Antimicrobial Drugs bacterial
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Selective Toxicity
selectively finding and destroying pathogens without damaging the host
The use of chemicals to treat a disease
Chemotherapy
A substance produced by a microbe that in small amounts, inhibits another microbe
Antibiotic
synthetic substance that interferes with any sort of microbe ex helminths, parasites etc.
Antimicrobial drugs
1928 Fleming
discovered penicillin, produced by Penicillium
1932 Prontosil red dye
used for streptococcal infections
First clinical trials of penicillin
1940
Currently in the history of chemotherapy
Growing problem of antibiotic resisitance
What is found in the soil and makes most of our antibiotics?
Streptomyces
drugs affecting a narrow range of microbial types (only kills either gram pos or gram neg)
Narrow spectrum of microbial activity
affecting a broad range of gram pos or gram neg bacteria
Broad -spectrum antibiotics
Superinfection
An overgrowth of normal microbiota that is resistance to antibiotics
Bactericidal
directly kills microbes
Bacteriostatic
-Prevents microbes from growing
Allows the immune system to take over and kill off bacteria eventually
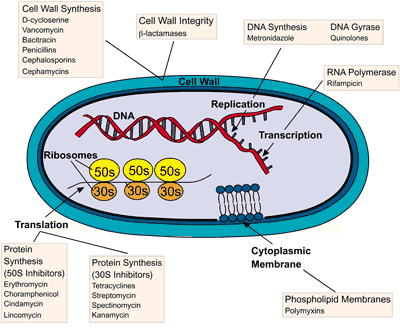
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Inhibition of protein synthesis
Inhibition of nucleic acid replication and transcriptions
Injury to plasma membrane
Inhibition of essential metabolite synthesis
what are the 5 modes of actions of antimicrobial drugs
What drug targets and inhibits cell wall synthesis and how
Penicillin- It prevents peptidoglycan walls from joining together , thus the cell wall is weakened.
Only actively growing cells affected
Best on gram positive ( think breaks links of a chain fence)
little toxicity to host
Targets bacterial 70S ribosomes
Blocks or prevents 1 part of the following
DNA/RNA/Transcription /Translation
Prevents amino acid chain formation
How does inhibiting protein synthesis work?
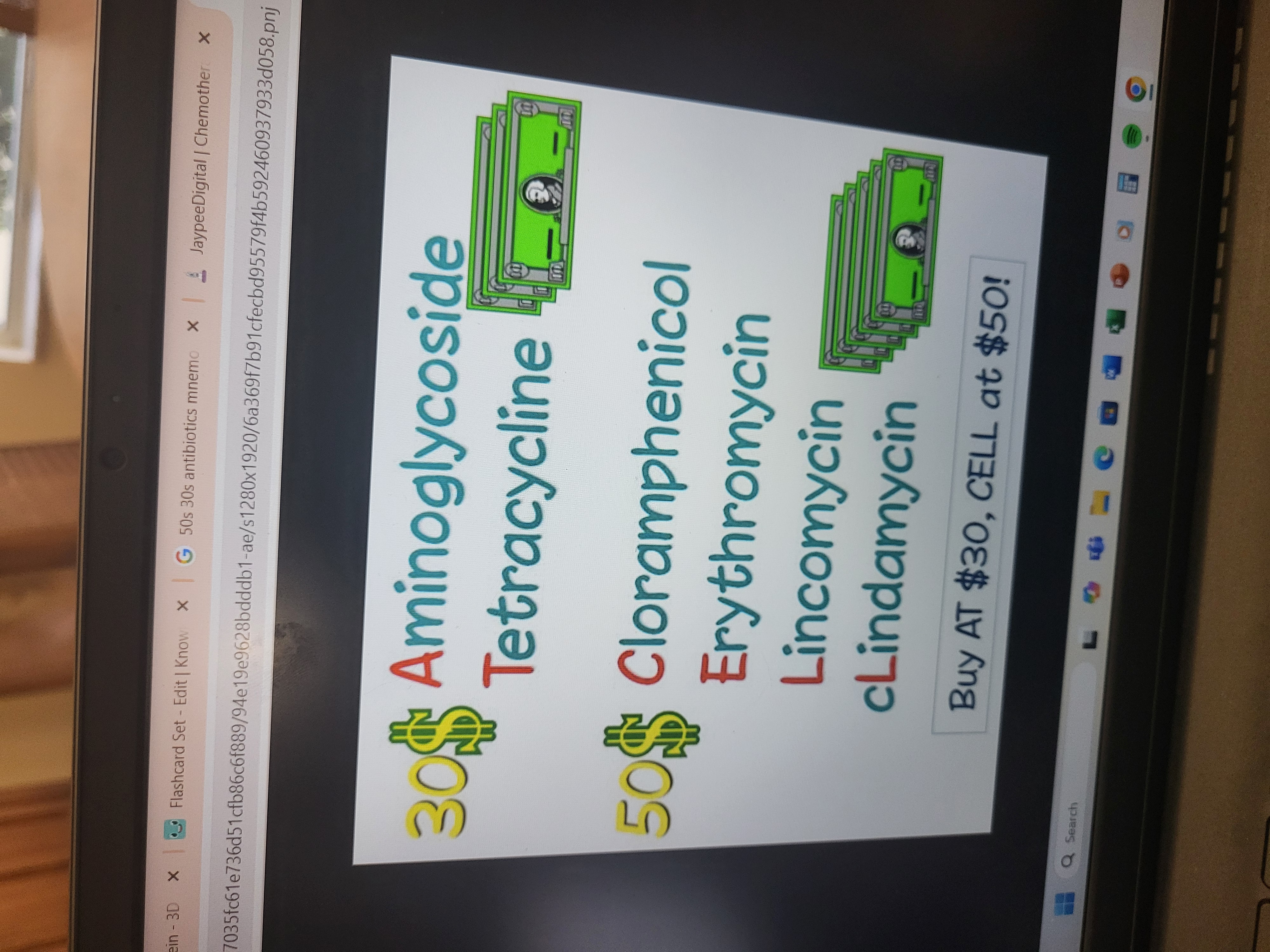
Examples of synthesis protein blocking drugs
Chloramphenicol
Erythromycin
Streptomycin
Tetracyclines
How do antimicrobials injure the plasma membrane?
Polypeptide antibiotics change the membrane permeability
Antifungal drugs combine with membrane sterols - only plants have sterols not bacterial cells
Ionophores (not for humans but cattle) allow uncontrolled movement of cations
How does antimicrobial drugs inhibit nucleic acid synthesis?
Interferes with DNA replication and transcription
Sulfa drugs
inhibiting the synthesis of essential metabolites
antimetabolite
competes with normal substrates for an enzyme
Without the correct enzyme fitting, cell cannot continue to replicate
sulfas competes with PABA stopping the synthesis of folic acid
folic acid is needed because
This is a precursor for DNA and RNA replication
without folic acid
DNA/RNA cannot be created in order to replicate
competing for PABA , sulfa is what action of antimicrobial drugs
Inhibition of creating and synthesizing nucleic acid
Penicillin- disrupts cell wall synthesis because
contains a B -lactam ring
B Lactam rings are
chemical sides attached to the side of the ring and prevent peptidoglycans to link together (think of chain link fence, each individual link is the peptidoglycan)
penicillinase
arch enemy of penicillin
enzyme that can work around the action of penicillin
allows peptidoglycan to hook up
is a limitation of natural penicillin
synthetic penicillins
lab created penicillin that can resist penicillinase
examples of synthetic penicillin that can resist penicillinase
methicillin
oxacillin
(think MO)
These have B lactam ring inhibitors
another name for broad spectrum
extended spectrum
clavulanic acid
The superhero that can inhibit the evil penicillinase and put in broad spectrum antibiotics
Methicillin is
The first penicillinase - resistant drug to be developed
carbapenems
Changes structure to penicillin
Adds double bonds to penicillin nucleus
Substitutes C and S
This makes it harder to break down the penicillin
Broad spectrum
Primaxin, doripenem
Examples of carbapenems (penicillin with stronger bonds)
Monobactam (single ring)
Penicillin with single ring instead of B lactam double ring
Low toxicity
only works against gram negatives
Aztreonam is an example of what kind of penicillin?
Monobactam
Bacitracin
Vancomycin
Teixobactin
Examples of polypeptide antibiotics that inhibit cell wall synthesis
works against gram positive and topical (OTC)
Bacitracin
Vancomycin
Glycopeptide
Last line of defense against MRSA
Teixobactin
New class of antibiotics fights gram positive
Antimycobacterial antibiotics
Prevents mycolic acid formation in the acid fast positive bacterial strains from forming
Isoniazid (INH)
Inhibits mycolic acid synthesis
Ethanbutal
allows for mycolic acid to be made but does not allow it to be used in the actual cell wall
Attacks & effects either 30S, 50S ribosome disrupting protein synthesis
How antimicrobics work against protein synthesis
What drug is converted to intermediates targeting ribosomal proteins?
Nitrofurantoin
methods of how antibiotics target growth
How to remember what drug effects what ribosome
50S ribosomal unit and 30 ribosomal unit in prokaryote cells
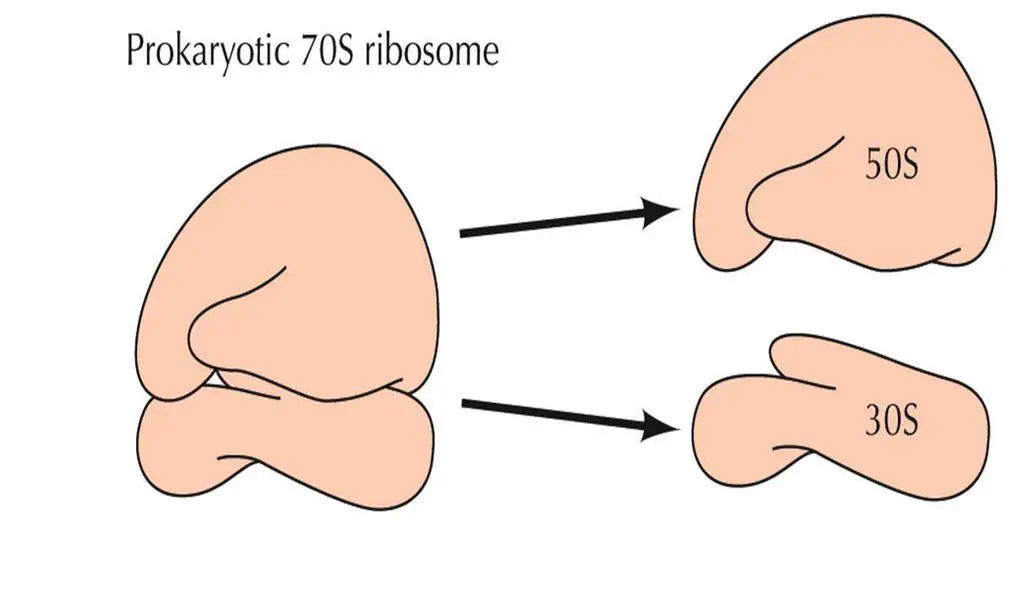
what are peptide bonds?
The bonds that links the amino acids so they stay together in formation
Chloramphenicol
drug that prevents peptide bonds from forming
binds to the 50S (big unit) of the entire ribosome
Broad spectrum
Chloramphenicol side effects
suppress bone marrow
affect blood cell formation
Aminoglycosides
Blocks tRNA from brining in amino acid sequence so protein sequence cannot be created
Bacteriostatic
Changes shape of the 30S (bottom) ribosomal unit
Aminoglycoside examples and side effects
streptomycin, neomycin, gentamycin
can cause permanent auditory damage
Streptomyces spp produces what?
Tetracyclines
Tetracycline action and is
Does not allow for the tRNA to attach to the ribosome
Broad spectrum & penetrates tissues
Because tetracycline is broad spectrum and penetrates tissues it is used for ____________ and side effect is _______________
against rikettsias, chlamydia and side effect is suppression of normal microbiota
Glycyclines
Newer class of protein synthesis inhibor
Binds to 30S ribosomal unit
Administered via IV
Useful against MRSA
Macrolides
Freezes the 50S ribosomal unit from moving along to read the mRNA unit, thus preventing the formation of proteins
Contains a macrocyclic lactone ring
Narrow spectrum - Gram pos targets
an example of a macrolide drug
Erythromycin
S.O.P (Last resort of drugs if other drugs used did not work in order of severity)
Bringing out the big guns
Inhibitors of protein synthesis
Streptogramins
Oxazolidinones
Pleuromutilins
Streptogramins mode of action
Attach to the 50S subunit
work against gram positives resistance to other antibiotics
Oxazolidinones mode of action
Bind to both 50S and 30S ribosomal unit
Combat MRSA
Pleuromutilins
Retapamulin: Topical and effective against gram pos.
Treats impetigo
Lipopetides
effects the plasma cell membrane
Daptomycin
Polymyxin B
Polymyxin E
All drugs that affect the plasma membrane
Daptomycin
Treats only gram +
Attacks the bacterial cell membrane
Produced by streptomycetes
for skin infections
Polymyxin B (B negative)
Topical
Bacteriocidal
Fights Gram negative
OTC combined w/bacitracin and neomycin ointments
Polymyxin E (colistin brand name)
Effective against gram negative
mostly to fight resistance / respirators and more broad
Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitors
prevents mRNA from doing its job during transcription thus preventing new DNA from being formed
Rifamycin
Quinolone and Fluoroquinolones
Examples of drugs blocking nucleic acid synthesis
Inhibits mRNA synthesis
penetrates tissues
antitubercular activity ( fights TB)
side effect of turning urine orange
Rifamycin uses and mechanism of action
Quinolone and Fluoroquinolones examples and uses
Nalidixic acid- synthetic, inhibiting DNA gyrase
Norfloxacin and ciprofloxacin- Broad spectrum, relatively non toxic