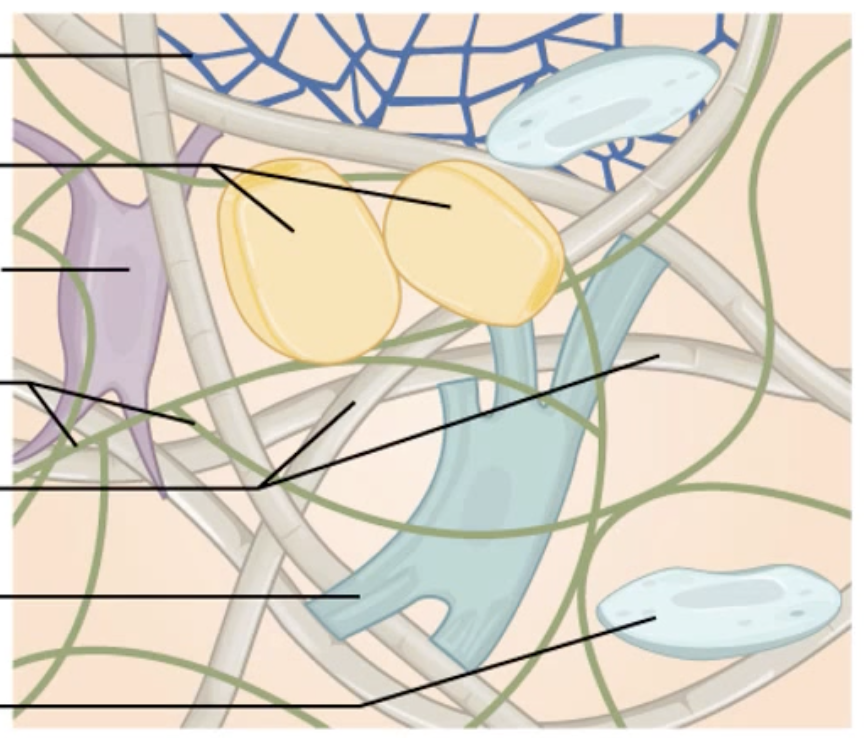
Connective tissue
Cells dispersed within a non-cellular matrix
Functions to connect, protect and support other tissues
3 Types:
Connective tissue proper:
a. Loose connective tissue (adipose tissue)
b. Dense connective tissue (tendons/ligaments)
Supportive connective tissue (cartilage & bone)
Fluid connective tissue (blood & lymph)
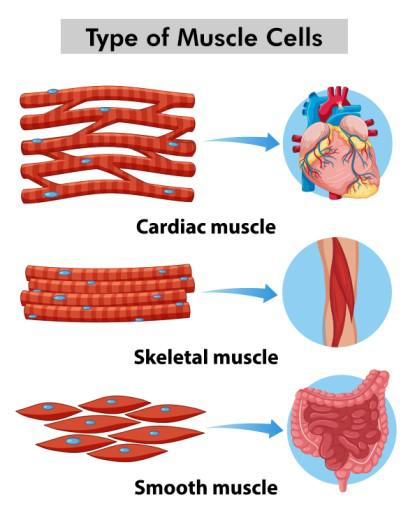
Muscle Tissue
Excitable contractile tissue. Can be electrically stimulated and can contract.
3 Types:
Skeletal muscle tissue
Majority is attached to the skeleton
All skeletal muscle tissue can be voluntarily moved
Produces head to protect organs
Smooth muscle tissue
Muscle of internal organs
Involuntary control
Cardiac muscle tissue
Heart muscles that pump blood
Involuntary control
Nervous Tissue
Excitable, non-contractile tissue. Can be electrically stimulated but cannot contract.
Sends & receives chemical and electrical signals
2 Types:
Neurons - Propagates signals through the nervous system
Neuroglia - Supports neuron function